User login
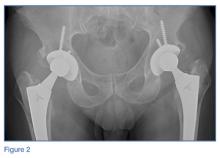
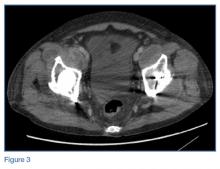
Laboratory studies revealed leukocytosis with a left shift. Chest radiographs were negative for pneumonia. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the lumbar spine was obtained to evaluate for diskitis osteomyelitis. A radiograph of the pelvis was also obtained to evaluate the patient’s THAs, and a computed tomography scan (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast was obtained for further evaluation. Representative CT, radiographic, and MRI images are shown at left (Figures 1-3).
What is the suspected diagnosis?
Answer
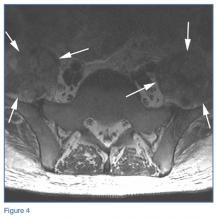
The MRI of the lumbar spine demonstrated no evidence of diskitis osteomyelitis. However, T2-weighted axial images showed enlarged heterogeneous bilateral psoas muscles with bright signal, indicating the presence of fluid (white arrows, Figure 4).
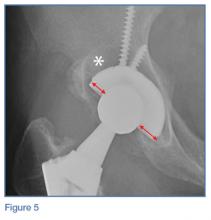
On the pelvic radiographs, both femoral heads appeared off-center within the acetabular cups (red arrows, Figure 5). This eccentric positioning indicated wear of the polyethylene in the THAs that normally occupies the space between the acetabular cup and the femoral head. In addition, focal lucency in the right acetabulum indicated breakdown of the bone, a condition referred to as osteolysis (white asterisk, Figure 5).
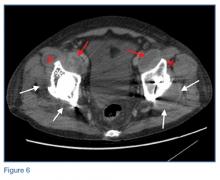
An abdominopelvic CT scan with contrast was performed and confirmed the findings of polyethylene wear and osteolysis. The CT scan also demonstrated large bilateral hip joint effusions (white arrows, Figure 6), decompressed along distended bilateral iliopsoas bursae (red asterisks, Figure 6), and communicating with the bilateral psoas muscle collections (red arrows, Figure 6).
Osteolysis With Iliopsoas Bursitis
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs lined by synovial tissue located throughout the body to reduce friction at sites of movement between muscles, bones, and tendons. Bursitis develops when these sacs become inflamed and/or infected and fill with fluid. The iliopsoas bursa lies between the anterior capsule of the hip and the psoas tendon, iliacus tendon, and muscle fibers.1,2 This bursa frequently communicates with the hip joint.3,4 Iliopsoas bursal distension has been reported following THA in the setting of polyethylene wear,5 and aseptic bursitis is a commonly seen incidental finding at the time of revision surgery.6
In this patient, long-standing polyethylene-induced synovitis had markedly expanded the hip joints and iliopsoas bursae, eventually resulting in superinfection, which accounted for the patient’s symptoms.
Treatment
Based on the imaging findings, interventional radiology services were contacted. The interventional radiologist drained the bilateral psoas abscesses. Cultures of the fluid were positive for both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA). The patient was admitted to the hospital for treatment of MRSA and MSSA with intravenous antibiotic therapy. He recovered from the infection and was discharged on hospital day 2, with instructions to follow up with an orthopedic surgeon to discuss eventual revision of the bilateral THAs.
1. Chandler SB. The iliopsoas bursa in man. Anatom Record. 1934;58(3),235-240. doi:10.1002/ar.1090580304.
2. Tatu L, Parratte B, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Descriptive anatomy of the femoral portion of the iliopsoas muscle. Anatomical basis of anterior snapping of the hip. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23(6):371-374.
3. Meaney JF, Cassar-Pullicino VN, Etherington R, Ritchie DA, McCall IW, Whitehouse GH. Ilio-psoas bursa enlargement. Clin Radiol. 1992;45(3):161-168.
