User login
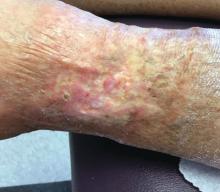
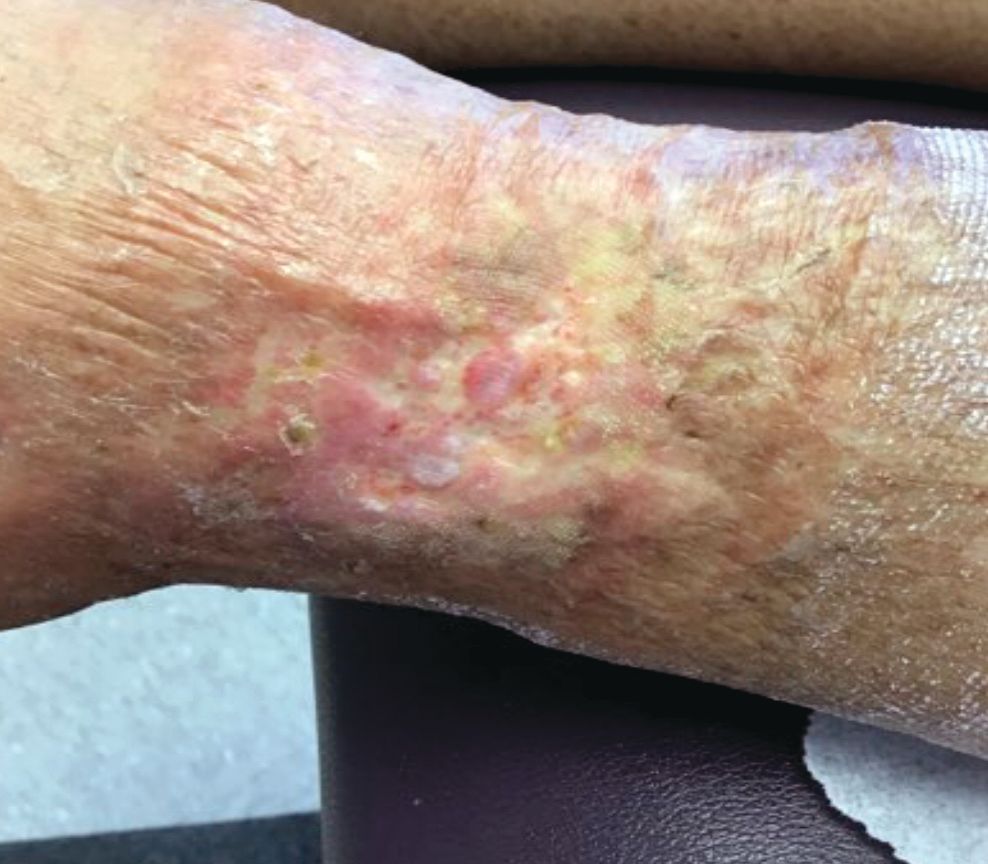
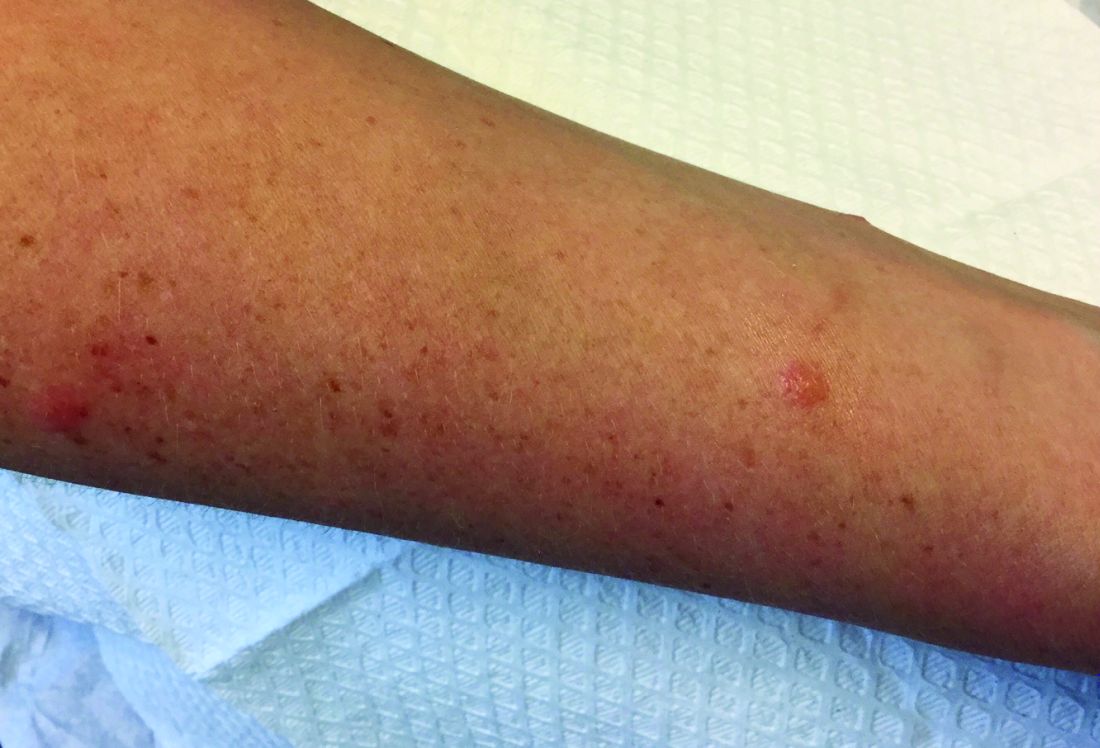
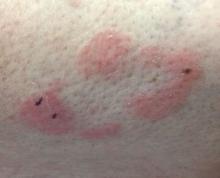
A 60-year-old white woman presented with a 3-month history of a painful, nonhealing ulceration on her left lateral lower leg
It is a vasculopathy rather than a vasculitis as the former is caused by occlusion of blood vessels and the latter results from inflammation of the vessels. Middle-aged women tend to be affected more frequently. Although the exact cause is unclear, systemic diseases, such as hypercoagulable states, may predispose vessels to develop occlusion. Associated disorders include antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C deficiency, factor V mutation, arteriosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, and hepatitis C.
Typically, lesions begin as painful purpura or reticulated macules on the lower extremities that ulcerate and heal very slowly. Ankles, particularly malleoli, are more frequently affected. When they heal, they form painless white stellate scars typical of atrophie blanche. Surrounding erythema, telangiectasias, and sclerosis may be present; livedo reticularis may be seen as well.
Histologically, the epidermis may be atrophic or necrotic. Hyaline thickening of the blood vessel walls is seen. Thrombi may be present. Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin may be positive for complement C3 and immunoglobulin (IgM) in dermal blood vessels.
Livedoid vasculopathy can be difficult to treat. Treatment is aimed at reducing clotting and improving blood flow and includes antiplatelet drugs (low-dose aspirin, dipyridamole), anticoagulants, and vasodilating agents (nifedipine). Pentoxifylline two or three times daily may help by altering blood viscosity. A recent literature search reports success in topical dapsone applied to lesions twice daily under occlusion. Leg elevation and compression stockings help healing. Livedoid vasculopathy may have periods of activity and remission.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com
It is a vasculopathy rather than a vasculitis as the former is caused by occlusion of blood vessels and the latter results from inflammation of the vessels. Middle-aged women tend to be affected more frequently. Although the exact cause is unclear, systemic diseases, such as hypercoagulable states, may predispose vessels to develop occlusion. Associated disorders include antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C deficiency, factor V mutation, arteriosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, and hepatitis C.
Typically, lesions begin as painful purpura or reticulated macules on the lower extremities that ulcerate and heal very slowly. Ankles, particularly malleoli, are more frequently affected. When they heal, they form painless white stellate scars typical of atrophie blanche. Surrounding erythema, telangiectasias, and sclerosis may be present; livedo reticularis may be seen as well.
Histologically, the epidermis may be atrophic or necrotic. Hyaline thickening of the blood vessel walls is seen. Thrombi may be present. Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin may be positive for complement C3 and immunoglobulin (IgM) in dermal blood vessels.
Livedoid vasculopathy can be difficult to treat. Treatment is aimed at reducing clotting and improving blood flow and includes antiplatelet drugs (low-dose aspirin, dipyridamole), anticoagulants, and vasodilating agents (nifedipine). Pentoxifylline two or three times daily may help by altering blood viscosity. A recent literature search reports success in topical dapsone applied to lesions twice daily under occlusion. Leg elevation and compression stockings help healing. Livedoid vasculopathy may have periods of activity and remission.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com
It is a vasculopathy rather than a vasculitis as the former is caused by occlusion of blood vessels and the latter results from inflammation of the vessels. Middle-aged women tend to be affected more frequently. Although the exact cause is unclear, systemic diseases, such as hypercoagulable states, may predispose vessels to develop occlusion. Associated disorders include antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C deficiency, factor V mutation, arteriosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, and hepatitis C.
Typically, lesions begin as painful purpura or reticulated macules on the lower extremities that ulcerate and heal very slowly. Ankles, particularly malleoli, are more frequently affected. When they heal, they form painless white stellate scars typical of atrophie blanche. Surrounding erythema, telangiectasias, and sclerosis may be present; livedo reticularis may be seen as well.
Histologically, the epidermis may be atrophic or necrotic. Hyaline thickening of the blood vessel walls is seen. Thrombi may be present. Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin may be positive for complement C3 and immunoglobulin (IgM) in dermal blood vessels.
Livedoid vasculopathy can be difficult to treat. Treatment is aimed at reducing clotting and improving blood flow and includes antiplatelet drugs (low-dose aspirin, dipyridamole), anticoagulants, and vasodilating agents (nifedipine). Pentoxifylline two or three times daily may help by altering blood viscosity. A recent literature search reports success in topical dapsone applied to lesions twice daily under occlusion. Leg elevation and compression stockings help healing. Livedoid vasculopathy may have periods of activity and remission.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com
December 2018
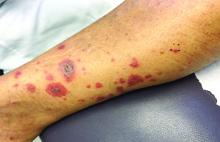
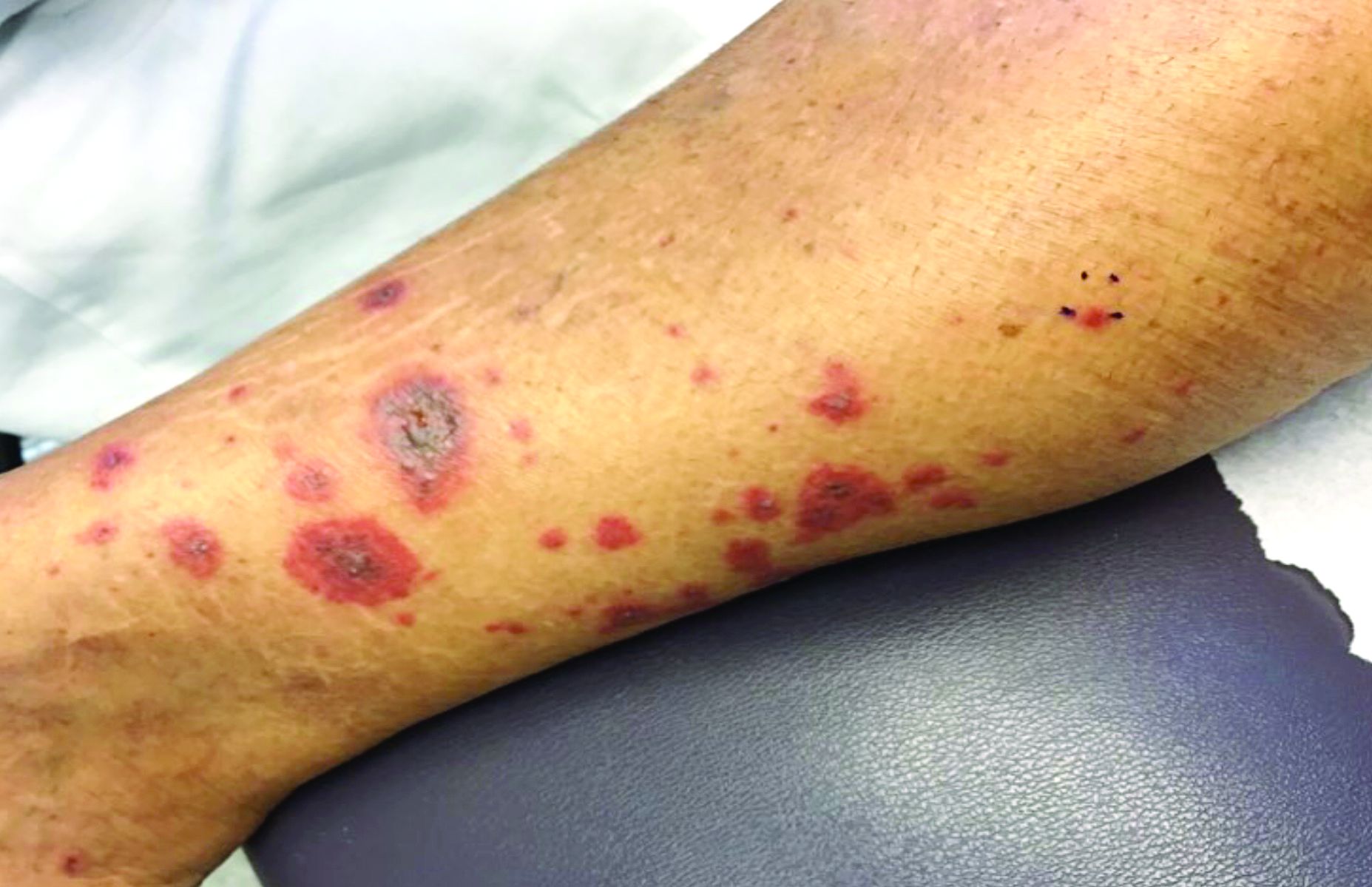
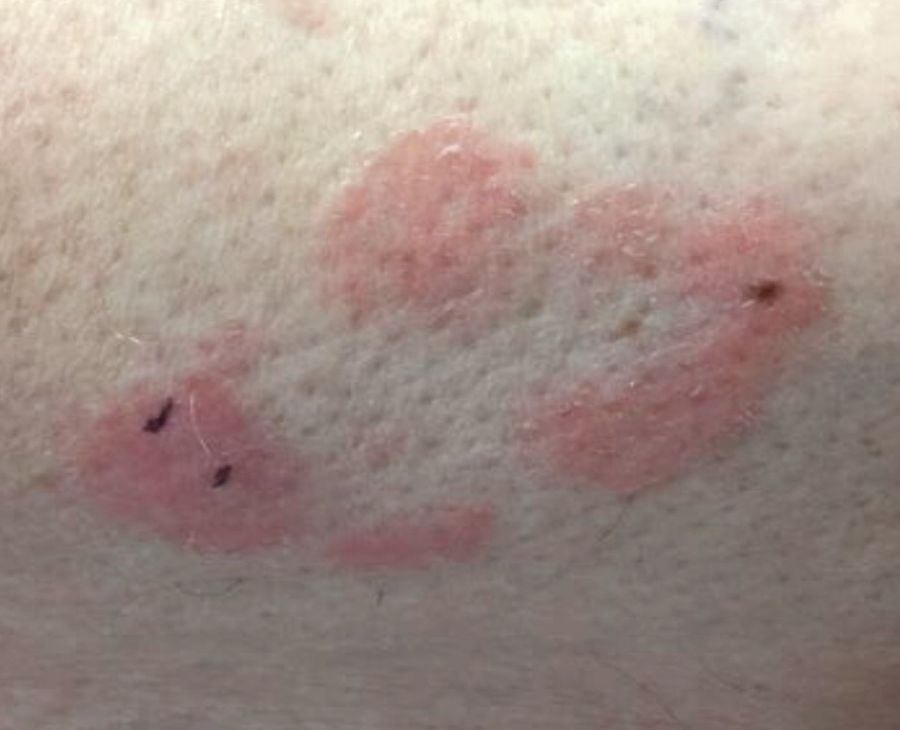
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Vasculitis is a process in which blood vessels become inflamed and necrotic. Classic small-vessel vasculitis reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis and most commonly presents as palpable purpura. In addition to skin, organs such as joints, kidneys, and intestines can be involved.
where immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the vessel walls. It is the most common form of vasculitis in children (usually aged 4-8 years). The incidence is higher in the winter. Some patients experience a prodrome of fever, colicky abdominal pain, and joint pain prior to the development of cutaneous symptoms. Disease in children tends to be self-limited. Adults may present with HSP as well, and often exhibit more severe disease that may become chronic with relapses and is more difficult to treat. In both children and adults, infectious causes, such as streptococcus pharyngitis, are the most common trigger. In adults, malignancy may be associated with HSP. A literature search revealed medications implicated in HSP such as antibiotics (vancomycin, penicillin, cephalosporins, clarithromycin), ACE inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Many cases of HSP are idiopathic.
Patients present with erythematous macules that progress to purpura on the extremities. Lesions may be vesicular or bullous and may become necrotic and ulcerate. Arthralgias, often of lower-extremity joints, may be present. Abdominal pain and renal disease may occur in both children and adults. Adults are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease and must be followed carefully with serial blood work and urinalysis to evaluate for hematuria and proteinuria. Severe abdominal pain is an emergency as intussusception may occur.
Histologically, leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels is present. On direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin, IgA, C3, and fibrin deposits can be seen. Serum IgA is unreliable and may be seen in healthy adults as well.
Treatment is generally supportive as the disease is self-limited. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. This may be effective for joint inflammation, abdominal disease, active nephritis, and ulcerated skin lesions, but doesn’t prevent the recurrence of skin lesions. Dapsone or colchicine can be used for resistant cutaneous lesions. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin may be warranted.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
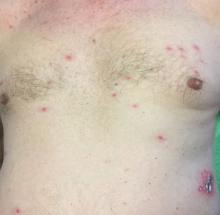
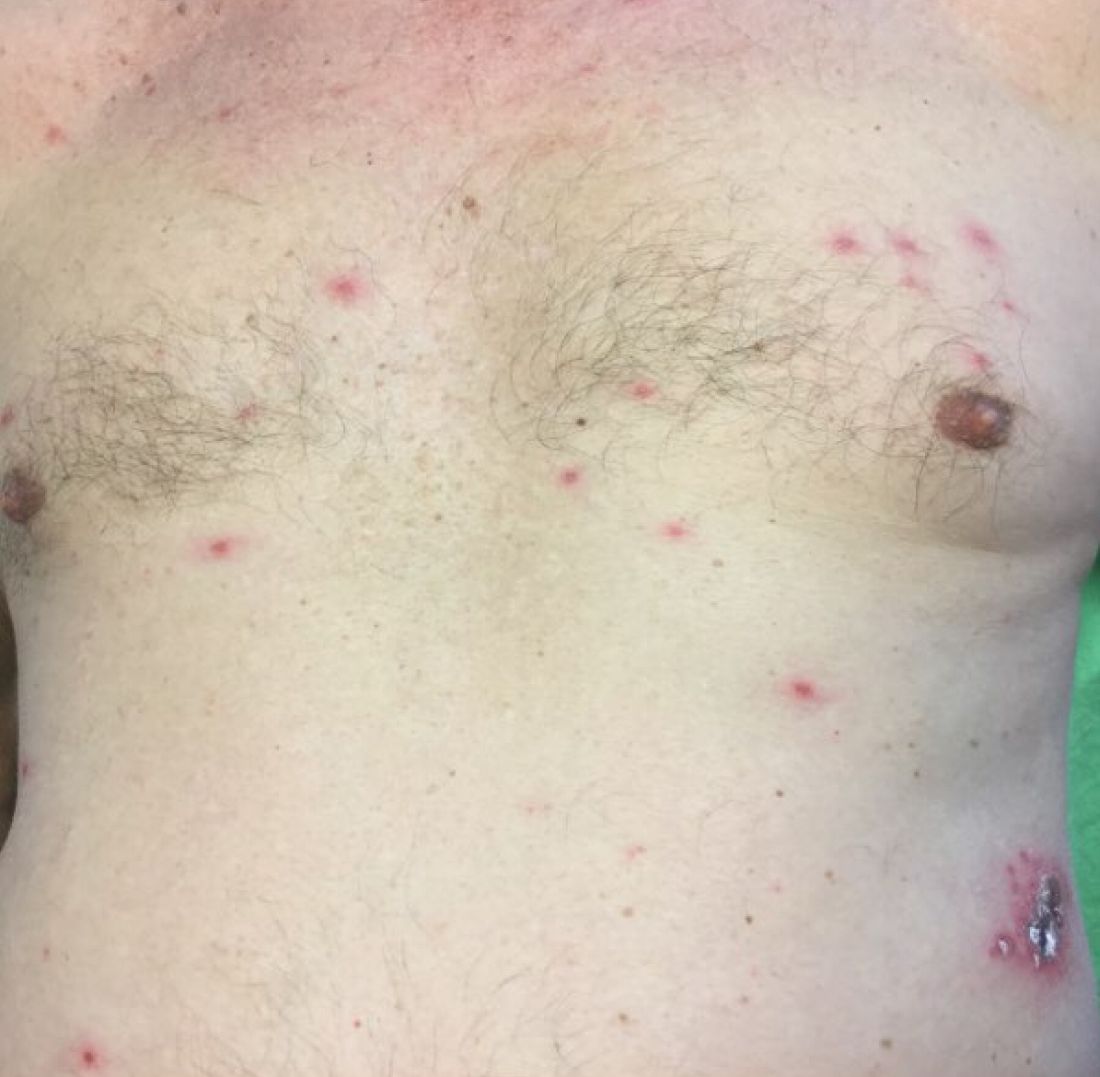
A 63-year-old white female presented with a 2-week history of hemorrhagic purpuric lesions and necrotic vesicles on the bilateral lower extremities.
Nearly 1 year prior to presentation, the patient underwent surgical resection for lung cancer. The patient also complained of joint swelling and pain in her ankles. She denied abdominal pain. She denied recent illness, including sore throat and upper respiratory infection. Skin biopsies were performed, including for direct immunofluorescence.
December 2018
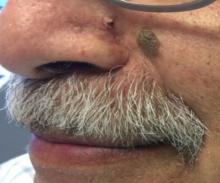
. White individuals over aged 50 years are more frequently affected. Both genders are equally affected, and 25% of cases occur on the covered areas (trunk or extremities) of younger patients. Clinically, lesions present as pink to red plaques or nodules that exhibit rapid growth. Ulceration or crusting may be present. Causes of AFX include ultraviolet radiation and ionizing radiation. AFX is considered a superficial variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH), the most common soft tissue sarcoma of adults. Clinically, MFH involves deeper tissues than does AFX, often on the thighs or buttocks. MFH is a more aggressive malignancy that regularly metastasizes.
Histologically, the tumor occurs as a dermal proliferation of “bizarre” spindle cells, epithelioid cells, and atypical histiocytes. Vesicular changes may be present in the nucleus or cytoplasm of the spindle cells. Mitotic figures are present. Multinucleated giant cells may be present. Solar elastosis is often seen, as well. Vimentin and histiocyte stains are positive. Unlike melanoma, S-100 staining is minimal. Unlike squamous cell carcinoma, prekeratin staining is negative. CD34 is negative. AFX resembles MFH histologically.
Surgical excision by the Mohs procedure is preferred over wide excision as there is a risk of recurrence. AFX rarely metastasizes. This is more likely if inadequately excised or the patient is immunosuppressed. Sun protective practices, such as applying and reapplying sunscreen regularly, wearing sun protective clothing, and avoiding excessive UV exposure during peak hours is recommended.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
. White individuals over aged 50 years are more frequently affected. Both genders are equally affected, and 25% of cases occur on the covered areas (trunk or extremities) of younger patients. Clinically, lesions present as pink to red plaques or nodules that exhibit rapid growth. Ulceration or crusting may be present. Causes of AFX include ultraviolet radiation and ionizing radiation. AFX is considered a superficial variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH), the most common soft tissue sarcoma of adults. Clinically, MFH involves deeper tissues than does AFX, often on the thighs or buttocks. MFH is a more aggressive malignancy that regularly metastasizes.
Histologically, the tumor occurs as a dermal proliferation of “bizarre” spindle cells, epithelioid cells, and atypical histiocytes. Vesicular changes may be present in the nucleus or cytoplasm of the spindle cells. Mitotic figures are present. Multinucleated giant cells may be present. Solar elastosis is often seen, as well. Vimentin and histiocyte stains are positive. Unlike melanoma, S-100 staining is minimal. Unlike squamous cell carcinoma, prekeratin staining is negative. CD34 is negative. AFX resembles MFH histologically.
Surgical excision by the Mohs procedure is preferred over wide excision as there is a risk of recurrence. AFX rarely metastasizes. This is more likely if inadequately excised or the patient is immunosuppressed. Sun protective practices, such as applying and reapplying sunscreen regularly, wearing sun protective clothing, and avoiding excessive UV exposure during peak hours is recommended.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
. White individuals over aged 50 years are more frequently affected. Both genders are equally affected, and 25% of cases occur on the covered areas (trunk or extremities) of younger patients. Clinically, lesions present as pink to red plaques or nodules that exhibit rapid growth. Ulceration or crusting may be present. Causes of AFX include ultraviolet radiation and ionizing radiation. AFX is considered a superficial variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH), the most common soft tissue sarcoma of adults. Clinically, MFH involves deeper tissues than does AFX, often on the thighs or buttocks. MFH is a more aggressive malignancy that regularly metastasizes.
Histologically, the tumor occurs as a dermal proliferation of “bizarre” spindle cells, epithelioid cells, and atypical histiocytes. Vesicular changes may be present in the nucleus or cytoplasm of the spindle cells. Mitotic figures are present. Multinucleated giant cells may be present. Solar elastosis is often seen, as well. Vimentin and histiocyte stains are positive. Unlike melanoma, S-100 staining is minimal. Unlike squamous cell carcinoma, prekeratin staining is negative. CD34 is negative. AFX resembles MFH histologically.
Surgical excision by the Mohs procedure is preferred over wide excision as there is a risk of recurrence. AFX rarely metastasizes. This is more likely if inadequately excised or the patient is immunosuppressed. Sun protective practices, such as applying and reapplying sunscreen regularly, wearing sun protective clothing, and avoiding excessive UV exposure during peak hours is recommended.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
November 2018
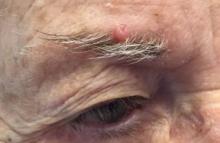
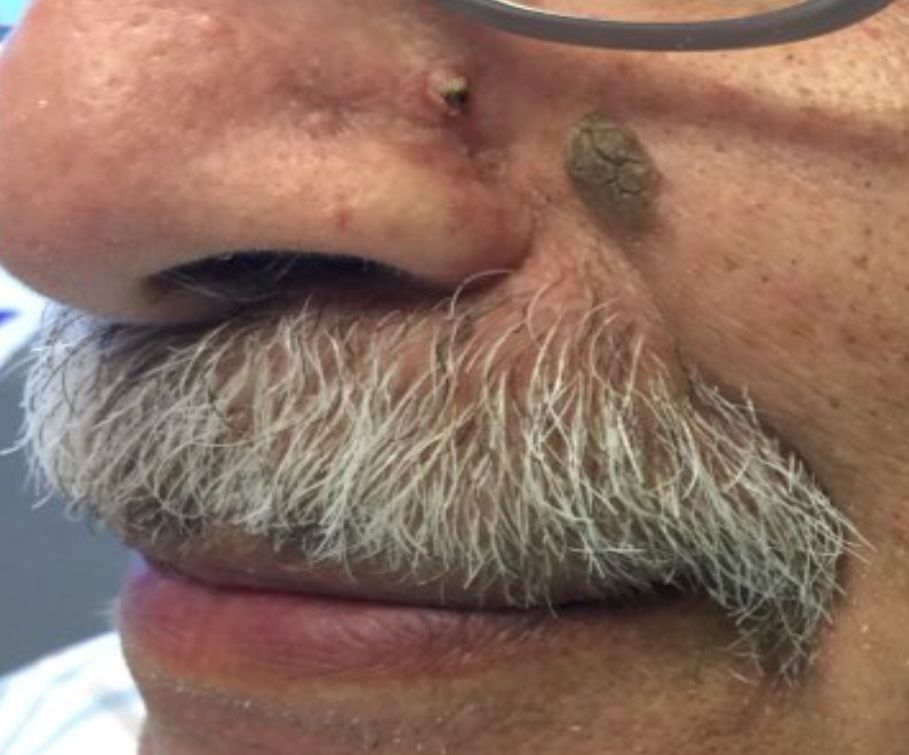
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma
that presents as a solitary, skin colored lesion on the midface. Lesions may appear smooth or verrucous. Lesions may occur alongside trichoepitheliomas. They may also occur on genital skin and resemble condyloma acuminata.
Histopathology reveals downward lobular growth of the epidermis. Keratinocytes are clear secondary to periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)–positive glycogen in the cells. In desmoplastic trichilemmoma, small clusters of cells are arranged in an infiltrative pattern that resembles invasive carcinoma. Often, the desmoplastic areas are surrounded by benign-appearing trichilemmomas, which helps to make the diagnosis. Desmoplastic trichilemmomas can also occur within nevus sebaceous. As trichilemmoma is a benign growth; no treatment is needed. However, if further removal is desired, electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, shave removal, or excision are treatment options. Rarely seen, the malignant counterpart to trichilemmomas is a trichilemmal carcinoma, which requires surgical excision or Mohs.
The appearance of multiple trichilemmomas is a marker for Cowden syndrome. Cowden syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder in which there is a mutation in a tumor-suppressor gene called PTEN. Patients may have oral mucosal papillomas, sclerotic fibromas, acral keratotic papules, and are at risk for the development of adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, and thyroid.
Trichoepithelioma is a benign neoplasm derived from follicular germ cells that presents as a skin-colored papule on the midface, especially the nose. Multiple trichoepitheliomas are a marker for Brooke-Spiegler syndrome. A desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is a variant that has stromal sclerosis on pathology. It is a benign lesion, although may be difficult to differentiate from sclerosing basal cell or microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
Angiofibroma, or fibrous papule, is a commonly seen, benign, skin-colored papule also often occurring on the nose. They can be treated for cosmetic purposes. Multiple lesions are associated with tuberous sclerosis.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma
that presents as a solitary, skin colored lesion on the midface. Lesions may appear smooth or verrucous. Lesions may occur alongside trichoepitheliomas. They may also occur on genital skin and resemble condyloma acuminata.
Histopathology reveals downward lobular growth of the epidermis. Keratinocytes are clear secondary to periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)–positive glycogen in the cells. In desmoplastic trichilemmoma, small clusters of cells are arranged in an infiltrative pattern that resembles invasive carcinoma. Often, the desmoplastic areas are surrounded by benign-appearing trichilemmomas, which helps to make the diagnosis. Desmoplastic trichilemmomas can also occur within nevus sebaceous. As trichilemmoma is a benign growth; no treatment is needed. However, if further removal is desired, electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, shave removal, or excision are treatment options. Rarely seen, the malignant counterpart to trichilemmomas is a trichilemmal carcinoma, which requires surgical excision or Mohs.
The appearance of multiple trichilemmomas is a marker for Cowden syndrome. Cowden syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder in which there is a mutation in a tumor-suppressor gene called PTEN. Patients may have oral mucosal papillomas, sclerotic fibromas, acral keratotic papules, and are at risk for the development of adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, and thyroid.
Trichoepithelioma is a benign neoplasm derived from follicular germ cells that presents as a skin-colored papule on the midface, especially the nose. Multiple trichoepitheliomas are a marker for Brooke-Spiegler syndrome. A desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is a variant that has stromal sclerosis on pathology. It is a benign lesion, although may be difficult to differentiate from sclerosing basal cell or microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
Angiofibroma, or fibrous papule, is a commonly seen, benign, skin-colored papule also often occurring on the nose. They can be treated for cosmetic purposes. Multiple lesions are associated with tuberous sclerosis.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma
that presents as a solitary, skin colored lesion on the midface. Lesions may appear smooth or verrucous. Lesions may occur alongside trichoepitheliomas. They may also occur on genital skin and resemble condyloma acuminata.
Histopathology reveals downward lobular growth of the epidermis. Keratinocytes are clear secondary to periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)–positive glycogen in the cells. In desmoplastic trichilemmoma, small clusters of cells are arranged in an infiltrative pattern that resembles invasive carcinoma. Often, the desmoplastic areas are surrounded by benign-appearing trichilemmomas, which helps to make the diagnosis. Desmoplastic trichilemmomas can also occur within nevus sebaceous. As trichilemmoma is a benign growth; no treatment is needed. However, if further removal is desired, electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, shave removal, or excision are treatment options. Rarely seen, the malignant counterpart to trichilemmomas is a trichilemmal carcinoma, which requires surgical excision or Mohs.
The appearance of multiple trichilemmomas is a marker for Cowden syndrome. Cowden syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder in which there is a mutation in a tumor-suppressor gene called PTEN. Patients may have oral mucosal papillomas, sclerotic fibromas, acral keratotic papules, and are at risk for the development of adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, and thyroid.
Trichoepithelioma is a benign neoplasm derived from follicular germ cells that presents as a skin-colored papule on the midface, especially the nose. Multiple trichoepitheliomas are a marker for Brooke-Spiegler syndrome. A desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is a variant that has stromal sclerosis on pathology. It is a benign lesion, although may be difficult to differentiate from sclerosing basal cell or microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
Angiofibroma, or fibrous papule, is a commonly seen, benign, skin-colored papule also often occurring on the nose. They can be treated for cosmetic purposes. Multiple lesions are associated with tuberous sclerosis.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
October 2018
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can affect individuals regardless of age, race, or sex, but ACD accounts for 20% of all contact dermatitis reactions. ACD results in an inflammatory reaction in those who have been previously sensitized to an allergen. This type of delayed hypersensitivity reaction is known as cell-mediated hypersensitivity. Generally, no reaction is elicited upon the first exposure to the allergen. In fact, it may take years of exposure to allergens for someone to develop an allergic contact dermatitis.
Once sensitized, epidermal antigen-presenting cells (APCs) called Langerhans cells process the allergen and present it in a complex on the surface of the cell to a CD4+ T cell. Subsequently, inflammatory cytokines and mediators are released, resulting in an allergic cutaneous (eczematous) reaction. Lesions may appear to be vesicular or bullous. Occasionally, a generalized eruption may occur. With repeated exposure, reactions may be acute or chronic.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include toxicodendron plants (poison ivy, oak, and sumac; cashew nut tree; and mango), metals (nickel and gold), topical antibiotics (neomycin and bacitracin), fragrance and Balsam of Peru, deodorant, preservatives (formaldehyde), and rubber (elastic and gloves).
Patch testing is the standard means of detecting which allergen is causing the sensitization in an individual. The Thin-Layer Rapid Use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test or individually prepared aluminum (Finn) chambers containing the most common allergens are applied to the patient’s upper back. The patches are removed after 48 hours and read, and then reevaluated at day 4 or 5. Positive reactions appear as eczematous or vesicular papules or plaques.
Treatment includes avoidance of the allergens. Topical corticosteroid creams are helpful. For severe or generalized reactions, oral prednisone may be used. It is important to note that patient may be allergic to topical steroids. Patch testing can be performed to elucidate such allergens.
In contrast, 80% of contact dermatitis reactions are irritant, not allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results is a local inflammatory reaction in people who have come into contact with a substance. Previous sensitization is not required. The reaction usually occurs immediately after exposure. Common causes include alkalis (detergents, soaps), acids (often found as an industrial work exposure), metals, solvents (occupational dermatitis), hydrocarbons, and chlorinated compounds.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can affect individuals regardless of age, race, or sex, but ACD accounts for 20% of all contact dermatitis reactions. ACD results in an inflammatory reaction in those who have been previously sensitized to an allergen. This type of delayed hypersensitivity reaction is known as cell-mediated hypersensitivity. Generally, no reaction is elicited upon the first exposure to the allergen. In fact, it may take years of exposure to allergens for someone to develop an allergic contact dermatitis.
Once sensitized, epidermal antigen-presenting cells (APCs) called Langerhans cells process the allergen and present it in a complex on the surface of the cell to a CD4+ T cell. Subsequently, inflammatory cytokines and mediators are released, resulting in an allergic cutaneous (eczematous) reaction. Lesions may appear to be vesicular or bullous. Occasionally, a generalized eruption may occur. With repeated exposure, reactions may be acute or chronic.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include toxicodendron plants (poison ivy, oak, and sumac; cashew nut tree; and mango), metals (nickel and gold), topical antibiotics (neomycin and bacitracin), fragrance and Balsam of Peru, deodorant, preservatives (formaldehyde), and rubber (elastic and gloves).
Patch testing is the standard means of detecting which allergen is causing the sensitization in an individual. The Thin-Layer Rapid Use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test or individually prepared aluminum (Finn) chambers containing the most common allergens are applied to the patient’s upper back. The patches are removed after 48 hours and read, and then reevaluated at day 4 or 5. Positive reactions appear as eczematous or vesicular papules or plaques.
Treatment includes avoidance of the allergens. Topical corticosteroid creams are helpful. For severe or generalized reactions, oral prednisone may be used. It is important to note that patient may be allergic to topical steroids. Patch testing can be performed to elucidate such allergens.
In contrast, 80% of contact dermatitis reactions are irritant, not allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results is a local inflammatory reaction in people who have come into contact with a substance. Previous sensitization is not required. The reaction usually occurs immediately after exposure. Common causes include alkalis (detergents, soaps), acids (often found as an industrial work exposure), metals, solvents (occupational dermatitis), hydrocarbons, and chlorinated compounds.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can affect individuals regardless of age, race, or sex, but ACD accounts for 20% of all contact dermatitis reactions. ACD results in an inflammatory reaction in those who have been previously sensitized to an allergen. This type of delayed hypersensitivity reaction is known as cell-mediated hypersensitivity. Generally, no reaction is elicited upon the first exposure to the allergen. In fact, it may take years of exposure to allergens for someone to develop an allergic contact dermatitis.
Once sensitized, epidermal antigen-presenting cells (APCs) called Langerhans cells process the allergen and present it in a complex on the surface of the cell to a CD4+ T cell. Subsequently, inflammatory cytokines and mediators are released, resulting in an allergic cutaneous (eczematous) reaction. Lesions may appear to be vesicular or bullous. Occasionally, a generalized eruption may occur. With repeated exposure, reactions may be acute or chronic.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include toxicodendron plants (poison ivy, oak, and sumac; cashew nut tree; and mango), metals (nickel and gold), topical antibiotics (neomycin and bacitracin), fragrance and Balsam of Peru, deodorant, preservatives (formaldehyde), and rubber (elastic and gloves).
Patch testing is the standard means of detecting which allergen is causing the sensitization in an individual. The Thin-Layer Rapid Use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test or individually prepared aluminum (Finn) chambers containing the most common allergens are applied to the patient’s upper back. The patches are removed after 48 hours and read, and then reevaluated at day 4 or 5. Positive reactions appear as eczematous or vesicular papules or plaques.
Treatment includes avoidance of the allergens. Topical corticosteroid creams are helpful. For severe or generalized reactions, oral prednisone may be used. It is important to note that patient may be allergic to topical steroids. Patch testing can be performed to elucidate such allergens.
In contrast, 80% of contact dermatitis reactions are irritant, not allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results is a local inflammatory reaction in people who have come into contact with a substance. Previous sensitization is not required. The reaction usually occurs immediately after exposure. Common causes include alkalis (detergents, soaps), acids (often found as an industrial work exposure), metals, solvents (occupational dermatitis), hydrocarbons, and chlorinated compounds.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
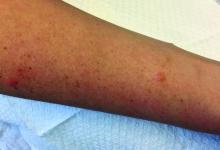
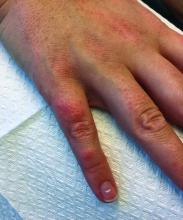
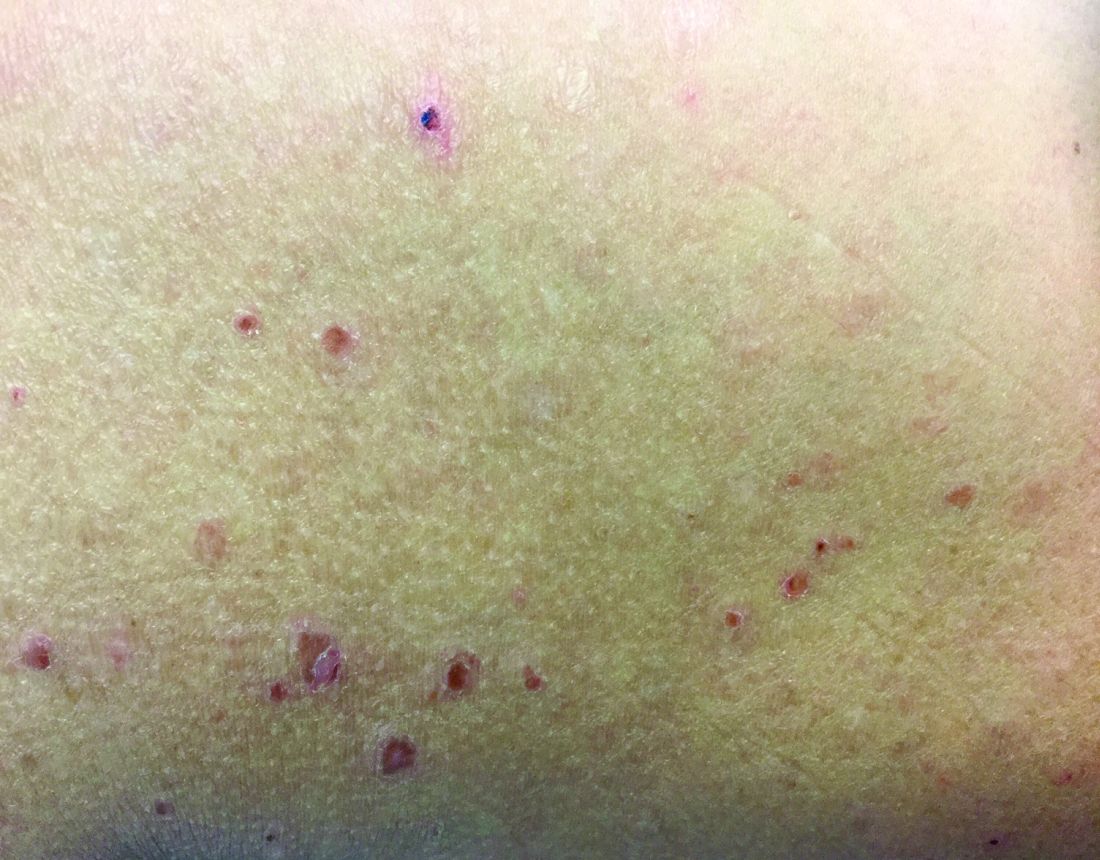
A 30-year-old female presented with 2 days of intensely pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles on her bilateral arms and hands. The lesions began appearing 1 day after a camping trip. Her neck, chest, and upper back were clear.
Make The Diagnosis - September 2018
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Make The Diagnosis - August 2018
respectively, of pityriasis lichenoides, an uncommon clonal T-cell disorder. The cause is unknown, although associations with infections have been reported. Pityriasis lichenoides more commonly affects children or young adults, usually before age 30 years. The disease can occur in all races.
In PLEVA, erythematous to brown papules and macules, in various stages of evolution, appear suddenly and in crops. The trunk and flexural areas are most often affected, but lesions may become widespread and may be pruritic or painful. Lesions may crust, ulcerate, or become necrotic and can heal with scarring. In general, patients don’t have constitutional symptoms. Lesions tend to resolve spontaneously over 1-3 years.
Rarely, PLEVA may develop into a more severe form called febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, a dermatologic emergency. Patients (more commonly, young males) may present with high fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy. Lesions become very painful, ulcerated, and necrotic, and extensive necrosis may be present. Changes in mental status, breathing difficulties, anemia, arthritis, abdominal pain, and sepsis may occur. Patients require hospitalization. There is a 25% mortality rate.
PLC is at the other end of this disease spectrum, representing the chronic, more mild stage of the disorder. Lesions present as indolent, asymptomatic, scaly macules and erythematous papules, favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions tend to be fewer in number than seen in PLEVA. They resolve over several months and may result in hypopigmentation, but usually don’t cause scarring. Patients may have long periods of remission between outbreaks. T-cell gene rearrangement may demonstrate monoclonality. PLC is generally considered a benign disease, although there are patients who have developed cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. For this reason, patients should be followed carefully for signs of malignant transformation.
Both forms share a common histologic picture. In PLEVA, focal parakeratosis and crusting is present. A dense, wedge-shaped infiltrate can be seen with prominent lymphocytic exocystosis in the epidermis. Necrotic keratinocytes are often seen. There may be spongiosis and intraepidermal vesicles. Extravasation of erythrocytes often occurs in the epidermis. PLC is histologically similar but far more subtle. There is less crusting, less spongiosis, fewer vesicles, and fewer necrotic keratinocytes. Generally, atypia of lymphocytes is absent.
Mucha-Habermann requires treatment with systemic steroids. Methotrexate, cyclosporine, or dapsone may be used as steroid-sparing agents. Upon treatment, lesions may resolve or revert back to more typical lesions of PLEVA. Treatment for PLEVA and PLC includes oral tetracycline or erythromycin, antihistamines (if pruritus is present), topical steroids, topical tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, or phototherapy. Low-dose weekly methotrexate may be helpful.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
respectively, of pityriasis lichenoides, an uncommon clonal T-cell disorder. The cause is unknown, although associations with infections have been reported. Pityriasis lichenoides more commonly affects children or young adults, usually before age 30 years. The disease can occur in all races.
In PLEVA, erythematous to brown papules and macules, in various stages of evolution, appear suddenly and in crops. The trunk and flexural areas are most often affected, but lesions may become widespread and may be pruritic or painful. Lesions may crust, ulcerate, or become necrotic and can heal with scarring. In general, patients don’t have constitutional symptoms. Lesions tend to resolve spontaneously over 1-3 years.
Rarely, PLEVA may develop into a more severe form called febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, a dermatologic emergency. Patients (more commonly, young males) may present with high fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy. Lesions become very painful, ulcerated, and necrotic, and extensive necrosis may be present. Changes in mental status, breathing difficulties, anemia, arthritis, abdominal pain, and sepsis may occur. Patients require hospitalization. There is a 25% mortality rate.
PLC is at the other end of this disease spectrum, representing the chronic, more mild stage of the disorder. Lesions present as indolent, asymptomatic, scaly macules and erythematous papules, favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions tend to be fewer in number than seen in PLEVA. They resolve over several months and may result in hypopigmentation, but usually don’t cause scarring. Patients may have long periods of remission between outbreaks. T-cell gene rearrangement may demonstrate monoclonality. PLC is generally considered a benign disease, although there are patients who have developed cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. For this reason, patients should be followed carefully for signs of malignant transformation.
Both forms share a common histologic picture. In PLEVA, focal parakeratosis and crusting is present. A dense, wedge-shaped infiltrate can be seen with prominent lymphocytic exocystosis in the epidermis. Necrotic keratinocytes are often seen. There may be spongiosis and intraepidermal vesicles. Extravasation of erythrocytes often occurs in the epidermis. PLC is histologically similar but far more subtle. There is less crusting, less spongiosis, fewer vesicles, and fewer necrotic keratinocytes. Generally, atypia of lymphocytes is absent.
Mucha-Habermann requires treatment with systemic steroids. Methotrexate, cyclosporine, or dapsone may be used as steroid-sparing agents. Upon treatment, lesions may resolve or revert back to more typical lesions of PLEVA. Treatment for PLEVA and PLC includes oral tetracycline or erythromycin, antihistamines (if pruritus is present), topical steroids, topical tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, or phototherapy. Low-dose weekly methotrexate may be helpful.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
respectively, of pityriasis lichenoides, an uncommon clonal T-cell disorder. The cause is unknown, although associations with infections have been reported. Pityriasis lichenoides more commonly affects children or young adults, usually before age 30 years. The disease can occur in all races.
In PLEVA, erythematous to brown papules and macules, in various stages of evolution, appear suddenly and in crops. The trunk and flexural areas are most often affected, but lesions may become widespread and may be pruritic or painful. Lesions may crust, ulcerate, or become necrotic and can heal with scarring. In general, patients don’t have constitutional symptoms. Lesions tend to resolve spontaneously over 1-3 years.
Rarely, PLEVA may develop into a more severe form called febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, a dermatologic emergency. Patients (more commonly, young males) may present with high fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy. Lesions become very painful, ulcerated, and necrotic, and extensive necrosis may be present. Changes in mental status, breathing difficulties, anemia, arthritis, abdominal pain, and sepsis may occur. Patients require hospitalization. There is a 25% mortality rate.
PLC is at the other end of this disease spectrum, representing the chronic, more mild stage of the disorder. Lesions present as indolent, asymptomatic, scaly macules and erythematous papules, favoring the trunk and proximal extremities. Lesions tend to be fewer in number than seen in PLEVA. They resolve over several months and may result in hypopigmentation, but usually don’t cause scarring. Patients may have long periods of remission between outbreaks. T-cell gene rearrangement may demonstrate monoclonality. PLC is generally considered a benign disease, although there are patients who have developed cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. For this reason, patients should be followed carefully for signs of malignant transformation.
Both forms share a common histologic picture. In PLEVA, focal parakeratosis and crusting is present. A dense, wedge-shaped infiltrate can be seen with prominent lymphocytic exocystosis in the epidermis. Necrotic keratinocytes are often seen. There may be spongiosis and intraepidermal vesicles. Extravasation of erythrocytes often occurs in the epidermis. PLC is histologically similar but far more subtle. There is less crusting, less spongiosis, fewer vesicles, and fewer necrotic keratinocytes. Generally, atypia of lymphocytes is absent.
