User login
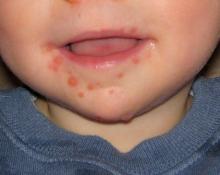
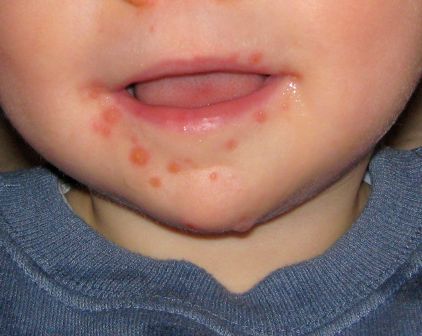
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has become a global challenge since its first description in 1957 in New Zealand and Canada. Clinicians readily recognize the characteristic syndrome in young children: fever associated with a papulovesicular rash affecting the palms or soles, or both, usually in spring, summer, or fall. In most cases the disease is self-limited, and brief. However, aseptic meningitis, brainstem encephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis or autonomic nervous system deregulation or cardiorespiratory failure may complicate the clinical course.
HFMD is caused by enterovirus A (formerly called human enterovirus A) which consists of 25 serotypes including multiple coxsackie A viruses, multiple enteroviruses, simian enteroviruses, and baboon enterovirus A13. The clinical spectrum spans from herpangina, characterized by fever and painful mouth ulcers most prominent in the posterior oral cavity (uvula, tonsils, soft plates, and anterior pharyngeal folds), to HFMD with papulovesicular rash on palms and soles with or without mouth ulcers/vesicles.1 In atypical cases, the rash may be maculopapular and may include the buttocks, knees or elbows.
In the United States, the predominant cause is coxsackie A16. However, coxsackie A6 appears to be emerging; often more than one HFMD causing virus is circulating concurrently and clinically indistinguishable. Globally, especially, in Asia, enterovirus 1 is a major cause of HFMD and more often associated with prominent central nervous system involvement. Disease can be sporadic or epidemic. An outbreak is usually defined as two or more cases within a defined geographic area; global epidemics as large as 1.5 million cases (Taiwan, 1998) have been reported, and outbreaks in China involving tens of thousands with multiple deaths have been reported.
In 2015, an outbreak of HFMD occurred during basic military training at Lackland Air Force Base, Bexar County, Texas, due to coxsackie A6.2 The illness was characterized by prodromal symptoms of fever and malaise followed by erosive stomatitis and a rash that began on the palms and soles. The rate of infection among trainees was 4.7% (50 of 1,054 persons).
The differential diagnosis includes aphthous ulcers and herpetic gingivostomatitis.3 Aphthous ulcers are seen more commonly in older children and adolescents, are often recurrent, are not seasonal, and are not associated with rash. Herpes simplex virus gingivostomatitis usually has a febrile prodrome, perioral lesions are frequent in addition to gum and tongue involvement, and gingival bleeding is common. HFMD usually has an incubation period of 3-5 days and fever, malaise, and myalgia prodrome followed by onset of oral and dermatologic manifestations in sequence. The skin rash has features that may overlap with varicella, erythema multiforme (EM) or drug eruption. Varicella usually involves the face before spreading to the extremities, and the lesions are characterized by umbilication and subsequent crusting. EM is characterized by target lesions and drug eruptions are morbilliform or maculopapular. The majority of cases of HFMD are diagnosed clinically; polymerase chain reaction testing is available and best performed on throat or vesicle specimens. Serologic testing for A16 and enterovirus 71 (IgM) is available. Infected patients shed virus for 2-4 weeks and virus is stable in the environment resulting in fecal-oral or oral-oral transmission.
Atypical features of HFMD include occurrence in the winter (outbreak in Alabama in 2011/2012) or an atypical distribution of rash involving the antecubital and popliteal fossae distribution of rash, or “eczema coxsackium” – the accentuation of rash in areas previously affected by atopic dermatitis. Additional features may include nail dystrophies that manifest as Beau lines (deep grooved lines that run from side to side on the fingernail or the toenail) and nail shedding.
A spectrum of neurologic complications has been observed, more frequently with EV71 and more frequently in Asia. The spectrum includes aseptic meningitis and brainstem encephalitis. Progressive cardiopulmonary failure also can be observed in severe cases. The hallmark of severe disease is often presentation with high fever, sweating, mottled skin, and tachycardia. Early signs of CNS involvement include myoclonic jerks, ataxia, and “wandering eyes.”3 Elevated white blood count and/or hyperglycemia may distinguish children with severe disease from benign disease. Anecdotal reports of response to treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone and intravenous immune globulin suggest that the neurologic disease may be an autoimmune phenomenon.
The clinician’s primary role is to accurately diagnose HFMD, provide supportive care for fever and dehydration, and identify those with early signs or laboratory features heralding a more severe course of disease.3 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends frequent hand washing after toileting and changing diapers, disinfecting surfaces such as toys, avoiding close contact with infected individuals or sharing of personal items for all affected patients. No antiviral treatment is available although improvement following early treatment with acyclovir has been reported anecdotally. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been used in severe cases in Asia with retrospective data analysis suggesting a potential for improvement when administered prior to cardiopulmonary arrest.1
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2014;81(9):537-43.
2. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report MMWR. 2016 Jul 8;65(26);678-80.
3. A Guide to clinical management and public health response for hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD).
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has become a global challenge since its first description in 1957 in New Zealand and Canada. Clinicians readily recognize the characteristic syndrome in young children: fever associated with a papulovesicular rash affecting the palms or soles, or both, usually in spring, summer, or fall. In most cases the disease is self-limited, and brief. However, aseptic meningitis, brainstem encephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis or autonomic nervous system deregulation or cardiorespiratory failure may complicate the clinical course.
HFMD is caused by enterovirus A (formerly called human enterovirus A) which consists of 25 serotypes including multiple coxsackie A viruses, multiple enteroviruses, simian enteroviruses, and baboon enterovirus A13. The clinical spectrum spans from herpangina, characterized by fever and painful mouth ulcers most prominent in the posterior oral cavity (uvula, tonsils, soft plates, and anterior pharyngeal folds), to HFMD with papulovesicular rash on palms and soles with or without mouth ulcers/vesicles.1 In atypical cases, the rash may be maculopapular and may include the buttocks, knees or elbows.
In the United States, the predominant cause is coxsackie A16. However, coxsackie A6 appears to be emerging; often more than one HFMD causing virus is circulating concurrently and clinically indistinguishable. Globally, especially, in Asia, enterovirus 1 is a major cause of HFMD and more often associated with prominent central nervous system involvement. Disease can be sporadic or epidemic. An outbreak is usually defined as two or more cases within a defined geographic area; global epidemics as large as 1.5 million cases (Taiwan, 1998) have been reported, and outbreaks in China involving tens of thousands with multiple deaths have been reported.
In 2015, an outbreak of HFMD occurred during basic military training at Lackland Air Force Base, Bexar County, Texas, due to coxsackie A6.2 The illness was characterized by prodromal symptoms of fever and malaise followed by erosive stomatitis and a rash that began on the palms and soles. The rate of infection among trainees was 4.7% (50 of 1,054 persons).
The differential diagnosis includes aphthous ulcers and herpetic gingivostomatitis.3 Aphthous ulcers are seen more commonly in older children and adolescents, are often recurrent, are not seasonal, and are not associated with rash. Herpes simplex virus gingivostomatitis usually has a febrile prodrome, perioral lesions are frequent in addition to gum and tongue involvement, and gingival bleeding is common. HFMD usually has an incubation period of 3-5 days and fever, malaise, and myalgia prodrome followed by onset of oral and dermatologic manifestations in sequence. The skin rash has features that may overlap with varicella, erythema multiforme (EM) or drug eruption. Varicella usually involves the face before spreading to the extremities, and the lesions are characterized by umbilication and subsequent crusting. EM is characterized by target lesions and drug eruptions are morbilliform or maculopapular. The majority of cases of HFMD are diagnosed clinically; polymerase chain reaction testing is available and best performed on throat or vesicle specimens. Serologic testing for A16 and enterovirus 71 (IgM) is available. Infected patients shed virus for 2-4 weeks and virus is stable in the environment resulting in fecal-oral or oral-oral transmission.
Atypical features of HFMD include occurrence in the winter (outbreak in Alabama in 2011/2012) or an atypical distribution of rash involving the antecubital and popliteal fossae distribution of rash, or “eczema coxsackium” – the accentuation of rash in areas previously affected by atopic dermatitis. Additional features may include nail dystrophies that manifest as Beau lines (deep grooved lines that run from side to side on the fingernail or the toenail) and nail shedding.
A spectrum of neurologic complications has been observed, more frequently with EV71 and more frequently in Asia. The spectrum includes aseptic meningitis and brainstem encephalitis. Progressive cardiopulmonary failure also can be observed in severe cases. The hallmark of severe disease is often presentation with high fever, sweating, mottled skin, and tachycardia. Early signs of CNS involvement include myoclonic jerks, ataxia, and “wandering eyes.”3 Elevated white blood count and/or hyperglycemia may distinguish children with severe disease from benign disease. Anecdotal reports of response to treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone and intravenous immune globulin suggest that the neurologic disease may be an autoimmune phenomenon.
The clinician’s primary role is to accurately diagnose HFMD, provide supportive care for fever and dehydration, and identify those with early signs or laboratory features heralding a more severe course of disease.3 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends frequent hand washing after toileting and changing diapers, disinfecting surfaces such as toys, avoiding close contact with infected individuals or sharing of personal items for all affected patients. No antiviral treatment is available although improvement following early treatment with acyclovir has been reported anecdotally. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been used in severe cases in Asia with retrospective data analysis suggesting a potential for improvement when administered prior to cardiopulmonary arrest.1
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2014;81(9):537-43.
2. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report MMWR. 2016 Jul 8;65(26);678-80.
3. A Guide to clinical management and public health response for hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD).
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has become a global challenge since its first description in 1957 in New Zealand and Canada. Clinicians readily recognize the characteristic syndrome in young children: fever associated with a papulovesicular rash affecting the palms or soles, or both, usually in spring, summer, or fall. In most cases the disease is self-limited, and brief. However, aseptic meningitis, brainstem encephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis or autonomic nervous system deregulation or cardiorespiratory failure may complicate the clinical course.
HFMD is caused by enterovirus A (formerly called human enterovirus A) which consists of 25 serotypes including multiple coxsackie A viruses, multiple enteroviruses, simian enteroviruses, and baboon enterovirus A13. The clinical spectrum spans from herpangina, characterized by fever and painful mouth ulcers most prominent in the posterior oral cavity (uvula, tonsils, soft plates, and anterior pharyngeal folds), to HFMD with papulovesicular rash on palms and soles with or without mouth ulcers/vesicles.1 In atypical cases, the rash may be maculopapular and may include the buttocks, knees or elbows.
In the United States, the predominant cause is coxsackie A16. However, coxsackie A6 appears to be emerging; often more than one HFMD causing virus is circulating concurrently and clinically indistinguishable. Globally, especially, in Asia, enterovirus 1 is a major cause of HFMD and more often associated with prominent central nervous system involvement. Disease can be sporadic or epidemic. An outbreak is usually defined as two or more cases within a defined geographic area; global epidemics as large as 1.5 million cases (Taiwan, 1998) have been reported, and outbreaks in China involving tens of thousands with multiple deaths have been reported.
In 2015, an outbreak of HFMD occurred during basic military training at Lackland Air Force Base, Bexar County, Texas, due to coxsackie A6.2 The illness was characterized by prodromal symptoms of fever and malaise followed by erosive stomatitis and a rash that began on the palms and soles. The rate of infection among trainees was 4.7% (50 of 1,054 persons).
The differential diagnosis includes aphthous ulcers and herpetic gingivostomatitis.3 Aphthous ulcers are seen more commonly in older children and adolescents, are often recurrent, are not seasonal, and are not associated with rash. Herpes simplex virus gingivostomatitis usually has a febrile prodrome, perioral lesions are frequent in addition to gum and tongue involvement, and gingival bleeding is common. HFMD usually has an incubation period of 3-5 days and fever, malaise, and myalgia prodrome followed by onset of oral and dermatologic manifestations in sequence. The skin rash has features that may overlap with varicella, erythema multiforme (EM) or drug eruption. Varicella usually involves the face before spreading to the extremities, and the lesions are characterized by umbilication and subsequent crusting. EM is characterized by target lesions and drug eruptions are morbilliform or maculopapular. The majority of cases of HFMD are diagnosed clinically; polymerase chain reaction testing is available and best performed on throat or vesicle specimens. Serologic testing for A16 and enterovirus 71 (IgM) is available. Infected patients shed virus for 2-4 weeks and virus is stable in the environment resulting in fecal-oral or oral-oral transmission.
Atypical features of HFMD include occurrence in the winter (outbreak in Alabama in 2011/2012) or an atypical distribution of rash involving the antecubital and popliteal fossae distribution of rash, or “eczema coxsackium” – the accentuation of rash in areas previously affected by atopic dermatitis. Additional features may include nail dystrophies that manifest as Beau lines (deep grooved lines that run from side to side on the fingernail or the toenail) and nail shedding.
A spectrum of neurologic complications has been observed, more frequently with EV71 and more frequently in Asia. The spectrum includes aseptic meningitis and brainstem encephalitis. Progressive cardiopulmonary failure also can be observed in severe cases. The hallmark of severe disease is often presentation with high fever, sweating, mottled skin, and tachycardia. Early signs of CNS involvement include myoclonic jerks, ataxia, and “wandering eyes.”3 Elevated white blood count and/or hyperglycemia may distinguish children with severe disease from benign disease. Anecdotal reports of response to treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone and intravenous immune globulin suggest that the neurologic disease may be an autoimmune phenomenon.
The clinician’s primary role is to accurately diagnose HFMD, provide supportive care for fever and dehydration, and identify those with early signs or laboratory features heralding a more severe course of disease.3 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends frequent hand washing after toileting and changing diapers, disinfecting surfaces such as toys, avoiding close contact with infected individuals or sharing of personal items for all affected patients. No antiviral treatment is available although improvement following early treatment with acyclovir has been reported anecdotally. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been used in severe cases in Asia with retrospective data analysis suggesting a potential for improvement when administered prior to cardiopulmonary arrest.1
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University. Dr. Pelton said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2014;81(9):537-43.
2. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report MMWR. 2016 Jul 8;65(26);678-80.
3. A Guide to clinical management and public health response for hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD).