User login
A Paradox? Higher Male Fertility Seen With Inflammatory Arthritis
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Men with an inflammatory arthritis (IA) diagnosis are less likely to be childless than healthy comparators, according to an epidemiological study.
METHODS:
- 10,865 men in the Norwegian Arthritis Registry were compared with 54,325 men without IA, matched by age and location.
- In the arthritis group, 37% had rheumatoid arthritis, 33% had psoriatic arthritis, and 30% had spondyloarthritis.
- Researchers used childlessness and number of children as proxies for male fertility.
TAKEAWAY:
- 21% of men with IA were childless compared with 27% in the healthy cohort (P < .001).
- On an average, a man with IA had 1.80 children whereas a man in the control group had 1.69 children (P < .001).
- These findings were consistent over time, but the most pronounced difference between groups was seen in men diagnosed after the year 2000.
IN PRACTICE:
The finding “is novel and generates new hypotheses regarding associations between fertility, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, and immune-modulating drugs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Gudrun David Sigmo, of the department of rheumatology at Stavanger (Norway) University Hospital, and colleagues had their work published online on January 23, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis relied on administrative data, and researchers did not have data on confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the nonprofit organizations Aslaug Anders fond, Astri og Edvard Riisøens legat, Det alminnelige medisinske forskningsfond, Pahles legat, and Fagsenter for medisins-ke kvalitetsregistre i Helse Vest. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tool Uses Genetics to Assist With Diagnosis of Early Inflammatory Arthritis
A new diagnostic tool can effectively discriminate different rheumatologic conditions and could potentially aid in the diagnosis of early inflammatory arthritis.
The algorithm — called Genetic Probability tool (G-PROB) — uses genetic information to calculate the probability of certain diseases.
“At such an early stage of disease, it’s not always easy to determine what the final outcome will be with respect to final diagnosis,” said John Bowes, PhD, a senior lecturer in the division of musculoskeletal & dermatological sciences at the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom. He was a senior author of the newest study of G-PROB. “What we are hoping for here is that genetics can help [clinicians] with the decision-making process and hopefully accelerate the correct diagnosis and get individuals onto the correct treatment as early as possible.”
Creating the Algorithm
G-PROB was first developed by an international group of scientists with the goal of using genetic risk scores to predict the probabilities of common diagnoses for patients with early signs of arthritis, such as synovitis and joint swelling. According to the study authors, about 80% of these types of patients are eventually diagnosed with the following conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and gout.
The algorithm combines existing knowledge about single-nucleotide polymorphisms from prior genomic studies to create genetic risk scores — also called polygenic risk score (PRS) — for multiple diseases. Using these scores, the program then calculates the probabilities of certain diagnoses for a patient, based on the assumption that at least one disease was present.
In this first study, researchers trained the tool on simulated data and then tested it in three patient cohorts totaling about 1700 individuals from the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics database and Mass General Brigham Biobank. In the initial study, G-PROB identified a likely diagnosis in 45% of patients, with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 64%. Adding these genetic scores to clinical data improved diagnostic accuracy from 39% to 51%.
Validating G-PROB
But data from these biobanks may not necessarily be representative of early arthritis in patients appearing in outpatient clinics, noted Dr. Bowes. In this new study, researchers sought to independently validate the original study’s findings using data from the Norfolk Arthritis Register, a community-based, long-term observational study on inflammatory polyarthritis. The team applied G-PROB in this cohort and then compared the tool’s probabilities for common rheumatic conditions to the final clinician diagnosis.
The study ultimately included 1047 individuals with early inflammatory arthritis with genotype data. In the cohort, more than 70% (756 individuals) were diagnosed with RA. Of the remaining patients, 104 had PsA, 18 had SLE, 16 had AS, and 12 had gout. The research team also added an “other diseases” category to the algorithm. A total of 141 patients fell into this category and were diagnosed with diseases including chronic pain syndrome (52 individuals), polymyalgia rheumatica (29 individuals), and Sjögren’s syndrome (9 individuals).
G-PROB was best at excluding diagnoses: Probabilities under 5% for a single disease corresponded to a negative predictive value (NPV) of 96%. If probabilities for two diseases were both < 5%, the NPV was 94%.
For patients with a single probability above 50%, the tool had a PPV of 70.3%. In 55.7% of all patients, the disease with the highest probability ended up being the final diagnosis.
Generally, PRSs, as well as tests using biomarkers, were better at excluding diagnoses than affirming them, noted Matthew Brown, MBBS, MD, a professor of medicine at King’s College London, who was not involved with the research. If disease prevalence is low, then a test aimed at diagnosis of that disease would be better at excluding a diagnosis than affirming it, he explained.
However, he noted that G-PROB’s PPV may have performed better if researchers had started by using established PRS scores to form the algorithm, rather than developing these genetic scores independently using internal datasets.
Can G-PROB Improve Diagnosis?
The new study’s key contribution was that it independently validated findings from a previous study, noted Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. She coauthored an accompanying editorial to the newest study and coauthored the original G-PROB paper.
This new study also brought up an important question about G-PROB that has yet to be tested: Will this tool help clinicians make more efficient and accurate diagnoses in practice?
A prospective trial would be necessary to begin answering this question, both Dr. Bowes and Dr. Liao agreed. For example, one clinician group would have access to G-PROB data, while another would not, and “see if that helps [the first group] make the diagnosis faster or more accurately,” Dr. Liao said.
Dr. Bowes was also interested in exploring if combining G-PROB with other clinical data would improve diagnostic performance.
“Genetics isn’t the full story,” he said. Dr. Bowes saw genetics as one additional, complementary tool in a clinician’s toolbox.
Future studies were needed to understand the clinical utility of genetic information in conjunction with current diagnostic practices, such as imaging, physical exams, and lab results, Dr. Liao and her editorial coauthors argued.
“For example, in cardiovascular disease, the clinical utility of polygenic risk scores has been defined by their ability to improve risk stratification beyond what is already achieved with more common risk factors and measures such as cholesterol levels, smoking status, and coronary calcium scores,” Dr. Liao and her coauthors wrote. “Similarly, a polygenic risk score for breast cancer would not be clinically implemented alone for risk prediction but rather as one risk factor among others, such as hormonal and reproductive factors and prior mammographic data.”
Future of Genetics in Rheumatology
An additional hurdle for using tools like G-PROB was that a patient must have undergone DNA sequencing, and these data must be available to clinicians. Even a decade ago, this type of testing may have seemed unrealistic to incorporate in daily practice, Dr. Liao noted, but technological advancements continue to make genetic sequencing more accessible to the public.
There are already efforts in the United Kingdom to incorporate genetics into healthcare, including trials for PRSs and heart disease, noted Dr. Bowes, as well as large-scale studies such as Our Future Health.
“As these population-based studies expand more, a high proportion of individuals should hopefully have access to this kind of data,” he said.
Brown added that genetic testing is already used to make rheumatology diagnoses.
“[HLA] B-27 testing, for example, is an extremely commonly used test to assist in the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Is it that different to change to a PRS as opposed to a straight HLA testing? I don’t think it is,” he said.
While there would need to be systematic training for clinicians to understand how to calculate and use PRSs in daily practice, Dr. Brown did not think this adjustment would be too difficult.
“There is a lot of exceptionalism about genetics, which is actually inappropriate,” he said. “This is actually just a quantitative score that should be easy for people to interpret.”
Dr. Bowes and Dr. Brown reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Liao worked as a consultant for UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new diagnostic tool can effectively discriminate different rheumatologic conditions and could potentially aid in the diagnosis of early inflammatory arthritis.
The algorithm — called Genetic Probability tool (G-PROB) — uses genetic information to calculate the probability of certain diseases.
“At such an early stage of disease, it’s not always easy to determine what the final outcome will be with respect to final diagnosis,” said John Bowes, PhD, a senior lecturer in the division of musculoskeletal & dermatological sciences at the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom. He was a senior author of the newest study of G-PROB. “What we are hoping for here is that genetics can help [clinicians] with the decision-making process and hopefully accelerate the correct diagnosis and get individuals onto the correct treatment as early as possible.”
Creating the Algorithm
G-PROB was first developed by an international group of scientists with the goal of using genetic risk scores to predict the probabilities of common diagnoses for patients with early signs of arthritis, such as synovitis and joint swelling. According to the study authors, about 80% of these types of patients are eventually diagnosed with the following conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and gout.
The algorithm combines existing knowledge about single-nucleotide polymorphisms from prior genomic studies to create genetic risk scores — also called polygenic risk score (PRS) — for multiple diseases. Using these scores, the program then calculates the probabilities of certain diagnoses for a patient, based on the assumption that at least one disease was present.
In this first study, researchers trained the tool on simulated data and then tested it in three patient cohorts totaling about 1700 individuals from the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics database and Mass General Brigham Biobank. In the initial study, G-PROB identified a likely diagnosis in 45% of patients, with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 64%. Adding these genetic scores to clinical data improved diagnostic accuracy from 39% to 51%.
Validating G-PROB
But data from these biobanks may not necessarily be representative of early arthritis in patients appearing in outpatient clinics, noted Dr. Bowes. In this new study, researchers sought to independently validate the original study’s findings using data from the Norfolk Arthritis Register, a community-based, long-term observational study on inflammatory polyarthritis. The team applied G-PROB in this cohort and then compared the tool’s probabilities for common rheumatic conditions to the final clinician diagnosis.
The study ultimately included 1047 individuals with early inflammatory arthritis with genotype data. In the cohort, more than 70% (756 individuals) were diagnosed with RA. Of the remaining patients, 104 had PsA, 18 had SLE, 16 had AS, and 12 had gout. The research team also added an “other diseases” category to the algorithm. A total of 141 patients fell into this category and were diagnosed with diseases including chronic pain syndrome (52 individuals), polymyalgia rheumatica (29 individuals), and Sjögren’s syndrome (9 individuals).
G-PROB was best at excluding diagnoses: Probabilities under 5% for a single disease corresponded to a negative predictive value (NPV) of 96%. If probabilities for two diseases were both < 5%, the NPV was 94%.
For patients with a single probability above 50%, the tool had a PPV of 70.3%. In 55.7% of all patients, the disease with the highest probability ended up being the final diagnosis.
Generally, PRSs, as well as tests using biomarkers, were better at excluding diagnoses than affirming them, noted Matthew Brown, MBBS, MD, a professor of medicine at King’s College London, who was not involved with the research. If disease prevalence is low, then a test aimed at diagnosis of that disease would be better at excluding a diagnosis than affirming it, he explained.
However, he noted that G-PROB’s PPV may have performed better if researchers had started by using established PRS scores to form the algorithm, rather than developing these genetic scores independently using internal datasets.
Can G-PROB Improve Diagnosis?
The new study’s key contribution was that it independently validated findings from a previous study, noted Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. She coauthored an accompanying editorial to the newest study and coauthored the original G-PROB paper.
This new study also brought up an important question about G-PROB that has yet to be tested: Will this tool help clinicians make more efficient and accurate diagnoses in practice?
A prospective trial would be necessary to begin answering this question, both Dr. Bowes and Dr. Liao agreed. For example, one clinician group would have access to G-PROB data, while another would not, and “see if that helps [the first group] make the diagnosis faster or more accurately,” Dr. Liao said.
Dr. Bowes was also interested in exploring if combining G-PROB with other clinical data would improve diagnostic performance.
“Genetics isn’t the full story,” he said. Dr. Bowes saw genetics as one additional, complementary tool in a clinician’s toolbox.
Future studies were needed to understand the clinical utility of genetic information in conjunction with current diagnostic practices, such as imaging, physical exams, and lab results, Dr. Liao and her editorial coauthors argued.
“For example, in cardiovascular disease, the clinical utility of polygenic risk scores has been defined by their ability to improve risk stratification beyond what is already achieved with more common risk factors and measures such as cholesterol levels, smoking status, and coronary calcium scores,” Dr. Liao and her coauthors wrote. “Similarly, a polygenic risk score for breast cancer would not be clinically implemented alone for risk prediction but rather as one risk factor among others, such as hormonal and reproductive factors and prior mammographic data.”
Future of Genetics in Rheumatology
An additional hurdle for using tools like G-PROB was that a patient must have undergone DNA sequencing, and these data must be available to clinicians. Even a decade ago, this type of testing may have seemed unrealistic to incorporate in daily practice, Dr. Liao noted, but technological advancements continue to make genetic sequencing more accessible to the public.
There are already efforts in the United Kingdom to incorporate genetics into healthcare, including trials for PRSs and heart disease, noted Dr. Bowes, as well as large-scale studies such as Our Future Health.
“As these population-based studies expand more, a high proportion of individuals should hopefully have access to this kind of data,” he said.
Brown added that genetic testing is already used to make rheumatology diagnoses.
“[HLA] B-27 testing, for example, is an extremely commonly used test to assist in the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Is it that different to change to a PRS as opposed to a straight HLA testing? I don’t think it is,” he said.
While there would need to be systematic training for clinicians to understand how to calculate and use PRSs in daily practice, Dr. Brown did not think this adjustment would be too difficult.
“There is a lot of exceptionalism about genetics, which is actually inappropriate,” he said. “This is actually just a quantitative score that should be easy for people to interpret.”
Dr. Bowes and Dr. Brown reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Liao worked as a consultant for UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new diagnostic tool can effectively discriminate different rheumatologic conditions and could potentially aid in the diagnosis of early inflammatory arthritis.
The algorithm — called Genetic Probability tool (G-PROB) — uses genetic information to calculate the probability of certain diseases.
“At such an early stage of disease, it’s not always easy to determine what the final outcome will be with respect to final diagnosis,” said John Bowes, PhD, a senior lecturer in the division of musculoskeletal & dermatological sciences at the University of Manchester in the United Kingdom. He was a senior author of the newest study of G-PROB. “What we are hoping for here is that genetics can help [clinicians] with the decision-making process and hopefully accelerate the correct diagnosis and get individuals onto the correct treatment as early as possible.”
Creating the Algorithm
G-PROB was first developed by an international group of scientists with the goal of using genetic risk scores to predict the probabilities of common diagnoses for patients with early signs of arthritis, such as synovitis and joint swelling. According to the study authors, about 80% of these types of patients are eventually diagnosed with the following conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and gout.
The algorithm combines existing knowledge about single-nucleotide polymorphisms from prior genomic studies to create genetic risk scores — also called polygenic risk score (PRS) — for multiple diseases. Using these scores, the program then calculates the probabilities of certain diagnoses for a patient, based on the assumption that at least one disease was present.
In this first study, researchers trained the tool on simulated data and then tested it in three patient cohorts totaling about 1700 individuals from the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics database and Mass General Brigham Biobank. In the initial study, G-PROB identified a likely diagnosis in 45% of patients, with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 64%. Adding these genetic scores to clinical data improved diagnostic accuracy from 39% to 51%.
Validating G-PROB
But data from these biobanks may not necessarily be representative of early arthritis in patients appearing in outpatient clinics, noted Dr. Bowes. In this new study, researchers sought to independently validate the original study’s findings using data from the Norfolk Arthritis Register, a community-based, long-term observational study on inflammatory polyarthritis. The team applied G-PROB in this cohort and then compared the tool’s probabilities for common rheumatic conditions to the final clinician diagnosis.
The study ultimately included 1047 individuals with early inflammatory arthritis with genotype data. In the cohort, more than 70% (756 individuals) were diagnosed with RA. Of the remaining patients, 104 had PsA, 18 had SLE, 16 had AS, and 12 had gout. The research team also added an “other diseases” category to the algorithm. A total of 141 patients fell into this category and were diagnosed with diseases including chronic pain syndrome (52 individuals), polymyalgia rheumatica (29 individuals), and Sjögren’s syndrome (9 individuals).
G-PROB was best at excluding diagnoses: Probabilities under 5% for a single disease corresponded to a negative predictive value (NPV) of 96%. If probabilities for two diseases were both < 5%, the NPV was 94%.
For patients with a single probability above 50%, the tool had a PPV of 70.3%. In 55.7% of all patients, the disease with the highest probability ended up being the final diagnosis.
Generally, PRSs, as well as tests using biomarkers, were better at excluding diagnoses than affirming them, noted Matthew Brown, MBBS, MD, a professor of medicine at King’s College London, who was not involved with the research. If disease prevalence is low, then a test aimed at diagnosis of that disease would be better at excluding a diagnosis than affirming it, he explained.
However, he noted that G-PROB’s PPV may have performed better if researchers had started by using established PRS scores to form the algorithm, rather than developing these genetic scores independently using internal datasets.
Can G-PROB Improve Diagnosis?
The new study’s key contribution was that it independently validated findings from a previous study, noted Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. She coauthored an accompanying editorial to the newest study and coauthored the original G-PROB paper.
This new study also brought up an important question about G-PROB that has yet to be tested: Will this tool help clinicians make more efficient and accurate diagnoses in practice?
A prospective trial would be necessary to begin answering this question, both Dr. Bowes and Dr. Liao agreed. For example, one clinician group would have access to G-PROB data, while another would not, and “see if that helps [the first group] make the diagnosis faster or more accurately,” Dr. Liao said.
Dr. Bowes was also interested in exploring if combining G-PROB with other clinical data would improve diagnostic performance.
“Genetics isn’t the full story,” he said. Dr. Bowes saw genetics as one additional, complementary tool in a clinician’s toolbox.
Future studies were needed to understand the clinical utility of genetic information in conjunction with current diagnostic practices, such as imaging, physical exams, and lab results, Dr. Liao and her editorial coauthors argued.
“For example, in cardiovascular disease, the clinical utility of polygenic risk scores has been defined by their ability to improve risk stratification beyond what is already achieved with more common risk factors and measures such as cholesterol levels, smoking status, and coronary calcium scores,” Dr. Liao and her coauthors wrote. “Similarly, a polygenic risk score for breast cancer would not be clinically implemented alone for risk prediction but rather as one risk factor among others, such as hormonal and reproductive factors and prior mammographic data.”
Future of Genetics in Rheumatology
An additional hurdle for using tools like G-PROB was that a patient must have undergone DNA sequencing, and these data must be available to clinicians. Even a decade ago, this type of testing may have seemed unrealistic to incorporate in daily practice, Dr. Liao noted, but technological advancements continue to make genetic sequencing more accessible to the public.