4. Warren R, Kaye JJ, Salvati EA. Arthrographic demonstration of an enlarged iliopsoas bursa complicating osteoarthritis of the hip. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(3):413-415.
5. Cheung YM, Gupte CM, Beverly MJ. Iliopsoas bursitis following total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(10):720-723. Epub 2004 Oct 23. doi:10.1007/s00402-004-0751-9.
6. Howie DW, Cain CM, Cornish BL. Pseudo-abscess of the psoas bursa in failed double-cup arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:29-32.
Laboratory studies revealed leukocytosis with a left shift. Chest radiographs were negative for pneumonia. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the lumbar spine was obtained to evaluate for diskitis osteomyelitis. A radiograph of the pelvis was also obtained to evaluate the patient’s THAs, and a computed tomography scan (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast was obtained for further evaluation. Representative CT, radiographic, and MRI images are shown at left (Figures 1-3).
What is the suspected diagnosis?
Answer
The MRI of the lumbar spine demonstrated no evidence of diskitis osteomyelitis. However, T2-weighted axial images showed enlarged heterogeneous bilateral psoas muscles with bright signal, indicating the presence of fluid (white arrows, Figure 4).
On the pelvic radiographs, both femoral heads appeared off-center within the acetabular cups (red arrows, Figure 5). This eccentric positioning indicated wear of the polyethylene in the THAs that normally occupies the space between the acetabular cup and the femoral head. In addition, focal lucency in the right acetabulum indicated breakdown of the bone, a condition referred to as osteolysis (white asterisk, Figure 5).
An abdominopelvic CT scan with contrast was performed and confirmed the findings of polyethylene wear and osteolysis. The CT scan also demonstrated large bilateral hip joint effusions (white arrows, Figure 6), decompressed along distended bilateral iliopsoas bursae (red asterisks, Figure 6), and communicating with the bilateral psoas muscle collections (red arrows, Figure 6).
Osteolysis With Iliopsoas Bursitis
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs lined by synovial tissue located throughout the body to reduce friction at sites of movement between muscles, bones, and tendons. Bursitis develops when these sacs become inflamed and/or infected and fill with fluid. The iliopsoas bursa lies between the anterior capsule of the hip and the psoas tendon, iliacus tendon, and muscle fibers.1,2 This bursa frequently communicates with the hip joint.3,4 Iliopsoas bursal distension has been reported following THA in the setting of polyethylene wear,5 and aseptic bursitis is a commonly seen incidental finding at the time of revision surgery.6
In this patient, long-standing polyethylene-induced synovitis had markedly expanded the hip joints and iliopsoas bursae, eventually resulting in superinfection, which accounted for the patient’s symptoms.
Treatment
Based on the imaging findings, interventional radiology services were contacted. The interventional radiologist drained the bilateral psoas abscesses. Cultures of the fluid were positive for both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA). The patient was admitted to the hospital for treatment of MRSA and MSSA with intravenous antibiotic therapy. He recovered from the infection and was discharged on hospital day 2, with instructions to follow up with an orthopedic surgeon to discuss eventual revision of the bilateral THAs.
Laboratory studies revealed leukocytosis with a left shift. Chest radiographs were negative for pneumonia. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the lumbar spine was obtained to evaluate for diskitis osteomyelitis. A radiograph of the pelvis was also obtained to evaluate the patient’s THAs, and a computed tomography scan (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast was obtained for further evaluation. Representative CT, radiographic, and MRI images are shown at left (Figures 1-3).
What is the suspected diagnosis?
Answer
The MRI of the lumbar spine demonstrated no evidence of diskitis osteomyelitis. However, T2-weighted axial images showed enlarged heterogeneous bilateral psoas muscles with bright signal, indicating the presence of fluid (white arrows, Figure 4).
