User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Which Emergencies Are Genuine Emergencies?
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal Trade Commission Bans Noncompete Agreements, Urges More Protections for Healthcare Workers
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
But business groups have vowed to challenge the decision in court.
The proposed final rule passed on a 3-2 vote, with the dissenting commissioners disputing the FTC’s authority to broadly ban noncompetes.
Tensions around noncompetes have been building for years. In 2021, President Biden issued an executive order supporting measures to improve economic competition, in which he urged the FTC to consider its rulemaking authority to address noncompete clauses that unfairly limit workers’ mobility. In January 2023, per that directive, the agency proposed ending the restrictive covenants.
While the FTC estimates that the final rule will reduce healthcare costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade and increase worker earnings by $300 million annually, the ruling faces legal hurdles.
US Chamber of Commerce president and CEO Suzanne P. Clark said in a statement that the move is a “blatant power grab” that will undermine competitive business practices, adding that the Chamber will sue to block the measure.
The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on noncompetes during the public feedback period, with about 25,000 supporting the measure, said Benjamin Cady, JD, an FTC attorney.
Mr. Cady called the feedback “compelling,” citing instances of workers who were forced to commute long distances, uproot their families, or risk expensive litigation for wanting to pursue job opportunities.
For example, a comment from a physician working in Appalachia highlights the potential real-life implications of the agreements. “With hospital systems merging, providers with aggressive noncompetes must abandon the community that they serve if they [choose] to leave their employer. Healthcare providers feel trapped in their current employment situation, leading to significant burnout that can shorten their [career] longevity.”
Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya said physicians have had their lives upended by cumbersome noncompetes, often having to move out of state to practice. “A pandemic killed a million people in this country, and there are doctors who cannot work because of a noncompete,” he said.
It’s unclear whether physicians and others who work for nonprofit healthcare groups or hospitals will be covered by the new ban. FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged that the agency’s jurisdictional limitations mean that employees of “certain nonprofit organizations” may not benefit from the rule.
“We want to be transparent about the limitation and recognize there are workers, especially healthcare workers, who are bound by anticompetitive and unfair noncompete clauses, that our rule will struggle to reach,” she said. To cover nonprofit healthcare employees, Ms. Slaughter urged Congress to pass legislation banning noncompetes, such as the Workforce Mobility Act of 2021 and the Freedom to Compete Act of 2023.
The FTC final rule will take effect 120 days after it is published in the federal register, and new noncompete agreements will be banned as of this date. However, existing contracts for senior executives will remain in effect because these individuals are less likely to experience “acute harm” due to their ability to negotiate accordingly, said Mr. Cady.
States, AMA Take Aim at Noncompetes
Before the federal ban, several states had already passed legislation limiting the reach of noncompetes. According to a recent article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12 states prohibit noncompete clauses for physicians: Alabama, California, Colorado, Delaware, Massachusetts, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and South Dakota.
The remaining states allow noncompetes in some form, often excluding them for employees earning below a certain threshold. For example, in Oregon, noncompete agreements may apply to employees earning more than $113,241. Most states have provisions to adjust the threshold annually. The District of Columbia permits 2-year noncompetes for “medical specialists” earning over $250,000 annually.
Indiana employers can no longer enter into noncompete agreements with primary care providers. Other specialties may be subject to the clauses, except when the physician terminates the contract for cause or when an employer terminates the contract without cause.
Rachel Marcus, MD, a cardiologist in Washington, DC, found out how limiting her employment contract’s noncompete clause was when she wanted to leave a former position. Due to the restrictions, she told this news organization that she couldn’t work locally for a competitor for 2 years. The closest location she could seek employment without violating the agreement was Baltimore, approximately 40 miles away.
Dr. Marcus ultimately moved to another position within the same organization because of the company’s reputation for being “aggressive” in their enforcement actions.
Although the American Medical Association (AMA) does not support a total ban, its House of Delegates adopted policies last year to support the prohibition of noncompete contracts for physicians employed by for-profit or nonprofit hospitals, hospital systems, or staffing companies.
Challenges Await
The American Hospital Association, which opposed the proposed rule, called it “bad policy.” The decision “will likely be short-lived, with courts almost certain to stop it before it can do damage to hospitals’ ability to care for their patients and communities,” the association said in a statement.
To ease the transition to the new rule, the FTC also released a model language for employers to use when discussing the changes with their employees. “All employers need to do to comply with the rule is to stop enforcing existing noncompetes with workers other than senior executives and provide notice to such workers,” he said.