There are already efforts in the United Kingdom to incorporate genetics into healthcare, including trials for PRSs and heart disease, noted Dr. Bowes, as well as large-scale studies such as Our Future Health.
“As these population-based studies expand more, a high proportion of individuals should hopefully have access to this kind of data,” he said.
Brown added that genetic testing is already used to make rheumatology diagnoses.
“[HLA] B-27 testing, for example, is an extremely commonly used test to assist in the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Is it that different to change to a PRS as opposed to a straight HLA testing? I don’t think it is,” he said.
While there would need to be systematic training for clinicians to understand how to calculate and use PRSs in daily practice, Dr. Brown did not think this adjustment would be too difficult.
“There is a lot of exceptionalism about genetics, which is actually inappropriate,” he said. “This is actually just a quantitative score that should be easy for people to interpret.”
Dr. Bowes and Dr. Brown reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Liao worked as a consultant for UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
IV secukinumab, alternative to self-injections, reaches primary endpoints in PsA, axSpA
SAN DIEGO – Monthly use of intravenously administered secukinumab (Cosentyx) proved its efficacy over placebo in treating psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in two industry-sponsored, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 trials of the drug’s second and newly approved route of administration.
The studies of the human monoclonal antibody secukinumab, an interleukin-17 inhibitor, were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. A subcutaneously injectable formulation of the drug is available, and the Food and Drug Administration approved the IV form for the conditions in October, although at a recommended lower monthly dose than the new trials examined.
In the PsA trial, 191 patients took IV secukinumab, and 190 took placebo. For the primary endpoint, the percentages who reached at least a 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR 50) at 16 weeks were 31.4% and 6.3%, respectively (P < .0001).
In the axSpA trial, 264 patients took IV secukinumab, and 262 took placebo. The primary endpoint, at least a 40% improvement in Assessment of the Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), was met at 16 weeks by 40.9% and 22.9%, respectively (P < .0001).
“Both studies appear to present clear efficacy of IV route administration of secukinumab with no clear increase in safety signals,” consultant rheumatologist Nicola Goodson, MBChB, PhD, of Aintree University Hospital in Liverpool, England, said in an interview.
“Offering IV administration as an option to patients is helpful,” added Dr. Goodson, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings.
As Dr. Goodson explained, secukinumab “was the first IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor used to treat spondyloarthropathies, and we have been using subcutaneous secukinumab to treat psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis/ankylosing spondylitis since 2016 in the U.K. Our experience with this medication has been good with similar efficacy to anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapy in axial spondyloarthritis. The medication is generally well-tolerated, and the subcutaneous pen injection device is easy for patients to use.”
However, IV treatment may speed up onset of action, she said, and it may be useful in situations when compliance is a challenge.
PsA trial details
In the PsA trial, known as INVIGORATE-2, researchers recruited patients who met the CASPAR criteria for active PsA with symptoms for ≥ 6 months, and had ≥ 3 tender joints out of 78 joints and ≥ 3 swollen joints out of 76.
Participants with a mean age of 48, including 55% females, were randomized 1:1 to receive placebo or secukinumab (6 mg/kg at baseline followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks). Those in the placebo group were switched to the same monthly doses of secukinumab at 16 weeks.
“Patients who switched from the placebo had a similar increase of efficacy as the original treated group,” rheumatologist Alan J. Kivitz, MD, of the Altoona Center for Clinical Research, in Duncansville, Penn., said in his presentation at the meeting. Specifically, at 52 weeks, the groups had similar ACR 50 response rates: 58% with secukinumab and 64% with placebo-to-secukinumab.
The fact that patients in the original placebo group who received 3 mg IV doses without 6-mg loading doses achieved ACR response rates similar to those who took secukinumab during the whole trial “could suggest that the IV loading dose may not be required. This would need to be explored in a randomized head-to-head study, but it’s an interesting observation that may reduce costs and exposure to higher doses of medication at the start of treatment,” Dr. Goodson said.
Among the patients who received secukinumab at any point in the study, 63% had a treatment-emergent adverse event, including 5.9% with serious events. One death was reported in the placebo group before week 16. No other deaths were reported.
AxSpA trial details
In the axSpA trial, called INVIGORATE-1, researchers recruited people aged ≥18 years with a diagnosis of active radiographic axSpA according to modified New York criteria or nonradiographic axSpA according to ASAS criteria, and all had inflammatory back pain for ≥6 months with an onset before age 45. They were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive IV secukinumab (6 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks) or placebo for 16 weeks. At that point, the placebo group switched to the same monthly doses of IV secukinumab.
Participants had a mean age of about 39, and about one-third were female.
Following the statistical superiority in ASAS 40 response rates seen with IV secukinumab at week 16, patients who from there switched from placebo to IV secukinumab achieved comparable ASAS 40 response rates to those of patients originally randomized to secukinumab by week 24, reaching 66.8% for those on secukinumab the whole time and 74.9% for those who switched.
Secondary outcome measures were similar in both groups at week 52.
Among all patients who took secukinumab – the percentage with any adverse event was 63.2%, and 6% had a nonfatal adverse event deemed serious. There was one death during secukinumab treatment not suspected to be related to treatment.
In a presentation about the axSpA study findings, Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, noted that “having an IV biologic available in the U.S. has some advantages. There are certain insurance providers such as Medicare where it is more economical for the patient to have an IV drug available.”
Dr. Deodhar also noted that in October the FDA approved a recommended lower dose for the IV treatment than in the study: 1.75 mg/kg instead of 3 mg/kg following the loading dose. That’s because the 3 mg/kg dose caused blood levels to be higher than those in the subcutaneous form, he said.
The FDA made the same dose recommendation for PsA.
Study limitations
Dr. Goodson, the U.K. consultant rheumatologist, noted a limitation of the trials: “It would have been interesting to compare IV to subcutaneous route secukinumab.” Still, the findings suggest that “the safety and efficacy of IV administration appears comparable,” she said.
“IV administration will have associated costs of attending hospital or infusion clinics,” she added, “and the cost of additional staff and administration need to be considered.”
Novartis, the maker of secukinumab, funded both studies. The PsA study authors report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Kivitz, have connections to Novartis. The axSpA study authors also report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Deodhar, have connections to Novartis. Some authors of both studies are Novartis employees. Dr. Goodson disclosed financial relationships with UCB and AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Monthly use of intravenously administered secukinumab (Cosentyx) proved its efficacy over placebo in treating psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in two industry-sponsored, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 trials of the drug’s second and newly approved route of administration.
The studies of the human monoclonal antibody secukinumab, an interleukin-17 inhibitor, were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. A subcutaneously injectable formulation of the drug is available, and the Food and Drug Administration approved the IV form for the conditions in October, although at a recommended lower monthly dose than the new trials examined.
In the PsA trial, 191 patients took IV secukinumab, and 190 took placebo. For the primary endpoint, the percentages who reached at least a 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR 50) at 16 weeks were 31.4% and 6.3%, respectively (P < .0001).
In the axSpA trial, 264 patients took IV secukinumab, and 262 took placebo. The primary endpoint, at least a 40% improvement in Assessment of the Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), was met at 16 weeks by 40.9% and 22.9%, respectively (P < .0001).
“Both studies appear to present clear efficacy of IV route administration of secukinumab with no clear increase in safety signals,” consultant rheumatologist Nicola Goodson, MBChB, PhD, of Aintree University Hospital in Liverpool, England, said in an interview.
“Offering IV administration as an option to patients is helpful,” added Dr. Goodson, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings.
As Dr. Goodson explained, secukinumab “was the first IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor used to treat spondyloarthropathies, and we have been using subcutaneous secukinumab to treat psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis/ankylosing spondylitis since 2016 in the U.K. Our experience with this medication has been good with similar efficacy to anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapy in axial spondyloarthritis. The medication is generally well-tolerated, and the subcutaneous pen injection device is easy for patients to use.”
However, IV treatment may speed up onset of action, she said, and it may be useful in situations when compliance is a challenge.
PsA trial details
In the PsA trial, known as INVIGORATE-2, researchers recruited patients who met the CASPAR criteria for active PsA with symptoms for ≥ 6 months, and had ≥ 3 tender joints out of 78 joints and ≥ 3 swollen joints out of 76.
Participants with a mean age of 48, including 55% females, were randomized 1:1 to receive placebo or secukinumab (6 mg/kg at baseline followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks). Those in the placebo group were switched to the same monthly doses of secukinumab at 16 weeks.
“Patients who switched from the placebo had a similar increase of efficacy as the original treated group,” rheumatologist Alan J. Kivitz, MD, of the Altoona Center for Clinical Research, in Duncansville, Penn., said in his presentation at the meeting. Specifically, at 52 weeks, the groups had similar ACR 50 response rates: 58% with secukinumab and 64% with placebo-to-secukinumab.
The fact that patients in the original placebo group who received 3 mg IV doses without 6-mg loading doses achieved ACR response rates similar to those who took secukinumab during the whole trial “could suggest that the IV loading dose may not be required. This would need to be explored in a randomized head-to-head study, but it’s an interesting observation that may reduce costs and exposure to higher doses of medication at the start of treatment,” Dr. Goodson said.
Among the patients who received secukinumab at any point in the study, 63% had a treatment-emergent adverse event, including 5.9% with serious events. One death was reported in the placebo group before week 16. No other deaths were reported.
AxSpA trial details
In the axSpA trial, called INVIGORATE-1, researchers recruited people aged ≥18 years with a diagnosis of active radiographic axSpA according to modified New York criteria or nonradiographic axSpA according to ASAS criteria, and all had inflammatory back pain for ≥6 months with an onset before age 45. They were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive IV secukinumab (6 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks) or placebo for 16 weeks. At that point, the placebo group switched to the same monthly doses of IV secukinumab.
Participants had a mean age of about 39, and about one-third were female.
Following the statistical superiority in ASAS 40 response rates seen with IV secukinumab at week 16, patients who from there switched from placebo to IV secukinumab achieved comparable ASAS 40 response rates to those of patients originally randomized to secukinumab by week 24, reaching 66.8% for those on secukinumab the whole time and 74.9% for those who switched.
Secondary outcome measures were similar in both groups at week 52.
Among all patients who took secukinumab – the percentage with any adverse event was 63.2%, and 6% had a nonfatal adverse event deemed serious. There was one death during secukinumab treatment not suspected to be related to treatment.
In a presentation about the axSpA study findings, Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, noted that “having an IV biologic available in the U.S. has some advantages. There are certain insurance providers such as Medicare where it is more economical for the patient to have an IV drug available.”
Dr. Deodhar also noted that in October the FDA approved a recommended lower dose for the IV treatment than in the study: 1.75 mg/kg instead of 3 mg/kg following the loading dose. That’s because the 3 mg/kg dose caused blood levels to be higher than those in the subcutaneous form, he said.
The FDA made the same dose recommendation for PsA.
Study limitations
Dr. Goodson, the U.K. consultant rheumatologist, noted a limitation of the trials: “It would have been interesting to compare IV to subcutaneous route secukinumab.” Still, the findings suggest that “the safety and efficacy of IV administration appears comparable,” she said.
“IV administration will have associated costs of attending hospital or infusion clinics,” she added, “and the cost of additional staff and administration need to be considered.”
Novartis, the maker of secukinumab, funded both studies. The PsA study authors report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Kivitz, have connections to Novartis. The axSpA study authors also report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Deodhar, have connections to Novartis. Some authors of both studies are Novartis employees. Dr. Goodson disclosed financial relationships with UCB and AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Monthly use of intravenously administered secukinumab (Cosentyx) proved its efficacy over placebo in treating psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in two industry-sponsored, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 trials of the drug’s second and newly approved route of administration.
The studies of the human monoclonal antibody secukinumab, an interleukin-17 inhibitor, were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. A subcutaneously injectable formulation of the drug is available, and the Food and Drug Administration approved the IV form for the conditions in October, although at a recommended lower monthly dose than the new trials examined.
In the PsA trial, 191 patients took IV secukinumab, and 190 took placebo. For the primary endpoint, the percentages who reached at least a 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR 50) at 16 weeks were 31.4% and 6.3%, respectively (P < .0001).
In the axSpA trial, 264 patients took IV secukinumab, and 262 took placebo. The primary endpoint, at least a 40% improvement in Assessment of the Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), was met at 16 weeks by 40.9% and 22.9%, respectively (P < .0001).
“Both studies appear to present clear efficacy of IV route administration of secukinumab with no clear increase in safety signals,” consultant rheumatologist Nicola Goodson, MBChB, PhD, of Aintree University Hospital in Liverpool, England, said in an interview.
“Offering IV administration as an option to patients is helpful,” added Dr. Goodson, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings.
As Dr. Goodson explained, secukinumab “was the first IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor used to treat spondyloarthropathies, and we have been using subcutaneous secukinumab to treat psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis/ankylosing spondylitis since 2016 in the U.K. Our experience with this medication has been good with similar efficacy to anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapy in axial spondyloarthritis. The medication is generally well-tolerated, and the subcutaneous pen injection device is easy for patients to use.”
However, IV treatment may speed up onset of action, she said, and it may be useful in situations when compliance is a challenge.
PsA trial details
In the PsA trial, known as INVIGORATE-2, researchers recruited patients who met the CASPAR criteria for active PsA with symptoms for ≥ 6 months, and had ≥ 3 tender joints out of 78 joints and ≥ 3 swollen joints out of 76.
Participants with a mean age of 48, including 55% females, were randomized 1:1 to receive placebo or secukinumab (6 mg/kg at baseline followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks). Those in the placebo group were switched to the same monthly doses of secukinumab at 16 weeks.
“Patients who switched from the placebo had a similar increase of efficacy as the original treated group,” rheumatologist Alan J. Kivitz, MD, of the Altoona Center for Clinical Research, in Duncansville, Penn., said in his presentation at the meeting. Specifically, at 52 weeks, the groups had similar ACR 50 response rates: 58% with secukinumab and 64% with placebo-to-secukinumab.
The fact that patients in the original placebo group who received 3 mg IV doses without 6-mg loading doses achieved ACR response rates similar to those who took secukinumab during the whole trial “could suggest that the IV loading dose may not be required. This would need to be explored in a randomized head-to-head study, but it’s an interesting observation that may reduce costs and exposure to higher doses of medication at the start of treatment,” Dr. Goodson said.
Among the patients who received secukinumab at any point in the study, 63% had a treatment-emergent adverse event, including 5.9% with serious events. One death was reported in the placebo group before week 16. No other deaths were reported.
AxSpA trial details
In the axSpA trial, called INVIGORATE-1, researchers recruited people aged ≥18 years with a diagnosis of active radiographic axSpA according to modified New York criteria or nonradiographic axSpA according to ASAS criteria, and all had inflammatory back pain for ≥6 months with an onset before age 45. They were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive IV secukinumab (6 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks) or placebo for 16 weeks. At that point, the placebo group switched to the same monthly doses of IV secukinumab.
Participants had a mean age of about 39, and about one-third were female.
Following the statistical superiority in ASAS 40 response rates seen with IV secukinumab at week 16, patients who from there switched from placebo to IV secukinumab achieved comparable ASAS 40 response rates to those of patients originally randomized to secukinumab by week 24, reaching 66.8% for those on secukinumab the whole time and 74.9% for those who switched.
Secondary outcome measures were similar in both groups at week 52.
Among all patients who took secukinumab – the percentage with any adverse event was 63.2%, and 6% had a nonfatal adverse event deemed serious. There was one death during secukinumab treatment not suspected to be related to treatment.
In a presentation about the axSpA study findings, Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, noted that “having an IV biologic available in the U.S. has some advantages. There are certain insurance providers such as Medicare where it is more economical for the patient to have an IV drug available.”
Dr. Deodhar also noted that in October the FDA approved a recommended lower dose for the IV treatment than in the study: 1.75 mg/kg instead of 3 mg/kg following the loading dose. That’s because the 3 mg/kg dose caused blood levels to be higher than those in the subcutaneous form, he said.
The FDA made the same dose recommendation for PsA.
Study limitations
Dr. Goodson, the U.K. consultant rheumatologist, noted a limitation of the trials: “It would have been interesting to compare IV to subcutaneous route secukinumab.” Still, the findings suggest that “the safety and efficacy of IV administration appears comparable,” she said.
“IV administration will have associated costs of attending hospital or infusion clinics,” she added, “and the cost of additional staff and administration need to be considered.”
Novartis, the maker of secukinumab, funded both studies. The PsA study authors report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Kivitz, have connections to Novartis. The axSpA study authors also report multiple relationships with industry, and some, such as Dr. Deodhar, have connections to Novartis. Some authors of both studies are Novartis employees. Dr. Goodson disclosed financial relationships with UCB and AbbVie.
AT ACR 2023
First referral guide issued for axial spondyloarthritis
SAN DIEGO – The Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) has created the first referral recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
The draft recommendations use a points scoring system, with the goal that at least one in three patients referred would be diagnosed with axSpA, an inflammatory arthritis that affects the central skeleton and shares a genetic overlap with skin psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammatory eye disease.
Patients with axSpA can wait 10 years after symptom onset to be diagnosed with the condition. There are currently no guidelines to advise clinicians on when to refer to a rheumatologist, and with the rheumatology workforce shortage, “it is impossible for rheumatologists to evaluate the 20% of adults in the U.S. who have chronic back pain,” said Maureen Dubreuil, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston University. She presented the work at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
To address this issue, Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues conducted a literature review to determine how predictive different spondyloarthritis features were of eventual axSpA diagnosis. The interdisciplinary team identified 38 studies published before March 2022, and uncovered 28 individual potential features associated with axSpA, including pain sites, family history of axSpA and related conditions, blood markers of inflammation, genetic testing, and imaging findings.
Inflammatory back pain elements had the lower predictive values, with positive likelihood ratios (LR+) ranging from 1.15 to 2.32, while imaging findings were the most predictive (LR+s from 6.40 to 10.02).
