User login
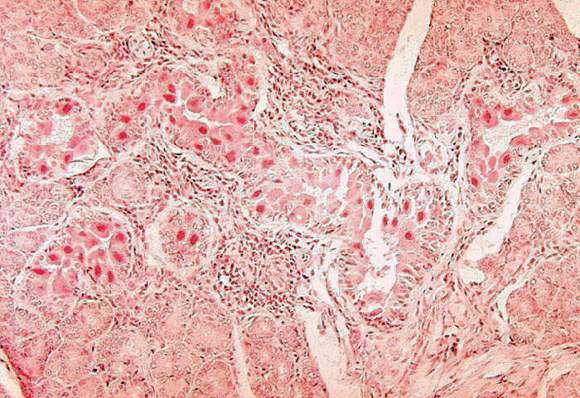
Data are mixed on cancerous transformation of cardiac mucosa in Barrett’s esophagus
CHICAGO – If scouring data is what makes a gastroenterologist feel good about risk assessment, there may be a lot of unhappy gastroenterologists out there, at least when it comes to the risk of cancer arising from cardiac mucosa in Barrett’s esophagus, according to Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD.
The risk arising from this nonintestinal metaplasia growth is probably quite low in real life, but the extant literature gives doctors a lot of contradictions, he said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
“The risk of cancer with cardiac mucosa is unclear,” said Dr. Shaheen of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Some data do suggest that, at least when present in the tubular esophagus in patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, there may be a risk of adenocarcinoma close to what’s seen in patients with intestinal metaplasia. Other data suggest the risk is quite low, perhaps even approximating that of the general population.”
The reasons for what Dr. Shaheen called “remarkable variability” in these data probably arise more from sampling error than real life. The studies are retrospective, and many lack long-term follow-up data, are plagued with insufficient numbers, and – perhaps most importantly – are not grounded in any standard clinical methodology.
“People who do endoscopy for a living understand that the stuff you read about systematic biopsy protocols is hardly ever honored in the breach. None of these studies ever reports the biopsy protocol from which the samples were taken.”
This lack of protocol means that studies on the cancer risk of columnar lined esophagus (CLE), which is negative for intestinal metaplasia are probably flawed from the beginning.
“The truth is that most gastroenterologists do a lousy job of biopsying Barrett’s, so there is probably a lot of sampling error in these studies, and they are contaminated with a high rate of intestinal metaplasia [IM],” said Dr. Shaheen.
And these studies do not report on the length of the CLE segment from which the biopsy was taken. “The likelihood of finding goblet cells [a characteristic of cardiac mucosa] increases with the length of Barrett’s. None of the studies is normalized for Barrett’s length. When we see studies saying the cancer risk is higher in the presence of goblet cells, length could be a partially confounding association.”
A 2009 study with a small sample size of 68 CLE patients found that abnormal DNA was just as likely in IM-negative samples as IM-positive ones. All of the samples were significantly different from the control samples, suggesting that any metaplasia in the CLE may already be on the path to cancer, Dr. Shaheen said (Am J Gastro. 2009;104:816-24)
In fact, a 2007 Scandinavian study supported the idea that IM isn’t even necessary for neoplastic progression of CLE (Scand J Gastroenterol 2007;42:1271-4). The investigators followed 712 patients for 12 years, and found that the adenocarcinoma rate was about 0.4 per patient per year whether the sample was IM positive or not.
“This study was enough to put a little shudder in the endoscopy community. If IM doesn’t matter, you’re talking about increasing the work in the endoscopy lab by 100%, because there are twice as many non-IM patients as those with IM.”
A 2008 study seemingly found something similar – but with a caveat, Dr. Shaheen said. The CLE patients in this study were followed for 3.5 years, and the cancer rate was virtually identical. But as the follow-up progressed, more and more biopsies turned up IM positive. “A first negative biopsy looked like it was associated with disease-free survival, but almost all IM-negative samples eventually became IM positive, so this didn’t really answer our question.”
Other studies have found that non-IM CLE has a very low neoplastic risk, and that IM is almost always a prerequisite for cancer to develop. The largest of these was conducted in the Northern Ireland Barrett’s Esophagus Registry in 2011. It followed more than 8,000 patients for 7 years. Patients with IM were 3.5 times more likely to develop a related adenocarcinoma than were those without IM (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1049-57).
The contradictory evidence leads Dr. Shaheen to suggest a specific biopsy protocol for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
“In my opinion, if you see a long segment of Barrett’s – more than 2 cm – and the biopsy is negative for IM, there is a good chance that you have a sampling error there, and a second endoscopy and biopsy are not unreasonable. If you see a short segment of Barrett’s and the biopsy is negative for IM, the cancer risk is unclear, but in general it’s probably pretty low, whether there are goblet cells there or not. I would say retaining these patients under endoscopic surveillance is of dubious value. [With] the likely low absolute risk of cancer in this patient population, no blanket recommendation for surveillance is advisable.”
Dr. Shaheen had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @Alz_Gal
CHICAGO – If scouring data is what makes a gastroenterologist feel good about risk assessment, there may be a lot of unhappy gastroenterologists out there, at least when it comes to the risk of cancer arising from cardiac mucosa in Barrett’s esophagus, according to Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD.
The risk arising from this nonintestinal metaplasia growth is probably quite low in real life, but the extant literature gives doctors a lot of contradictions, he said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
“The risk of cancer with cardiac mucosa is unclear,” said Dr. Shaheen of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Some data do suggest that, at least when present in the tubular esophagus in patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, there may be a risk of adenocarcinoma close to what’s seen in patients with intestinal metaplasia. Other data suggest the risk is quite low, perhaps even approximating that of the general population.”
The reasons for what Dr. Shaheen called “remarkable variability” in these data probably arise more from sampling error than real life. The studies are retrospective, and many lack long-term follow-up data, are plagued with insufficient numbers, and – perhaps most importantly – are not grounded in any standard clinical methodology.
“People who do endoscopy for a living understand that the stuff you read about systematic biopsy protocols is hardly ever honored in the breach. None of these studies ever reports the biopsy protocol from which the samples were taken.”
This lack of protocol means that studies on the cancer risk of columnar lined esophagus (CLE), which is negative for intestinal metaplasia are probably flawed from the beginning.
“The truth is that most gastroenterologists do a lousy job of biopsying Barrett’s, so there is probably a lot of sampling error in these studies, and they are contaminated with a high rate of intestinal metaplasia [IM],” said Dr. Shaheen.
And these studies do not report on the length of the CLE segment from which the biopsy was taken. “The likelihood of finding goblet cells [a characteristic of cardiac mucosa] increases with the length of Barrett’s. None of the studies is normalized for Barrett’s length. When we see studies saying the cancer risk is higher in the presence of goblet cells, length could be a partially confounding association.”
A 2009 study with a small sample size of 68 CLE patients found that abnormal DNA was just as likely in IM-negative samples as IM-positive ones. All of the samples were significantly different from the control samples, suggesting that any metaplasia in the CLE may already be on the path to cancer, Dr. Shaheen said (Am J Gastro. 2009;104:816-24)
In fact, a 2007 Scandinavian study supported the idea that IM isn’t even necessary for neoplastic progression of CLE (Scand J Gastroenterol 2007;42:1271-4). The investigators followed 712 patients for 12 years, and found that the adenocarcinoma rate was about 0.4 per patient per year whether the sample was IM positive or not.
“This study was enough to put a little shudder in the endoscopy community. If IM doesn’t matter, you’re talking about increasing the work in the endoscopy lab by 100%, because there are twice as many non-IM patients as those with IM.”
A 2008 study seemingly found something similar – but with a caveat, Dr. Shaheen said. The CLE patients in this study were followed for 3.5 years, and the cancer rate was virtually identical. But as the follow-up progressed, more and more biopsies turned up IM positive. “A first negative biopsy looked like it was associated with disease-free survival, but almost all IM-negative samples eventually became IM positive, so this didn’t really answer our question.”
Other studies have found that non-IM CLE has a very low neoplastic risk, and that IM is almost always a prerequisite for cancer to develop. The largest of these was conducted in the Northern Ireland Barrett’s Esophagus Registry in 2011. It followed more than 8,000 patients for 7 years. Patients with IM were 3.5 times more likely to develop a related adenocarcinoma than were those without IM (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1049-57).
The contradictory evidence leads Dr. Shaheen to suggest a specific biopsy protocol for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
“In my opinion, if you see a long segment of Barrett’s – more than 2 cm – and the biopsy is negative for IM, there is a good chance that you have a sampling error there, and a second endoscopy and biopsy are not unreasonable. If you see a short segment of Barrett’s and the biopsy is negative for IM, the cancer risk is unclear, but in general it’s probably pretty low, whether there are goblet cells there or not. I would say retaining these patients under endoscopic surveillance is of dubious value. [With] the likely low absolute risk of cancer in this patient population, no blanket recommendation for surveillance is advisable.”
Dr. Shaheen had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @Alz_Gal
CHICAGO – If scouring data is what makes a gastroenterologist feel good about risk assessment, there may be a lot of unhappy gastroenterologists out there, at least when it comes to the risk of cancer arising from cardiac mucosa in Barrett’s esophagus, according to Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD.
The risk arising from this nonintestinal metaplasia growth is probably quite low in real life, but the extant literature gives doctors a lot of contradictions, he said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association.
“The risk of cancer with cardiac mucosa is unclear,” said Dr. Shaheen of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Some data do suggest that, at least when present in the tubular esophagus in patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, there may be a risk of adenocarcinoma close to what’s seen in patients with intestinal metaplasia. Other data suggest the risk is quite low, perhaps even approximating that of the general population.”
The reasons for what Dr. Shaheen called “remarkable variability” in these data probably arise more from sampling error than real life. The studies are retrospective, and many lack long-term follow-up data, are plagued with insufficient numbers, and – perhaps most importantly – are not grounded in any standard clinical methodology.
“People who do endoscopy for a living understand that the stuff you read about systematic biopsy protocols is hardly ever honored in the breach. None of these studies ever reports the biopsy protocol from which the samples were taken.”
This lack of protocol means that studies on the cancer risk of columnar lined esophagus (CLE), which is negative for intestinal metaplasia are probably flawed from the beginning.
“The truth is that most gastroenterologists do a lousy job of biopsying Barrett’s, so there is probably a lot of sampling error in these studies, and they are contaminated with a high rate of intestinal metaplasia [IM],” said Dr. Shaheen.
And these studies do not report on the length of the CLE segment from which the biopsy was taken. “The likelihood of finding goblet cells [a characteristic of cardiac mucosa] increases with the length of Barrett’s. None of the studies is normalized for Barrett’s length. When we see studies saying the cancer risk is higher in the presence of goblet cells, length could be a partially confounding association.”
