User login
Mortality in ankylosing spondylitis: CV disease, drug abuse are big contributors
TOPLINE:
Drug use disorder increased the likelihood of in-hospital mortality more than 10-fold in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), compared with patients who did not die while hospitalized.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 2,125 adults with AS who were hospitalized between 2015 and 2017, using the Cerner Health Facts Database.
- The final analysis included 41 patients with AS who died while hospitalized and 260 random control patients with AS who did not die.
- The mean age of the deceased patients with AS was 70 years, 85% were male, and 81% were White; 71% had hypertension, 32% had kidney disease, and 22% had congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with AS, cardiovascular disease was the most frequent cause of death, followed by infection, respiratory failure, and fracture/trauma in 15, 14, 8, and 7 patients, respectively. (Some patients had more than one cause of death recorded in the discharge summary.)
- The most common cardiac causes of death were myocardial infarction and cardiac arrest, while the top causes of acute respiratory failure were pneumonia and pulmonary embolism.
- Drug abuse, including opioid dependence, was significantly associated with death among hospitalized patients with AS (adjusted odds ratio, 10.9; P = .001).
- Heart failure and kidney disease were the comorbidities most strongly associated with mortality; the odds of death in the presence of heart failure rose 2.76-fold, and it increased 2.46-fold in the presence of kidney disease.
IN PRACTICE:
Underlying comorbidities, especially cardiac and renal, are associated with mortality in AS, and patients should be screened early on for these comorbidities to help reduce the odds of death.
SOURCE:
First author Mohamad Bittar, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Rheumatology).
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked AS-specific data such as disease activity scores, which were not in the database. Also missing were variables linked to disease activity and mortality, including smoking, BMI levels, and C-reactive protein levels.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. Several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with UCB, Amgen, Pfizer, AbbVie, Novartis, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Drug use disorder increased the likelihood of in-hospital mortality more than 10-fold in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), compared with patients who did not die while hospitalized.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 2,125 adults with AS who were hospitalized between 2015 and 2017, using the Cerner Health Facts Database.
- The final analysis included 41 patients with AS who died while hospitalized and 260 random control patients with AS who did not die.
- The mean age of the deceased patients with AS was 70 years, 85% were male, and 81% were White; 71% had hypertension, 32% had kidney disease, and 22% had congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with AS, cardiovascular disease was the most frequent cause of death, followed by infection, respiratory failure, and fracture/trauma in 15, 14, 8, and 7 patients, respectively. (Some patients had more than one cause of death recorded in the discharge summary.)
- The most common cardiac causes of death were myocardial infarction and cardiac arrest, while the top causes of acute respiratory failure were pneumonia and pulmonary embolism.
- Drug abuse, including opioid dependence, was significantly associated with death among hospitalized patients with AS (adjusted odds ratio, 10.9; P = .001).
- Heart failure and kidney disease were the comorbidities most strongly associated with mortality; the odds of death in the presence of heart failure rose 2.76-fold, and it increased 2.46-fold in the presence of kidney disease.
IN PRACTICE:
Underlying comorbidities, especially cardiac and renal, are associated with mortality in AS, and patients should be screened early on for these comorbidities to help reduce the odds of death.
SOURCE:
First author Mohamad Bittar, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Rheumatology).
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked AS-specific data such as disease activity scores, which were not in the database. Also missing were variables linked to disease activity and mortality, including smoking, BMI levels, and C-reactive protein levels.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. Several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with UCB, Amgen, Pfizer, AbbVie, Novartis, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Drug use disorder increased the likelihood of in-hospital mortality more than 10-fold in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), compared with patients who did not die while hospitalized.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from 2,125 adults with AS who were hospitalized between 2015 and 2017, using the Cerner Health Facts Database.
- The final analysis included 41 patients with AS who died while hospitalized and 260 random control patients with AS who did not die.
- The mean age of the deceased patients with AS was 70 years, 85% were male, and 81% were White; 71% had hypertension, 32% had kidney disease, and 22% had congestive heart failure.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the patients with AS, cardiovascular disease was the most frequent cause of death, followed by infection, respiratory failure, and fracture/trauma in 15, 14, 8, and 7 patients, respectively. (Some patients had more than one cause of death recorded in the discharge summary.)
- The most common cardiac causes of death were myocardial infarction and cardiac arrest, while the top causes of acute respiratory failure were pneumonia and pulmonary embolism.
- Drug abuse, including opioid dependence, was significantly associated with death among hospitalized patients with AS (adjusted odds ratio, 10.9; P = .001).
- Heart failure and kidney disease were the comorbidities most strongly associated with mortality; the odds of death in the presence of heart failure rose 2.76-fold, and it increased 2.46-fold in the presence of kidney disease.
IN PRACTICE:
Underlying comorbidities, especially cardiac and renal, are associated with mortality in AS, and patients should be screened early on for these comorbidities to help reduce the odds of death.
SOURCE:
First author Mohamad Bittar, MD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Rheumatology).
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked AS-specific data such as disease activity scores, which were not in the database. Also missing were variables linked to disease activity and mortality, including smoking, BMI levels, and C-reactive protein levels.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. Several coauthors disclosed financial relationships with UCB, Amgen, Pfizer, AbbVie, Novartis, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fracture risk factors described in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
TOPLINE:
Opioid use, older age, and fracture history increase the risk for fractures in older adults with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) based on a review of registry and Medicare claims data.
METHODOLOGY:
- Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry data were linked to Medicare claims from 2016 to 2018; each patient had two AS International Classification of Diseases–9 and –10 codes at least 30 days apart.
- The study population included 1426 adults with AS (mean age, 69.4 years) who had continuous Medicare enrollment (Parts A and B) for the entire follow-up period but did not have Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C).
- The researchers used a logistic regression analysis to identify factors associated with fractures including age, sex, and body mass index.
TAKEAWAYS:
- The overall incidence of fractures was 76.7 per 1,000 person-years.
- Older age, history of fracture, and opioid use at a morphine-equivalent dose > 30 mg (at least one prescription 30 or more days prior to the index date) were significantly associated with increased risk for fracture (odds ratios, 2.8, 5.24, and 1.86, respectively).
- Fracture risk was equally likely for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
The study supports fracture risk-reduction strategies for men and women with AS and a fracture history, with added attention to opioid users.
SOURCE:
The first author of the study was Rachael Stovall, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published Aug. 22, 2023, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not include individuals younger than 65 years and references only first fractures. Some EHR data on variables including race, body mass index, national area deprivation index, and smoking status are incomplete.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by various grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Opioid use, older age, and fracture history increase the risk for fractures in older adults with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) based on a review of registry and Medicare claims data.
METHODOLOGY:
- Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry data were linked to Medicare claims from 2016 to 2018; each patient had two AS International Classification of Diseases–9 and –10 codes at least 30 days apart.
- The study population included 1426 adults with AS (mean age, 69.4 years) who had continuous Medicare enrollment (Parts A and B) for the entire follow-up period but did not have Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C).
- The researchers used a logistic regression analysis to identify factors associated with fractures including age, sex, and body mass index.
TAKEAWAYS:
- The overall incidence of fractures was 76.7 per 1,000 person-years.
- Older age, history of fracture, and opioid use at a morphine-equivalent dose > 30 mg (at least one prescription 30 or more days prior to the index date) were significantly associated with increased risk for fracture (odds ratios, 2.8, 5.24, and 1.86, respectively).
- Fracture risk was equally likely for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
The study supports fracture risk-reduction strategies for men and women with AS and a fracture history, with added attention to opioid users.
SOURCE:
The first author of the study was Rachael Stovall, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published Aug. 22, 2023, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not include individuals younger than 65 years and references only first fractures. Some EHR data on variables including race, body mass index, national area deprivation index, and smoking status are incomplete.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by various grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Opioid use, older age, and fracture history increase the risk for fractures in older adults with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) based on a review of registry and Medicare claims data.
METHODOLOGY:
- Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry data were linked to Medicare claims from 2016 to 2018; each patient had two AS International Classification of Diseases–9 and –10 codes at least 30 days apart.
- The study population included 1426 adults with AS (mean age, 69.4 years) who had continuous Medicare enrollment (Parts A and B) for the entire follow-up period but did not have Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C).
- The researchers used a logistic regression analysis to identify factors associated with fractures including age, sex, and body mass index.
TAKEAWAYS:
- The overall incidence of fractures was 76.7 per 1,000 person-years.
- Older age, history of fracture, and opioid use at a morphine-equivalent dose > 30 mg (at least one prescription 30 or more days prior to the index date) were significantly associated with increased risk for fracture (odds ratios, 2.8, 5.24, and 1.86, respectively).
- Fracture risk was equally likely for men and women.
IN PRACTICE:
The study supports fracture risk-reduction strategies for men and women with AS and a fracture history, with added attention to opioid users.
SOURCE:
The first author of the study was Rachael Stovall, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco. The study was published Aug. 22, 2023, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not include individuals younger than 65 years and references only first fractures. Some EHR data on variables including race, body mass index, national area deprivation index, and smoking status are incomplete.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by various grants from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rheumatology trials seem vulnerable to unblinding: Report
Until more is known about the potential for unblinding, clinicians need to keep in mind that patients and physicians could often guess accurately who was getting placebo or active drug, first author Cody Bruggemeyer, MD, a resident at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview.
“It’s important that rheumatologists be aware of this potential issue and use their clinical reasoning and their ability to critically assess papers to evaluate the study design” of research on treatments, he said in an interview.
Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors at the Medical College of Wisconsin presented their assessment of the potential for unblinding in a Viewpoint article in The Lancet Rheumatology.
A sample of pivotal clinical trials
The authors selected a sample of pivotal studies of 14 commonly prescribed drugs for rheumatic conditions for which double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the active ingredient with a placebo were available.
The 14 trials involved treatments classified as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), some of which were likely to produce side effects that placebos would not mimic, such as injection site and infusion reactions and difference in readings in lab reports, the authors wrote.
In their analysis, Dr. Bruggemeyer and colleagues evaluated discrepancies in the rates of adverse events reported between active drugs and placebos and classified the 14 studies as follows:
- High unblinding risk: Nine studies had a high estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of adalimumab with citrate (Humira), anakinra (Kineret), anifrolumab (Saphnelo), apremilast (Otezla), ixekizumab (Taltz), leflunomide (Arava), methotrexate, risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz).
- Moderate unblinding risk: Three studies had a moderate estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of azathioprine (Imuran), mycophenolate mofetil and tocilizumab (Actemra).
- Low unblinding risk: Two studies had a low estimated risk of unblinding. These involved tests of belimumab (Benlysta) and rituximab (Rituxan).
Many of the effectiveness measurements of treatments used in rheumatology depend on patients’ reports of relief of pain and other disease symptoms. For example, the widely used American College of Rheumatology 20% response for rheumatoid arthritis includes components that rely on patient and physician assessment of disease activity.
Unblinding risk to clinical trial validity
CTs are the highest level of evidence to establish efficacy, because the study design aims to mask whether the experimental treatment is a drug or placebo. In cases where patients and physicians are more likely to correctly detect use of an active drug, there can be biases that skew results toward reports of symptom improvement. Other patients’ views of their treatment may be distorted by accurate guesses that they have been given placebo, Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors wrote.
“The degree of these effects cannot be predicted, but they tend to erroneously inflate the perceived benefit of novel interventions,” they wrote.
The consequences of this unblinding may be minimal in cases where there’s a clear difference between the placebo and active drug, they said. As an example, they cited trials of interleukin-23 inhibitors for psoriasis, where skin clearance as measured by the Psoriatic Area and Severity Index 75 differed by more than 50% in absolute terms between the treatment and placebo groups.
But in other cases, there needs to be more attention paid to the potential role of unblinding, they wrote.
“Studies where effect sizes were small, contradictory, or dependent on subgroup analyses might be especially problematic, but commentary rarely reflects this issue or acknowledges the potential influence of unblinding,” they wrote.
In the paper, they call for more analysis of previous trials to look for unreported assessments of unblinding, while also asking that researchers consider surveying participants in future trials to evaluate the degree to which unblinding occurs.
“Advocacy from professional societies and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration itself might be necessary, but in the interim, rheumatologists should assume unblinding has occurred to some degree in most trials,” they wrote.
Unblinding measure needs validation
In an interview, Roy M. Fleischmann, MD, co–medical director of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center in Dallas, raised some objections to the paper. The paper addresses an interesting question about unblinding, but there should have been more work done, such as finding “a measure that is validated that can say whether you’ve been unblinded or not.”
He added that he was surprised the paper on unblinding in rheumatology trials was published in its current form.
“I would have sent it for a major rewrite” if asked to review this paper before publication, said Dr. Fleischmann, who as a reviewer for Lancet Rheumatology. “I would have said: ‘Okay, 90% of this paper is okay, but your gist is not correct.’ It should be: ‘Is this a problem?’ ”
Dr. Fleischmann said he would have recommended a different perspective to the paper. “That is, this could occur. Should we be looking at this, and how would we look at this?”
In the paper, the authors acknowledge their approach has not been validated, “but it highlights the potential effect of idiosyncratic adverse events,” they wrote.
There’s less funding in general for meta-research than for studies involving treatments, so researchers look for approaches that can be handled without requiring significant funding, and much of the research on the quality of research is conducted like this analysis of rheumatology trials, Michael Putman, MD, the corresponding author and is a rheumatologist and an assistant professor at the Medical College of Wisconsin, said in an interview.
“You’re mostly doing on a shoestring budget with yourself and trainees,” he said. Dr. Putman is an associate editor at the journal Rheumatology and also involved in meta-research, or efforts to understand how studies and trials answer questions about how medical treatments work.
In an Aug. 16 tweet, Dr. Putman said this issue of unintentional unblinding with rheumatology trials was something he’d “been ruminating about for awhile; took two all star trainees to push it over the top!”
One of the barriers to funding of meta-research is a tendency for major funding for medical studies to be focused on specific diseases or targets. With meta-research, it may be more difficult to explain how a specific project will advance efforts to treat or prevent a certain disease, Dr. Putman said.
“It’s a little more esoteric and maybe not quite as clear how these projects will move things forward,” Dr. Putman said.
In addition, the nature of meta-research is to question and often be critical of work that’s already been published, adding another hurdle in attempts to secure funding, he said.
Dr. Putman is supported by a Rheumatology Research Foundation Scientist Development Grant, receives research funding related to clinical trials by AbbVie and AstraZeneca, and consulting fees from Novartis. The other authors declared no competing interests.
Until more is known about the potential for unblinding, clinicians need to keep in mind that patients and physicians could often guess accurately who was getting placebo or active drug, first author Cody Bruggemeyer, MD, a resident at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview.
“It’s important that rheumatologists be aware of this potential issue and use their clinical reasoning and their ability to critically assess papers to evaluate the study design” of research on treatments, he said in an interview.
Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors at the Medical College of Wisconsin presented their assessment of the potential for unblinding in a Viewpoint article in The Lancet Rheumatology.
A sample of pivotal clinical trials
The authors selected a sample of pivotal studies of 14 commonly prescribed drugs for rheumatic conditions for which double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the active ingredient with a placebo were available.
The 14 trials involved treatments classified as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), some of which were likely to produce side effects that placebos would not mimic, such as injection site and infusion reactions and difference in readings in lab reports, the authors wrote.
In their analysis, Dr. Bruggemeyer and colleagues evaluated discrepancies in the rates of adverse events reported between active drugs and placebos and classified the 14 studies as follows:
- High unblinding risk: Nine studies had a high estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of adalimumab with citrate (Humira), anakinra (Kineret), anifrolumab (Saphnelo), apremilast (Otezla), ixekizumab (Taltz), leflunomide (Arava), methotrexate, risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz).
- Moderate unblinding risk: Three studies had a moderate estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of azathioprine (Imuran), mycophenolate mofetil and tocilizumab (Actemra).
- Low unblinding risk: Two studies had a low estimated risk of unblinding. These involved tests of belimumab (Benlysta) and rituximab (Rituxan).
Many of the effectiveness measurements of treatments used in rheumatology depend on patients’ reports of relief of pain and other disease symptoms. For example, the widely used American College of Rheumatology 20% response for rheumatoid arthritis includes components that rely on patient and physician assessment of disease activity.
Unblinding risk to clinical trial validity
CTs are the highest level of evidence to establish efficacy, because the study design aims to mask whether the experimental treatment is a drug or placebo. In cases where patients and physicians are more likely to correctly detect use of an active drug, there can be biases that skew results toward reports of symptom improvement. Other patients’ views of their treatment may be distorted by accurate guesses that they have been given placebo, Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors wrote.
“The degree of these effects cannot be predicted, but they tend to erroneously inflate the perceived benefit of novel interventions,” they wrote.
The consequences of this unblinding may be minimal in cases where there’s a clear difference between the placebo and active drug, they said. As an example, they cited trials of interleukin-23 inhibitors for psoriasis, where skin clearance as measured by the Psoriatic Area and Severity Index 75 differed by more than 50% in absolute terms between the treatment and placebo groups.
But in other cases, there needs to be more attention paid to the potential role of unblinding, they wrote.
“Studies where effect sizes were small, contradictory, or dependent on subgroup analyses might be especially problematic, but commentary rarely reflects this issue or acknowledges the potential influence of unblinding,” they wrote.
In the paper, they call for more analysis of previous trials to look for unreported assessments of unblinding, while also asking that researchers consider surveying participants in future trials to evaluate the degree to which unblinding occurs.
“Advocacy from professional societies and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration itself might be necessary, but in the interim, rheumatologists should assume unblinding has occurred to some degree in most trials,” they wrote.
Unblinding measure needs validation
In an interview, Roy M. Fleischmann, MD, co–medical director of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center in Dallas, raised some objections to the paper. The paper addresses an interesting question about unblinding, but there should have been more work done, such as finding “a measure that is validated that can say whether you’ve been unblinded or not.”
He added that he was surprised the paper on unblinding in rheumatology trials was published in its current form.
“I would have sent it for a major rewrite” if asked to review this paper before publication, said Dr. Fleischmann, who as a reviewer for Lancet Rheumatology. “I would have said: ‘Okay, 90% of this paper is okay, but your gist is not correct.’ It should be: ‘Is this a problem?’ ”
Dr. Fleischmann said he would have recommended a different perspective to the paper. “That is, this could occur. Should we be looking at this, and how would we look at this?”
In the paper, the authors acknowledge their approach has not been validated, “but it highlights the potential effect of idiosyncratic adverse events,” they wrote.
There’s less funding in general for meta-research than for studies involving treatments, so researchers look for approaches that can be handled without requiring significant funding, and much of the research on the quality of research is conducted like this analysis of rheumatology trials, Michael Putman, MD, the corresponding author and is a rheumatologist and an assistant professor at the Medical College of Wisconsin, said in an interview.
“You’re mostly doing on a shoestring budget with yourself and trainees,” he said. Dr. Putman is an associate editor at the journal Rheumatology and also involved in meta-research, or efforts to understand how studies and trials answer questions about how medical treatments work.
In an Aug. 16 tweet, Dr. Putman said this issue of unintentional unblinding with rheumatology trials was something he’d “been ruminating about for awhile; took two all star trainees to push it over the top!”
One of the barriers to funding of meta-research is a tendency for major funding for medical studies to be focused on specific diseases or targets. With meta-research, it may be more difficult to explain how a specific project will advance efforts to treat or prevent a certain disease, Dr. Putman said.
“It’s a little more esoteric and maybe not quite as clear how these projects will move things forward,” Dr. Putman said.
In addition, the nature of meta-research is to question and often be critical of work that’s already been published, adding another hurdle in attempts to secure funding, he said.
Dr. Putman is supported by a Rheumatology Research Foundation Scientist Development Grant, receives research funding related to clinical trials by AbbVie and AstraZeneca, and consulting fees from Novartis. The other authors declared no competing interests.
Until more is known about the potential for unblinding, clinicians need to keep in mind that patients and physicians could often guess accurately who was getting placebo or active drug, first author Cody Bruggemeyer, MD, a resident at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview.
“It’s important that rheumatologists be aware of this potential issue and use their clinical reasoning and their ability to critically assess papers to evaluate the study design” of research on treatments, he said in an interview.
Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors at the Medical College of Wisconsin presented their assessment of the potential for unblinding in a Viewpoint article in The Lancet Rheumatology.
A sample of pivotal clinical trials
The authors selected a sample of pivotal studies of 14 commonly prescribed drugs for rheumatic conditions for which double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the active ingredient with a placebo were available.
The 14 trials involved treatments classified as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), some of which were likely to produce side effects that placebos would not mimic, such as injection site and infusion reactions and difference in readings in lab reports, the authors wrote.
In their analysis, Dr. Bruggemeyer and colleagues evaluated discrepancies in the rates of adverse events reported between active drugs and placebos and classified the 14 studies as follows:
- High unblinding risk: Nine studies had a high estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of adalimumab with citrate (Humira), anakinra (Kineret), anifrolumab (Saphnelo), apremilast (Otezla), ixekizumab (Taltz), leflunomide (Arava), methotrexate, risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz).
- Moderate unblinding risk: Three studies had a moderate estimated risk of unblinding, including trials of azathioprine (Imuran), mycophenolate mofetil and tocilizumab (Actemra).
- Low unblinding risk: Two studies had a low estimated risk of unblinding. These involved tests of belimumab (Benlysta) and rituximab (Rituxan).
Many of the effectiveness measurements of treatments used in rheumatology depend on patients’ reports of relief of pain and other disease symptoms. For example, the widely used American College of Rheumatology 20% response for rheumatoid arthritis includes components that rely on patient and physician assessment of disease activity.
Unblinding risk to clinical trial validity
CTs are the highest level of evidence to establish efficacy, because the study design aims to mask whether the experimental treatment is a drug or placebo. In cases where patients and physicians are more likely to correctly detect use of an active drug, there can be biases that skew results toward reports of symptom improvement. Other patients’ views of their treatment may be distorted by accurate guesses that they have been given placebo, Dr. Bruggemeyer and coauthors wrote.
“The degree of these effects cannot be predicted, but they tend to erroneously inflate the perceived benefit of novel interventions,” they wrote.
The consequences of this unblinding may be minimal in cases where there’s a clear difference between the placebo and active drug, they said. As an example, they cited trials of interleukin-23 inhibitors for psoriasis, where skin clearance as measured by the Psoriatic Area and Severity Index 75 differed by more than 50% in absolute terms between the treatment and placebo groups.
But in other cases, there needs to be more attention paid to the potential role of unblinding, they wrote.
“Studies where effect sizes were small, contradictory, or dependent on subgroup analyses might be especially problematic, but commentary rarely reflects this issue or acknowledges the potential influence of unblinding,” they wrote.
In the paper, they call for more analysis of previous trials to look for unreported assessments of unblinding, while also asking that researchers consider surveying participants in future trials to evaluate the degree to which unblinding occurs.
“Advocacy from professional societies and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration itself might be necessary, but in the interim, rheumatologists should assume unblinding has occurred to some degree in most trials,” they wrote.
Unblinding measure needs validation
In an interview, Roy M. Fleischmann, MD, co–medical director of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center in Dallas, raised some objections to the paper. The paper addresses an interesting question about unblinding, but there should have been more work done, such as finding “a measure that is validated that can say whether you’ve been unblinded or not.”
He added that he was surprised the paper on unblinding in rheumatology trials was published in its current form.
“I would have sent it for a major rewrite” if asked to review this paper before publication, said Dr. Fleischmann, who as a reviewer for Lancet Rheumatology. “I would have said: ‘Okay, 90% of this paper is okay, but your gist is not correct.’ It should be: ‘Is this a problem?’ ”
Dr. Fleischmann said he would have recommended a different perspective to the paper. “That is, this could occur. Should we be looking at this, and how would we look at this?”
In the paper, the authors acknowledge their approach has not been validated, “but it highlights the potential effect of idiosyncratic adverse events,” they wrote.
There’s less funding in general for meta-research than for studies involving treatments, so researchers look for approaches that can be handled without requiring significant funding, and much of the research on the quality of research is conducted like this analysis of rheumatology trials, Michael Putman, MD, the corresponding author and is a rheumatologist and an assistant professor at the Medical College of Wisconsin, said in an interview.
“You’re mostly doing on a shoestring budget with yourself and trainees,” he said. Dr. Putman is an associate editor at the journal Rheumatology and also involved in meta-research, or efforts to understand how studies and trials answer questions about how medical treatments work.
In an Aug. 16 tweet, Dr. Putman said this issue of unintentional unblinding with rheumatology trials was something he’d “been ruminating about for awhile; took two all star trainees to push it over the top!”
One of the barriers to funding of meta-research is a tendency for major funding for medical studies to be focused on specific diseases or targets. With meta-research, it may be more difficult to explain how a specific project will advance efforts to treat or prevent a certain disease, Dr. Putman said.
“It’s a little more esoteric and maybe not quite as clear how these projects will move things forward,” Dr. Putman said.
In addition, the nature of meta-research is to question and often be critical of work that’s already been published, adding another hurdle in attempts to secure funding, he said.
Dr. Putman is supported by a Rheumatology Research Foundation Scientist Development Grant, receives research funding related to clinical trials by AbbVie and AstraZeneca, and consulting fees from Novartis. The other authors declared no competing interests.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
Structural changes may separate axial psoriatic arthritis from axial spondyloarthritis
Approximately 20% of adults with axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) show active or structural spinal changes without changes in the sacroiliac joint, based on imaging data from 106 individuals.
Axial PsA has been historically grouped with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but it has received more attention in recent years as a condition potentially distinct from axSpA, Henriette Käding, an MD and PhD student in the department of gastroenterology, infectiology, and rheumatology at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in her research presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). She added that the debate persists as to whether these conditions are on the same spectrum or should be separated.
Data from previous studies suggest differences in genetic, clinical, radiographic, and prognostic characteristics between axial PsA and axSpA that may affect patients’ response to available treatments. However, there are relatively little data available on distinguishing imaging and clinical features, and there’s a lack of classification criteria for axial PsA, Ms. Käding said.
Ms. Käding and colleagues prospectively collected data from 106 patients with axial PsA between August 2019 and June 2023 and presented the baseline data of this longitudinal project at the GRAPPA annual meeting in Dublin. At baseline, the researchers conducted clinical assessments of the participants, along with blood sampling, stool samples, and imaging protocols that included MRI of the whole spine and sacroiliac joint (SIJ).
The mean age of the included patients was 44.5 years; 55.7% were female. Inflammatory back pain was present in most of the patients at baseline (78.4%), and 48.1% were positive for HLA-B27, a genetic risk factor for both axSpA and axial PsA. Approximately one-third of the patients had elevated C-reactive protein (> 5 mg/L). In the baseline MRI scans, active inflammatory changes in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) were seen in 51.9% of the patients and structural changes in 72.1%. MRI spine scans showed active changes in 58.7% of the patients. Notably, active and/or structural changes of the spine without changes in the SIJ appeared in 20% of the patients, Ms. Käding said.
With regard to existing classification criteria, the researchers observed that 92% of the patients met the CASPAR (Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria for PsA, 73% met the ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria, while 66% of patients met both ASAS and CASPAR criteria.
The study will be the first to include longitudinal MRI scans of the whole spine and SIJ in addition to conventional radiographs, Ms. Käding said.
Better characterization should improve treatment
“Axial involvement in PsA might, on one hand, go unnoticed, but on the other hand, it could also be misdiagnosed in patients with degenerative spinal disease,” Denis Poddubnyy, MD, one of the study coauthors, also of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in an interview.
“By comprehending the unique characteristics, progression, and treatment responses within the axial domain, rheumatologists can customize interventions and therapies to effectively manage the psoriatic disease,” Dr. Poddubnyy said.
“One of the most significant findings [of the current study] is the relatively high frequency of spinal involvement without sacroiliac joint” involvement, Fabian Proft, MD, of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin and senior author of the study, said in an interview. “This finding holds importance as, in primary axial SpA, the disease typically originates in the sacroiliac joints. In contrast, in PsA, the scenario differs, which has implications for the diagnostic approach in clinical practice.”
“In individuals with PsA, spinal involvement can occur independently of sacroiliac joint [involvement]. As a result, imaging studies conducted on patients suspected of having axial PsA should encompass not only the sacroiliac joints but also the spine,” Dr. Poddubnyy explained. “It is important to note, however, that imaging findings such as bony spurs and bone marrow edema might be caused by degeneration or mechanical issues and, therefore, need to be interpreted with caution within the clinical context.”
The study was supported in part by an unrestricted research grant from Novartis. Dr. Poddubnyy and Dr. Proft disclosed receiving research grants and consultancy payments from Novartis and serving on speaker bureaus for the company.
Approximately 20% of adults with axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) show active or structural spinal changes without changes in the sacroiliac joint, based on imaging data from 106 individuals.
Axial PsA has been historically grouped with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but it has received more attention in recent years as a condition potentially distinct from axSpA, Henriette Käding, an MD and PhD student in the department of gastroenterology, infectiology, and rheumatology at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in her research presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). She added that the debate persists as to whether these conditions are on the same spectrum or should be separated.
Data from previous studies suggest differences in genetic, clinical, radiographic, and prognostic characteristics between axial PsA and axSpA that may affect patients’ response to available treatments. However, there are relatively little data available on distinguishing imaging and clinical features, and there’s a lack of classification criteria for axial PsA, Ms. Käding said.
Ms. Käding and colleagues prospectively collected data from 106 patients with axial PsA between August 2019 and June 2023 and presented the baseline data of this longitudinal project at the GRAPPA annual meeting in Dublin. At baseline, the researchers conducted clinical assessments of the participants, along with blood sampling, stool samples, and imaging protocols that included MRI of the whole spine and sacroiliac joint (SIJ).
The mean age of the included patients was 44.5 years; 55.7% were female. Inflammatory back pain was present in most of the patients at baseline (78.4%), and 48.1% were positive for HLA-B27, a genetic risk factor for both axSpA and axial PsA. Approximately one-third of the patients had elevated C-reactive protein (> 5 mg/L). In the baseline MRI scans, active inflammatory changes in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) were seen in 51.9% of the patients and structural changes in 72.1%. MRI spine scans showed active changes in 58.7% of the patients. Notably, active and/or structural changes of the spine without changes in the SIJ appeared in 20% of the patients, Ms. Käding said.
With regard to existing classification criteria, the researchers observed that 92% of the patients met the CASPAR (Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria for PsA, 73% met the ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria, while 66% of patients met both ASAS and CASPAR criteria.
The study will be the first to include longitudinal MRI scans of the whole spine and SIJ in addition to conventional radiographs, Ms. Käding said.
Better characterization should improve treatment
“Axial involvement in PsA might, on one hand, go unnoticed, but on the other hand, it could also be misdiagnosed in patients with degenerative spinal disease,” Denis Poddubnyy, MD, one of the study coauthors, also of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in an interview.
“By comprehending the unique characteristics, progression, and treatment responses within the axial domain, rheumatologists can customize interventions and therapies to effectively manage the psoriatic disease,” Dr. Poddubnyy said.
“One of the most significant findings [of the current study] is the relatively high frequency of spinal involvement without sacroiliac joint” involvement, Fabian Proft, MD, of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin and senior author of the study, said in an interview. “This finding holds importance as, in primary axial SpA, the disease typically originates in the sacroiliac joints. In contrast, in PsA, the scenario differs, which has implications for the diagnostic approach in clinical practice.”
“In individuals with PsA, spinal involvement can occur independently of sacroiliac joint [involvement]. As a result, imaging studies conducted on patients suspected of having axial PsA should encompass not only the sacroiliac joints but also the spine,” Dr. Poddubnyy explained. “It is important to note, however, that imaging findings such as bony spurs and bone marrow edema might be caused by degeneration or mechanical issues and, therefore, need to be interpreted with caution within the clinical context.”
The study was supported in part by an unrestricted research grant from Novartis. Dr. Poddubnyy and Dr. Proft disclosed receiving research grants and consultancy payments from Novartis and serving on speaker bureaus for the company.
Approximately 20% of adults with axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) show active or structural spinal changes without changes in the sacroiliac joint, based on imaging data from 106 individuals.
Axial PsA has been historically grouped with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but it has received more attention in recent years as a condition potentially distinct from axSpA, Henriette Käding, an MD and PhD student in the department of gastroenterology, infectiology, and rheumatology at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in her research presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). She added that the debate persists as to whether these conditions are on the same spectrum or should be separated.
Data from previous studies suggest differences in genetic, clinical, radiographic, and prognostic characteristics between axial PsA and axSpA that may affect patients’ response to available treatments. However, there are relatively little data available on distinguishing imaging and clinical features, and there’s a lack of classification criteria for axial PsA, Ms. Käding said.
Ms. Käding and colleagues prospectively collected data from 106 patients with axial PsA between August 2019 and June 2023 and presented the baseline data of this longitudinal project at the GRAPPA annual meeting in Dublin. At baseline, the researchers conducted clinical assessments of the participants, along with blood sampling, stool samples, and imaging protocols that included MRI of the whole spine and sacroiliac joint (SIJ).
The mean age of the included patients was 44.5 years; 55.7% were female. Inflammatory back pain was present in most of the patients at baseline (78.4%), and 48.1% were positive for HLA-B27, a genetic risk factor for both axSpA and axial PsA. Approximately one-third of the patients had elevated C-reactive protein (> 5 mg/L). In the baseline MRI scans, active inflammatory changes in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) were seen in 51.9% of the patients and structural changes in 72.1%. MRI spine scans showed active changes in 58.7% of the patients. Notably, active and/or structural changes of the spine without changes in the SIJ appeared in 20% of the patients, Ms. Käding said.
With regard to existing classification criteria, the researchers observed that 92% of the patients met the CASPAR (Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria for PsA, 73% met the ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria, while 66% of patients met both ASAS and CASPAR criteria.
The study will be the first to include longitudinal MRI scans of the whole spine and SIJ in addition to conventional radiographs, Ms. Käding said.
Better characterization should improve treatment
“Axial involvement in PsA might, on one hand, go unnoticed, but on the other hand, it could also be misdiagnosed in patients with degenerative spinal disease,” Denis Poddubnyy, MD, one of the study coauthors, also of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, said in an interview.
“By comprehending the unique characteristics, progression, and treatment responses within the axial domain, rheumatologists can customize interventions and therapies to effectively manage the psoriatic disease,” Dr. Poddubnyy said.
“One of the most significant findings [of the current study] is the relatively high frequency of spinal involvement without sacroiliac joint” involvement, Fabian Proft, MD, of Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin and senior author of the study, said in an interview. “This finding holds importance as, in primary axial SpA, the disease typically originates in the sacroiliac joints. In contrast, in PsA, the scenario differs, which has implications for the diagnostic approach in clinical practice.”
“In individuals with PsA, spinal involvement can occur independently of sacroiliac joint [involvement]. As a result, imaging studies conducted on patients suspected of having axial PsA should encompass not only the sacroiliac joints but also the spine,” Dr. Poddubnyy explained. “It is important to note, however, that imaging findings such as bony spurs and bone marrow edema might be caused by degeneration or mechanical issues and, therefore, need to be interpreted with caution within the clinical context.”
The study was supported in part by an unrestricted research grant from Novartis. Dr. Poddubnyy and Dr. Proft disclosed receiving research grants and consultancy payments from Novartis and serving on speaker bureaus for the company.
FROM GRAPPA 2023
Spondyloarthritis-related diseases share gut microbiota dysbiosis
TOPLINE:
Patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) experience similar gut microbiota dysbiosis with related inflammatory conditions, such as acute anterior uveitis (AAU) and Crohn’s disease (CD), new data show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed 16S rRNA sequencing on stool samples from 277 adult patients from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (102 with SpA, 72 with CD, and 103 with AAU) and 62 control patients with chronic back pain for whom SpA had been ruled out.
- Patients were treatment naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or had not received them for more than 3 months prior to study enrollment.
- The study is the first to identify the same microbiota in patients with SpA, AAU, and CD.
TAKEAWAY:
- “Our results showed a shared depletion of predominately Lachnospiraceae taxa, most notably Fusicatenibacter, which partially mediated increased CRP [C-reactive protein], and was most abundant in controls receiving NSAID monotherapy,” the researchers wrote.
- Among patients who tested positive for HLA-B27, an allele associated with SpA and other spondyloarthropathies, levels of Faecalibacterium were increased; among patients with SpA, levels of Collinsella were enriched; and among patients with CD, there was an abundance of beneficial Ruminococcus bacteria.
- The results suggest the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of the gut microbiome for mediating disease activity for patients with autoimmune diseases.
- Additional research is needed to clarify the roles of different bacteria in gut-joint inflammation and to understand the relationship between genetics and gut microbes.
IN PRACTICE:
The study is too preliminary to have applications for practice.
SOURCE:
Co–first authors Morgan Essex, MSc, and Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, of Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin and colleagues conducted the study, which was published online July 20, 2023, in Arthritis and Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
- The results were limited by several factors, including the restriction to amplicon sequencing, which prevented in-depth characterization of the gut microbiome.
- More studies are needed to validate the findings, especially regarding gut bacteria as potential mediators of inflammation or disease activity. The researchers recommended studies with whole-genome sequencing and fecal metabolite quantification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Additional funding came from the German Federal Ministry for Health and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Two patient cohorts were partially and separately supported by grants from Novartis and AbbVie.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) experience similar gut microbiota dysbiosis with related inflammatory conditions, such as acute anterior uveitis (AAU) and Crohn’s disease (CD), new data show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed 16S rRNA sequencing on stool samples from 277 adult patients from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (102 with SpA, 72 with CD, and 103 with AAU) and 62 control patients with chronic back pain for whom SpA had been ruled out.
- Patients were treatment naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or had not received them for more than 3 months prior to study enrollment.
- The study is the first to identify the same microbiota in patients with SpA, AAU, and CD.
TAKEAWAY:
- “Our results showed a shared depletion of predominately Lachnospiraceae taxa, most notably Fusicatenibacter, which partially mediated increased CRP [C-reactive protein], and was most abundant in controls receiving NSAID monotherapy,” the researchers wrote.
- Among patients who tested positive for HLA-B27, an allele associated with SpA and other spondyloarthropathies, levels of Faecalibacterium were increased; among patients with SpA, levels of Collinsella were enriched; and among patients with CD, there was an abundance of beneficial Ruminococcus bacteria.
- The results suggest the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of the gut microbiome for mediating disease activity for patients with autoimmune diseases.
- Additional research is needed to clarify the roles of different bacteria in gut-joint inflammation and to understand the relationship between genetics and gut microbes.
IN PRACTICE:
The study is too preliminary to have applications for practice.
SOURCE:
Co–first authors Morgan Essex, MSc, and Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, of Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin and colleagues conducted the study, which was published online July 20, 2023, in Arthritis and Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
- The results were limited by several factors, including the restriction to amplicon sequencing, which prevented in-depth characterization of the gut microbiome.
- More studies are needed to validate the findings, especially regarding gut bacteria as potential mediators of inflammation or disease activity. The researchers recommended studies with whole-genome sequencing and fecal metabolite quantification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Additional funding came from the German Federal Ministry for Health and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Two patient cohorts were partially and separately supported by grants from Novartis and AbbVie.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) experience similar gut microbiota dysbiosis with related inflammatory conditions, such as acute anterior uveitis (AAU) and Crohn’s disease (CD), new data show.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed 16S rRNA sequencing on stool samples from 277 adult patients from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (102 with SpA, 72 with CD, and 103 with AAU) and 62 control patients with chronic back pain for whom SpA had been ruled out.
- Patients were treatment naive to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or had not received them for more than 3 months prior to study enrollment.
- The study is the first to identify the same microbiota in patients with SpA, AAU, and CD.
TAKEAWAY:
- “Our results showed a shared depletion of predominately Lachnospiraceae taxa, most notably Fusicatenibacter, which partially mediated increased CRP [C-reactive protein], and was most abundant in controls receiving NSAID monotherapy,” the researchers wrote.
- Among patients who tested positive for HLA-B27, an allele associated with SpA and other spondyloarthropathies, levels of Faecalibacterium were increased; among patients with SpA, levels of Collinsella were enriched; and among patients with CD, there was an abundance of beneficial Ruminococcus bacteria.
- The results suggest the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of the gut microbiome for mediating disease activity for patients with autoimmune diseases.
- Additional research is needed to clarify the roles of different bacteria in gut-joint inflammation and to understand the relationship between genetics and gut microbes.
IN PRACTICE:
The study is too preliminary to have applications for practice.
SOURCE:
Co–first authors Morgan Essex, MSc, and Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, of Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin and colleagues conducted the study, which was published online July 20, 2023, in Arthritis and Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
- The results were limited by several factors, including the restriction to amplicon sequencing, which prevented in-depth characterization of the gut microbiome.
- More studies are needed to validate the findings, especially regarding gut bacteria as potential mediators of inflammation or disease activity. The researchers recommended studies with whole-genome sequencing and fecal metabolite quantification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Additional funding came from the German Federal Ministry for Health and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Two patient cohorts were partially and separately supported by grants from Novartis and AbbVie.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Could risk stratifying methotrexate users lead to less frequent testing?
A new model can predict which patients are more likely to experience side effects from long-term methotrexate (MTX) use, research suggests. Patients with a lower risk profile may benefit from less frequent testing, the authors hypothesize.
Most recommendations advise that patients initiating MTX therapy should get blood testing every 2-4 weeks to monitor for full blood count, liver function, urea electrolytes, and creatinine. After 6 months taking MTX, monitoring can be tapered to every 3 months. But Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust and colleagues argue that abnormal results after the initial 6 months of treatment are “infrequent,” and patients may benefit from fewer tests throughout the year.
“Unnecessary blood tests waste patients’ time and health care resources, including the time of general practitioners and phlebotomists,” Dr. Abhishek and associates write. “It would be beneficial to predict the risk of clinically significant abnormal blood test results during long-term methotrexate treatment to inform the frequency of testing for individuals.”
Stratifying risk
In the study, published in the BMJ, researchers used the UK’s Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) to identify the electronic medical records of over 37,000 adult patients with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease who were prescribed MTX during 2007-2019. All included patients were prescribed MTX for at least 6 months. The main outcome was discontinuation of methotrexate because of abnormal blood test results. Around 62% of patients had rheumatoid arthritis and 22% had psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis.
Using these anonymized data, the group developed a risk stratification model using 11 clinical predictors. “The factors that went in the model are simple things that most patients can self-report or doctors can get from their patient’s medical records,” Dr. Abhishek told this news organization, including methotrexate dose, age, sex, and comorbidities. Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the model should be used only in patients who have continued taking MTX for at least 6 months and have already undergone more frequent initial testing.
The strongest individual predictors were diabetes (hazard ratio, 1.25), chronic kidney disease stage 3 (HR, 2.01), and previous cytopenia or raised liver enzyme levels during the first 6 months of MTX therapy (HR, 2.97). However, Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the individual factors were less important, noting that the model sums the risks to predict outcomes more accurately. Most patients (68.4%) were sorted into the low-risk cohort, with a less than 10% estimated risk of discontinuing MTX over the next 5 years. About one-fifth (20.9%) were categorized as moderate risk (10%-20% estimated risk over 5 years), and 10.7% were high risk, with a greater than 20% estimated risk of discontinuing the drug over 5 years.
The authors argue that low-risk patients could receive less frequent testing – perhaps every 6 months or annually, while moderate-risk patients would continue to be tested every 3 months. High-risk patients could potentially be tested with even greater frequently.
More research needed
The research involved “incredibly sophisticated statistical analysis,” said Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study. However, the data do not yet support altering blood testing frequency based on this model.
“The hypothesis that not all patients have to be examined so frequently is a very reasonable hypothesis,” Dr. Furst said in an interview, and additional research is needed to corroborate it. The model also needs to be validated in patient populations outside of the United Kingdom, he added.
Dr. Abhishek agreed that validating the model in other patient populations is an important next step. “When we develop a tool [using] a one-nation data set, we want other researchers to then validate it in other countries’ data sets to make sure there is nothing odd about patients in the U.K. that makes the tool work well here but not in [the] U.S., Europe, or Asia, for example,” he said. Doing so should be relatively easy, he said, as the model is publicly available, and the information required is routinely collected during clinic visits.
To understand if less frequent testing might be appropriate for some patients, researchers would need to look at data registries like the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS) registry or CorEvitas registries “where the testing is done in a very regular way over the long haul,” Dr. Furst said. Analyzing these datasets, researchers could determine the testing intervals that would be most efficient for low- and high-risk patients.
A word of caution
While less frequent testing for long-term MTX therapy could likely have benefits, there is still some risk involved, cautioned Prabha Ranganathan, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Although most methotrexate toxicity occurs within the first 6 months of starting treatment, rare idiosyncratic toxicity can occur that does not correlate with the dose, duration, or method of how methotrexate is administered,” she wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Most rheumatologists can identify a handful of patients who receive methotrexate in their practice who develop sudden leukopenia or thrombocytopenia or transaminitis that is severe enough to warrant drug discontinuation.” While tools like this prediction model can be useful, clinicians need to consider each patient individually and use shared decision-making when monitoring for MTX toxicity, she advised.
“As in most of areas of medicine, the one-size-fits-all approach does not work for methotrexate users,” she noted.
This study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research and Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadila Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Furst and Dr. Ranganathan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new model can predict which patients are more likely to experience side effects from long-term methotrexate (MTX) use, research suggests. Patients with a lower risk profile may benefit from less frequent testing, the authors hypothesize.
Most recommendations advise that patients initiating MTX therapy should get blood testing every 2-4 weeks to monitor for full blood count, liver function, urea electrolytes, and creatinine. After 6 months taking MTX, monitoring can be tapered to every 3 months. But Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust and colleagues argue that abnormal results after the initial 6 months of treatment are “infrequent,” and patients may benefit from fewer tests throughout the year.
“Unnecessary blood tests waste patients’ time and health care resources, including the time of general practitioners and phlebotomists,” Dr. Abhishek and associates write. “It would be beneficial to predict the risk of clinically significant abnormal blood test results during long-term methotrexate treatment to inform the frequency of testing for individuals.”
Stratifying risk
In the study, published in the BMJ, researchers used the UK’s Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) to identify the electronic medical records of over 37,000 adult patients with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease who were prescribed MTX during 2007-2019. All included patients were prescribed MTX for at least 6 months. The main outcome was discontinuation of methotrexate because of abnormal blood test results. Around 62% of patients had rheumatoid arthritis and 22% had psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis.
Using these anonymized data, the group developed a risk stratification model using 11 clinical predictors. “The factors that went in the model are simple things that most patients can self-report or doctors can get from their patient’s medical records,” Dr. Abhishek told this news organization, including methotrexate dose, age, sex, and comorbidities. Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the model should be used only in patients who have continued taking MTX for at least 6 months and have already undergone more frequent initial testing.
The strongest individual predictors were diabetes (hazard ratio, 1.25), chronic kidney disease stage 3 (HR, 2.01), and previous cytopenia or raised liver enzyme levels during the first 6 months of MTX therapy (HR, 2.97). However, Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the individual factors were less important, noting that the model sums the risks to predict outcomes more accurately. Most patients (68.4%) were sorted into the low-risk cohort, with a less than 10% estimated risk of discontinuing MTX over the next 5 years. About one-fifth (20.9%) were categorized as moderate risk (10%-20% estimated risk over 5 years), and 10.7% were high risk, with a greater than 20% estimated risk of discontinuing the drug over 5 years.
The authors argue that low-risk patients could receive less frequent testing – perhaps every 6 months or annually, while moderate-risk patients would continue to be tested every 3 months. High-risk patients could potentially be tested with even greater frequently.
More research needed
The research involved “incredibly sophisticated statistical analysis,” said Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study. However, the data do not yet support altering blood testing frequency based on this model.
“The hypothesis that not all patients have to be examined so frequently is a very reasonable hypothesis,” Dr. Furst said in an interview, and additional research is needed to corroborate it. The model also needs to be validated in patient populations outside of the United Kingdom, he added.
Dr. Abhishek agreed that validating the model in other patient populations is an important next step. “When we develop a tool [using] a one-nation data set, we want other researchers to then validate it in other countries’ data sets to make sure there is nothing odd about patients in the U.K. that makes the tool work well here but not in [the] U.S., Europe, or Asia, for example,” he said. Doing so should be relatively easy, he said, as the model is publicly available, and the information required is routinely collected during clinic visits.
To understand if less frequent testing might be appropriate for some patients, researchers would need to look at data registries like the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS) registry or CorEvitas registries “where the testing is done in a very regular way over the long haul,” Dr. Furst said. Analyzing these datasets, researchers could determine the testing intervals that would be most efficient for low- and high-risk patients.
A word of caution
While less frequent testing for long-term MTX therapy could likely have benefits, there is still some risk involved, cautioned Prabha Ranganathan, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Although most methotrexate toxicity occurs within the first 6 months of starting treatment, rare idiosyncratic toxicity can occur that does not correlate with the dose, duration, or method of how methotrexate is administered,” she wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Most rheumatologists can identify a handful of patients who receive methotrexate in their practice who develop sudden leukopenia or thrombocytopenia or transaminitis that is severe enough to warrant drug discontinuation.” While tools like this prediction model can be useful, clinicians need to consider each patient individually and use shared decision-making when monitoring for MTX toxicity, she advised.
“As in most of areas of medicine, the one-size-fits-all approach does not work for methotrexate users,” she noted.
This study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research and Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadila Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Furst and Dr. Ranganathan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new model can predict which patients are more likely to experience side effects from long-term methotrexate (MTX) use, research suggests. Patients with a lower risk profile may benefit from less frequent testing, the authors hypothesize.
Most recommendations advise that patients initiating MTX therapy should get blood testing every 2-4 weeks to monitor for full blood count, liver function, urea electrolytes, and creatinine. After 6 months taking MTX, monitoring can be tapered to every 3 months. But Abhishek Abhishek, MD, PhD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust and colleagues argue that abnormal results after the initial 6 months of treatment are “infrequent,” and patients may benefit from fewer tests throughout the year.
“Unnecessary blood tests waste patients’ time and health care resources, including the time of general practitioners and phlebotomists,” Dr. Abhishek and associates write. “It would be beneficial to predict the risk of clinically significant abnormal blood test results during long-term methotrexate treatment to inform the frequency of testing for individuals.”
Stratifying risk
In the study, published in the BMJ, researchers used the UK’s Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) to identify the electronic medical records of over 37,000 adult patients with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease who were prescribed MTX during 2007-2019. All included patients were prescribed MTX for at least 6 months. The main outcome was discontinuation of methotrexate because of abnormal blood test results. Around 62% of patients had rheumatoid arthritis and 22% had psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis.
Using these anonymized data, the group developed a risk stratification model using 11 clinical predictors. “The factors that went in the model are simple things that most patients can self-report or doctors can get from their patient’s medical records,” Dr. Abhishek told this news organization, including methotrexate dose, age, sex, and comorbidities. Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the model should be used only in patients who have continued taking MTX for at least 6 months and have already undergone more frequent initial testing.
The strongest individual predictors were diabetes (hazard ratio, 1.25), chronic kidney disease stage 3 (HR, 2.01), and previous cytopenia or raised liver enzyme levels during the first 6 months of MTX therapy (HR, 2.97). However, Dr. Abhishek emphasized that the individual factors were less important, noting that the model sums the risks to predict outcomes more accurately. Most patients (68.4%) were sorted into the low-risk cohort, with a less than 10% estimated risk of discontinuing MTX over the next 5 years. About one-fifth (20.9%) were categorized as moderate risk (10%-20% estimated risk over 5 years), and 10.7% were high risk, with a greater than 20% estimated risk of discontinuing the drug over 5 years.
The authors argue that low-risk patients could receive less frequent testing – perhaps every 6 months or annually, while moderate-risk patients would continue to be tested every 3 months. High-risk patients could potentially be tested with even greater frequently.
More research needed
The research involved “incredibly sophisticated statistical analysis,” said Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor emeritus of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study. However, the data do not yet support altering blood testing frequency based on this model.
“The hypothesis that not all patients have to be examined so frequently is a very reasonable hypothesis,” Dr. Furst said in an interview, and additional research is needed to corroborate it. The model also needs to be validated in patient populations outside of the United Kingdom, he added.