Using a Delphi exercise and discrete choice experiments, members narrowed the checklist down to 10 features. These 10 features were assigned points, with a score of 3 points qualifying for a referral of adults 45 years or younger with chronic pain (3 or more months) in the back, hip, or buttock.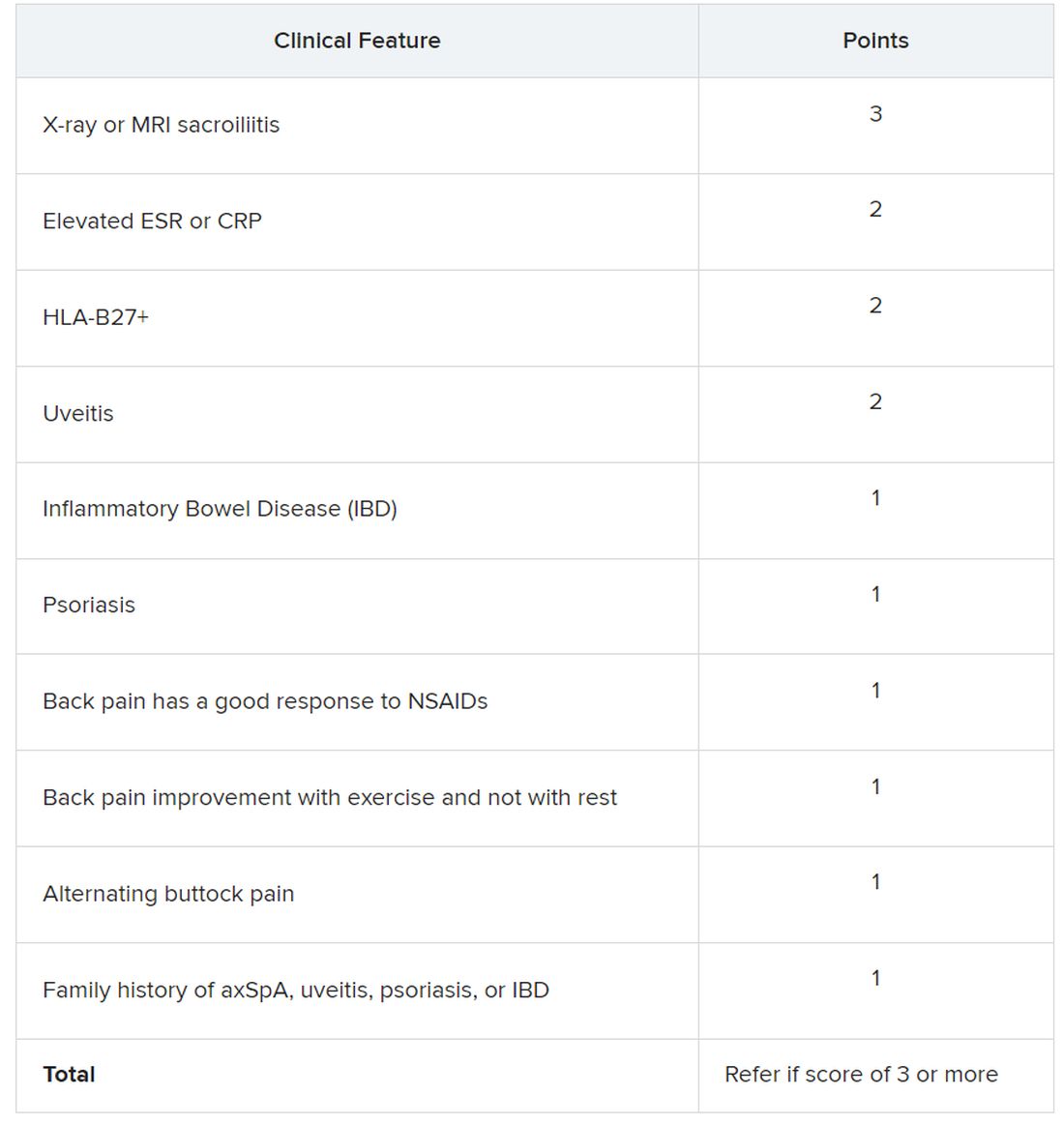
Sacroiliitis seen on imaging, either by x-ray or MRI, received the highest score of 3 points. Dr. Dubreuil emphasized that imaging was not required for a referral, but if a patient has received imaging “that shows sacroiliitis, that is sufficient for referral to a rheumatologist,” she said in her presentation.
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 positivity, and uveitis score 2 points. Inflammatory bowel disease; psoriasis; back pain with good response to NSAIDs; back pain improvement with exercise and not with rest; alternating buttock pain; and family history of axial spondyloarthritis, uveitis, psoriasis, or IBD score 1 point.
Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues expect that these criteria for referral will result in about one in three referred adults aged 45 years or younger with chronic back pain being diagnosed with axSpA. They also say additional research is necessary to understand if these recommendations increase probability of axSpA diagnosis and reduce diagnostic delays.
“We’re now getting to the stage where we are creating this screening tool, but [testing the] performance of the screening tool is going to be the major next step,” said Mark Hwang, MD, of UTHealth Houston in an interview with this news organization. He is a member of SPARTAN but was not involved with authoring the recommendations. “Will the screening tool enhance the ability on the back end to identify axSpA? We don’t know yet.”
Jon Chan, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, agreed that these recommendations “are a good first step,” but that more awareness about axSpA from nonrheumatologists would also be helpful in identifying new axSpA patients. He is also a member of SPARTAN and comoderated with Dr. Hwang the session where the new recommendations were presented. “I think other diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus have a lot more recognition in the nonrheumatology community,” he told this news organization.
Connecting with other health professionals who see a lot of patients with back pain – physiotherapists, chiropractors, and chronic pain physicians – could also be helpful, he added. “A lot of times, patients go straight to a physio and circumvent the doctor,” he said.
Dr. Chan reports success in educating other departments. “I put up a poster in the emergency department saying, ‘If you’re young with back pain and uveitis, you need to be seen by rheumatology,’ and we’ve identified a ton of axSpA patients that way,” he said. “Maybe their uveitis was very mild, but their back pain was quite severe, and no one really clued in.”
Dr. Dubreuil disclosed financial relationships with Amgen, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma. Her abstract coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hwang consults for UCB and has received research support from Janssen. Dr. Chan has relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB.
SAN DIEGO – The Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) has created the first referral recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
The draft recommendations use a points scoring system, with the goal that at least one in three patients referred would be diagnosed with axSpA, an inflammatory arthritis that affects the central skeleton and shares a genetic overlap with skin psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammatory eye disease.
Patients with axSpA can wait 10 years after symptom onset to be diagnosed with the condition. There are currently no guidelines to advise clinicians on when to refer to a rheumatologist, and with the rheumatology workforce shortage, “it is impossible for rheumatologists to evaluate the 20% of adults in the U.S. who have chronic back pain,” said Maureen Dubreuil, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston University. She presented the work at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
To address this issue, Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues conducted a literature review to determine how predictive different spondyloarthritis features were of eventual axSpA diagnosis. The interdisciplinary team identified 38 studies published before March 2022, and uncovered 28 individual potential features associated with axSpA, including pain sites, family history of axSpA and related conditions, blood markers of inflammation, genetic testing, and imaging findings.
Inflammatory back pain elements had the lower predictive values, with positive likelihood ratios (LR+) ranging from 1.15 to 2.32, while imaging findings were the most predictive (LR+s from 6.40 to 10.02).
Using a Delphi exercise and discrete choice experiments, members narrowed the checklist down to 10 features. These 10 features were assigned points, with a score of 3 points qualifying for a referral of adults 45 years or younger with chronic pain (3 or more months) in the back, hip, or buttock.
Sacroiliitis seen on imaging, either by x-ray or MRI, received the highest score of 3 points. Dr. Dubreuil emphasized that imaging was not required for a referral, but if a patient has received imaging “that shows sacroiliitis, that is sufficient for referral to a rheumatologist,” she said in her presentation.
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 positivity, and uveitis score 2 points. Inflammatory bowel disease; psoriasis; back pain with good response to NSAIDs; back pain improvement with exercise and not with rest; alternating buttock pain; and family history of axial spondyloarthritis, uveitis, psoriasis, or IBD score 1 point.
Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues expect that these criteria for referral will result in about one in three referred adults aged 45 years or younger with chronic back pain being diagnosed with axSpA. They also say additional research is necessary to understand if these recommendations increase probability of axSpA diagnosis and reduce diagnostic delays.
“We’re now getting to the stage where we are creating this screening tool, but [testing the] performance of the screening tool is going to be the major next step,” said Mark Hwang, MD, of UTHealth Houston in an interview with this news organization. He is a member of SPARTAN but was not involved with authoring the recommendations. “Will the screening tool enhance the ability on the back end to identify axSpA? We don’t know yet.”
Jon Chan, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, agreed that these recommendations “are a good first step,” but that more awareness about axSpA from nonrheumatologists would also be helpful in identifying new axSpA patients. He is also a member of SPARTAN and comoderated with Dr. Hwang the session where the new recommendations were presented. “I think other diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus have a lot more recognition in the nonrheumatology community,” he told this news organization.
Connecting with other health professionals who see a lot of patients with back pain – physiotherapists, chiropractors, and chronic pain physicians – could also be helpful, he added. “A lot of times, patients go straight to a physio and circumvent the doctor,” he said.
Dr. Chan reports success in educating other departments. “I put up a poster in the emergency department saying, ‘If you’re young with back pain and uveitis, you need to be seen by rheumatology,’ and we’ve identified a ton of axSpA patients that way,” he said. “Maybe their uveitis was very mild, but their back pain was quite severe, and no one really clued in.”
Dr. Dubreuil disclosed financial relationships with Amgen, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma. Her abstract coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hwang consults for UCB and has received research support from Janssen. Dr. Chan has relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB.
SAN DIEGO – The Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) has created the first referral recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
The draft recommendations use a points scoring system, with the goal that at least one in three patients referred would be diagnosed with axSpA, an inflammatory arthritis that affects the central skeleton and shares a genetic overlap with skin psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammatory eye disease.
Patients with axSpA can wait 10 years after symptom onset to be diagnosed with the condition. There are currently no guidelines to advise clinicians on when to refer to a rheumatologist, and with the rheumatology workforce shortage, “it is impossible for rheumatologists to evaluate the 20% of adults in the U.S. who have chronic back pain,” said Maureen Dubreuil, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston University. She presented the work at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
To address this issue, Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues conducted a literature review to determine how predictive different spondyloarthritis features were of eventual axSpA diagnosis. The interdisciplinary team identified 38 studies published before March 2022, and uncovered 28 individual potential features associated with axSpA, including pain sites, family history of axSpA and related conditions, blood markers of inflammation, genetic testing, and imaging findings.
Inflammatory back pain elements had the lower predictive values, with positive likelihood ratios (LR+) ranging from 1.15 to 2.32, while imaging findings were the most predictive (LR+s from 6.40 to 10.02).
Using a Delphi exercise and discrete choice experiments, members narrowed the checklist down to 10 features. These 10 features were assigned points, with a score of 3 points qualifying for a referral of adults 45 years or younger with chronic pain (3 or more months) in the back, hip, or buttock.
Sacroiliitis seen on imaging, either by x-ray or MRI, received the highest score of 3 points. Dr. Dubreuil emphasized that imaging was not required for a referral, but if a patient has received imaging “that shows sacroiliitis, that is sufficient for referral to a rheumatologist,” she said in her presentation.
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein, HLA-B27 positivity, and uveitis score 2 points. Inflammatory bowel disease; psoriasis; back pain with good response to NSAIDs; back pain improvement with exercise and not with rest; alternating buttock pain; and family history of axial spondyloarthritis, uveitis, psoriasis, or IBD score 1 point.
Dr. Dubreuil and colleagues expect that these criteria for referral will result in about one in three referred adults aged 45 years or younger with chronic back pain being diagnosed with axSpA. They also say additional research is necessary to understand if these recommendations increase probability of axSpA diagnosis and reduce diagnostic delays.
“We’re now getting to the stage where we are creating this screening tool, but [testing the] performance of the screening tool is going to be the major next step,” said Mark Hwang, MD, of UTHealth Houston in an interview with this news organization. He is a member of SPARTAN but was not involved with authoring the recommendations. “Will the screening tool enhance the ability on the back end to identify axSpA? We don’t know yet.”
Jon Chan, MD, a rheumatologist at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, agreed that these recommendations “are a good first step,” but that more awareness about axSpA from nonrheumatologists would also be helpful in identifying new axSpA patients. He is also a member of SPARTAN and comoderated with Dr. Hwang the session where the new recommendations were presented. “I think other diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus have a lot more recognition in the nonrheumatology community,” he told this news organization.
Connecting with other health professionals who see a lot of patients with back pain – physiotherapists, chiropractors, and chronic pain physicians – could also be helpful, he added. “A lot of times, patients go straight to a physio and circumvent the doctor,” he said.
Dr. Chan reports success in educating other departments. “I put up a poster in the emergency department saying, ‘If you’re young with back pain and uveitis, you need to be seen by rheumatology,’ and we’ve identified a ton of axSpA patients that way,” he said. “Maybe their uveitis was very mild, but their back pain was quite severe, and no one really clued in.”
Dr. Dubreuil disclosed financial relationships with Amgen, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma. Her abstract coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hwang consults for UCB and has received research support from Janssen. Dr. Chan has relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB.
AT ACR 2023
TNF blockers not associated with poorer pregnancy outcomes
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2023
Approximately 20% of U.S. adults are diagnosed with arthritis
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anemia, iron deficit common in rheumatic disease pregnancy
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a longitudinal cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from 368 pregnancies in women with rheumatic diseases during the period 2014-2022; nearly two-thirds (62%) had a connective tissue disease, 16% had rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis, 14% had spondyloarthritis, 3% had vasculitis, and 7% had other diseases.
- Patients were aged 17-44 years, with a median age of 32 years at the time of birth.
- Researchers examined the frequency of anemia and iron deficiency and the impact of anemia on adverse maternal and child outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of iron deficiency was 28%, 51%, and 62% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- The prevalence of anemia was 18%, 27%, and 33% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- There was an increased risk for fetal complications such as malformation, infections, small for gestational age, neonatal lupus, preterm birth, and abortion or stillbirth in association with maternal connective tissue disease (odds ratio, 2.14) and also with low maternal hemoglobin levels and maternal iron deficiency (ORs, 0.52 and 0.86, respectively).
- Lower maternal hemoglobin levels were associated with an increased risk for maternal complications (OR, 1.47) such as flare with adaption of rheumatic medication and pregnancy-related adverse events (preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, bleeding complications, and thromboembolism), but patients with connective tissue disease had a lower risk for maternal complications (OR, 0.51); mean serum ferritin had no significant impact on maternal complications (OR, 1.02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with rheumatic diseases suffer more often and already in early pregnancy from iron deficiency,” the researchers write. Therefore, early identification of anemia and iron deficiency in this population could inform prepregnancy counseling.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Ann-Christin Pecher, MD, of University Hospital Tübingen, Germany. The study was published online in Joint Bone Spine.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the use of a single dataset that might not be representative of all pregnant patients with rheumatic diseases. Other limitations included the lack of a standardized approach to iron supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the Medical Faculty of Tübingen Clinician-Scientist to the lead author. The researchers report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a longitudinal cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from 368 pregnancies in women with rheumatic diseases during the period 2014-2022; nearly two-thirds (62%) had a connective tissue disease, 16% had rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis, 14% had spondyloarthritis, 3% had vasculitis, and 7% had other diseases.
- Patients were aged 17-44 years, with a median age of 32 years at the time of birth.
- Researchers examined the frequency of anemia and iron deficiency and the impact of anemia on adverse maternal and child outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of iron deficiency was 28%, 51%, and 62% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- The prevalence of anemia was 18%, 27%, and 33% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- There was an increased risk for fetal complications such as malformation, infections, small for gestational age, neonatal lupus, preterm birth, and abortion or stillbirth in association with maternal connective tissue disease (odds ratio, 2.14) and also with low maternal hemoglobin levels and maternal iron deficiency (ORs, 0.52 and 0.86, respectively).
- Lower maternal hemoglobin levels were associated with an increased risk for maternal complications (OR, 1.47) such as flare with adaption of rheumatic medication and pregnancy-related adverse events (preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, bleeding complications, and thromboembolism), but patients with connective tissue disease had a lower risk for maternal complications (OR, 0.51); mean serum ferritin had no significant impact on maternal complications (OR, 1.02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with rheumatic diseases suffer more often and already in early pregnancy from iron deficiency,” the researchers write. Therefore, early identification of anemia and iron deficiency in this population could inform prepregnancy counseling.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Ann-Christin Pecher, MD, of University Hospital Tübingen, Germany. The study was published online in Joint Bone Spine.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the use of a single dataset that might not be representative of all pregnant patients with rheumatic diseases. Other limitations included the lack of a standardized approach to iron supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the Medical Faculty of Tübingen Clinician-Scientist to the lead author. The researchers report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a longitudinal cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from 368 pregnancies in women with rheumatic diseases during the period 2014-2022; nearly two-thirds (62%) had a connective tissue disease, 16% had rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis, 14% had spondyloarthritis, 3% had vasculitis, and 7% had other diseases.
- Patients were aged 17-44 years, with a median age of 32 years at the time of birth.
- Researchers examined the frequency of anemia and iron deficiency and the impact of anemia on adverse maternal and child outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of iron deficiency was 28%, 51%, and 62% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- The prevalence of anemia was 18%, 27%, and 33% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively.
- There was an increased risk for fetal complications such as malformation, infections, small for gestational age, neonatal lupus, preterm birth, and abortion or stillbirth in association with maternal connective tissue disease (odds ratio, 2.14) and also with low maternal hemoglobin levels and maternal iron deficiency (ORs, 0.52 and 0.86, respectively).
- Lower maternal hemoglobin levels were associated with an increased risk for maternal complications (OR, 1.47) such as flare with adaption of rheumatic medication and pregnancy-related adverse events (preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, bleeding complications, and thromboembolism), but patients with connective tissue disease had a lower risk for maternal complications (OR, 0.51); mean serum ferritin had no significant impact on maternal complications (OR, 1.02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with rheumatic diseases suffer more often and already in early pregnancy from iron deficiency,” the researchers write. Therefore, early identification of anemia and iron deficiency in this population could inform prepregnancy counseling.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Ann-Christin Pecher, MD, of University Hospital Tübingen, Germany. The study was published online in Joint Bone Spine.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the use of a single dataset that might not be representative of all pregnant patients with rheumatic diseases. Other limitations included the lack of a standardized approach to iron supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the Medical Faculty of Tübingen Clinician-Scientist to the lead author. The researchers report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are women and men with rheumatism treated equally?