A 2009 study with a small sample size of 68 CLE patients found that abnormal DNA was just as likely in IM-negative samples as IM-positive ones. All of the samples were significantly different from the control samples, suggesting that any metaplasia in the CLE may already be on the path to cancer, Dr. Shaheen said (Am J Gastro. 2009;104:816-24)
In fact, a 2007 Scandinavian study supported the idea that IM isn’t even necessary for neoplastic progression of CLE (Scand J Gastroenterol 2007;42:1271-4). The investigators followed 712 patients for 12 years, and found that the adenocarcinoma rate was about 0.4 per patient per year whether the sample was IM positive or not.
“This study was enough to put a little shudder in the endoscopy community. If IM doesn’t matter, you’re talking about increasing the work in the endoscopy lab by 100%, because there are twice as many non-IM patients as those with IM.”
A 2008 study seemingly found something similar – but with a caveat, Dr. Shaheen said. The CLE patients in this study were followed for 3.5 years, and the cancer rate was virtually identical. But as the follow-up progressed, more and more biopsies turned up IM positive. “A first negative biopsy looked like it was associated with disease-free survival, but almost all IM-negative samples eventually became IM positive, so this didn’t really answer our question.”
Other studies have found that non-IM CLE has a very low neoplastic risk, and that IM is almost always a prerequisite for cancer to develop. The largest of these was conducted in the Northern Ireland Barrett’s Esophagus Registry in 2011. It followed more than 8,000 patients for 7 years. Patients with IM were 3.5 times more likely to develop a related adenocarcinoma than were those without IM (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1049-57).
The contradictory evidence leads Dr. Shaheen to suggest a specific biopsy protocol for patients with Barrett’s esophagus.
“In my opinion, if you see a long segment of Barrett’s – more than 2 cm – and the biopsy is negative for IM, there is a good chance that you have a sampling error there, and a second endoscopy and biopsy are not unreasonable. If you see a short segment of Barrett’s and the biopsy is negative for IM, the cancer risk is unclear, but in general it’s probably pretty low, whether there are goblet cells there or not. I would say retaining these patients under endoscopic surveillance is of dubious value. [With] the likely low absolute risk of cancer in this patient population, no blanket recommendation for surveillance is advisable.”
Dr. Shaheen had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @Alz_Gal
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE 2016 JAMES W. FRESTON CONFERENCE
Whole brain radiotherapy not beneficial for NSCLC metastasis
Whole brain radiotherapy, a standard treatment for patients with metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer, provided no clinical benefit in a noninferiority trial specifically designed to assess both patient survival and quality of life.
The findings were published online Sept. 4 in the Lancet.
Whole brain radiotherapy, with or without concomitant steroid treatment, has been widely used for decades in that patient population, even though no sufficiently powered, definitive studies support the approach. It is likely that patients and clinicians alike continue to embrace it because of the absence of alternative treatment options.
The Quality of Life After Treatment for Brain Metastases (QUARTZ) trial was intended to assess whether any improvement in survival offered by whole brain radiotherapy is balanced by deterioration in quality of life, said Paula Mulvenna, MBBS, of the Northern Center for Cancer Care, Newcastle (England) Hospitals, and her associates (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30825-X).
QUARTZ involved 538 adults seen during a 7-year period who had NSCLC with brain metastases and who were not suited for either brain surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy. The median age was 66 years (range, 35-85 years), and 38% had a Karnofsky Performance Status score of less than 70.
The participants were randomly assigned to receive either optimal supportive care plus whole brain radiotherapy (269 patients) or optimal supportive care alone (269 patients) at 69 U.K. and 3 Australian medical centers. They reported on 20 symptoms and adverse effects, as well as health-related quality of life, approximately once per week.
The primary outcome measure – quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), which combines overall survival and quality of life – was 46.4 days with radiotherapy and 41.7 days without it.
Symptoms, adverse effects, and quality of life (QOL) were similar between the two study groups at 4 weeks, except that the radiotherapy group reported more moderate or severe episodes of drowsiness, hair loss, nausea, and dry or itchy scalp. The number and severity of serious adverse events were similar through 12 weeks of follow-up.
The percentage of patients whose QOL was either maintained or improved over time was similar between the two groups at 4 weeks (54% vs. 57%), 8 weeks (44% vs. 51%), and 12 weeks (44% vs. 49%). Changes in Karnofsky scores also were similar.
The study refuted the widely held belief that whole brain radiotherapy allows patients to reduce or discontinue steroid treatment, averting the associated adverse effects. Steroid doses were not significantly different between the two study groups through the first 8 weeks of treatment, which “challenges the dogma that whole brain radiotherapy can be seen as a steroid-sparing modality,” the investigators said.
Taken together, the findings “suggest that whole brain radiotherapy can be omitted and patients treated with optimal supportive care alone, without an important reduction in either overall survival or quality of life,” Dr. Mulvenna and her associates said.
The approximately 5-day difference between the two study groups in median overall survival highlights both the limited benefit offered by radiotherapy and the poor prognosis of this patient population, the researchers added.
Whole brain radiotherapy did offer a small survival benefit to the youngest patients who had good performance status and a “controlled” primary NSCLC. “For all other groups, [it] does not significantly affect QALY or overall survival,” they said.
Cancer Research U.K., the Medical Research Council in the U.K., the Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group, and the National Health and Medical Research Council Australia supported the study. Dr. Mulvenna and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Managing brain metastases from NSCLC is a challenge, because the lesions may well produce life-threatening symptoms and serious impairment, which could be ameliorated with whole brain radiotherapy.
This is a large and well designed trial, but it was limited in that the maximal benefit of radiotherapy is believed to occur 6 weeks after the end of treatment. Given that median overall survival was only 8 weeks and considering the time it took to deliver the treatment, approximately half of the patients in this study died before an optimal assessment of symptoms could be done.
This might also explain why radiotherapy didn’t have an effect on steroid use in this study. Many patients didn’t live long enough for radiotherapy’s steroid-sparing effect to be observed.
Cécile Le Pechoux, MD, is in the department of radiation oncology at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus in Villejuif, France. She and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures. They made these remarks in a comment accompanying the report on the QUARTZ trial (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[16]31391-5).
Managing brain metastases from NSCLC is a challenge, because the lesions may well produce life-threatening symptoms and serious impairment, which could be ameliorated with whole brain radiotherapy.
This is a large and well designed trial, but it was limited in that the maximal benefit of radiotherapy is believed to occur 6 weeks after the end of treatment. Given that median overall survival was only 8 weeks and considering the time it took to deliver the treatment, approximately half of the patients in this study died before an optimal assessment of symptoms could be done.
This might also explain why radiotherapy didn’t have an effect on steroid use in this study. Many patients didn’t live long enough for radiotherapy’s steroid-sparing effect to be observed.
Cécile Le Pechoux, MD, is in the department of radiation oncology at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus in Villejuif, France. She and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures. They made these remarks in a comment accompanying the report on the QUARTZ trial (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[16]31391-5).
Managing brain metastases from NSCLC is a challenge, because the lesions may well produce life-threatening symptoms and serious impairment, which could be ameliorated with whole brain radiotherapy.
This is a large and well designed trial, but it was limited in that the maximal benefit of radiotherapy is believed to occur 6 weeks after the end of treatment. Given that median overall survival was only 8 weeks and considering the time it took to deliver the treatment, approximately half of the patients in this study died before an optimal assessment of symptoms could be done.
This might also explain why radiotherapy didn’t have an effect on steroid use in this study. Many patients didn’t live long enough for radiotherapy’s steroid-sparing effect to be observed.
Cécile Le Pechoux, MD, is in the department of radiation oncology at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus in Villejuif, France. She and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures. They made these remarks in a comment accompanying the report on the QUARTZ trial (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[16]31391-5).
Whole brain radiotherapy, a standard treatment for patients with metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer, provided no clinical benefit in a noninferiority trial specifically designed to assess both patient survival and quality of life.
The findings were published online Sept. 4 in the Lancet.
Whole brain radiotherapy, with or without concomitant steroid treatment, has been widely used for decades in that patient population, even though no sufficiently powered, definitive studies support the approach. It is likely that patients and clinicians alike continue to embrace it because of the absence of alternative treatment options.
The Quality of Life After Treatment for Brain Metastases (QUARTZ) trial was intended to assess whether any improvement in survival offered by whole brain radiotherapy is balanced by deterioration in quality of life, said Paula Mulvenna, MBBS, of the Northern Center for Cancer Care, Newcastle (England) Hospitals, and her associates (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30825-X).
QUARTZ involved 538 adults seen during a 7-year period who had NSCLC with brain metastases and who were not suited for either brain surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy. The median age was 66 years (range, 35-85 years), and 38% had a Karnofsky Performance Status score of less than 70.
The participants were randomly assigned to receive either optimal supportive care plus whole brain radiotherapy (269 patients) or optimal supportive care alone (269 patients) at 69 U.K. and 3 Australian medical centers. They reported on 20 symptoms and adverse effects, as well as health-related quality of life, approximately once per week.
The primary outcome measure – quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), which combines overall survival and quality of life – was 46.4 days with radiotherapy and 41.7 days without it.
Symptoms, adverse effects, and quality of life (QOL) were similar between the two study groups at 4 weeks, except that the radiotherapy group reported more moderate or severe episodes of drowsiness, hair loss, nausea, and dry or itchy scalp. The number and severity of serious adverse events were similar through 12 weeks of follow-up.
The percentage of patients whose QOL was either maintained or improved over time was similar between the two groups at 4 weeks (54% vs. 57%), 8 weeks (44% vs. 51%), and 12 weeks (44% vs. 49%). Changes in Karnofsky scores also were similar.
The study refuted the widely held belief that whole brain radiotherapy allows patients to reduce or discontinue steroid treatment, averting the associated adverse effects. Steroid doses were not significantly different between the two study groups through the first 8 weeks of treatment, which “challenges the dogma that whole brain radiotherapy can be seen as a steroid-sparing modality,” the investigators said.
Taken together, the findings “suggest that whole brain radiotherapy can be omitted and patients treated with optimal supportive care alone, without an important reduction in either overall survival or quality of life,” Dr. Mulvenna and her associates said.
The approximately 5-day difference between the two study groups in median overall survival highlights both the limited benefit offered by radiotherapy and the poor prognosis of this patient population, the researchers added.
Whole brain radiotherapy did offer a small survival benefit to the youngest patients who had good performance status and a “controlled” primary NSCLC. “For all other groups, [it] does not significantly affect QALY or overall survival,” they said.
Cancer Research U.K., the Medical Research Council in the U.K., the Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group, and the National Health and Medical Research Council Australia supported the study. Dr. Mulvenna and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Whole brain radiotherapy, a standard treatment for patients with metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer, provided no clinical benefit in a noninferiority trial specifically designed to assess both patient survival and quality of life.
The findings were published online Sept. 4 in the Lancet.
Whole brain radiotherapy, with or without concomitant steroid treatment, has been widely used for decades in that patient population, even though no sufficiently powered, definitive studies support the approach. It is likely that patients and clinicians alike continue to embrace it because of the absence of alternative treatment options.
The Quality of Life After Treatment for Brain Metastases (QUARTZ) trial was intended to assess whether any improvement in survival offered by whole brain radiotherapy is balanced by deterioration in quality of life, said Paula Mulvenna, MBBS, of the Northern Center for Cancer Care, Newcastle (England) Hospitals, and her associates (Lancet 2016 Sep 4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30825-X).
