User login
A sizzling hybrid meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons
The 47th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS), like so many things in our modern world, endured many changes and had to stay nimble and evolve to changing times. In the end, however, SGS was able to adapt and succeed, just like a skilled gynecologic surgeon in the operating room, to deliver a fresh new type of meeting.
When we chose the meeting theme, “Working together: How collaboration enables us to better help our patients,” we anticipated a meeting discussing medical colleagues and consultants. In our forever-changed world, we knew we needed to reinterpret this to a broader social context. Our special lectures and panel discussions sought to open attendees’ eyes to disparities in health care for people of color and women.
While we highlighted the realities faced by colleagues in medicine, the topics addressed also were designed to grow awareness about struggles our patients encounter as well. Social disparities are sobering, long-standing, and sometimes require creative collaborations to achieve successful outcomes for all patients. The faculty of one of our postgraduate courses reviews in this special 2-part section to
The meeting also kicked off with a postgraduate course on fibroid management, with workshops on harnessing the power of social media and lessons on leadership from a female Fortune 500 CEO, Lori Ryerkerk, offered as well. As the scientific program launched, we were once again treated to strong science on gynecologic surgery, with only a small dip in abstract submissions, despite the challenges of research during a pandemic. Mark Walters, MD, gave the inaugural lecture in his name on the crucial topic of surgical education and teaching. We also heard a special report from the SGS SOCOVID research group, led by Dr. Rosanne Kho, on gynecologic surgery during the pandemic. We also convened a virtual panel for our hybrid attendees on the benefits to patients of a multidisciplinary approach to gynecologic surgery, presented here by Cecile Ferrando, MD.
As our practices continue to grow and evolve, the introduction of innovative technologies can pose a new challenge, as Miles Murphy, MD, and members of the panel on novel gynecologic office procedures will present in this series next month.
The TeLinde keynote speaker was Janet Dombrowski, who works as a coach for many surgeons in various disciplines across the country. She spoke to the resilience gained through community and collaboration.
While our meeting theme dated to the “before” pandemic era, those who were able to be in attendance in person can attest to the value we can all place now on community and personal interactions. With experience strengthened by science, I hope this meeting summary serves to highlight the many ways in which we can collaborate to improve outcomes for ourselves in medicine and for patients.
The 47th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS), like so many things in our modern world, endured many changes and had to stay nimble and evolve to changing times. In the end, however, SGS was able to adapt and succeed, just like a skilled gynecologic surgeon in the operating room, to deliver a fresh new type of meeting.
When we chose the meeting theme, “Working together: How collaboration enables us to better help our patients,” we anticipated a meeting discussing medical colleagues and consultants. In our forever-changed world, we knew we needed to reinterpret this to a broader social context. Our special lectures and panel discussions sought to open attendees’ eyes to disparities in health care for people of color and women.
While we highlighted the realities faced by colleagues in medicine, the topics addressed also were designed to grow awareness about struggles our patients encounter as well. Social disparities are sobering, long-standing, and sometimes require creative collaborations to achieve successful outcomes for all patients. The faculty of one of our postgraduate courses reviews in this special 2-part section to
The meeting also kicked off with a postgraduate course on fibroid management, with workshops on harnessing the power of social media and lessons on leadership from a female Fortune 500 CEO, Lori Ryerkerk, offered as well. As the scientific program launched, we were once again treated to strong science on gynecologic surgery, with only a small dip in abstract submissions, despite the challenges of research during a pandemic. Mark Walters, MD, gave the inaugural lecture in his name on the crucial topic of surgical education and teaching. We also heard a special report from the SGS SOCOVID research group, led by Dr. Rosanne Kho, on gynecologic surgery during the pandemic. We also convened a virtual panel for our hybrid attendees on the benefits to patients of a multidisciplinary approach to gynecologic surgery, presented here by Cecile Ferrando, MD.
As our practices continue to grow and evolve, the introduction of innovative technologies can pose a new challenge, as Miles Murphy, MD, and members of the panel on novel gynecologic office procedures will present in this series next month.
The TeLinde keynote speaker was Janet Dombrowski, who works as a coach for many surgeons in various disciplines across the country. She spoke to the resilience gained through community and collaboration.
While our meeting theme dated to the “before” pandemic era, those who were able to be in attendance in person can attest to the value we can all place now on community and personal interactions. With experience strengthened by science, I hope this meeting summary serves to highlight the many ways in which we can collaborate to improve outcomes for ourselves in medicine and for patients.
The 47th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS), like so many things in our modern world, endured many changes and had to stay nimble and evolve to changing times. In the end, however, SGS was able to adapt and succeed, just like a skilled gynecologic surgeon in the operating room, to deliver a fresh new type of meeting.
When we chose the meeting theme, “Working together: How collaboration enables us to better help our patients,” we anticipated a meeting discussing medical colleagues and consultants. In our forever-changed world, we knew we needed to reinterpret this to a broader social context. Our special lectures and panel discussions sought to open attendees’ eyes to disparities in health care for people of color and women.
While we highlighted the realities faced by colleagues in medicine, the topics addressed also were designed to grow awareness about struggles our patients encounter as well. Social disparities are sobering, long-standing, and sometimes require creative collaborations to achieve successful outcomes for all patients. The faculty of one of our postgraduate courses reviews in this special 2-part section to
The meeting also kicked off with a postgraduate course on fibroid management, with workshops on harnessing the power of social media and lessons on leadership from a female Fortune 500 CEO, Lori Ryerkerk, offered as well. As the scientific program launched, we were once again treated to strong science on gynecologic surgery, with only a small dip in abstract submissions, despite the challenges of research during a pandemic. Mark Walters, MD, gave the inaugural lecture in his name on the crucial topic of surgical education and teaching. We also heard a special report from the SGS SOCOVID research group, led by Dr. Rosanne Kho, on gynecologic surgery during the pandemic. We also convened a virtual panel for our hybrid attendees on the benefits to patients of a multidisciplinary approach to gynecologic surgery, presented here by Cecile Ferrando, MD.
As our practices continue to grow and evolve, the introduction of innovative technologies can pose a new challenge, as Miles Murphy, MD, and members of the panel on novel gynecologic office procedures will present in this series next month.
The TeLinde keynote speaker was Janet Dombrowski, who works as a coach for many surgeons in various disciplines across the country. She spoke to the resilience gained through community and collaboration.
While our meeting theme dated to the “before” pandemic era, those who were able to be in attendance in person can attest to the value we can all place now on community and personal interactions. With experience strengthened by science, I hope this meeting summary serves to highlight the many ways in which we can collaborate to improve outcomes for ourselves in medicine and for patients.
Closing the racial gap in minimally invasive gyn hysterectomy and myomectomy
The historical mistreatment of Black bodies in gynecologic care has bled into present day inequities—from surgeries performed on enslaved Black women and sterilization of low-income Black women under federally funded programs, to higher rates of adverse health-related outcomes among Black women compared with their non-Black counterparts.1-3 Not only is the foundation of gynecology imperfect, so too is its current-day structure.
It is not enough to identify and describe racial inequities in health care; action plans to provide equitable care are called for. In this report, we aim to 1) contextualize the data on disparities in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery, specifically hysterectomy and myomectomy candidates and postsurgical outcomes, and 2) provide recommendations to close racial gaps in gynecologic treatment for more equitable experiences for minority women.
Black women and uterine fibroids
Uterine leiomyomas, or fibroids, are not only the most common benign pelvic tumor but they also cause a significant medical and financial burden in the United States, with estimated direct costs of $4.1 ̶ 9.4 billion.4 Fibroids can affect fertility and cause pain, bulk symptoms, heavy bleeding, anemia requiring blood transfusion, and poor pregnancy outcomes. The burden of disease for uterine fibroids is greatest for Black women.
The incidence of fibroids is 2 to 3 times higher in Black women compared with White women.5 According to ultrasound-based studies, the prevalence of fibroids among women aged 18 to 30 years was 26% among Black and 7% among White asymptomatic women.6 Earlier onset and more severe symptoms mean that there is a larger potential for impact on fertility for Black women. This coupled with the historical context of mistreatment of Black bodies makes the need for personalized medicine and culturally sensitive care critical.
Inequitable management of uterine fibroids
Although tumor size, location, and patient risk factors are used to determine the best treatment approach, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines suggest that the use of alternative treatments to surgery should be first-line management instead of hysterectomy for most benign conditions.9 Conservative management will often help alleviate symptoms, slow the growth of fibroid(s), or bridge women to menopause, and treatment options include hormonal contraception, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, hysteroscopic resection, uterine artery embolization, magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound, and myomectomy.
The rate of conservative management prior to hysterectomy varies by setting, reflecting potential bias in treatment decisions. Some medical settings have reported a 29% alternative management rate prior to hysterectomy, while others report much higher rates.10 A study using patient data from Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) showed that, within a large, diverse, and integrated health care system, more than 80% of patients received alternative treatments before undergoing hysterectomy; for those with symptomatic leiomyomas, 74.1% used alternative treatments prior to hysterectomy, and in logistic regression there was not a difference by race.11 Nationally, Black women are more likely to have hysterectomy or myomectomy compared with a nonsurgical uterine-sparing therapy.12,13
With about 600,000 cases per year within the United States, the hysterectomy is the most frequently performed benign gynecologic surgery.14 The most common indication is for “symptomatic fibroid uterus.” The approach to decision making for route of hysterectomy involves multiple patient and surgeon factors, including history of vaginal delivery, body mass index, history of previous surgery, uterine size, informed patient preference, and surgeon volume.15-17 ACOG recommends a minimally invasive hysterectomy (MIH) whenever feasible given its benefits in postoperative pain, recovery time, and blood loss. Myomectomy, particularly among women in their reproductive years desiring management of leiomyomas, is a uterine-sparing procedure versus hysterectomy. Minimally invasive myomectomy (MIM), compared with an open abdominal route, provides for lower drop in hemoglobin levels, shorter hospital stay, less adhesion formation, and decreased postoperative pain.18
Racial variations in hysterectomy rates persist overall and according to hysterectomy type. Black women are 2 to 3 times more likely to undergo hysterectomy for leiomyomas than other racial groups.19 These differences in rates have been shown to persist even when burden of disease is the same. One study found that Black women had increased odds of hysterectomy compared with their White counterparts even when there was no difference in mean fibroid volume by race,20 calling into question provider bias. Even in a universal insurance setting, Black patients have been found to have higher rates of open hysterectomies.21 Previous studies found that, despite growing frequency of laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomies, patients of a minority race had decreased odds of undergoing a MIH compared with their White counterparts.22
While little data exist on route of myomectomy by race, a recent study found minority women were more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy compared with White women; Black women were twice as likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.7–2.0), Asian American women were more than twice as likely (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.8–2.8), and Hispanic American women were 50% more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (aOR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2–1.9) when compared with White women.23 These differences remained after controlling for potential confounders, and there appeared to be an interaction between race and fibroid weight such that racial bias alone may not explain the differences.
Finally, Black women have higher perioperative complication rates compared with non-Black women. Postoperative complications including blood transfusion after myomectomy have been shown to be twice as high among Black women compared with White women. However, once uterine size, comorbidities, and fibroid number were controlled, race was not associated with higher complications. Black women, compared with White women, have been found to have 50% increased odds of morbidity after an abdominal myomectomy.24
Continue to: How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management...
How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management
Eliminating disparities and providing equitable and patient-centered care for Black, Indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) women will require research, education, training, and targeted quality improvement initiatives.
Research into fibroids and comparative treatment outcomes
Uterine fibroids, despite their major public health impact, remain understudied. With Black women carrying the highest fibroid prevalence and severity burden, especially in their childbearing years, it is imperative that research efforts be focused on outcomes by race and ethnicity. Given the significant economic impact of fibroids, more efforts should be directed toward primary prevention of fibroid formation as well as secondary prevention and limitation of fibroid growth by affordable, effective, and safe means. For example, Bratka and colleagues researched the role of vitamin D in inhibiting growth of leiomyoma cells in animal models.25 Other innovative forms of management under investigation include aromatase inhibitors, green tea, cabergoline, elagolix, paricalcitol, and epigallocatechin gallate.26 Considerations such as stress, diet, and environmental risk factors have yet to be investigated in large studies.
Research contributing to evidence-based guidelines that address the needs of different patient populations affected by uterine fibroids is critical.8 Additionally, research conducted by Black women about Black women should be prioritized. In March 2021, the Stephanie Tubbs Jones Uterine Fibroid Research and Education Act of 2021 was introduced to fund $150 million in research supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This is an opportunity to develop a research database to inform evidence-based culturally informed care regarding fertility counseling, medical management, and optimal surgical approach, as well as to award funding to minority researchers. There are disparities in distribution of funds from the NIH to minority researchers. Under-represented minorities are awarded fewer NIH grants compared with their counterparts despite initiatives to increase funding. Furthermore, in 2011, Black applicants for NIH funding were two-thirds as likely as White applicants to receive grants from 2000 ̶ 2006, even when accounting for publication record and training.27 Funding BIPOC researchers fuels diversity-driven investigation and can be useful in the charge to increase fibroid research.
Education and training: Changing the work force
Achieving equity requires change in provider work force. In a study of trends across multiple specialties including obstetrics and gynecology, Blacks and Latinx are more under-represented in 2016 than in 1990 across all specialties except for Black women in obstetrics and gynecology.28 It is well documented that under-represented minorities are more likely to engage in practice, research, service, and mentorship activities aligned with their identity.29 As a higher proportion of under-represented minority obstetricians and gynecologists practice in medically underserved areas,30 this presents a unique opportunity for gynecologists to improve care for and increase research involvement among BIPOC women.
Increasing BIPOC representation in medical and health care institutions and practices is not enough, however, to achieve health equity. Data from the Association of American Medical Colleges demonstrate that between 1978 and 2017 the total number of full-time obstetrics and gynecology faculty rose nearly fourfold from 1,688 to 6,347; however, the greatest rise in proportion of faculty who were nontenured was among women who were under-represented minorities.31 Additionally, there are disparities in wage by race even after controlling for hours worked and state of residence.32 Medical and academic centers and health care institutions and practices should proactively and systematically engage in the recruitment and retention of under-represented minority physicians and people in leadership roles. This will involve creating safe and inclusive work environments, with equal pay and promotion structures.
Quality initiatives to address provider bias
Provider bias should be addressed in clinical decision making and counseling of patients. Studies focused on ultrasonography have shown an estimated cumulative incidence of fibroids by age 50 of greater than 80% for Black women and nearly 70% for White women.5 Due to the prevalence and burden of fibroids among Black women there may be a provider bias in approach to management. Addressing this bias requires quality improvement efforts and investigation into patient and provider factors in management of fibroids. Black women have been a vulnerable population in medicine due to instances of mistreatment, and often times mistrust can play a role in how a patient views his or her care decisions. A patient-centered strategy allows patient factors such as age, uterine size, and cultural background to be considered such that a provider can tailor an approach that is best for the patient. Previous minority women focus groups have demonstrated that women have a strong desire for elective treatment;33 therefore, providers should listen openly to patients about their values and their perspectives on how fibroids affect their lives. Provider bias toward surgical volume, incentive for surgery, and implicit bias need to be addressed at every institution to work toward equitable and cost-effective care.
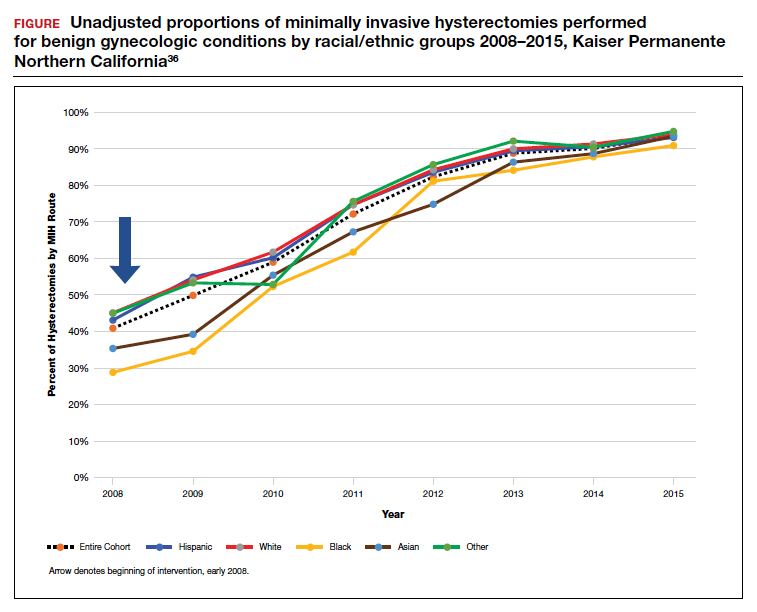
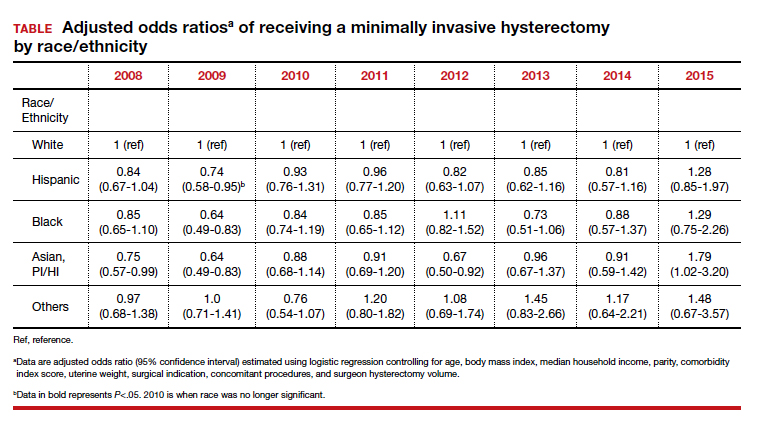
Integrated health care systems like Southern and Northern California Permanente Medical Group, using quality initiatives, have increased their minimally invasive surgery rates. Southern California Permanente Medical Group reached a 78% rate of MIH in a system of more than 350 surgeons performing benign indication hysterectomies as reported in 2011.34 Similarly, a study within KPNC, an institution with an MIH rate greater than 95%,35 found that racial disparities in route of MIH were eliminated through a quality improvement initiative described in detail in 2018 (FIGURE and TABLE).36
Conclusions
There are recognized successes in the gynecology field’s efforts to address racial disparities. Prior studies provide insight into opportunities to improve care in medical management of leiomyomas, minimally invasive route of hysterectomy and myomectomy, postsurgical outcomes, and institutional leadership. Particularly, when systemwide approaches are taken in the delivery of health care it is possible to significantly diminish racial disparities in gynecology.35 Much work remains to be done for our health care systems to provide equitable care.
- Ojanuga D. The medical ethics of the ‘father of gynaecology,’ Dr J Marion Sims. J Med Ethics. 1993;19:28-31. doi: 10.1136/jme.19.1.28.
- Borrero S, Zite N, Creinin MD. Federally funded sterilization: time to rethink policy? Am J Public Health. 2012;102:1822-1825.
- Eaglehouse YL, Georg MW, Shriver CD, et al. Racial differences in time to breast cancer surgery and overall survival in the US Military Health System. JAMA Surg. 2019;154:e185113. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.5113.
- Soliman AM, Yang H, Du EX, et al. The direct and indirect costs of uterine fibroid tumors: a systematic review of the literature between 2000 and 2013. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213:141-160.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(97)00534-6.