Mucha-Habermann requires treatment with systemic steroids. Methotrexate, cyclosporine, or dapsone may be used as steroid-sparing agents. Upon treatment, lesions may resolve or revert back to more typical lesions of PLEVA. Treatment for PLEVA and PLC includes oral tetracycline or erythromycin, antihistamines (if pruritus is present), topical steroids, topical tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, or phototherapy. Low-dose weekly methotrexate may be helpful.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
A 28-year-old white female with no significant past medical history presents with a 10-year history of asymptomatic erythematous papules and scaly patches that come and go. She has used topical steroids in the past.
Make the Diagnosis - June 2018
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Make the Diagnosis - May 2018
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Make The Diagnosis - April 2018
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
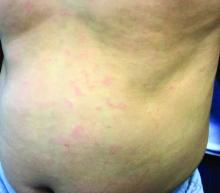
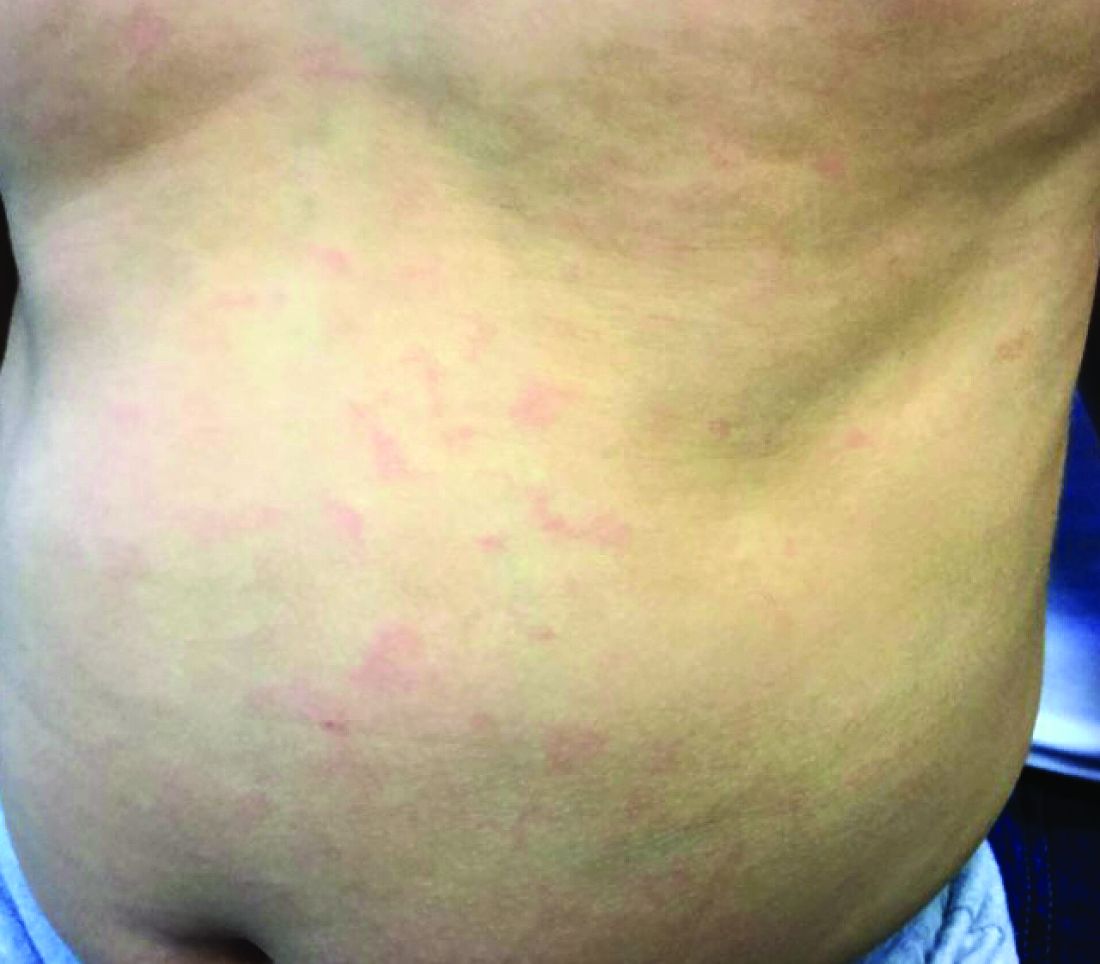
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
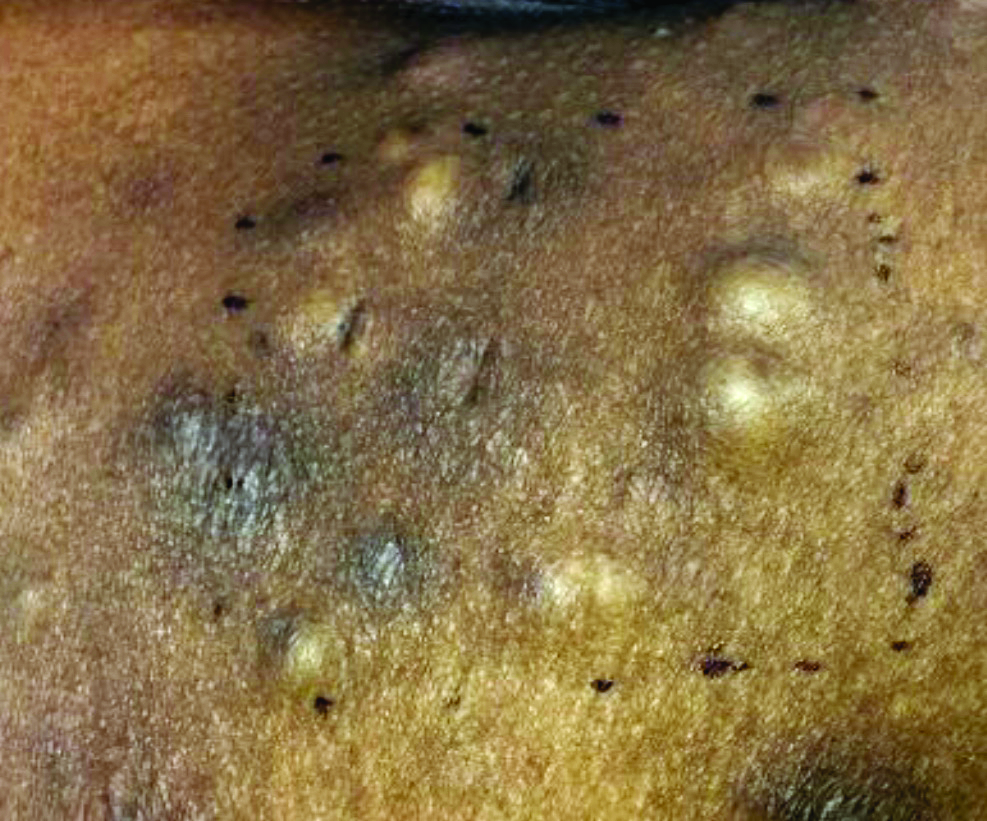
A healthy 70-year-old white male presented with an 8-day history of fatigue and a tingling, erythematous plaque with crusting on the left flank. Four days after the flank lesions appeared, he developed vesicles with an erythematous base on the right abdomen and back. There were more than 20 vesicles present on the abdomen and back, but there were no lesions on other parts of the body.