QUARTZ involved 538 adults seen during a 7-year period who had NSCLC with brain metastases and who were not suited for either brain surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy. The median age was 66 years (range, 35-85 years), and 38% had a Karnofsky Performance Status score of less than 70.
The participants were randomly assigned to receive either optimal supportive care plus whole brain radiotherapy (269 patients) or optimal supportive care alone (269 patients) at 69 U.K. and 3 Australian medical centers. They reported on 20 symptoms and adverse effects, as well as health-related quality of life, approximately once per week.
The primary outcome measure – quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), which combines overall survival and quality of life – was 46.4 days with radiotherapy and 41.7 days without it.
Symptoms, adverse effects, and quality of life (QOL) were similar between the two study groups at 4 weeks, except that the radiotherapy group reported more moderate or severe episodes of drowsiness, hair loss, nausea, and dry or itchy scalp. The number and severity of serious adverse events were similar through 12 weeks of follow-up.
The percentage of patients whose QOL was either maintained or improved over time was similar between the two groups at 4 weeks (54% vs. 57%), 8 weeks (44% vs. 51%), and 12 weeks (44% vs. 49%). Changes in Karnofsky scores also were similar.
The study refuted the widely held belief that whole brain radiotherapy allows patients to reduce or discontinue steroid treatment, averting the associated adverse effects. Steroid doses were not significantly different between the two study groups through the first 8 weeks of treatment, which “challenges the dogma that whole brain radiotherapy can be seen as a steroid-sparing modality,” the investigators said.
Taken together, the findings “suggest that whole brain radiotherapy can be omitted and patients treated with optimal supportive care alone, without an important reduction in either overall survival or quality of life,” Dr. Mulvenna and her associates said.
The approximately 5-day difference between the two study groups in median overall survival highlights both the limited benefit offered by radiotherapy and the poor prognosis of this patient population, the researchers added.
Whole brain radiotherapy did offer a small survival benefit to the youngest patients who had good performance status and a “controlled” primary NSCLC. “For all other groups, [it] does not significantly affect QALY or overall survival,” they said.
Cancer Research U.K., the Medical Research Council in the U.K., the Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group, and the National Health and Medical Research Council Australia supported the study. Dr. Mulvenna and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE LANCET
Key clinical point: Whole brain radiotherapy provided no clinically significant benefit for most patients with metastatic NSCLC.
Major finding: The primary outcome measure, quality-adjusted life-years, was 46.4 days with radiotherapy and 41.7 days without it.
Data source: An international, randomized, phase III noninferiority trial involving 538 patients treated during a 7-year period.
Disclosures: Cancer Research U.K., the Medical Research Council in the U.K., the Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group, and the Medical Research Council Australia supported the study. Dr. Mulvenna and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Antibiotic susceptibility differs in transplant recipients
Antibiotic susceptibility in bacteria cultured from transplant recipients at a single hospital differed markedly from that in hospital-wide antibiograms, according to a report published in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Understanding the differences in antibiotic susceptibility among these highly immunocompromised patients can help guide treatment when they develop infection, and reduce the delay before they begin receiving appropriate antibiotics, said Rossana Rosa, MD, of Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, and her associates.
The investigators examined the antibiotic susceptibility of 1,889 isolates from blood and urine specimens taken from patients who had received solid-organ transplants at a single tertiary-care teaching hospital and then developed bacterial infections during a 2-year period. These patients included both children and adults who had received kidney, pancreas, liver, heart, lung, or intestinal transplants and were treated in numerous, “geographically distributed” units throughout the hospital. Their culture results were compared with those from 10,439 other patients with bacterial infections, which comprised the hospital-wide antibiograms developed every 6 months during the study period.
The Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the transplant recipients showed markedly less susceptibility to first-line antibiotics than would have been predicted by the hospital-antibiograms. In particular, in the transplant recipients E. coli infections were resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, levofloxacin, and ceftriaxone; K. pneumoniae infections were resistant to every antibiotic except amikacin; and P. aeruginosa infections were resistant to levofloxacin, cefepime, and amikacin (Diag Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 25. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2016.08.018).
“We advocate for the development of antibiograms specific to solid-organ transplant recipients. This may allow intrahospital comparisons and intertransplant-center monitoring of trends in antimicrobial resistance over time,” Dr. Rosa and her associates said.
Antibiotic susceptibility in bacteria cultured from transplant recipients at a single hospital differed markedly from that in hospital-wide antibiograms, according to a report published in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Understanding the differences in antibiotic susceptibility among these highly immunocompromised patients can help guide treatment when they develop infection, and reduce the delay before they begin receiving appropriate antibiotics, said Rossana Rosa, MD, of Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, and her associates.
The investigators examined the antibiotic susceptibility of 1,889 isolates from blood and urine specimens taken from patients who had received solid-organ transplants at a single tertiary-care teaching hospital and then developed bacterial infections during a 2-year period. These patients included both children and adults who had received kidney, pancreas, liver, heart, lung, or intestinal transplants and were treated in numerous, “geographically distributed” units throughout the hospital. Their culture results were compared with those from 10,439 other patients with bacterial infections, which comprised the hospital-wide antibiograms developed every 6 months during the study period.
The Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the transplant recipients showed markedly less susceptibility to first-line antibiotics than would have been predicted by the hospital-antibiograms. In particular, in the transplant recipients E. coli infections were resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, levofloxacin, and ceftriaxone; K. pneumoniae infections were resistant to every antibiotic except amikacin; and P. aeruginosa infections were resistant to levofloxacin, cefepime, and amikacin (Diag Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 25. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2016.08.018).
“We advocate for the development of antibiograms specific to solid-organ transplant recipients. This may allow intrahospital comparisons and intertransplant-center monitoring of trends in antimicrobial resistance over time,” Dr. Rosa and her associates said.
Antibiotic susceptibility in bacteria cultured from transplant recipients at a single hospital differed markedly from that in hospital-wide antibiograms, according to a report published in Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease.
Understanding the differences in antibiotic susceptibility among these highly immunocompromised patients can help guide treatment when they develop infection, and reduce the delay before they begin receiving appropriate antibiotics, said Rossana Rosa, MD, of Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, and her associates.
The investigators examined the antibiotic susceptibility of 1,889 isolates from blood and urine specimens taken from patients who had received solid-organ transplants at a single tertiary-care teaching hospital and then developed bacterial infections during a 2-year period. These patients included both children and adults who had received kidney, pancreas, liver, heart, lung, or intestinal transplants and were treated in numerous, “geographically distributed” units throughout the hospital. Their culture results were compared with those from 10,439 other patients with bacterial infections, which comprised the hospital-wide antibiograms developed every 6 months during the study period.
The Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from the transplant recipients showed markedly less susceptibility to first-line antibiotics than would have been predicted by the hospital-antibiograms. In particular, in the transplant recipients E. coli infections were resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, levofloxacin, and ceftriaxone; K. pneumoniae infections were resistant to every antibiotic except amikacin; and P. aeruginosa infections were resistant to levofloxacin, cefepime, and amikacin (Diag Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 25. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2016.08.018).
“We advocate for the development of antibiograms specific to solid-organ transplant recipients. This may allow intrahospital comparisons and intertransplant-center monitoring of trends in antimicrobial resistance over time,” Dr. Rosa and her associates said.
FROM DIAGNOSTIC MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE
Key clinical point: Antibiotic susceptibility in bacteria cultured from transplant recipients differs markedly from that in hospital-wide antibiograms.
Major finding: In the transplant recipients, E. coli infections were resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, levofloxacin, and ceftriaxone; K. pneumoniae infections were resistant to every antibiotic except amikacin; and P. aeruginosa infections were resistant to levofloxacin, cefepime, and amikacin.
Data source: A single-center study comparing the antibiotic susceptibility of 1,889 bacterial isolates from transplant recipients with 10,439 isolates from other patients.
Disclosures: This study was not supported by funding from any public, commercial, or not-for-profit entities. Dr. Rosa and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
USPSTF: Screen for tuberculosis in those at greatest risk
Screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) can help prevent progression to active disease, and the availability of effective tests supports screening asymptomatic adults aged 18 years and older at increased risk for infection, according to new recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendations were published online Sept. 6 in JAMA.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that the net benefit of screening for LTBI in persons at increased risk for tuberculosis is moderate,” wrote lead author Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues (JAMA 2016 Sep 6;316[9]:962-9).
TB infection spreads through the coughing or sneezing of someone with active disease. Individuals at high risk for TB include those who are immunocompromised, residents of long-term care facilities or correctional facilities, or homeless individuals, as well as those born in countries known to have a high incidence of TB, including China, India, Mexico, and Vietnam.
Other populations at increased risk for TB are contacts of patients with active TB, health care workers, and workers in high-risk settings, the researchers noted.
TB remains a preventable disease in the United States, with a prevalence of approximately 5%, the researchers said. The two most effective screening tests, tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA), demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of 79% and 97%, and at least 80% and 95%, respectively.
The recommendations are supported by an evidence review, also published in JAMA (2016 Sep 6;316[9]:970-83). The review included 72 studies and 51,711 adults.
The studies in the evidence review did not assess the benefits vs. harms of TB screening, compared with no screening, noted Leila C. Kahwati, MD, of RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and her colleagues.
“The applicability of the evidence on accuracy and reliability of screening tests to primary care practice settings and populations is uncertain for several reasons,” the investigators said. However, the findings suggest that “treatment reduced the risk of active TB among the populations included in this review.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) can help prevent progression to active disease, and the availability of effective tests supports screening asymptomatic adults aged 18 years and older at increased risk for infection, according to new recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendations were published online Sept. 6 in JAMA.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that the net benefit of screening for LTBI in persons at increased risk for tuberculosis is moderate,” wrote lead author Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues (JAMA 2016 Sep 6;316[9]:962-9).
TB infection spreads through the coughing or sneezing of someone with active disease. Individuals at high risk for TB include those who are immunocompromised, residents of long-term care facilities or correctional facilities, or homeless individuals, as well as those born in countries known to have a high incidence of TB, including China, India, Mexico, and Vietnam.
Other populations at increased risk for TB are contacts of patients with active TB, health care workers, and workers in high-risk settings, the researchers noted.
TB remains a preventable disease in the United States, with a prevalence of approximately 5%, the researchers said. The two most effective screening tests, tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA), demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of 79% and 97%, and at least 80% and 95%, respectively.
The recommendations are supported by an evidence review, also published in JAMA (2016 Sep 6;316[9]:970-83). The review included 72 studies and 51,711 adults.
The studies in the evidence review did not assess the benefits vs. harms of TB screening, compared with no screening, noted Leila C. Kahwati, MD, of RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and her colleagues.
“The applicability of the evidence on accuracy and reliability of screening tests to primary care practice settings and populations is uncertain for several reasons,” the investigators said. However, the findings suggest that “treatment reduced the risk of active TB among the populations included in this review.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) can help prevent progression to active disease, and the availability of effective tests supports screening asymptomatic adults aged 18 years and older at increased risk for infection, according to new recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendations were published online Sept. 6 in JAMA.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that the net benefit of screening for LTBI in persons at increased risk for tuberculosis is moderate,” wrote lead author Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues (JAMA 2016 Sep 6;316[9]:962-9).
TB infection spreads through the coughing or sneezing of someone with active disease. Individuals at high risk for TB include those who are immunocompromised, residents of long-term care facilities or correctional facilities, or homeless individuals, as well as those born in countries known to have a high incidence of TB, including China, India, Mexico, and Vietnam.
Other populations at increased risk for TB are contacts of patients with active TB, health care workers, and workers in high-risk settings, the researchers noted.
TB remains a preventable disease in the United States, with a prevalence of approximately 5%, the researchers said. The two most effective screening tests, tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA), demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of 79% and 97%, and at least 80% and 95%, respectively.
The recommendations are supported by an evidence review, also published in JAMA (2016 Sep 6;316[9]:970-83). The review included 72 studies and 51,711 adults.
The studies in the evidence review did not assess the benefits vs. harms of TB screening, compared with no screening, noted Leila C. Kahwati, MD, of RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C., and her colleagues.
“The applicability of the evidence on accuracy and reliability of screening tests to primary care practice settings and populations is uncertain for several reasons,” the investigators said. However, the findings suggest that “treatment reduced the risk of active TB among the populations included in this review.”
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Latent tuberculosis infection is a significant problem, and both the tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA) were moderately sensitive and highly specific in areas with a low tuberculosis burden.
Major finding: Approximately 5%-10% of individuals with latent TB progress to active disease, according to the USPSTF, and treatment reduces the risk of progression.
Data source: An evidence review including 72 studies and 51,711 individuals.
Disclosures: The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Pneumonitis with nivolumab treatment shows common radiographic patterns
A study of cancer patients enrolled in trials of the programmed cell death-1 inhibiting medicine nivolumab found that among a minority who developed pneumonitis during treatment, distinct radiographic patterns were significantly associated with the level of pneumonitis severity.
Investigators found that cryptic organizing pneumonia pattern (COP) was the most common, though not the most severe. Led by Mizuki Nishino, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, the researchers looked at the 20 patients out of a cohort of 170 (11.8%) who had developed pneumonitis, and found that radiologic patterns indicating acute interstitial pneumonia/acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 2) had the highest severity grade on a scale of 1-5 (median 3), followed by those with COP pattern (n = 13, median grade 2), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (n = 2, median grade 1), and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (n = 3, median grade 1). The pattern was significantly associated with severity (P = .0006).
The study cohort included patients being treated with nivolumab for lung cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma; the COP patten was the most common across tumor types and observed in patients receiving monotherapy and combination therapy alike. Therapy with nivolumab was suspended for all 20 pneumonitis patients, and most (n = 17) received treatment for pneumonitis with corticosteroids with or without infliximab, for a median treatment time of 6 weeks. Seven patients were able to restart nivolumab, though pneumonitis recurred in two, the investigators reported (Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 17. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1320).
“Time from initiation of therapy to the development of pneumonitis had a wide range (0.5-11.5 months), indicating an importance of careful observation and follow-up for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis throughout treatment,” Dr. Nishino and colleagues wrote in their analysis, adding that shorter times were observed for lung cancer patients, possibly because of their higher pulmonary burden, a lower threshold for performing chest scans in these patients, or both. “In most patients, clinical and radiographic improvements were noted after treatment, indicating that [PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis], although potentially serious, is treatable if diagnosed and managed appropriately. The observation emphasizes the importance of timely recognition, accurate diagnosis, and early intervention.”
The lead author and several coauthors disclosed funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, which sponsored the trial, as well as from other manufacturers.
A study of cancer patients enrolled in trials of the programmed cell death-1 inhibiting medicine nivolumab found that among a minority who developed pneumonitis during treatment, distinct radiographic patterns were significantly associated with the level of pneumonitis severity.
Investigators found that cryptic organizing pneumonia pattern (COP) was the most common, though not the most severe. Led by Mizuki Nishino, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, the researchers looked at the 20 patients out of a cohort of 170 (11.8%) who had developed pneumonitis, and found that radiologic patterns indicating acute interstitial pneumonia/acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 2) had the highest severity grade on a scale of 1-5 (median 3), followed by those with COP pattern (n = 13, median grade 2), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (n = 2, median grade 1), and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (n = 3, median grade 1). The pattern was significantly associated with severity (P = .0006).
The study cohort included patients being treated with nivolumab for lung cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma; the COP patten was the most common across tumor types and observed in patients receiving monotherapy and combination therapy alike. Therapy with nivolumab was suspended for all 20 pneumonitis patients, and most (n = 17) received treatment for pneumonitis with corticosteroids with or without infliximab, for a median treatment time of 6 weeks. Seven patients were able to restart nivolumab, though pneumonitis recurred in two, the investigators reported (Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 17. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1320).
“Time from initiation of therapy to the development of pneumonitis had a wide range (0.5-11.5 months), indicating an importance of careful observation and follow-up for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis throughout treatment,” Dr. Nishino and colleagues wrote in their analysis, adding that shorter times were observed for lung cancer patients, possibly because of their higher pulmonary burden, a lower threshold for performing chest scans in these patients, or both. “In most patients, clinical and radiographic improvements were noted after treatment, indicating that [PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis], although potentially serious, is treatable if diagnosed and managed appropriately. The observation emphasizes the importance of timely recognition, accurate diagnosis, and early intervention.”
The lead author and several coauthors disclosed funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, which sponsored the trial, as well as from other manufacturers.
A study of cancer patients enrolled in trials of the programmed cell death-1 inhibiting medicine nivolumab found that among a minority who developed pneumonitis during treatment, distinct radiographic patterns were significantly associated with the level of pneumonitis severity.
Investigators found that cryptic organizing pneumonia pattern (COP) was the most common, though not the most severe. Led by Mizuki Nishino, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, the researchers looked at the 20 patients out of a cohort of 170 (11.8%) who had developed pneumonitis, and found that radiologic patterns indicating acute interstitial pneumonia/acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 2) had the highest severity grade on a scale of 1-5 (median 3), followed by those with COP pattern (n = 13, median grade 2), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (n = 2, median grade 1), and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (n = 3, median grade 1). The pattern was significantly associated with severity (P = .0006).
The study cohort included patients being treated with nivolumab for lung cancer, melanoma, and lymphoma; the COP patten was the most common across tumor types and observed in patients receiving monotherapy and combination therapy alike. Therapy with nivolumab was suspended for all 20 pneumonitis patients, and most (n = 17) received treatment for pneumonitis with corticosteroids with or without infliximab, for a median treatment time of 6 weeks. Seven patients were able to restart nivolumab, though pneumonitis recurred in two, the investigators reported (Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 17. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1320).
“Time from initiation of therapy to the development of pneumonitis had a wide range (0.5-11.5 months), indicating an importance of careful observation and follow-up for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis throughout treatment,” Dr. Nishino and colleagues wrote in their analysis, adding that shorter times were observed for lung cancer patients, possibly because of their higher pulmonary burden, a lower threshold for performing chest scans in these patients, or both. “In most patients, clinical and radiographic improvements were noted after treatment, indicating that [PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis], although potentially serious, is treatable if diagnosed and managed appropriately. The observation emphasizes the importance of timely recognition, accurate diagnosis, and early intervention.”
The lead author and several coauthors disclosed funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, which sponsored the trial, as well as from other manufacturers.
FROM CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
Key clinical point: Pneumonitis related to treatment with PD-1 inhibitors showed distinct radiographic patterns associated with severity; most cases resolved with corticosteroid treatment.
Major finding: Of 20 patients in nivolumab trials who developed pneumonitis, a COP pattern was seen in 13, and other patterns in 7; different patterns were significantly associated with pneumonitis severity (P = .006).
Data source: 170 patients with melanoma, lung cancer or lymphoma enrolled in single-site open-label clinical trial of nivolumab.
Disclosures: The lead author and several coauthors disclosed funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, which sponsored the trial, as well as from other manufacturers.
IPF Patient Registry will expand
The number of patients enrolled in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis–Prospective Outcomes (IPF-PRO) Registry will be increased to 1,500, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and the Duke Clinical Research Institute have announced.
The organizations plan to accomplish this goal by increasing the number of sites they use to gather IPF patient data, according to a statement; the patients enrolled in the registry will now come from 45 sites instead of 18 sites.
IPF-PRO, which was launched in June 2014, is the first multicenter longitudinal disease state registry in the United States focused specifically on IPF. It was designed for the purpose of studying the progression of IPF and the effectiveness of various treatment approaches for the disease. The registry includes a biorepository that stores blood samples that provide patient genetic material.
“In collecting data from a larger, more diverse group of patients ... this registry will allow us to better assess the impact of the disease over time on clinical and patient-centered outcomes,” said Scott M. Palmer, MD, director of pulmonary research at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., in the statement.
More information on the registry is available at clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01915511.
The number of patients enrolled in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis–Prospective Outcomes (IPF-PRO) Registry will be increased to 1,500, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and the Duke Clinical Research Institute have announced.
The organizations plan to accomplish this goal by increasing the number of sites they use to gather IPF patient data, according to a statement; the patients enrolled in the registry will now come from 45 sites instead of 18 sites.
IPF-PRO, which was launched in June 2014, is the first multicenter longitudinal disease state registry in the United States focused specifically on IPF. It was designed for the purpose of studying the progression of IPF and the effectiveness of various treatment approaches for the disease. The registry includes a biorepository that stores blood samples that provide patient genetic material.
“In collecting data from a larger, more diverse group of patients ... this registry will allow us to better assess the impact of the disease over time on clinical and patient-centered outcomes,” said Scott M. Palmer, MD, director of pulmonary research at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., in the statement.
More information on the registry is available at clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01915511.
The number of patients enrolled in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis–Prospective Outcomes (IPF-PRO) Registry will be increased to 1,500, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and the Duke Clinical Research Institute have announced.
The organizations plan to accomplish this goal by increasing the number of sites they use to gather IPF patient data, according to a statement; the patients enrolled in the registry will now come from 45 sites instead of 18 sites.
IPF-PRO, which was launched in June 2014, is the first multicenter longitudinal disease state registry in the United States focused specifically on IPF. It was designed for the purpose of studying the progression of IPF and the effectiveness of various treatment approaches for the disease. The registry includes a biorepository that stores blood samples that provide patient genetic material.
“In collecting data from a larger, more diverse group of patients ... this registry will allow us to better assess the impact of the disease over time on clinical and patient-centered outcomes,” said Scott M. Palmer, MD, director of pulmonary research at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., in the statement.
More information on the registry is available at clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01915511.
