User login
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
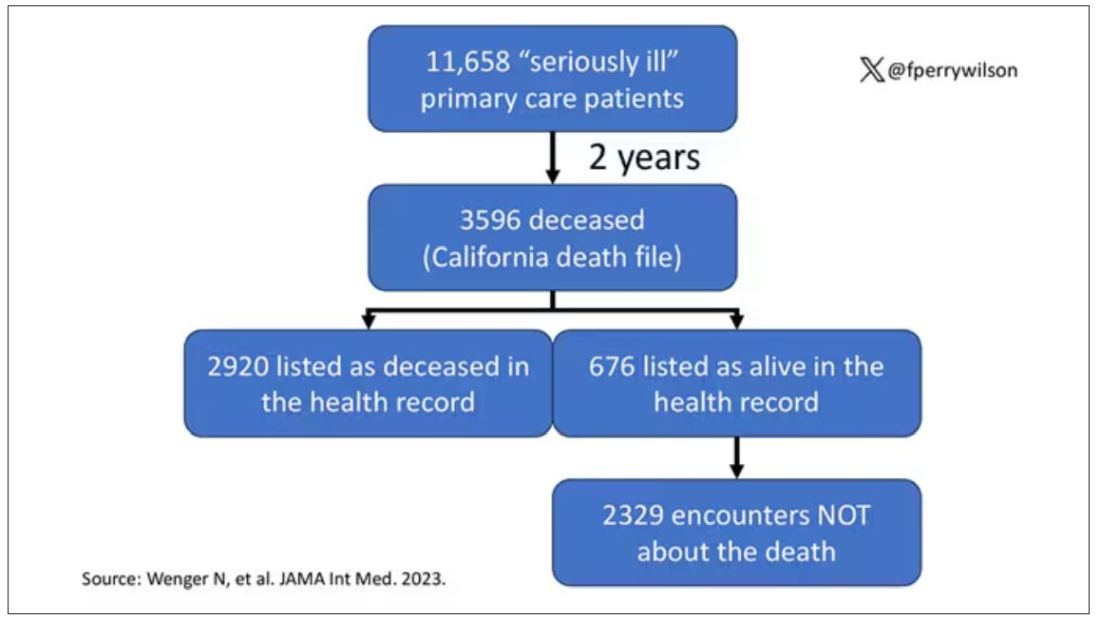
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.
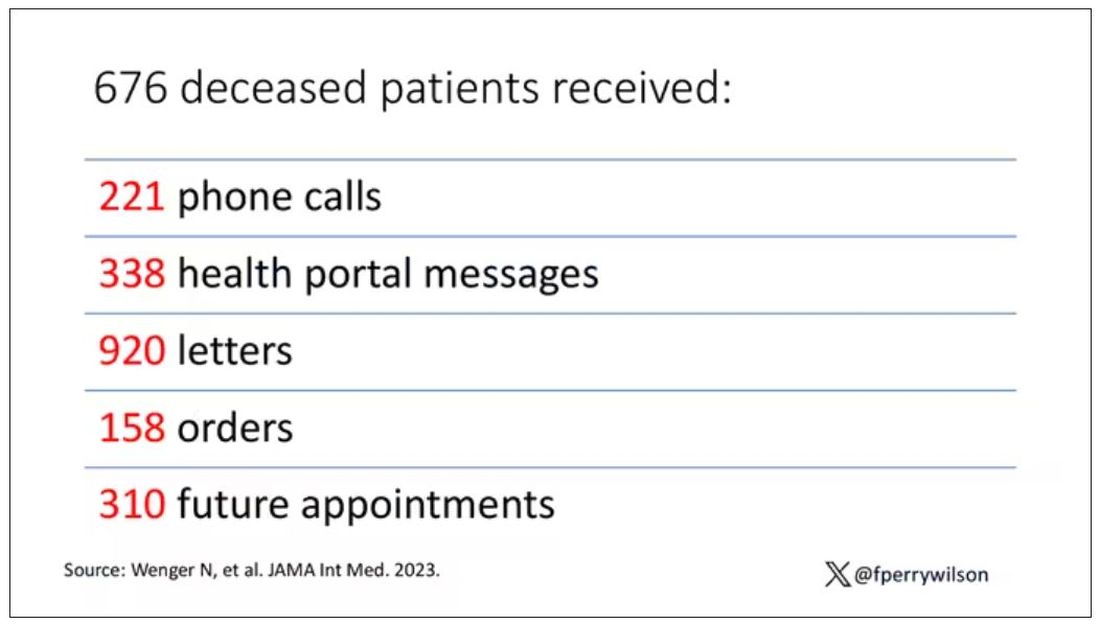
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Much of my research focuses on what is known as clinical decision support — prompts and messages to providers to help them make good decisions for their patients. I know that these things can be annoying, which is exactly why I study them — to figure out which ones actually help.