Dr. Marcus hopes the ban improves doctors’ lives. “Your employer is going to have to treat you better because they know that you can easily go across town to a place that has a higher salary, and your patient can go with you.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Are Women Better Doctors Than Men?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.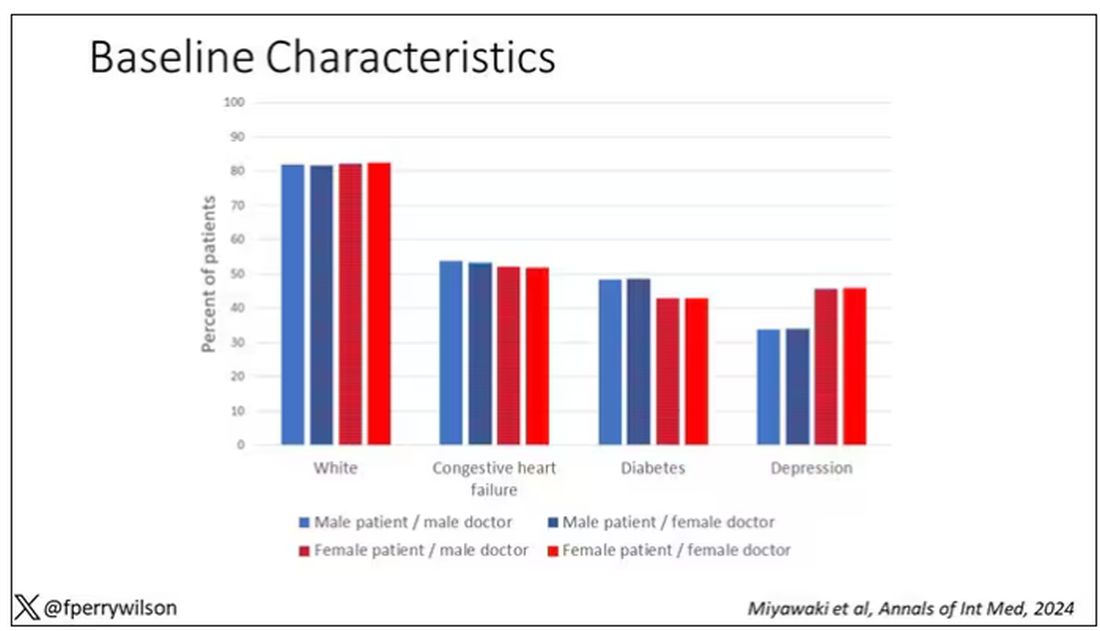
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 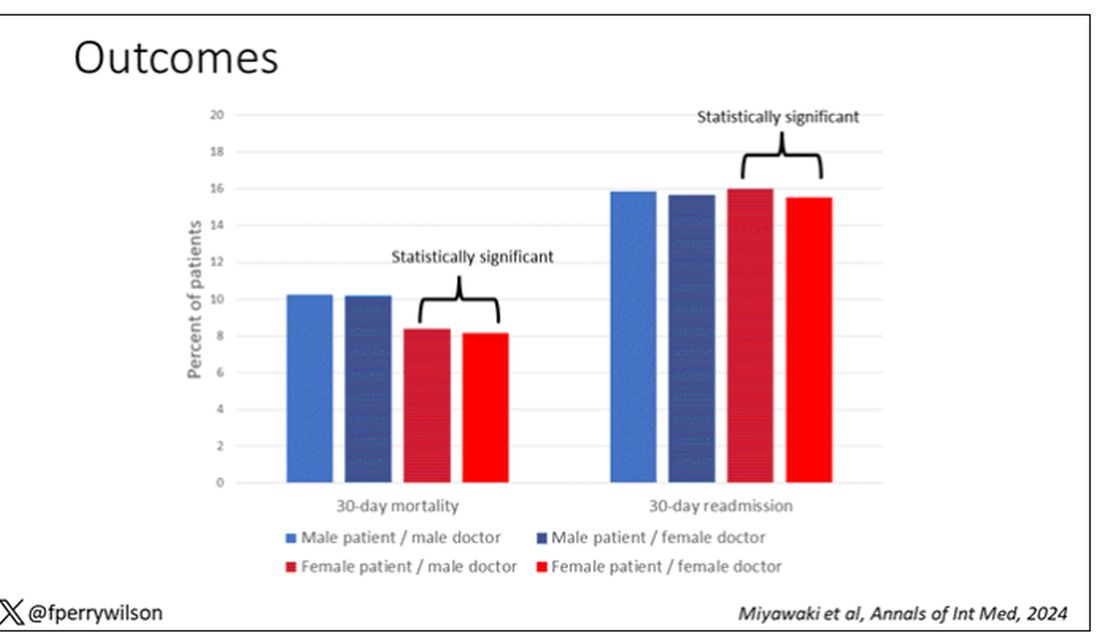
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding Life to Your Patients’ Years
Caring for older adults was one of the most rewarding parts of my years practicing as a clinical cardiologist. I appreciated their wisdom, humor, and, very often, their respect and appreciation for physicians. It was always upsetting to see them suffer a mild fall or episode of atrial fibrillation and recognize that it could have major health ramifications.
That is not just a question for geriatric care. With fewer than two practicing geriatricians for every 10,000 older individuals, it is obvious that geriatricians cannot shoulder this responsibility alone. Almost all primary care physicians and subspecialists should prepare to care for older individuals and help them age healthfully.
Susan Friedman, MD, a board-certified geriatrics and lifestyle medicine clinician at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, reviewed the literature on the connection between lifestyle and healthy aging and concluded that the integration of lifestyle medicine into medical care for older adults is key to compressing morbidity. The pillars of lifestyle medicine — optimal nutrition, physical activity, stress management, restorative sleep, positive social connections, and avoidance of risky substances — both individually or as a sum are associated with less chronic disease, improved engagement in life, better physical and cognitive function, less frailty, and less sarcopenia. Framing discussions with patients around the six pillars of lifestyle medicine can be an effective strategy.
Optimal Nutrition
For a variety of reasons, older adults, especially those living alone, often lose the desire to prepare a nourishing meal. Older adults require different protein intake than younger patients to offset age-related sarcopenia, but helping them select healthy sources of protein is imperative. Both adequate protein consumption and eating patterns high in vegetables, legumes, fruit, and nuts and low in saturated fat, red meat, and processed meat can lower the risk of developing frailty.
Asking a patient to share a 24-hour food recall, and based upon that, resourcing nutritional guidance, a lifestyle medicine program or specialist, and insurance or community resources for food-as-medicine services, is a good first step.
Physical Activity
Increasing general physical activity can be a tough ask for many older adults, and joint pain is a common reason they demur. Messaging around targeted exercises to mitigate falls, improve muscle strength, and reduce joint pain may be more appealing. Contemporary research demonstrates that exercise, particularly open-skill exercise that requires quick decisions (such as table tennis) can be powerful. Maintaining cognition, mood enhancement, and independence may also be motivating messages.
The first step is curiosity: What does your patient like to do? Referral to a physical therapist or an exercise specialist to provide stepwise guidance along with resourcing community opportunities can then follow.
Restorative Sleep
“I’m old. I don’t need as much sleep.” We’ve probably all heard older patients say this. But the National Sleep Foundation’s report on sleep health and aging indicates that the need to sleep does not decrease with age. The ability to sleep, however, may decline. Assessing and treating disordered sleep is another example of how each lifestyle medicine pillar, such as nutrition and physical activity, is multidimensional and interacts to support the functional integrity of older patients. It’s hard to feel motivated to go for a walk if you lack adequate sleep.
Stress Management
Exploring stress with patients can be very revealing. Do they experience stress that energizes and has a positive effect? How much of their day is spent in negatively impactful distress? Chronic stress has been shown to affect immune function in older individuals. Start conversations with your older patients to normalize the importance of stress as a health measure.
Positive Social Connections
Loneliness puts individuals at higher risk for heart disease, stroke, and dementia and even increases the risk for premature death by up to 60%. Yet, clinicians and patients rarely discuss social connections during medical appointments. Tools such as the UCLA Loneliness Scale exist for health practitioners to assess and identify patients at risk for loneliness, as do resources to integrate social care into the delivery of healthcare.
Avoidance of Risky Substances
Alcohol assessments are not just for younger patients. One study found that 5.6 million adults ages 65 or older engaged in binge drinking in the past month. Because of body changes, the negative effects of alcohol may be greater on older adults, including interactions between alcohol and commonly prescribed medications.
Conducting a lifestyle assessment is an important way to engage with older patients and allows clinicians to identify opportunities to improve health behaviors, understand obstacles, and support patients to make lifestyle changes. It may uncover ways to remove some of the pill and treatment burdens that older adults often experience. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) offers clinical practice resources to support clinicians as well as “Lifestyle Medicine and Food as Medicine Essentials,” a 5.5-hour complimentary CE/CME course on food and lifestyle medicine that introduces clinicians to the therapeutic use of lifestyle medicine. ACLM also offers members interest groups focused on geriatrics, fitness, and mental health, which may be beneficial to clinicians treating older adults.