Dr. Abhishek agreed that validating the model in other patient populations is an important next step. “When we develop a tool [using] a one-nation data set, we want other researchers to then validate it in other countries’ data sets to make sure there is nothing odd about patients in the U.K. that makes the tool work well here but not in [the] U.S., Europe, or Asia, for example,” he said. Doing so should be relatively easy, he said, as the model is publicly available, and the information required is routinely collected during clinic visits.
To understand if less frequent testing might be appropriate for some patients, researchers would need to look at data registries like the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS) registry or CorEvitas registries “where the testing is done in a very regular way over the long haul,” Dr. Furst said. Analyzing these datasets, researchers could determine the testing intervals that would be most efficient for low- and high-risk patients.
A word of caution
While less frequent testing for long-term MTX therapy could likely have benefits, there is still some risk involved, cautioned Prabha Ranganathan, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Although most methotrexate toxicity occurs within the first 6 months of starting treatment, rare idiosyncratic toxicity can occur that does not correlate with the dose, duration, or method of how methotrexate is administered,” she wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Most rheumatologists can identify a handful of patients who receive methotrexate in their practice who develop sudden leukopenia or thrombocytopenia or transaminitis that is severe enough to warrant drug discontinuation.” While tools like this prediction model can be useful, clinicians need to consider each patient individually and use shared decision-making when monitoring for MTX toxicity, she advised.
“As in most of areas of medicine, the one-size-fits-all approach does not work for methotrexate users,” she noted.
This study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Research and Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadila Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Furst and Dr. Ranganathan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ
Humira biosimilars: Five things to know
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.
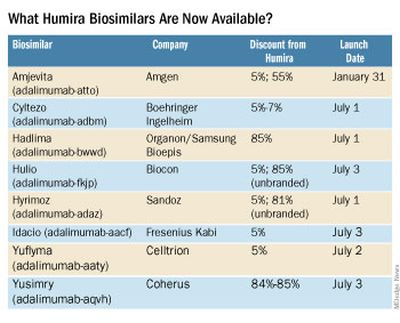
Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.

Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The best-selling drug Humira (adalimumab) now faces competition in the United States after a 20-year monopoly. The first adalimumab biosimilar, Amjevita, launched in the United States on January 31, and in July, seven additional biosimilars became available. These drugs have the potential to lower prescription drug prices, but when and by how much remains to be seen.
Here’s what you need to know about adalimumab biosimilars.
What Humira biosimilars are now available?
Eight different biosimilars have launched in 2023 with discounts as large at 85% from Humira’s list price of $6,922. A few companies also offer two price points.

Three of these biosimilars – Hadlima, Hyrimoz, and Yuflyma – are available in high concentration formulations. This high concentration formulation makes up 85% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report from Goodroot, a collection of companies focused on lowering health care costs.
Cyltezo is currently the only adalimumab biosimilar with an interchangeability designation, meaning that a pharmacist can substitute the biosimilar for an equivalent Humira prescription without the intervention of a clinician. A total of 47 states allow for these substitutions without prior approval from a clinician, according to Goodroot, and the clinician must be notified of the switch within a certain time frame. A total of 40 states require that patients be notified of the switch before substitution.
However, it’s not clear if this interchangeability designation will prove an advantage for Cyltezo, as it is interchangeable with the lower concentration version of Humira that makes up just 15% of prescriptions.
Most of the companies behind these biosimilars are pursuing interchangeability designations for their drugs, except for Fresenius Kabi (Idacio) and Coherus (Yusimry).
A ninth biosimilar, Pfizer’s adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), is not yet on the market and is currently awaiting an approval decision from the Food and Drug Administration to add an interchangeability designation to its prior approval for a low-concentration formulation.
Why are they priced differently?
The two price points offer different deals to payers. Pharmacy benefit managers make confidential agreements with drug manufacturers to get a discount – called a rebate – to get the drug on the PBM’s formulary. The PBM keeps a portion of that rebate, and the rest is passed on to the insurance company and patients. Biosimilars at a higher price point will likely offer larger rebates. Biosimilars offered at lower price points incorporate this discount up front in their list pricing and likely will not offer large rebates.
Will biosimilars be covered by payers?
Currently, biosimilars are being offered on formularies at parity with Humira, meaning they are on the same tier. The PBM companies OptumRx and Cigna Group’s Express Scripts will offer Amjevita (at both price points), Cyltezo, and Hyrimoz (at both price points).
“This decision allows our clients flexibility to provide access to the lower list price, so members in high-deductible plans and benefit designs with coinsurance can experience lower out-of-pocket costs,” said OptumRx spokesperson Isaac Sorensen in an email.
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company, which uses a direct-to-consumer model, will offer Yusimry for $567.27 on its website. SmithRx, a PBM based in San Francisco, announced it would partner with Cost Plus Drugs to offer Yusimry, adding that SmithRx members can use their insurance benefits to further reduce out-of-pocket costs. RxPreferred, another PBM, will also offer Yusimry through its partnership with Cuban’s company.
The news website Formulary Watch previously reported that CVS Caremark, another of the biggest PBMs, will be offering Amjevita, but as a nonpreferred brand, while Humira remains the preferred brand. CVS Caremark did not respond to a request for comment.
Will patients pay less?
Biosimilars have been touted as a potential solution to lower spending on biologic drugs, but it’s unknown if patients will ultimately benefit with lower out-of-pocket costs. It’s “impossible to predict” if the discount that third-party payers pay will be passed on to consumers, said Mark Fendrick, MD, who directs the University of Michigan Center for Value-based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor.
Generally, a consumer’s copay is a percentage of a drug’s list price, so it stands to reason that a low drug price would result in lower out-of-pocket payments. While this is mostly true, Humira has a successful copay assistance program to lower prescription costs for consumers. According to a 2022 IQVIA report, 82% of commercial prescriptions cost patients less than $10 for Humira because of this program.
To appeal to patients, biosimilar companies will need to offer similar savings, Dr. Fendrick added. “There will be some discontent if patients are actually asked to pay more out-of-pocket for a less expensive drug,” he said.
All eight companies behind these biosimilars are offering or will be launching copay saving programs, many which advertise copays as low as $0 per month for eligible patients.
How will Humira respond?
Marta Wosińska, PhD, a health care economist at the Brookings Institute, Washington, predicts payers will use these lower biosimilar prices to negotiate better deals with AbbVie, Humira’s manufacturer. “We have a lot of players coming into [the market] right now, so the competition is really fierce,” she said. In response, AbbVie will need to increase rebates on Humira and/or lower its price to compete with these biosimilars.
“The ball is in AbbVie’s court,” she said. “If [the company] is not willing to drop price sufficiently, then payers will start switching to biosimilars.”
Dr. Fendrick reported past financial relationships and consulting arrangements with AbbVie, Amgen, Arnold Ventures, Bayer, CareFirst, BlueCross BlueShield, and many other companies. Dr. Wosińska has received funding from Arnold Ventures and serves as an expert witness on antitrust cases involving generic medication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does colchicine have a role in treating excess ASCVD risk in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions?
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
The recent Food and Drug Administration approval of colchicine 0.5 mg (Lodoco) for use in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) prevention will possibly create opportunities to use the drug to treat residual risk for ASCVD in some patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, particularly in rheumatology.
Potential in rheumatology
The 0.5-mg dose is just a shade under the 0.6-mg, twice daily dosing rheumatologists typically prescribe for gout, Christie Bartels, MD, MS, chief of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said in an interview. Clinicians also use the 0.6-mg dose off-label for pseudogout or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), Dr. Bartels noted.
The new formulation opens the consideration for using colchicine more in patients with psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, she said. “I think we could certainly discuss it, particularly, in secondary prevention patients who already had an event or who are at the highest risk and already on optimal traditional agents,” she said.
She cited previous comments by Paul Ridker, MD, director of the center for cardiovascular disease prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and developer of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) test for measuring inflammatory markers. “We might not know the answer because Dr. Ridker pointed out he used colchicine 0.5 mg in patients that had a high-sensitivity CRP that was high; we need patients who have had inflammation of unknown origin, so those patients presumably weren’t already on another anti-inflammatory,” she said, noting that hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and some biologics provide some protection from cardiovascular risks.
However, a potential role for long-term colchicine 0.5 mg in ASCVD prevention may cause consideration for changing the drug’s role in gout treatment, Dr. Bartels said. “In gout, where we do have an FDA-approved indication for colchicine, we used to use it only for the first 6 months while we were getting patients to goal on allopurinol, which was usually then monotherapy after the first 6 months,” she said. “I think this will likely change how I treat gout patients in that I may also offer to continue both medications [colchicine and allopurinol] if they are tolerating them well.
“And then in patients where I’m using it off-label in CPPD, I might again share with them that in addition to possibly helping their CPPD, there may be this added benefit to reduce inflammation just in discussing the risks and benefits of the medicine.”
