User login
Can Cannabis Help to Reduce Diabetes Risk?
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , ongoing research suggests.
In the findings from the SONIC trial, Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and codirector of CUChange at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and colleagues hypothesized that “those inflammatory profiles would improve over the course of 4 weeks, particularly for those using a CBD [cannabidiol] as opposed to a THC [tetrahydrocannabinol] product.”
She presented the findings at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions.
Other recent work by Dr. Bryan and her colleagues focused on the public health implications of cannabis legalization. One study examined the acute effects of legal-market cannabis on regular users’ subjective responses while running and found that cannabis use prior to exercise may lead to more enjoyment and runner’s high symptoms, although it also led to feelings of greater exertion. The positive effects could make exercise more appealing to individuals — including those with or at risk for diabetes — who might not otherwise engage in it, Bryan suggested.
Another study found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
‘Complicated’ Connection to Diabetes
In the SONIC study, participants who were regular cannabis users had an average age of 30 years and had body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range; 86% were White individuals, and 59% were men. They were matched with a similar group of individuals who had not used cannabis for at least a year. At baseline, participants’ NSDR Healthy Eating Index score overall was 51.24, showing a “need for improvement/poor diet.”
“Folks were maybe not killing it in the dietary domain,” Dr. Bryan acknowledged. “However, they were absolutely killing it in the physical activity domain.”
The researchers did oral glucose tolerance tests to calculate participants’ Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity and measured inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL6), IL1 beta, IL12, interferon gamma, IL4, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1). In a “randomized encouragement” design, users were assigned to purchase and use a flower product for 4 weeks, however much they wanted. They completed daily assessments of their cannabis use, alcohol use, diet, and physical activity.
Between-group eating patterns were similar over the 4 weeks, with cannabis users reporting “marginally” more servings of salty snacks and food relative to nonusers. None of the daily associations were moderated by which cannabis product was used.
At 4 weeks, the team repeated the tests and, surprisingly, found no change in participants’ inflammatory markers. But what “popped out,” she said, was the “stark difference” between users and nonusers, with users having significantly lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers, circulating cytokines than the nonusers.
An exception were levels of MCP-1, which increased over time in the users but didn’t change in nonusers. Bryan said the finding is “perplexing” and asked the audience for thoughts, especially given that MCP-1 levels are positively associated with diabetes.
After controlling for BMI and inflammation, “we saw absolutely no effects of group or group by time interaction on the Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity,” she said. “Seemingly, there are no chronic effects of cannabis use on insulin sensitivity.”
Regarding limitations, Dr. Bryan acknowledged that the study is being conducted with “a very healthy sample of individuals who exercise a lot, and that might be factoring into our results, especially on insulin sensitivity.” The team could not use “gold standard” randomization because of the schedule-1 status of CannaVan cannabis, and the MCP-1 findings are difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, she noted, “our day-to-day level data show only slight differences in behavior between those who use cannabis and those who don’t and also very slight differences between users’ behavior on days that they use vs days that they don’t.
“I think all of this put together shows us that the relationship between cannabis use and potential implications for diabetes is a lot more complicated than just couch to couchlock [very deep relaxation/sedation] or runner’s high,” she said.
Bring On the CannaVan
The team’s next step, currently underway, is to get an acute response to cannabis with an oral glucose tolerance test that’s done immediately after the participant uses a product. Since cannabis is a schedule-1 drug, it can’t be taken into the laboratory. Therefore, the researchers are using a CannaVan — a mobile lab. “We drive it to their homes, they come out, we draw blood, and we send them back into their homes to use as much of their product as they want,” Bryan explained. “They come back out to the van. They do all the follow-up assessments. We take blood again to verify their exposure. And that’s how we collect those data.”
“Invite me back next year, and I will tell you what we found,” she quipped.
Dr. Bryan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Can Response to Semaglutide Be Predicted With a Genetic Test?
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — An analysis of data from 137 patients suggested testing whether people have a trait known as abnormal postprandial satiety (APS), or hungry gut, can predict how well they may respond to the obesity drug semaglutide, although it failed to establish this link for the somewhat similar tirzepatide.
At the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Scientific Sessions, Maria Daniela Hurtado Andrade, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, presented results of a study using the MyPhenome Hungry Gut test, which was developed through machine learning, a form of artificial intelligence.
The test is part of the MyPhenome obesity phenotyping portfolio from Phenomix Sciences, a company founded by Mayo Clinic physicians, scientists, and researchers Andres Acosta, MD, PhD, and Michael Camilleri, MD, DSc.
At the ADA meeting, Dr. Hurtado Andrade discussed a test of 137 adults: 91 were considered to have a positive biomarker for abnormal postprandial satiety (APS+), and 46 who did not have it were classified as APS−. These were patients of the Mayo Clinic who were already taking obesity drugs and agreed to phenotyping. Of this group, 113 were on semaglutide and 24 on tirzepatide.
, with a mean 19.4% body weight loss in the APS+ group and a mean loss of 22.1% in the APS− group.
Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical utility of these biomarkers, Dr. Hurtado Andrade said. But these findings do support “the use of precision medicine for obesity based on an individual’s genetic background,” she said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade’s presentation impressed fellow researchers who noted it as an early step toward the long-sought goal of more personalized medicine.
Daniel S. Hsia, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, who led the ADA session at which Dr. Hurtado Andrade presented, said it was good to see new information being presented about using genetic risk scoring in obesity.
“The numbers were very small for the tirzepatide group as compared to the semaglutide group, so it’s a little hard to really come to any significant conclusions,” Dr. Hsia said in an interview.
At the ADA meeting, Ajay D. Rao, MD, MMSc, of Temple University, Philadelphia, said clinicians are excited about the idea of having biomarkers to aid in decisions about approaches to obesity.
In a follow-up interview with this news organization, Dr. Rao said he too is looking to see more testing of this approach to care, while describing Hurtado Andrade’s work as a “very well-done study.”
“We still need to see more large-scale studies of responsiveness to certain interventions,” he said.
Dr. Hurtado Andrade noted that researchers at academic centers such as Mayo can try to hone in the combination of genetic and other factors that led to obesity, such as emotional eating patterns and abnormal postprandial satiety.
But this approach is not widely scalable, as it demands resources of time and staffing that not all clinicians and patients enjoy.
“To overcome this challenge, our team has been working on developing biomarkers” such as the machine-learning gene risk score used to predict abnormal postprandial satiety, she said.
Findings for a related project were presented in May at Digestive Disease Week, as this news organization reported earlier. In that study, researchers calculated the genetic risk score for 84 adults undergoing weight loss interventions at Mayo Clinic who were prescribed the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist semaglutide.
This news organization separately asked Phenomix about the sales of MyPhenome Test kits. These cost $499, and about 500 tests have been sold since commercialization started last year, a spokesperson said.
The study was funded by Phenomix Sciences. Separately, Dr. Hurtado Andrade has worked as a consultant for Novo Nordisk and received research support from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
GLP-1 Thyroid Warning Could Increase Overdiagnosis
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Florida — Clinicians should keep in mind concerns about overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer when prescribing glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) drugs, as the US boxed warning about this risk for this class of medicines for certain tumors in mice could trigger excess screening, an expert endocrinologist said.
Speaking at the annual American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, Elizabeth N. Pearce, MD, MSc, a professor of medicine at Boston University, Boston, reviewed the different approaches US and European regulators have taken for the GLP-1 drugs. She also explained the current concerns about the wide use of thyroid screening in general and how these intersect with the rapid uptake of the GLP-1 drugs.
said Dr. Pearce, who is also a former board president of the American Thyroid Association (ATA). “We do not want to contribute to this epidemic of overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer.”
The ATA and the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) are among the health organizations that have in recent years sought to boost public awareness of the potential risks for excess screening of thyroid nodules. In 2017, the USPSTF, which influences insurance coverage, recommended against routine screening for thyroid cancer in asymptomatic adults. At that time, the incidence of thyroid cancer detection had increased by 4.5% per year over a decade, faster than for any other cancer, but without a corresponding change in the mortality rate, USPSTF said.
“Unequivocally, the thyroid cancer mortality has not kept pace with thyroid cancer detection,” Dr. Pearce said at the ADA meeting. “We’ve been diagnosing a lot of small thyroid cancers that people would otherwise have been destined to die with and not die of.”
Dr. Pearce said clinicians should be careful not to overly restrict access to GLP-1 drugs due to concerns about thyroid cancer — and they should use care in screening nodules.
It’s possible that the weight loss experienced by people taking GLP-1 drugs may make preexisting thyroid nodules more prominent, Dr. Pearce said. It’s also likely that the US boxed warning on thyroid risk on GLP-1 drugs makes clinicians and patients more likely to look for these kinds of growths.
Dr. Pearce urged adherence to guidelines such as the ones the ATA published in 2015 for assessing nodules.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Pearce noted the frequency of CT scans in US medical practice in turning up many incidental thyroid nodules, a finding that can cause some panic for patients and their clinicians.
But it helps to put these findings in context, as by the age of 50, about 40% of women will have at least one thyroid nodule, making this a very common finding, she said.
“The vast majority are not malignant,” Dr. Pearce said. “When you explain this to patients, it alleviates anxiety.”
The US, European Union Differences
In the United States, the label for GLP-1 drugs starts with a boxed warning about thyroid C-cell tumors seen in rodents given these medicines in testing.
It’s unknown if the medicines could cause medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in humans, the label adds. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2, the boxed warning says. This is based largely on data seen in laboratory rats.
“It’s a big black box warning that gets people’s attention,” Dr. Pearce said. “Important to note that if you practice in Europe, you will not be familiar with this labeling because it doesn’t exist there. They’ve never had this warning on the European package.”
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) does include information about the results of rodent studies as part of the discussion of known and potential risks for GLP-1 drugs but has not emphasized it in the same way as the US drug labels do.
For example, the public assessment report posted on the EMA website for semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) notes that nonlethal thyroid C-cell tumors “observed in rodents are a class effect for GLP-1 receptor agonists.” It’s possible that these may be due to a particular sensitivity in rodents, the report said.
“The relevance for humans is considered to be low but cannot be completely excluded,” the EMA report said in the product information section of the report.
There has been ongoing interest in the issue.
The EMA’s Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) in October concluded that the available evidence does not support a causal association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.
The EMA’s PRAC safety committee said it began assessing the evidence about a possible connection following the publication of a study in 2022 in the journal Diabetes Care. That paper reported on an analysis that suggested increased risk for all thyroid cancer and medullary thyroid cancer with the use of GLP-1 drugs, particularly after 1-3 years of treatment.
The EMA’s PRAC said that in making its decision, it also considered other published papers on this topic as well as clinical and postmarketing data on GLP-1 drugs.
In an email interview, Jean-Luc Faillie, MD, PhD, corresponding author of the Diabetes Care paper, called for continued “vigilance and prudence in clinical practice” with GLP-1 drugs.
His paper reported on a case-control analysis on the basis of reports from the French national healthcare insurance system database, looking at people who had taken GLP-1 drugs and similar people who had not.
Due to a lack of a specific diagnostic code for medullary thyroid cancers, the researchers used a composite definition combining thyroid cancer diagnosis with several calcitonin tests, a carcinoembryonic antigen test, or a specific treatment (vandetanib) to identify potential cases of this cancer.
It’s possible that this method could have led to overestimation of MTC among the cases of thyroid cancer, wrote Dr. Faillie, who is a professor at France’s Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, and part of its pharmacological vigilance service.
“Nevertheless, it’s crucial to emphasize that any potential overestimation of MTC cases would likely apply equally to both GLP-1 receptor agonist–exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Faillie wrote. “Therefore, it should not significantly impact our main findings regarding the suggested increased risk associated with GLP-1 receptor agonist use.”
Dr. Pearce disclosed honoraria for speaking at the Merck China Forum. Dr. Faille and his coauthors reported no conflicts of interest in the publication of their study. Their research was supported by the French Medicines Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, grant 2019S015) in the context of a partnership with the Health Product Epidemiology Scientific Interest Group (EPI-PHARE). The study was part of France’s Drugs Systematized Assessment in Real-Life Environment (DRUGS-SAFEr) research program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Facial Temperature Can Reveal Age and Disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
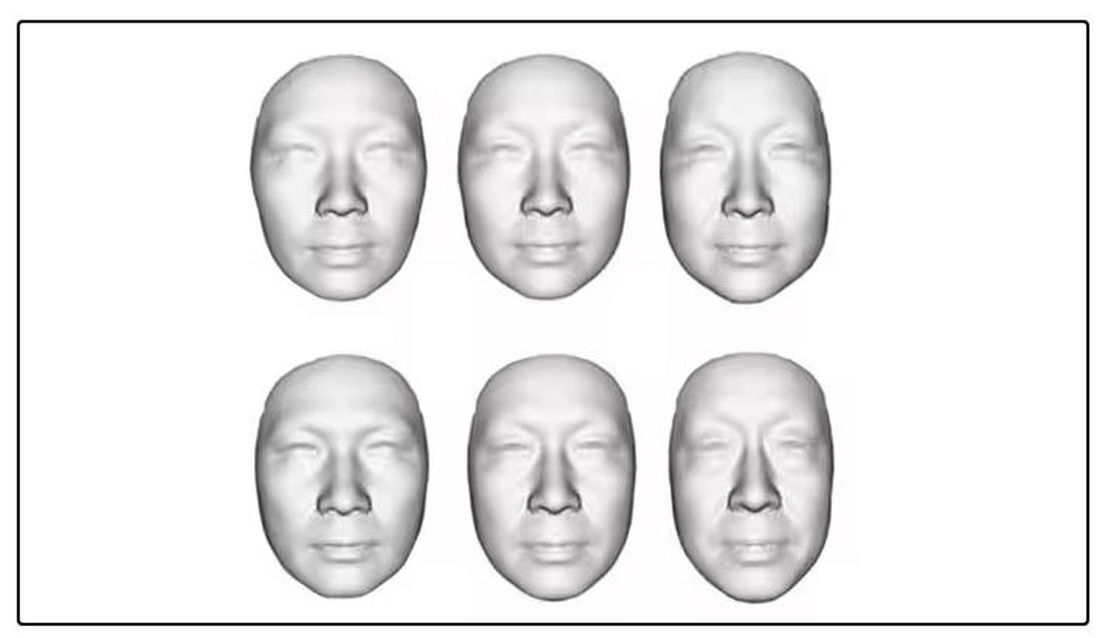
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those.
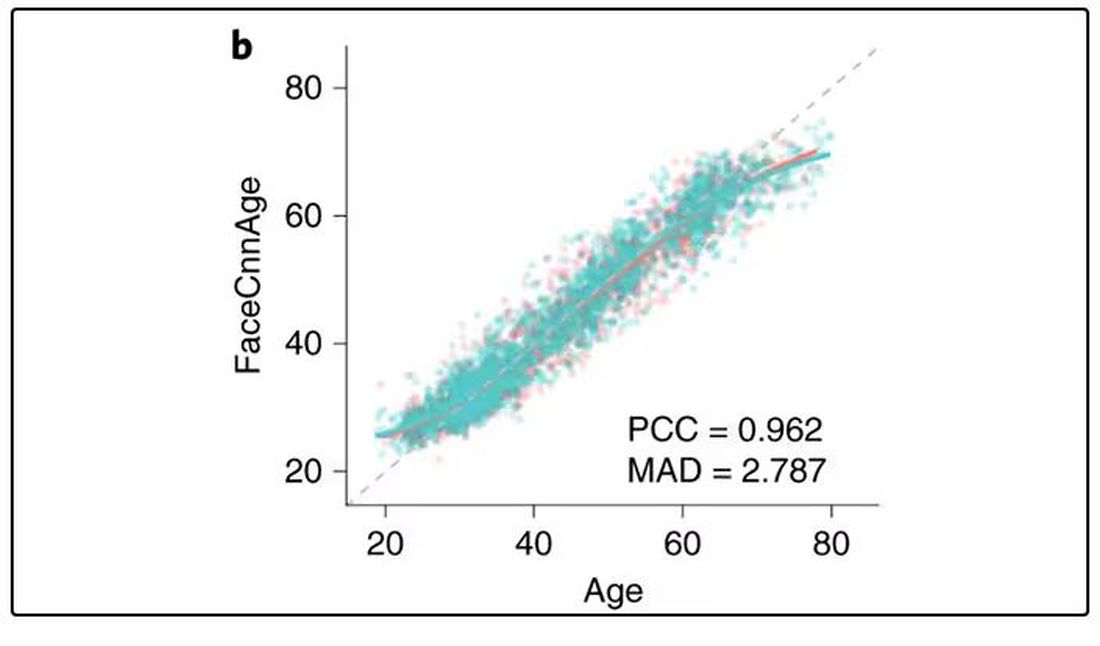
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally.
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
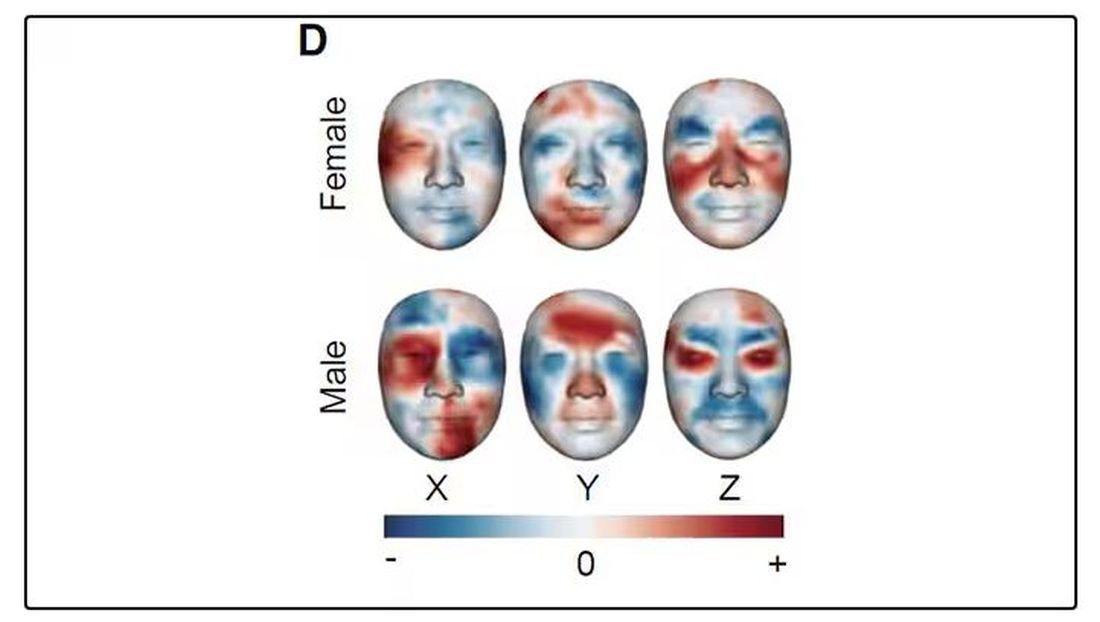
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
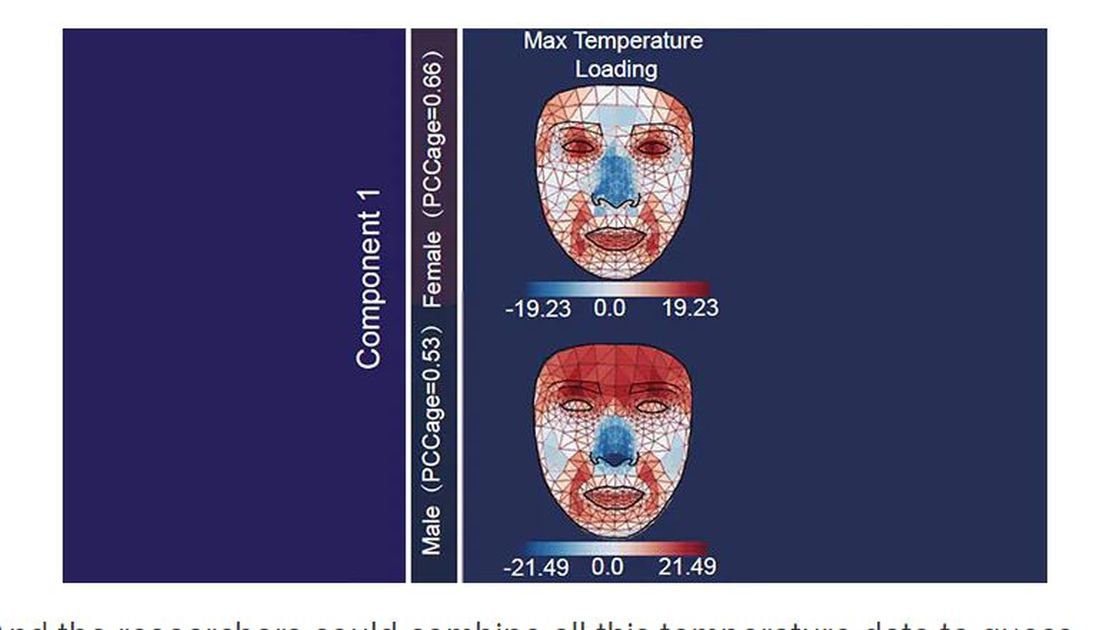
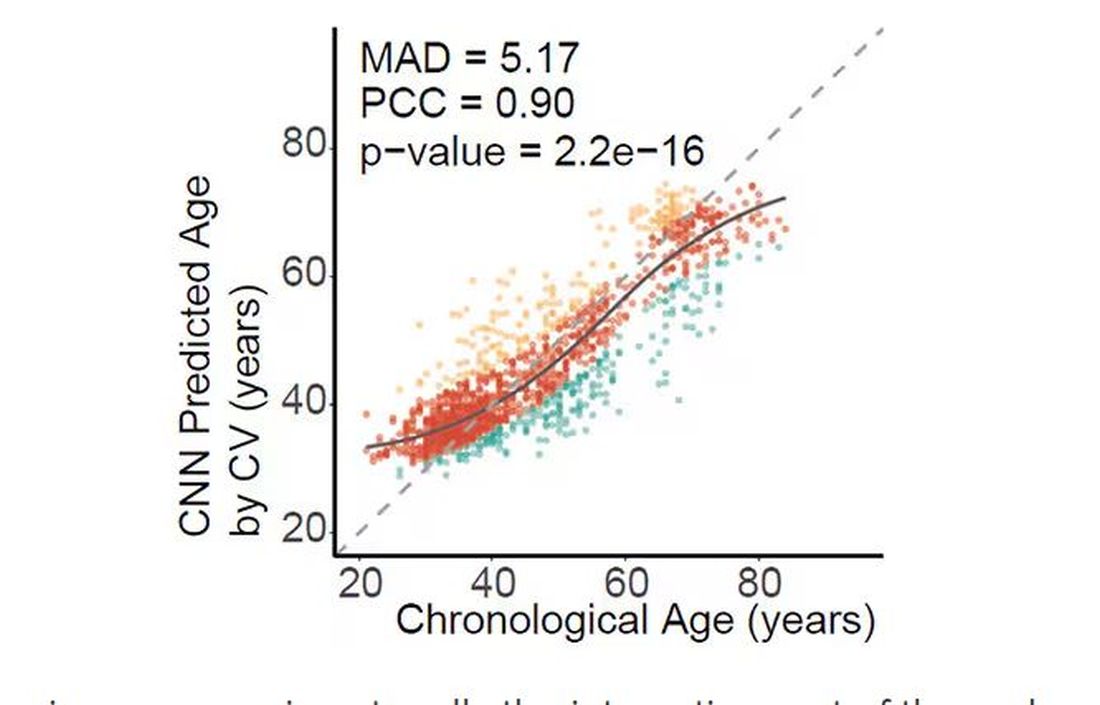
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
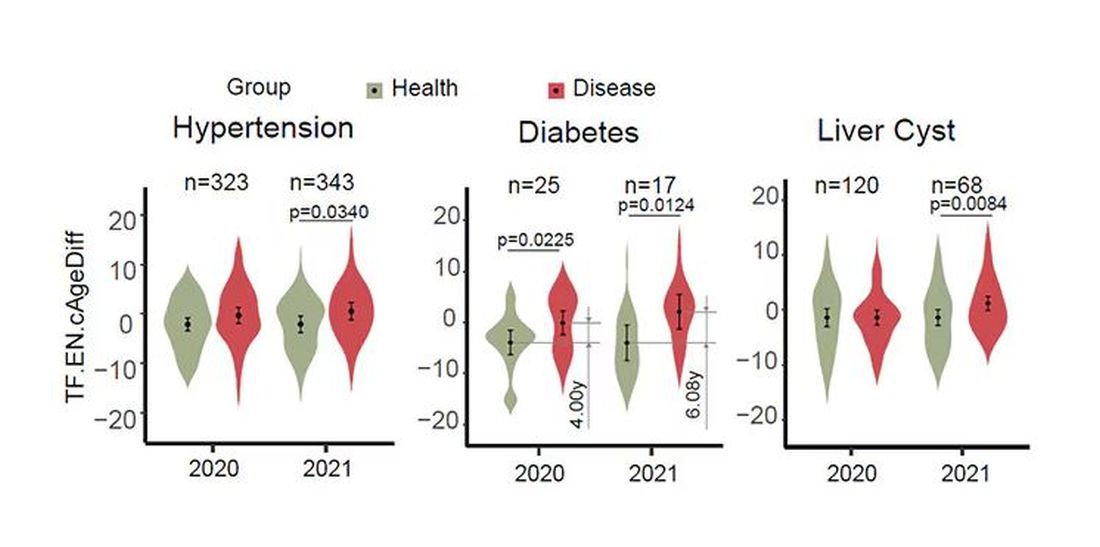
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.
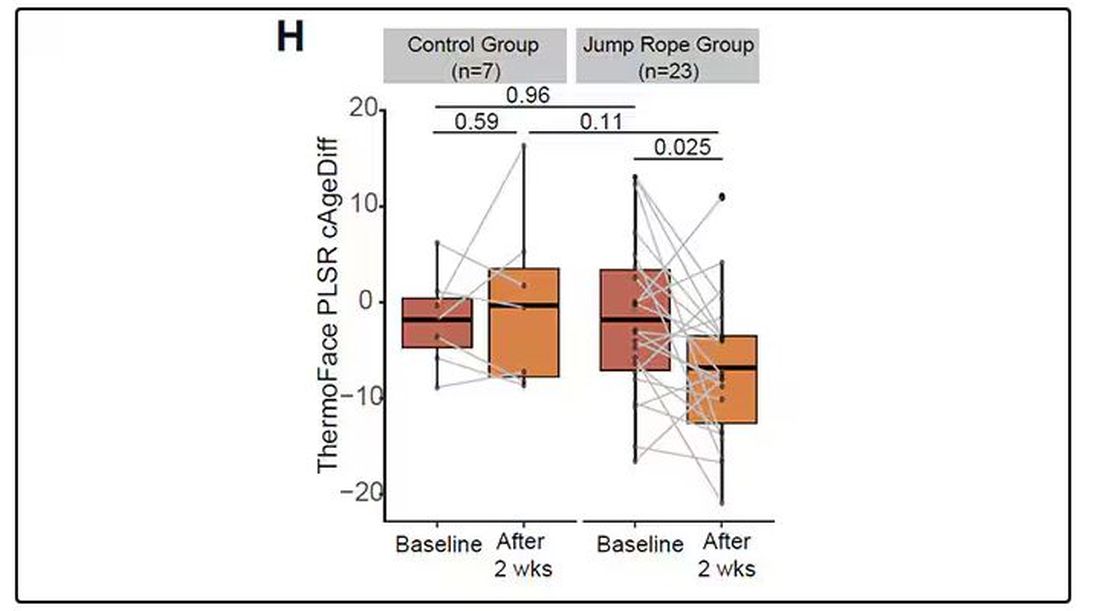
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those.
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally.
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
My oldest daughter is at sleepaway camp for a couple of weeks, and the camp has a photographer who goes around all day taking pictures of the kids, which get uploaded to a private Facebook group. In the past, I would go online every day (or, okay, several times a day) and scroll through all those pictures looking for one that features my kid.
I don’t have to do that anymore. This year, I simply uploaded a picture of my daughter to an app and artificial intelligence (AI) takes care of the rest, recognizing her face amidst the sea of smiling children, and flagging just those photos for me to peruse. It’s amazing, really. And a bit scary.
The fact that facial recognition has penetrated the summer camp market should tell you that the tech is truly ubiquitous. But today we’re going to think a bit more about what AI can do with a picture of your face, because the power of facial recognition is not just skin deep.