- Styer AK, Rueda BR. The epidemiology and genetics of uterine leiomyoma. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;34:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.11.018.
- Al-Hendy A, Myers ER, Stewart E. Uterine fibroids: burden and unmet medical need. Semin Reprod Med. 2017;35:473-480. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607264.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin. Alternatives to hysterectomy in the management of leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112(2 pt 1):387-400.
- Corona LE, Swenson CW, Sheetz KH, et al. Use of other treatments before hysterectomy for benign conditions in a statewide hospital collaborative. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:304.e1-e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.11.031.
- Nguyen NT, Merchant M, Ritterman Weintraub ML, et al. Alternative treatment utilization before hysterectomy for benign gynecologic conditions at a large integrated health system. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:847-855. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.08.013.
- Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Jacoby VL, Myers ER. Disparities in fibroid incidence, prognosis, and management. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.11.007.
- Borah BJ, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Myers ER, et al. Association between patient characteristics and treatment procedure among patients with uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:67-77.
- Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Jamieson DJ, et al. Inpatient hysterectomy surveillance in the United States, 2000-2004. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:34.e1-e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.039.
- Bardens D, Solomayer E, Baum S, et al. The impact of the body mass index (BMI) on laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign disease. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;289:803-807. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-3050-2.
- Seracchioli R, Venturoli S, Vianello F, et al. Total laparoscopic hysterectomy compared with abdominal hysterectomy in the presence of a large uterus. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2002;9:333-338. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60413.
- Boyd LR, Novetsky AP, Curtin JP. Effect of surgical volume on route of hysterectomy and short-term morbidity. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:909-915. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181f395d9.
- Jin C, Hu Y, Chen XC, et al. Laparoscopic versus open myomectomy—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.03.009.
- Wechter ME, Stewart EA, Myers ER, et al. Leiomyoma-related hospitalization and surgery: prevalence and predicted growth based on population trends. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;205:492.e1-e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.07.008.
- Bower JK, Schreiner PJ, Sternfeld B, et al. Black-White differences in hysterectomy prevalence: the CARDIA study. Am J Public Health. 2009;99:300-307. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.133702.
- Ranjit A, Sharma M, Romano A, et al. Does universal insurance mitigate racial differences in minimally invasive hysterectomy? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.03.016.
- Pollack LM, Olsen MA, Gehlert SJ, et al. Racial/ethnic disparities/differences in hysterectomy route in women likely eligible for minimally invasive surgery. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:1167-1177.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2019.09.003.
- Stentz NC, Cooney LG, Sammel MD, et al. Association of patient race with surgical practice and perioperative morbidity after myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:291-297. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002738.
- Roth TM, Gustilo-Ashby T, Barber MD, et al. Effects of race and clinical factors on short-term outcomes of abdominal myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101(5 pt 1):881-884. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00015-2.
- Bratka S, Diamond JS, Al-Hendy A, et al. The role of vitamin D in uterine fibroid biology. Fertil Steril. 2015;104:698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.05.031.
- Ciebiera M, Łukaszuk K, Męczekalski B, et al. Alternative oral agents in prophylaxis and therapy of uterine fibroids—an up-to-date review. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2586. doi:10.3390/ijms18122586.
- Hayden EC. Racial bias haunts NIH funding. Nature. 2015;527:145.
- Lett LA, Orji WU, Sebro R. Declining racial and ethnic representation in clinical academic medicine: a longitudinal study of 16 US medical specialties. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0207274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207274.
- Sánchez JP, Poll-Hunter N, Stern N, et al. Balancing two cultures: American Indian/Alaska Native medical students’ perceptions of academic medicine careers. J Community Health. 2016;41:871-880.
- Rayburn WF, Xierali IM, Castillo-Page L, et al. Racial and ethnic differences between obstetrician-gynecologists and other adult medical specialists. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:148-152. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001184.
- Esters D, Xierali IM, Nivet MA, et al. The rise of nontenured faculty in obstetrics and gynecology by sex and underrepresented in medicine status. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134 suppl 1:34S-39S. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003484.
- Ly DP, Seabury SA, Jena AB. Differences in incomes of physicians in the United States by race and sex: observational study. BMJ. 2016;I2923. doi:10.1136/bmj.i2923.
- Groff JY, Mullen PD, Byrd T, et al. Decision making, beliefs, and attitudes toward hysterectomy: a focus group study with medically underserved women in Texas. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9 suppl 2:S39-50. doi: 10.1089/152460900318759.
- Andryjowicz E, Wray T. Regional expansion of minimally invasive surgery for hysterectomy: implementation and methodology in a large multispecialty group. Perm J. 2011;15:42-46.
- Zaritsky E, Ojo A, Tucker LY, et al. Racial disparities in route of hysterectomy for benign indications within an integrated health care system. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e1917004. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17004.
- Abel MK, Kho KA, Walter A, et al. Measuring quality in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: what, how, and why? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:321-326. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.11.013.
The historical mistreatment of Black bodies in gynecologic care has bled into present day inequities—from surgeries performed on enslaved Black women and sterilization of low-income Black women under federally funded programs, to higher rates of adverse health-related outcomes among Black women compared with their non-Black counterparts.1-3 Not only is the foundation of gynecology imperfect, so too is its current-day structure.
It is not enough to identify and describe racial inequities in health care; action plans to provide equitable care are called for. In this report, we aim to 1) contextualize the data on disparities in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery, specifically hysterectomy and myomectomy candidates and postsurgical outcomes, and 2) provide recommendations to close racial gaps in gynecologic treatment for more equitable experiences for minority women.
Black women and uterine fibroids
Uterine leiomyomas, or fibroids, are not only the most common benign pelvic tumor but they also cause a significant medical and financial burden in the United States, with estimated direct costs of $4.1 ̶ 9.4 billion.4 Fibroids can affect fertility and cause pain, bulk symptoms, heavy bleeding, anemia requiring blood transfusion, and poor pregnancy outcomes. The burden of disease for uterine fibroids is greatest for Black women.
The incidence of fibroids is 2 to 3 times higher in Black women compared with White women.5 According to ultrasound-based studies, the prevalence of fibroids among women aged 18 to 30 years was 26% among Black and 7% among White asymptomatic women.6 Earlier onset and more severe symptoms mean that there is a larger potential for impact on fertility for Black women. This coupled with the historical context of mistreatment of Black bodies makes the need for personalized medicine and culturally sensitive care critical.
Inequitable management of uterine fibroids
Although tumor size, location, and patient risk factors are used to determine the best treatment approach, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines suggest that the use of alternative treatments to surgery should be first-line management instead of hysterectomy for most benign conditions.9 Conservative management will often help alleviate symptoms, slow the growth of fibroid(s), or bridge women to menopause, and treatment options include hormonal contraception, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, hysteroscopic resection, uterine artery embolization, magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound, and myomectomy.
The rate of conservative management prior to hysterectomy varies by setting, reflecting potential bias in treatment decisions. Some medical settings have reported a 29% alternative management rate prior to hysterectomy, while others report much higher rates.10 A study using patient data from Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) showed that, within a large, diverse, and integrated health care system, more than 80% of patients received alternative treatments before undergoing hysterectomy; for those with symptomatic leiomyomas, 74.1% used alternative treatments prior to hysterectomy, and in logistic regression there was not a difference by race.11 Nationally, Black women are more likely to have hysterectomy or myomectomy compared with a nonsurgical uterine-sparing therapy.12,13
With about 600,000 cases per year within the United States, the hysterectomy is the most frequently performed benign gynecologic surgery.14 The most common indication is for “symptomatic fibroid uterus.” The approach to decision making for route of hysterectomy involves multiple patient and surgeon factors, including history of vaginal delivery, body mass index, history of previous surgery, uterine size, informed patient preference, and surgeon volume.15-17 ACOG recommends a minimally invasive hysterectomy (MIH) whenever feasible given its benefits in postoperative pain, recovery time, and blood loss. Myomectomy, particularly among women in their reproductive years desiring management of leiomyomas, is a uterine-sparing procedure versus hysterectomy. Minimally invasive myomectomy (MIM), compared with an open abdominal route, provides for lower drop in hemoglobin levels, shorter hospital stay, less adhesion formation, and decreased postoperative pain.18
Racial variations in hysterectomy rates persist overall and according to hysterectomy type. Black women are 2 to 3 times more likely to undergo hysterectomy for leiomyomas than other racial groups.19 These differences in rates have been shown to persist even when burden of disease is the same. One study found that Black women had increased odds of hysterectomy compared with their White counterparts even when there was no difference in mean fibroid volume by race,20 calling into question provider bias. Even in a universal insurance setting, Black patients have been found to have higher rates of open hysterectomies.21 Previous studies found that, despite growing frequency of laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomies, patients of a minority race had decreased odds of undergoing a MIH compared with their White counterparts.22
While little data exist on route of myomectomy by race, a recent study found minority women were more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy compared with White women; Black women were twice as likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.7–2.0), Asian American women were more than twice as likely (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.8–2.8), and Hispanic American women were 50% more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (aOR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2–1.9) when compared with White women.23 These differences remained after controlling for potential confounders, and there appeared to be an interaction between race and fibroid weight such that racial bias alone may not explain the differences.
Finally, Black women have higher perioperative complication rates compared with non-Black women. Postoperative complications including blood transfusion after myomectomy have been shown to be twice as high among Black women compared with White women. However, once uterine size, comorbidities, and fibroid number were controlled, race was not associated with higher complications. Black women, compared with White women, have been found to have 50% increased odds of morbidity after an abdominal myomectomy.24
Continue to: How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management...
How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management
Eliminating disparities and providing equitable and patient-centered care for Black, Indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) women will require research, education, training, and targeted quality improvement initiatives.
Research into fibroids and comparative treatment outcomes
Uterine fibroids, despite their major public health impact, remain understudied. With Black women carrying the highest fibroid prevalence and severity burden, especially in their childbearing years, it is imperative that research efforts be focused on outcomes by race and ethnicity. Given the significant economic impact of fibroids, more efforts should be directed toward primary prevention of fibroid formation as well as secondary prevention and limitation of fibroid growth by affordable, effective, and safe means. For example, Bratka and colleagues researched the role of vitamin D in inhibiting growth of leiomyoma cells in animal models.25 Other innovative forms of management under investigation include aromatase inhibitors, green tea, cabergoline, elagolix, paricalcitol, and epigallocatechin gallate.26 Considerations such as stress, diet, and environmental risk factors have yet to be investigated in large studies.
Research contributing to evidence-based guidelines that address the needs of different patient populations affected by uterine fibroids is critical.8 Additionally, research conducted by Black women about Black women should be prioritized. In March 2021, the Stephanie Tubbs Jones Uterine Fibroid Research and Education Act of 2021 was introduced to fund $150 million in research supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This is an opportunity to develop a research database to inform evidence-based culturally informed care regarding fertility counseling, medical management, and optimal surgical approach, as well as to award funding to minority researchers. There are disparities in distribution of funds from the NIH to minority researchers. Under-represented minorities are awarded fewer NIH grants compared with their counterparts despite initiatives to increase funding. Furthermore, in 2011, Black applicants for NIH funding were two-thirds as likely as White applicants to receive grants from 2000 ̶ 2006, even when accounting for publication record and training.27 Funding BIPOC researchers fuels diversity-driven investigation and can be useful in the charge to increase fibroid research.
Education and training: Changing the work force
Achieving equity requires change in provider work force. In a study of trends across multiple specialties including obstetrics and gynecology, Blacks and Latinx are more under-represented in 2016 than in 1990 across all specialties except for Black women in obstetrics and gynecology.28 It is well documented that under-represented minorities are more likely to engage in practice, research, service, and mentorship activities aligned with their identity.29 As a higher proportion of under-represented minority obstetricians and gynecologists practice in medically underserved areas,30 this presents a unique opportunity for gynecologists to improve care for and increase research involvement among BIPOC women.
Increasing BIPOC representation in medical and health care institutions and practices is not enough, however, to achieve health equity. Data from the Association of American Medical Colleges demonstrate that between 1978 and 2017 the total number of full-time obstetrics and gynecology faculty rose nearly fourfold from 1,688 to 6,347; however, the greatest rise in proportion of faculty who were nontenured was among women who were under-represented minorities.31 Additionally, there are disparities in wage by race even after controlling for hours worked and state of residence.32 Medical and academic centers and health care institutions and practices should proactively and systematically engage in the recruitment and retention of under-represented minority physicians and people in leadership roles. This will involve creating safe and inclusive work environments, with equal pay and promotion structures.
Quality initiatives to address provider bias
Provider bias should be addressed in clinical decision making and counseling of patients. Studies focused on ultrasonography have shown an estimated cumulative incidence of fibroids by age 50 of greater than 80% for Black women and nearly 70% for White women.5 Due to the prevalence and burden of fibroids among Black women there may be a provider bias in approach to management. Addressing this bias requires quality improvement efforts and investigation into patient and provider factors in management of fibroids. Black women have been a vulnerable population in medicine due to instances of mistreatment, and often times mistrust can play a role in how a patient views his or her care decisions. A patient-centered strategy allows patient factors such as age, uterine size, and cultural background to be considered such that a provider can tailor an approach that is best for the patient. Previous minority women focus groups have demonstrated that women have a strong desire for elective treatment;33 therefore, providers should listen openly to patients about their values and their perspectives on how fibroids affect their lives. Provider bias toward surgical volume, incentive for surgery, and implicit bias need to be addressed at every institution to work toward equitable and cost-effective care.
Integrated health care systems like Southern and Northern California Permanente Medical Group, using quality initiatives, have increased their minimally invasive surgery rates. Southern California Permanente Medical Group reached a 78% rate of MIH in a system of more than 350 surgeons performing benign indication hysterectomies as reported in 2011.34 Similarly, a study within KPNC, an institution with an MIH rate greater than 95%,35 found that racial disparities in route of MIH were eliminated through a quality improvement initiative described in detail in 2018 (FIGURE and TABLE).36
Conclusions
There are recognized successes in the gynecology field’s efforts to address racial disparities. Prior studies provide insight into opportunities to improve care in medical management of leiomyomas, minimally invasive route of hysterectomy and myomectomy, postsurgical outcomes, and institutional leadership. Particularly, when systemwide approaches are taken in the delivery of health care it is possible to significantly diminish racial disparities in gynecology.35 Much work remains to be done for our health care systems to provide equitable care.


The historical mistreatment of Black bodies in gynecologic care has bled into present day inequities—from surgeries performed on enslaved Black women and sterilization of low-income Black women under federally funded programs, to higher rates of adverse health-related outcomes among Black women compared with their non-Black counterparts.1-3 Not only is the foundation of gynecology imperfect, so too is its current-day structure.
It is not enough to identify and describe racial inequities in health care; action plans to provide equitable care are called for. In this report, we aim to 1) contextualize the data on disparities in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery, specifically hysterectomy and myomectomy candidates and postsurgical outcomes, and 2) provide recommendations to close racial gaps in gynecologic treatment for more equitable experiences for minority women.
Black women and uterine fibroids
Uterine leiomyomas, or fibroids, are not only the most common benign pelvic tumor but they also cause a significant medical and financial burden in the United States, with estimated direct costs of $4.1 ̶ 9.4 billion.4 Fibroids can affect fertility and cause pain, bulk symptoms, heavy bleeding, anemia requiring blood transfusion, and poor pregnancy outcomes. The burden of disease for uterine fibroids is greatest for Black women.
The incidence of fibroids is 2 to 3 times higher in Black women compared with White women.5 According to ultrasound-based studies, the prevalence of fibroids among women aged 18 to 30 years was 26% among Black and 7% among White asymptomatic women.6 Earlier onset and more severe symptoms mean that there is a larger potential for impact on fertility for Black women. This coupled with the historical context of mistreatment of Black bodies makes the need for personalized medicine and culturally sensitive care critical.
Inequitable management of uterine fibroids
Although tumor size, location, and patient risk factors are used to determine the best treatment approach, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines suggest that the use of alternative treatments to surgery should be first-line management instead of hysterectomy for most benign conditions.9 Conservative management will often help alleviate symptoms, slow the growth of fibroid(s), or bridge women to menopause, and treatment options include hormonal contraception, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, hysteroscopic resection, uterine artery embolization, magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound, and myomectomy.
The rate of conservative management prior to hysterectomy varies by setting, reflecting potential bias in treatment decisions. Some medical settings have reported a 29% alternative management rate prior to hysterectomy, while others report much higher rates.10 A study using patient data from Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) showed that, within a large, diverse, and integrated health care system, more than 80% of patients received alternative treatments before undergoing hysterectomy; for those with symptomatic leiomyomas, 74.1% used alternative treatments prior to hysterectomy, and in logistic regression there was not a difference by race.11 Nationally, Black women are more likely to have hysterectomy or myomectomy compared with a nonsurgical uterine-sparing therapy.12,13
With about 600,000 cases per year within the United States, the hysterectomy is the most frequently performed benign gynecologic surgery.14 The most common indication is for “symptomatic fibroid uterus.” The approach to decision making for route of hysterectomy involves multiple patient and surgeon factors, including history of vaginal delivery, body mass index, history of previous surgery, uterine size, informed patient preference, and surgeon volume.15-17 ACOG recommends a minimally invasive hysterectomy (MIH) whenever feasible given its benefits in postoperative pain, recovery time, and blood loss. Myomectomy, particularly among women in their reproductive years desiring management of leiomyomas, is a uterine-sparing procedure versus hysterectomy. Minimally invasive myomectomy (MIM), compared with an open abdominal route, provides for lower drop in hemoglobin levels, shorter hospital stay, less adhesion formation, and decreased postoperative pain.18
Racial variations in hysterectomy rates persist overall and according to hysterectomy type. Black women are 2 to 3 times more likely to undergo hysterectomy for leiomyomas than other racial groups.19 These differences in rates have been shown to persist even when burden of disease is the same. One study found that Black women had increased odds of hysterectomy compared with their White counterparts even when there was no difference in mean fibroid volume by race,20 calling into question provider bias. Even in a universal insurance setting, Black patients have been found to have higher rates of open hysterectomies.21 Previous studies found that, despite growing frequency of laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomies, patients of a minority race had decreased odds of undergoing a MIH compared with their White counterparts.22
While little data exist on route of myomectomy by race, a recent study found minority women were more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy compared with White women; Black women were twice as likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.7–2.0), Asian American women were more than twice as likely (aOR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.8–2.8), and Hispanic American women were 50% more likely to undergo abdominal myomectomy (aOR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2–1.9) when compared with White women.23 These differences remained after controlling for potential confounders, and there appeared to be an interaction between race and fibroid weight such that racial bias alone may not explain the differences.
Finally, Black women have higher perioperative complication rates compared with non-Black women. Postoperative complications including blood transfusion after myomectomy have been shown to be twice as high among Black women compared with White women. However, once uterine size, comorbidities, and fibroid number were controlled, race was not associated with higher complications. Black women, compared with White women, have been found to have 50% increased odds of morbidity after an abdominal myomectomy.24
Continue to: How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management...
How to ensure that BIPOC women get the best management
Eliminating disparities and providing equitable and patient-centered care for Black, Indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) women will require research, education, training, and targeted quality improvement initiatives.
Research into fibroids and comparative treatment outcomes
Uterine fibroids, despite their major public health impact, remain understudied. With Black women carrying the highest fibroid prevalence and severity burden, especially in their childbearing years, it is imperative that research efforts be focused on outcomes by race and ethnicity. Given the significant economic impact of fibroids, more efforts should be directed toward primary prevention of fibroid formation as well as secondary prevention and limitation of fibroid growth by affordable, effective, and safe means. For example, Bratka and colleagues researched the role of vitamin D in inhibiting growth of leiomyoma cells in animal models.25 Other innovative forms of management under investigation include aromatase inhibitors, green tea, cabergoline, elagolix, paricalcitol, and epigallocatechin gallate.26 Considerations such as stress, diet, and environmental risk factors have yet to be investigated in large studies.
Research contributing to evidence-based guidelines that address the needs of different patient populations affected by uterine fibroids is critical.8 Additionally, research conducted by Black women about Black women should be prioritized. In March 2021, the Stephanie Tubbs Jones Uterine Fibroid Research and Education Act of 2021 was introduced to fund $150 million in research supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This is an opportunity to develop a research database to inform evidence-based culturally informed care regarding fertility counseling, medical management, and optimal surgical approach, as well as to award funding to minority researchers. There are disparities in distribution of funds from the NIH to minority researchers. Under-represented minorities are awarded fewer NIH grants compared with their counterparts despite initiatives to increase funding. Furthermore, in 2011, Black applicants for NIH funding were two-thirds as likely as White applicants to receive grants from 2000 ̶ 2006, even when accounting for publication record and training.27 Funding BIPOC researchers fuels diversity-driven investigation and can be useful in the charge to increase fibroid research.
Education and training: Changing the work force
Achieving equity requires change in provider work force. In a study of trends across multiple specialties including obstetrics and gynecology, Blacks and Latinx are more under-represented in 2016 than in 1990 across all specialties except for Black women in obstetrics and gynecology.28 It is well documented that under-represented minorities are more likely to engage in practice, research, service, and mentorship activities aligned with their identity.29 As a higher proportion of under-represented minority obstetricians and gynecologists practice in medically underserved areas,30 this presents a unique opportunity for gynecologists to improve care for and increase research involvement among BIPOC women.
Increasing BIPOC representation in medical and health care institutions and practices is not enough, however, to achieve health equity. Data from the Association of American Medical Colleges demonstrate that between 1978 and 2017 the total number of full-time obstetrics and gynecology faculty rose nearly fourfold from 1,688 to 6,347; however, the greatest rise in proportion of faculty who were nontenured was among women who were under-represented minorities.31 Additionally, there are disparities in wage by race even after controlling for hours worked and state of residence.32 Medical and academic centers and health care institutions and practices should proactively and systematically engage in the recruitment and retention of under-represented minority physicians and people in leadership roles. This will involve creating safe and inclusive work environments, with equal pay and promotion structures.
Quality initiatives to address provider bias
Provider bias should be addressed in clinical decision making and counseling of patients. Studies focused on ultrasonography have shown an estimated cumulative incidence of fibroids by age 50 of greater than 80% for Black women and nearly 70% for White women.5 Due to the prevalence and burden of fibroids among Black women there may be a provider bias in approach to management. Addressing this bias requires quality improvement efforts and investigation into patient and provider factors in management of fibroids. Black women have been a vulnerable population in medicine due to instances of mistreatment, and often times mistrust can play a role in how a patient views his or her care decisions. A patient-centered strategy allows patient factors such as age, uterine size, and cultural background to be considered such that a provider can tailor an approach that is best for the patient. Previous minority women focus groups have demonstrated that women have a strong desire for elective treatment;33 therefore, providers should listen openly to patients about their values and their perspectives on how fibroids affect their lives. Provider bias toward surgical volume, incentive for surgery, and implicit bias need to be addressed at every institution to work toward equitable and cost-effective care.
Integrated health care systems like Southern and Northern California Permanente Medical Group, using quality initiatives, have increased their minimally invasive surgery rates. Southern California Permanente Medical Group reached a 78% rate of MIH in a system of more than 350 surgeons performing benign indication hysterectomies as reported in 2011.34 Similarly, a study within KPNC, an institution with an MIH rate greater than 95%,35 found that racial disparities in route of MIH were eliminated through a quality improvement initiative described in detail in 2018 (FIGURE and TABLE).36
Conclusions
There are recognized successes in the gynecology field’s efforts to address racial disparities. Prior studies provide insight into opportunities to improve care in medical management of leiomyomas, minimally invasive route of hysterectomy and myomectomy, postsurgical outcomes, and institutional leadership. Particularly, when systemwide approaches are taken in the delivery of health care it is possible to significantly diminish racial disparities in gynecology.35 Much work remains to be done for our health care systems to provide equitable care.


- Ojanuga D. The medical ethics of the ‘father of gynaecology,’ Dr J Marion Sims. J Med Ethics. 1993;19:28-31. doi: 10.1136/jme.19.1.28.
- Borrero S, Zite N, Creinin MD. Federally funded sterilization: time to rethink policy? Am J Public Health. 2012;102:1822-1825.
- Eaglehouse YL, Georg MW, Shriver CD, et al. Racial differences in time to breast cancer surgery and overall survival in the US Military Health System. JAMA Surg. 2019;154:e185113. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.5113.
- Soliman AM, Yang H, Du EX, et al. The direct and indirect costs of uterine fibroid tumors: a systematic review of the literature between 2000 and 2013. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213:141-160.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(97)00534-6.
- Styer AK, Rueda BR. The epidemiology and genetics of uterine leiomyoma. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;34:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.11.018.
- Al-Hendy A, Myers ER, Stewart E. Uterine fibroids: burden and unmet medical need. Semin Reprod Med. 2017;35:473-480. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607264.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin. Alternatives to hysterectomy in the management of leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112(2 pt 1):387-400.
- Corona LE, Swenson CW, Sheetz KH, et al. Use of other treatments before hysterectomy for benign conditions in a statewide hospital collaborative. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:304.e1-e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.11.031.
- Nguyen NT, Merchant M, Ritterman Weintraub ML, et al. Alternative treatment utilization before hysterectomy for benign gynecologic conditions at a large integrated health system. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:847-855. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.08.013.
- Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Jacoby VL, Myers ER. Disparities in fibroid incidence, prognosis, and management. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.11.007.
- Borah BJ, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Myers ER, et al. Association between patient characteristics and treatment procedure among patients with uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:67-77.
- Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Jamieson DJ, et al. Inpatient hysterectomy surveillance in the United States, 2000-2004. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:34.e1-e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.039.
- Bardens D, Solomayer E, Baum S, et al. The impact of the body mass index (BMI) on laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign disease. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;289:803-807. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-3050-2.
- Seracchioli R, Venturoli S, Vianello F, et al. Total laparoscopic hysterectomy compared with abdominal hysterectomy in the presence of a large uterus. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2002;9:333-338. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60413.
- Boyd LR, Novetsky AP, Curtin JP. Effect of surgical volume on route of hysterectomy and short-term morbidity. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:909-915. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181f395d9.
- Jin C, Hu Y, Chen XC, et al. Laparoscopic versus open myomectomy—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.03.009.
- Wechter ME, Stewart EA, Myers ER, et al. Leiomyoma-related hospitalization and surgery: prevalence and predicted growth based on population trends. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;205:492.e1-e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.07.008.
- Bower JK, Schreiner PJ, Sternfeld B, et al. Black-White differences in hysterectomy prevalence: the CARDIA study. Am J Public Health. 2009;99:300-307. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.133702.
- Ranjit A, Sharma M, Romano A, et al. Does universal insurance mitigate racial differences in minimally invasive hysterectomy? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.03.016.
- Pollack LM, Olsen MA, Gehlert SJ, et al. Racial/ethnic disparities/differences in hysterectomy route in women likely eligible for minimally invasive surgery. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:1167-1177.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2019.09.003.
- Stentz NC, Cooney LG, Sammel MD, et al. Association of patient race with surgical practice and perioperative morbidity after myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:291-297. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002738.
- Roth TM, Gustilo-Ashby T, Barber MD, et al. Effects of race and clinical factors on short-term outcomes of abdominal myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101(5 pt 1):881-884. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00015-2.
- Bratka S, Diamond JS, Al-Hendy A, et al. The role of vitamin D in uterine fibroid biology. Fertil Steril. 2015;104:698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.05.031.
- Ciebiera M, Łukaszuk K, Męczekalski B, et al. Alternative oral agents in prophylaxis and therapy of uterine fibroids—an up-to-date review. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2586. doi:10.3390/ijms18122586.
- Hayden EC. Racial bias haunts NIH funding. Nature. 2015;527:145.
- Lett LA, Orji WU, Sebro R. Declining racial and ethnic representation in clinical academic medicine: a longitudinal study of 16 US medical specialties. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0207274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207274.
- Sánchez JP, Poll-Hunter N, Stern N, et al. Balancing two cultures: American Indian/Alaska Native medical students’ perceptions of academic medicine careers. J Community Health. 2016;41:871-880.
- Rayburn WF, Xierali IM, Castillo-Page L, et al. Racial and ethnic differences between obstetrician-gynecologists and other adult medical specialists. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:148-152. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001184.
- Esters D, Xierali IM, Nivet MA, et al. The rise of nontenured faculty in obstetrics and gynecology by sex and underrepresented in medicine status. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134 suppl 1:34S-39S. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003484.
- Ly DP, Seabury SA, Jena AB. Differences in incomes of physicians in the United States by race and sex: observational study. BMJ. 2016;I2923. doi:10.1136/bmj.i2923.
- Groff JY, Mullen PD, Byrd T, et al. Decision making, beliefs, and attitudes toward hysterectomy: a focus group study with medically underserved women in Texas. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9 suppl 2:S39-50. doi: 10.1089/152460900318759.
- Andryjowicz E, Wray T. Regional expansion of minimally invasive surgery for hysterectomy: implementation and methodology in a large multispecialty group. Perm J. 2011;15:42-46.
- Zaritsky E, Ojo A, Tucker LY, et al. Racial disparities in route of hysterectomy for benign indications within an integrated health care system. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e1917004. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17004.
- Abel MK, Kho KA, Walter A, et al. Measuring quality in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: what, how, and why? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:321-326. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.11.013.
- Ojanuga D. The medical ethics of the ‘father of gynaecology,’ Dr J Marion Sims. J Med Ethics. 1993;19:28-31. doi: 10.1136/jme.19.1.28.
- Borrero S, Zite N, Creinin MD. Federally funded sterilization: time to rethink policy? Am J Public Health. 2012;102:1822-1825.
- Eaglehouse YL, Georg MW, Shriver CD, et al. Racial differences in time to breast cancer surgery and overall survival in the US Military Health System. JAMA Surg. 2019;154:e185113. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.5113.
- Soliman AM, Yang H, Du EX, et al. The direct and indirect costs of uterine fibroid tumors: a systematic review of the literature between 2000 and 2013. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213:141-160.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstet Gynecol. 1997;90:967-973. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(97)00534-6.
- Styer AK, Rueda BR. The epidemiology and genetics of uterine leiomyoma. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;34:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.11.018.
- Al-Hendy A, Myers ER, Stewart E. Uterine fibroids: burden and unmet medical need. Semin Reprod Med. 2017;35:473-480. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607264.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin. Alternatives to hysterectomy in the management of leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112(2 pt 1):387-400.
- Corona LE, Swenson CW, Sheetz KH, et al. Use of other treatments before hysterectomy for benign conditions in a statewide hospital collaborative. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:304.e1-e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.11.031.
- Nguyen NT, Merchant M, Ritterman Weintraub ML, et al. Alternative treatment utilization before hysterectomy for benign gynecologic conditions at a large integrated health system. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:847-855. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.08.013.
- Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Jacoby VL, Myers ER. Disparities in fibroid incidence, prognosis, and management. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.11.007.
- Borah BJ, Laughlin-Tommaso SK, Myers ER, et al. Association between patient characteristics and treatment procedure among patients with uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:67-77.
- Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Jamieson DJ, et al. Inpatient hysterectomy surveillance in the United States, 2000-2004. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:34.e1-e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.039.
- Bardens D, Solomayer E, Baum S, et al. The impact of the body mass index (BMI) on laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign disease. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;289:803-807. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-3050-2.
- Seracchioli R, Venturoli S, Vianello F, et al. Total laparoscopic hysterectomy compared with abdominal hysterectomy in the presence of a large uterus. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 2002;9:333-338. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60413.
- Boyd LR, Novetsky AP, Curtin JP. Effect of surgical volume on route of hysterectomy and short-term morbidity. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:909-915. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181f395d9.
- Jin C, Hu Y, Chen XC, et al. Laparoscopic versus open myomectomy—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.03.009.
- Wechter ME, Stewart EA, Myers ER, et al. Leiomyoma-related hospitalization and surgery: prevalence and predicted growth based on population trends. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;205:492.e1-e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.07.008.
- Bower JK, Schreiner PJ, Sternfeld B, et al. Black-White differences in hysterectomy prevalence: the CARDIA study. Am J Public Health. 2009;99:300-307. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.133702.
- Ranjit A, Sharma M, Romano A, et al. Does universal insurance mitigate racial differences in minimally invasive hysterectomy? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2017.03.016.
- Pollack LM, Olsen MA, Gehlert SJ, et al. Racial/ethnic disparities/differences in hysterectomy route in women likely eligible for minimally invasive surgery. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:1167-1177.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2019.09.003.
- Stentz NC, Cooney LG, Sammel MD, et al. Association of patient race with surgical practice and perioperative morbidity after myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:291-297. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002738.
- Roth TM, Gustilo-Ashby T, Barber MD, et al. Effects of race and clinical factors on short-term outcomes of abdominal myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101(5 pt 1):881-884. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(03)00015-2.
- Bratka S, Diamond JS, Al-Hendy A, et al. The role of vitamin D in uterine fibroid biology. Fertil Steril. 2015;104:698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.05.031.
- Ciebiera M, Łukaszuk K, Męczekalski B, et al. Alternative oral agents in prophylaxis and therapy of uterine fibroids—an up-to-date review. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2586. doi:10.3390/ijms18122586.
- Hayden EC. Racial bias haunts NIH funding. Nature. 2015;527:145.
- Lett LA, Orji WU, Sebro R. Declining racial and ethnic representation in clinical academic medicine: a longitudinal study of 16 US medical specialties. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0207274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207274.
- Sánchez JP, Poll-Hunter N, Stern N, et al. Balancing two cultures: American Indian/Alaska Native medical students’ perceptions of academic medicine careers. J Community Health. 2016;41:871-880.
- Rayburn WF, Xierali IM, Castillo-Page L, et al. Racial and ethnic differences between obstetrician-gynecologists and other adult medical specialists. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:148-152. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001184.
- Esters D, Xierali IM, Nivet MA, et al. The rise of nontenured faculty in obstetrics and gynecology by sex and underrepresented in medicine status. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134 suppl 1:34S-39S. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003484.
- Ly DP, Seabury SA, Jena AB. Differences in incomes of physicians in the United States by race and sex: observational study. BMJ. 2016;I2923. doi:10.1136/bmj.i2923.
- Groff JY, Mullen PD, Byrd T, et al. Decision making, beliefs, and attitudes toward hysterectomy: a focus group study with medically underserved women in Texas. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9 suppl 2:S39-50. doi: 10.1089/152460900318759.
- Andryjowicz E, Wray T. Regional expansion of minimally invasive surgery for hysterectomy: implementation and methodology in a large multispecialty group. Perm J. 2011;15:42-46.
- Zaritsky E, Ojo A, Tucker LY, et al. Racial disparities in route of hysterectomy for benign indications within an integrated health care system. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e1917004. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17004.
- Abel MK, Kho KA, Walter A, et al. Measuring quality in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: what, how, and why? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:321-326. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.11.013.
Does prophylactic use of tranexamic acid reduce PPH from cesarean delivery when coupled with uterotonics?
Sentilhes L, Senat MV, Le Lous M, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after cesarean delivery. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1623-1634. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028788.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.1 Many preventive strategies, including tranexamic acid administration, have been studied in an attempt to reduce the risk of PPH. Tranexamic acid prevents the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, preventing the breakdown of fibrin, and ultimately stabilizing the fibrin matrix of clot.2 It has been shown to be an effective approach to treating hemorrhage in patients after trauma as well as cardiac surgery.3,4 The use of tranexamic acid in obstetric hemorrhage has reduced mortality in previous trials,5 but its prophylactic use has had mixed results in preventing obstetric hemorrhage.6-8
Recently, Sentilhes and colleagues published the largest prospective study to date addressing the efficacy of tranexamic acid for the primary prevention of PPH.
Details of the study
Multiple hospitals throughout France participated in the investigators’ double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Women undergoing CD at 34 or more weeks’ gestation (N = 4,551) were randomly assigned to receive 1 g of intravenous (IV) tranexamic acid or placebo after cord clamping. Both groups received IV prophylactic uterotonics. The primary outcome was PPH, defined by estimated blood loss (EBL) greater than 1 L or receipt of red blood cell transfusion within the first 2 days after surgery.
Results. The rate of PPH was significantly lower in women who received tranexamic acid compared with those who received placebo. Yet, the mean EBL between the 2 groups differed by only 100 mL. The rates of blood transfusions, additional uterotonic administration, arterial embolization, and hysterectomy did not differ between groups.
The clinicians responsible for the care of these patients did not observe a difference in the rate of “clinically significant” PPH between those who received tranexamic acid and those who received placebo. Women who received tranexamic acid were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting, but they did not have any increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease.
Study strengths and limitations
Sentilhes and colleagues’ study findings contradict those of an earlier meta-analysis on the topic.9 This may be due to the effect of publication bias on meta-analyses, which makes them prone to supporting the findings of published positive trials while missing data from negative trials that did not reach publication. The gold standard for addressing a research question such as this is a randomized controlled trial (RCT). The study reviewed here is an excellent example of a well-designed and executed RCT.
There may be a benefit to prophylactic tranexamic acid in certain populations not well captured among these study participants. The inclusion criteria were broad, including both prelabor and intrapartum CDs, making the results generalizable. However, the population studied, with a mean body mass index of 26 kg/m2 and age of 33, may not resemble some readers’ patient population. Prespecified subgroup analyses did not find a benefit to tranexamic acid in patients considered at high risk for PPH or in those undergoing intrapartum CD. ●
Prevention of PPH would reduce the burden of maternal morbidity and mortality dramatically. Unfortunately, the addition of tranexamic acid as a prophylactic agent at CD does not appear to have a clinically significant impact on the outcomes that matter to patients or providers. While tranexamic acid certainly has a role in the treatment of PPH, its benefit as a preventive agent has yet to be demonstrated.
JONATHAN S. HIRSHBERG, MD,
AND ALISON G. CAHILL, MD, MSCI
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e323-e333.
- Chauncey JM, Wieters JS. Tranexamic Acid. StatPearls Publishing LLC [internet]; 2021.
- Karski JM, Teasdale SJ, Norman P, et al. Prevention of bleeding after cardiopulmonary bypass with high-dose tranexamic acid. Double-blind, randomized clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;110:835-842.
- Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats T, et al. The CRASH-2 trial: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of the effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events and transfusion requirement in bleeding trauma patients. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17:1-79.
- WOMAN Trial Collaborators. Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage (WOMAN): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2105-2116.
- Sentilhes L, Winer N, Azria E, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after vaginal delivery. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:731-742.
- Shahid A, Khan A. Tranexamic acid in decreasing blood loss during and after caesarean section. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23;459-462.
- Simonazzi G, Bisulli M, Saccone G, et al. Tranexamic acid for preventing postpartum blood loss after cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016;95:28-37.
- Wang Y, Liu S, He L. Prophylactic use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion requirements in patients undergoing cesarean section: a meta-analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1562-1575.
Sentilhes L, Senat MV, Le Lous M, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after cesarean delivery. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1623-1634. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028788.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.1 Many preventive strategies, including tranexamic acid administration, have been studied in an attempt to reduce the risk of PPH. Tranexamic acid prevents the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, preventing the breakdown of fibrin, and ultimately stabilizing the fibrin matrix of clot.2 It has been shown to be an effective approach to treating hemorrhage in patients after trauma as well as cardiac surgery.3,4 The use of tranexamic acid in obstetric hemorrhage has reduced mortality in previous trials,5 but its prophylactic use has had mixed results in preventing obstetric hemorrhage.6-8
Recently, Sentilhes and colleagues published the largest prospective study to date addressing the efficacy of tranexamic acid for the primary prevention of PPH.
Details of the study
Multiple hospitals throughout France participated in the investigators’ double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Women undergoing CD at 34 or more weeks’ gestation (N = 4,551) were randomly assigned to receive 1 g of intravenous (IV) tranexamic acid or placebo after cord clamping. Both groups received IV prophylactic uterotonics. The primary outcome was PPH, defined by estimated blood loss (EBL) greater than 1 L or receipt of red blood cell transfusion within the first 2 days after surgery.
Results. The rate of PPH was significantly lower in women who received tranexamic acid compared with those who received placebo. Yet, the mean EBL between the 2 groups differed by only 100 mL. The rates of blood transfusions, additional uterotonic administration, arterial embolization, and hysterectomy did not differ between groups.
The clinicians responsible for the care of these patients did not observe a difference in the rate of “clinically significant” PPH between those who received tranexamic acid and those who received placebo. Women who received tranexamic acid were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting, but they did not have any increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease.
Study strengths and limitations
Sentilhes and colleagues’ study findings contradict those of an earlier meta-analysis on the topic.9 This may be due to the effect of publication bias on meta-analyses, which makes them prone to supporting the findings of published positive trials while missing data from negative trials that did not reach publication. The gold standard for addressing a research question such as this is a randomized controlled trial (RCT). The study reviewed here is an excellent example of a well-designed and executed RCT.
There may be a benefit to prophylactic tranexamic acid in certain populations not well captured among these study participants. The inclusion criteria were broad, including both prelabor and intrapartum CDs, making the results generalizable. However, the population studied, with a mean body mass index of 26 kg/m2 and age of 33, may not resemble some readers’ patient population. Prespecified subgroup analyses did not find a benefit to tranexamic acid in patients considered at high risk for PPH or in those undergoing intrapartum CD. ●
Prevention of PPH would reduce the burden of maternal morbidity and mortality dramatically. Unfortunately, the addition of tranexamic acid as a prophylactic agent at CD does not appear to have a clinically significant impact on the outcomes that matter to patients or providers. While tranexamic acid certainly has a role in the treatment of PPH, its benefit as a preventive agent has yet to be demonstrated.
JONATHAN S. HIRSHBERG, MD,
AND ALISON G. CAHILL, MD, MSCI
Sentilhes L, Senat MV, Le Lous M, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after cesarean delivery. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1623-1634. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028788.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.1 Many preventive strategies, including tranexamic acid administration, have been studied in an attempt to reduce the risk of PPH. Tranexamic acid prevents the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, preventing the breakdown of fibrin, and ultimately stabilizing the fibrin matrix of clot.2 It has been shown to be an effective approach to treating hemorrhage in patients after trauma as well as cardiac surgery.3,4 The use of tranexamic acid in obstetric hemorrhage has reduced mortality in previous trials,5 but its prophylactic use has had mixed results in preventing obstetric hemorrhage.6-8
Recently, Sentilhes and colleagues published the largest prospective study to date addressing the efficacy of tranexamic acid for the primary prevention of PPH.
Details of the study
Multiple hospitals throughout France participated in the investigators’ double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Women undergoing CD at 34 or more weeks’ gestation (N = 4,551) were randomly assigned to receive 1 g of intravenous (IV) tranexamic acid or placebo after cord clamping. Both groups received IV prophylactic uterotonics. The primary outcome was PPH, defined by estimated blood loss (EBL) greater than 1 L or receipt of red blood cell transfusion within the first 2 days after surgery.
Results. The rate of PPH was significantly lower in women who received tranexamic acid compared with those who received placebo. Yet, the mean EBL between the 2 groups differed by only 100 mL. The rates of blood transfusions, additional uterotonic administration, arterial embolization, and hysterectomy did not differ between groups.
The clinicians responsible for the care of these patients did not observe a difference in the rate of “clinically significant” PPH between those who received tranexamic acid and those who received placebo. Women who received tranexamic acid were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting, but they did not have any increased risk of venous thromboembolic disease.
Study strengths and limitations
Sentilhes and colleagues’ study findings contradict those of an earlier meta-analysis on the topic.9 This may be due to the effect of publication bias on meta-analyses, which makes them prone to supporting the findings of published positive trials while missing data from negative trials that did not reach publication. The gold standard for addressing a research question such as this is a randomized controlled trial (RCT). The study reviewed here is an excellent example of a well-designed and executed RCT.
There may be a benefit to prophylactic tranexamic acid in certain populations not well captured among these study participants. The inclusion criteria were broad, including both prelabor and intrapartum CDs, making the results generalizable. However, the population studied, with a mean body mass index of 26 kg/m2 and age of 33, may not resemble some readers’ patient population. Prespecified subgroup analyses did not find a benefit to tranexamic acid in patients considered at high risk for PPH or in those undergoing intrapartum CD. ●
Prevention of PPH would reduce the burden of maternal morbidity and mortality dramatically. Unfortunately, the addition of tranexamic acid as a prophylactic agent at CD does not appear to have a clinically significant impact on the outcomes that matter to patients or providers. While tranexamic acid certainly has a role in the treatment of PPH, its benefit as a preventive agent has yet to be demonstrated.
JONATHAN S. HIRSHBERG, MD,
AND ALISON G. CAHILL, MD, MSCI
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e323-e333.
- Chauncey JM, Wieters JS. Tranexamic Acid. StatPearls Publishing LLC [internet]; 2021.
- Karski JM, Teasdale SJ, Norman P, et al. Prevention of bleeding after cardiopulmonary bypass with high-dose tranexamic acid. Double-blind, randomized clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;110:835-842.
- Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats T, et al. The CRASH-2 trial: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of the effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events and transfusion requirement in bleeding trauma patients. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17:1-79.
- WOMAN Trial Collaborators. Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage (WOMAN): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2105-2116.
- Sentilhes L, Winer N, Azria E, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after vaginal delivery. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:731-742.
- Shahid A, Khan A. Tranexamic acid in decreasing blood loss during and after caesarean section. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23;459-462.
- Simonazzi G, Bisulli M, Saccone G, et al. Tranexamic acid for preventing postpartum blood loss after cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016;95:28-37.
- Wang Y, Liu S, He L. Prophylactic use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion requirements in patients undergoing cesarean section: a meta-analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1562-1575.
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e323-e333.
- Chauncey JM, Wieters JS. Tranexamic Acid. StatPearls Publishing LLC [internet]; 2021.
- Karski JM, Teasdale SJ, Norman P, et al. Prevention of bleeding after cardiopulmonary bypass with high-dose tranexamic acid. Double-blind, randomized clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;110:835-842.
- Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats T, et al. The CRASH-2 trial: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of the effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events and transfusion requirement in bleeding trauma patients. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17:1-79.
- WOMAN Trial Collaborators. Effect of early tranexamic acid administration on mortality, hysterectomy, and other morbidities in women with post-partum haemorrhage (WOMAN): an international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2105-2116.
- Sentilhes L, Winer N, Azria E, et al; Groupe de Recherche en Obstetrique et Gynecologie. Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after vaginal delivery. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:731-742.
- Shahid A, Khan A. Tranexamic acid in decreasing blood loss during and after caesarean section. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23;459-462.
- Simonazzi G, Bisulli M, Saccone G, et al. Tranexamic acid for preventing postpartum blood loss after cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2016;95:28-37.
- Wang Y, Liu S, He L. Prophylactic use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion requirements in patients undergoing cesarean section: a meta-analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1562-1575.
3 cases of hormone therapy optimized to match the patient problem
There are dozens of medications containing combinations of estrogen and progestin. I am often confused by the bewildering proliferation of generic brand names used to describe the same estrogen-progestin (E-P) regimen. For example, the combination medication containing ethinyl estradiol 20 µg plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 1 mg is available under at least 5 different names: Lo Estrin 1/20 (Warner Chilcot), Junel 1/20 (Teva Pharmaceuticals), Microgestin Fe 1/20 (Mayne Pharma), Gildess 1/20 (Qualitest Pharmaceuticals), and Larin 1/20 (Novast Laboratories). To reduce the confusion, it is often useful to select a single preferred estrogen and progestin and use the dose combinations that are available to treat a wide range of gynecology problems (TABLE). In this editorial I focus on using various dose combinations of ethinyl estradiol and NEA to treat 3 common gynecologic problems.
CASE 1 Polycystic ovary syndrome
A 19-year-old woman reports 4 spontaneous menses in the past year and bothersome facial hair and acne. Her total testosterone concentration is at the upper limit of normal (0.46 ng/mL) and her sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) concentration is at the lower limit of normal (35 nM). For treatment of the patient’s menstrual disorder, what is an optimal E-P combination?
Prioritize the use of an estrogen-dominant medication
Based on the Rotterdam criteria this woman has polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).1 In women with PCOS, luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion is increased, stimulating excessive ovarian production of testosterone.2 In addition, many women with PCOS have decreased hepatic secretion of SHBG, a binding protein that prevents testosterone from entering cells, resulting in excessive bioavailable testosterone.3 The Endocrine Society recommends that women with PCOS who have menstrual dysfunction or hirsutism be treated initially with a combination E-P hormone medication.1 Combination E-P medications suppress pituitary secretion of LH, thereby reducing ovarian production of testosterone, and ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic secretion of SHBG, reducing bioavailable testosterone. These two goals are best accomplished with an oral E-P hormone medication containing ethinyl estradiol doses of 20 µg to 30 µg per pill. An E-P hormone medication containing pills with an ethinyl estradiol dose ≤ 10 µg-daily may stimulate less hepatic production of SHBG than a pill with an ethinyl estradiol dose of 20 µg or 30 µg daily.4,5 In addition, E-P pills containing levonorgestrel suppress SHBG hormone secretion compared with E-P pills with other progestins.6 Therefore, levonorgestrel-containing E-P pills should not be prioritized for use in women with PCOS because the estrogen-induced increase in SHBG will be blunted by levonorgestrel.
CASE 2 Moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis lesions in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy showed endometriosis. Postoperatively, the patient was treated with an E-P pill containing 30 µg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg desogestrel per pill using a continuous-dosing protocol. During the year following the laparoscopy, her pelvic pain symptoms gradually increased until they became severe, preventing her from performing daily activities on multiple days per month. She was prescribed elagolix but her insurance did not approve the treatment. What alternative treatment would you prescribe?
Continue to: Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain...
Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain
Cellular activity in endometriosis lesions is stimulated by estradiol and inhibited by a high concentration of androgenic progestins or androgens. This simplified endocrine paradigm explains the effectiveness of hormonal treatments that suppress ovarian estradiol production, including leuprolide, elagolix, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and NEA. For the woman in the above case, I would advocate for elagolix treatment but, following the insurance denial of the prescription, an alternative treatment for moderate or severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis would be a progestin-dominant hormone medication (for example, NEA 5 mg daily). Norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily may be associated with bothersome adverse effects including weight gain (16% of patients; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%).7
I sometimes see women with moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis being treated with norethindrone 0.35 mg daily. This dose of norethindrone is suboptimal for pain treatment because it does not reliably suppress ovarian production of estradiol. In addition, the cells in endometriosis lesions are often resistant to the effects of progesterone, requiring higher dosages to produce secretory or decidual changes. In most situations, I recommend against the use of norethindrone 0.35 mg daily for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
Patients commonly ask if NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy. Although it is not approved at this dosage by the US Food and Drug Administration as a contraceptive,8 norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 Norethindrone acetate is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone (which is the FDA-approved dosage mentioned above). Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy, especially if there is good adherence with the daily medication.
CASE 3 Perimenopausal AUB
A 45-year-old woman reports varying menstrual cycle lengths from 24 to 60 days with very heavy menses in some cycles. Pelvic ultrasonography shows no abnormality. Endometrial biopsy shows a proliferative endometrium. Her serum progesterone level, obtained 1 week before the onset of menses, is < 3 ng/mL. She has no past history of heavy menses, easy bruising, excessive bleeding with procedures, or a family history of bleeding problems. She also reports occasional hot flashes that wake her from sleep.
Use an estrogen step-down regimen to manage postmenopause transition
This patient is likely in the perimenopause transition, and the abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is caused, in part, by oligo- or anovulation. Perimenopausal women with AUB may have cycles characterized by above normal ovarian estradiol production and below normal progesterone production, or frank anovulation.10 Elevated ovarian estrogen and low progesterone production sets the stage for heavy bleeding in the perimenopause, regardless of the presence of uterine pathology such as fibroids.
For perimenopausal women, one option for treatment of AUB due to anovulation is to prescribe an estrogen step-down regimen. For the 45-year-old woman in this case, initiating treatment with an E-P pill containing ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and NEA 1 mg will likely control the AUB and her occasional hot flash.11 As the woman ages, the ethinyl estradiol dose can be decreased to pills containing 5 µg and then 2.5 µg, covering the transition into postmenopause. Once the woman is in the postmenopause, treatment with transdermal estradiol and oral micronized progesterone is an option to treat menopausal vasomotor symptoms.
Optimize estrogen and progestin treatment for your patients
Many gynecologic problems are effectively treated by estrogen and/or progestin steroids. The dose of estrogen and progestin should be tailored to the specific problem. For PCOS, the estrogen dose selected should be sufficient to safely stimulate hepatic SHBG production. For endometriosis, if a GnRH antagonist is not available to the patient, a high-dose progestin, such as NEA 5 mg, may be an effective treatment. During the perimenopause transition in a woman with AUB, a treatment plan using a sequential E-P step-down program might control symptoms and help smoothly glide the patient into the postmenopause. ●
- Legro RS, Arslanian SA, Ehrmann DA, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:4565-4592. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2350.
- Rosenfield RL, Ehrmann DA. The pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): the hypothesis of PCOS as functional ovarian hyperandrogenism revisited. Endocr Rev. 2016;37:467-520. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1104.
- Zhu JL, Chen Z, Feng WJ, et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin and polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;499:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.010.
- Oner G, Muderris II. A prospective randomized trial comparing low-dose ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 24/4 combined oral contraceptive vs. ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 21/7 combined oral contraceptive in the treatment of hirsutism. Contraception. 2011;84:508-511. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.03.002.
- Boyd RA, Zegarac EA, Posvar EL, et al. Minimal androgenic activity of a new oral contraceptive containing norethindrone acetate and graduated doses of ethinyl estradiol. Contraception. 2001;63:71-76. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(01)00179-2.
- Thorneycroft IH, Stanczyk FZ, Bradshaw KD, et al. Effect of low-dose oral contraceptives on androgenic markers and acne. Contraception. 1999;60:255-262. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(99)00093-1.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2011.09.013.
- Aygestin [package insert]. Pomona, NY: Duramed Pharmaceuticals; 2007.
- Camila [package insert]. Greenville, NC; Mayne Pharma; 2018.
- Santoro N, Brown JR, Adel T, et al. Characterization of reproductive hormonal dynamics in the perimenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:1495-1501. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.4.8636357.
- Speroff L, Symons J, Kempfert N, et al; FemHrt Study Investigators. The effect of varying low-dose combinations of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol (Femhrt) on the frequency and intensity of vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2000;7:383-390. doi: 10.1097/00042192-200011000-00003.
There are dozens of medications containing combinations of estrogen and progestin. I am often confused by the bewildering proliferation of generic brand names used to describe the same estrogen-progestin (E-P) regimen. For example, the combination medication containing ethinyl estradiol 20 µg plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 1 mg is available under at least 5 different names: Lo Estrin 1/20 (Warner Chilcot), Junel 1/20 (Teva Pharmaceuticals), Microgestin Fe 1/20 (Mayne Pharma), Gildess 1/20 (Qualitest Pharmaceuticals), and Larin 1/20 (Novast Laboratories). To reduce the confusion, it is often useful to select a single preferred estrogen and progestin and use the dose combinations that are available to treat a wide range of gynecology problems (TABLE). In this editorial I focus on using various dose combinations of ethinyl estradiol and NEA to treat 3 common gynecologic problems.

CASE 1 Polycystic ovary syndrome
A 19-year-old woman reports 4 spontaneous menses in the past year and bothersome facial hair and acne. Her total testosterone concentration is at the upper limit of normal (0.46 ng/mL) and her sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) concentration is at the lower limit of normal (35 nM). For treatment of the patient’s menstrual disorder, what is an optimal E-P combination?
Prioritize the use of an estrogen-dominant medication
Based on the Rotterdam criteria this woman has polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).1 In women with PCOS, luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion is increased, stimulating excessive ovarian production of testosterone.2 In addition, many women with PCOS have decreased hepatic secretion of SHBG, a binding protein that prevents testosterone from entering cells, resulting in excessive bioavailable testosterone.3 The Endocrine Society recommends that women with PCOS who have menstrual dysfunction or hirsutism be treated initially with a combination E-P hormone medication.1 Combination E-P medications suppress pituitary secretion of LH, thereby reducing ovarian production of testosterone, and ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic secretion of SHBG, reducing bioavailable testosterone. These two goals are best accomplished with an oral E-P hormone medication containing ethinyl estradiol doses of 20 µg to 30 µg per pill. An E-P hormone medication containing pills with an ethinyl estradiol dose ≤ 10 µg-daily may stimulate less hepatic production of SHBG than a pill with an ethinyl estradiol dose of 20 µg or 30 µg daily.4,5 In addition, E-P pills containing levonorgestrel suppress SHBG hormone secretion compared with E-P pills with other progestins.6 Therefore, levonorgestrel-containing E-P pills should not be prioritized for use in women with PCOS because the estrogen-induced increase in SHBG will be blunted by levonorgestrel.
CASE 2 Moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis lesions in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy showed endometriosis. Postoperatively, the patient was treated with an E-P pill containing 30 µg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg desogestrel per pill using a continuous-dosing protocol. During the year following the laparoscopy, her pelvic pain symptoms gradually increased until they became severe, preventing her from performing daily activities on multiple days per month. She was prescribed elagolix but her insurance did not approve the treatment. What alternative treatment would you prescribe?
Continue to: Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain...
Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain
Cellular activity in endometriosis lesions is stimulated by estradiol and inhibited by a high concentration of androgenic progestins or androgens. This simplified endocrine paradigm explains the effectiveness of hormonal treatments that suppress ovarian estradiol production, including leuprolide, elagolix, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and NEA. For the woman in the above case, I would advocate for elagolix treatment but, following the insurance denial of the prescription, an alternative treatment for moderate or severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis would be a progestin-dominant hormone medication (for example, NEA 5 mg daily). Norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily may be associated with bothersome adverse effects including weight gain (16% of patients; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%).7
I sometimes see women with moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis being treated with norethindrone 0.35 mg daily. This dose of norethindrone is suboptimal for pain treatment because it does not reliably suppress ovarian production of estradiol. In addition, the cells in endometriosis lesions are often resistant to the effects of progesterone, requiring higher dosages to produce secretory or decidual changes. In most situations, I recommend against the use of norethindrone 0.35 mg daily for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
Patients commonly ask if NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy. Although it is not approved at this dosage by the US Food and Drug Administration as a contraceptive,8 norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 Norethindrone acetate is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone (which is the FDA-approved dosage mentioned above). Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy, especially if there is good adherence with the daily medication.