By engaging with older patients on their lifestyle behaviors, we can ensure that we are doing all we can to help them live longer — and live better.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Caring for older adults was one of the most rewarding parts of my years practicing as a clinical cardiologist. I appreciated their wisdom, humor, and, very often, their respect and appreciation for physicians. It was always upsetting to see them suffer a mild fall or episode of atrial fibrillation and recognize that it could have major health ramifications.
That is not just a question for geriatric care. With fewer than two practicing geriatricians for every 10,000 older individuals, it is obvious that geriatricians cannot shoulder this responsibility alone. Almost all primary care physicians and subspecialists should prepare to care for older individuals and help them age healthfully.
Susan Friedman, MD, a board-certified geriatrics and lifestyle medicine clinician at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, reviewed the literature on the connection between lifestyle and healthy aging and concluded that the integration of lifestyle medicine into medical care for older adults is key to compressing morbidity. The pillars of lifestyle medicine — optimal nutrition, physical activity, stress management, restorative sleep, positive social connections, and avoidance of risky substances — both individually or as a sum are associated with less chronic disease, improved engagement in life, better physical and cognitive function, less frailty, and less sarcopenia. Framing discussions with patients around the six pillars of lifestyle medicine can be an effective strategy.
Optimal Nutrition
For a variety of reasons, older adults, especially those living alone, often lose the desire to prepare a nourishing meal. Older adults require different protein intake than younger patients to offset age-related sarcopenia, but helping them select healthy sources of protein is imperative. Both adequate protein consumption and eating patterns high in vegetables, legumes, fruit, and nuts and low in saturated fat, red meat, and processed meat can lower the risk of developing frailty.
Asking a patient to share a 24-hour food recall, and based upon that, resourcing nutritional guidance, a lifestyle medicine program or specialist, and insurance or community resources for food-as-medicine services, is a good first step.
Physical Activity
Increasing general physical activity can be a tough ask for many older adults, and joint pain is a common reason they demur. Messaging around targeted exercises to mitigate falls, improve muscle strength, and reduce joint pain may be more appealing. Contemporary research demonstrates that exercise, particularly open-skill exercise that requires quick decisions (such as table tennis) can be powerful. Maintaining cognition, mood enhancement, and independence may also be motivating messages.
The first step is curiosity: What does your patient like to do? Referral to a physical therapist or an exercise specialist to provide stepwise guidance along with resourcing community opportunities can then follow.
Restorative Sleep
“I’m old. I don’t need as much sleep.” We’ve probably all heard older patients say this. But the National Sleep Foundation’s report on sleep health and aging indicates that the need to sleep does not decrease with age. The ability to sleep, however, may decline. Assessing and treating disordered sleep is another example of how each lifestyle medicine pillar, such as nutrition and physical activity, is multidimensional and interacts to support the functional integrity of older patients. It’s hard to feel motivated to go for a walk if you lack adequate sleep.
Stress Management
Exploring stress with patients can be very revealing. Do they experience stress that energizes and has a positive effect? How much of their day is spent in negatively impactful distress? Chronic stress has been shown to affect immune function in older individuals. Start conversations with your older patients to normalize the importance of stress as a health measure.
Positive Social Connections
Loneliness puts individuals at higher risk for heart disease, stroke, and dementia and even increases the risk for premature death by up to 60%. Yet, clinicians and patients rarely discuss social connections during medical appointments. Tools such as the UCLA Loneliness Scale exist for health practitioners to assess and identify patients at risk for loneliness, as do resources to integrate social care into the delivery of healthcare.
Avoidance of Risky Substances
Alcohol assessments are not just for younger patients. One study found that 5.6 million adults ages 65 or older engaged in binge drinking in the past month. Because of body changes, the negative effects of alcohol may be greater on older adults, including interactions between alcohol and commonly prescribed medications.
Conducting a lifestyle assessment is an important way to engage with older patients and allows clinicians to identify opportunities to improve health behaviors, understand obstacles, and support patients to make lifestyle changes. It may uncover ways to remove some of the pill and treatment burdens that older adults often experience. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) offers clinical practice resources to support clinicians as well as “Lifestyle Medicine and Food as Medicine Essentials,” a 5.5-hour complimentary CE/CME course on food and lifestyle medicine that introduces clinicians to the therapeutic use of lifestyle medicine. ACLM also offers members interest groups focused on geriatrics, fitness, and mental health, which may be beneficial to clinicians treating older adults.
By engaging with older patients on their lifestyle behaviors, we can ensure that we are doing all we can to help them live longer — and live better.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Caring for older adults was one of the most rewarding parts of my years practicing as a clinical cardiologist. I appreciated their wisdom, humor, and, very often, their respect and appreciation for physicians. It was always upsetting to see them suffer a mild fall or episode of atrial fibrillation and recognize that it could have major health ramifications.
That is not just a question for geriatric care. With fewer than two practicing geriatricians for every 10,000 older individuals, it is obvious that geriatricians cannot shoulder this responsibility alone. Almost all primary care physicians and subspecialists should prepare to care for older individuals and help them age healthfully.
Susan Friedman, MD, a board-certified geriatrics and lifestyle medicine clinician at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, reviewed the literature on the connection between lifestyle and healthy aging and concluded that the integration of lifestyle medicine into medical care for older adults is key to compressing morbidity. The pillars of lifestyle medicine — optimal nutrition, physical activity, stress management, restorative sleep, positive social connections, and avoidance of risky substances — both individually or as a sum are associated with less chronic disease, improved engagement in life, better physical and cognitive function, less frailty, and less sarcopenia. Framing discussions with patients around the six pillars of lifestyle medicine can be an effective strategy.
Optimal Nutrition
For a variety of reasons, older adults, especially those living alone, often lose the desire to prepare a nourishing meal. Older adults require different protein intake than younger patients to offset age-related sarcopenia, but helping them select healthy sources of protein is imperative. Both adequate protein consumption and eating patterns high in vegetables, legumes, fruit, and nuts and low in saturated fat, red meat, and processed meat can lower the risk of developing frailty.
Asking a patient to share a 24-hour food recall, and based upon that, resourcing nutritional guidance, a lifestyle medicine program or specialist, and insurance or community resources for food-as-medicine services, is a good first step.
Physical Activity
Increasing general physical activity can be a tough ask for many older adults, and joint pain is a common reason they demur. Messaging around targeted exercises to mitigate falls, improve muscle strength, and reduce joint pain may be more appealing. Contemporary research demonstrates that exercise, particularly open-skill exercise that requires quick decisions (such as table tennis) can be powerful. Maintaining cognition, mood enhancement, and independence may also be motivating messages.
The first step is curiosity: What does your patient like to do? Referral to a physical therapist or an exercise specialist to provide stepwise guidance along with resourcing community opportunities can then follow.
Restorative Sleep
“I’m old. I don’t need as much sleep.” We’ve probably all heard older patients say this. But the National Sleep Foundation’s report on sleep health and aging indicates that the need to sleep does not decrease with age. The ability to sleep, however, may decline. Assessing and treating disordered sleep is another example of how each lifestyle medicine pillar, such as nutrition and physical activity, is multidimensional and interacts to support the functional integrity of older patients. It’s hard to feel motivated to go for a walk if you lack adequate sleep.
Stress Management
Exploring stress with patients can be very revealing. Do they experience stress that energizes and has a positive effect? How much of their day is spent in negatively impactful distress? Chronic stress has been shown to affect immune function in older individuals. Start conversations with your older patients to normalize the importance of stress as a health measure.
Positive Social Connections
Loneliness puts individuals at higher risk for heart disease, stroke, and dementia and even increases the risk for premature death by up to 60%. Yet, clinicians and patients rarely discuss social connections during medical appointments. Tools such as the UCLA Loneliness Scale exist for health practitioners to assess and identify patients at risk for loneliness, as do resources to integrate social care into the delivery of healthcare.
Avoidance of Risky Substances
Alcohol assessments are not just for younger patients. One study found that 5.6 million adults ages 65 or older engaged in binge drinking in the past month. Because of body changes, the negative effects of alcohol may be greater on older adults, including interactions between alcohol and commonly prescribed medications.
Conducting a lifestyle assessment is an important way to engage with older patients and allows clinicians to identify opportunities to improve health behaviors, understand obstacles, and support patients to make lifestyle changes. It may uncover ways to remove some of the pill and treatment burdens that older adults often experience. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) offers clinical practice resources to support clinicians as well as “Lifestyle Medicine and Food as Medicine Essentials,” a 5.5-hour complimentary CE/CME course on food and lifestyle medicine that introduces clinicians to the therapeutic use of lifestyle medicine. ACLM also offers members interest groups focused on geriatrics, fitness, and mental health, which may be beneficial to clinicians treating older adults.
By engaging with older patients on their lifestyle behaviors, we can ensure that we are doing all we can to help them live longer — and live better.
Dr. Collings is director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How to Play Like a Masters Champ
You know what the happiest animal in the world is? A goldfish. You know why? It’s got a 10-second memory. Be a goldfish. — Ted Lasso
I don’t play much golf. When I do, it’s when my dad is in town. He shoots his age (78). I shoot double mine (52). He was recently here. We played and watched the Masters where he pointed out how I looked a lot like Scottie Scheffler, the now two-time Masters champion. On the 10th hole of his third round, you could see the resemblance. Scheffler’s third shot flew past the hole into the galley. He rifled the fourth past the hole on its way back toward the fairway. It was now a good distance further from the cup than a minute ago. He proceeded to misread his bogey putt, ending his misery with a double bogey. Scheffler went on to bogey the next hole and dropped from first on the leaderboard to fifth. Yes, I looked just like that on my last round. But here is where Scheffler and I differ. After a hole like that, I’d have been apoplectic, seething with self loathing. Scheffler was not. He kept moving. Head up, he sauntered to the next hole as if he had no awareness of what just transpired.
The ability to compartmentalize is useful not only to become the Masters champion, but also to become master of your day. In this way, golf is a nice approximation for life. The best golfers in the world will always have horrible shots and dreadful holes. The winning ones are often those who recover rather than continue in a downward spiral of one bad shot after another.
It’s easy to think of regular days that went just like Scheffler’s atrocious 10th hole. Getting pimped in front of distinguished faculty at Grand Rounds and whiffing (it was Sweet Syndrome). Calling a patient to let him know that his syphilis test did in fact come back positive (it was his father on the phone, also Mr. Rodham). Arguing with a patient that a biopsy was not needed for me to diagnose her with zoster (you’ve lost once, you’ve lost your temper). Each of these made me feel like slamming my club down, quitting the round right then and there. Losing control though, leads to flubbing the next question or arguing with the following patient. The masters let it go. Like goldfish, they live in the present without any thought of what happened 10 seconds ago.
We don’t have to take advice just from Ted Lasso here; there is plenty of research to support this concept of the critical relationship between resilience and psychological flexibility. Specifically, flexible cognitive control allows us to guide attention and to choose appropriate appraisal and good coping strategies. Ultimately, this leads to better performance. You might be a skilled athlete or presenter, but if you can’t regulate your emotions and something goes wrong, then you’ll perform as poorly as an amateur.
Scheffler went on to eagle the 13th hole on that round. He eventually won the 2024 Masters Tournament. Remember that the next time you find yourself in a day that feels like it is spiraling toward disaster. Close the door on the compartment that was the last miserable hole and saunter to the next patient like it never happened.
And maybe close the clubface a bit on address for your next drive.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
You know what the happiest animal in the world is? A goldfish. You know why? It’s got a 10-second memory. Be a goldfish. — Ted Lasso
I don’t play much golf. When I do, it’s when my dad is in town. He shoots his age (78). I shoot double mine (52). He was recently here. We played and watched the Masters where he pointed out how I looked a lot like Scottie Scheffler, the now two-time Masters champion. On the 10th hole of his third round, you could see the resemblance. Scheffler’s third shot flew past the hole into the galley. He rifled the fourth past the hole on its way back toward the fairway. It was now a good distance further from the cup than a minute ago. He proceeded to misread his bogey putt, ending his misery with a double bogey. Scheffler went on to bogey the next hole and dropped from first on the leaderboard to fifth. Yes, I looked just like that on my last round. But here is where Scheffler and I differ. After a hole like that, I’d have been apoplectic, seething with self loathing. Scheffler was not. He kept moving. Head up, he sauntered to the next hole as if he had no awareness of what just transpired.
The ability to compartmentalize is useful not only to become the Masters champion, but also to become master of your day. In this way, golf is a nice approximation for life. The best golfers in the world will always have horrible shots and dreadful holes. The winning ones are often those who recover rather than continue in a downward spiral of one bad shot after another.
It’s easy to think of regular days that went just like Scheffler’s atrocious 10th hole. Getting pimped in front of distinguished faculty at Grand Rounds and whiffing (it was Sweet Syndrome). Calling a patient to let him know that his syphilis test did in fact come back positive (it was his father on the phone, also Mr. Rodham). Arguing with a patient that a biopsy was not needed for me to diagnose her with zoster (you’ve lost once, you’ve lost your temper). Each of these made me feel like slamming my club down, quitting the round right then and there. Losing control though, leads to flubbing the next question or arguing with the following patient. The masters let it go. Like goldfish, they live in the present without any thought of what happened 10 seconds ago.
We don’t have to take advice just from Ted Lasso here; there is plenty of research to support this concept of the critical relationship between resilience and psychological flexibility. Specifically, flexible cognitive control allows us to guide attention and to choose appropriate appraisal and good coping strategies. Ultimately, this leads to better performance. You might be a skilled athlete or presenter, but if you can’t regulate your emotions and something goes wrong, then you’ll perform as poorly as an amateur.
Scheffler went on to eagle the 13th hole on that round. He eventually won the 2024 Masters Tournament. Remember that the next time you find yourself in a day that feels like it is spiraling toward disaster. Close the door on the compartment that was the last miserable hole and saunter to the next patient like it never happened.
And maybe close the clubface a bit on address for your next drive.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
You know what the happiest animal in the world is? A goldfish. You know why? It’s got a 10-second memory. Be a goldfish. — Ted Lasso
I don’t play much golf. When I do, it’s when my dad is in town. He shoots his age (78). I shoot double mine (52). He was recently here. We played and watched the Masters where he pointed out how I looked a lot like Scottie Scheffler, the now two-time Masters champion. On the 10th hole of his third round, you could see the resemblance. Scheffler’s third shot flew past the hole into the galley. He rifled the fourth past the hole on its way back toward the fairway. It was now a good distance further from the cup than a minute ago. He proceeded to misread his bogey putt, ending his misery with a double bogey. Scheffler went on to bogey the next hole and dropped from first on the leaderboard to fifth. Yes, I looked just like that on my last round. But here is where Scheffler and I differ. After a hole like that, I’d have been apoplectic, seething with self loathing. Scheffler was not. He kept moving. Head up, he sauntered to the next hole as if he had no awareness of what just transpired.
The ability to compartmentalize is useful not only to become the Masters champion, but also to become master of your day. In this way, golf is a nice approximation for life. The best golfers in the world will always have horrible shots and dreadful holes. The winning ones are often those who recover rather than continue in a downward spiral of one bad shot after another.
It’s easy to think of regular days that went just like Scheffler’s atrocious 10th hole. Getting pimped in front of distinguished faculty at Grand Rounds and whiffing (it was Sweet Syndrome). Calling a patient to let him know that his syphilis test did in fact come back positive (it was his father on the phone, also Mr. Rodham). Arguing with a patient that a biopsy was not needed for me to diagnose her with zoster (you’ve lost once, you’ve lost your temper). Each of these made me feel like slamming my club down, quitting the round right then and there. Losing control though, leads to flubbing the next question or arguing with the following patient. The masters let it go. Like goldfish, they live in the present without any thought of what happened 10 seconds ago.
We don’t have to take advice just from Ted Lasso here; there is plenty of research to support this concept of the critical relationship between resilience and psychological flexibility. Specifically, flexible cognitive control allows us to guide attention and to choose appropriate appraisal and good coping strategies. Ultimately, this leads to better performance. You might be a skilled athlete or presenter, but if you can’t regulate your emotions and something goes wrong, then you’ll perform as poorly as an amateur.
Scheffler went on to eagle the 13th hole on that round. He eventually won the 2024 Masters Tournament. Remember that the next time you find yourself in a day that feels like it is spiraling toward disaster. Close the door on the compartment that was the last miserable hole and saunter to the next patient like it never happened.
And maybe close the clubface a bit on address for your next drive.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on X. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Weighing the Benefits of Integrating AI-based Clinical Notes Into Your Practice
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Picture a healthcare system where physicians aren’t bogged down by excessive charting but are instead fully present with their patients, offering undivided attention and personalized care. In a recent X post, Stuart Blitz, COO and co-founder of Hone Health, sparked a thought-provoking conversation. “The problem with US healthcare is physicians are burned out since they spend way too much time charting, not enough with patients,” he wrote. “If you created a health system that did zero charting, you’d attract the best physicians and all patients would go there. Who is working on this?”
This resonates with many in the medical community, myself included, because the strain of extensive documentation detracts from patient care. Having worked in both large and small healthcare systems, I know the burden of extensive charting is a palpable challenge, often detracting from the time we can devote to our patients.
The first part of this two-part series examines the overarching benefits of artificial intelligence (AI)–based clinical documentation in modern healthcare, a field witnessing a paradigm shift thanks to advancements in AI.
Transformative Evolution of Clinical Documentation
The transition from manual documentation to AI-driven solutions marks a significant shift in the field, with a number of products in development including Nuance, Abridge, Ambience, ScribeAmerica, 3M, and DeepScribe. These tools use ambient clinical intelligence (ACI) to automate documentation, capturing patient conversations and translating them into structured clinical summaries. This innovation aligns with the vision of reducing charting burdens and enhancing patient-physician interactions.
How does it work? ACI refers to a sophisticated form of AI applied in healthcare settings, particularly focusing on enhancing the clinical documentation process without disrupting the natural flow of the consultation. Here’s a technical yet practical breakdown of ACI and the algorithms it typically employs:
Data capture and processing: ACI systems employ various sensors and processing units, typically integrated into clinical settings. These sensors, like microphones and cameras, gather diverse data such as audio from patient-doctor dialogues and visual cues. This information is then processed in real-time or near–real-time.
Natural language processing (NLP): A core component of ACI is advanced NLP algorithms. These algorithms analyze the captured audio data, transcribing spoken words into text. NLP goes beyond mere transcription; it involves understanding context, extracting relevant medical information (like symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans), and interpreting the nuances of human language.
Deep learning: Machine learning, particularly deep-learning techniques, are employed to improve the accuracy of ACI systems continually. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets of clinical interactions, enhancing their ability to transcribe and interpret future conversations accurately. As they learn, they become better at understanding different accents, complex medical terms, and variations in speech patterns.
Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): ACI systems are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems. They can automatically populate patient records with information from patient-clinician interactions, reducing manual entry and potential errors.
Customization and personalization: Many ACI systems offer customizable templates or allow clinicians to tailor documentation workflows. This flexibility ensures that the output aligns with the specific needs and preferences of healthcare providers.
Ethical and privacy considerations: ACI systems must navigate significant ethical and privacy concerns, especially related to patient consent and data security. These systems need to comply with healthcare privacy regulations such as HIPAA. They need to securely manage sensitive patient data and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Broad-Spectrum Benefits of AI in Documentation
- Reducing clinician burnout: By automating the documentation process, AI tools like DAX Copilot alleviate a significant contributor to physician burnout, enabling clinicians to focus more on patient care.
- Enhanced patient care: With AI handling documentation, clinicians can engage more with their patients, leading to improved care quality and patient satisfaction.
- Data accuracy and quality: AI-driven documentation captures detailed patient encounters accurately, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive medical records.
- Response to the growing need for efficient healthcare: AI-based documentation is a direct response to the growing call for more efficient healthcare practices, where clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more with patients.
The shift toward AI-based clinical documentation represents a critical step in addressing the inefficiencies in healthcare systems. It’s a move towards a more patient-centered approach, where clinicians can focus more on patient care by reducing the time spent on excessive charting. Hopefully, we can integrate these solutions into our clinics at a large enough scale to make such an impact.
In the next column, we will explore in-depth insights from Kenneth Harper at Nuance on the technical implementation of these tools, with DAX as an example.
I would love to read your comments on AI in clinical trials as well as other AI-related topics. Write me at Arturo.ai.medtech@gmail.com or find me on X @DrBonillaOnc.
Dr. Loaiza-Bonilla is the co-founder and chief medical officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as medical director of oncology research at Capital Health in New Jersey, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week. He has served as a consultant for Verify, PSI CRO, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Cardinal Health, BrightInsight, The Lynx Group, Fresenius, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Guardant; served as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Amgen, Guardant, Eisai, Ipsen, Natera, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca. He holds a 5% or greater equity interest in Massive Bio.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Federal Rule Delivers Workplace Support, Time Off for Pregnant Docs
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant physicians may receive more workplace accommodations and protection against discrimination thanks to an updated rule from the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). The guidelines could prevent women from losing critical career momentum.
The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) aims to help workers balance professional demands with healthy pregnancies. It requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for a “worker’s known limitations,” including physical or mental conditions associated with “pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.”
Reasonable accommodations vary but may involve time off to attend healthcare appointments or recover from childbirth, extra breaks during a shift, shorter work hours, or the ability to sit instead of stand. Private and public sector employers, including state and local governments, federal agencies, and employment agencies, must abide by the new guidelines unless they can provide evidence that doing so will cause undue hardship.
Female doctors have historically encountered significant barriers to family planning. Years of training cause them to delay having children, often leading to higher rates of infertility, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications than in the general population.
Some specialties, like surgeons, are particularly at risk, with 42% reporting at least one pregnancy loss. Most surgeons work their regular schedules until delivery despite desiring workload reductions, commonly citing unsupportive workplaces as a reason for not seeking accommodations.
Trauma surgeon Qaali Hussein, MD, became pregnant with her first child during her intern year in 2008. She told this news organization that her residency program didn’t even have a maternity policy at the time, and her male supervisor was certain that motherhood would end her surgical career.
She shared how “women usually waited until the end of their training to get pregnant. No one had ever gotten pregnant during the program and returned from maternity leave. I was the first to do so, so there wasn’t a policy or any program support to say, ‘What can we do to help?’ ”
Dr. Hussein used her vacation and sick time, returning to work 4 weeks after delivery. She had five more children, including twins her chief year and another baby during fellowship training in 2014.
Each subsequent pregnancy was met with the same response from program leadership, she recalled. “They’d say, ‘This is it. You may have been able to do the first and second child, but this one will be impossible.’ ”
After the PWFA regulations first became enforceable in June, the EEOC accepted public feedback. The guidelines received nearly 100,000 comments, spurred mainly by the inclusion of abortion care as a qualifying condition for which an employee could receive accommodations. About 54,000 comments called for abortion to be excluded from the final rule, and 40,000 supported keeping the clause.
The EEOC issued the final rule on April 15. It includes abortion care. However, the updated rule “does not require any employee to have — or not to have — an abortion, does not require taxpayers to pay for any abortions, and does not compel health care providers to provide any abortions,” the unpublished version of the final rule said. It is scheduled to take effect 60 days after its publication in the Federal Register on April 19.
Increasing Support for Doctor-Moms
The PWFA supplements other EEOC protections, such as pregnancy discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and access to reasonable accommodations under the Americans with Disabilities Act. In addition, it builds upon Department of Labor regulations, like the PUMP Act for breastfeeding employees and the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provides 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for the arrival of a child or certain medical conditions.
FMLA applies only to employees who have worked full-time for at least 12 months for an employer with 50 or more employees. Meanwhile, the unpaid, job-protected leave under the PWFA has no waiting period, lowers the required number of employees to 15, and permits accommodations for up to 40 weeks.
Employers are encouraged to honor “common and simple” requests, like using a closer parking space or pumping or nursing at work, without requiring a doctor’s note, the rule said.
Efforts to improve family leave policies for physicians and residents have been gaining traction. In 2021, the American Board of Medical Specialties began requiring its member boards with training programs lasting 2 or more years to allow at least 6 weeks off for parental, caregiver, and medical leave. This time can be taken without exhausting vacation or sick leave or requiring an extension in training. Over half of the 24 member boards permit leave beyond 6 weeks, including the American Boards of Allergy and Immunology, Emergency Medicine, Family Medicine, Radiology, and Surgery.
Estefania Oliveros, MD, MSc, cardiologist and assistant professor at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education also requires that residents and fellows receive 6 weeks of paid leave.
“We add to that vacation time, so it gives them at least 8 weeks,” she said. The school has created spaces for nursing mothers — something neither she nor Dr. Hussein had access to when breastfeeding — and encourages the attendings to be proactive in excusing pregnant fellows for appointments.
This differs significantly from her fellowship training experience 6 years ago at another institution, where she worked without accommodations until the day before her cesarean delivery. Dr. Oliveros had to use all her vacation time for recovery, returning to the program after 4 weeks instead of the recommended 6.
“And that’s the story you hear all the time. Not because people are ill-intended; I just don’t think the system is designed to accommodate women, so we lose a lot of talent that way,” said Dr. Oliveros, whose 2019 survey in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology called for more support and protections for pregnant doctors.
Both doctors believe the PWFA will be beneficial but only if leadership in the field takes up the cause.
“The cultures of these institutions determine whether women feel safe or even confident enough to have children in medical school or residency,” said Dr. Hussein.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AI Surpasses Harvard Docs on Clinical Reasoning Test
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The AI had more instances of incorrect reasoning than the doctors did but scored better overall.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 39 physicians from two academic medical centers in Boston and the generative AI model GPT-4.
- Participants were presented with 20 simulated clinical cases involving common problems such as pharyngitis, headache, abdominal pain, cough, and chest pain. Each case included sections describing the triage presentation, review of systems, physical examination, and diagnostic testing.
- The primary outcome was the Revised-IDEA (R-IDEA) score, a 10-point scale evaluating clinical reasoning documentation across four domains: Interpretive summary, differential diagnosis, explanation of the lead diagnosis, and alternative diagnoses.
TAKEAWAY:
- AI achieved a median R-IDEA score of 10, higher than attending physicians (median score, 9) and residents (8).
- The chatbot had a significantly higher estimated probability of achieving a high R-IDEA score of 8-10 (0.99) compared with attendings (0.76) and residents (0.56).
- AI provided more responses that contained instances of incorrect clinical reasoning (13.8%) than residents (2.8%) and attending physicians (12.5%). It performed similarly to physicians in diagnostic accuracy and inclusion of cannot-miss diagnoses.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should assess clinical reasoning of the LLM-physician interaction, as LLMs will more likely augment, not replace, the human reasoning process,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
Adam Rodman, MD, MPH, with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, was the corresponding author on the paper. The research was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Simulated clinical cases may not replicate performance in real-world scenarios. Further training could enhance the performance of the AI, so the study may underestimate its capabilities, the researchers noted.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center and Harvard University. Authors disclosed financial ties to publishing companies and Solera Health. Dr. Rodman received funding from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel PCSK9 Inhibitor Reduced LDL by 50%
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2024
Burnout
In last month’s column, I discussed employees who are “clock watchers” and how to address this issue in your practice if it exists. Here’s another scenario you may encounter from the Office Politics Forum at the recent American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting:
A 40-year-old dermatologist has practiced in the same office since residency and is loved by patients and staff. He remained with the practice through its takeover by a local hospital three years previously. Recently, over a 3-month period, everyone in the office notices a change in this dermatologist’s behavior. He no longer appears happy, is argumentative with staff and patients alike, often dismisses patients’ concerns, and calls in sick during the practice’s busiest days.
. According to the American Medical Association’s National Burnout Benchmarking report, over 50% of physicians report some characteristics of burnout, which include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a feeling of decreased personal achievement.
The causes of physician burnout are multifactorial and vary in importance, depending on the individual and on which authorities you consult. Here are some of the most prevalent, based on my experience and research:
Bureaucratic and Administrative Tasks: The burden of paperwork and other administrative responsibilities has increased, consuming time that could be spent on patient care or personal well-being.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Stress: As I (and many others) have predicted for decades, the demands of EHR documentation and the associated clerical tasks have become a major source of what is now called “technostress,” detracting from the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Insurance and Regulatory Demands: Navigating insurance appeals and prior authorizations, meeting regulatory requirements, and dealing with the complexities of healthcare reimbursement systems add to the stress and frustration experienced by physicians.
Lack of Autonomy and Control: As small practices consolidate, physicians often face constraints on their professional autonomy, with limited control over their work environment, schedules, and clinical decision-making, leading to feelings of helplessness and dissatisfaction.
Emotional Exhaustion from Patient Care: The emotional toll of caring for patients, especially in high-stakes or emotionally charged specialties, can lead to compassion fatigue and burnout. This may account for the results of a 2023 Medscape report in which physicians reporting the most burnout worked in emergency medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, obstetrics/gynecology, and infectious diseases.
Work-Life Imbalance: The demanding nature of the profession often leads to difficulties in balancing professional responsibilities with personal life, contributing to burnout.
Inadequate Support and Recognition: A lack of support from healthcare institutions and insufficient recognition of the challenges faced by physicians can exacerbate feelings of isolation and undervaluation.
Addressing physician burnout requires a systems-based approach that targets these root causes at all levels, from individual coping strategies to organizational and systemic changes in the healthcare industry. Here are some strategies that have worked for me and others:
Optimize Practice Efficiency: This is the consistent theme of this column over several decades: Streamline office processes to enhance the quality of care while reducing unnecessary workload. This can involve adopting efficient patient scheduling systems, improving clinic flow, and utilizing technology like patient portals judiciously to avoid increasing the task load without compensation.
Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage a culture that values work-life balance. This can include flexible scheduling, respecting off-duty hours by limiting non-emergency work communications, and using your vacation time. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.”
Implement Medical Scribes: I’ve written frequently about this, including a recent column on the new artificial intelligence (AI) scribes, such as DeepCura, DeepScribe, Nuance, Suki, Augmedix, Tali AI, Iodine Software, ScribeLink, and Amazon Web Services’ new HealthScribe product. Utilizing medical scribes to handle documentation can significantly reduce the administrative burden, allowing physicians to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork, potentially improving both physician and patient satisfaction. (As always, I have no financial interest in any product or service mentioned in this column.)
Provide Professional Development Opportunities: Offer opportunities for professional growth and development. This can include attending conferences, participating in research, or providing time and resources for continuing education. Such opportunities can reinvigorate a physician’s passion for medicine and improve job satisfaction.
Foster a Supportive Work Environment: Create a supportive work culture where staff and physicians feel comfortable discussing challenges and seeking support. Regular meetings or check-ins can help identify early signs of burnout and address them proactively.
Evaluate and Adjust Workloads: Regularly assess physician workloads to ensure they are manageable. Adjusting patient loads, redistributing tasks among team members, or hiring additional staff can help prevent burnout.
Leadership Training and Support: Provide training for leaders within the practice on recognizing signs of burnout and effective management strategies. Supportive leadership is crucial in creating an environment where physicians feel valued and heard.
Peer Support and Mentorship Programs: Establish peer support or mentorship programs where physicians can share experiences, offer advice, and provide emotional support to each other.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Managers should regularly solicit feedback from physicians regarding their workload, job satisfaction, and suggestions for improvements. Actively work on implementing feasible changes to address concerns.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
In last month’s column, I discussed employees who are “clock watchers” and how to address this issue in your practice if it exists. Here’s another scenario you may encounter from the Office Politics Forum at the recent American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting:
A 40-year-old dermatologist has practiced in the same office since residency and is loved by patients and staff. He remained with the practice through its takeover by a local hospital three years previously. Recently, over a 3-month period, everyone in the office notices a change in this dermatologist’s behavior. He no longer appears happy, is argumentative with staff and patients alike, often dismisses patients’ concerns, and calls in sick during the practice’s busiest days.
. According to the American Medical Association’s National Burnout Benchmarking report, over 50% of physicians report some characteristics of burnout, which include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a feeling of decreased personal achievement.
The causes of physician burnout are multifactorial and vary in importance, depending on the individual and on which authorities you consult. Here are some of the most prevalent, based on my experience and research:
Bureaucratic and Administrative Tasks: The burden of paperwork and other administrative responsibilities has increased, consuming time that could be spent on patient care or personal well-being.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Stress: As I (and many others) have predicted for decades, the demands of EHR documentation and the associated clerical tasks have become a major source of what is now called “technostress,” detracting from the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Insurance and Regulatory Demands: Navigating insurance appeals and prior authorizations, meeting regulatory requirements, and dealing with the complexities of healthcare reimbursement systems add to the stress and frustration experienced by physicians.
Lack of Autonomy and Control: As small practices consolidate, physicians often face constraints on their professional autonomy, with limited control over their work environment, schedules, and clinical decision-making, leading to feelings of helplessness and dissatisfaction.
Emotional Exhaustion from Patient Care: The emotional toll of caring for patients, especially in high-stakes or emotionally charged specialties, can lead to compassion fatigue and burnout. This may account for the results of a 2023 Medscape report in which physicians reporting the most burnout worked in emergency medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, obstetrics/gynecology, and infectious diseases.
Work-Life Imbalance: The demanding nature of the profession often leads to difficulties in balancing professional responsibilities with personal life, contributing to burnout.
Inadequate Support and Recognition: A lack of support from healthcare institutions and insufficient recognition of the challenges faced by physicians can exacerbate feelings of isolation and undervaluation.
Addressing physician burnout requires a systems-based approach that targets these root causes at all levels, from individual coping strategies to organizational and systemic changes in the healthcare industry. Here are some strategies that have worked for me and others:
Optimize Practice Efficiency: This is the consistent theme of this column over several decades: Streamline office processes to enhance the quality of care while reducing unnecessary workload. This can involve adopting efficient patient scheduling systems, improving clinic flow, and utilizing technology like patient portals judiciously to avoid increasing the task load without compensation.
Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage a culture that values work-life balance. This can include flexible scheduling, respecting off-duty hours by limiting non-emergency work communications, and using your vacation time. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.”
Implement Medical Scribes: I’ve written frequently about this, including a recent column on the new artificial intelligence (AI) scribes, such as DeepCura, DeepScribe, Nuance, Suki, Augmedix, Tali AI, Iodine Software, ScribeLink, and Amazon Web Services’ new HealthScribe product. Utilizing medical scribes to handle documentation can significantly reduce the administrative burden, allowing physicians to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork, potentially improving both physician and patient satisfaction. (As always, I have no financial interest in any product or service mentioned in this column.)
Provide Professional Development Opportunities: Offer opportunities for professional growth and development. This can include attending conferences, participating in research, or providing time and resources for continuing education. Such opportunities can reinvigorate a physician’s passion for medicine and improve job satisfaction.
Foster a Supportive Work Environment: Create a supportive work culture where staff and physicians feel comfortable discussing challenges and seeking support. Regular meetings or check-ins can help identify early signs of burnout and address them proactively.
Evaluate and Adjust Workloads: Regularly assess physician workloads to ensure they are manageable. Adjusting patient loads, redistributing tasks among team members, or hiring additional staff can help prevent burnout.
Leadership Training and Support: Provide training for leaders within the practice on recognizing signs of burnout and effective management strategies. Supportive leadership is crucial in creating an environment where physicians feel valued and heard.
Peer Support and Mentorship Programs: Establish peer support or mentorship programs where physicians can share experiences, offer advice, and provide emotional support to each other.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Managers should regularly solicit feedback from physicians regarding their workload, job satisfaction, and suggestions for improvements. Actively work on implementing feasible changes to address concerns.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
In last month’s column, I discussed employees who are “clock watchers” and how to address this issue in your practice if it exists. Here’s another scenario you may encounter from the Office Politics Forum at the recent American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting:
A 40-year-old dermatologist has practiced in the same office since residency and is loved by patients and staff. He remained with the practice through its takeover by a local hospital three years previously. Recently, over a 3-month period, everyone in the office notices a change in this dermatologist’s behavior. He no longer appears happy, is argumentative with staff and patients alike, often dismisses patients’ concerns, and calls in sick during the practice’s busiest days.
. According to the American Medical Association’s National Burnout Benchmarking report, over 50% of physicians report some characteristics of burnout, which include emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a feeling of decreased personal achievement.
The causes of physician burnout are multifactorial and vary in importance, depending on the individual and on which authorities you consult. Here are some of the most prevalent, based on my experience and research:
Bureaucratic and Administrative Tasks: The burden of paperwork and other administrative responsibilities has increased, consuming time that could be spent on patient care or personal well-being.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Stress: As I (and many others) have predicted for decades, the demands of EHR documentation and the associated clerical tasks have become a major source of what is now called “technostress,” detracting from the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Insurance and Regulatory Demands: Navigating insurance appeals and prior authorizations, meeting regulatory requirements, and dealing with the complexities of healthcare reimbursement systems add to the stress and frustration experienced by physicians.
Lack of Autonomy and Control: As small practices consolidate, physicians often face constraints on their professional autonomy, with limited control over their work environment, schedules, and clinical decision-making, leading to feelings of helplessness and dissatisfaction.
Emotional Exhaustion from Patient Care: The emotional toll of caring for patients, especially in high-stakes or emotionally charged specialties, can lead to compassion fatigue and burnout. This may account for the results of a 2023 Medscape report in which physicians reporting the most burnout worked in emergency medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, obstetrics/gynecology, and infectious diseases.
Work-Life Imbalance: The demanding nature of the profession often leads to difficulties in balancing professional responsibilities with personal life, contributing to burnout.
Inadequate Support and Recognition: A lack of support from healthcare institutions and insufficient recognition of the challenges faced by physicians can exacerbate feelings of isolation and undervaluation.
Addressing physician burnout requires a systems-based approach that targets these root causes at all levels, from individual coping strategies to organizational and systemic changes in the healthcare industry. Here are some strategies that have worked for me and others:
Optimize Practice Efficiency: This is the consistent theme of this column over several decades: Streamline office processes to enhance the quality of care while reducing unnecessary workload. This can involve adopting efficient patient scheduling systems, improving clinic flow, and utilizing technology like patient portals judiciously to avoid increasing the task load without compensation.
Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage a culture that values work-life balance. This can include flexible scheduling, respecting off-duty hours by limiting non-emergency work communications, and using your vacation time. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.”
Implement Medical Scribes: I’ve written frequently about this, including a recent column on the new artificial intelligence (AI) scribes, such as DeepCura, DeepScribe, Nuance, Suki, Augmedix, Tali AI, Iodine Software, ScribeLink, and Amazon Web Services’ new HealthScribe product. Utilizing medical scribes to handle documentation can significantly reduce the administrative burden, allowing physicians to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork, potentially improving both physician and patient satisfaction. (As always, I have no financial interest in any product or service mentioned in this column.)
Provide Professional Development Opportunities: Offer opportunities for professional growth and development. This can include attending conferences, participating in research, or providing time and resources for continuing education. Such opportunities can reinvigorate a physician’s passion for medicine and improve job satisfaction.
Foster a Supportive Work Environment: Create a supportive work culture where staff and physicians feel comfortable discussing challenges and seeking support. Regular meetings or check-ins can help identify early signs of burnout and address them proactively.
Evaluate and Adjust Workloads: Regularly assess physician workloads to ensure they are manageable. Adjusting patient loads, redistributing tasks among team members, or hiring additional staff can help prevent burnout.
Leadership Training and Support: Provide training for leaders within the practice on recognizing signs of burnout and effective management strategies. Supportive leadership is crucial in creating an environment where physicians feel valued and heard.
Peer Support and Mentorship Programs: Establish peer support or mentorship programs where physicians can share experiences, offer advice, and provide emotional support to each other.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Managers should regularly solicit feedback from physicians regarding their workload, job satisfaction, and suggestions for improvements. Actively work on implementing feasible changes to address concerns.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.





