User login
Pediatric Dermatology Consult - July 2018
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
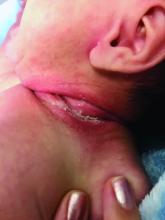
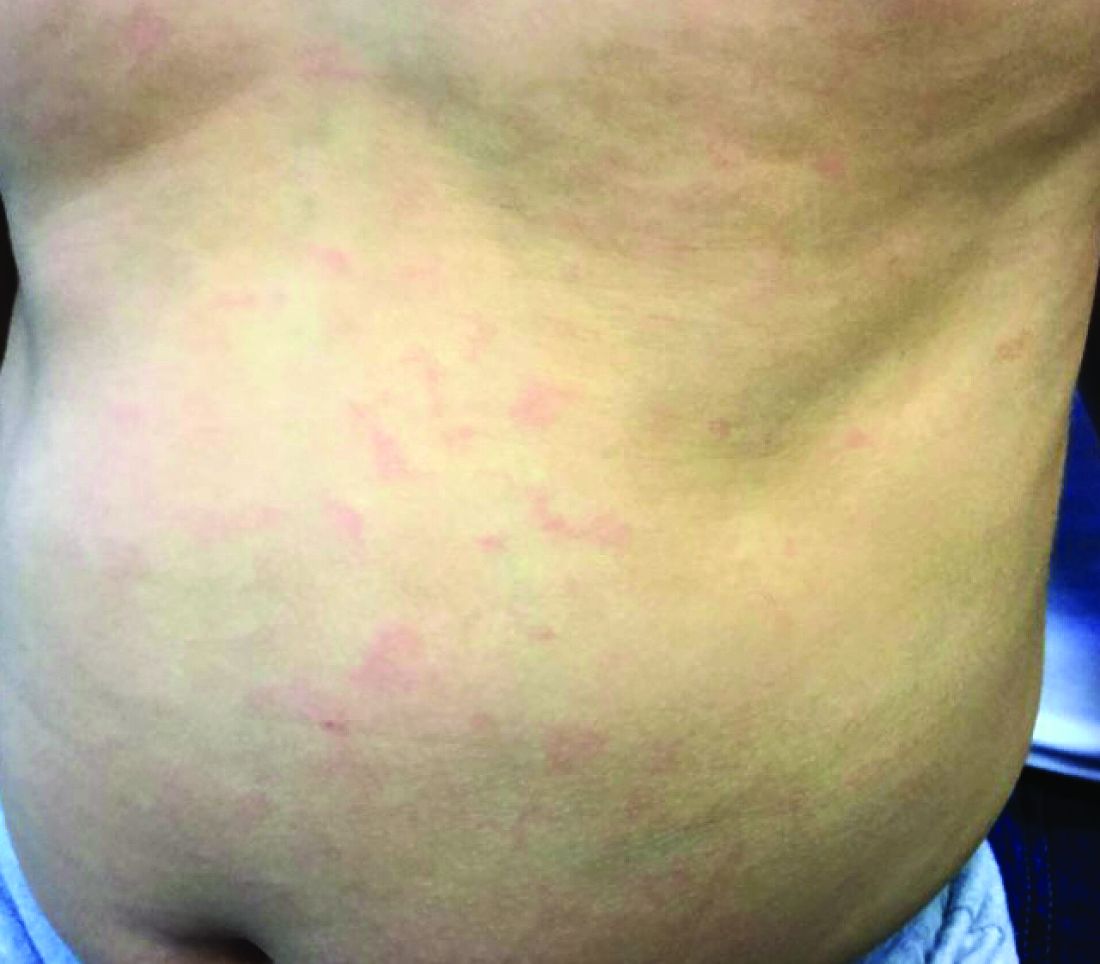
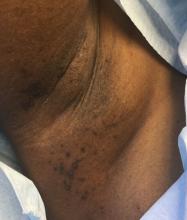
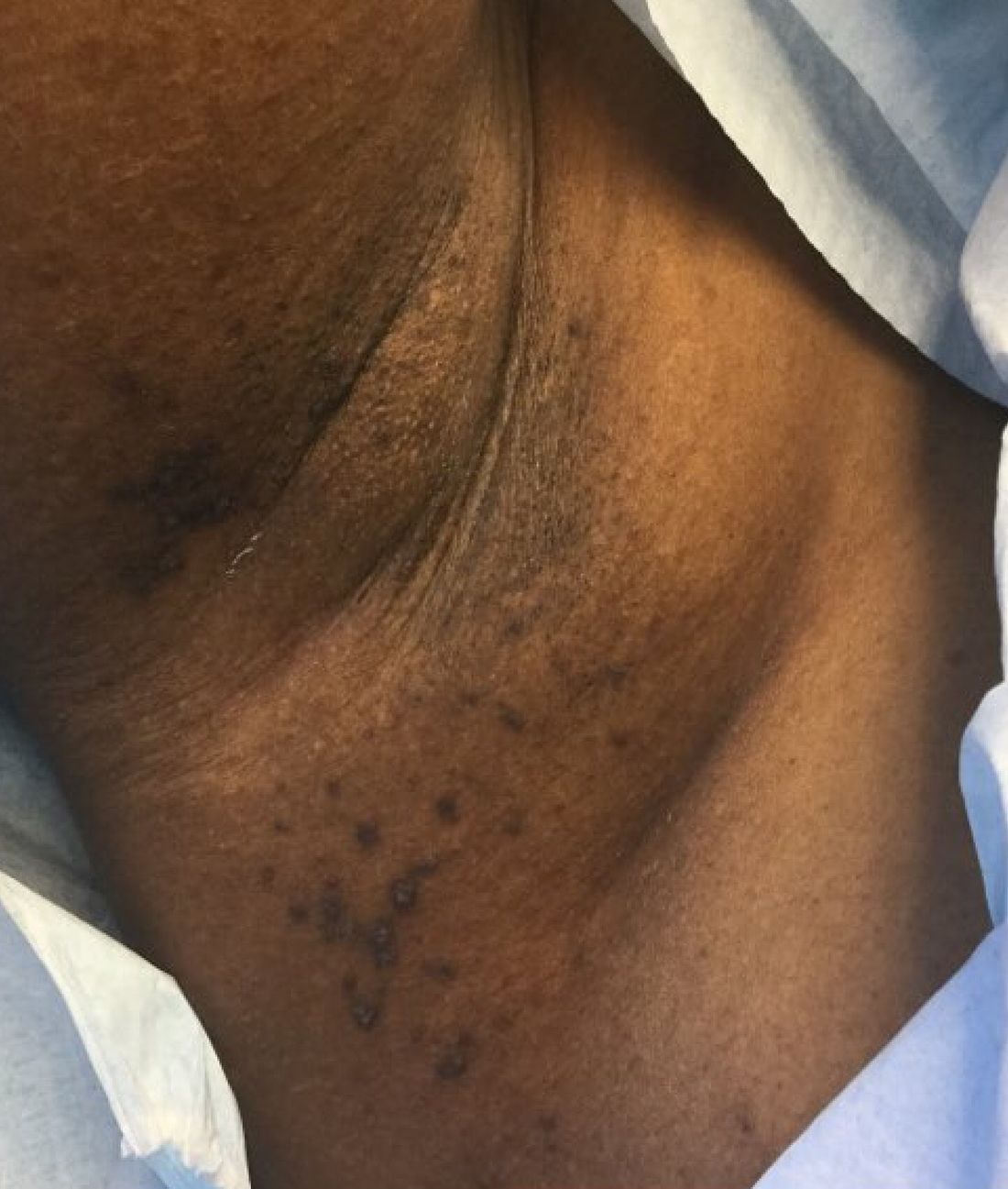
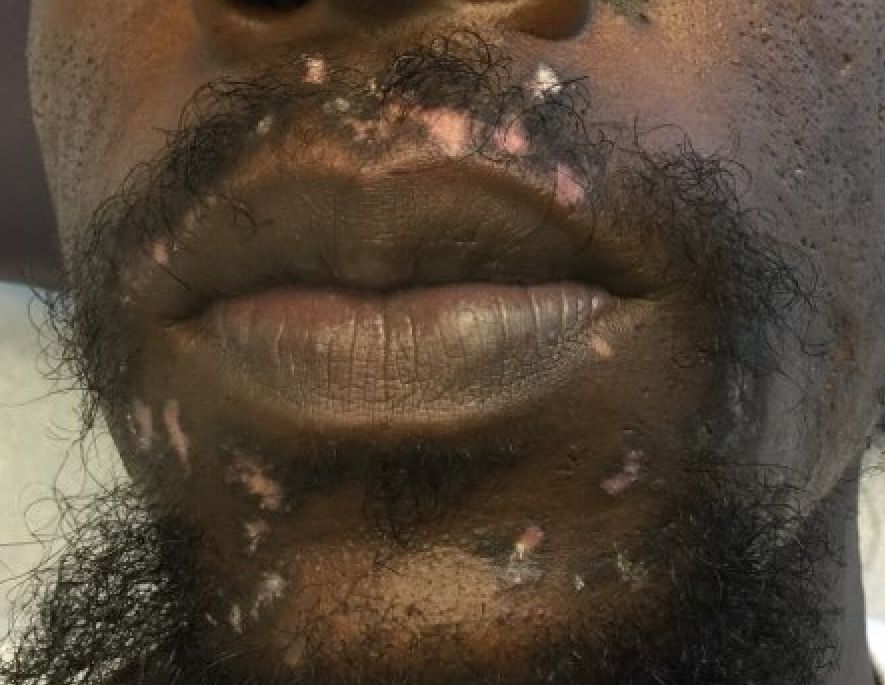
An 8-week-old male with a history of cradle cap presented for a second evaluation of an erythematous rash on the neck that started 1.5 weeks before, and it had since worsened. The parents note that their infant has been more irritable, but they otherwise deny any fever, diarrhea, constipation, or decrease in oral intake.
The patient’s first evaluation had been 3 days prior; nystatin cream was prescribed, and the parents applied it twice a day but without improvement to the rash. The patient also had a rash behind the ears bilaterally, which was treated with hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment with some improvement