CASE 3 Perimenopausal AUB
A 45-year-old woman reports varying menstrual cycle lengths from 24 to 60 days with very heavy menses in some cycles. Pelvic ultrasonography shows no abnormality. Endometrial biopsy shows a proliferative endometrium. Her serum progesterone level, obtained 1 week before the onset of menses, is < 3 ng/mL. She has no past history of heavy menses, easy bruising, excessive bleeding with procedures, or a family history of bleeding problems. She also reports occasional hot flashes that wake her from sleep.
Use an estrogen step-down regimen to manage postmenopause transition
This patient is likely in the perimenopause transition, and the abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is caused, in part, by oligo- or anovulation. Perimenopausal women with AUB may have cycles characterized by above normal ovarian estradiol production and below normal progesterone production, or frank anovulation.10 Elevated ovarian estrogen and low progesterone production sets the stage for heavy bleeding in the perimenopause, regardless of the presence of uterine pathology such as fibroids.
For perimenopausal women, one option for treatment of AUB due to anovulation is to prescribe an estrogen step-down regimen. For the 45-year-old woman in this case, initiating treatment with an E-P pill containing ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and NEA 1 mg will likely control the AUB and her occasional hot flash.11 As the woman ages, the ethinyl estradiol dose can be decreased to pills containing 5 µg and then 2.5 µg, covering the transition into postmenopause. Once the woman is in the postmenopause, treatment with transdermal estradiol and oral micronized progesterone is an option to treat menopausal vasomotor symptoms.
Optimize estrogen and progestin treatment for your patients
Many gynecologic problems are effectively treated by estrogen and/or progestin steroids. The dose of estrogen and progestin should be tailored to the specific problem. For PCOS, the estrogen dose selected should be sufficient to safely stimulate hepatic SHBG production. For endometriosis, if a GnRH antagonist is not available to the patient, a high-dose progestin, such as NEA 5 mg, may be an effective treatment. During the perimenopause transition in a woman with AUB, a treatment plan using a sequential E-P step-down program might control symptoms and help smoothly glide the patient into the postmenopause. ●
There are dozens of medications containing combinations of estrogen and progestin. I am often confused by the bewildering proliferation of generic brand names used to describe the same estrogen-progestin (E-P) regimen. For example, the combination medication containing ethinyl estradiol 20 µg plus norethindrone acetate (NEA) 1 mg is available under at least 5 different names: Lo Estrin 1/20 (Warner Chilcot), Junel 1/20 (Teva Pharmaceuticals), Microgestin Fe 1/20 (Mayne Pharma), Gildess 1/20 (Qualitest Pharmaceuticals), and Larin 1/20 (Novast Laboratories). To reduce the confusion, it is often useful to select a single preferred estrogen and progestin and use the dose combinations that are available to treat a wide range of gynecology problems (TABLE). In this editorial I focus on using various dose combinations of ethinyl estradiol and NEA to treat 3 common gynecologic problems.

CASE 1 Polycystic ovary syndrome
A 19-year-old woman reports 4 spontaneous menses in the past year and bothersome facial hair and acne. Her total testosterone concentration is at the upper limit of normal (0.46 ng/mL) and her sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) concentration is at the lower limit of normal (35 nM). For treatment of the patient’s menstrual disorder, what is an optimal E-P combination?
Prioritize the use of an estrogen-dominant medication
Based on the Rotterdam criteria this woman has polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).1 In women with PCOS, luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion is increased, stimulating excessive ovarian production of testosterone.2 In addition, many women with PCOS have decreased hepatic secretion of SHBG, a binding protein that prevents testosterone from entering cells, resulting in excessive bioavailable testosterone.3 The Endocrine Society recommends that women with PCOS who have menstrual dysfunction or hirsutism be treated initially with a combination E-P hormone medication.1 Combination E-P medications suppress pituitary secretion of LH, thereby reducing ovarian production of testosterone, and ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic secretion of SHBG, reducing bioavailable testosterone. These two goals are best accomplished with an oral E-P hormone medication containing ethinyl estradiol doses of 20 µg to 30 µg per pill. An E-P hormone medication containing pills with an ethinyl estradiol dose ≤ 10 µg-daily may stimulate less hepatic production of SHBG than a pill with an ethinyl estradiol dose of 20 µg or 30 µg daily.4,5 In addition, E-P pills containing levonorgestrel suppress SHBG hormone secretion compared with E-P pills with other progestins.6 Therefore, levonorgestrel-containing E-P pills should not be prioritized for use in women with PCOS because the estrogen-induced increase in SHBG will be blunted by levonorgestrel.
CASE 2 Moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
A 25-year-old woman (G0) with severe dysmenorrhea had a laparoscopy showing endometriosis lesions in the cul-de-sac and a peritoneal window near the left uterosacral ligament. Biopsy showed endometriosis. Postoperatively, the patient was treated with an E-P pill containing 30 µg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg desogestrel per pill using a continuous-dosing protocol. During the year following the laparoscopy, her pelvic pain symptoms gradually increased until they became severe, preventing her from performing daily activities on multiple days per month. She was prescribed elagolix but her insurance did not approve the treatment. What alternative treatment would you prescribe?
Continue to: Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain...
Use progestin-dominant pills to treat pelvic pain
Cellular activity in endometriosis lesions is stimulated by estradiol and inhibited by a high concentration of androgenic progestins or androgens. This simplified endocrine paradigm explains the effectiveness of hormonal treatments that suppress ovarian estradiol production, including leuprolide, elagolix, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and NEA. For the woman in the above case, I would advocate for elagolix treatment but, following the insurance denial of the prescription, an alternative treatment for moderate or severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis would be a progestin-dominant hormone medication (for example, NEA 5 mg daily). Norethindrone acetate 5 mg daily may be associated with bothersome adverse effects including weight gain (16% of patients; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%).7
I sometimes see women with moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis being treated with norethindrone 0.35 mg daily. This dose of norethindrone is suboptimal for pain treatment because it does not reliably suppress ovarian production of estradiol. In addition, the cells in endometriosis lesions are often resistant to the effects of progesterone, requiring higher dosages to produce secretory or decidual changes. In most situations, I recommend against the use of norethindrone 0.35 mg daily for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis.
Patients commonly ask if NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy. Although it is not approved at this dosage by the US Food and Drug Administration as a contraceptive,8 norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 Norethindrone acetate is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone (which is the FDA-approved dosage mentioned above). Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg daily has contraceptive efficacy, especially if there is good adherence with the daily medication.
CASE 3 Perimenopausal AUB
A 45-year-old woman reports varying menstrual cycle lengths from 24 to 60 days with very heavy menses in some cycles. Pelvic ultrasonography shows no abnormality. Endometrial biopsy shows a proliferative endometrium. Her serum progesterone level, obtained 1 week before the onset of menses, is < 3 ng/mL. She has no past history of heavy menses, easy bruising, excessive bleeding with procedures, or a family history of bleeding problems. She also reports occasional hot flashes that wake her from sleep.
Use an estrogen step-down regimen to manage postmenopause transition
This patient is likely in the perimenopause transition, and the abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is caused, in part, by oligo- or anovulation. Perimenopausal women with AUB may have cycles characterized by above normal ovarian estradiol production and below normal progesterone production, or frank anovulation.10 Elevated ovarian estrogen and low progesterone production sets the stage for heavy bleeding in the perimenopause, regardless of the presence of uterine pathology such as fibroids.
For perimenopausal women, one option for treatment of AUB due to anovulation is to prescribe an estrogen step-down regimen. For the 45-year-old woman in this case, initiating treatment with an E-P pill containing ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and NEA 1 mg will likely control the AUB and her occasional hot flash.11 As the woman ages, the ethinyl estradiol dose can be decreased to pills containing 5 µg and then 2.5 µg, covering the transition into postmenopause. Once the woman is in the postmenopause, treatment with transdermal estradiol and oral micronized progesterone is an option to treat menopausal vasomotor symptoms.
Optimize estrogen and progestin treatment for your patients
Many gynecologic problems are effectively treated by estrogen and/or progestin steroids. The dose of estrogen and progestin should be tailored to the specific problem. For PCOS, the estrogen dose selected should be sufficient to safely stimulate hepatic SHBG production. For endometriosis, if a GnRH antagonist is not available to the patient, a high-dose progestin, such as NEA 5 mg, may be an effective treatment. During the perimenopause transition in a woman with AUB, a treatment plan using a sequential E-P step-down program might control symptoms and help smoothly glide the patient into the postmenopause. ●
- Legro RS, Arslanian SA, Ehrmann DA, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:4565-4592. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2350.
- Rosenfield RL, Ehrmann DA. The pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): the hypothesis of PCOS as functional ovarian hyperandrogenism revisited. Endocr Rev. 2016;37:467-520. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1104.
- Zhu JL, Chen Z, Feng WJ, et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin and polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;499:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.010.
- Oner G, Muderris II. A prospective randomized trial comparing low-dose ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 24/4 combined oral contraceptive vs. ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 21/7 combined oral contraceptive in the treatment of hirsutism. Contraception. 2011;84:508-511. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.03.002.
- Boyd RA, Zegarac EA, Posvar EL, et al. Minimal androgenic activity of a new oral contraceptive containing norethindrone acetate and graduated doses of ethinyl estradiol. Contraception. 2001;63:71-76. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(01)00179-2.
- Thorneycroft IH, Stanczyk FZ, Bradshaw KD, et al. Effect of low-dose oral contraceptives on androgenic markers and acne. Contraception. 1999;60:255-262. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(99)00093-1.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2011.09.013.
- Aygestin [package insert]. Pomona, NY: Duramed Pharmaceuticals; 2007.
- Camila [package insert]. Greenville, NC; Mayne Pharma; 2018.
- Santoro N, Brown JR, Adel T, et al. Characterization of reproductive hormonal dynamics in the perimenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:1495-1501. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.4.8636357.
- Speroff L, Symons J, Kempfert N, et al; FemHrt Study Investigators. The effect of varying low-dose combinations of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol (Femhrt) on the frequency and intensity of vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2000;7:383-390. doi: 10.1097/00042192-200011000-00003.
- Legro RS, Arslanian SA, Ehrmann DA, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:4565-4592. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2350.
- Rosenfield RL, Ehrmann DA. The pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): the hypothesis of PCOS as functional ovarian hyperandrogenism revisited. Endocr Rev. 2016;37:467-520. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1104.
- Zhu JL, Chen Z, Feng WJ, et al. Sex hormone-binding globulin and polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;499:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.010.
- Oner G, Muderris II. A prospective randomized trial comparing low-dose ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 24/4 combined oral contraceptive vs. ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone 21/7 combined oral contraceptive in the treatment of hirsutism. Contraception. 2011;84:508-511. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.03.002.
- Boyd RA, Zegarac EA, Posvar EL, et al. Minimal androgenic activity of a new oral contraceptive containing norethindrone acetate and graduated doses of ethinyl estradiol. Contraception. 2001;63:71-76. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(01)00179-2.
- Thorneycroft IH, Stanczyk FZ, Bradshaw KD, et al. Effect of low-dose oral contraceptives on androgenic markers and acne. Contraception. 1999;60:255-262. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(99)00093-1.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2011.09.013.
- Aygestin [package insert]. Pomona, NY: Duramed Pharmaceuticals; 2007.
- Camila [package insert]. Greenville, NC; Mayne Pharma; 2018.
- Santoro N, Brown JR, Adel T, et al. Characterization of reproductive hormonal dynamics in the perimenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:1495-1501. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.4.8636357.
- Speroff L, Symons J, Kempfert N, et al; FemHrt Study Investigators. The effect of varying low-dose combinations of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol (Femhrt) on the frequency and intensity of vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2000;7:383-390. doi: 10.1097/00042192-200011000-00003.
Daily reporting from the 2021 Society of Gynecologic Surgeons Annual Meeting
TUESDAY, 6/29/21. DAY 3 AT SGS
The third day of the annual SGS meeting started with several academic roundtables hosted by experts in the field. These authorities shared their knowledge on a range of topics including endometriosis, building an academic career, diversity and equity in the workplace, and scientific publishing. The general session got underway with additional oral and video presentations highlighting advancements in our field. This year’s SGS President Dr. Miles Murphy gave the annual presidential address. He spoke genuinely and humbly about our field. Whitney Ross, MD, (@WRossMD), referred to his speech on Twitter as “Best. Presidential. Address. Ever.” –a sentiment felt by many in the crowd!
This year’s Telinde Lecture was given by Janet Dombrowski, the first ever non-physician to present this lecture. She spoke on resiliency in a lecture titled, “Cultivating Resilience: The Power in Connection & Collaboration.” It was an insightful and wise presentation on the power of connection and how connection bolsters our resiliency. She challenged us to all break down “thinking habits” that isolate us into silos and get in the way of powerful connection and collaboration. She reminded us of the African greeting “Sawubona” (I see you) and “Sikhona” (Because you see me, I am here). A gentle reminder that we feel our existence most tangibly when we are seen by others—an idea consistent with other important themes of this conference, focused on diversity, equity, and inclusion of all. The morning session was rounded out with a panel discussion on “Novel GYN Office Procedure,” featuring Drs. Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Abbas Shobeiri (@ShobeiriAbbas), Andrea Pezzela, and Eric Sokol.
The afternoon was filled with leisure activities in beautiful Palm Springs, including the SGS Golf Tournament, mountain biking, aerial tramway tour, and hike. The weather even cooperated with slightly cooler temperatures (think 100℉ instead of 120℉)! The evening was filled with food, drinks, and the excitement around the annual “SGS’ Got Talent” show! Everyone was able to let down, show off their dance moves, and enjoy some of that much needed connection time!
Tomorrow is the last day of #SGS2021! Excited to round out the conference with continued learning.
MONDAY, 6/28/21. DAY 2 AT SGS
The sun is up and working hard here in Palm Springs, and so are we!
Welcome and introduction of new members
The general session started with a warm welcome to the 12 new SGS members. A special shout out to Dr. Kelly Wright who is a new SGS Member and won the #SGS2021 tweetup! She ranked as a top influencer, prolific tweeter, and made more than 250K impressions leading up to SGS! Way to represent @MigsRunner.
General scientific sessions
There were several excellent oral and video presentations throughout the morning session. A range of topics were discussed, including postoperative pain management, strategies for cost-effective surgery, and how racial and ethnic disparities play into our medical education and patient outcomes. Dr. Eva Welch gave a stellar video presentation on straight-stick sacrocolpopexy techniques for the savvy surgeon. I personally will be incorporating some of her needle management tricks!
After a brief break with some refreshments and a stroll around the exhibit hall, the second scientific session initiated with a transformative lecture. Dr. Mark Walters presented "Insights on Surgical Education: How Can I Help You Get Better" in the inaugural Mark D. Walters Lectureship. Dr. Walters shared his experience and insights on how to transform oneself from a good surgeon to an expert and from a teacher to a coach in the operating room. His dedication to our field, years of experience, and wisdom earned him a standing ovation! Additional oral and video presentations followed. Dr. J. Wong shared correlations between surgeon gender and ergonomic strain with laparoscopic devices. Female surgeons more often reported inappropriate fit and expressed physical discomfort compared with male surgeons. Injuries and ergonomic strain lead to less operating and even disability for some surgeons. It is past time for us to have better--we need instruments that fit our hands!
The afternoon session started with a panel on "Perspectives on Race in GYN Surgery." It was another insightful discussion with thought- and action-provoking knowledge. The afternoon session included the SGS Prize Video by Dr. Angela DiCarlo-Meacham on excision of a vulvar cyst.
Fellows' Pelvic Research Network
After adjourning of the scientific sessions, the fellow-ran, multicenter research network (FPRN) met to give updates. This diverse group of both AUGS-SGS and FMIGS-SGS offers mentorship and relationships that are important for future careers and research. The collaboration allows the study of rare outcomes that may not be feasible at single sites. Dr. Amanda Yunker, fellowship director at Vanderbilt University, gave an amazing history lesson on the fields of OB and GYN, and the evolution of gynecologic surgery. We then had fun assigning a "report card grade" on how MIGS is doing comparatively with other subspecialties in the realms of academics and research.
VideoFest
The late afternoon was concluded with a surgical video session. What an amazing and talented group we are here at SGS!
President's awards ceremony and reception
The scientific focused day was rounded out with an evening of honors, awards, and social time as we celebrated all the achievements of our peers and colleagues. The president's reception was filled with food, laughter, networking, and reconnecting with friends and colleagues. We are looking forward to another day of education tomorrow!
Follow @JennaRehmerMD, @GynSurgery, and #SGS2021 on Twitter for updates.
SUNDAY, 6/27/21. DAY 1 AT SGS
Hello live from sunny Palm Spring, CA, and the Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS)! This year’s conference balances the long-awaited return to in-person events while simultaneously embracing virtual learning with their hybrid meeting format. You can follow me, @JennaRehmerMD, and #SGS2021 in real-time on Twitter.
Dismantling racism
We were incredibly fortunate to take a deep dive into dismantling racism in our personal and professional spheres. The postgraduate course was well researched and presented by Drs. Oluwateniola “Teni” Brown, Cassandra Carberry, Olivia Cardenas-Trowers (@otrowers_md), Annetta Madsen, Moiuri Siddique, and Blair Washington (@Dr_B_Washington). Each presentation provided a succinct and cohesive flow, taking us through what racism is, the historical and active structural racism in medicine, and the actions and steps of becoming anti-racist.
Dr. Brown discussed critical race theory. We learned that the engineered system of oppression is so advanced that it is often hidden in plain sight, and that one’s conscious awareness is not necessary in order to uphold the system of oppression. It is reinforced and supported with minimal effort. This is why not being racist is not enough; active anti-racism is needed to bring about change.
Fibroid management
Across the hall, Drs. Linda Bradley (@BradlelMD), Kimberly Kho (@KimberlyKho1), Cara King (@drcaraking), and Kelly Wright (@MigsRunner) broadened our armamentarium for uterine conservation in fibroid management. Dr. Bradley reviewed medical therapies, including novel treatments, as first-line or adjunct treatment options. Next, the course focused on surgical techniques for hysteroscopic myomectomies, optimization of minilaparotomy for myomectomy, and tissue extraction. Dr. King displayed true grit when giving her lecture from the airport after flight delays prevented her from being in person with us.
Multidisciplinary care within gyn surgery
In this virtual only postgraduate course, Drs. Risal Djohan (@DjohanMD), Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Marie Fidela Paraiso, Sandip Vasavada (@SandipVasavada), and Sarah Vogler showed us the importance of multidisciplinary care within gynecologic surgery practices. They explored how to streamline the approach so it complements your practice, how to co-bill for shared patient care, and tips and tricks for optimizing the surgical experience for the patient.
Industry presentations
Over lunch, Dr. Opoku-Akane presented on using ERAS (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocols for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain and how to optimize the use of alternative surgical modalities for endometriosis. Following this, Drs. Albert Huany and Craig McCoy taught about a new technology using electrical stimulation to optimize visualization of the ureter.
Harnessing the power of social media
This workshop, organized by SGS Social Media Committee Chair Dr. Amy Park (@dramypark) showed us the importance of having an online identity for the sharing of ideas, networking, professional development, and education. We learned how to optimize our online bios, proper use of GYN ontology for hashtags, and how to maintain professionalism on social media. We reviewed the data on how sharing publications on social media improves altmetric scores and discussed how our social media influence may be tied to performance in the future.
Lessons in leadership
We rounded out the day with after-dinner dessert and drinks at the evening SGS Women’s Council presentation. We had the great honor of hearing from Lori Ryerker, CEO of Celanese Corporation, a Fortune 500 global company. She provided much wisdom on being a leader. She shared several keys to creating a successful work environment:
- being a leader that “provides an environment where people feel like they can bring their best selves every day” (and that being your best self is being your whole self, without reservations)
- allowing all genders, sexual orientations, races, ethnicities, and ages to show up together without reservations (because only then can people feel safe to be their best, because their best self is their true self).
It was a wonderful and successful kick-off to the meeting. I look forward to a full day tomorrow! Follow along as this year’s Fellow Scholars, Drs. Tara Brah (@TaraBrah), Amr El Haraki (@drharaki), Sheena Galhotra (@SheenaGalhotra), Meenal Misal (@meenalmisalMD), and yours truly, post live updates daily.
TUESDAY, 6/29/21. DAY 3 AT SGS
The third day of the annual SGS meeting started with several academic roundtables hosted by experts in the field. These authorities shared their knowledge on a range of topics including endometriosis, building an academic career, diversity and equity in the workplace, and scientific publishing. The general session got underway with additional oral and video presentations highlighting advancements in our field. This year’s SGS President Dr. Miles Murphy gave the annual presidential address. He spoke genuinely and humbly about our field. Whitney Ross, MD, (@WRossMD), referred to his speech on Twitter as “Best. Presidential. Address. Ever.” –a sentiment felt by many in the crowd!
This year’s Telinde Lecture was given by Janet Dombrowski, the first ever non-physician to present this lecture. She spoke on resiliency in a lecture titled, “Cultivating Resilience: The Power in Connection & Collaboration.” It was an insightful and wise presentation on the power of connection and how connection bolsters our resiliency. She challenged us to all break down “thinking habits” that isolate us into silos and get in the way of powerful connection and collaboration. She reminded us of the African greeting “Sawubona” (I see you) and “Sikhona” (Because you see me, I am here). A gentle reminder that we feel our existence most tangibly when we are seen by others—an idea consistent with other important themes of this conference, focused on diversity, equity, and inclusion of all. The morning session was rounded out with a panel discussion on “Novel GYN Office Procedure,” featuring Drs. Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Abbas Shobeiri (@ShobeiriAbbas), Andrea Pezzela, and Eric Sokol.
The afternoon was filled with leisure activities in beautiful Palm Springs, including the SGS Golf Tournament, mountain biking, aerial tramway tour, and hike. The weather even cooperated with slightly cooler temperatures (think 100℉ instead of 120℉)! The evening was filled with food, drinks, and the excitement around the annual “SGS’ Got Talent” show! Everyone was able to let down, show off their dance moves, and enjoy some of that much needed connection time!
Tomorrow is the last day of #SGS2021! Excited to round out the conference with continued learning.
MONDAY, 6/28/21. DAY 2 AT SGS
The sun is up and working hard here in Palm Springs, and so are we!
Welcome and introduction of new members
The general session started with a warm welcome to the 12 new SGS members. A special shout out to Dr. Kelly Wright who is a new SGS Member and won the #SGS2021 tweetup! She ranked as a top influencer, prolific tweeter, and made more than 250K impressions leading up to SGS! Way to represent @MigsRunner.
General scientific sessions
There were several excellent oral and video presentations throughout the morning session. A range of topics were discussed, including postoperative pain management, strategies for cost-effective surgery, and how racial and ethnic disparities play into our medical education and patient outcomes. Dr. Eva Welch gave a stellar video presentation on straight-stick sacrocolpopexy techniques for the savvy surgeon. I personally will be incorporating some of her needle management tricks!
After a brief break with some refreshments and a stroll around the exhibit hall, the second scientific session initiated with a transformative lecture. Dr. Mark Walters presented "Insights on Surgical Education: How Can I Help You Get Better" in the inaugural Mark D. Walters Lectureship. Dr. Walters shared his experience and insights on how to transform oneself from a good surgeon to an expert and from a teacher to a coach in the operating room. His dedication to our field, years of experience, and wisdom earned him a standing ovation! Additional oral and video presentations followed. Dr. J. Wong shared correlations between surgeon gender and ergonomic strain with laparoscopic devices. Female surgeons more often reported inappropriate fit and expressed physical discomfort compared with male surgeons. Injuries and ergonomic strain lead to less operating and even disability for some surgeons. It is past time for us to have better--we need instruments that fit our hands!
The afternoon session started with a panel on "Perspectives on Race in GYN Surgery." It was another insightful discussion with thought- and action-provoking knowledge. The afternoon session included the SGS Prize Video by Dr. Angela DiCarlo-Meacham on excision of a vulvar cyst.
Fellows' Pelvic Research Network
After adjourning of the scientific sessions, the fellow-ran, multicenter research network (FPRN) met to give updates. This diverse group of both AUGS-SGS and FMIGS-SGS offers mentorship and relationships that are important for future careers and research. The collaboration allows the study of rare outcomes that may not be feasible at single sites. Dr. Amanda Yunker, fellowship director at Vanderbilt University, gave an amazing history lesson on the fields of OB and GYN, and the evolution of gynecologic surgery. We then had fun assigning a "report card grade" on how MIGS is doing comparatively with other subspecialties in the realms of academics and research.
VideoFest
The late afternoon was concluded with a surgical video session. What an amazing and talented group we are here at SGS!
President's awards ceremony and reception
The scientific focused day was rounded out with an evening of honors, awards, and social time as we celebrated all the achievements of our peers and colleagues. The president's reception was filled with food, laughter, networking, and reconnecting with friends and colleagues. We are looking forward to another day of education tomorrow!
Follow @JennaRehmerMD, @GynSurgery, and #SGS2021 on Twitter for updates.
SUNDAY, 6/27/21. DAY 1 AT SGS
Hello live from sunny Palm Spring, CA, and the Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS)! This year’s conference balances the long-awaited return to in-person events while simultaneously embracing virtual learning with their hybrid meeting format. You can follow me, @JennaRehmerMD, and #SGS2021 in real-time on Twitter.
Dismantling racism
We were incredibly fortunate to take a deep dive into dismantling racism in our personal and professional spheres. The postgraduate course was well researched and presented by Drs. Oluwateniola “Teni” Brown, Cassandra Carberry, Olivia Cardenas-Trowers (@otrowers_md), Annetta Madsen, Moiuri Siddique, and Blair Washington (@Dr_B_Washington). Each presentation provided a succinct and cohesive flow, taking us through what racism is, the historical and active structural racism in medicine, and the actions and steps of becoming anti-racist.
Dr. Brown discussed critical race theory. We learned that the engineered system of oppression is so advanced that it is often hidden in plain sight, and that one’s conscious awareness is not necessary in order to uphold the system of oppression. It is reinforced and supported with minimal effort. This is why not being racist is not enough; active anti-racism is needed to bring about change.
Fibroid management
Across the hall, Drs. Linda Bradley (@BradlelMD), Kimberly Kho (@KimberlyKho1), Cara King (@drcaraking), and Kelly Wright (@MigsRunner) broadened our armamentarium for uterine conservation in fibroid management. Dr. Bradley reviewed medical therapies, including novel treatments, as first-line or adjunct treatment options. Next, the course focused on surgical techniques for hysteroscopic myomectomies, optimization of minilaparotomy for myomectomy, and tissue extraction. Dr. King displayed true grit when giving her lecture from the airport after flight delays prevented her from being in person with us.
Multidisciplinary care within gyn surgery
In this virtual only postgraduate course, Drs. Risal Djohan (@DjohanMD), Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Marie Fidela Paraiso, Sandip Vasavada (@SandipVasavada), and Sarah Vogler showed us the importance of multidisciplinary care within gynecologic surgery practices. They explored how to streamline the approach so it complements your practice, how to co-bill for shared patient care, and tips and tricks for optimizing the surgical experience for the patient.
Industry presentations
Over lunch, Dr. Opoku-Akane presented on using ERAS (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocols for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain and how to optimize the use of alternative surgical modalities for endometriosis. Following this, Drs. Albert Huany and Craig McCoy taught about a new technology using electrical stimulation to optimize visualization of the ureter.
Harnessing the power of social media
This workshop, organized by SGS Social Media Committee Chair Dr. Amy Park (@dramypark) showed us the importance of having an online identity for the sharing of ideas, networking, professional development, and education. We learned how to optimize our online bios, proper use of GYN ontology for hashtags, and how to maintain professionalism on social media. We reviewed the data on how sharing publications on social media improves altmetric scores and discussed how our social media influence may be tied to performance in the future.
Lessons in leadership
We rounded out the day with after-dinner dessert and drinks at the evening SGS Women’s Council presentation. We had the great honor of hearing from Lori Ryerker, CEO of Celanese Corporation, a Fortune 500 global company. She provided much wisdom on being a leader. She shared several keys to creating a successful work environment:
- being a leader that “provides an environment where people feel like they can bring their best selves every day” (and that being your best self is being your whole self, without reservations)
- allowing all genders, sexual orientations, races, ethnicities, and ages to show up together without reservations (because only then can people feel safe to be their best, because their best self is their true self).
It was a wonderful and successful kick-off to the meeting. I look forward to a full day tomorrow! Follow along as this year’s Fellow Scholars, Drs. Tara Brah (@TaraBrah), Amr El Haraki (@drharaki), Sheena Galhotra (@SheenaGalhotra), Meenal Misal (@meenalmisalMD), and yours truly, post live updates daily.
TUESDAY, 6/29/21. DAY 3 AT SGS
The third day of the annual SGS meeting started with several academic roundtables hosted by experts in the field. These authorities shared their knowledge on a range of topics including endometriosis, building an academic career, diversity and equity in the workplace, and scientific publishing. The general session got underway with additional oral and video presentations highlighting advancements in our field. This year’s SGS President Dr. Miles Murphy gave the annual presidential address. He spoke genuinely and humbly about our field. Whitney Ross, MD, (@WRossMD), referred to his speech on Twitter as “Best. Presidential. Address. Ever.” –a sentiment felt by many in the crowd!
This year’s Telinde Lecture was given by Janet Dombrowski, the first ever non-physician to present this lecture. She spoke on resiliency in a lecture titled, “Cultivating Resilience: The Power in Connection & Collaboration.” It was an insightful and wise presentation on the power of connection and how connection bolsters our resiliency. She challenged us to all break down “thinking habits” that isolate us into silos and get in the way of powerful connection and collaboration. She reminded us of the African greeting “Sawubona” (I see you) and “Sikhona” (Because you see me, I am here). A gentle reminder that we feel our existence most tangibly when we are seen by others—an idea consistent with other important themes of this conference, focused on diversity, equity, and inclusion of all. The morning session was rounded out with a panel discussion on “Novel GYN Office Procedure,” featuring Drs. Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Abbas Shobeiri (@ShobeiriAbbas), Andrea Pezzela, and Eric Sokol.
The afternoon was filled with leisure activities in beautiful Palm Springs, including the SGS Golf Tournament, mountain biking, aerial tramway tour, and hike. The weather even cooperated with slightly cooler temperatures (think 100℉ instead of 120℉)! The evening was filled with food, drinks, and the excitement around the annual “SGS’ Got Talent” show! Everyone was able to let down, show off their dance moves, and enjoy some of that much needed connection time!
Tomorrow is the last day of #SGS2021! Excited to round out the conference with continued learning.
MONDAY, 6/28/21. DAY 2 AT SGS
The sun is up and working hard here in Palm Springs, and so are we!
Welcome and introduction of new members
The general session started with a warm welcome to the 12 new SGS members. A special shout out to Dr. Kelly Wright who is a new SGS Member and won the #SGS2021 tweetup! She ranked as a top influencer, prolific tweeter, and made more than 250K impressions leading up to SGS! Way to represent @MigsRunner.
General scientific sessions
There were several excellent oral and video presentations throughout the morning session. A range of topics were discussed, including postoperative pain management, strategies for cost-effective surgery, and how racial and ethnic disparities play into our medical education and patient outcomes. Dr. Eva Welch gave a stellar video presentation on straight-stick sacrocolpopexy techniques for the savvy surgeon. I personally will be incorporating some of her needle management tricks!
After a brief break with some refreshments and a stroll around the exhibit hall, the second scientific session initiated with a transformative lecture. Dr. Mark Walters presented "Insights on Surgical Education: How Can I Help You Get Better" in the inaugural Mark D. Walters Lectureship. Dr. Walters shared his experience and insights on how to transform oneself from a good surgeon to an expert and from a teacher to a coach in the operating room. His dedication to our field, years of experience, and wisdom earned him a standing ovation! Additional oral and video presentations followed. Dr. J. Wong shared correlations between surgeon gender and ergonomic strain with laparoscopic devices. Female surgeons more often reported inappropriate fit and expressed physical discomfort compared with male surgeons. Injuries and ergonomic strain lead to less operating and even disability for some surgeons. It is past time for us to have better--we need instruments that fit our hands!
The afternoon session started with a panel on "Perspectives on Race in GYN Surgery." It was another insightful discussion with thought- and action-provoking knowledge. The afternoon session included the SGS Prize Video by Dr. Angela DiCarlo-Meacham on excision of a vulvar cyst.
Fellows' Pelvic Research Network
After adjourning of the scientific sessions, the fellow-ran, multicenter research network (FPRN) met to give updates. This diverse group of both AUGS-SGS and FMIGS-SGS offers mentorship and relationships that are important for future careers and research. The collaboration allows the study of rare outcomes that may not be feasible at single sites. Dr. Amanda Yunker, fellowship director at Vanderbilt University, gave an amazing history lesson on the fields of OB and GYN, and the evolution of gynecologic surgery. We then had fun assigning a "report card grade" on how MIGS is doing comparatively with other subspecialties in the realms of academics and research.
VideoFest
The late afternoon was concluded with a surgical video session. What an amazing and talented group we are here at SGS!
President's awards ceremony and reception
The scientific focused day was rounded out with an evening of honors, awards, and social time as we celebrated all the achievements of our peers and colleagues. The president's reception was filled with food, laughter, networking, and reconnecting with friends and colleagues. We are looking forward to another day of education tomorrow!
Follow @JennaRehmerMD, @GynSurgery, and #SGS2021 on Twitter for updates.
SUNDAY, 6/27/21. DAY 1 AT SGS
Hello live from sunny Palm Spring, CA, and the Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons (SGS)! This year’s conference balances the long-awaited return to in-person events while simultaneously embracing virtual learning with their hybrid meeting format. You can follow me, @JennaRehmerMD, and #SGS2021 in real-time on Twitter.
Dismantling racism
We were incredibly fortunate to take a deep dive into dismantling racism in our personal and professional spheres. The postgraduate course was well researched and presented by Drs. Oluwateniola “Teni” Brown, Cassandra Carberry, Olivia Cardenas-Trowers (@otrowers_md), Annetta Madsen, Moiuri Siddique, and Blair Washington (@Dr_B_Washington). Each presentation provided a succinct and cohesive flow, taking us through what racism is, the historical and active structural racism in medicine, and the actions and steps of becoming anti-racist.
Dr. Brown discussed critical race theory. We learned that the engineered system of oppression is so advanced that it is often hidden in plain sight, and that one’s conscious awareness is not necessary in order to uphold the system of oppression. It is reinforced and supported with minimal effort. This is why not being racist is not enough; active anti-racism is needed to bring about change.
Fibroid management
Across the hall, Drs. Linda Bradley (@BradlelMD), Kimberly Kho (@KimberlyKho1), Cara King (@drcaraking), and Kelly Wright (@MigsRunner) broadened our armamentarium for uterine conservation in fibroid management. Dr. Bradley reviewed medical therapies, including novel treatments, as first-line or adjunct treatment options. Next, the course focused on surgical techniques for hysteroscopic myomectomies, optimization of minilaparotomy for myomectomy, and tissue extraction. Dr. King displayed true grit when giving her lecture from the airport after flight delays prevented her from being in person with us.
Multidisciplinary care within gyn surgery
In this virtual only postgraduate course, Drs. Risal Djohan (@DjohanMD), Cecile Ferrando (@CFerrandoMD), Marie Fidela Paraiso, Sandip Vasavada (@SandipVasavada), and Sarah Vogler showed us the importance of multidisciplinary care within gynecologic surgery practices. They explored how to streamline the approach so it complements your practice, how to co-bill for shared patient care, and tips and tricks for optimizing the surgical experience for the patient.
Industry presentations
Over lunch, Dr. Opoku-Akane presented on using ERAS (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocols for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain and how to optimize the use of alternative surgical modalities for endometriosis. Following this, Drs. Albert Huany and Craig McCoy taught about a new technology using electrical stimulation to optimize visualization of the ureter.
Harnessing the power of social media
This workshop, organized by SGS Social Media Committee Chair Dr. Amy Park (@dramypark) showed us the importance of having an online identity for the sharing of ideas, networking, professional development, and education. We learned how to optimize our online bios, proper use of GYN ontology for hashtags, and how to maintain professionalism on social media. We reviewed the data on how sharing publications on social media improves altmetric scores and discussed how our social media influence may be tied to performance in the future.
Lessons in leadership
We rounded out the day with after-dinner dessert and drinks at the evening SGS Women’s Council presentation. We had the great honor of hearing from Lori Ryerker, CEO of Celanese Corporation, a Fortune 500 global company. She provided much wisdom on being a leader. She shared several keys to creating a successful work environment:
- being a leader that “provides an environment where people feel like they can bring their best selves every day” (and that being your best self is being your whole self, without reservations)
- allowing all genders, sexual orientations, races, ethnicities, and ages to show up together without reservations (because only then can people feel safe to be their best, because their best self is their true self).
It was a wonderful and successful kick-off to the meeting. I look forward to a full day tomorrow! Follow along as this year’s Fellow Scholars, Drs. Tara Brah (@TaraBrah), Amr El Haraki (@drharaki), Sheena Galhotra (@SheenaGalhotra), Meenal Misal (@meenalmisalMD), and yours truly, post live updates daily.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes and later cardiovascular disease
Preconception health influences pregnancy outcomes, and in turn, both preconception health and an APO influence adult cardiometabolic health (FIGURE). This editorial is focused on the link between APOs and later cardiometabolic morbidity and mortality, recognizing that preconception health greatly influences the risk of an APO and lifetime cardiometabolic disease.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes
Major APOs include miscarriage, preterm birth (birth <37 weeks’ gestation), low birth weight (birth weight ≤2,500 g; 5.5 lb), gestational diabetes (GDM), preeclampsia, and placental abruption. In the United States, among all births, reported rates of the following APOs are:1-3
- preterm birth, 10.2%
- low birth weight, 8.3%
- GDM, 6%
- preeclampsia, 5%
- placental abruption, 1%.
