User login
Dear Dr. Mossman,
Last week, I hospitalized a patient against her will, based in part on what her family members told me she had threatened to do. The patient threatened to sue me and said I should have known that her relatives were lying. What if my patient is right? Could I face liability if I involuntarily hospitalized her based on bad collateral information?
Submitted by “Dr. R”
In all U.S. states, laws permit psychiatrists to involuntarily hospitalize persons who pose a danger to themselves or others because of mental illness.1 But taking this step can be tough. Deciding to hospitalize a patient against her will involves weighing her wants and freedom against your duty to look out for her long-term welfare and the community’s safety.2,3 Often, psychiatrists make these decisions under pressure because the family wants something done immediately, other patients also need attention, the clinical picture is incomplete, or potential dispositions (eg, crisis care and inpatient beds) are limited.3 Given such constraints, you can’t always make perfect decisions.
Dr. R’s question has 2 parts:
- What liabilities can a clinician face if a patient is wrongfully committed?
- What liabilities could arise from relying on inaccurate information or making a false petition in order to hospitalize a patient?
We hope that as you and Dr. R read our answers, you’ll have a clearer understanding of:
- the rationale for civil commitment
- how patients, doctors, and courts view civil commitment
- the role of collateral information in decision-making
- relevant legal concepts and case law.
Rationale for civil commitment
For centuries, society has used civil commitment as one of its legal methods for intervening when persons pose a danger to themselves or others because of their mental illness.4 Because incapacitation or death could result from a “false-negative” decision to release a dangerous patient, psychiatrists err on the side of caution and tolerate many “false-positive” hospitalizations of persons who wouldn’t have hurt anyone.5
We can never know if a patient would have done harm had she not been hospitalized. Measures of suicidality and hostility tend to subside during involuntary hospital treatment.6 After hospitalization, many patients cite protection from harm as a reason they are thankful for their treatment.7-9 Some involuntary inpatients want to be hospitalized but hide this for conscious or unconscious reasons,10,11 and involuntary treatment sometimes is the only way to help persons whose illness-induced anosognosia12 prevents them from understanding why they need treatment.13 Involuntary inpatient care leads to modest symptom reduction14,15 and produces treatment outcomes no worse than those of non-coerced patients.10
Patients’ views
Patients often view commitment as unjustified.16 They and their advocates object to what some view as the ultimate infringement on civil liberty.7,17 By its nature, involuntary commitment eliminates patients’ involvement in a major treatment decision,8 disempowers them,18 and influences their relationship with the treatment team.15
Some involuntary patients feel disrespected by staff members8 or experience inadvertent psychological harm, including “loss of self-esteem, identity, self-control, and self-efficacy, as well as diminished hope in the possibility of recovery.”15 Involuntary hospitalization also can have serious practical consequences. Commitment can lead to social stigma, loss of gun rights, increased risks of losing child custody, housing problems, and possible disqualification from some professions.19
Having seen many involuntary patients undergo a change of heart after treatment, psychiatrist Alan Stone proposed the “Thank You Theory” of civil commitment: involuntary hospitalization can be justified by showing that the patient is grateful after recovering.20 Studies show, however, that gratitude is far from universal.1
How coercion is experienced often depends on how it is communicated. The less coercion patients perceive, the better they feel about the treatment they received.21 Satisfaction is important because it leads to less compulsory readmission,22 and dissatisfaction makes malpractice lawsuits more likely.23
Commitment decision-making
States’ laws, judges’ attitudes, and court decisions establish each jurisdiction’s legal methods for instituting emergency holds and willingness to tolerate “false-positive” involuntary hospitalization,4,24 all of which create variation between and within states in how civil commitment laws are applied. As a result, clinicians’ decisions are influenced “by a range of social, political, and economic factors,”25 including patients’ sex, race, age, homelessness, employment status, living situation, diagnoses, previous involuntary treatment, and dissatisfaction with mental health treatment.22,26-32 Furthermore, the potential for coercion often blurs the line between an offer of voluntary admission and an involuntary hospitalization.18
Collateral information
Psychiatrists owe each patient a sound clinical assessment before deciding to initiate involuntarily hospitalization. During a psychiatric crisis, a patient might not be forthcoming or could have impaired memory or judgment. Information from friends or family can help fill in gaps in a patient’s self-report.33 As Dr. R’s question illustrates, adequate assessment often includes seeking information from persons familiar with the patient.1 A report on the Virginia Tech shootings by the Virginia Office of the Inspector General describes how collateral sources can provide otherwise missing evidence of dangerousness,34 and it often leads clinicians toward favoring admission.35
Yet clinicians should regard third-party reports with caution.36 As one attorney warns, “Psychiatrists should be cautious of the underlying motives of well-meaning family members and relatives.”37 If you make a decision to hospitalize a patient involuntarily based on collateral information that turns out to be flawed, are you at fault and potentially liable for harm to the patient?
False petitions and liability
If you’re in a situation similar to the one Dr. R describes, you can take solace in knowing that courts generally provide immunity to a psychiatrist who makes a reasonable, well-intentioned decision to commit someone. The degree of immunity offered varies by jurisdiction. Table 1 provides examples of immunity language from several states’ statutes.
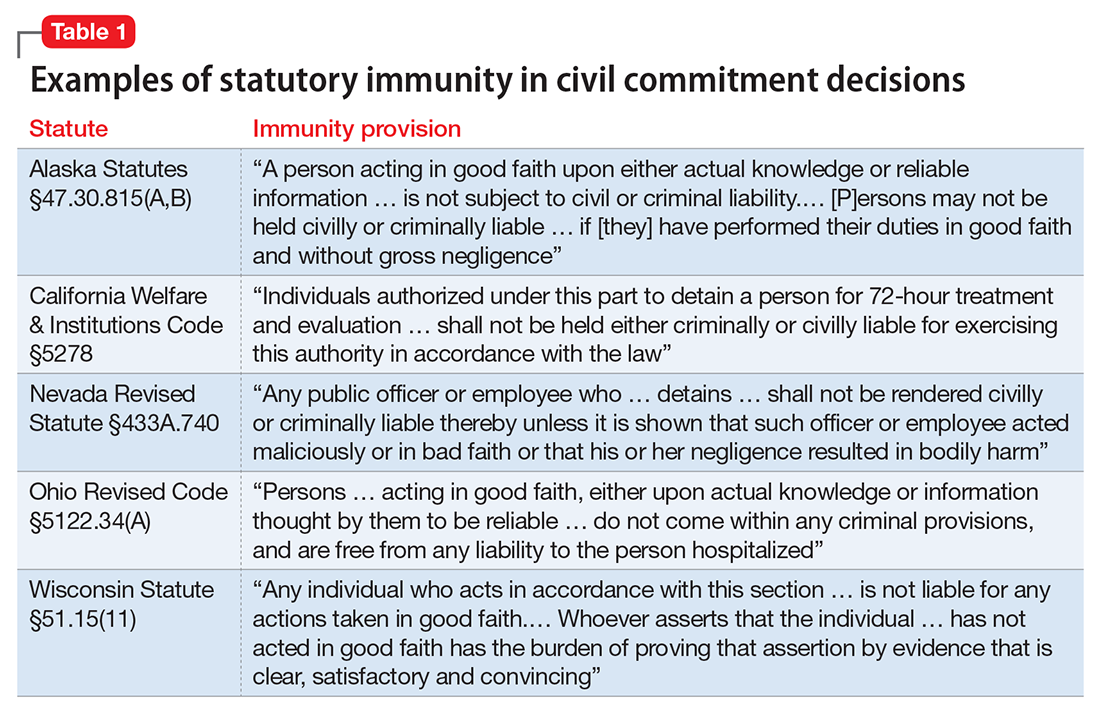
Many states’ statutes also lay out the potential consequences if a psychiatrist takes action to involuntarily hospitalize someone in bad faith or with malicious intent. In some jurisdictions, such actions can lead to criminal sanctions against the doctor or against the party who made a false petition (eg, a devious family member) (Table 2). Commenting on Texas’s statute, attorney Jeffrey Anderson explains, “The touchstone for causes of action based upon a wrongful civil commitment require that the psychiatrist[’s] conduct be found to be unreasonable and negligent. [Immunity…] still requires that a psychiatrist[’s] diagnosis of a patient[’s] threat to harm himself or others be a reasonable and prudent one.”37
The immunity extended through such statutes usually is limited to claims arising directly from the detention. For example, in the California case of Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, a patient under a 72-hour hold fell and fractured her leg, and she sought damages. The trial court dismissed the suit under the immunity statute applicable to commitment decisions, but the appellate court held that “the immunity did not extend to other negligent acts.… The trial court erred in assuming that … the hospital was exempt from all liability for any negligence that occurred during the lawful hold.”38
Bingham v Cedars-Sinai Health Systems illustrates how physicians can lose immunity.39 A nurse contacted her supervisor to report a colleague who had stolen narcotics from work and compromised patient care. In response, the supervisor, hospital, and several physicians agreed to have her involuntarily committed. Later, it was confirmed that the colleague had taken the narcotics. She later sued the hospital system, claiming—in addition to malpractice—retaliation, invasion of privacy, assault and battery, false imprisonment, defamation, intentional infliction of emotional distress, disability-based harassment, and violation of her civil rights. Citing California’s immunity statute, the trial court granted summary judgment to the clinicians and hospital system. On appeal, however, the appellate court reversed the judgment, holding that the defendants had not shown that “the decision to detain Bingham was based on probable cause, a prerequisite to the exemption from liability,” and that Bingham had some legitimate grounds for her lawsuit.
A key point for Dr. R to consider is that, although some states provide immunity if the psychiatrist’s admitting decision was based on an evaluation “performed in good faith,”40 other states’ immunity provisions apply only if the psychiatrist had probable cause to make a decision to detain.41
Ways to reduce liability risk
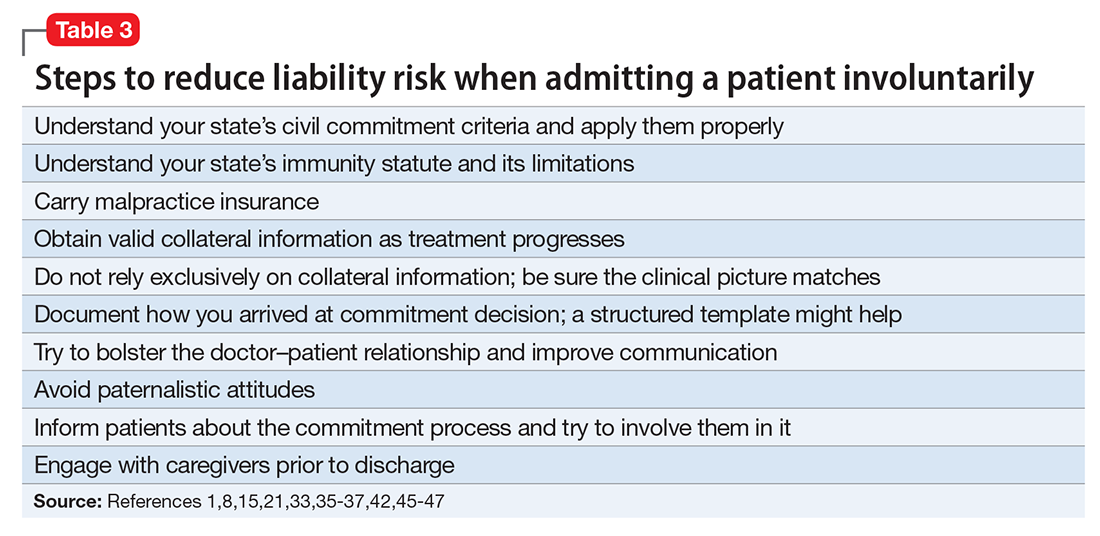
Although an involuntary hospitalization could have an uncertain basis, psychiatrists can reduce the risk of legal liability for their decisions. Good documentation is important. Admitting psychiatrists usually make sound decisions, but the corresponding documentation frequently lacks clinical justification.42-44 As the rate of appropriate documentation of admission decision-making improves, the rate of commitment falls,44 and patients’ legal rights enjoy greater protection.43 Poor communication can decrease the quality of care and increase the risk of a malpractice lawsuit.45 This is just one of many reasons why you should explain your reasons for involuntary hospitalization and inform patients of the procedures for judicial review.8,9 Table 3 summarizes other steps to reduce liability risk when committing patients to the hospital.1,8,15,21,33,35-37,42,45-47
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for civil commitment: best practices for forensic mental health assessments. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2011.
2. Testa M, West SG. Civil commitment in the United States. Psychiatry (Edgemont). 2010;7(10):30-40.
3. Hedman LC, Petrila J, Fisher WH, et al. State laws on emergency holds for mental health stabilization. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):529-535.
4. Groendyk Z. “It takes a lot to get into Bellevue”: a pro-rights critique of New York’s involuntary commitment law. Fordham Urban Law J. 2013;40(1):548-585.
5. Brooks RA. U.S. psychiatrists’ beliefs and wants about involuntary civil commitment grounds. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2006;29(1):13-21.
6. Giacco D, Priebe S. Suicidality and hostility following involuntary hospital treatment. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0154458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154458.
7. Wyder M, Bland R, Herriot A, et al. The experiences of the legal processes of involuntary treatment orders: tension between the legal and medical frameworks. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2015;38:44-50.
8. Valenti E, Giacco D, Katasakou C, et al. Which values are important for patients during involuntary treatment? A qualitative study with psychiatric inpatients. J Med Ethics. 2014;40(12):832-836.
9. Katsakou C, Rose D, Amos T, et al. Psychiatric patients’ views on why their involuntary hospitalisation was right or wrong: a qualitative study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;42(7):1169-1179.
10. Kaltiala-Heino R, Laippala P, Salokangas RK. Impact of coercion on treatment outcome. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(3):311-322.
11. Hoge SK, Lidz CW, Eisenberg M, et al. Perceptions of coercion in the admission of voluntary and involuntary psychiatric patients. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(2):167-181.
12. Lehrer DS, Lorenz J. Anosognosia in schizophrenia: hidden in plain sight. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2014;11(5-6):10-17. 13. Gordon S. The danger zone: how the dangerousness standard in civil commitment proceedings harms people with serious mental illness. Case Western Reserve Law Review. 2016;66(3):657-700.
14. Kallert TW, Katsakou C, Adamowski T, et al. Coerced hospital admission and symptom change—a prospective observational multi-centre study. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028191.
15. Danzer G, Wilkus-Stone A. The give and take of freedom: the role of involuntary hospitalization and treatment in recovery from mental illness. Bull Menninger Clin. 2015;79(3):255-280.
16. Roe D, Weishut DJ, Jaglom M, et al. Patients’ and staff members’ attitudes about the rights of hospitalized psychiatric patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):87-91.
17. Amidov T. Involuntary commitment is unnecessary and discriminatory. In: Berlatsky N, ed. Mental illness. Farmington Hills, MI: Greenhaven Press; 2016;140-145.
18. Monahan J, Hoge SK, Lidz C, et al. Coercion and commitment: understanding involuntary mental hospital admission. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1995;18(3):249-263.
19. Guest Pryal KR. Heller’s scapegoats. North Carolina Law Review. 2015;93(5):1439-1473.
20. Stone AA. Mental health and law: a system in transition. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office; 1975:75-176.
21. Katsakou C, Bowers L, Amos T, et al. Coercion and treatment satisfaction among involuntary patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(3):286-292.
22. Setkowski K, van der Post LF, Peen J, et al. Changing patient perspectives after compulsory admission and the risk of re-admission during 5 years of follow-up: the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry IX. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2016;62(6):578-588.
23. Stelfox HT, Gandhi TK, Orav EJ, et al. The relation of patient satisfaction with complaints against physicians and malpractice lawsuits. Am J Med. 2005;118(10):1126-1133.
24. Goldman A. Continued overreliance on involuntary commitment: the need for a less restrictive alternative. J Leg Med. 2015;36(2):233-251.
25. Fisher WH, Grisso T. Commentary: civil commitment statutes—40 years of circumvention. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2010;38(3):365-368.
26. Curley A, Agada E, Emechebe A, et al. Exploring and explaining involuntary care: the relationship between psychiatric admission status, gender and other demographic and clinical variables. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2016;47:53-59.
27. Muroff JR, Jackson JS, Mowbray CT, et al. The influence of gender, patient volume and time on clinical diagnostic decision making in psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2007;29(6):481-488.
28. Muroff JR, Edelsohn GA, Joe S, et al. The role of race in diagnostic and disposition decision making in a pediatric psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008;30(3):269-276.
29. Unick GJ, Kessell E, Woodard EK, et al. Factors affecting psychiatric inpatient hospitalization from a psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(6):618-625.
30. Ng XT, Kelly BD. Voluntary and involuntary care: three-year study of demographic and diagnostic admission statistics at an inner-city adult psychiatry unit. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2012;35(4):317-326.
31. Lo TT, Woo BK. The impact of unemployment on utilization of psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(3):e7-e8. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.10.010.
32. van der Post LFM, Peen J, Dekker JJ. A prediction model for the incidence of civil detention for crisis patients with psychiatric illnesses; the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry VII. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(2):283-290.
33. Heilbrun K, NeMoyer A, King C, et al. Using third-party information in forensic mental health assessment: a critical review. Court Review. 2015;51(1):16-35.
34. Mass shootings at Virginia Tech, April 16, 2007 report of the Virginia Tech Review Panel presented to Timothy M. Kaine, Governor, Commonwealth of Virginia. http://cdm16064.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p266901coll4/id/904. Accessed February 2, 2017.
35. Segal SP, Laurie TA, Segal MJ. Factors in the use of coercive retention in civil commitment evaluations in psychiatric emergency services. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(4):514-520.
36. Lincoln A, Allen MH. The influence of collateral information on access to inpatient psychiatric services. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation. 2002;6:99-108.
37. Anderson JC. How I decided to sue you: misadventures in psychiatry. Reprinted in part from: Moody CE, Smith MT, Maedgen BJ. Litigation of psychiatric malpractice claims. Presented at: Medical Malpractice Conference; April 15, 1993; San Antonio, TX. http://www.texaslawfirm.com/Articles/How_I_Decided_to_Sue_You__Misadventrues_in_Psychiatry.pdf. Accessed December 27, 2016.
38. Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, 108 Cal App 4th 69, 133 Cal Rptr 2d9 (2003).
39. Bingham v Cedars Sinai Health Systems, WL 2137442, Cal App 2 Dist (2004).
40. Ohio Revised Code §5122.34.
41. California Welfare & Institutions Code §5150(E).
42. Hashmi A, Shad M, Rhoades HM, et al. Involuntary detention: do psychiatrists clinically justify continuing involuntary hospitalization? Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):285-293.
43. Brayley J, Alston A, Rogers K. Legal criteria for involuntary mental health admission: clinician performance in recording grounds for decision. Med J Aust. 2015;203(8):334.
44. Perrigo TL, Williams KA. Implementation of an evidence based guideline for assessment and documentation of the civil commitment process. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(8):1033-1036.
45. Mor S, Rabinovich-Einy O. Relational malpractice. Seton Hall Law Rev. 2012;42(2):601-642.
46. Tate v Kaiser Foundation Hospitals, WL 176625, U.S. Dist. LEXIS 5891 (CD Cal 2014).
47. Ranieri V, Madigan K, Roche E, et al. Caregivers’ perceptions of coercion in psychiatric hospital admission. Psychiatry Res. 2015;22(3)8:380-385.
Dear Dr. Mossman,
Last week, I hospitalized a patient against her will, based in part on what her family members told me she had threatened to do. The patient threatened to sue me and said I should have known that her relatives were lying. What if my patient is right? Could I face liability if I involuntarily hospitalized her based on bad collateral information?
Submitted by “Dr. R”
In all U.S. states, laws permit psychiatrists to involuntarily hospitalize persons who pose a danger to themselves or others because of mental illness.1 But taking this step can be tough. Deciding to hospitalize a patient against her will involves weighing her wants and freedom against your duty to look out for her long-term welfare and the community’s safety.2,3 Often, psychiatrists make these decisions under pressure because the family wants something done immediately, other patients also need attention, the clinical picture is incomplete, or potential dispositions (eg, crisis care and inpatient beds) are limited.3 Given such constraints, you can’t always make perfect decisions.
Dr. R’s question has 2 parts:
- What liabilities can a clinician face if a patient is wrongfully committed?
- What liabilities could arise from relying on inaccurate information or making a false petition in order to hospitalize a patient?
We hope that as you and Dr. R read our answers, you’ll have a clearer understanding of:
- the rationale for civil commitment
- how patients, doctors, and courts view civil commitment
- the role of collateral information in decision-making
- relevant legal concepts and case law.
Rationale for civil commitment
For centuries, society has used civil commitment as one of its legal methods for intervening when persons pose a danger to themselves or others because of their mental illness.4 Because incapacitation or death could result from a “false-negative” decision to release a dangerous patient, psychiatrists err on the side of caution and tolerate many “false-positive” hospitalizations of persons who wouldn’t have hurt anyone.5
We can never know if a patient would have done harm had she not been hospitalized. Measures of suicidality and hostility tend to subside during involuntary hospital treatment.6 After hospitalization, many patients cite protection from harm as a reason they are thankful for their treatment.7-9 Some involuntary inpatients want to be hospitalized but hide this for conscious or unconscious reasons,10,11 and involuntary treatment sometimes is the only way to help persons whose illness-induced anosognosia12 prevents them from understanding why they need treatment.13 Involuntary inpatient care leads to modest symptom reduction14,15 and produces treatment outcomes no worse than those of non-coerced patients.10
Patients’ views
Patients often view commitment as unjustified.16 They and their advocates object to what some view as the ultimate infringement on civil liberty.7,17 By its nature, involuntary commitment eliminates patients’ involvement in a major treatment decision,8 disempowers them,18 and influences their relationship with the treatment team.15
Some involuntary patients feel disrespected by staff members8 or experience inadvertent psychological harm, including “loss of self-esteem, identity, self-control, and self-efficacy, as well as diminished hope in the possibility of recovery.”15 Involuntary hospitalization also can have serious practical consequences. Commitment can lead to social stigma, loss of gun rights, increased risks of losing child custody, housing problems, and possible disqualification from some professions.19
Having seen many involuntary patients undergo a change of heart after treatment, psychiatrist Alan Stone proposed the “Thank You Theory” of civil commitment: involuntary hospitalization can be justified by showing that the patient is grateful after recovering.20 Studies show, however, that gratitude is far from universal.1
How coercion is experienced often depends on how it is communicated. The less coercion patients perceive, the better they feel about the treatment they received.21 Satisfaction is important because it leads to less compulsory readmission,22 and dissatisfaction makes malpractice lawsuits more likely.23
Commitment decision-making
States’ laws, judges’ attitudes, and court decisions establish each jurisdiction’s legal methods for instituting emergency holds and willingness to tolerate “false-positive” involuntary hospitalization,4,24 all of which create variation between and within states in how civil commitment laws are applied. As a result, clinicians’ decisions are influenced “by a range of social, political, and economic factors,”25 including patients’ sex, race, age, homelessness, employment status, living situation, diagnoses, previous involuntary treatment, and dissatisfaction with mental health treatment.22,26-32 Furthermore, the potential for coercion often blurs the line between an offer of voluntary admission and an involuntary hospitalization.18
Collateral information
Psychiatrists owe each patient a sound clinical assessment before deciding to initiate involuntarily hospitalization. During a psychiatric crisis, a patient might not be forthcoming or could have impaired memory or judgment. Information from friends or family can help fill in gaps in a patient’s self-report.33 As Dr. R’s question illustrates, adequate assessment often includes seeking information from persons familiar with the patient.1 A report on the Virginia Tech shootings by the Virginia Office of the Inspector General describes how collateral sources can provide otherwise missing evidence of dangerousness,34 and it often leads clinicians toward favoring admission.35
Yet clinicians should regard third-party reports with caution.36 As one attorney warns, “Psychiatrists should be cautious of the underlying motives of well-meaning family members and relatives.”37 If you make a decision to hospitalize a patient involuntarily based on collateral information that turns out to be flawed, are you at fault and potentially liable for harm to the patient?
False petitions and liability
If you’re in a situation similar to the one Dr. R describes, you can take solace in knowing that courts generally provide immunity to a psychiatrist who makes a reasonable, well-intentioned decision to commit someone. The degree of immunity offered varies by jurisdiction. Table 1 provides examples of immunity language from several states’ statutes.

Many states’ statutes also lay out the potential consequences if a psychiatrist takes action to involuntarily hospitalize someone in bad faith or with malicious intent. In some jurisdictions, such actions can lead to criminal sanctions against the doctor or against the party who made a false petition (eg, a devious family member) (Table 2). Commenting on Texas’s statute, attorney Jeffrey Anderson explains, “The touchstone for causes of action based upon a wrongful civil commitment require that the psychiatrist[’s] conduct be found to be unreasonable and negligent. [Immunity…] still requires that a psychiatrist[’s] diagnosis of a patient[’s] threat to harm himself or others be a reasonable and prudent one.”37
The immunity extended through such statutes usually is limited to claims arising directly from the detention. For example, in the California case of Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, a patient under a 72-hour hold fell and fractured her leg, and she sought damages. The trial court dismissed the suit under the immunity statute applicable to commitment decisions, but the appellate court held that “the immunity did not extend to other negligent acts.… The trial court erred in assuming that … the hospital was exempt from all liability for any negligence that occurred during the lawful hold.”38
Bingham v Cedars-Sinai Health Systems illustrates how physicians can lose immunity.39 A nurse contacted her supervisor to report a colleague who had stolen narcotics from work and compromised patient care. In response, the supervisor, hospital, and several physicians agreed to have her involuntarily committed. Later, it was confirmed that the colleague had taken the narcotics. She later sued the hospital system, claiming—in addition to malpractice—retaliation, invasion of privacy, assault and battery, false imprisonment, defamation, intentional infliction of emotional distress, disability-based harassment, and violation of her civil rights. Citing California’s immunity statute, the trial court granted summary judgment to the clinicians and hospital system. On appeal, however, the appellate court reversed the judgment, holding that the defendants had not shown that “the decision to detain Bingham was based on probable cause, a prerequisite to the exemption from liability,” and that Bingham had some legitimate grounds for her lawsuit.
A key point for Dr. R to consider is that, although some states provide immunity if the psychiatrist’s admitting decision was based on an evaluation “performed in good faith,”40 other states’ immunity provisions apply only if the psychiatrist had probable cause to make a decision to detain.41
Ways to reduce liability risk
Although an involuntary hospitalization could have an uncertain basis, psychiatrists can reduce the risk of legal liability for their decisions. Good documentation is important. Admitting psychiatrists usually make sound decisions, but the corresponding documentation frequently lacks clinical justification.42-44 As the rate of appropriate documentation of admission decision-making improves, the rate of commitment falls,44 and patients’ legal rights enjoy greater protection.43 Poor communication can decrease the quality of care and increase the risk of a malpractice lawsuit.45 This is just one of many reasons why you should explain your reasons for involuntary hospitalization and inform patients of the procedures for judicial review.8,9 Table 3 summarizes other steps to reduce liability risk when committing patients to the hospital.1,8,15,21,33,35-37,42,45-47

Dear Dr. Mossman,
Last week, I hospitalized a patient against her will, based in part on what her family members told me she had threatened to do. The patient threatened to sue me and said I should have known that her relatives were lying. What if my patient is right? Could I face liability if I involuntarily hospitalized her based on bad collateral information?
Submitted by “Dr. R”
In all U.S. states, laws permit psychiatrists to involuntarily hospitalize persons who pose a danger to themselves or others because of mental illness.1 But taking this step can be tough. Deciding to hospitalize a patient against her will involves weighing her wants and freedom against your duty to look out for her long-term welfare and the community’s safety.2,3 Often, psychiatrists make these decisions under pressure because the family wants something done immediately, other patients also need attention, the clinical picture is incomplete, or potential dispositions (eg, crisis care and inpatient beds) are limited.3 Given such constraints, you can’t always make perfect decisions.
Dr. R’s question has 2 parts:
- What liabilities can a clinician face if a patient is wrongfully committed?
- What liabilities could arise from relying on inaccurate information or making a false petition in order to hospitalize a patient?
We hope that as you and Dr. R read our answers, you’ll have a clearer understanding of:
- the rationale for civil commitment
- how patients, doctors, and courts view civil commitment
- the role of collateral information in decision-making
- relevant legal concepts and case law.
Rationale for civil commitment
For centuries, society has used civil commitment as one of its legal methods for intervening when persons pose a danger to themselves or others because of their mental illness.4 Because incapacitation or death could result from a “false-negative” decision to release a dangerous patient, psychiatrists err on the side of caution and tolerate many “false-positive” hospitalizations of persons who wouldn’t have hurt anyone.5
We can never know if a patient would have done harm had she not been hospitalized. Measures of suicidality and hostility tend to subside during involuntary hospital treatment.6 After hospitalization, many patients cite protection from harm as a reason they are thankful for their treatment.7-9 Some involuntary inpatients want to be hospitalized but hide this for conscious or unconscious reasons,10,11 and involuntary treatment sometimes is the only way to help persons whose illness-induced anosognosia12 prevents them from understanding why they need treatment.13 Involuntary inpatient care leads to modest symptom reduction14,15 and produces treatment outcomes no worse than those of non-coerced patients.10
Patients’ views
Patients often view commitment as unjustified.16 They and their advocates object to what some view as the ultimate infringement on civil liberty.7,17 By its nature, involuntary commitment eliminates patients’ involvement in a major treatment decision,8 disempowers them,18 and influences their relationship with the treatment team.15
Some involuntary patients feel disrespected by staff members8 or experience inadvertent psychological harm, including “loss of self-esteem, identity, self-control, and self-efficacy, as well as diminished hope in the possibility of recovery.”15 Involuntary hospitalization also can have serious practical consequences. Commitment can lead to social stigma, loss of gun rights, increased risks of losing child custody, housing problems, and possible disqualification from some professions.19
Having seen many involuntary patients undergo a change of heart after treatment, psychiatrist Alan Stone proposed the “Thank You Theory” of civil commitment: involuntary hospitalization can be justified by showing that the patient is grateful after recovering.20 Studies show, however, that gratitude is far from universal.1
How coercion is experienced often depends on how it is communicated. The less coercion patients perceive, the better they feel about the treatment they received.21 Satisfaction is important because it leads to less compulsory readmission,22 and dissatisfaction makes malpractice lawsuits more likely.23
Commitment decision-making
States’ laws, judges’ attitudes, and court decisions establish each jurisdiction’s legal methods for instituting emergency holds and willingness to tolerate “false-positive” involuntary hospitalization,4,24 all of which create variation between and within states in how civil commitment laws are applied. As a result, clinicians’ decisions are influenced “by a range of social, political, and economic factors,”25 including patients’ sex, race, age, homelessness, employment status, living situation, diagnoses, previous involuntary treatment, and dissatisfaction with mental health treatment.22,26-32 Furthermore, the potential for coercion often blurs the line between an offer of voluntary admission and an involuntary hospitalization.18
Collateral information
Psychiatrists owe each patient a sound clinical assessment before deciding to initiate involuntarily hospitalization. During a psychiatric crisis, a patient might not be forthcoming or could have impaired memory or judgment. Information from friends or family can help fill in gaps in a patient’s self-report.33 As Dr. R’s question illustrates, adequate assessment often includes seeking information from persons familiar with the patient.1 A report on the Virginia Tech shootings by the Virginia Office of the Inspector General describes how collateral sources can provide otherwise missing evidence of dangerousness,34 and it often leads clinicians toward favoring admission.35
Yet clinicians should regard third-party reports with caution.36 As one attorney warns, “Psychiatrists should be cautious of the underlying motives of well-meaning family members and relatives.”37 If you make a decision to hospitalize a patient involuntarily based on collateral information that turns out to be flawed, are you at fault and potentially liable for harm to the patient?
False petitions and liability
If you’re in a situation similar to the one Dr. R describes, you can take solace in knowing that courts generally provide immunity to a psychiatrist who makes a reasonable, well-intentioned decision to commit someone. The degree of immunity offered varies by jurisdiction. Table 1 provides examples of immunity language from several states’ statutes.

Many states’ statutes also lay out the potential consequences if a psychiatrist takes action to involuntarily hospitalize someone in bad faith or with malicious intent. In some jurisdictions, such actions can lead to criminal sanctions against the doctor or against the party who made a false petition (eg, a devious family member) (Table 2). Commenting on Texas’s statute, attorney Jeffrey Anderson explains, “The touchstone for causes of action based upon a wrongful civil commitment require that the psychiatrist[’s] conduct be found to be unreasonable and negligent. [Immunity…] still requires that a psychiatrist[’s] diagnosis of a patient[’s] threat to harm himself or others be a reasonable and prudent one.”37
The immunity extended through such statutes usually is limited to claims arising directly from the detention. For example, in the California case of Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, a patient under a 72-hour hold fell and fractured her leg, and she sought damages. The trial court dismissed the suit under the immunity statute applicable to commitment decisions, but the appellate court held that “the immunity did not extend to other negligent acts.… The trial court erred in assuming that … the hospital was exempt from all liability for any negligence that occurred during the lawful hold.”38
Bingham v Cedars-Sinai Health Systems illustrates how physicians can lose immunity.39 A nurse contacted her supervisor to report a colleague who had stolen narcotics from work and compromised patient care. In response, the supervisor, hospital, and several physicians agreed to have her involuntarily committed. Later, it was confirmed that the colleague had taken the narcotics. She later sued the hospital system, claiming—in addition to malpractice—retaliation, invasion of privacy, assault and battery, false imprisonment, defamation, intentional infliction of emotional distress, disability-based harassment, and violation of her civil rights. Citing California’s immunity statute, the trial court granted summary judgment to the clinicians and hospital system. On appeal, however, the appellate court reversed the judgment, holding that the defendants had not shown that “the decision to detain Bingham was based on probable cause, a prerequisite to the exemption from liability,” and that Bingham had some legitimate grounds for her lawsuit.
A key point for Dr. R to consider is that, although some states provide immunity if the psychiatrist’s admitting decision was based on an evaluation “performed in good faith,”40 other states’ immunity provisions apply only if the psychiatrist had probable cause to make a decision to detain.41
Ways to reduce liability risk
Although an involuntary hospitalization could have an uncertain basis, psychiatrists can reduce the risk of legal liability for their decisions. Good documentation is important. Admitting psychiatrists usually make sound decisions, but the corresponding documentation frequently lacks clinical justification.42-44 As the rate of appropriate documentation of admission decision-making improves, the rate of commitment falls,44 and patients’ legal rights enjoy greater protection.43 Poor communication can decrease the quality of care and increase the risk of a malpractice lawsuit.45 This is just one of many reasons why you should explain your reasons for involuntary hospitalization and inform patients of the procedures for judicial review.8,9 Table 3 summarizes other steps to reduce liability risk when committing patients to the hospital.1,8,15,21,33,35-37,42,45-47

1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for civil commitment: best practices for forensic mental health assessments. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2011.
2. Testa M, West SG. Civil commitment in the United States. Psychiatry (Edgemont). 2010;7(10):30-40.
3. Hedman LC, Petrila J, Fisher WH, et al. State laws on emergency holds for mental health stabilization. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):529-535.
4. Groendyk Z. “It takes a lot to get into Bellevue”: a pro-rights critique of New York’s involuntary commitment law. Fordham Urban Law J. 2013;40(1):548-585.
5. Brooks RA. U.S. psychiatrists’ beliefs and wants about involuntary civil commitment grounds. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2006;29(1):13-21.
6. Giacco D, Priebe S. Suicidality and hostility following involuntary hospital treatment. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0154458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154458.
7. Wyder M, Bland R, Herriot A, et al. The experiences of the legal processes of involuntary treatment orders: tension between the legal and medical frameworks. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2015;38:44-50.
8. Valenti E, Giacco D, Katasakou C, et al. Which values are important for patients during involuntary treatment? A qualitative study with psychiatric inpatients. J Med Ethics. 2014;40(12):832-836.
9. Katsakou C, Rose D, Amos T, et al. Psychiatric patients’ views on why their involuntary hospitalisation was right or wrong: a qualitative study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;42(7):1169-1179.
10. Kaltiala-Heino R, Laippala P, Salokangas RK. Impact of coercion on treatment outcome. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(3):311-322.
11. Hoge SK, Lidz CW, Eisenberg M, et al. Perceptions of coercion in the admission of voluntary and involuntary psychiatric patients. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(2):167-181.
12. Lehrer DS, Lorenz J. Anosognosia in schizophrenia: hidden in plain sight. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2014;11(5-6):10-17. 13. Gordon S. The danger zone: how the dangerousness standard in civil commitment proceedings harms people with serious mental illness. Case Western Reserve Law Review. 2016;66(3):657-700.
14. Kallert TW, Katsakou C, Adamowski T, et al. Coerced hospital admission and symptom change—a prospective observational multi-centre study. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028191.
15. Danzer G, Wilkus-Stone A. The give and take of freedom: the role of involuntary hospitalization and treatment in recovery from mental illness. Bull Menninger Clin. 2015;79(3):255-280.
16. Roe D, Weishut DJ, Jaglom M, et al. Patients’ and staff members’ attitudes about the rights of hospitalized psychiatric patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):87-91.
17. Amidov T. Involuntary commitment is unnecessary and discriminatory. In: Berlatsky N, ed. Mental illness. Farmington Hills, MI: Greenhaven Press; 2016;140-145.
18. Monahan J, Hoge SK, Lidz C, et al. Coercion and commitment: understanding involuntary mental hospital admission. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1995;18(3):249-263.
19. Guest Pryal KR. Heller’s scapegoats. North Carolina Law Review. 2015;93(5):1439-1473.
20. Stone AA. Mental health and law: a system in transition. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office; 1975:75-176.
21. Katsakou C, Bowers L, Amos T, et al. Coercion and treatment satisfaction among involuntary patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(3):286-292.
22. Setkowski K, van der Post LF, Peen J, et al. Changing patient perspectives after compulsory admission and the risk of re-admission during 5 years of follow-up: the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry IX. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2016;62(6):578-588.
23. Stelfox HT, Gandhi TK, Orav EJ, et al. The relation of patient satisfaction with complaints against physicians and malpractice lawsuits. Am J Med. 2005;118(10):1126-1133.
24. Goldman A. Continued overreliance on involuntary commitment: the need for a less restrictive alternative. J Leg Med. 2015;36(2):233-251.
25. Fisher WH, Grisso T. Commentary: civil commitment statutes—40 years of circumvention. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2010;38(3):365-368.
26. Curley A, Agada E, Emechebe A, et al. Exploring and explaining involuntary care: the relationship between psychiatric admission status, gender and other demographic and clinical variables. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2016;47:53-59.
27. Muroff JR, Jackson JS, Mowbray CT, et al. The influence of gender, patient volume and time on clinical diagnostic decision making in psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2007;29(6):481-488.
28. Muroff JR, Edelsohn GA, Joe S, et al. The role of race in diagnostic and disposition decision making in a pediatric psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008;30(3):269-276.
29. Unick GJ, Kessell E, Woodard EK, et al. Factors affecting psychiatric inpatient hospitalization from a psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(6):618-625.
30. Ng XT, Kelly BD. Voluntary and involuntary care: three-year study of demographic and diagnostic admission statistics at an inner-city adult psychiatry unit. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2012;35(4):317-326.
31. Lo TT, Woo BK. The impact of unemployment on utilization of psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(3):e7-e8. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.10.010.
32. van der Post LFM, Peen J, Dekker JJ. A prediction model for the incidence of civil detention for crisis patients with psychiatric illnesses; the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry VII. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(2):283-290.
33. Heilbrun K, NeMoyer A, King C, et al. Using third-party information in forensic mental health assessment: a critical review. Court Review. 2015;51(1):16-35.
34. Mass shootings at Virginia Tech, April 16, 2007 report of the Virginia Tech Review Panel presented to Timothy M. Kaine, Governor, Commonwealth of Virginia. http://cdm16064.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p266901coll4/id/904. Accessed February 2, 2017.
35. Segal SP, Laurie TA, Segal MJ. Factors in the use of coercive retention in civil commitment evaluations in psychiatric emergency services. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(4):514-520.
36. Lincoln A, Allen MH. The influence of collateral information on access to inpatient psychiatric services. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation. 2002;6:99-108.
37. Anderson JC. How I decided to sue you: misadventures in psychiatry. Reprinted in part from: Moody CE, Smith MT, Maedgen BJ. Litigation of psychiatric malpractice claims. Presented at: Medical Malpractice Conference; April 15, 1993; San Antonio, TX. http://www.texaslawfirm.com/Articles/How_I_Decided_to_Sue_You__Misadventrues_in_Psychiatry.pdf. Accessed December 27, 2016.
38. Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, 108 Cal App 4th 69, 133 Cal Rptr 2d9 (2003).
39. Bingham v Cedars Sinai Health Systems, WL 2137442, Cal App 2 Dist (2004).
40. Ohio Revised Code §5122.34.
41. California Welfare & Institutions Code §5150(E).
42. Hashmi A, Shad M, Rhoades HM, et al. Involuntary detention: do psychiatrists clinically justify continuing involuntary hospitalization? Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):285-293.
43. Brayley J, Alston A, Rogers K. Legal criteria for involuntary mental health admission: clinician performance in recording grounds for decision. Med J Aust. 2015;203(8):334.
44. Perrigo TL, Williams KA. Implementation of an evidence based guideline for assessment and documentation of the civil commitment process. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(8):1033-1036.
45. Mor S, Rabinovich-Einy O. Relational malpractice. Seton Hall Law Rev. 2012;42(2):601-642.
46. Tate v Kaiser Foundation Hospitals, WL 176625, U.S. Dist. LEXIS 5891 (CD Cal 2014).
47. Ranieri V, Madigan K, Roche E, et al. Caregivers’ perceptions of coercion in psychiatric hospital admission. Psychiatry Res. 2015;22(3)8:380-385.
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for civil commitment: best practices for forensic mental health assessments. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2011.
2. Testa M, West SG. Civil commitment in the United States. Psychiatry (Edgemont). 2010;7(10):30-40.
3. Hedman LC, Petrila J, Fisher WH, et al. State laws on emergency holds for mental health stabilization. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):529-535.
4. Groendyk Z. “It takes a lot to get into Bellevue”: a pro-rights critique of New York’s involuntary commitment law. Fordham Urban Law J. 2013;40(1):548-585.
5. Brooks RA. U.S. psychiatrists’ beliefs and wants about involuntary civil commitment grounds. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2006;29(1):13-21.
6. Giacco D, Priebe S. Suicidality and hostility following involuntary hospital treatment. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0154458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154458.
7. Wyder M, Bland R, Herriot A, et al. The experiences of the legal processes of involuntary treatment orders: tension between the legal and medical frameworks. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2015;38:44-50.
8. Valenti E, Giacco D, Katasakou C, et al. Which values are important for patients during involuntary treatment? A qualitative study with psychiatric inpatients. J Med Ethics. 2014;40(12):832-836.
9. Katsakou C, Rose D, Amos T, et al. Psychiatric patients’ views on why their involuntary hospitalisation was right or wrong: a qualitative study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;42(7):1169-1179.
10. Kaltiala-Heino R, Laippala P, Salokangas RK. Impact of coercion on treatment outcome. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(3):311-322.
11. Hoge SK, Lidz CW, Eisenberg M, et al. Perceptions of coercion in the admission of voluntary and involuntary psychiatric patients. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1997;20(2):167-181.
12. Lehrer DS, Lorenz J. Anosognosia in schizophrenia: hidden in plain sight. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2014;11(5-6):10-17. 13. Gordon S. The danger zone: how the dangerousness standard in civil commitment proceedings harms people with serious mental illness. Case Western Reserve Law Review. 2016;66(3):657-700.
14. Kallert TW, Katsakou C, Adamowski T, et al. Coerced hospital admission and symptom change—a prospective observational multi-centre study. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028191.
15. Danzer G, Wilkus-Stone A. The give and take of freedom: the role of involuntary hospitalization and treatment in recovery from mental illness. Bull Menninger Clin. 2015;79(3):255-280.
16. Roe D, Weishut DJ, Jaglom M, et al. Patients’ and staff members’ attitudes about the rights of hospitalized psychiatric patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):87-91.
17. Amidov T. Involuntary commitment is unnecessary and discriminatory. In: Berlatsky N, ed. Mental illness. Farmington Hills, MI: Greenhaven Press; 2016;140-145.
18. Monahan J, Hoge SK, Lidz C, et al. Coercion and commitment: understanding involuntary mental hospital admission. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1995;18(3):249-263.
19. Guest Pryal KR. Heller’s scapegoats. North Carolina Law Review. 2015;93(5):1439-1473.
20. Stone AA. Mental health and law: a system in transition. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office; 1975:75-176.
21. Katsakou C, Bowers L, Amos T, et al. Coercion and treatment satisfaction among involuntary patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(3):286-292.
22. Setkowski K, van der Post LF, Peen J, et al. Changing patient perspectives after compulsory admission and the risk of re-admission during 5 years of follow-up: the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry IX. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2016;62(6):578-588.
23. Stelfox HT, Gandhi TK, Orav EJ, et al. The relation of patient satisfaction with complaints against physicians and malpractice lawsuits. Am J Med. 2005;118(10):1126-1133.
24. Goldman A. Continued overreliance on involuntary commitment: the need for a less restrictive alternative. J Leg Med. 2015;36(2):233-251.
25. Fisher WH, Grisso T. Commentary: civil commitment statutes—40 years of circumvention. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2010;38(3):365-368.
26. Curley A, Agada E, Emechebe A, et al. Exploring and explaining involuntary care: the relationship between psychiatric admission status, gender and other demographic and clinical variables. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2016;47:53-59.
27. Muroff JR, Jackson JS, Mowbray CT, et al. The influence of gender, patient volume and time on clinical diagnostic decision making in psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2007;29(6):481-488.
28. Muroff JR, Edelsohn GA, Joe S, et al. The role of race in diagnostic and disposition decision making in a pediatric psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008;30(3):269-276.
29. Unick GJ, Kessell E, Woodard EK, et al. Factors affecting psychiatric inpatient hospitalization from a psychiatric emergency service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(6):618-625.
30. Ng XT, Kelly BD. Voluntary and involuntary care: three-year study of demographic and diagnostic admission statistics at an inner-city adult psychiatry unit. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2012;35(4):317-326.
31. Lo TT, Woo BK. The impact of unemployment on utilization of psychiatric emergency services. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33(3):e7-e8. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2010.10.010.
32. van der Post LFM, Peen J, Dekker JJ. A prediction model for the incidence of civil detention for crisis patients with psychiatric illnesses; the Amsterdam study of acute psychiatry VII. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(2):283-290.
33. Heilbrun K, NeMoyer A, King C, et al. Using third-party information in forensic mental health assessment: a critical review. Court Review. 2015;51(1):16-35.
34. Mass shootings at Virginia Tech, April 16, 2007 report of the Virginia Tech Review Panel presented to Timothy M. Kaine, Governor, Commonwealth of Virginia. http://cdm16064.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p266901coll4/id/904. Accessed February 2, 2017.
35. Segal SP, Laurie TA, Segal MJ. Factors in the use of coercive retention in civil commitment evaluations in psychiatric emergency services. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(4):514-520.
36. Lincoln A, Allen MH. The influence of collateral information on access to inpatient psychiatric services. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation. 2002;6:99-108.
37. Anderson JC. How I decided to sue you: misadventures in psychiatry. Reprinted in part from: Moody CE, Smith MT, Maedgen BJ. Litigation of psychiatric malpractice claims. Presented at: Medical Malpractice Conference; April 15, 1993; San Antonio, TX. http://www.texaslawfirm.com/Articles/How_I_Decided_to_Sue_You__Misadventrues_in_Psychiatry.pdf. Accessed December 27, 2016.
38. Jacobs v Grossmont Hospital, 108 Cal App 4th 69, 133 Cal Rptr 2d9 (2003).
39. Bingham v Cedars Sinai Health Systems, WL 2137442, Cal App 2 Dist (2004).
40. Ohio Revised Code §5122.34.
41. California Welfare & Institutions Code §5150(E).
42. Hashmi A, Shad M, Rhoades HM, et al. Involuntary detention: do psychiatrists clinically justify continuing involuntary hospitalization? Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):285-293.
43. Brayley J, Alston A, Rogers K. Legal criteria for involuntary mental health admission: clinician performance in recording grounds for decision. Med J Aust. 2015;203(8):334.
44. Perrigo TL, Williams KA. Implementation of an evidence based guideline for assessment and documentation of the civil commitment process. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(8):1033-1036.
45. Mor S, Rabinovich-Einy O. Relational malpractice. Seton Hall Law Rev. 2012;42(2):601-642.
46. Tate v Kaiser Foundation Hospitals, WL 176625, U.S. Dist. LEXIS 5891 (CD Cal 2014).
47. Ranieri V, Madigan K, Roche E, et al. Caregivers’ perceptions of coercion in psychiatric hospital admission. Psychiatry Res. 2015;22(3)8:380-385.