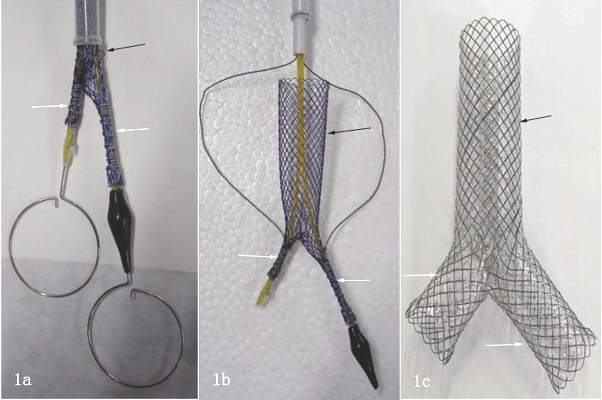
A dual Y-shaped stent can improve QOL with airway fistulas
Airway fistula is a rare but life-threatening complication of esophageal surgery, but an innovative technique using two custom-made, Y-shaped metallic stents can preserve airway patency, researchers at Zhengzhou University in China reported in the August issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:557-63).
The study involved 10 patients who received Y-shaped stents to treat gastrotracheal or gastrobronchial fistulas (GTFs and GBFs, respectively) after esophageal surgery from 2010 through 2014. “Our patients tolerated the stents well and had good palliation of their symptoms,” wrote Teng-Fei Li, MD, and colleagues.
Six patients died within 8 months for unrelated reasons – either tumors (four patients), or hemoptysis or pulmonary infection (one each). In one patient, the carinal fistula enlarged 4 months after stenting, but the researchers successfully placed an additional small Y-shaped stent. At the publication of the paper, this patient and three others had survived, Dr. Li and colleagues said.
After esophagectomy, fistulas can form between the tracheobronchial tree and stomach for a variety of reasons. A metallic stent would seem the logical choice after fistula formation, but it can be problematic, Dr. Li and colleagues pointed out. “Most often the clinician faces a situation in which the esophageal stent should have a larger diameter on the gastric side, making stenting the alimentary side of the fistula insufficient,” they said. The risk of stent migration is high, and the bifurcated structure of the trachea and main bronchi can cause leakage and stent displacement.
The researchers noted that Y-shaped self-expanding stents have been used for sealing airway fistulas, but they don’t always fully seal large GTFs and GBFs. Their primary objective in studying the combined-type Y-shaped covered metallic stent was to determine the safety and feasibility of the technique; the secondary aim was to evaluate long-term patency and complication rates.
They designed a Y-shaped stent delivery system (Micro-Tech) and used a combined bundle-and-push to insert the main body of the stent. In all, they inserted 20 Y-shaped stents in the 10 patients, although two stents did not fully expand and were dilated with a balloon. The researchers reported resolution of coughing during eating, toleration of liquid or semiliquid diet, and no complications after insertion.
Dr. Li and colleagues also developed strategies to avoid complications of Y-shaped stents, which have been known to retain secretions because they hinder cilia function. “To avoid this, we provided sputum suction and administered continuous high-concentration oxygen during the procedure,” they noted. Also, speed and agility in placement are important. “The operation should be performed as rapidly and gently as possible to avoid irritation to the airway,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. The postoperative course involved IV expectorants and antiasthma agents and aerosol inhalation of terbutaline. Surveillance bronchoscopes and debridement of granulation tissue helped avoid stent obstruction.
Nonetheless, the researches acknowledged limitations of the retrospective study, namely its small sample size and lack of a control group.
Dr. Li and colleagues had no financial relationships to disclose.
The Zhengzhou University investigators provide an opportunity to “think outside the box” when managing complex airway fistulas, Waël C. Hanna, MDCM, of McMaster University and St. Joseph’s Healthcare in Hamilton, Ontario, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:564).
 |
Dr. Waël Hanna |
Dr. Hanna credited a couple of innovations in their technique to overcome the challenge of Y stents that “remain notoriously difficult to position”: eliminating rigid bronchoscopy and using angiography-guided oral delivery; and developing the hybrid deployment mechanism.
Dr. Hanna also noted two “important nuances” of the technique: The stents are custom-made based on the length and location of the fistula; and the routine placement of two stents, with a limb of the smaller Y stent projecting through a limb of the larger Y stent to seal the entire airway. “This Y-en-Y technique using perfectly fitted stents is likely what caused the excellent outcomes that are reported in this series,” Dr. Hanna said.
But their approach may not be a practical solution to complex airway fistulas soon, he said. “Most of us who see the occasional case are unlikely to be able to commission custom-made Y stents,” he said. What’s more, the deployment mechanism is complicated, and the effect on patient quality of life is unclear.
Dr. Hanna had no financial relationships to disclose.
The Zhengzhou University investigators provide an opportunity to “think outside the box” when managing complex airway fistulas, Waël C. Hanna, MDCM, of McMaster University and St. Joseph’s Healthcare in Hamilton, Ontario, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:564).
 |
Dr. Waël Hanna |
Dr. Hanna credited a couple of innovations in their technique to overcome the challenge of Y stents that “remain notoriously difficult to position”: eliminating rigid bronchoscopy and using angiography-guided oral delivery; and developing the hybrid deployment mechanism.
Dr. Hanna also noted two “important nuances” of the technique: The stents are custom-made based on the length and location of the fistula; and the routine placement of two stents, with a limb of the smaller Y stent projecting through a limb of the larger Y stent to seal the entire airway. “This Y-en-Y technique using perfectly fitted stents is likely what caused the excellent outcomes that are reported in this series,” Dr. Hanna said.
But their approach may not be a practical solution to complex airway fistulas soon, he said. “Most of us who see the occasional case are unlikely to be able to commission custom-made Y stents,” he said. What’s more, the deployment mechanism is complicated, and the effect on patient quality of life is unclear.
Dr. Hanna had no financial relationships to disclose.
The Zhengzhou University investigators provide an opportunity to “think outside the box” when managing complex airway fistulas, Waël C. Hanna, MDCM, of McMaster University and St. Joseph’s Healthcare in Hamilton, Ontario, said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:564).
 |
Dr. Waël Hanna |
Dr. Hanna credited a couple of innovations in their technique to overcome the challenge of Y stents that “remain notoriously difficult to position”: eliminating rigid bronchoscopy and using angiography-guided oral delivery; and developing the hybrid deployment mechanism.
Dr. Hanna also noted two “important nuances” of the technique: The stents are custom-made based on the length and location of the fistula; and the routine placement of two stents, with a limb of the smaller Y stent projecting through a limb of the larger Y stent to seal the entire airway. “This Y-en-Y technique using perfectly fitted stents is likely what caused the excellent outcomes that are reported in this series,” Dr. Hanna said.
But their approach may not be a practical solution to complex airway fistulas soon, he said. “Most of us who see the occasional case are unlikely to be able to commission custom-made Y stents,” he said. What’s more, the deployment mechanism is complicated, and the effect on patient quality of life is unclear.
Dr. Hanna had no financial relationships to disclose.
Airway fistula is a rare but life-threatening complication of esophageal surgery, but an innovative technique using two custom-made, Y-shaped metallic stents can preserve airway patency, researchers at Zhengzhou University in China reported in the August issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:557-63).
The study involved 10 patients who received Y-shaped stents to treat gastrotracheal or gastrobronchial fistulas (GTFs and GBFs, respectively) after esophageal surgery from 2010 through 2014. “Our patients tolerated the stents well and had good palliation of their symptoms,” wrote Teng-Fei Li, MD, and colleagues.
Six patients died within 8 months for unrelated reasons – either tumors (four patients), or hemoptysis or pulmonary infection (one each). In one patient, the carinal fistula enlarged 4 months after stenting, but the researchers successfully placed an additional small Y-shaped stent. At the publication of the paper, this patient and three others had survived, Dr. Li and colleagues said.
After esophagectomy, fistulas can form between the tracheobronchial tree and stomach for a variety of reasons. A metallic stent would seem the logical choice after fistula formation, but it can be problematic, Dr. Li and colleagues pointed out. “Most often the clinician faces a situation in which the esophageal stent should have a larger diameter on the gastric side, making stenting the alimentary side of the fistula insufficient,” they said. The risk of stent migration is high, and the bifurcated structure of the trachea and main bronchi can cause leakage and stent displacement.
The researchers noted that Y-shaped self-expanding stents have been used for sealing airway fistulas, but they don’t always fully seal large GTFs and GBFs. Their primary objective in studying the combined-type Y-shaped covered metallic stent was to determine the safety and feasibility of the technique; the secondary aim was to evaluate long-term patency and complication rates.
They designed a Y-shaped stent delivery system (Micro-Tech) and used a combined bundle-and-push to insert the main body of the stent. In all, they inserted 20 Y-shaped stents in the 10 patients, although two stents did not fully expand and were dilated with a balloon. The researchers reported resolution of coughing during eating, toleration of liquid or semiliquid diet, and no complications after insertion.
Dr. Li and colleagues also developed strategies to avoid complications of Y-shaped stents, which have been known to retain secretions because they hinder cilia function. “To avoid this, we provided sputum suction and administered continuous high-concentration oxygen during the procedure,” they noted. Also, speed and agility in placement are important. “The operation should be performed as rapidly and gently as possible to avoid irritation to the airway,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. The postoperative course involved IV expectorants and antiasthma agents and aerosol inhalation of terbutaline. Surveillance bronchoscopes and debridement of granulation tissue helped avoid stent obstruction.
Nonetheless, the researches acknowledged limitations of the retrospective study, namely its small sample size and lack of a control group.
Dr. Li and colleagues had no financial relationships to disclose.
Airway fistula is a rare but life-threatening complication of esophageal surgery, but an innovative technique using two custom-made, Y-shaped metallic stents can preserve airway patency, researchers at Zhengzhou University in China reported in the August issue of the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152:557-63).
The study involved 10 patients who received Y-shaped stents to treat gastrotracheal or gastrobronchial fistulas (GTFs and GBFs, respectively) after esophageal surgery from 2010 through 2014. “Our patients tolerated the stents well and had good palliation of their symptoms,” wrote Teng-Fei Li, MD, and colleagues.
Six patients died within 8 months for unrelated reasons – either tumors (four patients), or hemoptysis or pulmonary infection (one each). In one patient, the carinal fistula enlarged 4 months after stenting, but the researchers successfully placed an additional small Y-shaped stent. At the publication of the paper, this patient and three others had survived, Dr. Li and colleagues said.
After esophagectomy, fistulas can form between the tracheobronchial tree and stomach for a variety of reasons. A metallic stent would seem the logical choice after fistula formation, but it can be problematic, Dr. Li and colleagues pointed out. “Most often the clinician faces a situation in which the esophageal stent should have a larger diameter on the gastric side, making stenting the alimentary side of the fistula insufficient,” they said. The risk of stent migration is high, and the bifurcated structure of the trachea and main bronchi can cause leakage and stent displacement.
The researchers noted that Y-shaped self-expanding stents have been used for sealing airway fistulas, but they don’t always fully seal large GTFs and GBFs. Their primary objective in studying the combined-type Y-shaped covered metallic stent was to determine the safety and feasibility of the technique; the secondary aim was to evaluate long-term patency and complication rates.
They designed a Y-shaped stent delivery system (Micro-Tech) and used a combined bundle-and-push to insert the main body of the stent. In all, they inserted 20 Y-shaped stents in the 10 patients, although two stents did not fully expand and were dilated with a balloon. The researchers reported resolution of coughing during eating, toleration of liquid or semiliquid diet, and no complications after insertion.
Dr. Li and colleagues also developed strategies to avoid complications of Y-shaped stents, which have been known to retain secretions because they hinder cilia function. “To avoid this, we provided sputum suction and administered continuous high-concentration oxygen during the procedure,” they noted. Also, speed and agility in placement are important. “The operation should be performed as rapidly and gently as possible to avoid irritation to the airway,” Dr. Li and colleagues wrote. The postoperative course involved IV expectorants and antiasthma agents and aerosol inhalation of terbutaline. Surveillance bronchoscopes and debridement of granulation tissue helped avoid stent obstruction.
Nonetheless, the researches acknowledged limitations of the retrospective study, namely its small sample size and lack of a control group.
Dr. Li and colleagues had no financial relationships to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: A combined type Y-shaped self-expandable coated metallic stent is a new approach for treatment of airway fistulas.
Major finding: Ten patients received the stents; all of them reported improved quality of life. Six died within 8 months because of unrelated factors.
Data source: Single-institution retrospective review of 10 patients with gastrotracheal or gastrobronchial fistulas who received the stent to reopen the airway.
Disclosures: Dr. Li and coauthors had no financial relationships to disclose. The study received support from the National High-Tech R&D Program of China.
Don’t delay treatment for patients with TB and HIV
Clinicians should treat patients diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis for both conditions immediately, according to new guidelines on the treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis.
The clinical practice guidelines were issued collectively by three organizations: the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and published online in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
The guidelines recommend starting TB treatment for all patients as soon as an infection is suspected, rather than waiting for test results, and focusing on daily therapy to reduce the risk of relapse. In addition, all TB patients should receive comprehensive care, including direct observed therapy (DOT) when appropriate (Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 10. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw376).
“Treatment of tuberculosis is focused on both curing the individual patient and minimizing the transmission,” wrote Payam Nahid, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and his colleagues on the guidelines committee.
The guidelines’ section on treatment of tuberculosis in special situations addresses management of TB in patients with conditions including HIV, extrapulmonary TB, culture-negative pulmonary TB, pregnancy, renal disease, and hepatic disease, as well as treatment of children and the elderly.
With regard to HIV, the guidelines recommend the standard 6-month daily TB treatment for HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy. This treatment includes 2 months of isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB), followed by a continuation phase of 4 months of INH and RIF.
“Patients with HIV infection and tuberculosis are at an increased risk of developing paradoxical worsening of symptoms, signs, or clinical manifestations of tuberculosis after beginning antituberculosis and antiretroviral treatments,” according to the guidelines. These responses are defined as Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS). However, IRIS does not appear to impact the simultaneous treatment of TB and HIV, and the condition can be managed symptomatically if it occurs, the researchers noted.
The guidelines identified several areas in need of further study, including new TB drugs and treatment plans; the effects of biomarkers to help design individual therapy; TB in special populations including HIV patients, pregnant women, and children; and treatment delivery strategies.
The guidelines also are endorsed by the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the U.S. National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NCTA).
The American Thoracic Society, the Infections Diseases Society of America, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provided financial support. Lead author Dr. Nahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Clinicians should treat patients diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis for both conditions immediately, according to new guidelines on the treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis.
The clinical practice guidelines were issued collectively by three organizations: the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and published online in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
The guidelines recommend starting TB treatment for all patients as soon as an infection is suspected, rather than waiting for test results, and focusing on daily therapy to reduce the risk of relapse. In addition, all TB patients should receive comprehensive care, including direct observed therapy (DOT) when appropriate (Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 10. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw376).
“Treatment of tuberculosis is focused on both curing the individual patient and minimizing the transmission,” wrote Payam Nahid, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and his colleagues on the guidelines committee.
The guidelines’ section on treatment of tuberculosis in special situations addresses management of TB in patients with conditions including HIV, extrapulmonary TB, culture-negative pulmonary TB, pregnancy, renal disease, and hepatic disease, as well as treatment of children and the elderly.
With regard to HIV, the guidelines recommend the standard 6-month daily TB treatment for HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy. This treatment includes 2 months of isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB), followed by a continuation phase of 4 months of INH and RIF.
“Patients with HIV infection and tuberculosis are at an increased risk of developing paradoxical worsening of symptoms, signs, or clinical manifestations of tuberculosis after beginning antituberculosis and antiretroviral treatments,” according to the guidelines. These responses are defined as Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS). However, IRIS does not appear to impact the simultaneous treatment of TB and HIV, and the condition can be managed symptomatically if it occurs, the researchers noted.
The guidelines identified several areas in need of further study, including new TB drugs and treatment plans; the effects of biomarkers to help design individual therapy; TB in special populations including HIV patients, pregnant women, and children; and treatment delivery strategies.
The guidelines also are endorsed by the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the U.S. National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NCTA).
The American Thoracic Society, the Infections Diseases Society of America, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provided financial support. Lead author Dr. Nahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Clinicians should treat patients diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis for both conditions immediately, according to new guidelines on the treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis.
The clinical practice guidelines were issued collectively by three organizations: the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and published online in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
The guidelines recommend starting TB treatment for all patients as soon as an infection is suspected, rather than waiting for test results, and focusing on daily therapy to reduce the risk of relapse. In addition, all TB patients should receive comprehensive care, including direct observed therapy (DOT) when appropriate (Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 10. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw376).
“Treatment of tuberculosis is focused on both curing the individual patient and minimizing the transmission,” wrote Payam Nahid, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and his colleagues on the guidelines committee.
The guidelines’ section on treatment of tuberculosis in special situations addresses management of TB in patients with conditions including HIV, extrapulmonary TB, culture-negative pulmonary TB, pregnancy, renal disease, and hepatic disease, as well as treatment of children and the elderly.
With regard to HIV, the guidelines recommend the standard 6-month daily TB treatment for HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy. This treatment includes 2 months of isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB), followed by a continuation phase of 4 months of INH and RIF.
“Patients with HIV infection and tuberculosis are at an increased risk of developing paradoxical worsening of symptoms, signs, or clinical manifestations of tuberculosis after beginning antituberculosis and antiretroviral treatments,” according to the guidelines. These responses are defined as Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS). However, IRIS does not appear to impact the simultaneous treatment of TB and HIV, and the condition can be managed symptomatically if it occurs, the researchers noted.
The guidelines identified several areas in need of further study, including new TB drugs and treatment plans; the effects of biomarkers to help design individual therapy; TB in special populations including HIV patients, pregnant women, and children; and treatment delivery strategies.
The guidelines also are endorsed by the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the U.S. National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NCTA).
The American Thoracic Society, the Infections Diseases Society of America, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provided financial support. Lead author Dr. Nahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Key clinical point: Clinicians should treat patients diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis for both conditions immediately.
Major finding: A four-drug regimen of INH, RIF, PZA, and EMB remains the preferred initial treatment for drug-susceptible pulmonary tuberculosis. Treatment should be initiated promptly even before diagnostic test results are known in patients with high likelihood of having tuberculosis.
Data source: Nine PICO (population, intervention, comparators, outcomes) questions and associated recommendations for the treatment of patients diagnosed with both HIV and TB, developed based on the evidence appraised using GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) methodology.
Disclosures: The American Thoracic Society, the Infections Diseases Society of America, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provided financial support. Lead author Dr. Nahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
CMV viremia not culprit in high mortality of TB/HIV coinfection
DURBAN, SOUTH AFRICA – Cytomegalovirus viremia is common among patients hospitalized for HIV-associated tuberculosis, but it appears to be a bystander rather than a contributor to the high mortality seen in this population, Amy Ward, MD, said at the 21st International AIDS Conference.
“CMV [cytomegalovirus] viremia is likely a marker of more severe immunodeficiency rather than a direct contributor to mortality,” she concluded based upon the findings of her prospective cohort study. The finding means therapies for CMV viremia will not open up a new avenue of potentially life-saving treatments for these patients.
In other severe immunodeficiency conditions, such as after organ transplant, CMV viremia is directly related to increased mortality, and ganciclovir therapy can prevent progression to clinical disease and death, explained Dr. Ward of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
She presented a prospective cohort study of 256 HIV-infected South African adults, median age 36 years, who were hospitalized with a new diagnosis of TB. At enrollment, their median CD4 count was 64 cells/mm3. Only 35% were on antiretroviral therapy (ART); 44% had previously been on ART, 21% were ART-naive, and 41% had a positive TB blood culture.
CMV viremia was present in 31%, and CMV viral load was 1,000 copies/mL or more in half of them. None had CMV retinitis, based on panoptic fundoscopy at enrollment. HIV-related retinal pathologies at enrollment included disseminated cryptococcal disease, ocular TB granules, and HIV retinitis.
The primary endpoint of the study was mortality at 12 weeks on anti-TB therapy. The mortality rate was 38% in the CMV viremic group, significantly higher than the 17.8% mortality rate seen in the CMV-negative patients.
In a univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, CMV viremia was associated with a 2.1-fold increased risk for 12-week mortality. But advancing age, a low CD4 count, and decreasing serum albumin were also risk factors.
When these variables were incorporated in a multivariate regression analysis along with HIV viral load, tuberculosis blood culture results, and gender, CMV viremia was no longer a significant risk factor for 12-week mortality. Age was the sole significant predictor of death. Patients who were at least 36 years old had a 32.8% mortality rate, compared with a 14.1% rate in those who were younger. The CD4 count didn’t differ significantly by age; however, the prevalence of CMV viremia was 38% in the older group and 26.3% in patients under age 36.
“Those patients who were 36 years old and above had a higher mortality and were more likely to have CMV viremia, both findings perhaps reflecting premature aging of the immune system,” Dr. Ward said.
Also, no dose-response was seen between CMV viral load and mortality risk. The 12-week mortality rate was 33.3% in patients with a CMV viral load below 1,000 copies/mL and similar at 34.1% in those with a viral load above that cutpoint, she noted.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the South African Medical Research Council. Dr. Ward reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
DURBAN, SOUTH AFRICA – Cytomegalovirus viremia is common among patients hospitalized for HIV-associated tuberculosis, but it appears to be a bystander rather than a contributor to the high mortality seen in this population, Amy Ward, MD, said at the 21st International AIDS Conference.
“CMV [cytomegalovirus] viremia is likely a marker of more severe immunodeficiency rather than a direct contributor to mortality,” she concluded based upon the findings of her prospective cohort study. The finding means therapies for CMV viremia will not open up a new avenue of potentially life-saving treatments for these patients.
In other severe immunodeficiency conditions, such as after organ transplant, CMV viremia is directly related to increased mortality, and ganciclovir therapy can prevent progression to clinical disease and death, explained Dr. Ward of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
She presented a prospective cohort study of 256 HIV-infected South African adults, median age 36 years, who were hospitalized with a new diagnosis of TB. At enrollment, their median CD4 count was 64 cells/mm3. Only 35% were on antiretroviral therapy (ART); 44% had previously been on ART, 21% were ART-naive, and 41% had a positive TB blood culture.
CMV viremia was present in 31%, and CMV viral load was 1,000 copies/mL or more in half of them. None had CMV retinitis, based on panoptic fundoscopy at enrollment. HIV-related retinal pathologies at enrollment included disseminated cryptococcal disease, ocular TB granules, and HIV retinitis.
The primary endpoint of the study was mortality at 12 weeks on anti-TB therapy. The mortality rate was 38% in the CMV viremic group, significantly higher than the 17.8% mortality rate seen in the CMV-negative patients.
In a univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, CMV viremia was associated with a 2.1-fold increased risk for 12-week mortality. But advancing age, a low CD4 count, and decreasing serum albumin were also risk factors.
When these variables were incorporated in a multivariate regression analysis along with HIV viral load, tuberculosis blood culture results, and gender, CMV viremia was no longer a significant risk factor for 12-week mortality. Age was the sole significant predictor of death. Patients who were at least 36 years old had a 32.8% mortality rate, compared with a 14.1% rate in those who were younger. The CD4 count didn’t differ significantly by age; however, the prevalence of CMV viremia was 38% in the older group and 26.3% in patients under age 36.
“Those patients who were 36 years old and above had a higher mortality and were more likely to have CMV viremia, both findings perhaps reflecting premature aging of the immune system,” Dr. Ward said.
Also, no dose-response was seen between CMV viral load and mortality risk. The 12-week mortality rate was 33.3% in patients with a CMV viral load below 1,000 copies/mL and similar at 34.1% in those with a viral load above that cutpoint, she noted.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the South African Medical Research Council. Dr. Ward reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
DURBAN, SOUTH AFRICA – Cytomegalovirus viremia is common among patients hospitalized for HIV-associated tuberculosis, but it appears to be a bystander rather than a contributor to the high mortality seen in this population, Amy Ward, MD, said at the 21st International AIDS Conference.
“CMV [cytomegalovirus] viremia is likely a marker of more severe immunodeficiency rather than a direct contributor to mortality,” she concluded based upon the findings of her prospective cohort study. The finding means therapies for CMV viremia will not open up a new avenue of potentially life-saving treatments for these patients.
In other severe immunodeficiency conditions, such as after organ transplant, CMV viremia is directly related to increased mortality, and ganciclovir therapy can prevent progression to clinical disease and death, explained Dr. Ward of the University of Cape Town, South Africa.
She presented a prospective cohort study of 256 HIV-infected South African adults, median age 36 years, who were hospitalized with a new diagnosis of TB. At enrollment, their median CD4 count was 64 cells/mm3. Only 35% were on antiretroviral therapy (ART); 44% had previously been on ART, 21% were ART-naive, and 41% had a positive TB blood culture.
CMV viremia was present in 31%, and CMV viral load was 1,000 copies/mL or more in half of them. None had CMV retinitis, based on panoptic fundoscopy at enrollment. HIV-related retinal pathologies at enrollment included disseminated cryptococcal disease, ocular TB granules, and HIV retinitis.
The primary endpoint of the study was mortality at 12 weeks on anti-TB therapy. The mortality rate was 38% in the CMV viremic group, significantly higher than the 17.8% mortality rate seen in the CMV-negative patients.
In a univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, CMV viremia was associated with a 2.1-fold increased risk for 12-week mortality. But advancing age, a low CD4 count, and decreasing serum albumin were also risk factors.
When these variables were incorporated in a multivariate regression analysis along with HIV viral load, tuberculosis blood culture results, and gender, CMV viremia was no longer a significant risk factor for 12-week mortality. Age was the sole significant predictor of death. Patients who were at least 36 years old had a 32.8% mortality rate, compared with a 14.1% rate in those who were younger. The CD4 count didn’t differ significantly by age; however, the prevalence of CMV viremia was 38% in the older group and 26.3% in patients under age 36.
“Those patients who were 36 years old and above had a higher mortality and were more likely to have CMV viremia, both findings perhaps reflecting premature aging of the immune system,” Dr. Ward said.
Also, no dose-response was seen between CMV viral load and mortality risk. The 12-week mortality rate was 33.3% in patients with a CMV viral load below 1,000 copies/mL and similar at 34.1% in those with a viral load above that cutpoint, she noted.
The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the South African Medical Research Council. Dr. Ward reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
AT AIDS 2016
Key clinical point: Cytomegalovirus viremia is common in patients hospitalized for HIV-associated tuberculosis, but treating the CMV infection is unlikely to reduce the coinfected group’s high mortality rate.
Major finding: Cytomegalovirus viremia was present in nearly one-third of a group of hospitalized patients with HIV infection and tuberculosis, but was not an independent risk factor for their 23% mortality rate at 12 weeks.
Data source: This was a prospective cohort study including 256 hospitalized patients coinfected with HIV and newly diagnosed tuberculosis.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Wellcome Trust and the South African Medical Research Council. The presenter reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
Thymectomy improves clinical outcomes for myasthenia gravis
Thymectomy improved 3-year clinical outcomes and proved superior to medical therapy for mild to severe nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis, according to a report published online Aug. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Compared with standard prednisone therapy, thymectomy plus prednisone decreased the number and severity of symptoms, allowed the lowering of steroid doses, decreased the number and length of hospitalizations for disease exacerbations, reduced the need for immunosuppressive agents, and improved health-related quality of life in an international, randomized clinical trial, said Gil I. Wolfe, MD, of the department of neurology, State University of New York at Buffalo and his associates.
Until now, thymectomy was known to be beneficial in some cases of myasthenia gravis “but with widely varying rates of clinical improvement or remission.” And the success of immunotherapy has raised the question of whether an invasive surgery is necessary. Data from randomized, controlled studies have been sparse.
Moreover, thymectomy rarely causes adverse effects, but “the procedure can cost up to $80,000 and can be associated with operative complications that need to be weighed against benefits.” In comparison, medical therapy with glucocorticoids and other immunosuppressive agents is less invasive but is definitely associated with adverse events, including some that are life threatening, and negatively impacts quality of life, the investigators said.
To address the lack of randomized controlled trial data, they assessed 3-year outcomes in 126 patients treated at 67 medical centers in 18 countries during a 6-year period. The study participants were aged 18-65 years, had a disease duration of less than 5 years at enrollment (median duration, 1 year), and had class II (mild generalized disease) to class IV (severe generalized disease) myasthenia gravis. These patients were randomly assigned to undergo thymectomy and receive standard prednisone therapy (66 participants) or to receive standard prednisone alone (60 participants).
Thymectomy was performed using a median sternotomy “with the goal of an en bloc resection of all mediastinal tissue that could anatomically contain gross or microscopic thymus.”
At follow-up, time-weighted average scores on the Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis scale were significantly lower by 2.85 points, indicating improved clinical status, in the thymectomy group than in the control group. Time-weighted average prednisone dose also was significantly lower, at an average alternate-day dose of 44 mg in the thymectomy group and 60 mg in the control group, Dr. Wolfe and his associates said (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602489).
On a measure of treatment-related complications, scores favored thymectomy with regard to the number of patients with symptoms, the total number of symptoms, and the distress level related to symptoms throughout the study period. Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required hospitalization for exacerbations of myasthenia gravis (9% vs. 37%), and the mean cumulative number of hospital days was lower with thymectomy (8.4 vs. 19.2).
In addition, scores on the Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living scale favored thymectomy (2.24 vs. 3.41). Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required azathioprine (17% vs. 0.48%). And the percentage of patients who reported having minimal manifestations of the disease at 3 years was significantly higher with thymectomy (67%) than with prednisone alone (47%).
This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, and the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America and received no commercial support. Dr. Wolfe reported ties to Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Alpha Cancer Technologies, Argenx, Baxalta, CSL Behring, Grifols, and UCB, and his associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Landmark trial establishes effectiveness of thymectomy in myasthenia gravis
One of the many challenges of treating patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) is the fluctuating nature of symptoms and deficits. The neurologist or neuromuscular specialist must decide whether the disease is truly worsening, whether the patient is experiencing more pronounced symptoms from intercurrent illness or the effects of a medication known to affect the neuromuscular junction adversely, or whether the patient is concerned that there might be worsening disease when all objective measures indicate stability. These factors make treatment decisions more difficult in MG than for many other neuromuscular disorders.
Similarly, researchers considering a trial investigating treatment efficacy in MG face the complex issues of disease fluctuation in cohorts of individuals with the disease, varying levels of corticosteroid and immunosuppressant doses in different MG patients, and thorny ethical dilemmas in providing accepted therapies but not withholding effective treatments from those in need.
Dr. Wolfe and his colleagues demonstrate that they have navigated these treacherous waters. They have succeeded in completing a landmark controlled clinical trial which establishes the effectiveness of transsternal thymectomy with adjuvant corticosteroid therapy in nonthymomatous MG vs. oral prednisone without surgery. While this international 36-center trial managed to recruit 126 subjects over a 6-year period, using sound inclusion and exclusion criteria and a meticulous trial design, the number of patients is not sufficient to allow for as robust a subgroup analysis for age, gender, and a variety of clinical variables reflecting severity of disease as would have been hoped for by the MG community.
Nonetheless, this paper sets the use of thymectomy in nonthymomatous MG on firmer ground going forward. The investigators will doubtless be presenting further data from the trial, including clinical-pathologic correlates and other relevant novel observations. In addition, Wolfe et al. have opened the door for future trials of thymectomy in MG to address such issues as the benefits vs. risks of performing the operation via the traditional transsternal vs. alternative non–sternal splitting approaches.
Benn E. Smith, MD, is an associate professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz. and is the director of the sensory laboratory there. Dr. Smith is on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Neurology News.
End to an 80-year controversy
These findings from Wolfe et al. end an 80-year controversy over the effectiveness of thymectomy for patients with myasthenia gravis.
Perhaps the most important benefit for patients is that even when they require prednisone following the surgery, they can take lower doses, endure fewer glucocorticoid-related symptoms, and experience less distress from those symptoms than patients who don’t undergo thymectomy.
Unfortunately, the study results cannot offer further clarity regarding patient selection for thymectomy. The patient population in this trial was so small that subgroup analyses couldn’t allow conclusions regarding the relative effectiveness of thymectomy in men vs. women or younger vs. older patients.
Allan H. Ropper, MD, is in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. His financial disclosures are available at NEJM.org. Dr. Ropper made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wolfe’s report (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1607953).
Landmark trial establishes effectiveness of thymectomy in myasthenia gravis
One of the many challenges of treating patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) is the fluctuating nature of symptoms and deficits. The neurologist or neuromuscular specialist must decide whether the disease is truly worsening, whether the patient is experiencing more pronounced symptoms from intercurrent illness or the effects of a medication known to affect the neuromuscular junction adversely, or whether the patient is concerned that there might be worsening disease when all objective measures indicate stability. These factors make treatment decisions more difficult in MG than for many other neuromuscular disorders.
Similarly, researchers considering a trial investigating treatment efficacy in MG face the complex issues of disease fluctuation in cohorts of individuals with the disease, varying levels of corticosteroid and immunosuppressant doses in different MG patients, and thorny ethical dilemmas in providing accepted therapies but not withholding effective treatments from those in need.
Dr. Wolfe and his colleagues demonstrate that they have navigated these treacherous waters. They have succeeded in completing a landmark controlled clinical trial which establishes the effectiveness of transsternal thymectomy with adjuvant corticosteroid therapy in nonthymomatous MG vs. oral prednisone without surgery. While this international 36-center trial managed to recruit 126 subjects over a 6-year period, using sound inclusion and exclusion criteria and a meticulous trial design, the number of patients is not sufficient to allow for as robust a subgroup analysis for age, gender, and a variety of clinical variables reflecting severity of disease as would have been hoped for by the MG community.
Nonetheless, this paper sets the use of thymectomy in nonthymomatous MG on firmer ground going forward. The investigators will doubtless be presenting further data from the trial, including clinical-pathologic correlates and other relevant novel observations. In addition, Wolfe et al. have opened the door for future trials of thymectomy in MG to address such issues as the benefits vs. risks of performing the operation via the traditional transsternal vs. alternative non–sternal splitting approaches.
Benn E. Smith, MD, is an associate professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz. and is the director of the sensory laboratory there. Dr. Smith is on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Neurology News.
End to an 80-year controversy
These findings from Wolfe et al. end an 80-year controversy over the effectiveness of thymectomy for patients with myasthenia gravis.
Perhaps the most important benefit for patients is that even when they require prednisone following the surgery, they can take lower doses, endure fewer glucocorticoid-related symptoms, and experience less distress from those symptoms than patients who don’t undergo thymectomy.
Unfortunately, the study results cannot offer further clarity regarding patient selection for thymectomy. The patient population in this trial was so small that subgroup analyses couldn’t allow conclusions regarding the relative effectiveness of thymectomy in men vs. women or younger vs. older patients.
Allan H. Ropper, MD, is in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. His financial disclosures are available at NEJM.org. Dr. Ropper made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wolfe’s report (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1607953).
Landmark trial establishes effectiveness of thymectomy in myasthenia gravis
One of the many challenges of treating patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) is the fluctuating nature of symptoms and deficits. The neurologist or neuromuscular specialist must decide whether the disease is truly worsening, whether the patient is experiencing more pronounced symptoms from intercurrent illness or the effects of a medication known to affect the neuromuscular junction adversely, or whether the patient is concerned that there might be worsening disease when all objective measures indicate stability. These factors make treatment decisions more difficult in MG than for many other neuromuscular disorders.
Similarly, researchers considering a trial investigating treatment efficacy in MG face the complex issues of disease fluctuation in cohorts of individuals with the disease, varying levels of corticosteroid and immunosuppressant doses in different MG patients, and thorny ethical dilemmas in providing accepted therapies but not withholding effective treatments from those in need.
Dr. Wolfe and his colleagues demonstrate that they have navigated these treacherous waters. They have succeeded in completing a landmark controlled clinical trial which establishes the effectiveness of transsternal thymectomy with adjuvant corticosteroid therapy in nonthymomatous MG vs. oral prednisone without surgery. While this international 36-center trial managed to recruit 126 subjects over a 6-year period, using sound inclusion and exclusion criteria and a meticulous trial design, the number of patients is not sufficient to allow for as robust a subgroup analysis for age, gender, and a variety of clinical variables reflecting severity of disease as would have been hoped for by the MG community.
Nonetheless, this paper sets the use of thymectomy in nonthymomatous MG on firmer ground going forward. The investigators will doubtless be presenting further data from the trial, including clinical-pathologic correlates and other relevant novel observations. In addition, Wolfe et al. have opened the door for future trials of thymectomy in MG to address such issues as the benefits vs. risks of performing the operation via the traditional transsternal vs. alternative non–sternal splitting approaches.
Benn E. Smith, MD, is an associate professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz. and is the director of the sensory laboratory there. Dr. Smith is on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Neurology News.
End to an 80-year controversy
These findings from Wolfe et al. end an 80-year controversy over the effectiveness of thymectomy for patients with myasthenia gravis.
Perhaps the most important benefit for patients is that even when they require prednisone following the surgery, they can take lower doses, endure fewer glucocorticoid-related symptoms, and experience less distress from those symptoms than patients who don’t undergo thymectomy.
Unfortunately, the study results cannot offer further clarity regarding patient selection for thymectomy. The patient population in this trial was so small that subgroup analyses couldn’t allow conclusions regarding the relative effectiveness of thymectomy in men vs. women or younger vs. older patients.
Allan H. Ropper, MD, is in the department of neurology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. His financial disclosures are available at NEJM.org. Dr. Ropper made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wolfe’s report (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1607953).
Thymectomy improved 3-year clinical outcomes and proved superior to medical therapy for mild to severe nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis, according to a report published online Aug. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Compared with standard prednisone therapy, thymectomy plus prednisone decreased the number and severity of symptoms, allowed the lowering of steroid doses, decreased the number and length of hospitalizations for disease exacerbations, reduced the need for immunosuppressive agents, and improved health-related quality of life in an international, randomized clinical trial, said Gil I. Wolfe, MD, of the department of neurology, State University of New York at Buffalo and his associates.
Until now, thymectomy was known to be beneficial in some cases of myasthenia gravis “but with widely varying rates of clinical improvement or remission.” And the success of immunotherapy has raised the question of whether an invasive surgery is necessary. Data from randomized, controlled studies have been sparse.
Moreover, thymectomy rarely causes adverse effects, but “the procedure can cost up to $80,000 and can be associated with operative complications that need to be weighed against benefits.” In comparison, medical therapy with glucocorticoids and other immunosuppressive agents is less invasive but is definitely associated with adverse events, including some that are life threatening, and negatively impacts quality of life, the investigators said.
To address the lack of randomized controlled trial data, they assessed 3-year outcomes in 126 patients treated at 67 medical centers in 18 countries during a 6-year period. The study participants were aged 18-65 years, had a disease duration of less than 5 years at enrollment (median duration, 1 year), and had class II (mild generalized disease) to class IV (severe generalized disease) myasthenia gravis. These patients were randomly assigned to undergo thymectomy and receive standard prednisone therapy (66 participants) or to receive standard prednisone alone (60 participants).
Thymectomy was performed using a median sternotomy “with the goal of an en bloc resection of all mediastinal tissue that could anatomically contain gross or microscopic thymus.”
At follow-up, time-weighted average scores on the Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis scale were significantly lower by 2.85 points, indicating improved clinical status, in the thymectomy group than in the control group. Time-weighted average prednisone dose also was significantly lower, at an average alternate-day dose of 44 mg in the thymectomy group and 60 mg in the control group, Dr. Wolfe and his associates said (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602489).
On a measure of treatment-related complications, scores favored thymectomy with regard to the number of patients with symptoms, the total number of symptoms, and the distress level related to symptoms throughout the study period. Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required hospitalization for exacerbations of myasthenia gravis (9% vs. 37%), and the mean cumulative number of hospital days was lower with thymectomy (8.4 vs. 19.2).
In addition, scores on the Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living scale favored thymectomy (2.24 vs. 3.41). Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required azathioprine (17% vs. 0.48%). And the percentage of patients who reported having minimal manifestations of the disease at 3 years was significantly higher with thymectomy (67%) than with prednisone alone (47%).
This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, and the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America and received no commercial support. Dr. Wolfe reported ties to Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Alpha Cancer Technologies, Argenx, Baxalta, CSL Behring, Grifols, and UCB, and his associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Thymectomy improved 3-year clinical outcomes and proved superior to medical therapy for mild to severe nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis, according to a report published online Aug. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Compared with standard prednisone therapy, thymectomy plus prednisone decreased the number and severity of symptoms, allowed the lowering of steroid doses, decreased the number and length of hospitalizations for disease exacerbations, reduced the need for immunosuppressive agents, and improved health-related quality of life in an international, randomized clinical trial, said Gil I. Wolfe, MD, of the department of neurology, State University of New York at Buffalo and his associates.
Until now, thymectomy was known to be beneficial in some cases of myasthenia gravis “but with widely varying rates of clinical improvement or remission.” And the success of immunotherapy has raised the question of whether an invasive surgery is necessary. Data from randomized, controlled studies have been sparse.
Moreover, thymectomy rarely causes adverse effects, but “the procedure can cost up to $80,000 and can be associated with operative complications that need to be weighed against benefits.” In comparison, medical therapy with glucocorticoids and other immunosuppressive agents is less invasive but is definitely associated with adverse events, including some that are life threatening, and negatively impacts quality of life, the investigators said.
To address the lack of randomized controlled trial data, they assessed 3-year outcomes in 126 patients treated at 67 medical centers in 18 countries during a 6-year period. The study participants were aged 18-65 years, had a disease duration of less than 5 years at enrollment (median duration, 1 year), and had class II (mild generalized disease) to class IV (severe generalized disease) myasthenia gravis. These patients were randomly assigned to undergo thymectomy and receive standard prednisone therapy (66 participants) or to receive standard prednisone alone (60 participants).
Thymectomy was performed using a median sternotomy “with the goal of an en bloc resection of all mediastinal tissue that could anatomically contain gross or microscopic thymus.”
At follow-up, time-weighted average scores on the Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis scale were significantly lower by 2.85 points, indicating improved clinical status, in the thymectomy group than in the control group. Time-weighted average prednisone dose also was significantly lower, at an average alternate-day dose of 44 mg in the thymectomy group and 60 mg in the control group, Dr. Wolfe and his associates said (N Engl J Med. 2016 Aug 11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602489).
On a measure of treatment-related complications, scores favored thymectomy with regard to the number of patients with symptoms, the total number of symptoms, and the distress level related to symptoms throughout the study period. Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required hospitalization for exacerbations of myasthenia gravis (9% vs. 37%), and the mean cumulative number of hospital days was lower with thymectomy (8.4 vs. 19.2).
In addition, scores on the Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living scale favored thymectomy (2.24 vs. 3.41). Fewer patients in the thymectomy group required azathioprine (17% vs. 0.48%). And the percentage of patients who reported having minimal manifestations of the disease at 3 years was significantly higher with thymectomy (67%) than with prednisone alone (47%).
This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, and the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America and received no commercial support. Dr. Wolfe reported ties to Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Alpha Cancer Technologies, Argenx, Baxalta, CSL Behring, Grifols, and UCB, and his associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Thymectomy improved 3-year clinical outcomes and was superior to medical therapy for mild to severe nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis.
Major finding: Scores on the Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis scale were significantly lower by 2.85 points, indicating improved clinical status, in the thymectomy group than in the control group.
Data source: An international, randomized, medication-controlled trial involving 126 patients at 67 medical centers.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, and the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America and received no commercial support. Dr. Wolfe reported ties to Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Alpha Cancer Technologies, Argenx, Baxalta, CSL Behring, Grifols, and UCB, and his associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.