Miscarriage occurs in approximately 10% to 15% of pregnancies, influenced by both the age of the woman and the method used to diagnose pregnancy.4 Miscarriage, preterm birth, low birth weight, GDM, preeclampsia, and placental abruption have been reported to be associated with an increased risk of later cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
APOs and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) affects the majority of people past the age of 60 years and includes 4 major subcategories:
- coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, angina, and heart failure
- CVD, stroke, and transient ischemic attack
- peripheral artery disease
- atherosclerosis of the aorta leading to aortic aneurysm.
Multiple meta-analyses report that APOs are associated with CVD in later life. A comprehensive review reported that the risk of CVD was increased following a pregnancy with one of these APOs: severe preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 2.74), GDM (OR, 1.68), preterm birth (OR, 1.93), low birth weight (OR, 1.29), and placental abruption (OR, 1.82).5
The link between APOs and CVD may be explained in part by the association of APOs with multiple risk factors for CVD, including chronic hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and dyslipidemia. A meta-analysis of 43 studies reported that, compared with controls, women with a history of preeclampsia have a 3.13 times greater risk of developing chronic hypertension.6 Among women with preeclampsia, approximately 20% will develop hypertension within 15 years.7 A meta-analysis of 20 studies reported that women with a history of GDM had a 9.51-times greater risk of developing T2DM than women without GDM.8 Among women with a history of GDM, over 16 years of follow-up, T2DM was diagnosed in 16.2%, compared with 1.9% of control women.8
CVD prevention—Breastfeeding: An antidote for APOs
Pregnancy stresses both the cardiovascular and metabolic systems. Breastfeeding is an antidote to the stresses imposed by pregnancy. Breastfeeding women have lower blood glucose9 and blood pressure.10
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of CVD. In a study of 100,864 parous Australian women, with a mean age of 60 years, ever breastfeeding was associated a lower risk of CVD hospitalization (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78–0.96; P = .005) and CVD mortality (aHR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.49–0.89; P = .006).11
Continue to: CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations...
CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations
The American Heart Association12 recommends lifestyle interventions to reduce the risk of CVD, including:
- Eat a high-quality diet that includes vegetables, fruit, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based protein, lean animal protein, and fish.
- Limit intake of sugary drinks and foods, fatty or processed meats, full-fat dairy products, eggs, highly processed foods, and tropical oils.
- Exercise at least 150 minutes weekly at a moderate activity level, including muscle-strengthening activity.
- Reduce prolonged intervals of sitting.
- Live a tobacco- and nicotine-free life.
- Strive to maintain a normal body mass index.
- Consider using an activity tracker to monitor activity level.
- After 40 years of age calculate CVD risk using a validated calculator such as the American Cardiology Association risk calculator.13 This calculator uses age, gender, and lipid and blood pressure measurements to calculate the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic CVD, including coronary death, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
Medications to reduce CVD risk
Historically, ObGyns have not routinely prescribed medications to treat hypertension, dyslipidemia, or to prevent diabetes. The recent increase in the valuation of return ambulatory visits and a reduction in the valuation assigned to procedural care may provide ObGyn practices the additional resources needed to manage some chronic diseases. Physician assistants and nurse practitioners may help ObGyn practices to manage hypertension, dyslipidemia, and prediabetes.
Prior to initiating a medicine, counseling about healthy living, including smoking cessation, exercise, heart-healthy diet, and achieving an optimal body mass index is warranted.
For treatment of stage II hypertension, defined as blood pressure (BP) measurements with systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg and diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg, therapeutic lifestyle interventions include: optimizing weight, following the DASH diet, restricting dietary sodium, physical activity, and reducing alcohol consumption. Medication treatment for essential hypertension is guided by the magnitude of BP reduction needed to achieve normotension. For women with hypertension needing antihypertensive medication and planning another pregnancy in the near future, labetalol or extended-release nifedipine may be first-line medications. For women who have completed their families or who have no immediate plans for pregnancy, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or thiazide diuretic are commonly prescribed.14
For the treatment of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in women who have not had a cardiovascular event, statin therapy is often warranted when both the LDL cholesterol is >100 mg/dL and the woman has a calculated 10-year risk of >10% for a cardiovascular event using the American Heart Association or American College of Cardiology calculator. Most women who meet these criteria will be older than age 40 years and many will be under the care of an internal medicine or family medicine specialist, limiting the role of the ObGyn.15-17
For prevention of diabetes in women with a history of GDM, both weight loss and metformin (1,750 mg daily) have been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of developing T2DM.18 Among 350 women with a history of GDM who were followed for 10 years, metformin 850 mg twice daily reduced the risk of developing T2DM by 40% compared with placebo.19 In the same study, lifestyle changes without metformin, including loss of 7% of body weight plus 150 minutes of exercise weekly was associated with a 35% reduction in the risk of developing T2DM.19 Metformin is one of the least expensive prescription medications and is cost-effective for the prevention of T2DM.18
Low-dose aspirin treatment for the prevention of CVD in women who have not had a cardiovascular event must balance a modest reduction in cardiovascular events with a small increased risk of bleeding events. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends low-dose aspirin for a limited group of women, those aged 50 to 59 years of age with a 10-year risk of a cardiovascular event >10% who are willing to take aspirin for 10 years. The USPSTF concluded that there is insufficient evidence to recommend low-dose aspirin prevention of CVD in women aged <50 years.20
Continue to: Beyond the fourth trimester...
Beyond the fourth trimester
The fourth trimester is the 12-week period following birth. At the comprehensive postpartum visit, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that women with APOs be counseled about their increased lifetime risk of maternal cardiometabolic disease.21 In addition, ACOG recommends that at this visit the clinician who will assume primary responsibility for the woman’s ongoing medical care in her primary medical home be clarified. One option is to ensure a high-quality hand-off to an internal medicine or family medicine clinician. Another option is for a clinician in the ObGyn’s office practice, including a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or office-based ObGyn, to assume some role in the primary care of the woman.
An APO is not only a pregnancy problem
An APO reverberates across a woman’s lifetime, increasing the risk of CVD and diabetes. In the United States the mean age at first birth is 27 years.1 The mean life expectancy of US women is 81 years.22 Following a birth complicated by an APO there are 5 decades of opportunity to improve health through lifestyle changes and medication treatment of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and hyperglycemia, thereby reducing the risk of CVD.
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ, et al. Births: final data for 2019. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-51.
- Deputy NP, Kim SY, Conrey EJ, et al. Prevalence and changes in preexisting diabetes and gestational diabetes among women who had a live birth—United States, 2012-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:1201-1207. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6743a2.
- Fingar KR, Mabry-Hernandez I, Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Delivery hospitalizations involving preeclampsia and eclampsia, 2005–2014. Statistical brief #222. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD; April 2017.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken NH, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Parikh NI, Gonzalez JM, Anderson CAM, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes and cardiovascular disease risk: unique opportunities for cardiovascular disease prevention in women. Circulation. 2021;143:e902-e916. doi: 10.1161 /CIR.0000000000000961.
- Brown MC, Best KE, Pearce MS, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk in women with pre-eclampsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;28:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013- 9762-6.
- Groenfol TK, Zoet GA, Franx A, et al; on behalf of the PREVENT Group. Trajectory of cardiovascular risk factors after hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertension. 2019;73:171-178. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11726.
- Vounzoulaki E, Khunti K, Abner SC, et al. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;369:m1361. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1361.
- Tarrant M, Chooniedass R, Fan HSL, et al. Breastfeeding and postpartum glucose regulation among women with prior gestational diabetes: a systematic review. J Hum Lact. 2020;36:723-738. doi: 10.1177/0890334420950259.
- Park S, Choi NK. Breastfeeding and maternal hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31:615-621. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx219.
- Nguyen B, Gale J, Nassar N, et al. Breastfeeding and cardiovascular disease hospitalization and mortality in parous women: evidence from a large Australian cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e011056. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011056.
- Eight things you can do to prevent heart disease and stroke. American Heart Association website. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living /healthy-lifestyle/prevent-heart-disease-andstroke. Last Reviewed March 14, 2019. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- ASCVD risk estimator plus. American College of Cardiology website. https://tools.acc.org /ascvd-risk-estimator-plus/#!/calculate /estimate/. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- Ferdinand KC, Nasser SA. Management of essential hypertension. Cardiol Clin. 2017;35:231-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.12.005.
- Packard CJ. LDL cholesterol: how low to go? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018;28:348-354. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.12.011.
- Simons L. An updated review of lipid-modifying therapy. Med J Aust. 2019;211:87-92. doi: 10.5694 /mja2.50142.
- Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, et al. Statins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:2008. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.15629.
- Moin T, Schmittdiel JA, Flory JH, et al. Review of metformin use for type 2 diabetes mellitus prevention. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55:565-574. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.038.
- Aorda VR, Christophi CA, Edelstein SL, et al, for the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The effect of lifestyle intervention and metformin on preventing or delaying diabetes among women with and without gestational diabetes: the Diabetes Prevention Program outcomes study 10-year follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1646- 1653. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3761.
- Bibbins-Domingo K, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Aspirin use of the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Int Med. 2016; 164: 836-845. doi: 10.7326/M16-0577.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000002633.
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2017: Table 015. Hyattsville, MD; 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /hus/2017/015.pdf. Accessed May 18, 2021.
Preconception health influences pregnancy outcomes, and in turn, both preconception health and an APO influence adult cardiometabolic health (FIGURE). This editorial is focused on the link between APOs and later cardiometabolic morbidity and mortality, recognizing that preconception health greatly influences the risk of an APO and lifetime cardiometabolic disease.

Adverse pregnancy outcomes
Major APOs include miscarriage, preterm birth (birth <37 weeks’ gestation), low birth weight (birth weight ≤2,500 g; 5.5 lb), gestational diabetes (GDM), preeclampsia, and placental abruption. In the United States, among all births, reported rates of the following APOs are:1-3
- preterm birth, 10.2%
- low birth weight, 8.3%
- GDM, 6%
- preeclampsia, 5%
- placental abruption, 1%.
Miscarriage occurs in approximately 10% to 15% of pregnancies, influenced by both the age of the woman and the method used to diagnose pregnancy.4 Miscarriage, preterm birth, low birth weight, GDM, preeclampsia, and placental abruption have been reported to be associated with an increased risk of later cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
APOs and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) affects the majority of people past the age of 60 years and includes 4 major subcategories:
- coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, angina, and heart failure
- CVD, stroke, and transient ischemic attack
- peripheral artery disease
- atherosclerosis of the aorta leading to aortic aneurysm.
Multiple meta-analyses report that APOs are associated with CVD in later life. A comprehensive review reported that the risk of CVD was increased following a pregnancy with one of these APOs: severe preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 2.74), GDM (OR, 1.68), preterm birth (OR, 1.93), low birth weight (OR, 1.29), and placental abruption (OR, 1.82).5
The link between APOs and CVD may be explained in part by the association of APOs with multiple risk factors for CVD, including chronic hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and dyslipidemia. A meta-analysis of 43 studies reported that, compared with controls, women with a history of preeclampsia have a 3.13 times greater risk of developing chronic hypertension.6 Among women with preeclampsia, approximately 20% will develop hypertension within 15 years.7 A meta-analysis of 20 studies reported that women with a history of GDM had a 9.51-times greater risk of developing T2DM than women without GDM.8 Among women with a history of GDM, over 16 years of follow-up, T2DM was diagnosed in 16.2%, compared with 1.9% of control women.8
CVD prevention—Breastfeeding: An antidote for APOs
Pregnancy stresses both the cardiovascular and metabolic systems. Breastfeeding is an antidote to the stresses imposed by pregnancy. Breastfeeding women have lower blood glucose9 and blood pressure.10
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of CVD. In a study of 100,864 parous Australian women, with a mean age of 60 years, ever breastfeeding was associated a lower risk of CVD hospitalization (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78–0.96; P = .005) and CVD mortality (aHR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.49–0.89; P = .006).11
Continue to: CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations...
CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations
The American Heart Association12 recommends lifestyle interventions to reduce the risk of CVD, including:
- Eat a high-quality diet that includes vegetables, fruit, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based protein, lean animal protein, and fish.
- Limit intake of sugary drinks and foods, fatty or processed meats, full-fat dairy products, eggs, highly processed foods, and tropical oils.
- Exercise at least 150 minutes weekly at a moderate activity level, including muscle-strengthening activity.
- Reduce prolonged intervals of sitting.
- Live a tobacco- and nicotine-free life.
- Strive to maintain a normal body mass index.
- Consider using an activity tracker to monitor activity level.
- After 40 years of age calculate CVD risk using a validated calculator such as the American Cardiology Association risk calculator.13 This calculator uses age, gender, and lipid and blood pressure measurements to calculate the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic CVD, including coronary death, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
Medications to reduce CVD risk
Historically, ObGyns have not routinely prescribed medications to treat hypertension, dyslipidemia, or to prevent diabetes. The recent increase in the valuation of return ambulatory visits and a reduction in the valuation assigned to procedural care may provide ObGyn practices the additional resources needed to manage some chronic diseases. Physician assistants and nurse practitioners may help ObGyn practices to manage hypertension, dyslipidemia, and prediabetes.
Prior to initiating a medicine, counseling about healthy living, including smoking cessation, exercise, heart-healthy diet, and achieving an optimal body mass index is warranted.
For treatment of stage II hypertension, defined as blood pressure (BP) measurements with systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg and diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg, therapeutic lifestyle interventions include: optimizing weight, following the DASH diet, restricting dietary sodium, physical activity, and reducing alcohol consumption. Medication treatment for essential hypertension is guided by the magnitude of BP reduction needed to achieve normotension. For women with hypertension needing antihypertensive medication and planning another pregnancy in the near future, labetalol or extended-release nifedipine may be first-line medications. For women who have completed their families or who have no immediate plans for pregnancy, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or thiazide diuretic are commonly prescribed.14
For the treatment of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in women who have not had a cardiovascular event, statin therapy is often warranted when both the LDL cholesterol is >100 mg/dL and the woman has a calculated 10-year risk of >10% for a cardiovascular event using the American Heart Association or American College of Cardiology calculator. Most women who meet these criteria will be older than age 40 years and many will be under the care of an internal medicine or family medicine specialist, limiting the role of the ObGyn.15-17
For prevention of diabetes in women with a history of GDM, both weight loss and metformin (1,750 mg daily) have been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of developing T2DM.18 Among 350 women with a history of GDM who were followed for 10 years, metformin 850 mg twice daily reduced the risk of developing T2DM by 40% compared with placebo.19 In the same study, lifestyle changes without metformin, including loss of 7% of body weight plus 150 minutes of exercise weekly was associated with a 35% reduction in the risk of developing T2DM.19 Metformin is one of the least expensive prescription medications and is cost-effective for the prevention of T2DM.18
Low-dose aspirin treatment for the prevention of CVD in women who have not had a cardiovascular event must balance a modest reduction in cardiovascular events with a small increased risk of bleeding events. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends low-dose aspirin for a limited group of women, those aged 50 to 59 years of age with a 10-year risk of a cardiovascular event >10% who are willing to take aspirin for 10 years. The USPSTF concluded that there is insufficient evidence to recommend low-dose aspirin prevention of CVD in women aged <50 years.20
Continue to: Beyond the fourth trimester...
Beyond the fourth trimester
The fourth trimester is the 12-week period following birth. At the comprehensive postpartum visit, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that women with APOs be counseled about their increased lifetime risk of maternal cardiometabolic disease.21 In addition, ACOG recommends that at this visit the clinician who will assume primary responsibility for the woman’s ongoing medical care in her primary medical home be clarified. One option is to ensure a high-quality hand-off to an internal medicine or family medicine clinician. Another option is for a clinician in the ObGyn’s office practice, including a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or office-based ObGyn, to assume some role in the primary care of the woman.
An APO is not only a pregnancy problem
An APO reverberates across a woman’s lifetime, increasing the risk of CVD and diabetes. In the United States the mean age at first birth is 27 years.1 The mean life expectancy of US women is 81 years.22 Following a birth complicated by an APO there are 5 decades of opportunity to improve health through lifestyle changes and medication treatment of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and hyperglycemia, thereby reducing the risk of CVD.

Preconception health influences pregnancy outcomes, and in turn, both preconception health and an APO influence adult cardiometabolic health (FIGURE). This editorial is focused on the link between APOs and later cardiometabolic morbidity and mortality, recognizing that preconception health greatly influences the risk of an APO and lifetime cardiometabolic disease.

Adverse pregnancy outcomes
Major APOs include miscarriage, preterm birth (birth <37 weeks’ gestation), low birth weight (birth weight ≤2,500 g; 5.5 lb), gestational diabetes (GDM), preeclampsia, and placental abruption. In the United States, among all births, reported rates of the following APOs are:1-3
- preterm birth, 10.2%
- low birth weight, 8.3%
- GDM, 6%
- preeclampsia, 5%
- placental abruption, 1%.
Miscarriage occurs in approximately 10% to 15% of pregnancies, influenced by both the age of the woman and the method used to diagnose pregnancy.4 Miscarriage, preterm birth, low birth weight, GDM, preeclampsia, and placental abruption have been reported to be associated with an increased risk of later cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
APOs and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) affects the majority of people past the age of 60 years and includes 4 major subcategories:
- coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, angina, and heart failure
- CVD, stroke, and transient ischemic attack
- peripheral artery disease
- atherosclerosis of the aorta leading to aortic aneurysm.
Multiple meta-analyses report that APOs are associated with CVD in later life. A comprehensive review reported that the risk of CVD was increased following a pregnancy with one of these APOs: severe preeclampsia (odds ratio [OR], 2.74), GDM (OR, 1.68), preterm birth (OR, 1.93), low birth weight (OR, 1.29), and placental abruption (OR, 1.82).5
The link between APOs and CVD may be explained in part by the association of APOs with multiple risk factors for CVD, including chronic hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and dyslipidemia. A meta-analysis of 43 studies reported that, compared with controls, women with a history of preeclampsia have a 3.13 times greater risk of developing chronic hypertension.6 Among women with preeclampsia, approximately 20% will develop hypertension within 15 years.7 A meta-analysis of 20 studies reported that women with a history of GDM had a 9.51-times greater risk of developing T2DM than women without GDM.8 Among women with a history of GDM, over 16 years of follow-up, T2DM was diagnosed in 16.2%, compared with 1.9% of control women.8
CVD prevention—Breastfeeding: An antidote for APOs
Pregnancy stresses both the cardiovascular and metabolic systems. Breastfeeding is an antidote to the stresses imposed by pregnancy. Breastfeeding women have lower blood glucose9 and blood pressure.10
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of CVD. In a study of 100,864 parous Australian women, with a mean age of 60 years, ever breastfeeding was associated a lower risk of CVD hospitalization (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78–0.96; P = .005) and CVD mortality (aHR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.49–0.89; P = .006).11
Continue to: CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations...
CVD prevention—American Heart Association recommendations
The American Heart Association12 recommends lifestyle interventions to reduce the risk of CVD, including:
- Eat a high-quality diet that includes vegetables, fruit, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based protein, lean animal protein, and fish.
- Limit intake of sugary drinks and foods, fatty or processed meats, full-fat dairy products, eggs, highly processed foods, and tropical oils.
- Exercise at least 150 minutes weekly at a moderate activity level, including muscle-strengthening activity.
- Reduce prolonged intervals of sitting.
- Live a tobacco- and nicotine-free life.
- Strive to maintain a normal body mass index.
- Consider using an activity tracker to monitor activity level.
- After 40 years of age calculate CVD risk using a validated calculator such as the American Cardiology Association risk calculator.13 This calculator uses age, gender, and lipid and blood pressure measurements to calculate the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic CVD, including coronary death, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
Medications to reduce CVD risk
Historically, ObGyns have not routinely prescribed medications to treat hypertension, dyslipidemia, or to prevent diabetes. The recent increase in the valuation of return ambulatory visits and a reduction in the valuation assigned to procedural care may provide ObGyn practices the additional resources needed to manage some chronic diseases. Physician assistants and nurse practitioners may help ObGyn practices to manage hypertension, dyslipidemia, and prediabetes.
Prior to initiating a medicine, counseling about healthy living, including smoking cessation, exercise, heart-healthy diet, and achieving an optimal body mass index is warranted.
For treatment of stage II hypertension, defined as blood pressure (BP) measurements with systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg and diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg, therapeutic lifestyle interventions include: optimizing weight, following the DASH diet, restricting dietary sodium, physical activity, and reducing alcohol consumption. Medication treatment for essential hypertension is guided by the magnitude of BP reduction needed to achieve normotension. For women with hypertension needing antihypertensive medication and planning another pregnancy in the near future, labetalol or extended-release nifedipine may be first-line medications. For women who have completed their families or who have no immediate plans for pregnancy, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, calcium channel blocker, or thiazide diuretic are commonly prescribed.14
For the treatment of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in women who have not had a cardiovascular event, statin therapy is often warranted when both the LDL cholesterol is >100 mg/dL and the woman has a calculated 10-year risk of >10% for a cardiovascular event using the American Heart Association or American College of Cardiology calculator. Most women who meet these criteria will be older than age 40 years and many will be under the care of an internal medicine or family medicine specialist, limiting the role of the ObGyn.15-17
For prevention of diabetes in women with a history of GDM, both weight loss and metformin (1,750 mg daily) have been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of developing T2DM.18 Among 350 women with a history of GDM who were followed for 10 years, metformin 850 mg twice daily reduced the risk of developing T2DM by 40% compared with placebo.19 In the same study, lifestyle changes without metformin, including loss of 7% of body weight plus 150 minutes of exercise weekly was associated with a 35% reduction in the risk of developing T2DM.19 Metformin is one of the least expensive prescription medications and is cost-effective for the prevention of T2DM.18
Low-dose aspirin treatment for the prevention of CVD in women who have not had a cardiovascular event must balance a modest reduction in cardiovascular events with a small increased risk of bleeding events. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends low-dose aspirin for a limited group of women, those aged 50 to 59 years of age with a 10-year risk of a cardiovascular event >10% who are willing to take aspirin for 10 years. The USPSTF concluded that there is insufficient evidence to recommend low-dose aspirin prevention of CVD in women aged <50 years.20
Continue to: Beyond the fourth trimester...
Beyond the fourth trimester
The fourth trimester is the 12-week period following birth. At the comprehensive postpartum visit, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that women with APOs be counseled about their increased lifetime risk of maternal cardiometabolic disease.21 In addition, ACOG recommends that at this visit the clinician who will assume primary responsibility for the woman’s ongoing medical care in her primary medical home be clarified. One option is to ensure a high-quality hand-off to an internal medicine or family medicine clinician. Another option is for a clinician in the ObGyn’s office practice, including a physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or office-based ObGyn, to assume some role in the primary care of the woman.
An APO is not only a pregnancy problem
An APO reverberates across a woman’s lifetime, increasing the risk of CVD and diabetes. In the United States the mean age at first birth is 27 years.1 The mean life expectancy of US women is 81 years.22 Following a birth complicated by an APO there are 5 decades of opportunity to improve health through lifestyle changes and medication treatment of obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and hyperglycemia, thereby reducing the risk of CVD.

- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ, et al. Births: final data for 2019. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-51.
- Deputy NP, Kim SY, Conrey EJ, et al. Prevalence and changes in preexisting diabetes and gestational diabetes among women who had a live birth—United States, 2012-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:1201-1207. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6743a2.
- Fingar KR, Mabry-Hernandez I, Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Delivery hospitalizations involving preeclampsia and eclampsia, 2005–2014. Statistical brief #222. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD; April 2017.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken NH, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Parikh NI, Gonzalez JM, Anderson CAM, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes and cardiovascular disease risk: unique opportunities for cardiovascular disease prevention in women. Circulation. 2021;143:e902-e916. doi: 10.1161 /CIR.0000000000000961.
- Brown MC, Best KE, Pearce MS, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk in women with pre-eclampsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;28:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013- 9762-6.
- Groenfol TK, Zoet GA, Franx A, et al; on behalf of the PREVENT Group. Trajectory of cardiovascular risk factors after hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertension. 2019;73:171-178. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11726.
- Vounzoulaki E, Khunti K, Abner SC, et al. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;369:m1361. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1361.
- Tarrant M, Chooniedass R, Fan HSL, et al. Breastfeeding and postpartum glucose regulation among women with prior gestational diabetes: a systematic review. J Hum Lact. 2020;36:723-738. doi: 10.1177/0890334420950259.
- Park S, Choi NK. Breastfeeding and maternal hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31:615-621. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx219.
- Nguyen B, Gale J, Nassar N, et al. Breastfeeding and cardiovascular disease hospitalization and mortality in parous women: evidence from a large Australian cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e011056. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011056.
- Eight things you can do to prevent heart disease and stroke. American Heart Association website. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living /healthy-lifestyle/prevent-heart-disease-andstroke. Last Reviewed March 14, 2019. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- ASCVD risk estimator plus. American College of Cardiology website. https://tools.acc.org /ascvd-risk-estimator-plus/#!/calculate /estimate/. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- Ferdinand KC, Nasser SA. Management of essential hypertension. Cardiol Clin. 2017;35:231-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.12.005.
- Packard CJ. LDL cholesterol: how low to go? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018;28:348-354. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.12.011.
- Simons L. An updated review of lipid-modifying therapy. Med J Aust. 2019;211:87-92. doi: 10.5694 /mja2.50142.
- Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, et al. Statins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:2008. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.15629.
- Moin T, Schmittdiel JA, Flory JH, et al. Review of metformin use for type 2 diabetes mellitus prevention. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55:565-574. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.038.
- Aorda VR, Christophi CA, Edelstein SL, et al, for the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The effect of lifestyle intervention and metformin on preventing or delaying diabetes among women with and without gestational diabetes: the Diabetes Prevention Program outcomes study 10-year follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1646- 1653. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3761.
- Bibbins-Domingo K, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Aspirin use of the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Int Med. 2016; 164: 836-845. doi: 10.7326/M16-0577.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000002633.
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2017: Table 015. Hyattsville, MD; 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /hus/2017/015.pdf. Accessed May 18, 2021.
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ, et al. Births: final data for 2019. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-51.
- Deputy NP, Kim SY, Conrey EJ, et al. Prevalence and changes in preexisting diabetes and gestational diabetes among women who had a live birth—United States, 2012-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:1201-1207. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6743a2.
- Fingar KR, Mabry-Hernandez I, Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Delivery hospitalizations involving preeclampsia and eclampsia, 2005–2014. Statistical brief #222. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD; April 2017.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken NH, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Parikh NI, Gonzalez JM, Anderson CAM, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes and cardiovascular disease risk: unique opportunities for cardiovascular disease prevention in women. Circulation. 2021;143:e902-e916. doi: 10.1161 /CIR.0000000000000961.
- Brown MC, Best KE, Pearce MS, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk in women with pre-eclampsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;28:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013- 9762-6.
- Groenfol TK, Zoet GA, Franx A, et al; on behalf of the PREVENT Group. Trajectory of cardiovascular risk factors after hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertension. 2019;73:171-178. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11726.
- Vounzoulaki E, Khunti K, Abner SC, et al. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;369:m1361. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1361.
- Tarrant M, Chooniedass R, Fan HSL, et al. Breastfeeding and postpartum glucose regulation among women with prior gestational diabetes: a systematic review. J Hum Lact. 2020;36:723-738. doi: 10.1177/0890334420950259.
- Park S, Choi NK. Breastfeeding and maternal hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31:615-621. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx219.
- Nguyen B, Gale J, Nassar N, et al. Breastfeeding and cardiovascular disease hospitalization and mortality in parous women: evidence from a large Australian cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e011056. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011056.
- Eight things you can do to prevent heart disease and stroke. American Heart Association website. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living /healthy-lifestyle/prevent-heart-disease-andstroke. Last Reviewed March 14, 2019. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- ASCVD risk estimator plus. American College of Cardiology website. https://tools.acc.org /ascvd-risk-estimator-plus/#!/calculate /estimate/. Accessed May 19, 2021.
- Ferdinand KC, Nasser SA. Management of essential hypertension. Cardiol Clin. 2017;35:231-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.12.005.
- Packard CJ. LDL cholesterol: how low to go? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018;28:348-354. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.12.011.
- Simons L. An updated review of lipid-modifying therapy. Med J Aust. 2019;211:87-92. doi: 10.5694 /mja2.50142.
- Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, et al. Statins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;316:2008. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.15629.
- Moin T, Schmittdiel JA, Flory JH, et al. Review of metformin use for type 2 diabetes mellitus prevention. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55:565-574. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.038.
- Aorda VR, Christophi CA, Edelstein SL, et al, for the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The effect of lifestyle intervention and metformin on preventing or delaying diabetes among women with and without gestational diabetes: the Diabetes Prevention Program outcomes study 10-year follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1646- 1653. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3761.
- Bibbins-Domingo K, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Aspirin use of the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Int Med. 2016; 164: 836-845. doi: 10.7326/M16-0577.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000002633.
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2017: Table 015. Hyattsville, MD; 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /hus/2017/015.pdf. Accessed May 18, 2021.
COVID-19 vaccination and pregnancy: Benefits outweigh the risks, for now
Vaccines have been a lifesaving public health measure since 1000 CE, when the Chinese first used smallpox inoculations to induce immunity.1 Work by pioneers such as Edward Jenner, Louis Pasteur, and Maurice Hilleman has averted countless millions of vaccine-preventable illnesses and deaths, and vaccines have become a routine part of health maintenance throughout the human life cycle.
Pregnant patients who receive vaccines often have an added benefit of protection provided to their infants through passive transfer of antibodies. Several vaccine platforms have been utilized in pregnancy with well-documented improvements in maternal and obstetric outcomes as well as improved neonatal outcomes in the first several months of life.
Risks of COVID-19 in pregnancy
The COVID-19 pandemic placed a spotlight on medically at-risk groups. Pregnant women are 3 times more likely to require admission to the intensive care unit, have increased requirement for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment, and are up to 70% more likely to die than nonpregnant peers—and this risk increases with the presence of additional comorbidities.
In the case of COVID-19, vaccination trials that have shaped worldwide clinical practice unfortunately followed the historical trend of excluding pregnant patients from participation. This has required clinicians to guide their patients through the decision of whether or not to accept vaccination without having the same reassurances regarding safety and effectiveness afforded to their nonpregnant counterparts. With more than 86,000 pregnant women infected with COVID-19 through April 19, 2021, this lack of information regarding vaccine safety in pregnancy is a significant public health gap.2
COVID-19 vaccines
The current COVID-19 vaccines approved for use in the United States under an Emergency Use Authorization issued by the US Food and Drug Administration are nonreplicating and thus cannot cause infection in the mother or fetus. These are the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine, and the Janssen Biotech Inc. monovalent vaccine. Furthermore, in animal studies that included the Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Janssen COVID-19 vaccines, no fetal, embryonal, female reproductive, or postnatal development safety concerns were demonstrated.
As of April 19, 2021, 94,335 pregnant women had received a COVID-19 vaccination, and 4,622 of these enrolled in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) V-safe Vaccine Pregnancy Registry.3 The data reported noted no unexpected pregnancy or infant outcomes related to COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy. Adverse effects of the vaccine were similar to those in nonpregnant cohorts. Additionally, emerging data suggest passage of immunity to neonates, with maternal antibodies demonstrated in cord blood at time of delivery as well as in breast milk.4 To date, these data mainly have come from women immunized with the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccines.
Counseling pregnant patients
Our counseling aligns with that of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in that COVID-19 vaccination should not be withheld from pregnant patients or patients who want to become pregnant. In pregnant patients with comorbidities that place them at higher risk for severe COVID-19 infection, all available formulations of the COVID-19 vaccination should be strongly considered.
As evidence for vaccination safety continues to emerge, patients should continue to discuss their individual needs for vaccination in a shared decision-making format with their obstetric providers.
Boylston A. The origins of inoculation. J R Soc Med. 2012;105:309-313.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID data tracker. Data on COVID-19 during pregnancy: severity of maternal illness. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pregnant-population. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. V-safe COVID-19 Vaccine Pregnancy Registry. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019- ncov/vaccines/safety/vsafepregnancyregistry.html. Updated May 3, 2021. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Gray KJ, Bordt EA, Atyeo C, et al. COVID-19 vaccine response in pregnant and lactating women: a cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;S0002-9378(21)00187-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.023
Vaccines have been a lifesaving public health measure since 1000 CE, when the Chinese first used smallpox inoculations to induce immunity.1 Work by pioneers such as Edward Jenner, Louis Pasteur, and Maurice Hilleman has averted countless millions of vaccine-preventable illnesses and deaths, and vaccines have become a routine part of health maintenance throughout the human life cycle.
Pregnant patients who receive vaccines often have an added benefit of protection provided to their infants through passive transfer of antibodies. Several vaccine platforms have been utilized in pregnancy with well-documented improvements in maternal and obstetric outcomes as well as improved neonatal outcomes in the first several months of life.
Risks of COVID-19 in pregnancy
The COVID-19 pandemic placed a spotlight on medically at-risk groups. Pregnant women are 3 times more likely to require admission to the intensive care unit, have increased requirement for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment, and are up to 70% more likely to die than nonpregnant peers—and this risk increases with the presence of additional comorbidities.
In the case of COVID-19, vaccination trials that have shaped worldwide clinical practice unfortunately followed the historical trend of excluding pregnant patients from participation. This has required clinicians to guide their patients through the decision of whether or not to accept vaccination without having the same reassurances regarding safety and effectiveness afforded to their nonpregnant counterparts. With more than 86,000 pregnant women infected with COVID-19 through April 19, 2021, this lack of information regarding vaccine safety in pregnancy is a significant public health gap.2
COVID-19 vaccines
The current COVID-19 vaccines approved for use in the United States under an Emergency Use Authorization issued by the US Food and Drug Administration are nonreplicating and thus cannot cause infection in the mother or fetus. These are the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine, and the Janssen Biotech Inc. monovalent vaccine. Furthermore, in animal studies that included the Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Janssen COVID-19 vaccines, no fetal, embryonal, female reproductive, or postnatal development safety concerns were demonstrated.
As of April 19, 2021, 94,335 pregnant women had received a COVID-19 vaccination, and 4,622 of these enrolled in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) V-safe Vaccine Pregnancy Registry.3 The data reported noted no unexpected pregnancy or infant outcomes related to COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy. Adverse effects of the vaccine were similar to those in nonpregnant cohorts. Additionally, emerging data suggest passage of immunity to neonates, with maternal antibodies demonstrated in cord blood at time of delivery as well as in breast milk.4 To date, these data mainly have come from women immunized with the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccines.
Counseling pregnant patients
Our counseling aligns with that of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in that COVID-19 vaccination should not be withheld from pregnant patients or patients who want to become pregnant. In pregnant patients with comorbidities that place them at higher risk for severe COVID-19 infection, all available formulations of the COVID-19 vaccination should be strongly considered.
As evidence for vaccination safety continues to emerge, patients should continue to discuss their individual needs for vaccination in a shared decision-making format with their obstetric providers.
Vaccines have been a lifesaving public health measure since 1000 CE, when the Chinese first used smallpox inoculations to induce immunity.1 Work by pioneers such as Edward Jenner, Louis Pasteur, and Maurice Hilleman has averted countless millions of vaccine-preventable illnesses and deaths, and vaccines have become a routine part of health maintenance throughout the human life cycle.
Pregnant patients who receive vaccines often have an added benefit of protection provided to their infants through passive transfer of antibodies. Several vaccine platforms have been utilized in pregnancy with well-documented improvements in maternal and obstetric outcomes as well as improved neonatal outcomes in the first several months of life.
Risks of COVID-19 in pregnancy
The COVID-19 pandemic placed a spotlight on medically at-risk groups. Pregnant women are 3 times more likely to require admission to the intensive care unit, have increased requirement for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment, and are up to 70% more likely to die than nonpregnant peers—and this risk increases with the presence of additional comorbidities.
In the case of COVID-19, vaccination trials that have shaped worldwide clinical practice unfortunately followed the historical trend of excluding pregnant patients from participation. This has required clinicians to guide their patients through the decision of whether or not to accept vaccination without having the same reassurances regarding safety and effectiveness afforded to their nonpregnant counterparts. With more than 86,000 pregnant women infected with COVID-19 through April 19, 2021, this lack of information regarding vaccine safety in pregnancy is a significant public health gap.2
COVID-19 vaccines
The current COVID-19 vaccines approved for use in the United States under an Emergency Use Authorization issued by the US Food and Drug Administration are nonreplicating and thus cannot cause infection in the mother or fetus. These are the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine, and the Janssen Biotech Inc. monovalent vaccine. Furthermore, in animal studies that included the Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Janssen COVID-19 vaccines, no fetal, embryonal, female reproductive, or postnatal development safety concerns were demonstrated.
As of April 19, 2021, 94,335 pregnant women had received a COVID-19 vaccination, and 4,622 of these enrolled in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) V-safe Vaccine Pregnancy Registry.3 The data reported noted no unexpected pregnancy or infant outcomes related to COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy. Adverse effects of the vaccine were similar to those in nonpregnant cohorts. Additionally, emerging data suggest passage of immunity to neonates, with maternal antibodies demonstrated in cord blood at time of delivery as well as in breast milk.4 To date, these data mainly have come from women immunized with the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccines.
Counseling pregnant patients
Our counseling aligns with that of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in that COVID-19 vaccination should not be withheld from pregnant patients or patients who want to become pregnant. In pregnant patients with comorbidities that place them at higher risk for severe COVID-19 infection, all available formulations of the COVID-19 vaccination should be strongly considered.
As evidence for vaccination safety continues to emerge, patients should continue to discuss their individual needs for vaccination in a shared decision-making format with their obstetric providers.
Boylston A. The origins of inoculation. J R Soc Med. 2012;105:309-313.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID data tracker. Data on COVID-19 during pregnancy: severity of maternal illness. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pregnant-population. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. V-safe COVID-19 Vaccine Pregnancy Registry. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019- ncov/vaccines/safety/vsafepregnancyregistry.html. Updated May 3, 2021. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Gray KJ, Bordt EA, Atyeo C, et al. COVID-19 vaccine response in pregnant and lactating women: a cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;S0002-9378(21)00187-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.023
Boylston A. The origins of inoculation. J R Soc Med. 2012;105:309-313.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID data tracker. Data on COVID-19 during pregnancy: severity of maternal illness. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pregnant-population. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. V-safe COVID-19 Vaccine Pregnancy Registry. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019- ncov/vaccines/safety/vsafepregnancyregistry.html. Updated May 3, 2021. Accessed April 19, 2021.
Gray KJ, Bordt EA, Atyeo C, et al. COVID-19 vaccine response in pregnant and lactating women: a cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;S0002-9378(21)00187-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.03.023