When I got started on this about 10 years ago, we were learning a lot about how best to message providers about their patients. My team had developed a simple alert for acute kidney injury (AKI). We knew that providers often missed the diagnosis, so maybe letting them know would improve patient outcomes.
As we tested the alert, we got feedback, and I have kept an email from an ICU doctor from those early days. It read:
Dear Dr. Wilson: Thank you for the automated alert informing me that my patient had AKI. Regrettably, the alert fired about an hour after the patient had died. I feel that the information is less than actionable at this time.
Our early system had neglected to add a conditional flag ensuring that the patient was still alive at the time it sent the alert message. A small oversight, but one that had very large implications. Future studies would show that “false positive” alerts like this seriously degrade physician confidence in the system. And why wouldn’t they?
Not knowing the vital status of a patient can have major consequences.
Health systems send messages to their patients all the time: reminders of appointments, reminders for preventive care, reminders for vaccinations, and so on.
But what if the patient being reminded has died? It’s a waste of resources, of course, but more than that, it can be painful for their families and reflects poorly on the health care system. Of all the people who should know whether someone is alive or dead, shouldn’t their doctor be at the top of the list?
A new study in JAMA Internal Medicine quantifies this very phenomenon.
Researchers examined 11,658 primary care patients in their health system who met the criteria of being “seriously ill” and followed them for 2 years. During that period of time, 25% were recorded as deceased in the electronic health record. But 30.8% had died. That left 676 patients who had died, but were not known to have died, left in the system.
And those 676 were not left to rest in peace. They received 221 telephone and 338 health portal messages not related to death, and 920 letters reminding them about unmet primary care metrics like flu shots and cancer screening. Orders were entered into the health record for things like vaccines and routine screenings for 158 patients, and 310 future appointments — destined to be no-shows — were still on the books. One can only imagine the frustration of families checking their mail and finding yet another letter reminding their deceased loved one to get a mammogram.
How did the researchers figure out who had died? It turns out it’s not that hard. California keeps a record of all deaths in the state; they simply had to search it. Like all state death records, they tend to lag a bit so it’s not clinically terribly useful, but it works. California and most other states also have a very accurate and up-to-date death file which can only be used by law enforcement to investigate criminal activity and fraud; health care is left in the lurch.
Nationwide, there is the real-time fact of death service, supported by the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems. This allows employers to verify, in real time, whether the person applying for a job is alive. Healthcare systems are not allowed to use it.
Let’s also remember that very few people die in this country without some health care agency knowing about it and recording it. But sharing of medical information is so poor in the United States that your patient could die in a hospital one city away from you and you might not find out until you’re calling them to see why they missed a scheduled follow-up appointment.
These events — the embarrassing lack of knowledge about the very vital status of our patients — highlight a huge problem with health care in our country. The fragmented health care system is terrible at data sharing, in part because of poor protocols, in part because of unfounded concerns about patient privacy, and in part because of a tendency to hoard data that might be valuable in the future. It has to stop. We need to know how our patients are doing even when they are not sitting in front of us. When it comes to life and death, the knowledge is out there; we just can’t access it. Seems like a pretty easy fix.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .