User login
Why Is Mom’s Type 1 Diabetes Half as Likely as Dad’s to Pass to Child?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Individuals with a family history of type 1 diabetes face 8-15 times higher risk for this condition than the general population, with the risk of inheritance from mothers with type 1 diabetes being about half that of fathers with type 1 diabetes; however, it is unclear if the effect continues past childhood and what is responsible for the difference in risk.
- Researchers performed a meta-analysis across five cohort studies involving 11,475 individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes aged 0-88 years to evaluate if maternal type 1 diabetes conferred relative protection only to young children.
- They compared the proportion of individuals with type 1 diabetes with affected fathers versus mothers and explored if this comparison was altered by the age at diagnosis and the timing of parental diagnosis relative to the birth of the offspring.
- Lastly, the inherited genetic risk for type 1 diabetes was compared between those with affected mothers versus fathers using a risk score composed of more than 60 different gene variants associated with type 1 diabetes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes were almost twice as likely to have a father with the condition than a mother (odds ratio, 1.79; P < .0001).
- The protective effect of maternal diabetes was seen regardless of whether the individuals were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes before or after age 18 years (P < .0001).
- Maternal diabetes was linked to a lower risk for type 1 diabetes in children only if the mother had type 1 diabetes during pregnancy.
- The genetic risk score for type 1 diabetes was not significantly different between those with affected fathers versus mothers (P = .31).
IN PRACTICE:
“Understanding why having a mother compared with a father with type 1 diabetes offers a relative protection against type 1 diabetes could help us develop new ways to prevent type 1 diabetes, such as treatments that mimic some of the protective elements from mothers,” study author Lowri Allen, MBChB, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Allen from the Diabetes Research Group, Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, and was published as an early release from the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
LIMITATIONS:
This abstract did not discuss any limitations. The number of individuals and parents with type 1 diabetes in the meta-analysis was not disclosed. The baseline risk for type 1 diabetes among individuals with a mother, father, or both or no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. The number of people with type 1 diabetes under and over age 18 was not disclosed, nor were the numbers of mothers and fathers with type 1 diabetes. The relative risk in individuals having no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. Moreover, the race and ethnicity of the study populations were not disclosed.
DISCLOSURES:
The Wellcome Trust supported this study. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Individuals with a family history of type 1 diabetes face 8-15 times higher risk for this condition than the general population, with the risk of inheritance from mothers with type 1 diabetes being about half that of fathers with type 1 diabetes; however, it is unclear if the effect continues past childhood and what is responsible for the difference in risk.
- Researchers performed a meta-analysis across five cohort studies involving 11,475 individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes aged 0-88 years to evaluate if maternal type 1 diabetes conferred relative protection only to young children.
- They compared the proportion of individuals with type 1 diabetes with affected fathers versus mothers and explored if this comparison was altered by the age at diagnosis and the timing of parental diagnosis relative to the birth of the offspring.
- Lastly, the inherited genetic risk for type 1 diabetes was compared between those with affected mothers versus fathers using a risk score composed of more than 60 different gene variants associated with type 1 diabetes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes were almost twice as likely to have a father with the condition than a mother (odds ratio, 1.79; P < .0001).
- The protective effect of maternal diabetes was seen regardless of whether the individuals were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes before or after age 18 years (P < .0001).
- Maternal diabetes was linked to a lower risk for type 1 diabetes in children only if the mother had type 1 diabetes during pregnancy.
- The genetic risk score for type 1 diabetes was not significantly different between those with affected fathers versus mothers (P = .31).
IN PRACTICE:
“Understanding why having a mother compared with a father with type 1 diabetes offers a relative protection against type 1 diabetes could help us develop new ways to prevent type 1 diabetes, such as treatments that mimic some of the protective elements from mothers,” study author Lowri Allen, MBChB, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Allen from the Diabetes Research Group, Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, and was published as an early release from the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
LIMITATIONS:
This abstract did not discuss any limitations. The number of individuals and parents with type 1 diabetes in the meta-analysis was not disclosed. The baseline risk for type 1 diabetes among individuals with a mother, father, or both or no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. The number of people with type 1 diabetes under and over age 18 was not disclosed, nor were the numbers of mothers and fathers with type 1 diabetes. The relative risk in individuals having no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. Moreover, the race and ethnicity of the study populations were not disclosed.
DISCLOSURES:
The Wellcome Trust supported this study. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Individuals with a family history of type 1 diabetes face 8-15 times higher risk for this condition than the general population, with the risk of inheritance from mothers with type 1 diabetes being about half that of fathers with type 1 diabetes; however, it is unclear if the effect continues past childhood and what is responsible for the difference in risk.
- Researchers performed a meta-analysis across five cohort studies involving 11,475 individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes aged 0-88 years to evaluate if maternal type 1 diabetes conferred relative protection only to young children.
- They compared the proportion of individuals with type 1 diabetes with affected fathers versus mothers and explored if this comparison was altered by the age at diagnosis and the timing of parental diagnosis relative to the birth of the offspring.
- Lastly, the inherited genetic risk for type 1 diabetes was compared between those with affected mothers versus fathers using a risk score composed of more than 60 different gene variants associated with type 1 diabetes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes were almost twice as likely to have a father with the condition than a mother (odds ratio, 1.79; P < .0001).
- The protective effect of maternal diabetes was seen regardless of whether the individuals were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes before or after age 18 years (P < .0001).
- Maternal diabetes was linked to a lower risk for type 1 diabetes in children only if the mother had type 1 diabetes during pregnancy.
- The genetic risk score for type 1 diabetes was not significantly different between those with affected fathers versus mothers (P = .31).
IN PRACTICE:
“Understanding why having a mother compared with a father with type 1 diabetes offers a relative protection against type 1 diabetes could help us develop new ways to prevent type 1 diabetes, such as treatments that mimic some of the protective elements from mothers,” study author Lowri Allen, MBChB, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Allen from the Diabetes Research Group, Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, and was published as an early release from the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
LIMITATIONS:
This abstract did not discuss any limitations. The number of individuals and parents with type 1 diabetes in the meta-analysis was not disclosed. The baseline risk for type 1 diabetes among individuals with a mother, father, or both or no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. The number of people with type 1 diabetes under and over age 18 was not disclosed, nor were the numbers of mothers and fathers with type 1 diabetes. The relative risk in individuals having no parent with type 1 diabetes was not disclosed. Moreover, the race and ethnicity of the study populations were not disclosed.
DISCLOSURES:
The Wellcome Trust supported this study. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Non-Prescription Semaglutide Purchased Online Poses Risks
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide products sold online without a prescription may pose multiple risks to consumers, new research found.
Of six test purchases of semaglutide products offered online without a prescription, only three were actually received. The other three vendors demanded additional payment. Of the three delivered, one was potentially contaminated, and all three contained higher concentrations of semaglutide than indicated on the label, potentially resulting in an overdose.
“Semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products,” wrote Amir Reza Ashraf, PharmD, of the University of Pécs, Hungary, and colleagues in their paper, published online on August 2, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted in July 2023, but its publication comes a week after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an alert about dosing errors in compounded semaglutide, which typically does require a prescription.
Study coauthor Tim K. Mackey, PhD, told this news organization, “Compounding pharmacies are another element of this risk that has become more prominent now but arguably have more controls if prescribed appropriately, while the traditional ‘no-prescription’ online market still exists and will continue to evolve.”
Overall, said Dr. Mackey, professor of global health at the University of California San Diego and director of the Global Health Policy and Data Institute,
He advises clinicians to actively discuss with their patients the risks associated with semaglutide and, specifically, the dangers of buying it online. “Clinicians can act as a primary information source for patient safety information by letting their patients know about these risks ... and also asking where patients get their medications in case they are concerned about reports of adverse events or other patient safety issues.”
Buyer Beware: Online Semaglutide Purchases Not as They Seem
The investigators began by searching online for websites advertising semaglutide without a prescription. They ordered products from six online vendors that showed up prominently in the searches. Of those, three offered prefilled 0.25 mg/dose semaglutide injection pens, while the other three sold vials of lyophilized semaglutide powder to be reconstituted to solution for injection. Prices for the smallest dose and quantity ranged from $113 to $360.
Only three of the ordered products — all vials — actually showed up. The advertised prefilled pens were all nondelivery scams, with requests for an extra payment of $650-$1200 purportedly to clear customs. This was confirmed as fraudulent by customs agencies, the authors noted.
The three vial products were received and assessed physically, of both the packaging and the actual product, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to determine purity and peptide concentration, and microbiologically, to examine sterility.
Using a checklist from the International Pharmaceutical Federation, Dr. Ashraf and colleagues found “clear discrepancies in regulatory registration information, accurate labeling, and evidence products were likely unregistered or unlicensed.”
Quality testing showed that one sample had an elevated presence of endotoxin suggesting possible contamination. While all three actually did contain semaglutide, the measured content exceeded the labeled amount by 29%-39%, posing a risk that users could receive up to 39% more than intended per injection, “particularly concerning if a consumer has to reconstitute and self-inject,” Dr. Mackey noted.
At least one of these sites in this study, “semaspace.com,” was subsequently sent a warning letter by the FDA for unauthorized semaglutide sale, Mackey noted.
Unfortunately, he told this news organization, these dangers are likely to persist. “There is a strong market opportunity to introduce counterfeit and unauthorized versions of semaglutide. Counterfeiters will continue to innovate with where they sell products, what products they offer, and how they mislead consumers about the safety and legality of what they are offering online. We are likely just at the beginning of counterfeiting of semaglutide, and it is likely that these false products will become endemic in our supply chain.”
The research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund. The authors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ozempic Curbs Hunger – And Not Just for Food
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 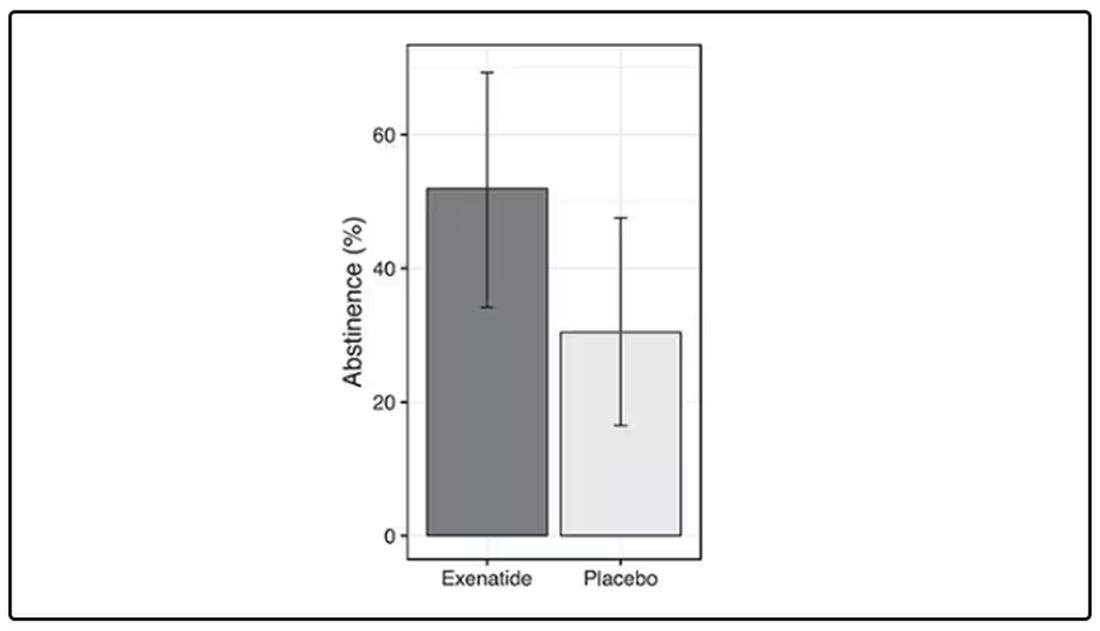
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.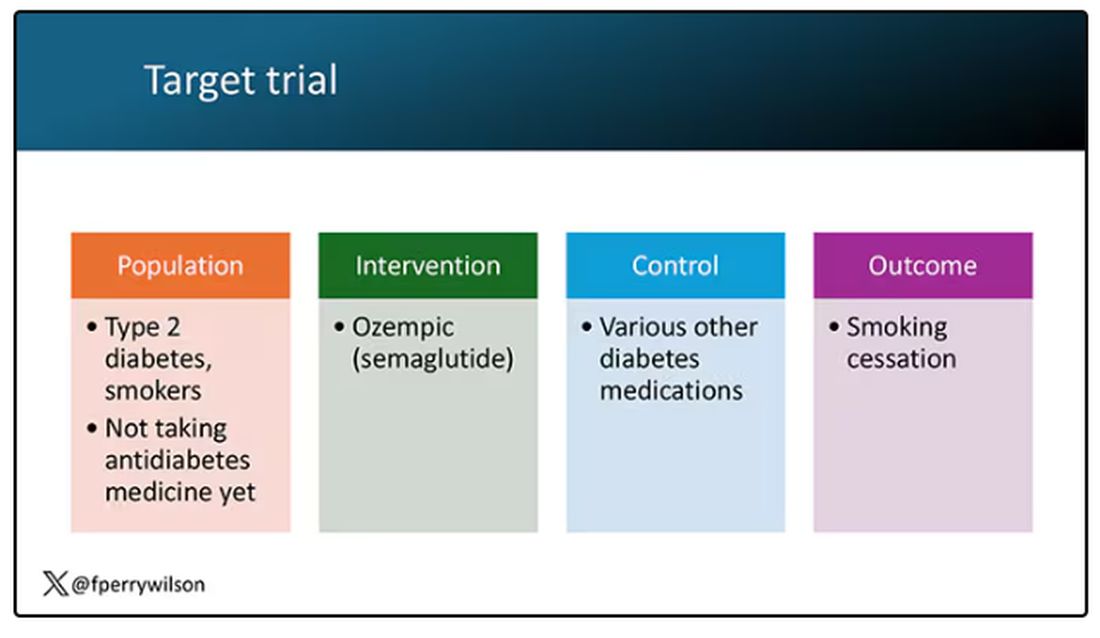
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.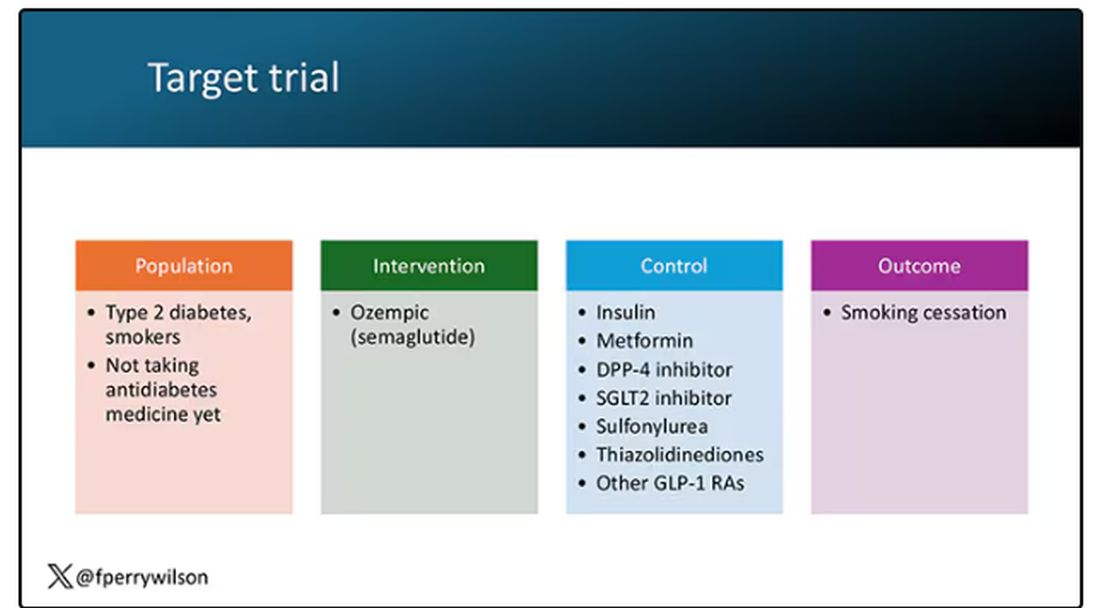
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 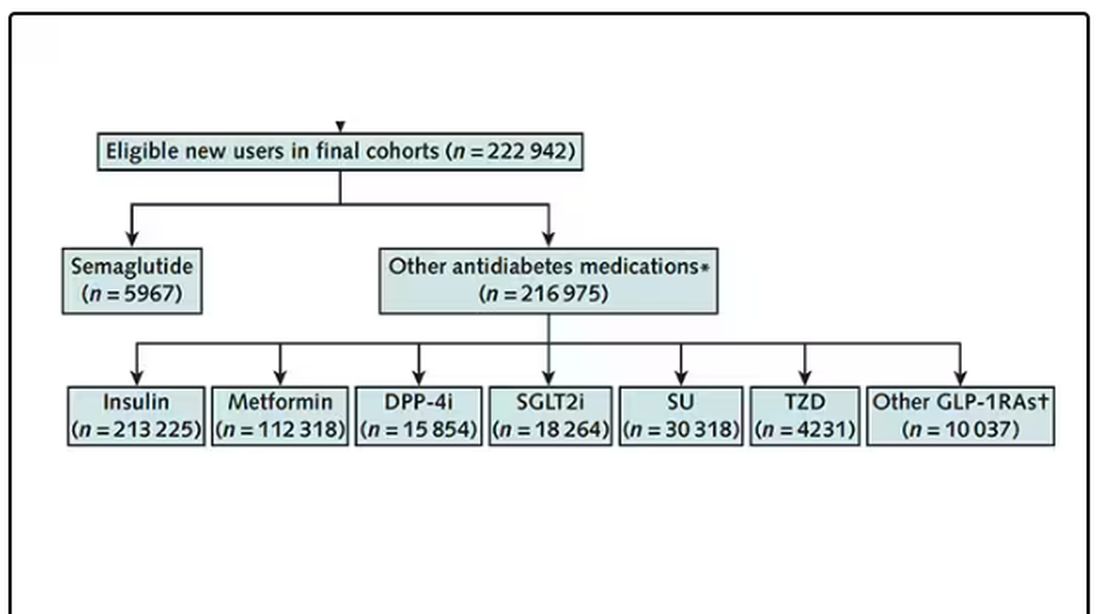
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 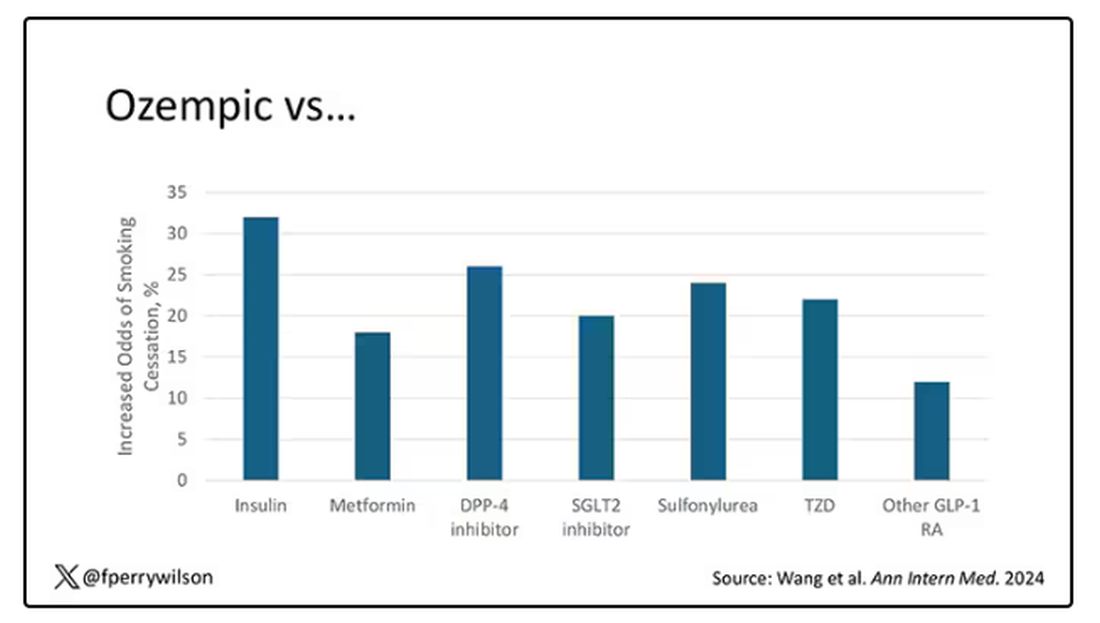
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
If you’ve been paying attention only to the headlines, when you think of “Ozempic” you’ll think of a few things: a blockbuster weight loss drug or the tip of the spear of a completely new industry — why not? A drug so popular that the people it was invented for (those with diabetes) can’t even get it.
Ozempic and other GLP-1 receptor agonists are undeniable game changers. Insofar as obesity is the number-one public health risk in the United States, antiobesity drugs hold immense promise even if all they do is reduce obesity.
In 2023, an article in Scientific Reports presented data suggesting that people on Ozempic might be reducing their alcohol intake, not just their total calories.
A 2024 article in Molecular Psychiatry found that the drug might positively impact cannabis use disorder. An article from Brain Sciences suggests that the drug reduces compulsive shopping.
A picture is starting to form, a picture that suggests these drugs curb hunger both literally and figuratively. That GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro are fundamentally anticonsumption drugs. In a society that — some would argue — is plagued by overconsumption, these drugs might be just what the doctor ordered.
If only they could stop people from smoking.
Oh, wait — they can.
At least it seems they can, based on a new study appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Before we get too excited, this is not a randomized trial. There actually was a small randomized trial of exenatide (Byetta), which is in the same class as Ozempic but probably a bit less potent, with promising results for smoking cessation. 
But Byetta is the weaker drug in this class; the market leader is Ozempic. So how can you figure out whether Ozempic can reduce smoking without doing a huge and expensive randomized trial? You can do what Nora Volkow and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse did: a target trial emulation study.
A target trial emulation study is more or less what it sounds like. First, you decide what your dream randomized controlled trial would be and you plan it all out in great detail. You define the population you would recruit, with all the relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria. You define the intervention and the control, and you define the outcome.
But you don’t actually do the trial. You could if someone would lend you $10-$50 million, but assuming you don’t have that lying around, you do the next best thing, which is to dig into a medical record database to find all the people who would be eligible for your imaginary trial. And you analyze them.
The authors wanted to study the effect of Ozempic on smoking among people with diabetes; that’s why all the comparator agents are antidiabetes drugs. They figured out whether these folks were smoking on the basis of a medical record diagnosis of tobacco use disorder before they started one of the drugs of interest. This code is fairly specific: If a patient has it, you can be pretty sure they are smoking. But it’s not very sensitive; not every smoker has this diagnostic code. This is an age-old limitation of using EHR data instead of asking patients, but it’s part of the tradeoff for not having to spend $50 million.
After applying all those inclusion and exclusion criteria, they have a defined population who could be in their dream trial. And, as luck would have it, some of those people really were treated with Ozempic and some really were treated with those other agents. Although decisions about what to prescribe were not randomized, the authors account for this confounding-by-indication using propensity-score matching. You can find a little explainer on propensity-score matching in an earlier column here. 
It’s easy enough, using the EHR, to figure out who has diabetes and who got which drug. But how do you know who quit smoking? Remember, everyone had a diagnosis code for tobacco use disorder prior to starting Ozempic or a comparator drug. The authors decided that if the patient had a medical visit where someone again coded tobacco-use disorder, they were still smoking. If someone prescribed smoking cessation meds like a nicotine patch or varenicline, they were obviously still smoking. If someone billed for tobacco-cessation counseling, the patient is still smoking. We’ll get back to the implications of this outcome definition in a minute.
Let’s talk about the results, which are pretty intriguing. 
When Ozempic is compared with insulin among smokers with diabetes, those on Ozempic were about 30% more likely to quit smoking. They were about 18% more likely to quit smoking than those who took metformin. They were even slightly more likely to quit smoking than those on other GLP-1 receptor antagonists, though I should note that Mounjaro, which is probably the more potent GLP-1 drug in terms of weight loss, was not among the comparators.
This is pretty impressive for a drug that was not designed to be a smoking cessation drug. It speaks to this emerging idea that these drugs do more than curb appetite by slowing down gastric emptying or something. They work in the brain, modulating some of the reward circuitry that keeps us locked into our bad habits.
There are, of course, some caveats. As I pointed out, this study captured the idea of “still smoking” through the use of administrative codes in the EHR and prescription of smoking cessation aids. You could see similar results if taking Ozempic makes people less likely to address their smoking at all; maybe they shut down the doctor before they even talk about it, or there is too much to discuss during these visits to even get to the subject of smoking. You could also see results like this if people taking Ozempic had fewer visits overall, but the authors showed that that, at least, was not the case.
I’m inclined to believe that this effect is real, simply because we keep seeing signals from multiple sources. If that turns out to be the case, these new “weight loss” drugs may prove to be much more than that; they may turn out to be the drugs that can finally save us from ourselves.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HDL Cholesterol Increases Kidney Disease Risk in T2D
TOPLINE:
Very high and very low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are linked to a higher risk for kidney disease in women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), but not in men.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have reported a strong association between low HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, but whether higher HDL-C levels can influence the risk for diabetic kidney disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional observational study of 936 patients with T2D (mean age, about 60 years; 41% women; 33% with diabetic kidney disease) from the Endocrinology Department at the Jinhua Hospital between September 2020 and July 2021.
- To examine the relationship between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, researchers used logistic regression to assess the continuous and categorical associations and a restricted cubic spline curve to assess the nonlinear association.
- HDL-C levels were categorized into four groups, with 0.40-0.96 mmol/L corresponding to the lowest quartile and 1.32-6.27 mmol/L corresponding to the highest quartile.
- The researchers observed a U-shaped association between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease (Pnonlinear = .010) and selected two threshold values of 0.95 and 1.54 mmol/L.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for diabetic kidney disease was higher when the HDL-C levels were < 0.95 mmol/L or > 1.54 mmol/L.
- Compared with patients with HDL-C levels in the range of 0.95-1.54 mmol/L, those with very high and very low HDL-C levels had a 128% and 77% increased risk for diabetic kidney disease, respectively.
- The association was significant in women (P = .006) and not in men (P = .054), after adjusting for confounding factors.
- HDL-C level as a continuous variable was not associated with the risk for kidney disease (P = .902).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although HDL-C is generally considered a cardiovascular protective factor, at very high levels, this protective effect does not seem to hold true and may be associated with an increased DKD [diabetic kidney disease] risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huabin Wang, from the Department of Clinical Laboratory, Jinhua Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Jinhua, China, and was published online in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the ability to establish a causal relationship between high HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease. The sample size of the study was relatively small at the higher end of the HDL-C concentration spectrum. Moreover, the study did not consider other potential confounding factors such as diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, genetic diseases, drug effects on HDL-C levels, and fluctuating estrogen levels, which could affect the overall findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, China, and The Science and Technology Bureau of Jinhua City. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Very high and very low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are linked to a higher risk for kidney disease in women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), but not in men.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have reported a strong association between low HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, but whether higher HDL-C levels can influence the risk for diabetic kidney disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional observational study of 936 patients with T2D (mean age, about 60 years; 41% women; 33% with diabetic kidney disease) from the Endocrinology Department at the Jinhua Hospital between September 2020 and July 2021.
- To examine the relationship between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, researchers used logistic regression to assess the continuous and categorical associations and a restricted cubic spline curve to assess the nonlinear association.
- HDL-C levels were categorized into four groups, with 0.40-0.96 mmol/L corresponding to the lowest quartile and 1.32-6.27 mmol/L corresponding to the highest quartile.
- The researchers observed a U-shaped association between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease (Pnonlinear = .010) and selected two threshold values of 0.95 and 1.54 mmol/L.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for diabetic kidney disease was higher when the HDL-C levels were < 0.95 mmol/L or > 1.54 mmol/L.
- Compared with patients with HDL-C levels in the range of 0.95-1.54 mmol/L, those with very high and very low HDL-C levels had a 128% and 77% increased risk for diabetic kidney disease, respectively.
- The association was significant in women (P = .006) and not in men (P = .054), after adjusting for confounding factors.
- HDL-C level as a continuous variable was not associated with the risk for kidney disease (P = .902).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although HDL-C is generally considered a cardiovascular protective factor, at very high levels, this protective effect does not seem to hold true and may be associated with an increased DKD [diabetic kidney disease] risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huabin Wang, from the Department of Clinical Laboratory, Jinhua Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Jinhua, China, and was published online in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the ability to establish a causal relationship between high HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease. The sample size of the study was relatively small at the higher end of the HDL-C concentration spectrum. Moreover, the study did not consider other potential confounding factors such as diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, genetic diseases, drug effects on HDL-C levels, and fluctuating estrogen levels, which could affect the overall findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, China, and The Science and Technology Bureau of Jinhua City. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Very high and very low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are linked to a higher risk for kidney disease in women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), but not in men.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies have reported a strong association between low HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, but whether higher HDL-C levels can influence the risk for diabetic kidney disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional observational study of 936 patients with T2D (mean age, about 60 years; 41% women; 33% with diabetic kidney disease) from the Endocrinology Department at the Jinhua Hospital between September 2020 and July 2021.
- To examine the relationship between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease, researchers used logistic regression to assess the continuous and categorical associations and a restricted cubic spline curve to assess the nonlinear association.
- HDL-C levels were categorized into four groups, with 0.40-0.96 mmol/L corresponding to the lowest quartile and 1.32-6.27 mmol/L corresponding to the highest quartile.
- The researchers observed a U-shaped association between HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease (Pnonlinear = .010) and selected two threshold values of 0.95 and 1.54 mmol/L.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for diabetic kidney disease was higher when the HDL-C levels were < 0.95 mmol/L or > 1.54 mmol/L.
- Compared with patients with HDL-C levels in the range of 0.95-1.54 mmol/L, those with very high and very low HDL-C levels had a 128% and 77% increased risk for diabetic kidney disease, respectively.
- The association was significant in women (P = .006) and not in men (P = .054), after adjusting for confounding factors.
- HDL-C level as a continuous variable was not associated with the risk for kidney disease (P = .902).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although HDL-C is generally considered a cardiovascular protective factor, at very high levels, this protective effect does not seem to hold true and may be associated with an increased DKD [diabetic kidney disease] risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Huabin Wang, from the Department of Clinical Laboratory, Jinhua Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Jinhua, China, and was published online in Scientific Reports.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the ability to establish a causal relationship between high HDL-C levels and the risk for diabetic kidney disease. The sample size of the study was relatively small at the higher end of the HDL-C concentration spectrum. Moreover, the study did not consider other potential confounding factors such as diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, genetic diseases, drug effects on HDL-C levels, and fluctuating estrogen levels, which could affect the overall findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology of Zhejiang Province, China, and The Science and Technology Bureau of Jinhua City. The authors declared no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Medium-Chain Fatty Acids Reduce Diabetes Risk?
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of some serum medium-chain fatty acids found in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and milk products are associated with a reduced risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D). This inverse relationship is more pronounced in individuals with a high genetic risk or physical inactivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies reporting a link between dietary medium-chain fatty acids and a reduced risk for T2D have been based on food intake questionnaires, but serum samples are likely to be a more precise and objective basis for understanding metabolic relationships.
- To assess the association between medium-chain fatty acids and T2D risk, the researchers conducted a nested case-control study within the prospective China Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer Cohort Study.
- They included 1707 individuals who developed diabetes during a median follow-up of 3.03 years and added a propensity-matched normoglycemic control group for a total of 3414 individuals (mean age, 57.56 years; 59.4% women), all with normal glucose regulation at baseline.
- Researchers investigated associations of baseline levels of five serum medium-chain fatty acids — octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, decanoic acid, undecanoic acid, and lauric acid — between individuals with T2D and control participants and stratified by risk factors, including diabetes genetic susceptibility.
- The genetic risk scores were calculated as a weighted sum of 86 T2D-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an inverse association, each standard deviation increase in the baseline serum levels of octanoic acid and nonanoic acid decreased the odds of T2D by 10% and 16%, respectively (odds ratio [OR], 0.90; 95% CI, 0.82-0.98 and OR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.74-0.95, respectively; all P < .05).
- , with significant interactions observed for octanoic, nonanoic, and decanoic acids (P for interaction = .042, .034, and .037, respectively).
- Moreover, the negative relationship between octanoic acid and the risk for diabetes was stronger in those with a high genetic risk, with a significant interaction (P for interaction = .003).
- No significant associations were observed between the levels of decanoic, undecanoic, and lauric acids and the overall risk for incident diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings generally support the protective effect of MCFAs [medium-chain fatty acids] but also emphasize the personalized approaches in improving serum MCFA profiles for T2D prevention, which could be tailored according to individuals’ genetic and lifestyle profiles,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xiaojing Jia, MD, and Hong Lin, PhD, of the Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s follow-up duration of 3 years was short, which may have compromised the statistical power of the analysis. The long-term effects of medium-chain fatty acids on the risk for diabetes may not be captured as they were assessed only at baseline. The study population was limited to Chinese adults older than 40 years, which may affect the generalizability of the findings to other ethnicities and age groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of some serum medium-chain fatty acids found in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and milk products are associated with a reduced risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D). This inverse relationship is more pronounced in individuals with a high genetic risk or physical inactivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies reporting a link between dietary medium-chain fatty acids and a reduced risk for T2D have been based on food intake questionnaires, but serum samples are likely to be a more precise and objective basis for understanding metabolic relationships.
- To assess the association between medium-chain fatty acids and T2D risk, the researchers conducted a nested case-control study within the prospective China Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer Cohort Study.
- They included 1707 individuals who developed diabetes during a median follow-up of 3.03 years and added a propensity-matched normoglycemic control group for a total of 3414 individuals (mean age, 57.56 years; 59.4% women), all with normal glucose regulation at baseline.
- Researchers investigated associations of baseline levels of five serum medium-chain fatty acids — octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, decanoic acid, undecanoic acid, and lauric acid — between individuals with T2D and control participants and stratified by risk factors, including diabetes genetic susceptibility.
- The genetic risk scores were calculated as a weighted sum of 86 T2D-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an inverse association, each standard deviation increase in the baseline serum levels of octanoic acid and nonanoic acid decreased the odds of T2D by 10% and 16%, respectively (odds ratio [OR], 0.90; 95% CI, 0.82-0.98 and OR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.74-0.95, respectively; all P < .05).
- , with significant interactions observed for octanoic, nonanoic, and decanoic acids (P for interaction = .042, .034, and .037, respectively).
- Moreover, the negative relationship between octanoic acid and the risk for diabetes was stronger in those with a high genetic risk, with a significant interaction (P for interaction = .003).
- No significant associations were observed between the levels of decanoic, undecanoic, and lauric acids and the overall risk for incident diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings generally support the protective effect of MCFAs [medium-chain fatty acids] but also emphasize the personalized approaches in improving serum MCFA profiles for T2D prevention, which could be tailored according to individuals’ genetic and lifestyle profiles,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xiaojing Jia, MD, and Hong Lin, PhD, of the Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s follow-up duration of 3 years was short, which may have compromised the statistical power of the analysis. The long-term effects of medium-chain fatty acids on the risk for diabetes may not be captured as they were assessed only at baseline. The study population was limited to Chinese adults older than 40 years, which may affect the generalizability of the findings to other ethnicities and age groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of some serum medium-chain fatty acids found in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and milk products are associated with a reduced risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D). This inverse relationship is more pronounced in individuals with a high genetic risk or physical inactivity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies reporting a link between dietary medium-chain fatty acids and a reduced risk for T2D have been based on food intake questionnaires, but serum samples are likely to be a more precise and objective basis for understanding metabolic relationships.
- To assess the association between medium-chain fatty acids and T2D risk, the researchers conducted a nested case-control study within the prospective China Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer Cohort Study.
- They included 1707 individuals who developed diabetes during a median follow-up of 3.03 years and added a propensity-matched normoglycemic control group for a total of 3414 individuals (mean age, 57.56 years; 59.4% women), all with normal glucose regulation at baseline.
- Researchers investigated associations of baseline levels of five serum medium-chain fatty acids — octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, decanoic acid, undecanoic acid, and lauric acid — between individuals with T2D and control participants and stratified by risk factors, including diabetes genetic susceptibility.
- The genetic risk scores were calculated as a weighted sum of 86 T2D-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an inverse association, each standard deviation increase in the baseline serum levels of octanoic acid and nonanoic acid decreased the odds of T2D by 10% and 16%, respectively (odds ratio [OR], 0.90; 95% CI, 0.82-0.98 and OR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.74-0.95, respectively; all P < .05).
- , with significant interactions observed for octanoic, nonanoic, and decanoic acids (P for interaction = .042, .034, and .037, respectively).
- Moreover, the negative relationship between octanoic acid and the risk for diabetes was stronger in those with a high genetic risk, with a significant interaction (P for interaction = .003).
- No significant associations were observed between the levels of decanoic, undecanoic, and lauric acids and the overall risk for incident diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings generally support the protective effect of MCFAs [medium-chain fatty acids] but also emphasize the personalized approaches in improving serum MCFA profiles for T2D prevention, which could be tailored according to individuals’ genetic and lifestyle profiles,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xiaojing Jia, MD, and Hong Lin, PhD, of the Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s follow-up duration of 3 years was short, which may have compromised the statistical power of the analysis. The long-term effects of medium-chain fatty acids on the risk for diabetes may not be captured as they were assessed only at baseline. The study population was limited to Chinese adults older than 40 years, which may affect the generalizability of the findings to other ethnicities and age groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Compounded Semaglutide Overdoses Tied to Hospitalizations
Patients are overdosing on compounded semaglutide due to errors in measuring and self-administering the drug and due to clinicians miscalculating doses that may differ from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products.
The FDA published an alert on July 26 after receiving reports of dosing errors involving compounded semaglutide injectable products dispensed in multidose vials. Adverse events included gastrointestinal effects, fainting, dehydration, headache, gallstones, and acute pancreatitis. Some patients required hospitalization.
Why the Risks?
FDA-approved semaglutide injectable products are dosed in milligrams, have standard concentrations, and are currently only available in prefilled pens.
Compounded semaglutide products may differ from approved products in ways that contribute to potential errors — for example, in multidose vials and prefilled syringes. In addition, product concentrations may vary depending on the compounder, and even a single compounder may offer multiple concentrations of semaglutide.
Instructions for a compounded drug, if provided, may tell users to administer semaglutide injections in “units,” the volume of which may vary depending on the concentration — rather than in milligrams. In some instances, patients received syringes significantly larger than the prescribed volume.
Common Errors
The FDA has received reports related to patients mistakenly taking more than the prescribed dose from a multidose vial — sometimes 5-20 times more than the intended dose.
Several reports described clinicians incorrectly calculating the intended dose when converting from milligrams to units or milliliters. In one case, a patient couldn’t get clarity on dosing instructions from the telemedicine provider who prescribed the compounded semaglutide, leading the patient to search online for medical advice. This resulted in the patient taking five times the intended dose.
In another example, one clinician prescribed 20 units instead of two units, affecting three patients who, after receiving 10 times the intended dose, experienced nausea and vomiting.
Another clinician, who also takes semaglutide himself, tried to recalculate his own dose in units and ended up self-administering a dose 10 times higher than intended.
The FDA previously warned about potential risks from the use of compounded drugs during a shortage as is the case with semaglutide. While compounded drugs can “sometimes” be helpful, according to the agency, “compounded drugs pose a higher risk to patients than FDA-approved drugs because compounded drugs do not undergo FDA premarket review for safety, effectiveness, or quality.”
Patients are overdosing on compounded semaglutide due to errors in measuring and self-administering the drug and due to clinicians miscalculating doses that may differ from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products.
The FDA published an alert on July 26 after receiving reports of dosing errors involving compounded semaglutide injectable products dispensed in multidose vials. Adverse events included gastrointestinal effects, fainting, dehydration, headache, gallstones, and acute pancreatitis. Some patients required hospitalization.
Why the Risks?
FDA-approved semaglutide injectable products are dosed in milligrams, have standard concentrations, and are currently only available in prefilled pens.
Compounded semaglutide products may differ from approved products in ways that contribute to potential errors — for example, in multidose vials and prefilled syringes. In addition, product concentrations may vary depending on the compounder, and even a single compounder may offer multiple concentrations of semaglutide.
Instructions for a compounded drug, if provided, may tell users to administer semaglutide injections in “units,” the volume of which may vary depending on the concentration — rather than in milligrams. In some instances, patients received syringes significantly larger than the prescribed volume.
Common Errors
The FDA has received reports related to patients mistakenly taking more than the prescribed dose from a multidose vial — sometimes 5-20 times more than the intended dose.
Several reports described clinicians incorrectly calculating the intended dose when converting from milligrams to units or milliliters. In one case, a patient couldn’t get clarity on dosing instructions from the telemedicine provider who prescribed the compounded semaglutide, leading the patient to search online for medical advice. This resulted in the patient taking five times the intended dose.
In another example, one clinician prescribed 20 units instead of two units, affecting three patients who, after receiving 10 times the intended dose, experienced nausea and vomiting.
Another clinician, who also takes semaglutide himself, tried to recalculate his own dose in units and ended up self-administering a dose 10 times higher than intended.
The FDA previously warned about potential risks from the use of compounded drugs during a shortage as is the case with semaglutide. While compounded drugs can “sometimes” be helpful, according to the agency, “compounded drugs pose a higher risk to patients than FDA-approved drugs because compounded drugs do not undergo FDA premarket review for safety, effectiveness, or quality.”
Patients are overdosing on compounded semaglutide due to errors in measuring and self-administering the drug and due to clinicians miscalculating doses that may differ from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products.
The FDA published an alert on July 26 after receiving reports of dosing errors involving compounded semaglutide injectable products dispensed in multidose vials. Adverse events included gastrointestinal effects, fainting, dehydration, headache, gallstones, and acute pancreatitis. Some patients required hospitalization.
Why the Risks?
FDA-approved semaglutide injectable products are dosed in milligrams, have standard concentrations, and are currently only available in prefilled pens.
Compounded semaglutide products may differ from approved products in ways that contribute to potential errors — for example, in multidose vials and prefilled syringes. In addition, product concentrations may vary depending on the compounder, and even a single compounder may offer multiple concentrations of semaglutide.
Instructions for a compounded drug, if provided, may tell users to administer semaglutide injections in “units,” the volume of which may vary depending on the concentration — rather than in milligrams. In some instances, patients received syringes significantly larger than the prescribed volume.
Common Errors
The FDA has received reports related to patients mistakenly taking more than the prescribed dose from a multidose vial — sometimes 5-20 times more than the intended dose.
Several reports described clinicians incorrectly calculating the intended dose when converting from milligrams to units or milliliters. In one case, a patient couldn’t get clarity on dosing instructions from the telemedicine provider who prescribed the compounded semaglutide, leading the patient to search online for medical advice. This resulted in the patient taking five times the intended dose.
In another example, one clinician prescribed 20 units instead of two units, affecting three patients who, after receiving 10 times the intended dose, experienced nausea and vomiting.
Another clinician, who also takes semaglutide himself, tried to recalculate his own dose in units and ended up self-administering a dose 10 times higher than intended.
The FDA previously warned about potential risks from the use of compounded drugs during a shortage as is the case with semaglutide. While compounded drugs can “sometimes” be helpful, according to the agency, “compounded drugs pose a higher risk to patients than FDA-approved drugs because compounded drugs do not undergo FDA premarket review for safety, effectiveness, or quality.”
What Time of Day Is Best to Eat to Reduce Diabetes Risk?
TOPLINE:
Higher energy intake and glycemic load in the late morning are associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Hispanic/Latino adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Glucose tolerance peaks in the morning and declines in the afternoon and evening in individuals without diabetes.
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study enrolling 8868 Hispanic/Latino adults (mean age, 38.7 years; 51.5% women) without diabetes across four US communities between 2008 and 2011, with a second clinic examination conducted between 2014 and 2017.
- Meal timing was categorized into five periods: Early morning (6:00-8:59 AM), late morning (9:00-11:59 AM), afternoon (12:00-5:59 PM), evening (6:00-11:59 PM), and night (0:00-5:59 AM).
- Participants’ energy intake and glycemic load for each period were assessed at baseline using two 24-hour dietary recalls.
- Incident diabetes was identified through annual follow-up calls or at the second clinic examination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 100-kcal increment in energy intake and 10-unit increment in glycemic load in the late morning was associated with a 6% and 7% lower risk for T2D, respectively (both P = .001), independent of total energy intake, diet quality, and other confounders.
- No such association was found between energy intake and glycemic load in early morning, afternoon, evening, or night meal timings and the risk for diabetes.