What’s got me hot and bothered about facial images is this paper, appearing in Cell Metabolism, which adds a new layer to the standard facial-analysis playbook: facial temperature.
To understand this paper, you need to understand a whole field of research that is developing various different “clocks” for age.
It turns out that age really is just a number. Our cells, our proteins, our biochemistry can be analyzed to give different numbers. These “clocks,” as distinct from the calendar we usually use to measure our age, might have more predictive power than the number itself.
There are numerous molecular clocks, such as telomere length, that not only correlate with calendar age but are superior to calendar age in predicting age-related complications. Testing telomere length typically requires a blood sample — and remains costly. But we can use other sources to estimate age; how about a photo?
I mean, we do this all the time when we meet someone new or, as a physician, when we meet a new patient. I have often written that a patient “appears younger than their stated age,” and we’ve all had the experience of hearing how old someone is and being shocked. I mean, have you seen Sharon Stone recently? She’s 66 years old. Okay — to be fair, there might be some outside help there. But you get the point.
Back to the Cell Metabolism paper. Researchers report on multiple algorithms to obtain an “age” from a picture of an individual’s face.
The first algorithm is pretty straightforward. Researchers collected 2811 images, all of Han Chinese individuals ranging in age from 20 to 90 years, and reconstructed a 3D facial map from those.
They then trained a convolutional neural network to predict the individuals’ ages from the pictures. It was quite accurate, as you can see here.
In the AI age, this may not seem that impressive. A brief search online turned up dozens of apps that promised to guess my age from a photo.
I sent this rather unflattering picture of myself to ChatGPT which, after initially demurring and saying it was not designed to guess ages, pegged me at somewhere between 35 and 45, which I am taking as a major victory.
But the Cell Metabolism paper goes deeper. Literally.
And this is where things start to get interesting. Because sure, the visible part of your face can change depending on makeup, expression, plastic surgery, and the like. But the temperature? That’s harder to fake.
It turns out that the temperature distribution in your face changes as you get older. There is a cooling of the nose and the cheeks, for example.
And the researchers could combine all this temperature data to guess someone’s calendar age fairly accurately, though notably not as accurately as the model that just looks at the pictures.
But guessing your age is not really the interesting part of thermal imaging of the face. It’s guessing — or, rather, predicting — the state of your metabolism. All these study participants had extensive metabolic testing performed, as well as detailed analysis of their lifestyle behaviors. And facial images could be used to predict those factors.
For example, the 3D reconstruction of the faces could predict who ate seafood (they tend to look younger than their actual age) compared with who ate poultry and meat (they tend to look older). The thermal imaging could predict who got more sleep (they look younger from a temperature perspective) and who ate more yogurt (also younger-appearing, temperature-wise). Facial temperature patterns could identify those with higher BMI, higher blood pressure, higher fasting glucose.
The researchers used the difference between actual and predicted age as a metric to measure illness as well. You can see here how, on average, individuals with hypertension, diabetes, and even liver cysts are “older,” at least by face temperature.
It may even be possible to use facial temperature as biofeedback. In a small study, the researchers measured the difference between facial temperature age and real age before and after 2 weeks of jump-roping. It turns out that 2 weeks of jump-roping can make you look about 5 years younger, at least as judged by a thermal camera. Or like the Predator.
Okay, this is all very cool, but I’m not saying we’ll all be doing facial temperature tests in the near future. No; what this study highlights for me is how much information about ourselves is available to those who know how to decode it. Maybe those data come from the wrinkles in our faces, or the angles of our smiles, or the speed with which we type, or the temperature of our elbows. The data have always been there, actually, but we’ve never had the tools powerful enough to analyze them until now.
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with Star Trek — I know, you’re shocked — and, of course, the famous tricorder, a scanner that could tell everything about someone’s state of health in 5 seconds from 3 feet away. That’s how I thought medicine really would be in the future. Once I got to medical school, I was disabused of that notion. But the age of data, the age of AI, may mean the tricorder age is not actually that far away.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What Should Be Prioritized in Managing Early Diabetes?
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — What to prioritize first in managing early diabetes? That was the question debated on an expert panel at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, with impassioned responses ranging from a plea to “treat obesity first,” to a James Carville–inspired counterpoint of “it’s the glucose, stupid.”
With a focus on preventing complications and inducing remission rounding out the four positions argued,
“In clinical decision-making [for early diabetes], we are faced with weighing each of these variables for the individual patient, and while all are good options, strong arguments can be made for prioritizing each — with the potential of each choice to influence or improve all of the others,” Dr. Retnakaran told this news organization.
Which to Prioritize First?
Making the obesity first argument, Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, associate professor and director of the Yale Obesity Research Center at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, noted the striking statistic that nearly 90% of people with type 2 diabetes have overweight or obesity and discussed the ever-expanding data showing the benefits of drugs including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists not just in weight loss but also in kidney, cardiovascular, and, as presented at the meeting, sleep apnea improvement.
She contrasted the experiences of two patients with obesity: One treated for the obesity upon type 2 diagnosis — who had a quick normalization of lipids and hypertension soon after the obesity treatment — and the other presenting after 10 years with type 2 diabetes — who was on therapy for hypertension and hyperlipidemia but not for obesity and whose diseases were not as easily treated by that point.
“Why are we treating all the downstream effects and we’re not treating the disease that is potentially the root cause of all these other diseases?” Dr. Jastreboff said.
Complications?
Arguing in favor of focusing on complications, Roopa Mehta, MD, PhD, with the department of endocrinology and metabolism at Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán (INCMNSZ), Mexico City, made the case that stakes don’t get any higher in diabetes than when it comes the looming threat of potentially fatal complications.
Acute myocardial infarction, stroke, amputation, and end-stage renal disease are all on the list of unwanted outcomes and need to be considered even in the earliest stages, as data show early onset type 2 diabetes is linked to life expectancy.
“The main goal of management has always been to prevent complications,” she noted. Citing ADA guidelines, Dr. Mehta underscored the benefits of first- and second-line therapy of metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists for most patients.
Remission?
Discussing the priority of putting patients into disease remission, Roy Taylor, MD, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University and Newcastle Hospitals NHS in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and author of the book Life Without Diabetes, focused on an evidence-based alternative to achieving remission — a nonpharmacologic approach that avoids costly and sometimes inaccessible drugs.
In the intervention, described in the DiRECT randomized trial and subsequently in the UK National Health Service Type 2 Diabetes Path to Remission Program, patients with overweight or obesity were placed on a highly restrictive diet of just 800-900 calories a day for 12-20 weeks, followed by maintenance for 12 months, and they not only achieved weight loss but also achieved diabetes remission, in some cases long term.
Acknowledging that “this is not for everyone,” Dr. Taylor asserted that “we have to realize there is a substantial minority of people who want to be healthy but who don’t want to be medicalized,” he said.
“They want their health, and they can do extremely well.”
Glucose?
In taking his self-titled “it’s the glucose, stupid” stand, David M. Nathan, MD, of the Diabetes Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, in Boston, cited extensive evidence showing that early intensive blood glucose control with treatment including sulfonylureas, insulin, or metformin significantly reduced the risk for complications in type 2 diabetes 15 or more years later, including renal failure, blindness, amputation, and myocardial infarctions, in addition to a reduction in diabetes-related death.
“In many of these studies, you saw the benefit even in the setting of weight-gain,” Dr. Nathan underscored.
He further noted the “sobering” findings of the Look AHEAD study, which had to be stopped due to futility when an intensive lifestyle/weight loss intervention showed no significant benefits in terms of cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes at a median follow-up of 9.6 years.
Ultimately, “diabetes, type 1 and type 2, remains a gluco-centric disease,” Dr. Nathan asserted. “Hyperglycemia is the only universal link between all forms of diabetes and mortality, and the long-term complications of diabetes are intimately associated with hyperglycemia.”
Tackling the Caveats
The ensuing panel discussion did not fail to deliver in delving into key areas of contention, particularly in terms of GLP-1 treatment.
Regarding a lack of data on the potential long-term effects of GLP-1s: “Yes, there are a huge number of studies [on GLP-1 receptor agonists], but they are, in general, over short periods of time and driven by pharma, who get in and get out as quickly as they can and have little in the way of interest to do comparative effectiveness studies,” Dr. Nathan argued.
“Meanwhile, this is like the crack cocaine of medications — patients have to stay on it for a lifetime or they will regain the weight — are you concerned at all about a lifetime of exposure to GLP-1 [drugs]?” he asked the panel.
Dr. Jastreboff responded that the first GLP-1 receptor agonist medications were approved in 2005, nearly 20 years ago, by the US Food and Drug Administration.
“Do I think we need long-term lifetime data? Absolutely,” she said. “We need to do our due diligence, we need to be careful, we need to monitor patients, and when and if there are signals, we need to follow them.”
What about the notorious gastrointestinal side effects of the drugs? “A majority of them are mitigated by slow up-titration,” Dr. Jastreboff noted.
“If patients have nausea, I do not go up [in dose]. I invite patients to tell me if they’re having vomiting because I don’t want anybody to have it, and I can count on one hand how many of my patients do.”
Dr. Mehta added the concern that as the drugs’ popularity soars, “a lot of doctors don’t know when they need to put the brakes on [weight coming off too quickly].”
She underscored that “we are not treating obesity for weight loss or for cosmetic reasons — this is about optimizing health.”
Dr. Jastreboff noted that in her practice, “I down-titrate if they’re losing weight too quickly.”
“If the patient is losing more than 1% per week of their body weight, then I slow down to make sure they’re getting the nutrients that they need, that they have enough energy to exercise, and that they’re prioritizing protein and fruits and vegetables in their diet.
“We just need to go slow, and yes, we need to follow them long term,” she said.
Chiming in from the audience, Julio Rosenstock, MD, a recognized thought leader in type 2 diabetes, offered his own take on the issues, describing Dr. Taylor’s very low–calorie diet suggestion as “not realistic” and Dr. Nathan’s glucose-first argument to be “stuck in the past.”
Based on modern-day evidence, “there is no reason on earth to start [diabetes treatment] with only metformin,” asserted Dr. Rosenstock, director of the Velocity Clinical Research center at Medical City and clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“We need to start at the very least with metformin and a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor from day 1, and then, if it’s affordable and there is access, with a GLP-1 receptor agonist,” he said.
“There is nothing better these days than those agents that consistently have shown a reduction of cardiovascular events and slowing of kidney disease progression.”
Overall, however, “I think you are all right,” he added, a sentiment shared by most.
Noting that the discussion as a whole represents a virtual sea change from the evidence-based options that would have been discussed only a decade ago, Dr. Retnakaran summed up his take-home message: “Stay tuned.
“You could easily see things changing in the next decade to come as we get more data and evidence to support what we ultimately should prioritize an early type 2 diabetes, so this is an exciting time.”
Dr. Retnakaran disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jastreboff disclosed ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regeneron, Scholar Rock, Structure Therapeutics, Terms Pharmaceutical, Weight Watchers, and Zealand Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Roopa had relationships with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Silanes, and Sanofi. Dr. Taylor received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, Abbott, and Nestle Health and research funding from Diabetes UK and is an advisor to Fast800. Dr. Rosenstock reported relationships with Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Biomea Fusion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Hanmi, Merck, Oramed, Structure Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Ragor, and Sanofi. Dr. Nathan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — What to prioritize first in managing early diabetes? That was the question debated on an expert panel at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, with impassioned responses ranging from a plea to “treat obesity first,” to a James Carville–inspired counterpoint of “it’s the glucose, stupid.”
With a focus on preventing complications and inducing remission rounding out the four positions argued,
“In clinical decision-making [for early diabetes], we are faced with weighing each of these variables for the individual patient, and while all are good options, strong arguments can be made for prioritizing each — with the potential of each choice to influence or improve all of the others,” Dr. Retnakaran told this news organization.
Which to Prioritize First?
Making the obesity first argument, Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, associate professor and director of the Yale Obesity Research Center at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, noted the striking statistic that nearly 90% of people with type 2 diabetes have overweight or obesity and discussed the ever-expanding data showing the benefits of drugs including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists not just in weight loss but also in kidney, cardiovascular, and, as presented at the meeting, sleep apnea improvement.
She contrasted the experiences of two patients with obesity: One treated for the obesity upon type 2 diagnosis — who had a quick normalization of lipids and hypertension soon after the obesity treatment — and the other presenting after 10 years with type 2 diabetes — who was on therapy for hypertension and hyperlipidemia but not for obesity and whose diseases were not as easily treated by that point.
“Why are we treating all the downstream effects and we’re not treating the disease that is potentially the root cause of all these other diseases?” Dr. Jastreboff said.
Complications?
Arguing in favor of focusing on complications, Roopa Mehta, MD, PhD, with the department of endocrinology and metabolism at Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán (INCMNSZ), Mexico City, made the case that stakes don’t get any higher in diabetes than when it comes the looming threat of potentially fatal complications.
Acute myocardial infarction, stroke, amputation, and end-stage renal disease are all on the list of unwanted outcomes and need to be considered even in the earliest stages, as data show early onset type 2 diabetes is linked to life expectancy.
“The main goal of management has always been to prevent complications,” she noted. Citing ADA guidelines, Dr. Mehta underscored the benefits of first- and second-line therapy of metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists for most patients.
Remission?
Discussing the priority of putting patients into disease remission, Roy Taylor, MD, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University and Newcastle Hospitals NHS in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and author of the book Life Without Diabetes, focused on an evidence-based alternative to achieving remission — a nonpharmacologic approach that avoids costly and sometimes inaccessible drugs.
In the intervention, described in the DiRECT randomized trial and subsequently in the UK National Health Service Type 2 Diabetes Path to Remission Program, patients with overweight or obesity were placed on a highly restrictive diet of just 800-900 calories a day for 12-20 weeks, followed by maintenance for 12 months, and they not only achieved weight loss but also achieved diabetes remission, in some cases long term.
Acknowledging that “this is not for everyone,” Dr. Taylor asserted that “we have to realize there is a substantial minority of people who want to be healthy but who don’t want to be medicalized,” he said.
“They want their health, and they can do extremely well.”
Glucose?
In taking his self-titled “it’s the glucose, stupid” stand, David M. Nathan, MD, of the Diabetes Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, in Boston, cited extensive evidence showing that early intensive blood glucose control with treatment including sulfonylureas, insulin, or metformin significantly reduced the risk for complications in type 2 diabetes 15 or more years later, including renal failure, blindness, amputation, and myocardial infarctions, in addition to a reduction in diabetes-related death.
“In many of these studies, you saw the benefit even in the setting of weight-gain,” Dr. Nathan underscored.
He further noted the “sobering” findings of the Look AHEAD study, which had to be stopped due to futility when an intensive lifestyle/weight loss intervention showed no significant benefits in terms of cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes at a median follow-up of 9.6 years.
Ultimately, “diabetes, type 1 and type 2, remains a gluco-centric disease,” Dr. Nathan asserted. “Hyperglycemia is the only universal link between all forms of diabetes and mortality, and the long-term complications of diabetes are intimately associated with hyperglycemia.”
Tackling the Caveats
The ensuing panel discussion did not fail to deliver in delving into key areas of contention, particularly in terms of GLP-1 treatment.
Regarding a lack of data on the potential long-term effects of GLP-1s: “Yes, there are a huge number of studies [on GLP-1 receptor agonists], but they are, in general, over short periods of time and driven by pharma, who get in and get out as quickly as they can and have little in the way of interest to do comparative effectiveness studies,” Dr. Nathan argued.
“Meanwhile, this is like the crack cocaine of medications — patients have to stay on it for a lifetime or they will regain the weight — are you concerned at all about a lifetime of exposure to GLP-1 [drugs]?” he asked the panel.
Dr. Jastreboff responded that the first GLP-1 receptor agonist medications were approved in 2005, nearly 20 years ago, by the US Food and Drug Administration.
“Do I think we need long-term lifetime data? Absolutely,” she said. “We need to do our due diligence, we need to be careful, we need to monitor patients, and when and if there are signals, we need to follow them.”
What about the notorious gastrointestinal side effects of the drugs? “A majority of them are mitigated by slow up-titration,” Dr. Jastreboff noted.
“If patients have nausea, I do not go up [in dose]. I invite patients to tell me if they’re having vomiting because I don’t want anybody to have it, and I can count on one hand how many of my patients do.”
Dr. Mehta added the concern that as the drugs’ popularity soars, “a lot of doctors don’t know when they need to put the brakes on [weight coming off too quickly].”
She underscored that “we are not treating obesity for weight loss or for cosmetic reasons — this is about optimizing health.”
Dr. Jastreboff noted that in her practice, “I down-titrate if they’re losing weight too quickly.”
“If the patient is losing more than 1% per week of their body weight, then I slow down to make sure they’re getting the nutrients that they need, that they have enough energy to exercise, and that they’re prioritizing protein and fruits and vegetables in their diet.
“We just need to go slow, and yes, we need to follow them long term,” she said.
Chiming in from the audience, Julio Rosenstock, MD, a recognized thought leader in type 2 diabetes, offered his own take on the issues, describing Dr. Taylor’s very low–calorie diet suggestion as “not realistic” and Dr. Nathan’s glucose-first argument to be “stuck in the past.”
Based on modern-day evidence, “there is no reason on earth to start [diabetes treatment] with only metformin,” asserted Dr. Rosenstock, director of the Velocity Clinical Research center at Medical City and clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“We need to start at the very least with metformin and a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor from day 1, and then, if it’s affordable and there is access, with a GLP-1 receptor agonist,” he said.
“There is nothing better these days than those agents that consistently have shown a reduction of cardiovascular events and slowing of kidney disease progression.”
Overall, however, “I think you are all right,” he added, a sentiment shared by most.
Noting that the discussion as a whole represents a virtual sea change from the evidence-based options that would have been discussed only a decade ago, Dr. Retnakaran summed up his take-home message: “Stay tuned.
“You could easily see things changing in the next decade to come as we get more data and evidence to support what we ultimately should prioritize an early type 2 diabetes, so this is an exciting time.”
Dr. Retnakaran disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jastreboff disclosed ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regeneron, Scholar Rock, Structure Therapeutics, Terms Pharmaceutical, Weight Watchers, and Zealand Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Roopa had relationships with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Silanes, and Sanofi. Dr. Taylor received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, Abbott, and Nestle Health and research funding from Diabetes UK and is an advisor to Fast800. Dr. Rosenstock reported relationships with Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Biomea Fusion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Hanmi, Merck, Oramed, Structure Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Ragor, and Sanofi. Dr. Nathan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — What to prioritize first in managing early diabetes? That was the question debated on an expert panel at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions, with impassioned responses ranging from a plea to “treat obesity first,” to a James Carville–inspired counterpoint of “it’s the glucose, stupid.”
With a focus on preventing complications and inducing remission rounding out the four positions argued,
“In clinical decision-making [for early diabetes], we are faced with weighing each of these variables for the individual patient, and while all are good options, strong arguments can be made for prioritizing each — with the potential of each choice to influence or improve all of the others,” Dr. Retnakaran told this news organization.
Which to Prioritize First?
Making the obesity first argument, Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, associate professor and director of the Yale Obesity Research Center at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, noted the striking statistic that nearly 90% of people with type 2 diabetes have overweight or obesity and discussed the ever-expanding data showing the benefits of drugs including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists not just in weight loss but also in kidney, cardiovascular, and, as presented at the meeting, sleep apnea improvement.
She contrasted the experiences of two patients with obesity: One treated for the obesity upon type 2 diagnosis — who had a quick normalization of lipids and hypertension soon after the obesity treatment — and the other presenting after 10 years with type 2 diabetes — who was on therapy for hypertension and hyperlipidemia but not for obesity and whose diseases were not as easily treated by that point.
“Why are we treating all the downstream effects and we’re not treating the disease that is potentially the root cause of all these other diseases?” Dr. Jastreboff said.
Complications?
Arguing in favor of focusing on complications, Roopa Mehta, MD, PhD, with the department of endocrinology and metabolism at Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán (INCMNSZ), Mexico City, made the case that stakes don’t get any higher in diabetes than when it comes the looming threat of potentially fatal complications.
Acute myocardial infarction, stroke, amputation, and end-stage renal disease are all on the list of unwanted outcomes and need to be considered even in the earliest stages, as data show early onset type 2 diabetes is linked to life expectancy.
“The main goal of management has always been to prevent complications,” she noted. Citing ADA guidelines, Dr. Mehta underscored the benefits of first- and second-line therapy of metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists for most patients.
Remission?
Discussing the priority of putting patients into disease remission, Roy Taylor, MD, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University and Newcastle Hospitals NHS in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and author of the book Life Without Diabetes, focused on an evidence-based alternative to achieving remission — a nonpharmacologic approach that avoids costly and sometimes inaccessible drugs.
In the intervention, described in the DiRECT randomized trial and subsequently in the UK National Health Service Type 2 Diabetes Path to Remission Program, patients with overweight or obesity were placed on a highly restrictive diet of just 800-900 calories a day for 12-20 weeks, followed by maintenance for 12 months, and they not only achieved weight loss but also achieved diabetes remission, in some cases long term.
Acknowledging that “this is not for everyone,” Dr. Taylor asserted that “we have to realize there is a substantial minority of people who want to be healthy but who don’t want to be medicalized,” he said.
“They want their health, and they can do extremely well.”
Glucose?
In taking his self-titled “it’s the glucose, stupid” stand, David M. Nathan, MD, of the Diabetes Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, in Boston, cited extensive evidence showing that early intensive blood glucose control with treatment including sulfonylureas, insulin, or metformin significantly reduced the risk for complications in type 2 diabetes 15 or more years later, including renal failure, blindness, amputation, and myocardial infarctions, in addition to a reduction in diabetes-related death.
“In many of these studies, you saw the benefit even in the setting of weight-gain,” Dr. Nathan underscored.
He further noted the “sobering” findings of the Look AHEAD study, which had to be stopped due to futility when an intensive lifestyle/weight loss intervention showed no significant benefits in terms of cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes at a median follow-up of 9.6 years.
Ultimately, “diabetes, type 1 and type 2, remains a gluco-centric disease,” Dr. Nathan asserted. “Hyperglycemia is the only universal link between all forms of diabetes and mortality, and the long-term complications of diabetes are intimately associated with hyperglycemia.”
Tackling the Caveats
The ensuing panel discussion did not fail to deliver in delving into key areas of contention, particularly in terms of GLP-1 treatment.
Regarding a lack of data on the potential long-term effects of GLP-1s: “Yes, there are a huge number of studies [on GLP-1 receptor agonists], but they are, in general, over short periods of time and driven by pharma, who get in and get out as quickly as they can and have little in the way of interest to do comparative effectiveness studies,” Dr. Nathan argued.
“Meanwhile, this is like the crack cocaine of medications — patients have to stay on it for a lifetime or they will regain the weight — are you concerned at all about a lifetime of exposure to GLP-1 [drugs]?” he asked the panel.
Dr. Jastreboff responded that the first GLP-1 receptor agonist medications were approved in 2005, nearly 20 years ago, by the US Food and Drug Administration.
“Do I think we need long-term lifetime data? Absolutely,” she said. “We need to do our due diligence, we need to be careful, we need to monitor patients, and when and if there are signals, we need to follow them.”
What about the notorious gastrointestinal side effects of the drugs? “A majority of them are mitigated by slow up-titration,” Dr. Jastreboff noted.
“If patients have nausea, I do not go up [in dose]. I invite patients to tell me if they’re having vomiting because I don’t want anybody to have it, and I can count on one hand how many of my patients do.”
Dr. Mehta added the concern that as the drugs’ popularity soars, “a lot of doctors don’t know when they need to put the brakes on [weight coming off too quickly].”
She underscored that “we are not treating obesity for weight loss or for cosmetic reasons — this is about optimizing health.”
Dr. Jastreboff noted that in her practice, “I down-titrate if they’re losing weight too quickly.”
