User login
Dry cough and dyspnea
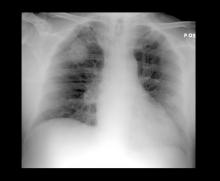
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 58-year-old man with a 20-year–pack history of smoking initially presented with a persistent dry cough and dyspnea. Clubbing was noted on physical examination and breath sounds in the right upper lung were weak. Other than hypertension, which the patient manages with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, medical history is unremarkable. The patient notes that this medication has always made him cough, but dyspnea has only developed over the past 6 weeks. Respiratory symptoms prompted a chest radiograph which revealed a mass in the upper lobe of the right lung. Transbronchial lung biopsy of the right lung reveals components of adenocarcinoma; the specimen is otherwise squamous.
NSCLC Treatment Basics
Cough and moderate hoarseness
Based on the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC accounts for about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma, in particular, is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases. This subtype is also the most common histology among nonsmokers. Still, individuals aged 55 to 77 years with a smoking history of 30 pack-years or more are considered to be the highest-risk group for lung cancer; those who quit less than 15 years ago — like the patient in the present case — are still considered to be in this risk group. Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage when symptoms have already begun to manifest. However, it should be noted that women are more likely to develop adenocarcinoma, are generally younger when they present with symptoms, and are more likely to present with localized disease. It remains to be proven whether the use of HRT affects the risk for lung cancer in women. Deaths from lung cancer, and in particular NSCLC, were shown to be higher among patients undergoing HRT, though no increase in lung cancer death was reported in women receiving estrogen alone.
In addition to the imaging described in this case, workup for NSCLC should include immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor therapy or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. Management of NSCLC is primarily informed by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes. KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with a history of smoking and are considered prognostic biomarkers. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, patients who are confirmed to be harboring KRAS mutations will likely not benefit from additional molecular testing. Presence of the KRAS mutation suggests a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, though it does not appear to impact chemotherapeutic efficacy. Although no targeted therapies are yet available for this population, immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma be tested for EGFR mutations and that DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Based on the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC accounts for about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma, in particular, is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases. This subtype is also the most common histology among nonsmokers. Still, individuals aged 55 to 77 years with a smoking history of 30 pack-years or more are considered to be the highest-risk group for lung cancer; those who quit less than 15 years ago — like the patient in the present case — are still considered to be in this risk group. Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage when symptoms have already begun to manifest. However, it should be noted that women are more likely to develop adenocarcinoma, are generally younger when they present with symptoms, and are more likely to present with localized disease. It remains to be proven whether the use of HRT affects the risk for lung cancer in women. Deaths from lung cancer, and in particular NSCLC, were shown to be higher among patients undergoing HRT, though no increase in lung cancer death was reported in women receiving estrogen alone.
In addition to the imaging described in this case, workup for NSCLC should include immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor therapy or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. Management of NSCLC is primarily informed by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes. KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with a history of smoking and are considered prognostic biomarkers. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, patients who are confirmed to be harboring KRAS mutations will likely not benefit from additional molecular testing. Presence of the KRAS mutation suggests a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, though it does not appear to impact chemotherapeutic efficacy. Although no targeted therapies are yet available for this population, immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma be tested for EGFR mutations and that DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Based on the patient's presentation, history, and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC accounts for about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma, in particular, is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases. This subtype is also the most common histology among nonsmokers. Still, individuals aged 55 to 77 years with a smoking history of 30 pack-years or more are considered to be the highest-risk group for lung cancer; those who quit less than 15 years ago — like the patient in the present case — are still considered to be in this risk group. Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage when symptoms have already begun to manifest. However, it should be noted that women are more likely to develop adenocarcinoma, are generally younger when they present with symptoms, and are more likely to present with localized disease. It remains to be proven whether the use of HRT affects the risk for lung cancer in women. Deaths from lung cancer, and in particular NSCLC, were shown to be higher among patients undergoing HRT, though no increase in lung cancer death was reported in women receiving estrogen alone.
In addition to the imaging described in this case, workup for NSCLC should include immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor therapy or programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. Management of NSCLC is primarily informed by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes. KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with a history of smoking and are considered prognostic biomarkers. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, patients who are confirmed to be harboring KRAS mutations will likely not benefit from additional molecular testing. Presence of the KRAS mutation suggests a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, though it does not appear to impact chemotherapeutic efficacy. Although no targeted therapies are yet available for this population, immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial. National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma be tested for EGFR mutations and that DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
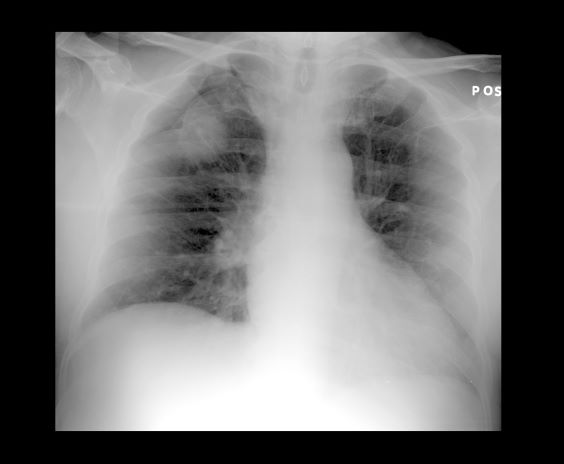
A 56-year-old woman presents with dyspnea, a persistent cough, and moderate hoarseness. She has no significant medical history other than thyroiditis. Her current medications include hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Although the patient reports a 20–pack-year history of smoking tobacco, she notes that she quit 11 years ago and has not been previously screened for lung cancer. A chest radiograph is ordered, which demonstrates a mass in the upper lobe of the right lung.
NSCLC Diagnosis
Woman with dyspnea and persistent cough
On the basis of the patient's presentation and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC makes up about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma in particular is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases, and it is the most common histology among nonsmokers. Women are more likely to develop this subtype of NSCLC and are generally younger when they present with symptoms. This type of cancer arises from the bronchial mucosal glands and usually develops in a peripheral location within the lung.
In the course of workup, immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses are used to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether ALK inhibitor therapy or programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. NCCN guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma should be tested for EGFR mutations, and DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method for assessment. Patients should also undergo routine biomarker testing, with an eye toward ALK, RET, and ROS1 rearrangements, BRAF mutations, c-MET and exon 14 skipping mutations, and PD-L1 expression levels. For patients with metastatic NSCLC, PD-L1 IHC testing is recommended.
Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage, when symptoms have already begun to manifest. Of note, however, women with adenocarcinoma are more likely to present with localized disease. Treatment is largely influenced by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes.
For patients who are EGFR mutation positive (exon 10 deletion or L858R), osimertinib is the recommended first-line therapy. For patients who are positive for the EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate; the preferred regimen being pembrolizumab-carboplatin-pemetrexed if there are no contraindications to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or PD-L1 inhibitors.
KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with smoking. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, identification of KRAS mutations suggests that these patients will not benefit from additional molecular testing. Again, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate, but the presence of KRAS mutation predicts a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The FDA approved a KRAS inhibitor in June 2021 and immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial in this population.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
On the basis of the patient's presentation and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC makes up about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma in particular is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases, and it is the most common histology among nonsmokers. Women are more likely to develop this subtype of NSCLC and are generally younger when they present with symptoms. This type of cancer arises from the bronchial mucosal glands and usually develops in a peripheral location within the lung.
In the course of workup, immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses are used to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether ALK inhibitor therapy or programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. NCCN guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma should be tested for EGFR mutations, and DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method for assessment. Patients should also undergo routine biomarker testing, with an eye toward ALK, RET, and ROS1 rearrangements, BRAF mutations, c-MET and exon 14 skipping mutations, and PD-L1 expression levels. For patients with metastatic NSCLC, PD-L1 IHC testing is recommended.
Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage, when symptoms have already begun to manifest. Of note, however, women with adenocarcinoma are more likely to present with localized disease. Treatment is largely influenced by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes.
For patients who are EGFR mutation positive (exon 10 deletion or L858R), osimertinib is the recommended first-line therapy. For patients who are positive for the EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate; the preferred regimen being pembrolizumab-carboplatin-pemetrexed if there are no contraindications to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or PD-L1 inhibitors.
KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with smoking. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, identification of KRAS mutations suggests that these patients will not benefit from additional molecular testing. Again, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate, but the presence of KRAS mutation predicts a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The FDA approved a KRAS inhibitor in June 2021 and immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial in this population.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
On the basis of the patient's presentation and imaging results, the likely diagnosis is non–small cell cancer (NSCLC) of an adenocarcinoma subtype. NSCLC makes up about 80% of all lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma in particular is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States, accounting for about 40% of cases, and it is the most common histology among nonsmokers. Women are more likely to develop this subtype of NSCLC and are generally younger when they present with symptoms. This type of cancer arises from the bronchial mucosal glands and usually develops in a peripheral location within the lung.
In the course of workup, immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses are used to identify tumor type and lineage (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, metastatic malignancy, or primary pleural mesothelioma). Separate IHC analyses are then used to guide treatment decisions, identifying whether ALK inhibitor therapy or programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor therapy would be appropriate.
Tissue should also be conserved for molecular testing. NCCN guidelines advise that all patients with adenocarcinoma should be tested for EGFR mutations, and DNA mutational analysis is the preferred method for assessment. Patients should also undergo routine biomarker testing, with an eye toward ALK, RET, and ROS1 rearrangements, BRAF mutations, c-MET and exon 14 skipping mutations, and PD-L1 expression levels. For patients with metastatic NSCLC, PD-L1 IHC testing is recommended.
Most cases of lung cancer are diagnosed at a late stage, when symptoms have already begun to manifest. Of note, however, women with adenocarcinoma are more likely to present with localized disease. Treatment is largely influenced by the presence of targetable mutations. Among adenocarcinoma cases, the most common mutations are in the EGFR and KRAS genes.
For patients who are EGFR mutation positive (exon 10 deletion or L858R), osimertinib is the recommended first-line therapy. For patients who are positive for the EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate; the preferred regimen being pembrolizumab-carboplatin-pemetrexed if there are no contraindications to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or PD-L1 inhibitors.
KRAS mutations, unlike EGFR mutations, are associated with smoking. Because overlapping targetable alterations are uncommon, identification of KRAS mutations suggests that these patients will not benefit from additional molecular testing. Again, initial systemic therapy options for adenocarcinoma are appropriate, but the presence of KRAS mutation predicts a poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The FDA approved a KRAS inhibitor in June 2021 and immune checkpoint inhibitors appear to be beneficial in this population.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
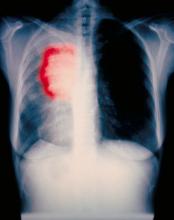
A 52-year-old woman presents with dyspnea and a persistent cough. She is 5 ft 5 in and weighs 155 lb, with no recent significant weight loss. She has been experiencing symptoms for a few months, which she originally thought might be related to her history of GERD. She reports that she was a light smoker before she had children but has not smoked regularly in about 20 years. Because of the patient's respiratory symptoms, chest radiography is ordered.
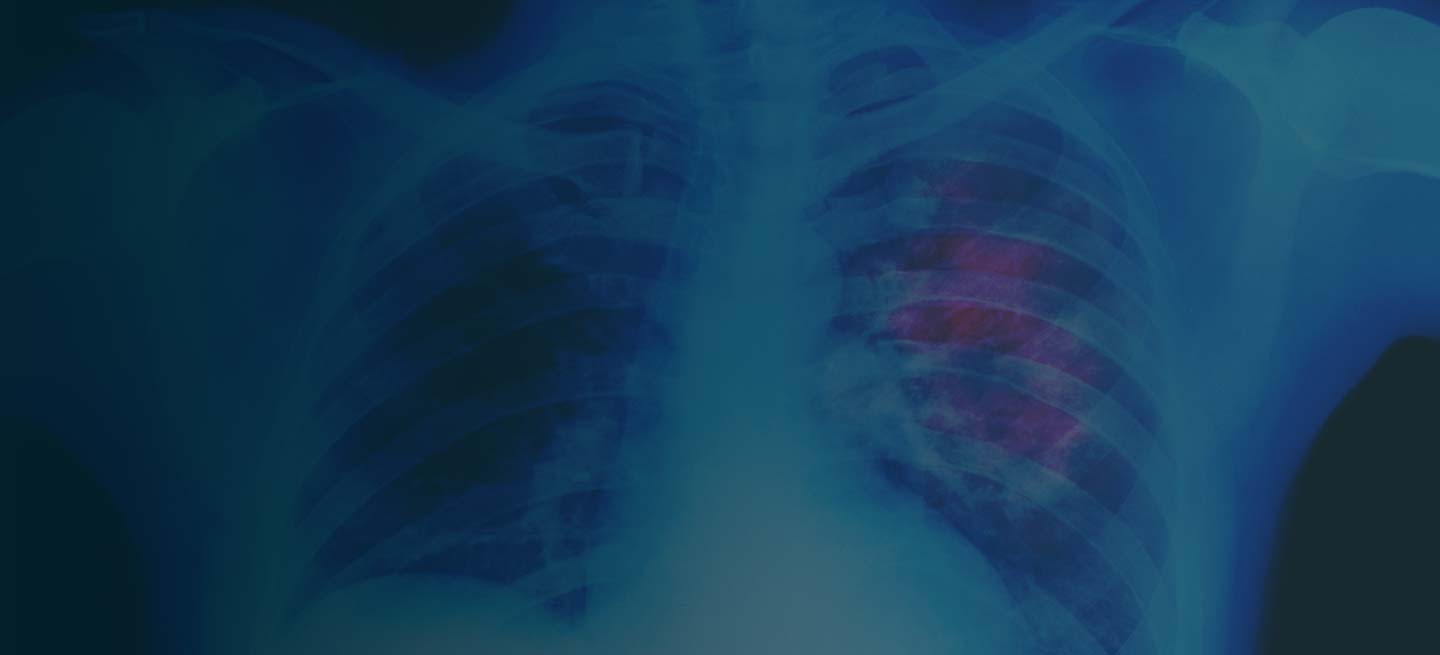
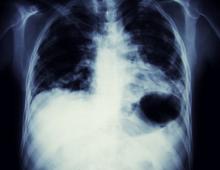
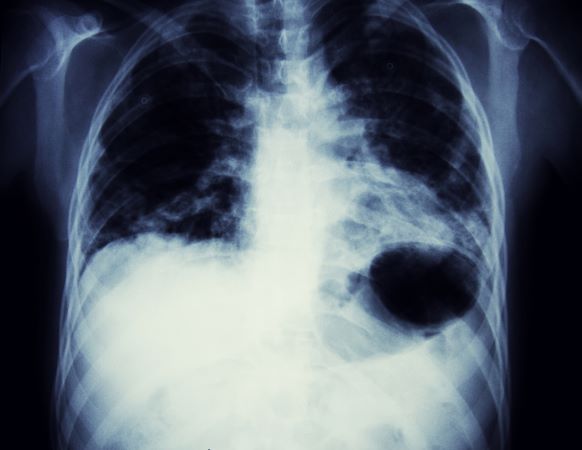
This frontal projection chest radiography clearly demonstrates a mass in the upper lobe of the right lung that represents the appearance of lung cancer (malignancy).
History of dysphagia and abdominal pain
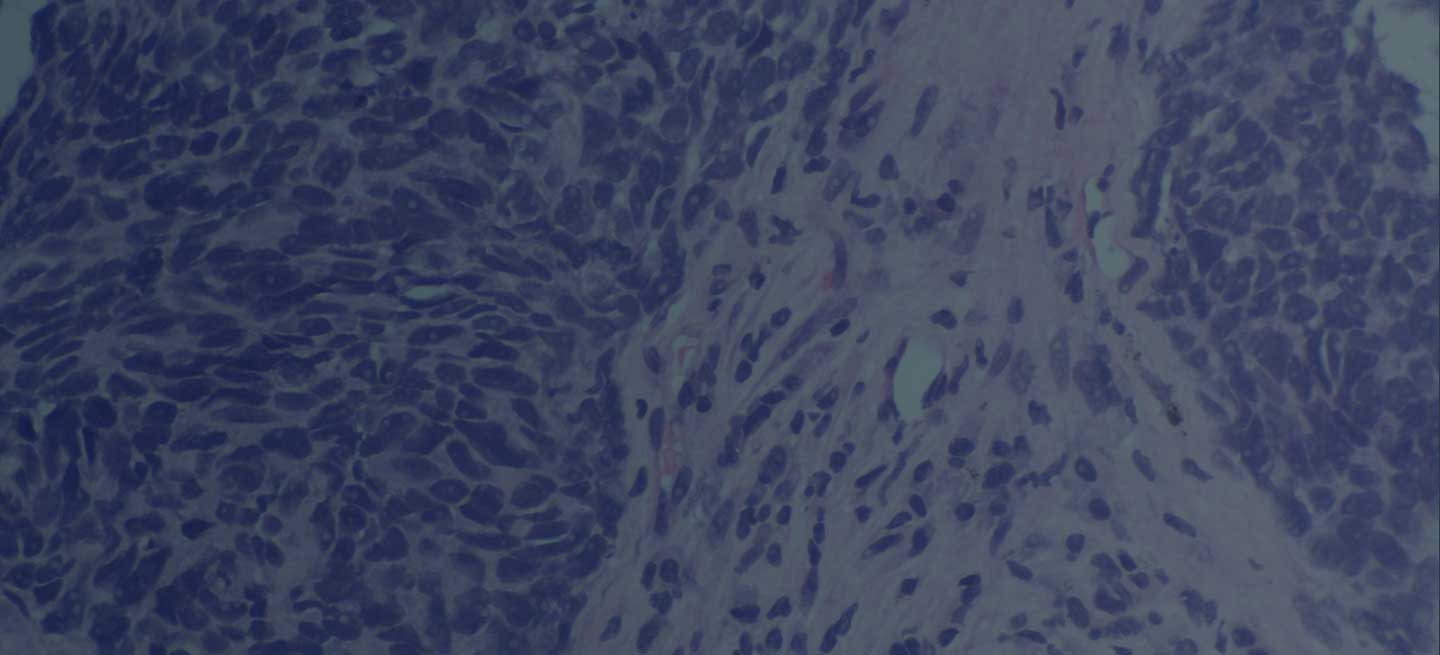
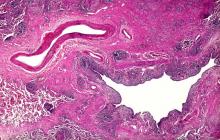
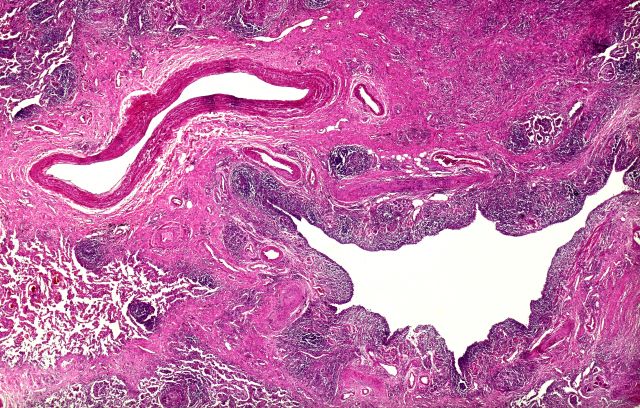
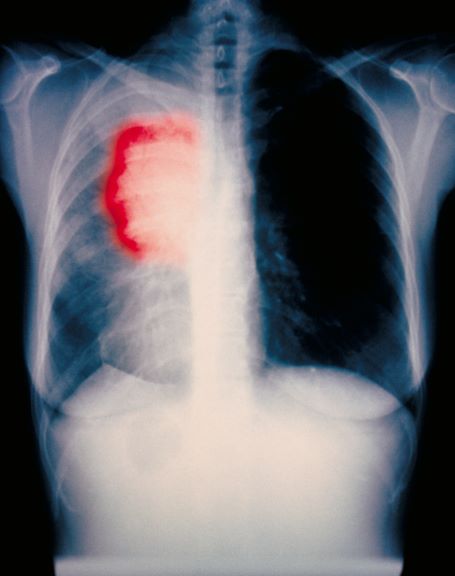
The diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma. A central or hilar mass is most likely to be a squamous cell carcinoma or a small cell tumor and less commonly an adenocarcinoma. Histologically, when there is lack of cohesion among the epithelial cells due to malignant changes, the cells get arranged in a concentric manner. The fate of a squamous cell is to form keratin, so these cells lay down keratin in a concentric manner and then appear as keratin pearls.