LEIPZIG, GERMANY – Women eat more healthily, visit their physician more often, and accept offers of prophylactic treatment more frequently than their male counterparts. Nevertheless, they are generally diagnosed with a rheumatic disease much later. “With systemic sclerosis for example, diagnosis occurs a whole year later than for male patients,” said Uta Kiltz, MD, senior physician at the Ruhrgebiet Rheumatism Center in Bochum, Germany, at a press conference for the annual congress of the German Society for Rheumatology.
In addition, certain markers and antibodies can be detected earlier in men’s blood – for example in systemic sclerosis. “What’s more, women exhibit a more diverse array of symptoms, which can make an unequivocal diagnosis difficult,” Dr. Kiltz explained.
Differences between the sexes in terms of disease progression and clinical presentation have been described for most rheumatic diseases. Roughly speaking, women often exhibit a much wider range of symptoms and report a higher disease burden, whereas men tend to experience a more severe progression of the disease.
Comorbidities also occur at different rates between the sexes. Whereas women with rheumatoid arthritis suffer more frequently from osteoporosis and depression, men are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Gender-sensitive approach
Like Dr. Kiltz, Susanna Späthling-Mestekemper, MD, PhD, of the Munich-Pasing (Germany) Rheumatology Practice, also advocates a gender-sensitive approach to diagnosis and therapy. Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper referred to this during the conference, stating that women are still treated more poorly than men. The difference in treatment quality results from gaps in knowledge in the following areas:
- Sex-specific differences in the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases and in basic and clinical research
- Sex-specific differences in communication between male and female patients and between male and female physicians.
Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper used axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) as a “prominent example” of false diagnoses. “Men more commonly fulfill the modified New York criteria – involvement of the axial skeleton, the lumbar spine, and increasing radiological progression.”
In contrast, women with axSpA exhibit the following differences:
- It is more likely for the cervical spine to be affected.
- Women are more likely to suffer from peripheral joint involvement.
- They suffer more from whole body pain.
- They have fatigue and exhaustion.
- They exhibit fewer humoral signs of inflammation (lower C-reactive protein).
- They are rarely HLA-B27 positive.
“We also have to completely rethink how we make the diagnosis in women,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. The current approach leads to women with axSpA being diagnosed much later than men. “Depending on the study, the difference can range from 7 months to 2 years,” according to Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
A 2018 Spanish study reported that the most common incorrect diagnoses in women with axSpA were sciatica, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
However, it is not just in axSpA that there are significant differences between men and women. There is evidence that women with systemic lupus erythematosus suffer more from musculoskeletal symptoms, while men with lupus exhibit more severe organ involvement (especially more serositis and nephritis).
For systemic sclerosis, women have the higher survival rate. They also exhibit skin involvement more frequently. Men, however, are more likely to have organ involvement, especially with the lungs.
TNF blockers
Using the example of axSpA, Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper also showed that men and women respond differently to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker therapy. “The duration of therapy with TNF blockers is shorter for women: 33.4 months versus 44.9 months. They respond less to this therapy; they stop and change more frequently.”
Data from March 2023 show that, in contrast, there is no evidence of a difference in response to Janus kinase inhibitor treatment.
The presence of enthesitis has been discussed as one reason for the worse response to TNF blockers in women, since they have it more often than men do. “In fact, a better response to TNF blockers is associated with HLA-B27 positivity, with the absence of enthesitis and with TNF blocker naivety. In women, higher fat-mass index could also play a part, or even abdominal weight gain, which also increases in women after menopause,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
She mentioned the following other potential reasons for a delayed therapy response to biological drugs in women:
- Genetic, physical, or hormonal causes
- Widespread pain or fibromyalgia
- Late diagnosis or late application of therapy, which lowers the chances of remission.
Even the science itself has shown the following sex-specific shortcomings:
- Disregarding sex-specific differences in animal-experimental studies (which, until recently, were only conducted in male mice to avoid hormone fluctuations)
- Women in clinical studies are still underrepresented: only 37% of the populations in phase 3 studies are women; 64% of studies do not describe any sex-specific differences
- Most of the data come from epidemiological analyses (not from basic research)
- Gaps in medical textbooks
Communication differences
Female patients are looking for explanations, whereas male patients describe specific symptoms. Female physicians talk, while male physicians treat. They sound like stereotypes, but they have been substantiated in multiple studies, said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. In general, the study results show that male patients behave in the following ways:
- Describe their symptoms in terms of specifics
- Do not like to admit having mental health issues
- Are three to five times more likely to commit suicide because of depression than women
On the other hand, female patients behave in the following ways:
- Look for an explanation for their symptoms
- Often do not have their physical symptoms taken seriously
- Are often pushed in a psychosomatic direction.
Female physicians focus on the following questions:
- Prevention, communication, shared decision-making, open-ended questions, “positive” discussions, patient self-management (chronic diseases such as diabetes: female physicians are better at reaching the therapy goals set by the ADA guidelines than male physicians)
- Psychosocial situations: consultations last 1 minute longer (10%).
Male physicians focus on the following questions:
- Medical history
- Physical examination (cardiac catheterizations after a heart attack are arranged much more commonly by male rather than female physicians)
- Diagnostics
Recognition and training
A large-scale surgical study in 2021 made a few waves. The study analyzed whether it makes a difference if women are operated on by men or by women. The results showed that women who had been operated on by men exhibited a higher level of risk after the surgery, compared with men who had been operated on by men or by women. The risk took the following forms:
- 15% higher risk for a worse surgery result
- 16% higher risk for complications
- 11% higher risk for repeat hospitalization
- 20% higher risk for a longer period of hospitalization
- 32% higher risk for mortality
The study authors provided the following potential reasons for these differences:
- Male physicians underestimate the severity of symptoms in their female patients
- Women are less comfortable indicating their postoperative pain to a male physician
- Different working style and treatment decisions between female and male physicians
- Unconsciously incorporated role patterns and preconceptions
“Our potential solutions are recognition and training. We need a personalized style of medicine; we need to have a closer look. We owe our male and female patients as much,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
LEIPZIG, GERMANY – Women eat more healthily, visit their physician more often, and accept offers of prophylactic treatment more frequently than their male counterparts. Nevertheless, they are generally diagnosed with a rheumatic disease much later. “With systemic sclerosis for example, diagnosis occurs a whole year later than for male patients,” said Uta Kiltz, MD, senior physician at the Ruhrgebiet Rheumatism Center in Bochum, Germany, at a press conference for the annual congress of the German Society for Rheumatology.
In addition, certain markers and antibodies can be detected earlier in men’s blood – for example in systemic sclerosis. “What’s more, women exhibit a more diverse array of symptoms, which can make an unequivocal diagnosis difficult,” Dr. Kiltz explained.
Differences between the sexes in terms of disease progression and clinical presentation have been described for most rheumatic diseases. Roughly speaking, women often exhibit a much wider range of symptoms and report a higher disease burden, whereas men tend to experience a more severe progression of the disease.
Comorbidities also occur at different rates between the sexes. Whereas women with rheumatoid arthritis suffer more frequently from osteoporosis and depression, men are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Gender-sensitive approach
Like Dr. Kiltz, Susanna Späthling-Mestekemper, MD, PhD, of the Munich-Pasing (Germany) Rheumatology Practice, also advocates a gender-sensitive approach to diagnosis and therapy. Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper referred to this during the conference, stating that women are still treated more poorly than men. The difference in treatment quality results from gaps in knowledge in the following areas:
- Sex-specific differences in the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases and in basic and clinical research
- Sex-specific differences in communication between male and female patients and between male and female physicians.
Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper used axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) as a “prominent example” of false diagnoses. “Men more commonly fulfill the modified New York criteria – involvement of the axial skeleton, the lumbar spine, and increasing radiological progression.”
In contrast, women with axSpA exhibit the following differences:
- It is more likely for the cervical spine to be affected.
- Women are more likely to suffer from peripheral joint involvement.
- They suffer more from whole body pain.
- They have fatigue and exhaustion.
- They exhibit fewer humoral signs of inflammation (lower C-reactive protein).
- They are rarely HLA-B27 positive.
“We also have to completely rethink how we make the diagnosis in women,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. The current approach leads to women with axSpA being diagnosed much later than men. “Depending on the study, the difference can range from 7 months to 2 years,” according to Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
A 2018 Spanish study reported that the most common incorrect diagnoses in women with axSpA were sciatica, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
However, it is not just in axSpA that there are significant differences between men and women. There is evidence that women with systemic lupus erythematosus suffer more from musculoskeletal symptoms, while men with lupus exhibit more severe organ involvement (especially more serositis and nephritis).
For systemic sclerosis, women have the higher survival rate. They also exhibit skin involvement more frequently. Men, however, are more likely to have organ involvement, especially with the lungs.
TNF blockers
Using the example of axSpA, Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper also showed that men and women respond differently to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker therapy. “The duration of therapy with TNF blockers is shorter for women: 33.4 months versus 44.9 months. They respond less to this therapy; they stop and change more frequently.”
Data from March 2023 show that, in contrast, there is no evidence of a difference in response to Janus kinase inhibitor treatment.
The presence of enthesitis has been discussed as one reason for the worse response to TNF blockers in women, since they have it more often than men do. “In fact, a better response to TNF blockers is associated with HLA-B27 positivity, with the absence of enthesitis and with TNF blocker naivety. In women, higher fat-mass index could also play a part, or even abdominal weight gain, which also increases in women after menopause,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
She mentioned the following other potential reasons for a delayed therapy response to biological drugs in women:
- Genetic, physical, or hormonal causes
- Widespread pain or fibromyalgia
- Late diagnosis or late application of therapy, which lowers the chances of remission.
Even the science itself has shown the following sex-specific shortcomings:
- Disregarding sex-specific differences in animal-experimental studies (which, until recently, were only conducted in male mice to avoid hormone fluctuations)
- Women in clinical studies are still underrepresented: only 37% of the populations in phase 3 studies are women; 64% of studies do not describe any sex-specific differences
- Most of the data come from epidemiological analyses (not from basic research)
- Gaps in medical textbooks
Communication differences
Female patients are looking for explanations, whereas male patients describe specific symptoms. Female physicians talk, while male physicians treat. They sound like stereotypes, but they have been substantiated in multiple studies, said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. In general, the study results show that male patients behave in the following ways:
- Describe their symptoms in terms of specifics
- Do not like to admit having mental health issues
- Are three to five times more likely to commit suicide because of depression than women
On the other hand, female patients behave in the following ways:
- Look for an explanation for their symptoms
- Often do not have their physical symptoms taken seriously
- Are often pushed in a psychosomatic direction.
Female physicians focus on the following questions:
- Prevention, communication, shared decision-making, open-ended questions, “positive” discussions, patient self-management (chronic diseases such as diabetes: female physicians are better at reaching the therapy goals set by the ADA guidelines than male physicians)
- Psychosocial situations: consultations last 1 minute longer (10%).
Male physicians focus on the following questions:
- Medical history
- Physical examination (cardiac catheterizations after a heart attack are arranged much more commonly by male rather than female physicians)
- Diagnostics
Recognition and training
A large-scale surgical study in 2021 made a few waves. The study analyzed whether it makes a difference if women are operated on by men or by women. The results showed that women who had been operated on by men exhibited a higher level of risk after the surgery, compared with men who had been operated on by men or by women. The risk took the following forms:
- 15% higher risk for a worse surgery result
- 16% higher risk for complications
- 11% higher risk for repeat hospitalization
- 20% higher risk for a longer period of hospitalization
- 32% higher risk for mortality
The study authors provided the following potential reasons for these differences:
- Male physicians underestimate the severity of symptoms in their female patients
- Women are less comfortable indicating their postoperative pain to a male physician
- Different working style and treatment decisions between female and male physicians
- Unconsciously incorporated role patterns and preconceptions
“Our potential solutions are recognition and training. We need a personalized style of medicine; we need to have a closer look. We owe our male and female patients as much,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
LEIPZIG, GERMANY – Women eat more healthily, visit their physician more often, and accept offers of prophylactic treatment more frequently than their male counterparts. Nevertheless, they are generally diagnosed with a rheumatic disease much later. “With systemic sclerosis for example, diagnosis occurs a whole year later than for male patients,” said Uta Kiltz, MD, senior physician at the Ruhrgebiet Rheumatism Center in Bochum, Germany, at a press conference for the annual congress of the German Society for Rheumatology.
In addition, certain markers and antibodies can be detected earlier in men’s blood – for example in systemic sclerosis. “What’s more, women exhibit a more diverse array of symptoms, which can make an unequivocal diagnosis difficult,” Dr. Kiltz explained.
Differences between the sexes in terms of disease progression and clinical presentation have been described for most rheumatic diseases. Roughly speaking, women often exhibit a much wider range of symptoms and report a higher disease burden, whereas men tend to experience a more severe progression of the disease.
Comorbidities also occur at different rates between the sexes. Whereas women with rheumatoid arthritis suffer more frequently from osteoporosis and depression, men are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Gender-sensitive approach
Like Dr. Kiltz, Susanna Späthling-Mestekemper, MD, PhD, of the Munich-Pasing (Germany) Rheumatology Practice, also advocates a gender-sensitive approach to diagnosis and therapy. Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper referred to this during the conference, stating that women are still treated more poorly than men. The difference in treatment quality results from gaps in knowledge in the following areas:
- Sex-specific differences in the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases and in basic and clinical research
- Sex-specific differences in communication between male and female patients and between male and female physicians.
Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper used axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) as a “prominent example” of false diagnoses. “Men more commonly fulfill the modified New York criteria – involvement of the axial skeleton, the lumbar spine, and increasing radiological progression.”
In contrast, women with axSpA exhibit the following differences:
- It is more likely for the cervical spine to be affected.
- Women are more likely to suffer from peripheral joint involvement.
- They suffer more from whole body pain.
- They have fatigue and exhaustion.
- They exhibit fewer humoral signs of inflammation (lower C-reactive protein).
- They are rarely HLA-B27 positive.
“We also have to completely rethink how we make the diagnosis in women,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. The current approach leads to women with axSpA being diagnosed much later than men. “Depending on the study, the difference can range from 7 months to 2 years,” according to Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
A 2018 Spanish study reported that the most common incorrect diagnoses in women with axSpA were sciatica, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
However, it is not just in axSpA that there are significant differences between men and women. There is evidence that women with systemic lupus erythematosus suffer more from musculoskeletal symptoms, while men with lupus exhibit more severe organ involvement (especially more serositis and nephritis).
For systemic sclerosis, women have the higher survival rate. They also exhibit skin involvement more frequently. Men, however, are more likely to have organ involvement, especially with the lungs.
TNF blockers
Using the example of axSpA, Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper also showed that men and women respond differently to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker therapy. “The duration of therapy with TNF blockers is shorter for women: 33.4 months versus 44.9 months. They respond less to this therapy; they stop and change more frequently.”
Data from March 2023 show that, in contrast, there is no evidence of a difference in response to Janus kinase inhibitor treatment.
The presence of enthesitis has been discussed as one reason for the worse response to TNF blockers in women, since they have it more often than men do. “In fact, a better response to TNF blockers is associated with HLA-B27 positivity, with the absence of enthesitis and with TNF blocker naivety. In women, higher fat-mass index could also play a part, or even abdominal weight gain, which also increases in women after menopause,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
She mentioned the following other potential reasons for a delayed therapy response to biological drugs in women:
- Genetic, physical, or hormonal causes
- Widespread pain or fibromyalgia
- Late diagnosis or late application of therapy, which lowers the chances of remission.
Even the science itself has shown the following sex-specific shortcomings:
- Disregarding sex-specific differences in animal-experimental studies (which, until recently, were only conducted in male mice to avoid hormone fluctuations)
- Women in clinical studies are still underrepresented: only 37% of the populations in phase 3 studies are women; 64% of studies do not describe any sex-specific differences
- Most of the data come from epidemiological analyses (not from basic research)
- Gaps in medical textbooks
Communication differences
Female patients are looking for explanations, whereas male patients describe specific symptoms. Female physicians talk, while male physicians treat. They sound like stereotypes, but they have been substantiated in multiple studies, said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper. In general, the study results show that male patients behave in the following ways:
- Describe their symptoms in terms of specifics
- Do not like to admit having mental health issues
- Are three to five times more likely to commit suicide because of depression than women
On the other hand, female patients behave in the following ways:
- Look for an explanation for their symptoms
- Often do not have their physical symptoms taken seriously
- Are often pushed in a psychosomatic direction.
Female physicians focus on the following questions:
- Prevention, communication, shared decision-making, open-ended questions, “positive” discussions, patient self-management (chronic diseases such as diabetes: female physicians are better at reaching the therapy goals set by the ADA guidelines than male physicians)
- Psychosocial situations: consultations last 1 minute longer (10%).
Male physicians focus on the following questions:
- Medical history
- Physical examination (cardiac catheterizations after a heart attack are arranged much more commonly by male rather than female physicians)
- Diagnostics
Recognition and training
A large-scale surgical study in 2021 made a few waves. The study analyzed whether it makes a difference if women are operated on by men or by women. The results showed that women who had been operated on by men exhibited a higher level of risk after the surgery, compared with men who had been operated on by men or by women. The risk took the following forms:
- 15% higher risk for a worse surgery result
- 16% higher risk for complications
- 11% higher risk for repeat hospitalization
- 20% higher risk for a longer period of hospitalization
- 32% higher risk for mortality
The study authors provided the following potential reasons for these differences:
- Male physicians underestimate the severity of symptoms in their female patients
- Women are less comfortable indicating their postoperative pain to a male physician
- Different working style and treatment decisions between female and male physicians
- Unconsciously incorporated role patterns and preconceptions
“Our potential solutions are recognition and training. We need a personalized style of medicine; we need to have a closer look. We owe our male and female patients as much,” said Dr. Späthling-Mestekemper.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE GERMAN RHEUMATOLOGY CONGRESS 2023
Intravenous formulation of secukinumab gets FDA approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves ninth Humira biosimilar, with interchangeability
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.