- Substituting 100 kcal of energy intake from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents was associated with a 5% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
- Similarly, substituting 10 units of energy-adjusted glycemic load from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents yielded a 7%-9% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings further enhance the existing literature by demonstrating the potential long-term promise of eating in alignment with the diurnal rhythm of glucose tolerance for diabetes prevention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jin Dai, PhD, Fielding School of Public Health, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on only two 24-hour self-reported dietary recalls may have introduced measurement error. Diabetes was self-reported, which may have led to outcome misclassification. The study’s relatively short follow-up time may have introduced reverse causation bias. As most patients had T2D, the findings predominately apply to this diabetes subtype.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher energy intake and glycemic load in the late morning are associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Hispanic/Latino adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Glucose tolerance peaks in the morning and declines in the afternoon and evening in individuals without diabetes.
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study enrolling 8868 Hispanic/Latino adults (mean age, 38.7 years; 51.5% women) without diabetes across four US communities between 2008 and 2011, with a second clinic examination conducted between 2014 and 2017.
- Meal timing was categorized into five periods: Early morning (6:00-8:59 AM), late morning (9:00-11:59 AM), afternoon (12:00-5:59 PM), evening (6:00-11:59 PM), and night (0:00-5:59 AM).
- Participants’ energy intake and glycemic load for each period were assessed at baseline using two 24-hour dietary recalls.
- Incident diabetes was identified through annual follow-up calls or at the second clinic examination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 100-kcal increment in energy intake and 10-unit increment in glycemic load in the late morning was associated with a 6% and 7% lower risk for T2D, respectively (both P = .001), independent of total energy intake, diet quality, and other confounders.
- No such association was found between energy intake and glycemic load in early morning, afternoon, evening, or night meal timings and the risk for diabetes.
- Substituting 100 kcal of energy intake from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents was associated with a 5% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
- Similarly, substituting 10 units of energy-adjusted glycemic load from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents yielded a 7%-9% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings further enhance the existing literature by demonstrating the potential long-term promise of eating in alignment with the diurnal rhythm of glucose tolerance for diabetes prevention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jin Dai, PhD, Fielding School of Public Health, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on only two 24-hour self-reported dietary recalls may have introduced measurement error. Diabetes was self-reported, which may have led to outcome misclassification. The study’s relatively short follow-up time may have introduced reverse causation bias. As most patients had T2D, the findings predominately apply to this diabetes subtype.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher energy intake and glycemic load in the late morning are associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Hispanic/Latino adults.
METHODOLOGY:
- Glucose tolerance peaks in the morning and declines in the afternoon and evening in individuals without diabetes.
- Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study enrolling 8868 Hispanic/Latino adults (mean age, 38.7 years; 51.5% women) without diabetes across four US communities between 2008 and 2011, with a second clinic examination conducted between 2014 and 2017.
- Meal timing was categorized into five periods: Early morning (6:00-8:59 AM), late morning (9:00-11:59 AM), afternoon (12:00-5:59 PM), evening (6:00-11:59 PM), and night (0:00-5:59 AM).
- Participants’ energy intake and glycemic load for each period were assessed at baseline using two 24-hour dietary recalls.
- Incident diabetes was identified through annual follow-up calls or at the second clinic examination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 100-kcal increment in energy intake and 10-unit increment in glycemic load in the late morning was associated with a 6% and 7% lower risk for T2D, respectively (both P = .001), independent of total energy intake, diet quality, and other confounders.
- No such association was found between energy intake and glycemic load in early morning, afternoon, evening, or night meal timings and the risk for diabetes.
- Substituting 100 kcal of energy intake from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents was associated with a 5% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
- Similarly, substituting 10 units of energy-adjusted glycemic load from the early morning, afternoon, or evening with late-morning equivalents yielded a 7%-9% lower risk for diabetes (all P < .05).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings further enhance the existing literature by demonstrating the potential long-term promise of eating in alignment with the diurnal rhythm of glucose tolerance for diabetes prevention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jin Dai, PhD, Fielding School of Public Health, University of California, Los Angeles. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on only two 24-hour self-reported dietary recalls may have introduced measurement error. Diabetes was self-reported, which may have led to outcome misclassification. The study’s relatively short follow-up time may have introduced reverse causation bias. As most patients had T2D, the findings predominately apply to this diabetes subtype.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Guide to Eating Healthy While Working in Healthcare
Eat as fast as you can whenever you can.
That was the med student mindset around food, as Catherine Harmon Toomer, MD, discovered during her school years. “Without a good system in place to counter that,” she explains, “unhealthy eating can get out of control, and that’s what happened to me.”
After med school, things got worse for Dr. Toomer. By her second year in practice as a family medicine physician, she’d gained a lot of weight and had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and cardiomyopathy. At 36, she went into congestive heart failure and was told she likely had 5 years to live.
A moment she described as “a huge wake-up call.”
Dr. Toomer is far from alone in her struggles to balance working in medicine and eating healthfully.
internist and cofounder of ChefMD and founder of Chef Clinic.
There is also the culture of medicine, which Dr. Toomer said looks down on self-care. “Even with break times, patient needs come before our own.” So, you sit down to eat, and there’s an emergency. Your clinic closes for lunch, but the phones still ring, and patients continue to email questions. Charting is also so time-consuming that “everything else gets put on the back burner.”
Sticking to a nutritious diet in this context can feel hopeless. But it isn’t. Really. Here are some doctor-tested, real-life ways you can nourish yourself while getting it all done.
Something Is Always Better Than Nothing
Sure, you might not be able to eat a balanced lunch or dinner while at work, conceded Amy Margulies, RD, LDN, owner of The Rebellious RD. But try to focus on the bigger picture and take small steps.
First, make sure you eat something, Ms. Margulies advised. “Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and negatively impact energy levels and concentration.”
Lisa Andrews, MEd, RD, LD, owner of Sound Bites Nutrition, recalled one of her patients, a gastrointestinal surgeon with reactive hypoglycemia and fatigue. “She was experiencing energy crashes mid-afternoon,” she said. It was only after starting to eat every 4-5 hours that her patient felt better.
Of course, this is easier said than done. “When you are running from one patient to the other and trying to keep on time with your schedule, there is very little time for eating and no time at all for cooking or even heating up food,” recalled Hélène Bertrand, MD, author of Low Back Pain: 3 Steps to Relief in 2 Minutes.
But during her 55 years as a family medicine physician, Dr. Bertrand found ways to improve (if not perfect) the situation. She lunched on nuts or seeds during the day or grabbed a 95% cacao chocolate bar — higher in antioxidants and lower in sugar than a candy bar.
If you don’t have time for breakfast, try drinking a complete protein shake while driving to work, Dr. Toomer recommended. “It’s not ideal, but it’s better than nothing.” Similarly, if the only way you’ll eat a high-protein, lower-carb snack like hummus is with potato chips, go for it, she said.
Basically, don’t be type A striving for perfection. Take good enough when you can and balance the rest when you have time.
Torpedo Temptation
From free treats in the break room to always-present pizza for residents, high-fat, high-sugar, low-nutrient fare is a constant temptation. “I worked with a physician who would bring a balanced lunch to work every day, then find whatever sweet was around for his afternoon treat,” recalled Ms. Margulies.“The cookies, cakes, and donuts were starting to add up — and stopping at one wasn’t working for him.”
What did work was Ms. Margulies’ suggestion to bring a single serving of dark chocolate and fruit to savor during a longer break. “Bringing your favorite treats in appropriate portions can help you stick with your plan throughout the day,” she explained, and you’ll have an easier time resisting what’s in the break room. “When you desire a treat, tell yourself you have what you need and don’t need to indulge in the ‘free food’ just because it’s there. You have power over your choices.”
How about tricking yourself into perceiving cherry tomatoes as treats? That might be unusual, but one of Dr. La Puma’s physician patients did just that, displaying the produce in a candy dish on his office counter. Not only did this strategy help remind him to snack healthfully, it also prompted his patients to ask about eating better, he said.
Preparation Is Still Underrated
Many people find meal prepping intimidating. But it doesn’t need to be complicated. For instance, try purchasing precut veggies, cooked chicken breasts, or other healthy convenience options. You can then combine them in packable containers to prep a few meals at a time. For less busy weeks, consider cooking the protein yourself and whipping up basic sauces (like pesto and vinaigrette) to jazz up your meals.
“I worked with a resident who was gaining weight each month,” recalled Ms. Margulies. “She would skip lunch, grab a random snack, then wait until she got home to eat anything she could find.”
Encouraged by Ms. Margulies, she prepared and portioned one or two balanced dinners each week, which she’d later reheat. She also bought fresh and dried fruit and high-protein snacks, keeping single servings in her car to eat on the way home.
Similarly, Jess DeGore, RD, LDN, CDCES, CHWC, a diabetes educator and owner of Dietitian Jess Nutrition, recalled an ob.gyn. client who constantly skipped meals and relied on vending machine snacks. To combat her resulting energy crashes, she followed Ms. DeGore’s advice to prep workday lunches (like quinoa salads) over the weekend and bring fruit and nut snacks to work.
Automate as Much as You Can
If healthy is already on hand, you’ll eat healthy, said Ms. Andrews. Build up a snack stash focusing on fiber and protein. Tote a lunch bag with a cooler pack if needed. Some suggestions:
- Oatmeal packets
- Individual Greek yogurt cups or drinkable yogurts
- Protein bars
- Protein shakes
- Fresh fruit
- Fresh veggie sticks
- Nuts, dried chickpeas, or edamame
- Trail mix
- Single servings of hummus, nut butter, or guacamole
- Dried seaweed snacks
- Whole grain crackers
- Hard-boiled eggs
- String cheese
- Peanut butter sandwich
- 95% cacao chocolate bar
Try a Meal Delivery Service
Meal delivery services can be pricey, but potentially worth the expense. By bringing meals or having them sent to your office, you won’t have to find time to go to the cafeteria and stand in line, noted Janese S. Laster, MD, an internal medicine, gastroenterology, obesity medicine, and nutrition physician and founder of Gut Theory Total Digestive Care. Instead, “you’ll have something to warm up and eat while writing notes or in between patients,” she said. Plus, “you won’t have an excuse to skip meals.”
Hydration Yes, Junk Drinks No
The following can be filed in the Doctors-Know-It-But-Don’t-Always-Do-It section: “Hunger can be mistaken for thirst,” said Ms. Margulies. “Staying hydrated will help you better assess whether you’re hungry or thirsty.” Choose water over soda or energy drinks, she added, to hydrate your body without unnecessary extra sugars, sugar substitutes, calories, caffeine, or sodium — all of which can affect how you feel.
Advocate for Your Health
Convincing your institution to make changes might be difficult or even impossible, but consider asking your workplace to implement initiatives like these to boost provider nutrition, suggested Jabe Brown, BHSc (Nat), founder of Melbourne Functional Medicine:
- Establish protected break times when doctors can step away from their duties to eat
- Add more nutritious cafeteria options, like salads, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Overhaul vending machine offerings
- Offer educational workshops on nutrition
Be Tenacious About Good Eating
For Dr. Toomer, that meant taking several years off from work to improve her health. After losing more than 100 pounds, she founded TOTAL Weight Care Institute to help other healthcare professionals follow in her footsteps.
For you, the path toward a healthier diet might be gradual — grabbing a more nutritious snack, spending an extra hour per week on food shopping or prep, remembering a water bottle. Whatever it looks like, make realistic lifestyle tweaks that work for you.
Maybe even try that apple-a-day thing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eat as fast as you can whenever you can.
That was the med student mindset around food, as Catherine Harmon Toomer, MD, discovered during her school years. “Without a good system in place to counter that,” she explains, “unhealthy eating can get out of control, and that’s what happened to me.”
After med school, things got worse for Dr. Toomer. By her second year in practice as a family medicine physician, she’d gained a lot of weight and had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and cardiomyopathy. At 36, she went into congestive heart failure and was told she likely had 5 years to live.
A moment she described as “a huge wake-up call.”
Dr. Toomer is far from alone in her struggles to balance working in medicine and eating healthfully.
internist and cofounder of ChefMD and founder of Chef Clinic.
There is also the culture of medicine, which Dr. Toomer said looks down on self-care. “Even with break times, patient needs come before our own.” So, you sit down to eat, and there’s an emergency. Your clinic closes for lunch, but the phones still ring, and patients continue to email questions. Charting is also so time-consuming that “everything else gets put on the back burner.”
Sticking to a nutritious diet in this context can feel hopeless. But it isn’t. Really. Here are some doctor-tested, real-life ways you can nourish yourself while getting it all done.
Something Is Always Better Than Nothing
Sure, you might not be able to eat a balanced lunch or dinner while at work, conceded Amy Margulies, RD, LDN, owner of The Rebellious RD. But try to focus on the bigger picture and take small steps.
First, make sure you eat something, Ms. Margulies advised. “Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and negatively impact energy levels and concentration.”
Lisa Andrews, MEd, RD, LD, owner of Sound Bites Nutrition, recalled one of her patients, a gastrointestinal surgeon with reactive hypoglycemia and fatigue. “She was experiencing energy crashes mid-afternoon,” she said. It was only after starting to eat every 4-5 hours that her patient felt better.
Of course, this is easier said than done. “When you are running from one patient to the other and trying to keep on time with your schedule, there is very little time for eating and no time at all for cooking or even heating up food,” recalled Hélène Bertrand, MD, author of Low Back Pain: 3 Steps to Relief in 2 Minutes.
But during her 55 years as a family medicine physician, Dr. Bertrand found ways to improve (if not perfect) the situation. She lunched on nuts or seeds during the day or grabbed a 95% cacao chocolate bar — higher in antioxidants and lower in sugar than a candy bar.
If you don’t have time for breakfast, try drinking a complete protein shake while driving to work, Dr. Toomer recommended. “It’s not ideal, but it’s better than nothing.” Similarly, if the only way you’ll eat a high-protein, lower-carb snack like hummus is with potato chips, go for it, she said.
Basically, don’t be type A striving for perfection. Take good enough when you can and balance the rest when you have time.
Torpedo Temptation
From free treats in the break room to always-present pizza for residents, high-fat, high-sugar, low-nutrient fare is a constant temptation. “I worked with a physician who would bring a balanced lunch to work every day, then find whatever sweet was around for his afternoon treat,” recalled Ms. Margulies.“The cookies, cakes, and donuts were starting to add up — and stopping at one wasn’t working for him.”
What did work was Ms. Margulies’ suggestion to bring a single serving of dark chocolate and fruit to savor during a longer break. “Bringing your favorite treats in appropriate portions can help you stick with your plan throughout the day,” she explained, and you’ll have an easier time resisting what’s in the break room. “When you desire a treat, tell yourself you have what you need and don’t need to indulge in the ‘free food’ just because it’s there. You have power over your choices.”
How about tricking yourself into perceiving cherry tomatoes as treats? That might be unusual, but one of Dr. La Puma’s physician patients did just that, displaying the produce in a candy dish on his office counter. Not only did this strategy help remind him to snack healthfully, it also prompted his patients to ask about eating better, he said.
Preparation Is Still Underrated
Many people find meal prepping intimidating. But it doesn’t need to be complicated. For instance, try purchasing precut veggies, cooked chicken breasts, or other healthy convenience options. You can then combine them in packable containers to prep a few meals at a time. For less busy weeks, consider cooking the protein yourself and whipping up basic sauces (like pesto and vinaigrette) to jazz up your meals.
“I worked with a resident who was gaining weight each month,” recalled Ms. Margulies. “She would skip lunch, grab a random snack, then wait until she got home to eat anything she could find.”
Encouraged by Ms. Margulies, she prepared and portioned one or two balanced dinners each week, which she’d later reheat. She also bought fresh and dried fruit and high-protein snacks, keeping single servings in her car to eat on the way home.
Similarly, Jess DeGore, RD, LDN, CDCES, CHWC, a diabetes educator and owner of Dietitian Jess Nutrition, recalled an ob.gyn. client who constantly skipped meals and relied on vending machine snacks. To combat her resulting energy crashes, she followed Ms. DeGore’s advice to prep workday lunches (like quinoa salads) over the weekend and bring fruit and nut snacks to work.
Automate as Much as You Can
If healthy is already on hand, you’ll eat healthy, said Ms. Andrews. Build up a snack stash focusing on fiber and protein. Tote a lunch bag with a cooler pack if needed. Some suggestions:
- Oatmeal packets
- Individual Greek yogurt cups or drinkable yogurts
- Protein bars
- Protein shakes
- Fresh fruit
- Fresh veggie sticks
- Nuts, dried chickpeas, or edamame
- Trail mix
- Single servings of hummus, nut butter, or guacamole
- Dried seaweed snacks
- Whole grain crackers
- Hard-boiled eggs
- String cheese
- Peanut butter sandwich
- 95% cacao chocolate bar
Try a Meal Delivery Service
Meal delivery services can be pricey, but potentially worth the expense. By bringing meals or having them sent to your office, you won’t have to find time to go to the cafeteria and stand in line, noted Janese S. Laster, MD, an internal medicine, gastroenterology, obesity medicine, and nutrition physician and founder of Gut Theory Total Digestive Care. Instead, “you’ll have something to warm up and eat while writing notes or in between patients,” she said. Plus, “you won’t have an excuse to skip meals.”
Hydration Yes, Junk Drinks No
The following can be filed in the Doctors-Know-It-But-Don’t-Always-Do-It section: “Hunger can be mistaken for thirst,” said Ms. Margulies. “Staying hydrated will help you better assess whether you’re hungry or thirsty.” Choose water over soda or energy drinks, she added, to hydrate your body without unnecessary extra sugars, sugar substitutes, calories, caffeine, or sodium — all of which can affect how you feel.
Advocate for Your Health
Convincing your institution to make changes might be difficult or even impossible, but consider asking your workplace to implement initiatives like these to boost provider nutrition, suggested Jabe Brown, BHSc (Nat), founder of Melbourne Functional Medicine:
- Establish protected break times when doctors can step away from their duties to eat
- Add more nutritious cafeteria options, like salads, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Overhaul vending machine offerings
- Offer educational workshops on nutrition
Be Tenacious About Good Eating
For Dr. Toomer, that meant taking several years off from work to improve her health. After losing more than 100 pounds, she founded TOTAL Weight Care Institute to help other healthcare professionals follow in her footsteps.
For you, the path toward a healthier diet might be gradual — grabbing a more nutritious snack, spending an extra hour per week on food shopping or prep, remembering a water bottle. Whatever it looks like, make realistic lifestyle tweaks that work for you.
Maybe even try that apple-a-day thing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eat as fast as you can whenever you can.
That was the med student mindset around food, as Catherine Harmon Toomer, MD, discovered during her school years. “Without a good system in place to counter that,” she explains, “unhealthy eating can get out of control, and that’s what happened to me.”
After med school, things got worse for Dr. Toomer. By her second year in practice as a family medicine physician, she’d gained a lot of weight and had been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and cardiomyopathy. At 36, she went into congestive heart failure and was told she likely had 5 years to live.
A moment she described as “a huge wake-up call.”
Dr. Toomer is far from alone in her struggles to balance working in medicine and eating healthfully.
internist and cofounder of ChefMD and founder of Chef Clinic.
There is also the culture of medicine, which Dr. Toomer said looks down on self-care. “Even with break times, patient needs come before our own.” So, you sit down to eat, and there’s an emergency. Your clinic closes for lunch, but the phones still ring, and patients continue to email questions. Charting is also so time-consuming that “everything else gets put on the back burner.”
Sticking to a nutritious diet in this context can feel hopeless. But it isn’t. Really. Here are some doctor-tested, real-life ways you can nourish yourself while getting it all done.
Something Is Always Better Than Nothing
Sure, you might not be able to eat a balanced lunch or dinner while at work, conceded Amy Margulies, RD, LDN, owner of The Rebellious RD. But try to focus on the bigger picture and take small steps.
First, make sure you eat something, Ms. Margulies advised. “Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and negatively impact energy levels and concentration.”
Lisa Andrews, MEd, RD, LD, owner of Sound Bites Nutrition, recalled one of her patients, a gastrointestinal surgeon with reactive hypoglycemia and fatigue. “She was experiencing energy crashes mid-afternoon,” she said. It was only after starting to eat every 4-5 hours that her patient felt better.
Of course, this is easier said than done. “When you are running from one patient to the other and trying to keep on time with your schedule, there is very little time for eating and no time at all for cooking or even heating up food,” recalled Hélène Bertrand, MD, author of Low Back Pain: 3 Steps to Relief in 2 Minutes.
But during her 55 years as a family medicine physician, Dr. Bertrand found ways to improve (if not perfect) the situation. She lunched on nuts or seeds during the day or grabbed a 95% cacao chocolate bar — higher in antioxidants and lower in sugar than a candy bar.
If you don’t have time for breakfast, try drinking a complete protein shake while driving to work, Dr. Toomer recommended. “It’s not ideal, but it’s better than nothing.” Similarly, if the only way you’ll eat a high-protein, lower-carb snack like hummus is with potato chips, go for it, she said.
Basically, don’t be type A striving for perfection. Take good enough when you can and balance the rest when you have time.
Torpedo Temptation
From free treats in the break room to always-present pizza for residents, high-fat, high-sugar, low-nutrient fare is a constant temptation. “I worked with a physician who would bring a balanced lunch to work every day, then find whatever sweet was around for his afternoon treat,” recalled Ms. Margulies.“The cookies, cakes, and donuts were starting to add up — and stopping at one wasn’t working for him.”
What did work was Ms. Margulies’ suggestion to bring a single serving of dark chocolate and fruit to savor during a longer break. “Bringing your favorite treats in appropriate portions can help you stick with your plan throughout the day,” she explained, and you’ll have an easier time resisting what’s in the break room. “When you desire a treat, tell yourself you have what you need and don’t need to indulge in the ‘free food’ just because it’s there. You have power over your choices.”
How about tricking yourself into perceiving cherry tomatoes as treats? That might be unusual, but one of Dr. La Puma’s physician patients did just that, displaying the produce in a candy dish on his office counter. Not only did this strategy help remind him to snack healthfully, it also prompted his patients to ask about eating better, he said.
Preparation Is Still Underrated
Many people find meal prepping intimidating. But it doesn’t need to be complicated. For instance, try purchasing precut veggies, cooked chicken breasts, or other healthy convenience options. You can then combine them in packable containers to prep a few meals at a time. For less busy weeks, consider cooking the protein yourself and whipping up basic sauces (like pesto and vinaigrette) to jazz up your meals.
“I worked with a resident who was gaining weight each month,” recalled Ms. Margulies. “She would skip lunch, grab a random snack, then wait until she got home to eat anything she could find.”
Encouraged by Ms. Margulies, she prepared and portioned one or two balanced dinners each week, which she’d later reheat. She also bought fresh and dried fruit and high-protein snacks, keeping single servings in her car to eat on the way home.
Similarly, Jess DeGore, RD, LDN, CDCES, CHWC, a diabetes educator and owner of Dietitian Jess Nutrition, recalled an ob.gyn. client who constantly skipped meals and relied on vending machine snacks. To combat her resulting energy crashes, she followed Ms. DeGore’s advice to prep workday lunches (like quinoa salads) over the weekend and bring fruit and nut snacks to work.
Automate as Much as You Can
If healthy is already on hand, you’ll eat healthy, said Ms. Andrews. Build up a snack stash focusing on fiber and protein. Tote a lunch bag with a cooler pack if needed. Some suggestions:
- Oatmeal packets
- Individual Greek yogurt cups or drinkable yogurts
- Protein bars
- Protein shakes
- Fresh fruit
- Fresh veggie sticks
- Nuts, dried chickpeas, or edamame
- Trail mix
- Single servings of hummus, nut butter, or guacamole
- Dried seaweed snacks
- Whole grain crackers
- Hard-boiled eggs
- String cheese
- Peanut butter sandwich
- 95% cacao chocolate bar
Try a Meal Delivery Service
Meal delivery services can be pricey, but potentially worth the expense. By bringing meals or having them sent to your office, you won’t have to find time to go to the cafeteria and stand in line, noted Janese S. Laster, MD, an internal medicine, gastroenterology, obesity medicine, and nutrition physician and founder of Gut Theory Total Digestive Care. Instead, “you’ll have something to warm up and eat while writing notes or in between patients,” she said. Plus, “you won’t have an excuse to skip meals.”
Hydration Yes, Junk Drinks No
The following can be filed in the Doctors-Know-It-But-Don’t-Always-Do-It section: “Hunger can be mistaken for thirst,” said Ms. Margulies. “Staying hydrated will help you better assess whether you’re hungry or thirsty.” Choose water over soda or energy drinks, she added, to hydrate your body without unnecessary extra sugars, sugar substitutes, calories, caffeine, or sodium — all of which can affect how you feel.
Advocate for Your Health
Convincing your institution to make changes might be difficult or even impossible, but consider asking your workplace to implement initiatives like these to boost provider nutrition, suggested Jabe Brown, BHSc (Nat), founder of Melbourne Functional Medicine:
- Establish protected break times when doctors can step away from their duties to eat
- Add more nutritious cafeteria options, like salads, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Overhaul vending machine offerings
- Offer educational workshops on nutrition
Be Tenacious About Good Eating
For Dr. Toomer, that meant taking several years off from work to improve her health. After losing more than 100 pounds, she founded TOTAL Weight Care Institute to help other healthcare professionals follow in her footsteps.
For you, the path toward a healthier diet might be gradual — grabbing a more nutritious snack, spending an extra hour per week on food shopping or prep, remembering a water bottle. Whatever it looks like, make realistic lifestyle tweaks that work for you.
Maybe even try that apple-a-day thing.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High Blood Sugar May Drive Dementia, German Researchers Warn
On World Brain Day (July 22, 2024), the German Society of Neurology (DGN) and the German Brain Foundation pointed out that too much sugar can harm the brain. The current results of the Global Burden of Diseases study shows that stroke and dementia are among the top 10 causes of death. A healthy, active lifestyle with sufficient exercise and sleep, along with the avoidance of harmful substances like alcohol, nicotine, or excessive sugar, protects the brain.
“Of course, the dose makes the poison as the brain, being the body’s powerhouse, needs glucose to function,” said Frank Erbguth, MD, PhD, president of the German Brain Foundation, in a press release from DGN and the German Brain Foundation. “However, with a permanent increase in blood sugar levels due to too many, too lavish meals and constant snacking on the side, we overload the system and fuel the development of neurologic diseases, particularly dementia and stroke.”
The per capita consumption of sugar was 33.2 kg in 2021/2022, which is almost twice the recommended amount. The German Nutrition Society recommends that no more than 10% of energy come from sugar. With a goal of 2000 kilocalories, that’s 50 g per day, or 18 kg per year. This total includes not only added sugar but also naturally occurring sugar, such as in fruits, honey, or juices.
What’s the Mechanism?
In Germany, around 250,000 people are diagnosed with dementia annually, and 15%-25% have vascular dementia. That proportion represents between 40,000 and 60,000 new cases each year.
In addition, glycosaminoglycans, which are complex sugar molecules, can directly impair cognition. They affect the function of synapses between nerve cells and, thus, affect neuronal plasticity. Experimental data presented at the 2023 American Chemical Society Congress have shown this phenomenon.
Twenty years ago, a study provided evidence that a diet high in fat and sugar disrupts neuronal plasticity and can impair the function of the hippocampus in the long term. A recent meta-analysis confirms these findings: Although mental performance improves at 2-12 hours after sugar consumption, sustained sugar intake can permanently damage cognitive function.
Diabetes mellitus can indirectly cause brain damage. Since the 1990s, it has been known that patients with type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk for dementia. It is suspected that glucose metabolism is also disrupted in neurons, thus contributing to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Insulin also plays a role in the formation of Alzheimer’s plaques.
The Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research demonstrated in 2023 that regular consumption of high-sugar and high-fat foods can change the brain. This leads to an increased craving for high-sugar and high-fat foods, which in turn promotes the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Reduce Sugar Consumption
DGN and the German Brain Foundation advise minimizing sugar consumption. This process is often challenging, as even a small dose of sugar can trigger the gut to send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve, thus causing a strong craving for more sugar. “This could be the reason why some people quickly eat a whole chocolate bar after just one piece,” said Dr. Erbguth. In addition, dopamine, a “feel-good hormone,” is released in the brain when consuming sugar, thus leading to a desire for more.
“It is wise to break free from this cycle by largely avoiding sugar,” said Peter Berlit, MD, secretary general and spokesperson for DGN. “The effort is worth it, as 40% of all dementia cases and 90% of all strokes are preventable, with many of them linked to industrial sugar,” said Dr. Berlit. DGN and the German Brain Foundation support the call for a tax on particularly sugary beverages. They also pointed out that foods like yogurt or tomato ketchup contain sugar, and alcohol can also significantly raise blood sugar levels.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On World Brain Day (July 22, 2024), the German Society of Neurology (DGN) and the German Brain Foundation pointed out that too much sugar can harm the brain. The current results of the Global Burden of Diseases study shows that stroke and dementia are among the top 10 causes of death. A healthy, active lifestyle with sufficient exercise and sleep, along with the avoidance of harmful substances like alcohol, nicotine, or excessive sugar, protects the brain.
“Of course, the dose makes the poison as the brain, being the body’s powerhouse, needs glucose to function,” said Frank Erbguth, MD, PhD, president of the German Brain Foundation, in a press release from DGN and the German Brain Foundation. “However, with a permanent increase in blood sugar levels due to too many, too lavish meals and constant snacking on the side, we overload the system and fuel the development of neurologic diseases, particularly dementia and stroke.”
The per capita consumption of sugar was 33.2 kg in 2021/2022, which is almost twice the recommended amount. The German Nutrition Society recommends that no more than 10% of energy come from sugar. With a goal of 2000 kilocalories, that’s 50 g per day, or 18 kg per year. This total includes not only added sugar but also naturally occurring sugar, such as in fruits, honey, or juices.
What’s the Mechanism?
In Germany, around 250,000 people are diagnosed with dementia annually, and 15%-25% have vascular dementia. That proportion represents between 40,000 and 60,000 new cases each year.
In addition, glycosaminoglycans, which are complex sugar molecules, can directly impair cognition. They affect the function of synapses between nerve cells and, thus, affect neuronal plasticity. Experimental data presented at the 2023 American Chemical Society Congress have shown this phenomenon.
Twenty years ago, a study provided evidence that a diet high in fat and sugar disrupts neuronal plasticity and can impair the function of the hippocampus in the long term. A recent meta-analysis confirms these findings: Although mental performance improves at 2-12 hours after sugar consumption, sustained sugar intake can permanently damage cognitive function.
Diabetes mellitus can indirectly cause brain damage. Since the 1990s, it has been known that patients with type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk for dementia. It is suspected that glucose metabolism is also disrupted in neurons, thus contributing to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Insulin also plays a role in the formation of Alzheimer’s plaques.
The Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research demonstrated in 2023 that regular consumption of high-sugar and high-fat foods can change the brain. This leads to an increased craving for high-sugar and high-fat foods, which in turn promotes the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Reduce Sugar Consumption
DGN and the German Brain Foundation advise minimizing sugar consumption. This process is often challenging, as even a small dose of sugar can trigger the gut to send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve, thus causing a strong craving for more sugar. “This could be the reason why some people quickly eat a whole chocolate bar after just one piece,” said Dr. Erbguth. In addition, dopamine, a “feel-good hormone,” is released in the brain when consuming sugar, thus leading to a desire for more.
“It is wise to break free from this cycle by largely avoiding sugar,” said Peter Berlit, MD, secretary general and spokesperson for DGN. “The effort is worth it, as 40% of all dementia cases and 90% of all strokes are preventable, with many of them linked to industrial sugar,” said Dr. Berlit. DGN and the German Brain Foundation support the call for a tax on particularly sugary beverages. They also pointed out that foods like yogurt or tomato ketchup contain sugar, and alcohol can also significantly raise blood sugar levels.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On World Brain Day (July 22, 2024), the German Society of Neurology (DGN) and the German Brain Foundation pointed out that too much sugar can harm the brain. The current results of the Global Burden of Diseases study shows that stroke and dementia are among the top 10 causes of death. A healthy, active lifestyle with sufficient exercise and sleep, along with the avoidance of harmful substances like alcohol, nicotine, or excessive sugar, protects the brain.
“Of course, the dose makes the poison as the brain, being the body’s powerhouse, needs glucose to function,” said Frank Erbguth, MD, PhD, president of the German Brain Foundation, in a press release from DGN and the German Brain Foundation. “However, with a permanent increase in blood sugar levels due to too many, too lavish meals and constant snacking on the side, we overload the system and fuel the development of neurologic diseases, particularly dementia and stroke.”
The per capita consumption of sugar was 33.2 kg in 2021/2022, which is almost twice the recommended amount. The German Nutrition Society recommends that no more than 10% of energy come from sugar. With a goal of 2000 kilocalories, that’s 50 g per day, or 18 kg per year. This total includes not only added sugar but also naturally occurring sugar, such as in fruits, honey, or juices.
What’s the Mechanism?
In Germany, around 250,000 people are diagnosed with dementia annually, and 15%-25% have vascular dementia. That proportion represents between 40,000 and 60,000 new cases each year.
In addition, glycosaminoglycans, which are complex sugar molecules, can directly impair cognition. They affect the function of synapses between nerve cells and, thus, affect neuronal plasticity. Experimental data presented at the 2023 American Chemical Society Congress have shown this phenomenon.
Twenty years ago, a study provided evidence that a diet high in fat and sugar disrupts neuronal plasticity and can impair the function of the hippocampus in the long term. A recent meta-analysis confirms these findings: Although mental performance improves at 2-12 hours after sugar consumption, sustained sugar intake can permanently damage cognitive function.
Diabetes mellitus can indirectly cause brain damage. Since the 1990s, it has been known that patients with type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk for dementia. It is suspected that glucose metabolism is also disrupted in neurons, thus contributing to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Insulin also plays a role in the formation of Alzheimer’s plaques.
The Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research demonstrated in 2023 that regular consumption of high-sugar and high-fat foods can change the brain. This leads to an increased craving for high-sugar and high-fat foods, which in turn promotes the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Reduce Sugar Consumption
DGN and the German Brain Foundation advise minimizing sugar consumption. This process is often challenging, as even a small dose of sugar can trigger the gut to send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve, thus causing a strong craving for more sugar. “This could be the reason why some people quickly eat a whole chocolate bar after just one piece,” said Dr. Erbguth. In addition, dopamine, a “feel-good hormone,” is released in the brain when consuming sugar, thus leading to a desire for more.
“It is wise to break free from this cycle by largely avoiding sugar,” said Peter Berlit, MD, secretary general and spokesperson for DGN. “The effort is worth it, as 40% of all dementia cases and 90% of all strokes are preventable, with many of them linked to industrial sugar,” said Dr. Berlit. DGN and the German Brain Foundation support the call for a tax on particularly sugary beverages. They also pointed out that foods like yogurt or tomato ketchup contain sugar, and alcohol can also significantly raise blood sugar levels.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Two Diets Linked to Improved Cognition, Slowed Brain Aging
An intermittent fasting (IF) diet and a standard healthy living (HL) diet focused on healthy foods both lead to weight loss, reduced insulin resistance (IR), and slowed brain aging in older overweight adults with IR, new research showed. However, neither diet has an effect on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) biomarkers.
Although investigators found both diets were beneficial, some outcomes were more robust with the IF diet.
“The study provides a blueprint for assessing brain effects of dietary interventions and motivates further research on intermittent fasting and continuous diets for brain health optimization,” wrote the investigators, led by Dimitrios Kapogiannis, MD, chief, human neuroscience section, National Institute on Aging, and adjunct associate professor of neurology, the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
The findings were published online in Cell Metabolism.
Cognitive Outcomes
The prevalence of IR — reduced cellular sensitivity to insulin that’s a hallmark of type 2 diabetes — increases with age and obesity, adding to an increased risk for accelerated brain aging as well as AD and related dementias (ADRD) in older adults who have overweight.
Studies reported healthy diets promote overall health, but it’s unclear whether, and to what extent, they improve brain health beyond general health enhancement.
Researchers used multiple brain and cognitive measures to assess dietary effects on brain health, including peripherally harvested neuron-derived extracellular vesicles (NDEVs) to probe neuronal insulin signaling; MRI to investigate the pace of brain aging; magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure brain glucose, metabolites, and neurotransmitters; and NDEVs and cerebrospinal fluid to derive biomarkers for AD/ADRD.
The study included 40 cognitively intact overweight participants with IR, mean age 63.2 years, 60% women, and 62.5% White. Their mean body weight was 97.1 kg and mean body mass index (BMI) was 34.4.
Participants were randomly assigned to 8 weeks of an IF diet or a HL diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy and limits added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
The IF diet involved following the HL diet for 5 days per week and restricting calories to a quarter of the recommended daily intake for 2 consecutive days.
Both diets reduced neuronal IR and had comparable effects in improving insulin signaling biomarkers in NDEVs, reducing brain glucose on MRS, and improving blood biomarkers of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Using MRI, researchers also assessed brain age, an indication of whether the brain appears older or younger than an individual’s chronological age. There was a decrease of 2.63 years with the IF diet (P = .05) and 2.42 years with the HL diet (P < .001) in the anterior cingulate and ventromedial prefrontal cortex.
Both diets improved executive function and memory, with those following the IF diet benefiting more in strategic planning, switching between two cognitively demanding tasks, cued recall, and other areas.
Hypothesis-Generating Research
AD biomarkers including amyloid beta 42 (Aß42), Aß40, and plasma phosphorylated-tau181 did not change with either diet, a finding that investigators speculated may be due to the short duration of the study. Light-chain neurofilaments increased across groups with no differences between the diets.
In other findings, BMI decreased by 1.41 with the IF diet and by 0.80 with the HL diet, and a similar pattern was observed for weight. Waist circumference decreased in both groups with no significant differences between diets.
An exploratory analysis showed executive function improved with the IF diet but not with the HL diet in women, whereas it improved with both diets in men. BMI and apolipoprotein E and SLC16A7 genotypes also modulated diet effects.
Both diets were well tolerated. The most frequent adverse events were gastrointestinal and occurred only with the IF diet.
The authors noted the findings are preliminary and results are hypothesis generating. Study limitations included the study’s short duration and its power to detect anything other than large to moderate effect size changes and differences between the diets. Researchers also didn’t acquire data on dietary intake, so lapses in adherence can’t be excluded. However, the large decreases in BMI, weight, and waist circumference with both diets indicated high adherence.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging. The authors reported no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An intermittent fasting (IF) diet and a standard healthy living (HL) diet focused on healthy foods both lead to weight loss, reduced insulin resistance (IR), and slowed brain aging in older overweight adults with IR, new research showed. However, neither diet has an effect on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) biomarkers.
Although investigators found both diets were beneficial, some outcomes were more robust with the IF diet.
“The study provides a blueprint for assessing brain effects of dietary interventions and motivates further research on intermittent fasting and continuous diets for brain health optimization,” wrote the investigators, led by Dimitrios Kapogiannis, MD, chief, human neuroscience section, National Institute on Aging, and adjunct associate professor of neurology, the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
The findings were published online in Cell Metabolism.
Cognitive Outcomes
The prevalence of IR — reduced cellular sensitivity to insulin that’s a hallmark of type 2 diabetes — increases with age and obesity, adding to an increased risk for accelerated brain aging as well as AD and related dementias (ADRD) in older adults who have overweight.
Studies reported healthy diets promote overall health, but it’s unclear whether, and to what extent, they improve brain health beyond general health enhancement.
Researchers used multiple brain and cognitive measures to assess dietary effects on brain health, including peripherally harvested neuron-derived extracellular vesicles (NDEVs) to probe neuronal insulin signaling; MRI to investigate the pace of brain aging; magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure brain glucose, metabolites, and neurotransmitters; and NDEVs and cerebrospinal fluid to derive biomarkers for AD/ADRD.
The study included 40 cognitively intact overweight participants with IR, mean age 63.2 years, 60% women, and 62.5% White. Their mean body weight was 97.1 kg and mean body mass index (BMI) was 34.4.
Participants were randomly assigned to 8 weeks of an IF diet or a HL diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy and limits added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
The IF diet involved following the HL diet for 5 days per week and restricting calories to a quarter of the recommended daily intake for 2 consecutive days.
Both diets reduced neuronal IR and had comparable effects in improving insulin signaling biomarkers in NDEVs, reducing brain glucose on MRS, and improving blood biomarkers of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Using MRI, researchers also assessed brain age, an indication of whether the brain appears older or younger than an individual’s chronological age. There was a decrease of 2.63 years with the IF diet (P = .05) and 2.42 years with the HL diet (P < .001) in the anterior cingulate and ventromedial prefrontal cortex.
Both diets improved executive function and memory, with those following the IF diet benefiting more in strategic planning, switching between two cognitively demanding tasks, cued recall, and other areas.
Hypothesis-Generating Research
AD biomarkers including amyloid beta 42 (Aß42), Aß40, and plasma phosphorylated-tau181 did not change with either diet, a finding that investigators speculated may be due to the short duration of the study. Light-chain neurofilaments increased across groups with no differences between the diets.
In other findings, BMI decreased by 1.41 with the IF diet and by 0.80 with the HL diet, and a similar pattern was observed for weight. Waist circumference decreased in both groups with no significant differences between diets.
An exploratory analysis showed executive function improved with the IF diet but not with the HL diet in women, whereas it improved with both diets in men. BMI and apolipoprotein E and SLC16A7 genotypes also modulated diet effects.
Both diets were well tolerated. The most frequent adverse events were gastrointestinal and occurred only with the IF diet.
The authors noted the findings are preliminary and results are hypothesis generating. Study limitations included the study’s short duration and its power to detect anything other than large to moderate effect size changes and differences between the diets. Researchers also didn’t acquire data on dietary intake, so lapses in adherence can’t be excluded. However, the large decreases in BMI, weight, and waist circumference with both diets indicated high adherence.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging. The authors reported no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An intermittent fasting (IF) diet and a standard healthy living (HL) diet focused on healthy foods both lead to weight loss, reduced insulin resistance (IR), and slowed brain aging in older overweight adults with IR, new research showed. However, neither diet has an effect on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) biomarkers.
Although investigators found both diets were beneficial, some outcomes were more robust with the IF diet.
“The study provides a blueprint for assessing brain effects of dietary interventions and motivates further research on intermittent fasting and continuous diets for brain health optimization,” wrote the investigators, led by Dimitrios Kapogiannis, MD, chief, human neuroscience section, National Institute on Aging, and adjunct associate professor of neurology, the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
The findings were published online in Cell Metabolism.
Cognitive Outcomes
The prevalence of IR — reduced cellular sensitivity to insulin that’s a hallmark of type 2 diabetes — increases with age and obesity, adding to an increased risk for accelerated brain aging as well as AD and related dementias (ADRD) in older adults who have overweight.
Studies reported healthy diets promote overall health, but it’s unclear whether, and to what extent, they improve brain health beyond general health enhancement.
Researchers used multiple brain and cognitive measures to assess dietary effects on brain health, including peripherally harvested neuron-derived extracellular vesicles (NDEVs) to probe neuronal insulin signaling; MRI to investigate the pace of brain aging; magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure brain glucose, metabolites, and neurotransmitters; and NDEVs and cerebrospinal fluid to derive biomarkers for AD/ADRD.
The study included 40 cognitively intact overweight participants with IR, mean age 63.2 years, 60% women, and 62.5% White. Their mean body weight was 97.1 kg and mean body mass index (BMI) was 34.4.
Participants were randomly assigned to 8 weeks of an IF diet or a HL diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy and limits added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
The IF diet involved following the HL diet for 5 days per week and restricting calories to a quarter of the recommended daily intake for 2 consecutive days.
Both diets reduced neuronal IR and had comparable effects in improving insulin signaling biomarkers in NDEVs, reducing brain glucose on MRS, and improving blood biomarkers of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Using MRI, researchers also assessed brain age, an indication of whether the brain appears older or younger than an individual’s chronological age. There was a decrease of 2.63 years with the IF diet (P = .05) and 2.42 years with the HL diet (P < .001) in the anterior cingulate and ventromedial prefrontal cortex.
Both diets improved executive function and memory, with those following the IF diet benefiting more in strategic planning, switching between two cognitively demanding tasks, cued recall, and other areas.
Hypothesis-Generating Research
AD biomarkers including amyloid beta 42 (Aß42), Aß40, and plasma phosphorylated-tau181 did not change with either diet, a finding that investigators speculated may be due to the short duration of the study. Light-chain neurofilaments increased across groups with no differences between the diets.
In other findings, BMI decreased by 1.41 with the IF diet and by 0.80 with the HL diet, and a similar pattern was observed for weight. Waist circumference decreased in both groups with no significant differences between diets.
An exploratory analysis showed executive function improved with the IF diet but not with the HL diet in women, whereas it improved with both diets in men. BMI and apolipoprotein E and SLC16A7 genotypes also modulated diet effects.
Both diets were well tolerated. The most frequent adverse events were gastrointestinal and occurred only with the IF diet.
The authors noted the findings are preliminary and results are hypothesis generating. Study limitations included the study’s short duration and its power to detect anything other than large to moderate effect size changes and differences between the diets. Researchers also didn’t acquire data on dietary intake, so lapses in adherence can’t be excluded. However, the large decreases in BMI, weight, and waist circumference with both diets indicated high adherence.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging. The authors reported no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL METABOLISM