“If the patient is losing more than 1% per week of their body weight, then I slow down to make sure they’re getting the nutrients that they need, that they have enough energy to exercise, and that they’re prioritizing protein and fruits and vegetables in their diet.
“We just need to go slow, and yes, we need to follow them long term,” she said.
Chiming in from the audience, Julio Rosenstock, MD, a recognized thought leader in type 2 diabetes, offered his own take on the issues, describing Dr. Taylor’s very low–calorie diet suggestion as “not realistic” and Dr. Nathan’s glucose-first argument to be “stuck in the past.”
Based on modern-day evidence, “there is no reason on earth to start [diabetes treatment] with only metformin,” asserted Dr. Rosenstock, director of the Velocity Clinical Research center at Medical City and clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“We need to start at the very least with metformin and a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor from day 1, and then, if it’s affordable and there is access, with a GLP-1 receptor agonist,” he said.
“There is nothing better these days than those agents that consistently have shown a reduction of cardiovascular events and slowing of kidney disease progression.”
Overall, however, “I think you are all right,” he added, a sentiment shared by most.
Noting that the discussion as a whole represents a virtual sea change from the evidence-based options that would have been discussed only a decade ago, Dr. Retnakaran summed up his take-home message: “Stay tuned.
“You could easily see things changing in the next decade to come as we get more data and evidence to support what we ultimately should prioritize an early type 2 diabetes, so this is an exciting time.”
Dr. Retnakaran disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jastreboff disclosed ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Regeneron, Scholar Rock, Structure Therapeutics, Terms Pharmaceutical, Weight Watchers, and Zealand Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Roopa had relationships with Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Silanes, and Sanofi. Dr. Taylor received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, Abbott, and Nestle Health and research funding from Diabetes UK and is an advisor to Fast800. Dr. Rosenstock reported relationships with Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Biomea Fusion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Hanmi, Merck, Oramed, Structure Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Ragor, and Sanofi. Dr. Nathan had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triple Therapy May Be Effective in Drug-Naive T2D
TOPLINE:
A triple combination therapy (TCT) of metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin is an effective and safe treatment option for drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared with stepwise add-on therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Current guidelines recommend early combination therapy to extend the time to treatment failure, reduce the risk for diabetic complications, and prevent clinical inertia in patients with T2D.
- This randomized controlled open-label trial conducted at nine sites in South Korea included 105 drug-naive patients with T2D (mean age, 49.5 years; 32.4% women) who either received triple therapy (metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin) or stepwise add-on therapy (initiated with metformin, followed by glimepiride and sitagliptin for those with baseline hemoglobin A1c levels < 9.0% or with initial dual metformin and glimepiride in those with A1c levels ≥ 9.0% followed by sitagliptin).
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who achieved A1c levels < 6.5% without hypoglycemia, weight gain ≥ 5%, or discontinuation of drugs because of adverse events at week 104.
- The secondary outcomes were the proportion of patients whose A1c levels dropped to < 7.0% at weeks 56 and 104 and dropped to < 6.5% at week 56, all without hypoglycemia, weight gain, nor discontinuation due to adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 104, a higher proportion of patients in the triple therapy group achieved the primary outcome than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (39.0% vs 17.1%; P = .027).
- In both groups, a similar proportion of patients (46.3%) achieved A1c levels < 6.5% at week 104, but the proportion of patients without hypoglycemia, weight gain, or discontinuation because of adverse events was higher in the triple therapy group than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (83.3% vs 38.0%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote: “Although the glycemic efficacy of each drug in the TCT was modest, the combination of these drugs resulted in a 2-year durable glycemic efficacy, with greater than a 2.5% reduction in A1c levels from baseline. The overall results of this study suggest a novel strategy for initial combination therapy in newly diagnosed T2D patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nam Hoon Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul. It was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a relatively small sample size as compared with previous clinical trials. More people in the standard therapy group had A1c levels ≥ 9.0%, which resulted in more than double the number of people receiving dual combination therapy over monotherapy in that group. The trial duration was insufficient to evaluate the cardiovascular outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Some authors reported financial ties with AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical and medical device companies as members of advisory boards or recipients of grants, consulting fees, honoraria, or lecture fees.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A triple combination therapy (TCT) of metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin is an effective and safe treatment option for drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared with stepwise add-on therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Current guidelines recommend early combination therapy to extend the time to treatment failure, reduce the risk for diabetic complications, and prevent clinical inertia in patients with T2D.
- This randomized controlled open-label trial conducted at nine sites in South Korea included 105 drug-naive patients with T2D (mean age, 49.5 years; 32.4% women) who either received triple therapy (metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin) or stepwise add-on therapy (initiated with metformin, followed by glimepiride and sitagliptin for those with baseline hemoglobin A1c levels < 9.0% or with initial dual metformin and glimepiride in those with A1c levels ≥ 9.0% followed by sitagliptin).
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who achieved A1c levels < 6.5% without hypoglycemia, weight gain ≥ 5%, or discontinuation of drugs because of adverse events at week 104.
- The secondary outcomes were the proportion of patients whose A1c levels dropped to < 7.0% at weeks 56 and 104 and dropped to < 6.5% at week 56, all without hypoglycemia, weight gain, nor discontinuation due to adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 104, a higher proportion of patients in the triple therapy group achieved the primary outcome than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (39.0% vs 17.1%; P = .027).
- In both groups, a similar proportion of patients (46.3%) achieved A1c levels < 6.5% at week 104, but the proportion of patients without hypoglycemia, weight gain, or discontinuation because of adverse events was higher in the triple therapy group than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (83.3% vs 38.0%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote: “Although the glycemic efficacy of each drug in the TCT was modest, the combination of these drugs resulted in a 2-year durable glycemic efficacy, with greater than a 2.5% reduction in A1c levels from baseline. The overall results of this study suggest a novel strategy for initial combination therapy in newly diagnosed T2D patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nam Hoon Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul. It was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a relatively small sample size as compared with previous clinical trials. More people in the standard therapy group had A1c levels ≥ 9.0%, which resulted in more than double the number of people receiving dual combination therapy over monotherapy in that group. The trial duration was insufficient to evaluate the cardiovascular outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Some authors reported financial ties with AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical and medical device companies as members of advisory boards or recipients of grants, consulting fees, honoraria, or lecture fees.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A triple combination therapy (TCT) of metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin is an effective and safe treatment option for drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared with stepwise add-on therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Current guidelines recommend early combination therapy to extend the time to treatment failure, reduce the risk for diabetic complications, and prevent clinical inertia in patients with T2D.
- This randomized controlled open-label trial conducted at nine sites in South Korea included 105 drug-naive patients with T2D (mean age, 49.5 years; 32.4% women) who either received triple therapy (metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin) or stepwise add-on therapy (initiated with metformin, followed by glimepiride and sitagliptin for those with baseline hemoglobin A1c levels < 9.0% or with initial dual metformin and glimepiride in those with A1c levels ≥ 9.0% followed by sitagliptin).
- The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who achieved A1c levels < 6.5% without hypoglycemia, weight gain ≥ 5%, or discontinuation of drugs because of adverse events at week 104.
- The secondary outcomes were the proportion of patients whose A1c levels dropped to < 7.0% at weeks 56 and 104 and dropped to < 6.5% at week 56, all without hypoglycemia, weight gain, nor discontinuation due to adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 104, a higher proportion of patients in the triple therapy group achieved the primary outcome than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (39.0% vs 17.1%; P = .027).
- In both groups, a similar proportion of patients (46.3%) achieved A1c levels < 6.5% at week 104, but the proportion of patients without hypoglycemia, weight gain, or discontinuation because of adverse events was higher in the triple therapy group than those in the stepwise add-on therapy group (83.3% vs 38.0%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote: “Although the glycemic efficacy of each drug in the TCT was modest, the combination of these drugs resulted in a 2-year durable glycemic efficacy, with greater than a 2.5% reduction in A1c levels from baseline. The overall results of this study suggest a novel strategy for initial combination therapy in newly diagnosed T2D patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nam Hoon Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul. It was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a relatively small sample size as compared with previous clinical trials. More people in the standard therapy group had A1c levels ≥ 9.0%, which resulted in more than double the number of people receiving dual combination therapy over monotherapy in that group. The trial duration was insufficient to evaluate the cardiovascular outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Some authors reported financial ties with AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical and medical device companies as members of advisory boards or recipients of grants, consulting fees, honoraria, or lecture fees.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Exercise Plus GLP-1 RAs Upped Weight Loss, Bone Retention
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Semaglutide Reduce Inflammation?
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic Gene Therapy: A ‘One-and-Done’ GLP-1 Treatment?
TOPLINE:
An experimental pancreatic gene therapy given to a mouse model of obesity as a one-time, single-dose treatment showed improvements in body composition and fasting glucose comparable with those achieved with the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide, without the reversal of fat-loss and glycemia improvements that are a key concern with the withdrawal of GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- With initial preclinical research showing benefits in Yucatan pigs, the authors tested the pancreatic gene therapy in mice representing a validated model of diet-induced obesity.
- The mice were randomized to receive either a single-dose administration of the pancreatic gene therapy (n = 10), daily subcutaneous semaglutide injections (n = 10; 10 nmol/kg/d for 4 weeks), pancreatic gene therapy placebo (n = 8), or a semaglutide placebo (n = 8).
- The gene therapy is designed to be delivered directly to the pancreas with a needle puncture, using a proprietary endoscopic delivery method that is similar to procedures commonly performed by gastrointestinal endoscopists, limiting systemic exposure.
- At 4 weeks, semaglutide was discontinued, and 5 of the 10 mice in that group were randomized to the gene therapy, while the other 5 received placebo.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 4, the pancreatic gene therapy arm had a reduction in fat mass of 21%, compared with 16% with semaglutide (P < .05; both P < .0001 vs placebo)
- The pancreatic gene therapy and semaglutide groups each preserved lean mass, with a loss of only 5% of body weight (both P < .0001 vs placebo).
- At week 8, mice withdrawn from semaglutide had nearly a full reversal of the fat and lean mass losses observed at 4 weeks, returning to within 1% and 2% below baseline, respectively, while the semaglutide-withdrawn mice treated with gene therapy maintained a fat reduction of 17% (P < .01) and lean mass of 5% (P < .0001).
- Significant improvements in fasting glucose were observed in the gene therapy and semaglutide-treated mice at week 4 (both 18%; P < .0001).
- While semaglutide-withdrawal resulted in a rebound of fasting glucose to baseline at week 8, those who had initially received gene therapy or were switched over to the therapy maintained fasting glucose reductions of 21% and 22% at 8 weeks (P < .0001 and P < .001), respectively.
- No indications of pancreatic inflammation or injury were observed in any of the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
The results suggest the therapy could represent “a reliable, ‘off ramp’ from chronic GLP-1 drugs that allows people to maintain the weight loss and blood sugar benefits, even as they stop taking these medicines,” said first author Harith Rajagopalan, MD, PhD, cofounder and chief executive officer of Fractyl Health, which is developing the gene therapy, in a press statement issued by the company.
The therapy is being developed as a candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and plans are underway for the first in-human study in type 2 diabetes in 2025, Dr. Rajagopalan noted while presenting the results at the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s 84th scientific sessions.
SOURCE:
The study was presented on June 23, 2024, at the annual meeting of the ADA’s 84th scientific sessions (Abstract #261-OR).
LIMITATIONS:
The pancreatic gene therapy is in early development and has not been assessed by any regulatory body for investigational or commercial use.
Asked by an audience member at the ADA presentation if the therapy would be reversible if complications were to arise, Dr. Rajagopalan responded that “there are ways to tune this effect in order to prevent complications from occurring, which we will discuss in due course.”
Also asked about the potential for a positive feedback loop with GLP-1 signaling and insulin signaling, Dr. Rajagopalan noted that “I don’t believe that we have seen any evidence of that risk so far. One could hypothesize, but we have not seen anything [in that regard] that would be a cause for concern.”
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Fractyl Health, and Dr. Rajagopalan and the authors declared being employees and stockholders/shareholders of the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An experimental pancreatic gene therapy given to a mouse model of obesity as a one-time, single-dose treatment showed improvements in body composition and fasting glucose comparable with those achieved with the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide, without the reversal of fat-loss and glycemia improvements that are a key concern with the withdrawal of GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- With initial preclinical research showing benefits in Yucatan pigs, the authors tested the pancreatic gene therapy in mice representing a validated model of diet-induced obesity.
- The mice were randomized to receive either a single-dose administration of the pancreatic gene therapy (n = 10), daily subcutaneous semaglutide injections (n = 10; 10 nmol/kg/d for 4 weeks), pancreatic gene therapy placebo (n = 8), or a semaglutide placebo (n = 8).
- The gene therapy is designed to be delivered directly to the pancreas with a needle puncture, using a proprietary endoscopic delivery method that is similar to procedures commonly performed by gastrointestinal endoscopists, limiting systemic exposure.
- At 4 weeks, semaglutide was discontinued, and 5 of the 10 mice in that group were randomized to the gene therapy, while the other 5 received placebo.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 4, the pancreatic gene therapy arm had a reduction in fat mass of 21%, compared with 16% with semaglutide (P < .05; both P < .0001 vs placebo)
- The pancreatic gene therapy and semaglutide groups each preserved lean mass, with a loss of only 5% of body weight (both P < .0001 vs placebo).
- At week 8, mice withdrawn from semaglutide had nearly a full reversal of the fat and lean mass losses observed at 4 weeks, returning to within 1% and 2% below baseline, respectively, while the semaglutide-withdrawn mice treated with gene therapy maintained a fat reduction of 17% (P < .01) and lean mass of 5% (P < .0001).
- Significant improvements in fasting glucose were observed in the gene therapy and semaglutide-treated mice at week 4 (both 18%; P < .0001).
- While semaglutide-withdrawal resulted in a rebound of fasting glucose to baseline at week 8, those who had initially received gene therapy or were switched over to the therapy maintained fasting glucose reductions of 21% and 22% at 8 weeks (P < .0001 and P < .001), respectively.
- No indications of pancreatic inflammation or injury were observed in any of the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
The results suggest the therapy could represent “a reliable, ‘off ramp’ from chronic GLP-1 drugs that allows people to maintain the weight loss and blood sugar benefits, even as they stop taking these medicines,” said first author Harith Rajagopalan, MD, PhD, cofounder and chief executive officer of Fractyl Health, which is developing the gene therapy, in a press statement issued by the company.
The therapy is being developed as a candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and plans are underway for the first in-human study in type 2 diabetes in 2025, Dr. Rajagopalan noted while presenting the results at the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s 84th scientific sessions.
SOURCE:
The study was presented on June 23, 2024, at the annual meeting of the ADA’s 84th scientific sessions (Abstract #261-OR).
LIMITATIONS:
The pancreatic gene therapy is in early development and has not been assessed by any regulatory body for investigational or commercial use.
Asked by an audience member at the ADA presentation if the therapy would be reversible if complications were to arise, Dr. Rajagopalan responded that “there are ways to tune this effect in order to prevent complications from occurring, which we will discuss in due course.”
Also asked about the potential for a positive feedback loop with GLP-1 signaling and insulin signaling, Dr. Rajagopalan noted that “I don’t believe that we have seen any evidence of that risk so far. One could hypothesize, but we have not seen anything [in that regard] that would be a cause for concern.”
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Fractyl Health, and Dr. Rajagopalan and the authors declared being employees and stockholders/shareholders of the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An experimental pancreatic gene therapy given to a mouse model of obesity as a one-time, single-dose treatment showed improvements in body composition and fasting glucose comparable with those achieved with the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide, without the reversal of fat-loss and glycemia improvements that are a key concern with the withdrawal of GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- With initial preclinical research showing benefits in Yucatan pigs, the authors tested the pancreatic gene therapy in mice representing a validated model of diet-induced obesity.
- The mice were randomized to receive either a single-dose administration of the pancreatic gene therapy (n = 10), daily subcutaneous semaglutide injections (n = 10; 10 nmol/kg/d for 4 weeks), pancreatic gene therapy placebo (n = 8), or a semaglutide placebo (n = 8).
- The gene therapy is designed to be delivered directly to the pancreas with a needle puncture, using a proprietary endoscopic delivery method that is similar to procedures commonly performed by gastrointestinal endoscopists, limiting systemic exposure.
- At 4 weeks, semaglutide was discontinued, and 5 of the 10 mice in that group were randomized to the gene therapy, while the other 5 received placebo.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 4, the pancreatic gene therapy arm had a reduction in fat mass of 21%, compared with 16% with semaglutide (P < .05; both P < .0001 vs placebo)
- The pancreatic gene therapy and semaglutide groups each preserved lean mass, with a loss of only 5% of body weight (both P < .0001 vs placebo).
- At week 8, mice withdrawn from semaglutide had nearly a full reversal of the fat and lean mass losses observed at 4 weeks, returning to within 1% and 2% below baseline, respectively, while the semaglutide-withdrawn mice treated with gene therapy maintained a fat reduction of 17% (P < .01) and lean mass of 5% (P < .0001).
- Significant improvements in fasting glucose were observed in the gene therapy and semaglutide-treated mice at week 4 (both 18%; P < .0001).
- While semaglutide-withdrawal resulted in a rebound of fasting glucose to baseline at week 8, those who had initially received gene therapy or were switched over to the therapy maintained fasting glucose reductions of 21% and 22% at 8 weeks (P < .0001 and P < .001), respectively.
- No indications of pancreatic inflammation or injury were observed in any of the groups.
IN PRACTICE:
The results suggest the therapy could represent “a reliable, ‘off ramp’ from chronic GLP-1 drugs that allows people to maintain the weight loss and blood sugar benefits, even as they stop taking these medicines,” said first author Harith Rajagopalan, MD, PhD, cofounder and chief executive officer of Fractyl Health, which is developing the gene therapy, in a press statement issued by the company.
The therapy is being developed as a candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and plans are underway for the first in-human study in type 2 diabetes in 2025, Dr. Rajagopalan noted while presenting the results at the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s 84th scientific sessions.
SOURCE:
The study was presented on June 23, 2024, at the annual meeting of the ADA’s 84th scientific sessions (Abstract #261-OR).
LIMITATIONS:
The pancreatic gene therapy is in early development and has not been assessed by any regulatory body for investigational or commercial use.
Asked by an audience member at the ADA presentation if the therapy would be reversible if complications were to arise, Dr. Rajagopalan responded that “there are ways to tune this effect in order to prevent complications from occurring, which we will discuss in due course.”
Also asked about the potential for a positive feedback loop with GLP-1 signaling and insulin signaling, Dr. Rajagopalan noted that “I don’t believe that we have seen any evidence of that risk so far. One could hypothesize, but we have not seen anything [in that regard] that would be a cause for concern.”
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Fractyl Health, and Dr. Rajagopalan and the authors declared being employees and stockholders/shareholders of the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Compounded Semaglutide: How to Better Ensure Its Safety
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide (marketed as Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes and as Wegovy for obesity) slow down digestion and curb hunger by working on the brain’s dopamine reward center. They are prescribed to promote weight loss, metabolic health in type 2 diabetes, and heart health in coronary artery disease.
Semaglutide can be prescribed in two forms: the brand-name version, which is approved and confirmed as safe and effective by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the versions that can be obtained from a compounding pharmacy. Compounding pharmacies are permitted by the FDA to produce what is “ essentially a copy” of approved medications when there’s an official shortage, which is currently the case with semaglutide and other GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Patients are often drawn to compounding pharmacies for pricing-related reasons. If semaglutide is prescribed for a clear indication like diabetes and is covered by insurance, the brand-name version is commonly dispensed. However, if it’s not covered, patients need to pay out of pocket for branded versions, which carry a monthly cost of $1000 or more. Alternatively, their doctors can prescribe compounded semaglutide, which some telehealth companies advertise at costs of approximately $150-$300 per month.
Potential Issues With Compounded Semaglutide
Compounding pharmacies produce drugs from raw materials containing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Although compounders use many of the same ingredients found in brand-name medications, for drugs like semaglutide, they may opt for specific salts that are not identical to those involved in the production of the standard versions. These salts are typically reserved for research purposes and may not be suitable for general use.
In late 2023, the FDA issued a letter asking the public to exercise caution when using compounded products containing semaglutide or semaglutide salts. This was followed in January 2024 by an FDA communication citing adverse events reported with the use of compounded semaglutide and advising patients to avoid these versions if an approved form of the drug is available.
Compound Pharmacies: A Closer Look
Compounding pharmacies have exploded in popularity in the past several decades. The compounding pharmacy market is expected to grow at 7.8% per year over the next decade.
Historically, compounding pharmacies have filled a niche for specialty vitamins for intravenous administration as well as chemotherapy medications. They also offer controlled substances, such as ketamine lozenges and nasal sprays, which are unavailable or are in short supply from traditional manufacturers.
Compounding pharmacies fall into two categories. First are compounding pharmacies covered under Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act; these drugs are neither tested nor monitored. Such facilities do not have to report adverse events to the FDA. The second category is Section 503B outsourcing facilities. These pharmacies choose to be tested by, to be inspected by, and to report adverse events to the FDA.
The FDA’s Latest Update on This Issue
This news organization contacted the FDA for an update on the adverse events reported about compounded semaglutide. From August 8, 2021, to March 31, 2024, they received more than 20,000 adverse events reports for FDA-approved semaglutide. Comparatively, there were 210 adverse events reported on compounded semaglutide products.
The FDA went on to describe that many of the adverse events reported were consistent with known reactions in the labeling, like nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Yet, they added that, “the FDA is unable to determine how, or if, other factors may have contributed to these adverse events, such as differences in ingredients and formulation between FDA-approved and compounded semaglutide products.” They also noted there was variation in the data quality in the reports they have received, which came only from 503B compounding pharmacies.
In conclusion, given the concerns about compounded semaglutide, it is prudent for the prescribing physicians as well as the patients taking the medication to know that risks are “higher” according to the FDA. We eagerly await more specific information from the FDA to better understand reported adverse events.
How to Help Patients Receive Safe Compounded Semaglutide
For clinicians considering prescribing semaglutide from compounding pharmacies, there are several questions worth asking, according to the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding. First, find out whether the pharmacy complies with United States Pharmacopeia compounding standards and whether they source their APIs from FDA-registered facilities, the latter being required by federal law. It’s also important to ensure that these facilities undergo periodic third-party testing to verify medication purity and dosing.
Ask whether the pharmacy is accredited by the Pharmacy Compounding Accreditation Board (PCAB). Accreditation from the PCAB means that pharmacies have been assessed for processes related to continuous quality improvement. In addition, ask whether the pharmacy is designated as a 503B compounder and if not, why.
Finally, interviewing the pharmacist themselves can provide useful information about staffing, training, and their methods of preparing medications. For example, if they are preparing a sterile eye drop, it is important to ask about sterility testing.
Jesse M. Pines, MD, MBA, MSCE, is a clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, and a professor in the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University College of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Pines is also the chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Pines reported conflicts of interest with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide (marketed as Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes and as Wegovy for obesity) slow down digestion and curb hunger by working on the brain’s dopamine reward center. They are prescribed to promote weight loss, metabolic health in type 2 diabetes, and heart health in coronary artery disease.
Semaglutide can be prescribed in two forms: the brand-name version, which is approved and confirmed as safe and effective by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the versions that can be obtained from a compounding pharmacy. Compounding pharmacies are permitted by the FDA to produce what is “ essentially a copy” of approved medications when there’s an official shortage, which is currently the case with semaglutide and other GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Patients are often drawn to compounding pharmacies for pricing-related reasons. If semaglutide is prescribed for a clear indication like diabetes and is covered by insurance, the brand-name version is commonly dispensed. However, if it’s not covered, patients need to pay out of pocket for branded versions, which carry a monthly cost of $1000 or more. Alternatively, their doctors can prescribe compounded semaglutide, which some telehealth companies advertise at costs of approximately $150-$300 per month.
Potential Issues With Compounded Semaglutide
Compounding pharmacies produce drugs from raw materials containing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Although compounders use many of the same ingredients found in brand-name medications, for drugs like semaglutide, they may opt for specific salts that are not identical to those involved in the production of the standard versions. These salts are typically reserved for research purposes and may not be suitable for general use.
In late 2023, the FDA issued a letter asking the public to exercise caution when using compounded products containing semaglutide or semaglutide salts. This was followed in January 2024 by an FDA communication citing adverse events reported with the use of compounded semaglutide and advising patients to avoid these versions if an approved form of the drug is available.
Compound Pharmacies: A Closer Look
Compounding pharmacies have exploded in popularity in the past several decades. The compounding pharmacy market is expected to grow at 7.8% per year over the next decade.
Historically, compounding pharmacies have filled a niche for specialty vitamins for intravenous administration as well as chemotherapy medications. They also offer controlled substances, such as ketamine lozenges and nasal sprays, which are unavailable or are in short supply from traditional manufacturers.
Compounding pharmacies fall into two categories. First are compounding pharmacies covered under Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act; these drugs are neither tested nor monitored. Such facilities do not have to report adverse events to the FDA. The second category is Section 503B outsourcing facilities. These pharmacies choose to be tested by, to be inspected by, and to report adverse events to the FDA.
The FDA’s Latest Update on This Issue
This news organization contacted the FDA for an update on the adverse events reported about compounded semaglutide. From August 8, 2021, to March 31, 2024, they received more than 20,000 adverse events reports for FDA-approved semaglutide. Comparatively, there were 210 adverse events reported on compounded semaglutide products.
The FDA went on to describe that many of the adverse events reported were consistent with known reactions in the labeling, like nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Yet, they added that, “the FDA is unable to determine how, or if, other factors may have contributed to these adverse events, such as differences in ingredients and formulation between FDA-approved and compounded semaglutide products.” They also noted there was variation in the data quality in the reports they have received, which came only from 503B compounding pharmacies.
In conclusion, given the concerns about compounded semaglutide, it is prudent for the prescribing physicians as well as the patients taking the medication to know that risks are “higher” according to the FDA. We eagerly await more specific information from the FDA to better understand reported adverse events.
How to Help Patients Receive Safe Compounded Semaglutide
For clinicians considering prescribing semaglutide from compounding pharmacies, there are several questions worth asking, according to the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding. First, find out whether the pharmacy complies with United States Pharmacopeia compounding standards and whether they source their APIs from FDA-registered facilities, the latter being required by federal law. It’s also important to ensure that these facilities undergo periodic third-party testing to verify medication purity and dosing.
Ask whether the pharmacy is accredited by the Pharmacy Compounding Accreditation Board (PCAB). Accreditation from the PCAB means that pharmacies have been assessed for processes related to continuous quality improvement. In addition, ask whether the pharmacy is designated as a 503B compounder and if not, why.
Finally, interviewing the pharmacist themselves can provide useful information about staffing, training, and their methods of preparing medications. For example, if they are preparing a sterile eye drop, it is important to ask about sterility testing.
Jesse M. Pines, MD, MBA, MSCE, is a clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, and a professor in the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University College of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Pines is also the chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Pines reported conflicts of interest with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists such as semaglutide (marketed as Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes and as Wegovy for obesity) slow down digestion and curb hunger by working on the brain’s dopamine reward center. They are prescribed to promote weight loss, metabolic health in type 2 diabetes, and heart health in coronary artery disease.
Semaglutide can be prescribed in two forms: the brand-name version, which is approved and confirmed as safe and effective by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the versions that can be obtained from a compounding pharmacy. Compounding pharmacies are permitted by the FDA to produce what is “ essentially a copy” of approved medications when there’s an official shortage, which is currently the case with semaglutide and other GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Patients are often drawn to compounding pharmacies for pricing-related reasons. If semaglutide is prescribed for a clear indication like diabetes and is covered by insurance, the brand-name version is commonly dispensed. However, if it’s not covered, patients need to pay out of pocket for branded versions, which carry a monthly cost of $1000 or more. Alternatively, their doctors can prescribe compounded semaglutide, which some telehealth companies advertise at costs of approximately $150-$300 per month.
Potential Issues With Compounded Semaglutide
Compounding pharmacies produce drugs from raw materials containing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Although compounders use many of the same ingredients found in brand-name medications, for drugs like semaglutide, they may opt for specific salts that are not identical to those involved in the production of the standard versions. These salts are typically reserved for research purposes and may not be suitable for general use.
In late 2023, the FDA issued a letter asking the public to exercise caution when using compounded products containing semaglutide or semaglutide salts. This was followed in January 2024 by an FDA communication citing adverse events reported with the use of compounded semaglutide and advising patients to avoid these versions if an approved form of the drug is available.
Compound Pharmacies: A Closer Look
Compounding pharmacies have exploded in popularity in the past several decades. The compounding pharmacy market is expected to grow at 7.8% per year over the next decade.
Historically, compounding pharmacies have filled a niche for specialty vitamins for intravenous administration as well as chemotherapy medications. They also offer controlled substances, such as ketamine lozenges and nasal sprays, which are unavailable or are in short supply from traditional manufacturers.
Compounding pharmacies fall into two categories. First are compounding pharmacies covered under Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act; these drugs are neither tested nor monitored. Such facilities do not have to report adverse events to the FDA. The second category is Section 503B outsourcing facilities. These pharmacies choose to be tested by, to be inspected by, and to report adverse events to the FDA.
The FDA’s Latest Update on This Issue
This news organization contacted the FDA for an update on the adverse events reported about compounded semaglutide. From August 8, 2021, to March 31, 2024, they received more than 20,000 adverse events reports for FDA-approved semaglutide. Comparatively, there were 210 adverse events reported on compounded semaglutide products.
The FDA went on to describe that many of the adverse events reported were consistent with known reactions in the labeling, like nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Yet, they added that, “the FDA is unable to determine how, or if, other factors may have contributed to these adverse events, such as differences in ingredients and formulation between FDA-approved and compounded semaglutide products.” They also noted there was variation in the data quality in the reports they have received, which came only from 503B compounding pharmacies.
In conclusion, given the concerns about compounded semaglutide, it is prudent for the prescribing physicians as well as the patients taking the medication to know that risks are “higher” according to the FDA. We eagerly await more specific information from the FDA to better understand reported adverse events.
How to Help Patients Receive Safe Compounded Semaglutide
For clinicians considering prescribing semaglutide from compounding pharmacies, there are several questions worth asking, according to the Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding. First, find out whether the pharmacy complies with United States Pharmacopeia compounding standards and whether they source their APIs from FDA-registered facilities, the latter being required by federal law. It’s also important to ensure that these facilities undergo periodic third-party testing to verify medication purity and dosing.
Ask whether the pharmacy is accredited by the Pharmacy Compounding Accreditation Board (PCAB). Accreditation from the PCAB means that pharmacies have been assessed for processes related to continuous quality improvement. In addition, ask whether the pharmacy is designated as a 503B compounder and if not, why.
Finally, interviewing the pharmacist themselves can provide useful information about staffing, training, and their methods of preparing medications. For example, if they are preparing a sterile eye drop, it is important to ask about sterility testing.
Jesse M. Pines, MD, MBA, MSCE, is a clinical professor of emergency medicine at George Washington University in Washington, and a professor in the department of emergency medicine at Drexel University College of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Dr. Pines is also the chief of clinical innovation at US Acute Care Solutions in Canton, Ohio. Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Pines reported conflicts of interest with CSL Behring and Abbott Point-of-Care. Dr. Glatter reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.