This patient's tumor is found to have programmed cell death–ligand 1 ≥ 1% and has no actionable molecular markers. The patient has a performance status score of 1. In a patient with advanced or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma with a performance status score of 1, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends pembrolizumab/carboplatin/paclitaxel or pembrolizumab/carboplatin/albumin-bound paclitaxel as preferred regimens. The pembrolizumab component is based on the results of the KEYNOTE-407 trial. In patients with previously untreated metastatic, squamous non-small cell lung cancer, the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy with carboplatin plus paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel resulted in significantly longer overall survival and progression-free survival than chemotherapy alone.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
The diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma. A central or hilar mass is most likely to be a squamous cell carcinoma or a small cell tumor and less commonly an adenocarcinoma. Histologically, when there is lack of cohesion among the epithelial cells due to malignant changes, the cells get arranged in a concentric manner. The fate of a squamous cell is to form keratin, so these cells lay down keratin in a concentric manner and then appear as keratin pearls.
This patient's tumor is found to have programmed cell death–ligand 1 ≥ 1% and has no actionable molecular markers. The patient has a performance status score of 1. In a patient with advanced or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma with a performance status score of 1, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends pembrolizumab/carboplatin/paclitaxel or pembrolizumab/carboplatin/albumin-bound paclitaxel as preferred regimens. The pembrolizumab component is based on the results of the KEYNOTE-407 trial. In patients with previously untreated metastatic, squamous non-small cell lung cancer, the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy with carboplatin plus paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel resulted in significantly longer overall survival and progression-free survival than chemotherapy alone.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
The diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma. A central or hilar mass is most likely to be a squamous cell carcinoma or a small cell tumor and less commonly an adenocarcinoma. Histologically, when there is lack of cohesion among the epithelial cells due to malignant changes, the cells get arranged in a concentric manner. The fate of a squamous cell is to form keratin, so these cells lay down keratin in a concentric manner and then appear as keratin pearls.
This patient's tumor is found to have programmed cell death–ligand 1 ≥ 1% and has no actionable molecular markers. The patient has a performance status score of 1. In a patient with advanced or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma with a performance status score of 1, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends pembrolizumab/carboplatin/paclitaxel or pembrolizumab/carboplatin/albumin-bound paclitaxel as preferred regimens. The pembrolizumab component is based on the results of the KEYNOTE-407 trial. In patients with previously untreated metastatic, squamous non-small cell lung cancer, the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy with carboplatin plus paclitaxel or nab-paclitaxel resulted in significantly longer overall survival and progression-free survival than chemotherapy alone.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
A 59-year-old woman presents with a 4-month history of dysphagia when eating solids in addition to nausea and abdominal pain. She also reports recent hemoptysis and the onset of hoarseness. She has had an unintentional 22-lb weight loss over the past 6 months. She has a history of emphysema. She takes no medication. She has a 26 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. She is 5 feet 4 in tall and weighs 105 lb, with a BMI of 18. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Chest auscultation reveals diminished breath sounds over the right lung fields. Chest radiography reveals a right-sided 6-cm hilar mass. Laboratory studies show a serum calcium level of 12 mg/dL (normal range, 8.5-10.5 mg/dL). A CT scan revealed a spiculated lesion and hepatic metastases. A biopsy was performed. Keratinization was found in the form of keratin pearls.