On the pelvic radiographs, both femoral heads appeared off-center within the acetabular cups (red arrows, Figure 5). This eccentric positioning indicated wear of the polyethylene in the THAs that normally occupies the space between the acetabular cup and the femoral head. In addition, focal lucency in the right acetabulum indicated breakdown of the bone, a condition referred to as osteolysis (white asterisk, Figure 5).
An abdominopelvic CT scan with contrast was performed and confirmed the findings of polyethylene wear and osteolysis. The CT scan also demonstrated large bilateral hip joint effusions (white arrows, Figure 6), decompressed along distended bilateral iliopsoas bursae (red asterisks, Figure 6), and communicating with the bilateral psoas muscle collections (red arrows, Figure 6).
Osteolysis With Iliopsoas Bursitis
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs lined by synovial tissue located throughout the body to reduce friction at sites of movement between muscles, bones, and tendons. Bursitis develops when these sacs become inflamed and/or infected and fill with fluid. The iliopsoas bursa lies between the anterior capsule of the hip and the psoas tendon, iliacus tendon, and muscle fibers.1,2 This bursa frequently communicates with the hip joint.3,4 Iliopsoas bursal distension has been reported following THA in the setting of polyethylene wear,5 and aseptic bursitis is a commonly seen incidental finding at the time of revision surgery.6
In this patient, long-standing polyethylene-induced synovitis had markedly expanded the hip joints and iliopsoas bursae, eventually resulting in superinfection, which accounted for the patient’s symptoms.
Treatment
Based on the imaging findings, interventional radiology services were contacted. The interventional radiologist drained the bilateral psoas abscesses. Cultures of the fluid were positive for both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA). The patient was admitted to the hospital for treatment of MRSA and MSSA with intravenous antibiotic therapy. He recovered from the infection and was discharged on hospital day 2, with instructions to follow up with an orthopedic surgeon to discuss eventual revision of the bilateral THAs.
1. Chandler SB. The iliopsoas bursa in man. Anatom Record. 1934;58(3),235-240. doi:10.1002/ar.1090580304.
2. Tatu L, Parratte B, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Descriptive anatomy of the femoral portion of the iliopsoas muscle. Anatomical basis of anterior snapping of the hip. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23(6):371-374.
3. Meaney JF, Cassar-Pullicino VN, Etherington R, Ritchie DA, McCall IW, Whitehouse GH. Ilio-psoas bursa enlargement. Clin Radiol. 1992;45(3):161-168.
4. Warren R, Kaye JJ, Salvati EA. Arthrographic demonstration of an enlarged iliopsoas bursa complicating osteoarthritis of the hip. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(3):413-415.
5. Cheung YM, Gupte CM, Beverly MJ. Iliopsoas bursitis following total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(10):720-723. Epub 2004 Oct 23. doi:10.1007/s00402-004-0751-9.
6. Howie DW, Cain CM, Cornish BL. Pseudo-abscess of the psoas bursa in failed double-cup arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:29-32.
1. Chandler SB. The iliopsoas bursa in man. Anatom Record. 1934;58(3),235-240. doi:10.1002/ar.1090580304.
2. Tatu L, Parratte B, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Descriptive anatomy of the femoral portion of the iliopsoas muscle. Anatomical basis of anterior snapping of the hip. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23(6):371-374.
3. Meaney JF, Cassar-Pullicino VN, Etherington R, Ritchie DA, McCall IW, Whitehouse GH. Ilio-psoas bursa enlargement. Clin Radiol. 1992;45(3):161-168.
4. Warren R, Kaye JJ, Salvati EA. Arthrographic demonstration of an enlarged iliopsoas bursa complicating osteoarthritis of the hip. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(3):413-415.
5. Cheung YM, Gupte CM, Beverly MJ. Iliopsoas bursitis following total hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(10):720-723. Epub 2004 Oct 23. doi:10.1007/s00402-004-0751-9.
6. Howie DW, Cain CM, Cornish BL. Pseudo-abscess of the psoas bursa in failed double-cup arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:29-32.