On physical exam, the central neck is covered by a bright, beefy red, erythematous plaque with distinct borders and strong odor. There is faint scale and superficial desquamation between the skin folds. There are no surrounding papules or pustules. The patient’s chin is moist with drool. In the postauricular skin folds bilaterally, there are fainter but still erythematous plaques with mild scale.
Make the Diagnosis - June 2018
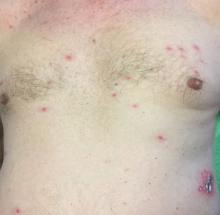
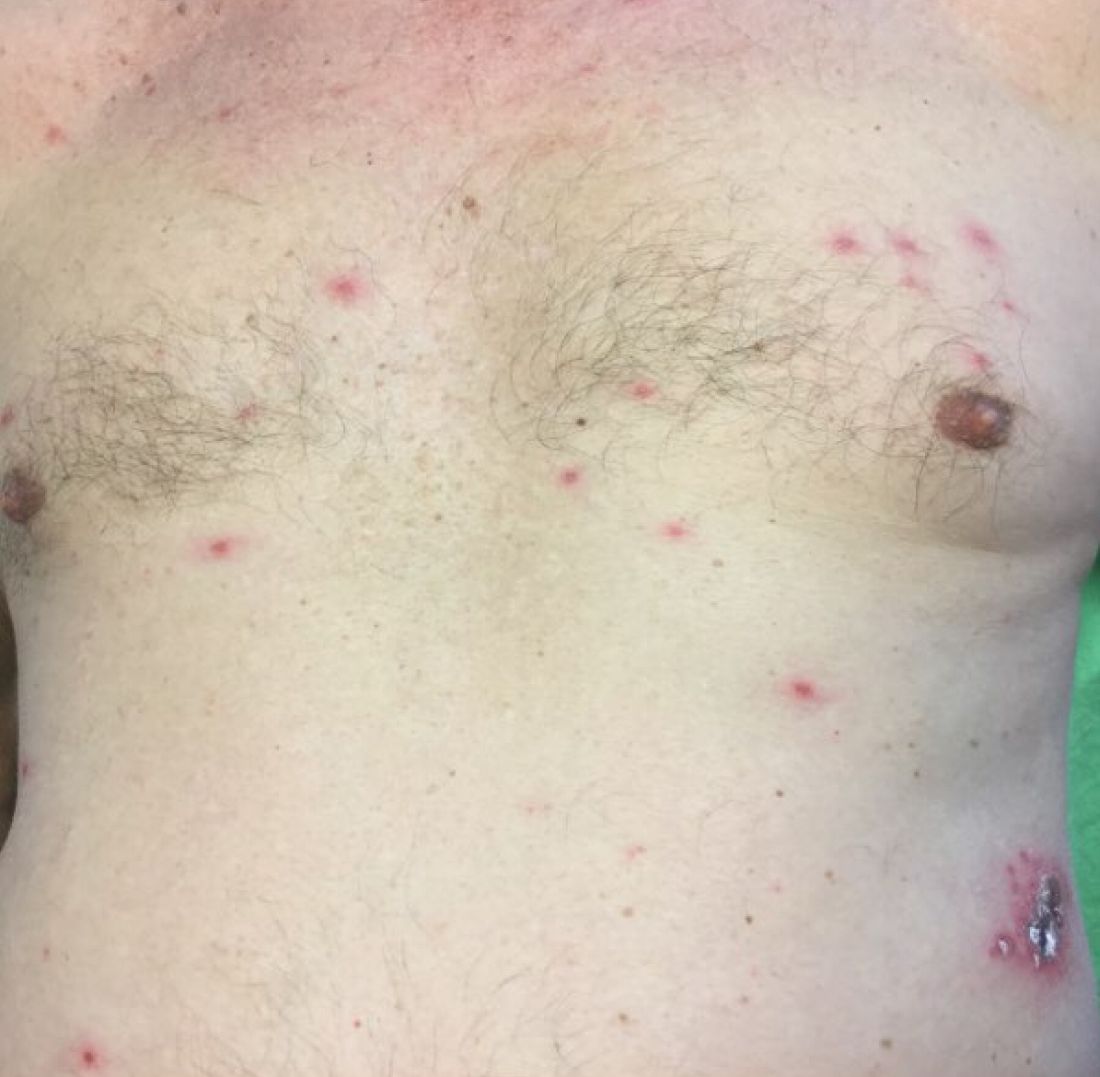
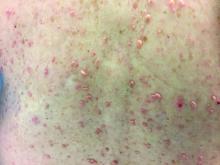
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Make the Diagnosis - May 2018
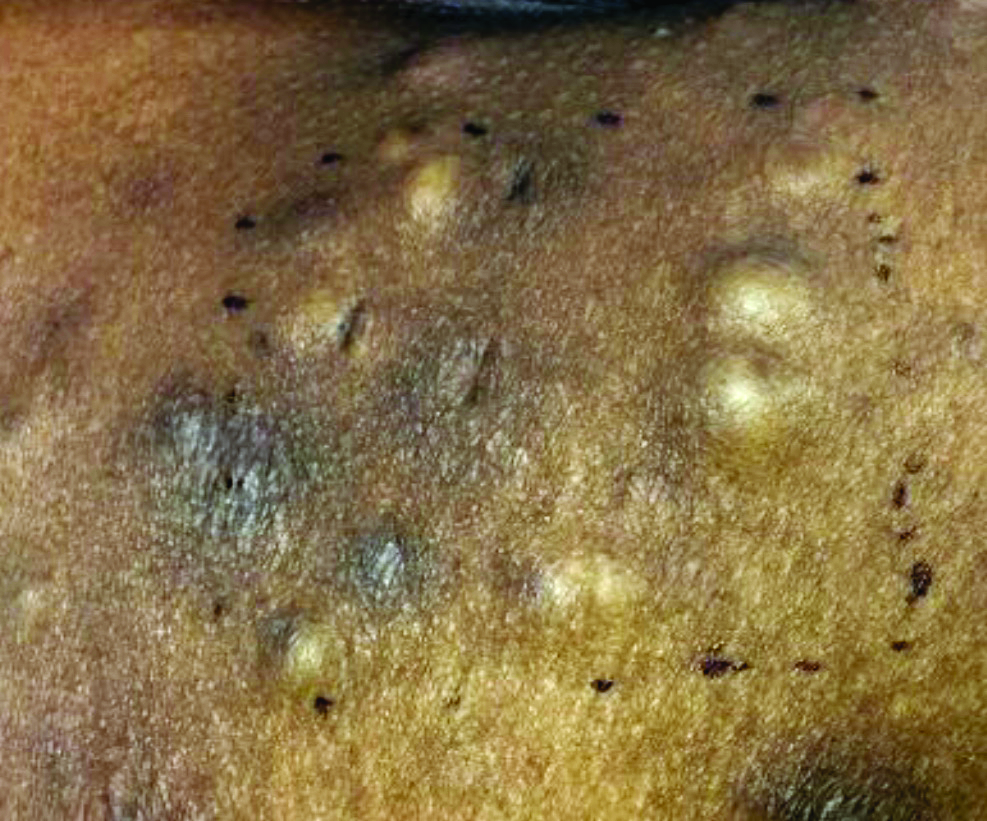
and through close skin contact, as well as contaminated clothes and bedding. Adult lice can live up to 36 hours away from its host. Pubic areas most commonly are affected, although other hair-bearing parts of the body often are affected, including eyelashes.
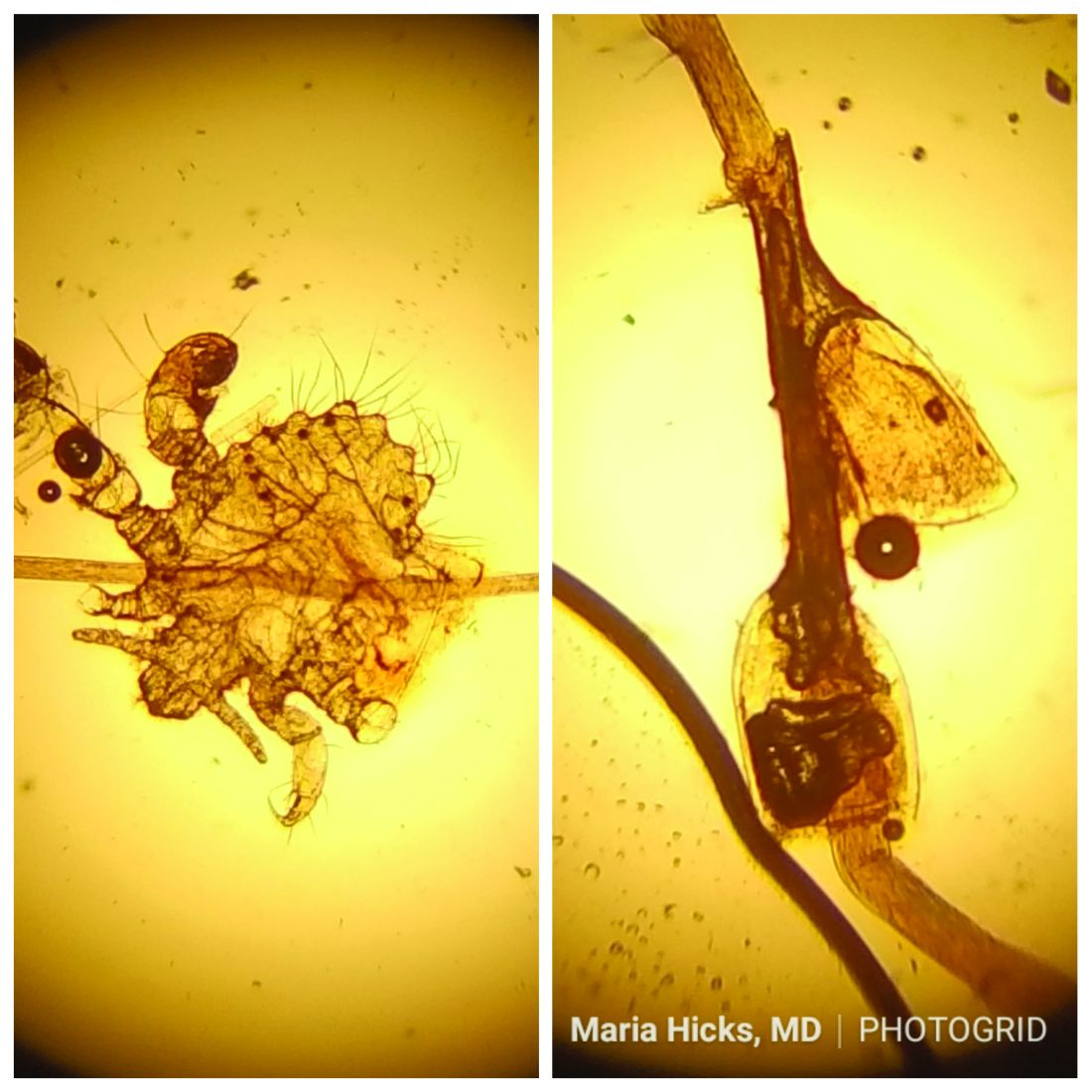
Pruritus can be severe. Secondary bacterial infections may occur as maculae ceruleae, or blue-colored macules, on the skin. The lice are visible to the naked eye and are approximately 1 mm in length. They have a crablike appearance, six legs, and a wide body. Nits may be present on the hair shaft. Unlike hair casts, which can be moved up and down along the hair shaft, nits firmly adhere to the hair. Diagnosis should prompt a workup for other sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV.
Treatment for patients and their sexual partners include permethrin topically; and laundering of clothing and bedding. Lice on the eyelashes can be treated with 8 days of twice-daily applications of petrolatum. Ivermectin can be used when topical therapy fails, although this is an off-label treatment (not approved by the Food and Drug Administration).
Pediculosis corporis – body lice or clothing lice – is also known as “vagabond’s disease” and is caused by Pediculus humanus var corporis. Body lice lay their eggs in clothing seams and can live in clothing for up to 1 month without feeding on human blood. Often homeless individuals and those living in overcrowded areas can be affected. The louse and nits also are visible to the naked eye. They have a longer, narrower body than Phthirus pubis and are more similar in appearance to head lice. They rarely are found on the skin.
Body lice may carry disease such as epidemic typhus, relapsing fever, and trench fever or endocarditis. Permethrin is the most widely used treatment to kill both lice and ova. Other treatments include Malathion, Lindane, and Crotamiton. Clothing and bedding should be laundered.
Scabies is a mite infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. Unlike lice, scabies often affects the hands and feet. Characteristic linear burrows may be seen in the finger web spaces. The circle of Hebra describes the areas commonly infected by mites: axillae, antecubital fossa, wrists, hands, and the groin. Pruritus may be severe and worse at night. Patients may be afflicted with both lice and scabies at the same time. Mites are not visible to the naked eye but can be seen microscopically. Topical permethrin cream is used most often for treatment. All household contacts should be treated at the same time. As in louse infestations, clothing and bedding should be laundered. Ivermectin can be used for crusted scabies, although this is an off-label treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Maria Hicks, MD, Advanced Dermatology and Cosmetic Surgery, Tampa, and Dr. Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
and through close skin contact, as well as contaminated clothes and bedding. Adult lice can live up to 36 hours away from its host. Pubic areas most commonly are affected, although other hair-bearing parts of the body often are affected, including eyelashes.
Pruritus can be severe. Secondary bacterial infections may occur as maculae ceruleae, or blue-colored macules, on the skin. The lice are visible to the naked eye and are approximately 1 mm in length. They have a crablike appearance, six legs, and a wide body. Nits may be present on the hair shaft. Unlike hair casts, which can be moved up and down along the hair shaft, nits firmly adhere to the hair. Diagnosis should prompt a workup for other sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV.
Treatment for patients and their sexual partners include permethrin topically; and laundering of clothing and bedding. Lice on the eyelashes can be treated with 8 days of twice-daily applications of petrolatum. Ivermectin can be used when topical therapy fails, although this is an off-label treatment (not approved by the Food and Drug Administration).
Pediculosis corporis – body lice or clothing lice – is also known as “vagabond’s disease” and is caused by Pediculus humanus var corporis. Body lice lay their eggs in clothing seams and can live in clothing for up to 1 month without feeding on human blood. Often homeless individuals and those living in overcrowded areas can be affected. The louse and nits also are visible to the naked eye. They have a longer, narrower body than Phthirus pubis and are more similar in appearance to head lice. They rarely are found on the skin.
Body lice may carry disease such as epidemic typhus, relapsing fever, and trench fever or endocarditis. Permethrin is the most widely used treatment to kill both lice and ova. Other treatments include Malathion, Lindane, and Crotamiton. Clothing and bedding should be laundered.
Scabies is a mite infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. Unlike lice, scabies often affects the hands and feet. Characteristic linear burrows may be seen in the finger web spaces. The circle of Hebra describes the areas commonly infected by mites: axillae, antecubital fossa, wrists, hands, and the groin. Pruritus may be severe and worse at night. Patients may be afflicted with both lice and scabies at the same time. Mites are not visible to the naked eye but can be seen microscopically. Topical permethrin cream is used most often for treatment. All household contacts should be treated at the same time. As in louse infestations, clothing and bedding should be laundered. Ivermectin can be used for crusted scabies, although this is an off-label treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Maria Hicks, MD, Advanced Dermatology and Cosmetic Surgery, Tampa, and Dr. Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
and through close skin contact, as well as contaminated clothes and bedding. Adult lice can live up to 36 hours away from its host. Pubic areas most commonly are affected, although other hair-bearing parts of the body often are affected, including eyelashes.
Pruritus can be severe. Secondary bacterial infections may occur as maculae ceruleae, or blue-colored macules, on the skin. The lice are visible to the naked eye and are approximately 1 mm in length. They have a crablike appearance, six legs, and a wide body. Nits may be present on the hair shaft. Unlike hair casts, which can be moved up and down along the hair shaft, nits firmly adhere to the hair. Diagnosis should prompt a workup for other sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV.
Treatment for patients and their sexual partners include permethrin topically; and laundering of clothing and bedding. Lice on the eyelashes can be treated with 8 days of twice-daily applications of petrolatum. Ivermectin can be used when topical therapy fails, although this is an off-label treatment (not approved by the Food and Drug Administration).
Pediculosis corporis – body lice or clothing lice – is also known as “vagabond’s disease” and is caused by Pediculus humanus var corporis. Body lice lay their eggs in clothing seams and can live in clothing for up to 1 month without feeding on human blood. Often homeless individuals and those living in overcrowded areas can be affected. The louse and nits also are visible to the naked eye. They have a longer, narrower body than Phthirus pubis and are more similar in appearance to head lice. They rarely are found on the skin.
Body lice may carry disease such as epidemic typhus, relapsing fever, and trench fever or endocarditis. Permethrin is the most widely used treatment to kill both lice and ova. Other treatments include Malathion, Lindane, and Crotamiton. Clothing and bedding should be laundered.
Scabies is a mite infestation caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. Unlike lice, scabies often affects the hands and feet. Characteristic linear burrows may be seen in the finger web spaces. The circle of Hebra describes the areas commonly infected by mites: axillae, antecubital fossa, wrists, hands, and the groin. Pruritus may be severe and worse at night. Patients may be afflicted with both lice and scabies at the same time. Mites are not visible to the naked eye but can be seen microscopically. Topical permethrin cream is used most often for treatment. All household contacts should be treated at the same time. As in louse infestations, clothing and bedding should be laundered. Ivermectin can be used for crusted scabies, although this is an off-label treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Maria Hicks, MD, Advanced Dermatology and Cosmetic Surgery, Tampa, and Dr. Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
A 40-year-old HIV-positive male presented with a 1-month history of severely pruritic papules on his chest. The patient reported that he "removes bugs" from his skin. Microscopic examination of a hair clipping was performed.
Make the Diagnosis:
Make the Diagnosis - May 2018
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Generally, school-aged children are most often affected. Infections are more likely in late winter and early spring. The virus is spread via respiratory secretions, blood products, and transmission from mother to fetus. The cutaneous findings occur about 10 days after exposure to the virus. By that time, the risk of being contagious is low.
Healthy individuals have no sequelae from fifth disease and require no treatment. However, in patients with hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease, an aplastic crisis can be triggered. In patients with deficient immune systems, parvovirus B19 may cause infection and anemia, requiring hospitalization. Pregnant women exposed to parvovirus B19 are at risk for hydrops fetalis and rarely, fetal malformations or fetal demise. Other uncommon associations include hepatitis, vasculitides, and neurologic disease.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Make The Diagnosis - April 2018
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Once an individual has been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, either from primary infection (chickenpox) or vaccination, the virus remains dormant in dorsal root ganglion cells. It may become reactivated at a later time, which results in herpes zoster. Typically, immunosuppression (hematologic malignancy and HIV infection) and age are factors that play a role in reactivation, although young people may develop shingles as well. Older age increases the incidence of herpes zoster.
More than 90% of patients will experience a prodrome of pain, burning, or tingling in the dermatome prior to the development of cutaneous lesions. Occasionally, there will be no symptoms prior. Papules and plaques begin to form, which quickly develop into vesicles and blisters. After a few days, lesions become crusted. Bullae or necrosis may occur in more severe cases. Typically, the condition resolves in 2-3 weeks, but can take 6 weeks or longer in elderly patients. In zoster sine herpete, patients have pain but no skin lesions.
In typical herpes zoster, lesions can be scattered outside the dermatome as well. When more than 20 lesions are scattered outside the area of primary or adjacent dermatomes, this is defined as disseminated herpes zoster. This occurs more commonly in debilitated or immune-compromised individuals. The outlying vesicles are often singular, not grouped, and resemble the “dew drop on a rose petal” look of varicella-zoster lesions. Dissemination necessitates systemic antiviral therapy, preferably intravenous followed by oral treatment once stable. Central nervous system and pulmonary involvement can occur.
Complications of zoster can occur. Postherpetic neuralgia and pain is more common in patients over the age of 50 and may become chronic. Ramsay Hunt syndrome may result in facial paralysis and hearing loss when there is involvement of the facial or auditory nerve. Occasionally, inflammatory lesions can occur within the affected area after the infection has resolved. Secondary bacterial infection, scarring, and motor paralysis can occur.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com. This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
A healthy 70-year-old white male presented with an 8-day history of fatigue and a tingling, erythematous plaque with crusting on the left flank. Four days after the flank lesions appeared, he developed vesicles with an erythematous base on the right abdomen and back. There were more than 20 vesicles present on the abdomen and back, but there were no lesions on other parts of the body.
Make the Diagnosis - March 2018
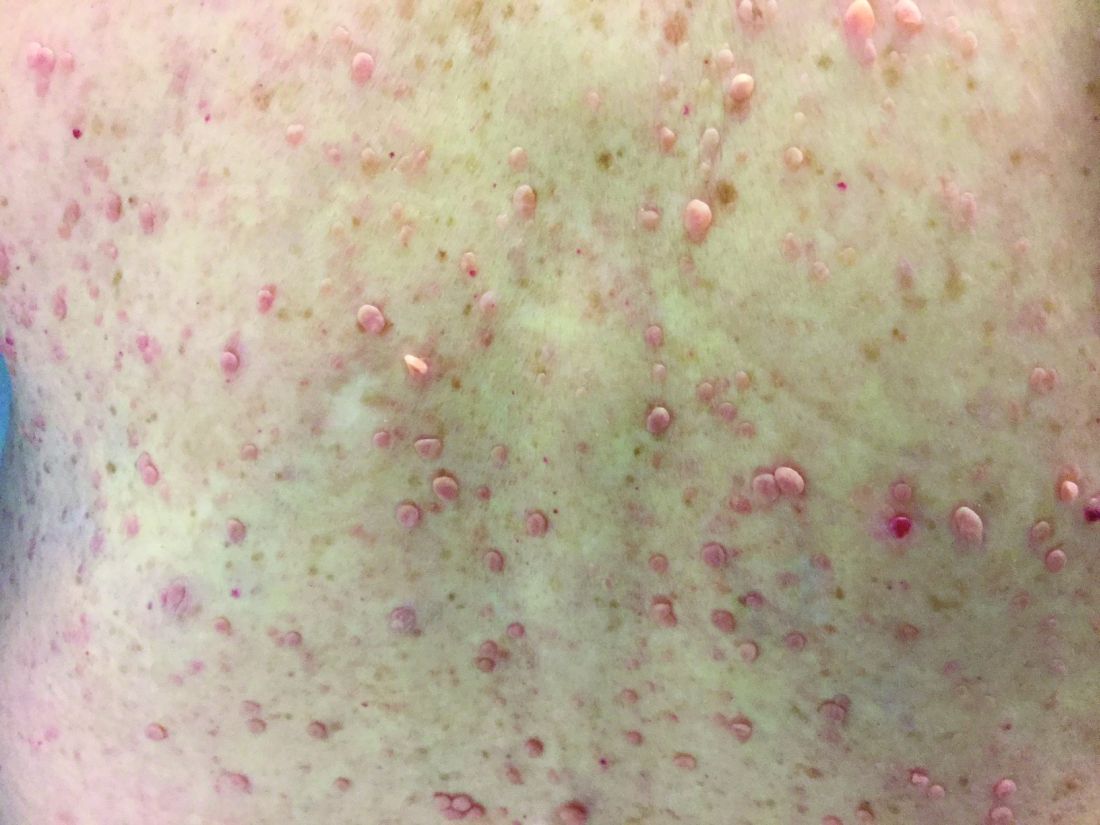
Familial benign chronic pemphigus, also known as Hailey-Hailey disease, is an uncommon autosomal dominant genetic condition. A mutation in the calcium ATPase (ATP2C1) gene on chromosome 3q21 interferes with calcium signaling and results in a loss of keratinocyte adhesion. Generally, the onset of the condition is in the second or third decade. There are two clinical subtypes of the disease: segmental type 1 and segmental type 2.
Histology reveals groups of acantholytic cells that resemble a “dilapidated brick wall.” Direct immunofluorescence is negative, unlike pemphigus vulgaris.
As hyperhidrosis is a known aggravating factor, injection with botulinum toxin (this is off-label use not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration) in affected areas to decrease sweating has been reported to be effective.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Familial benign chronic pemphigus, also known as Hailey-Hailey disease, is an uncommon autosomal dominant genetic condition. A mutation in the calcium ATPase (ATP2C1) gene on chromosome 3q21 interferes with calcium signaling and results in a loss of keratinocyte adhesion. Generally, the onset of the condition is in the second or third decade. There are two clinical subtypes of the disease: segmental type 1 and segmental type 2.
Histology reveals groups of acantholytic cells that resemble a “dilapidated brick wall.” Direct immunofluorescence is negative, unlike pemphigus vulgaris.
As hyperhidrosis is a known aggravating factor, injection with botulinum toxin (this is off-label use not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration) in affected areas to decrease sweating has been reported to be effective.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Familial benign chronic pemphigus, also known as Hailey-Hailey disease, is an uncommon autosomal dominant genetic condition. A mutation in the calcium ATPase (ATP2C1) gene on chromosome 3q21 interferes with calcium signaling and results in a loss of keratinocyte adhesion. Generally, the onset of the condition is in the second or third decade. There are two clinical subtypes of the disease: segmental type 1 and segmental type 2.
Histology reveals groups of acantholytic cells that resemble a “dilapidated brick wall.” Direct immunofluorescence is negative, unlike pemphigus vulgaris.
As hyperhidrosis is a known aggravating factor, injection with botulinum toxin (this is off-label use not yet approved by the Food and Drug Administration) in affected areas to decrease sweating has been reported to be effective.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
A 39-year-old healthy black woman presented with itchy, painful lesions in the bilateral axillae and groin. The lesions have come and gone for 15 years and flare when the patient perspires. Her mother and grandmother have the same condition.
Make the Diagnosis - February 2018
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is an autosomal dominant genetic neurocutaneous disorder. There are eight subtypes of NF: NF type 1-7 and NF-NOS, or not otherwise specified. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen disease, is the most common and is a result of a genetic mutation on chromosome 17 that is involved in producing a protein called neurofibromin. Neurofibromin is a tumor suppressor that suppresses products of ras proto-oncogenes. When it is absent, tumor progression may occur.
Von Recklinghausen NF-1 appears in childhood, usually by age 10. Diagnosis requires the presence of at least 2 of the following 7 criteria:
•Six or more café au lait macules measuring 5 mm in diameter or greater in prepubertal children and measuring greater than 15 mm in postpubertal children.
•Axillary or inguinal freckling (Crowe’s sign).
•Two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma.
•Optic nerve glioma.
•Two or more iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules).
•Sphenoid dysplasia or long-bone abnormalities, such as pseudoarthrosis.
•First degree relative with NF-1.
The diagnosis is usually made via physical examination. Supportive tests include an ophthalmologic exam to detect Lisch nodules and cataracts. A neurological evaluation is essential. Imaging examinations can identify bony abnormalities and tumor growths. Also, genetic testing to identify genetic mutations can be performed.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 results from a genetic mutation located on chromosome 22 that produces a protein called merlin and occurs in adolescence. Acoustic or vestibular neuromas may occur; these interfere with the transmission of sound and maintaining balance. Symptoms include gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, poor balance, and headaches. Radiosurgery and cochlear implants have shown a role for symptomatic treatment in patients with NF-2.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is an autosomal dominant genetic neurocutaneous disorder. There are eight subtypes of NF: NF type 1-7 and NF-NOS, or not otherwise specified. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen disease, is the most common and is a result of a genetic mutation on chromosome 17 that is involved in producing a protein called neurofibromin. Neurofibromin is a tumor suppressor that suppresses products of ras proto-oncogenes. When it is absent, tumor progression may occur.
Von Recklinghausen NF-1 appears in childhood, usually by age 10. Diagnosis requires the presence of at least 2 of the following 7 criteria:
•Six or more café au lait macules measuring 5 mm in diameter or greater in prepubertal children and measuring greater than 15 mm in postpubertal children.
•Axillary or inguinal freckling (Crowe’s sign).
•Two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma.
•Optic nerve glioma.
•Two or more iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules).
•Sphenoid dysplasia or long-bone abnormalities, such as pseudoarthrosis.
•First degree relative with NF-1.
The diagnosis is usually made via physical examination. Supportive tests include an ophthalmologic exam to detect Lisch nodules and cataracts. A neurological evaluation is essential. Imaging examinations can identify bony abnormalities and tumor growths. Also, genetic testing to identify genetic mutations can be performed.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 results from a genetic mutation located on chromosome 22 that produces a protein called merlin and occurs in adolescence. Acoustic or vestibular neuromas may occur; these interfere with the transmission of sound and maintaining balance. Symptoms include gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, poor balance, and headaches. Radiosurgery and cochlear implants have shown a role for symptomatic treatment in patients with NF-2.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is an autosomal dominant genetic neurocutaneous disorder. There are eight subtypes of NF: NF type 1-7 and NF-NOS, or not otherwise specified. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen disease, is the most common and is a result of a genetic mutation on chromosome 17 that is involved in producing a protein called neurofibromin. Neurofibromin is a tumor suppressor that suppresses products of ras proto-oncogenes. When it is absent, tumor progression may occur.
Von Recklinghausen NF-1 appears in childhood, usually by age 10. Diagnosis requires the presence of at least 2 of the following 7 criteria:
•Six or more café au lait macules measuring 5 mm in diameter or greater in prepubertal children and measuring greater than 15 mm in postpubertal children.
•Axillary or inguinal freckling (Crowe’s sign).
•Two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma.
•Optic nerve glioma.
•Two or more iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules).
•Sphenoid dysplasia or long-bone abnormalities, such as pseudoarthrosis.
•First degree relative with NF-1.
The diagnosis is usually made via physical examination. Supportive tests include an ophthalmologic exam to detect Lisch nodules and cataracts. A neurological evaluation is essential. Imaging examinations can identify bony abnormalities and tumor growths. Also, genetic testing to identify genetic mutations can be performed.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 results from a genetic mutation located on chromosome 22 that produces a protein called merlin and occurs in adolescence. Acoustic or vestibular neuromas may occur; these interfere with the transmission of sound and maintaining balance. Symptoms include gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, poor balance, and headaches. Radiosurgery and cochlear implants have shown a role for symptomatic treatment in patients with NF-2.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Make the diagnosis - January 2018
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus can be classified into acute, subacute, and chronic lesions. Chronic cutaneous lupus, or discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They are one of the more common skin presentations seen in lupus. Young adults are typically affected, with a female-to-male ratio of 2:1. Progression from DLE to SLE is uncommon. However, patients with SLE will frequently develop discoid lesions.
The differential diagnosis includes: subacute cutaneous lupus, lichen planus, seborrheic dermatitis, Jessner’s lymphocytic infiltrate, polymorphous light eruption, rosacea, granuloma faciale, and sarcoidosis. Histology of DLE may reveal hyperkeratosis, a thin epidermis with effacement of the rete ridges, a lichenoid and vacuolar interface dermatitis, and follicular plugging. Damaged keratinocytes called colloid bodies may be present. Increased mucin and thickening of the basement membrane are commonly seen. Active lesions will exhibit more of an inflammatory infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in more than 75% of cases.
This case and the photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus can be classified into acute, subacute, and chronic lesions. Chronic cutaneous lupus, or discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They are one of the more common skin presentations seen in lupus. Young adults are typically affected, with a female-to-male ratio of 2:1. Progression from DLE to SLE is uncommon. However, patients with SLE will frequently develop discoid lesions.
The differential diagnosis includes: subacute cutaneous lupus, lichen planus, seborrheic dermatitis, Jessner’s lymphocytic infiltrate, polymorphous light eruption, rosacea, granuloma faciale, and sarcoidosis. Histology of DLE may reveal hyperkeratosis, a thin epidermis with effacement of the rete ridges, a lichenoid and vacuolar interface dermatitis, and follicular plugging. Damaged keratinocytes called colloid bodies may be present. Increased mucin and thickening of the basement membrane are commonly seen. Active lesions will exhibit more of an inflammatory infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in more than 75% of cases.
This case and the photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus can be classified into acute, subacute, and chronic lesions. Chronic cutaneous lupus, or discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), may occur independently of or in combination with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They are one of the more common skin presentations seen in lupus. Young adults are typically affected, with a female-to-male ratio of 2:1. Progression from DLE to SLE is uncommon. However, patients with SLE will frequently develop discoid lesions.
The differential diagnosis includes: subacute cutaneous lupus, lichen planus, seborrheic dermatitis, Jessner’s lymphocytic infiltrate, polymorphous light eruption, rosacea, granuloma faciale, and sarcoidosis. Histology of DLE may reveal hyperkeratosis, a thin epidermis with effacement of the rete ridges, a lichenoid and vacuolar interface dermatitis, and follicular plugging. Damaged keratinocytes called colloid bodies may be present. Increased mucin and thickening of the basement membrane are commonly seen. Active lesions will exhibit more of an inflammatory infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence of lesional skin is positive in more than 75% of cases.
This case and the photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
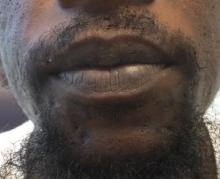
A 32-year-old male with no significant past medical history presented with a 2-year history of asymptomatic perioral lesions. On physical examination, multiple erythematous to hypopigmented atrophic plaques with peripheral hyperpigmentation were present.
Make The Diagnosis - November 2017
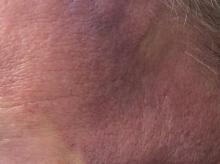
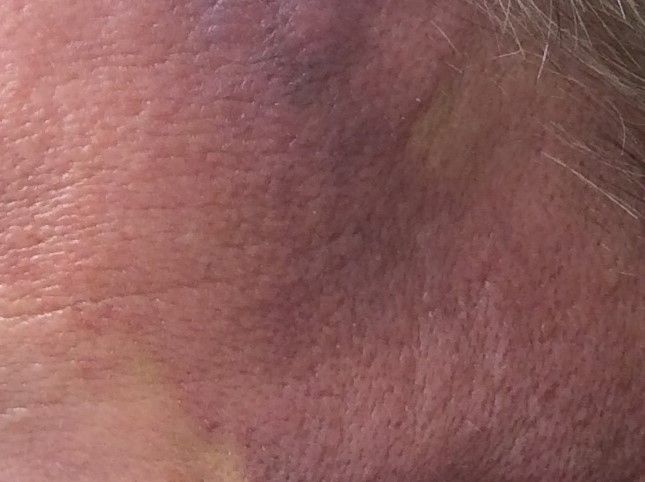
Angiosarcoma is also known as malignant hemangioendothelioma, hemangiosarcoma, and lymphangiosarcoma. It is an uncommon, high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm of the inner lining of blood vessels. Unlike most sarcomas, it occurs more superficially, most often on the head and neck (particularly on the scalp). This neoplasm occurs twice as often in males as it does in females. Angiosarcomas can occur in the breast after radiation therapy, as well as in the liver and spleen, but 60% are cutaneous.
Clinical exam findings may show a violaceous lesion similar to a bruise on the head and neck that does not heal or bleeds when scratched; this is of particular concern when the lesion has appeared in an area of prior radiation therapy. Deeper tumors may be felt as a soft nodule. Ulceration may be present. Biopsy of the lesion will show hyperchromatic, pleomorphic tumor cells that dissect between collagen bundles with endothelial cells that are multilayered along with hemorrhage. Malignant cells stain positive for CD31, CD34, ERG, and FLI1.
For localized disease, surgery with wide local excision plus adjuvant radiation therapy can be used. For metastatic disease, chemotherapy is the treatment modality of choice. Unfortunately, prognosis is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of about 35% in nonmetastatic angiosarcoma cases. The majority of recurrences – approximately 75% – occur within 24 months of local treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and at Barnes-Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Susannah McClain, MD, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Angiosarcoma is also known as malignant hemangioendothelioma, hemangiosarcoma, and lymphangiosarcoma. It is an uncommon, high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm of the inner lining of blood vessels. Unlike most sarcomas, it occurs more superficially, most often on the head and neck (particularly on the scalp). This neoplasm occurs twice as often in males as it does in females. Angiosarcomas can occur in the breast after radiation therapy, as well as in the liver and spleen, but 60% are cutaneous.
Clinical exam findings may show a violaceous lesion similar to a bruise on the head and neck that does not heal or bleeds when scratched; this is of particular concern when the lesion has appeared in an area of prior radiation therapy. Deeper tumors may be felt as a soft nodule. Ulceration may be present. Biopsy of the lesion will show hyperchromatic, pleomorphic tumor cells that dissect between collagen bundles with endothelial cells that are multilayered along with hemorrhage. Malignant cells stain positive for CD31, CD34, ERG, and FLI1.
For localized disease, surgery with wide local excision plus adjuvant radiation therapy can be used. For metastatic disease, chemotherapy is the treatment modality of choice. Unfortunately, prognosis is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of about 35% in nonmetastatic angiosarcoma cases. The majority of recurrences – approximately 75% – occur within 24 months of local treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and at Barnes-Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Susannah McClain, MD, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Angiosarcoma is also known as malignant hemangioendothelioma, hemangiosarcoma, and lymphangiosarcoma. It is an uncommon, high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm of the inner lining of blood vessels. Unlike most sarcomas, it occurs more superficially, most often on the head and neck (particularly on the scalp). This neoplasm occurs twice as often in males as it does in females. Angiosarcomas can occur in the breast after radiation therapy, as well as in the liver and spleen, but 60% are cutaneous.
Clinical exam findings may show a violaceous lesion similar to a bruise on the head and neck that does not heal or bleeds when scratched; this is of particular concern when the lesion has appeared in an area of prior radiation therapy. Deeper tumors may be felt as a soft nodule. Ulceration may be present. Biopsy of the lesion will show hyperchromatic, pleomorphic tumor cells that dissect between collagen bundles with endothelial cells that are multilayered along with hemorrhage. Malignant cells stain positive for CD31, CD34, ERG, and FLI1.
For localized disease, surgery with wide local excision plus adjuvant radiation therapy can be used. For metastatic disease, chemotherapy is the treatment modality of choice. Unfortunately, prognosis is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of about 35% in nonmetastatic angiosarcoma cases. The majority of recurrences – approximately 75% – occur within 24 months of local treatment.
This case and photo were submitted by Parteek Singla, MD, of the division of dermatology at Washington University and at Barnes-Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis, and by Susannah McClain, MD, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
A 62-year-old healthy man presented with a skin lesion located on the left scalp. The lesion was swollen and painful and had been present for 4 months. This lesion had not been treated in the past.
Make the Diagnosis - October 2017
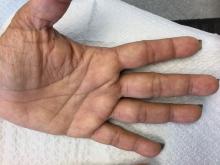
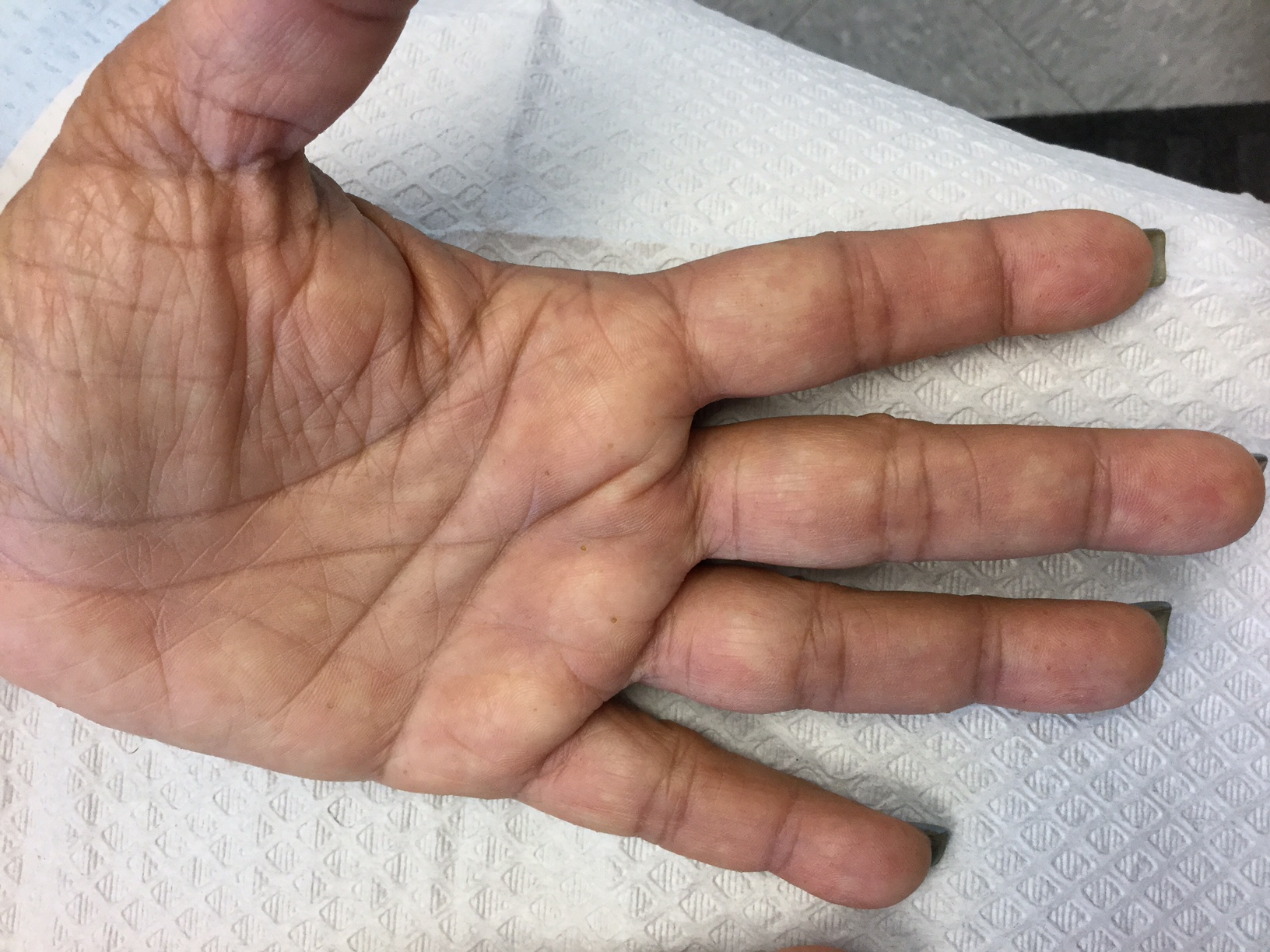
Palmoplantar keratoderma
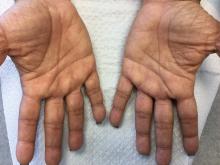
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is made of a group of benign disorders that cause thickening of the palms and soles. It is generally divided into three categories: diffuse PPK, with involvement of the whole palmoplantar surface; focal and striate PPK, usually located mainly on pressure points; and punctate PPK, featuring multiple small hyperkeratotic papules, nodules, or spicules. This patient’s lesions are most consistent with punctate palmoplantar keratoderma (PPPK).
PPPK is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, although acquired cases can be seen. It is also called Buschke-Fischer-Brauer syndrome, or keratodermia palmoplantaris papulosa. The condition affects men and women equally. Lesions usually appear during adolescence or after, unlike other forms of keratoderma, which may occur during childhood. While any race may be affected, in those of African descent, lesions are more common in the palmar creases. The condition is likely due to an aberration in proteins involved in keratin filament assembly. A mutation in the AAGAB gene can be at fault. PPPK can be associated with Darier’s disease and Cowden disease. Familial PPPK may be associated with Hodgkin disease, squamous cell carcinoma, kidney, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer.
Upon physical exam, multiple keratotic, punctate papules are present on the palms and soles, which may appear clear or more opaque. They may also have a verrucous appearance. Some lesions may have a central keratotic core and appear more comedonal. Most often, lesions are nontransgradient, meaning they only involve the palms and soles. Sometimes lesions may extend to the top of the hands and feet as well, which is called transgradient. Lesions are typically asymptomatic, although larger lesions can become painful with friction. Other types of PPPKs include filiform keratoderma and marginal keratoderma.
Histologic evaluation reveals columns of hyperkeratosis with an increased granular layer. There is no dermal inflammation. Clinically, the differential diagnosis is limited. Verruca vulgaris will reveal bleeding points upon paring with a blade. In spiny keratoderma, also called punctate porokeratosis of the palms and soles, lesions protrude more and resemble “music box spines.” Histologically, columnar parakeratosis is seen. Pitted keratolysis have reduced stratum corneum and a distinct clinical appearance.
If treatment is desired, emollients, keratolytics such as topical retinoids, salicylic acid, lactic acid, and urea may be used. Oral retinoids may be useful in symptomatic patients. Surgery and CO2 laser may be an option for resistant lesions.
This case and photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Palmoplantar keratoderma
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is made of a group of benign disorders that cause thickening of the palms and soles. It is generally divided into three categories: diffuse PPK, with involvement of the whole palmoplantar surface; focal and striate PPK, usually located mainly on pressure points; and punctate PPK, featuring multiple small hyperkeratotic papules, nodules, or spicules. This patient’s lesions are most consistent with punctate palmoplantar keratoderma (PPPK).
PPPK is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, although acquired cases can be seen. It is also called Buschke-Fischer-Brauer syndrome, or keratodermia palmoplantaris papulosa. The condition affects men and women equally. Lesions usually appear during adolescence or after, unlike other forms of keratoderma, which may occur during childhood. While any race may be affected, in those of African descent, lesions are more common in the palmar creases. The condition is likely due to an aberration in proteins involved in keratin filament assembly. A mutation in the AAGAB gene can be at fault. PPPK can be associated with Darier’s disease and Cowden disease. Familial PPPK may be associated with Hodgkin disease, squamous cell carcinoma, kidney, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer.
Upon physical exam, multiple keratotic, punctate papules are present on the palms and soles, which may appear clear or more opaque. They may also have a verrucous appearance. Some lesions may have a central keratotic core and appear more comedonal. Most often, lesions are nontransgradient, meaning they only involve the palms and soles. Sometimes lesions may extend to the top of the hands and feet as well, which is called transgradient. Lesions are typically asymptomatic, although larger lesions can become painful with friction. Other types of PPPKs include filiform keratoderma and marginal keratoderma.
Histologic evaluation reveals columns of hyperkeratosis with an increased granular layer. There is no dermal inflammation. Clinically, the differential diagnosis is limited. Verruca vulgaris will reveal bleeding points upon paring with a blade. In spiny keratoderma, also called punctate porokeratosis of the palms and soles, lesions protrude more and resemble “music box spines.” Histologically, columnar parakeratosis is seen. Pitted keratolysis have reduced stratum corneum and a distinct clinical appearance.
If treatment is desired, emollients, keratolytics such as topical retinoids, salicylic acid, lactic acid, and urea may be used. Oral retinoids may be useful in symptomatic patients. Surgery and CO2 laser may be an option for resistant lesions.
This case and photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Palmoplantar keratoderma
Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is made of a group of benign disorders that cause thickening of the palms and soles. It is generally divided into three categories: diffuse PPK, with involvement of the whole palmoplantar surface; focal and striate PPK, usually located mainly on pressure points; and punctate PPK, featuring multiple small hyperkeratotic papules, nodules, or spicules. This patient’s lesions are most consistent with punctate palmoplantar keratoderma (PPPK).
PPPK is usually inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, although acquired cases can be seen. It is also called Buschke-Fischer-Brauer syndrome, or keratodermia palmoplantaris papulosa. The condition affects men and women equally. Lesions usually appear during adolescence or after, unlike other forms of keratoderma, which may occur during childhood. While any race may be affected, in those of African descent, lesions are more common in the palmar creases. The condition is likely due to an aberration in proteins involved in keratin filament assembly. A mutation in the AAGAB gene can be at fault. PPPK can be associated with Darier’s disease and Cowden disease. Familial PPPK may be associated with Hodgkin disease, squamous cell carcinoma, kidney, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer.
Upon physical exam, multiple keratotic, punctate papules are present on the palms and soles, which may appear clear or more opaque. They may also have a verrucous appearance. Some lesions may have a central keratotic core and appear more comedonal. Most often, lesions are nontransgradient, meaning they only involve the palms and soles. Sometimes lesions may extend to the top of the hands and feet as well, which is called transgradient. Lesions are typically asymptomatic, although larger lesions can become painful with friction. Other types of PPPKs include filiform keratoderma and marginal keratoderma.
Histologic evaluation reveals columns of hyperkeratosis with an increased granular layer. There is no dermal inflammation. Clinically, the differential diagnosis is limited. Verruca vulgaris will reveal bleeding points upon paring with a blade. In spiny keratoderma, also called punctate porokeratosis of the palms and soles, lesions protrude more and resemble “music box spines.” Histologically, columnar parakeratosis is seen. Pitted keratolysis have reduced stratum corneum and a distinct clinical appearance.
If treatment is desired, emollients, keratolytics such as topical retinoids, salicylic acid, lactic acid, and urea may be used. Oral retinoids may be useful in symptomatic patients. Surgery and CO2 laser may be an option for resistant lesions.
This case and photos were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.