However, rheumatologists must be careful in using colchicine beyond the typical 6-month cycle, Dr. Bartels said. “One of the tricky things with colchicine, and part of the reason we did not traditionally continue it specifically past the first 6 months, was that it can cause myopathies or cytopenias, so we still have to counsel patients regarding these risks and monitor that,” she said.
Additionally, colchicine can have drug interactions with statins or calcium channel blockers that can change colchicine levels. “I think the dose here is so low, the 0.5 mg, that it’s probably still safe, but again, it’s something that we have to take a look at in the patient’s whole picture and the rest of their burden of their meds in order to make a decision with them,” Dr. Bartels said.
Possibilities in dermatology
The LoDoCo2 trial one of two major randomized trials that supported approval of colchicine 0.5 mg, reported that treated patients had a 60% lower rate of gout than the placebo group (1.4% vs. 3.4%). Joel Gelfand, MD, MSCE, the James J. Leyden professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, pointed to this in evaluating the dermatologic implications of the drug’s approval. “This may be of particular interest as people with psoriasis have an increased risk of gout,” he said in emailed comments.
Colchicine’s mechanism of action to reduce inflammation parallels that of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors used for dermatologic indications, namely by inhibiting leukocyte adhesion to disrupt the downregulation of TNF receptors, Dr. Gelfand said.
“Interestingly, observational data suggests biologics that target TNF such as adalimumab, etanercept, etc., are associated with a reduction in CV events, and in placebo-controlled trials we conducted in psoriasis patients, it reduced key inflammatory mediators of cardiovascular disease, including IL [interleukin]-6,” he said. “Randomized clinical trials to evaluate the ability of TNF inhibitors, which are now available as biosimilars, to prevent cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, should be conducted, and more work is needed to identify which additional immune-targeted treatments may lower CV risk with an acceptable safety profile.”
Colchicine currently has few indications for rare conditions in dermatology, Dr. Gelfand said, including Sweets syndrome, subcorneal pustular dermatosis, and cutaneous vasculitis. “There are some reports to suggest it may help psoriatic disease, but current data are limited and insufficient to recommend its use for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis,” he said.
The approval of colchicine 0.5 mg for ASCVD could be meaningful for people with psoriasis who are also being treated for CV risk factors, Dr. Gelfand said. “Additional considerations such as signs of residual inflammation (elevated hsCRP) and CV imaging findings may be used to further guide shared decision-making for optimal use,” he said.
Another consideration he noted: “This is also a novel 0.5-mg formulation, and thus cost may be an issue.”
Would side effects bar use in gastroenterology?
Colchicine 0.5 mg may not move the needle much for expanding treatment of ASCVD in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and potentially other gastrointestinal conditions, Edward Loftus Jr., MD, the Maxine and Jack Zarrow Family professor of gastroenterology specifically for IBD at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told MDEdge in emailed comments. “Given the GI side effect profile [of colchicine], I am not sure I would go there,” he said.
“Hopefully, the prescribers of this low-dose formulation are aware of the gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and nausea, and educate patients about these side effects so that a proper risk-benefit discussion can ensue,” he said.
Dr. Bartels reporting a previous financial relationship with Pfizer. Dr. Gelfand said he has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celldex, GlaxoSmithKline, Twill, Lilly, Leo, Moonlake, Janssen Biologics, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Neuroderm, and Veolia North America. Dr. Loftus disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Alvotech, Amgen, Arena, Avalo, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene/Receptos, Celltrion Healthcare, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Iterative Health, Janssen, KSL Diagnostics, Morphic, Ono, Pfizer, Sun, Surrozen, Takeda, Theravance, and UCB.
Methotrexate does not impair sperm quality, small study finds
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methotrexate (MTX) is not associated with testicular toxicity, so therapy can be safety started in men pursuing parenthood, a small study finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Lack of evidence regarding MTX’s effect on sperm quality has resulted in inconsistent recommendations for men actively pursuing parenthood.
- Researchers enrolled 20 men aged 18 years or older with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID) who were about to begin MTX therapy and 25 healthy men as controls.
- Participants provided semen samples prior to beginning MTX therapy and 13 weeks after beginning therapy.
- Researchers tested samples in both groups for markers of testicular toxicity.
- Also evaluated whether MTX polyglutamates could be detected in sperm of seminal fluid, as a secondary outcome.
TAKEAWAY:
- Found no significant differences in conventional semen parameters, sperm DNA damage, or male reproductive endocrine axis between the MTX group and controls.
- The concentration of MTX polyglutamates is low in both sperm and seminal fluid and is particularly low in sperm.
IN PRACTICE:
“Therapy with MTX can be safely started or continued in men diagnosed with an IMID and with an active wish to become a father,” the authors write.
STUDY DETAILS:
Luis Fernando Perez-Garcia, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the research. The study was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases on June 1, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The small number of participants and that the study included only MTX starters and not those who have taken MTX longer term.
DISCLOSURES:
Grants from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation, The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia funded the project. Researchers disclosed financial relationships with Galapagos NV and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After Yusimry’s steep discount, little clarity on future adalimumab biosimilar pricing
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, enjoyed a long run as one of the world’s best-selling medicines. But its 20-year, competition-free period has ended, and despite its best efforts to delay their arrival, drug manufacturer AbbVie now faces increasing competition from biosimilars entering the marketplace.
But one biosimilar about to be launched may be something of a game changer. Coherus BioSciences has announced plans to market its biosimilar Yusimry (adalimumab-aqvh) at a cost of $995 for two autoinjectors. This represents an approximate 85% discount over Humira’s sale list price of $6922.
This price, however, is slated to plunge even further as Coherus has also revealed that it will work with the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC) to offer an even lower price. When Yusimry launches in July, it will sell for about $579 for two autoinjectors, making it the lowest-priced adalimumab biosimilar on the market.
“Coherus and Cost Plus Drug Company share a common mission, to increase access to high-quality medicine for patients at an affordable price,” said Dennis Lanfear, MBA, president, CEO and chairman of Coherus. “Mark Cuban and his team offer innovative solutions to health care problems, and Coherus is also a highly innovative company focused on unmet patient needs.”
He noted that, with adalimumab biosimilar pricing, this translates to a low list price approach. “We are pleased that Yusimry will be a part of that, as the first biologic they carry,” Mr. Lanfear said.
MCCPDC prices are based on the cost of ingredients and manufacturing plus 15% margin, a $3 pharmacy dispensing fee, and a $5 shipping fee. The company has expanded its inventory from 100 generics to more than 350 medications since it launched in January 2022. While MCCPDC is primarily directed to people who are paying cash for drugs, it does take insurance from select plans. And even for people who are covered by other insurers, the cost of drugs from Mr. Cuban’s company may be less than their out-of-pocket costs if they did go through their payer.
The low pricing of Yusimry is welcome, said Marcus Snow, MD, an assistant professor in the division of rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, but he pointed out that it is still a very expensive drug. “For patients who can’t afford Humira due to poor insurance coverage and high out-of-pocket costs, it is a welcome option. But it’s also unclear how many patients who lack adequate health insurance coverage can afford to pay $579 a month out of their own pockets.”
The biosimilars are coming
By early December 2022, the Food and Drug Administration had approved seven Humira biosimilars, and Amgen launched the first biosimilar to come on the market, Amjevita, soon afterward. By July 2023, half a dozen more are expected to enter the marketplace, said Steven Horvitz, managing director of EMC Analytics Group, a pharmaceutical research firm.
Mr. Horvitz agrees that the system is out of control, but it is unclear how much of an effect the low price tag on the Coherus product will have. “Some insurers may say, ‘we want the lowest price, and we don’t care about rebates,’ and will go with it,” he said. “PBMs [pharmacy benefit managers] are all about economics, so we have to see how many of their major clients will ask for the lowest price.”
Amgen has more or less followed the status quo on pricing for its biosimilar, but with a twist. It›s being offered at two different prices: $85,494 a year, which is only a 5% discount from Humira’s list price, or at $40,497 a year, a 55% discount. However, to date, the lower price has generally not been granted favorable formulary placement by PBMs. The plans that adopt the higher-priced biosimilar will get bigger rebates, but patients with coinsurance and deductibles will pay more out of pocket.
It is yet unknown how the pricing on Yusimry will affect the biosimilars ready to launch. “Will it give them pause for thought or not make any difference?” Mr. Horvitz said. “The companies do not reveal their pricing before the fact, so we have to wait and see.”
Large PBMs have not jumped at the opportunity to offer the Coherus biosimilar, but SmithRx, which bills itself as “next-generation pharmacy benefits management,” announced that it will offer Yusimry to its members at a discount of more than 90%.
“Unlike traditional PBMs, SmithRx prioritizes transparency and up-front cost savings. Humira is often an employer’s top drug expense so offering a low-cost alternative will have significant impact,” Jake Frenz, CEO and founder of SmithRx, said in a statement. “We’re excited to work with Cost Plus Drugs to bring this biosimilar to our members – and significantly reduce costs for them and their employers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.