User login
Recurrent Cutaneous Exophiala Phaeohyphomycosis in an Immunosuppressed Patient
To the Editor:
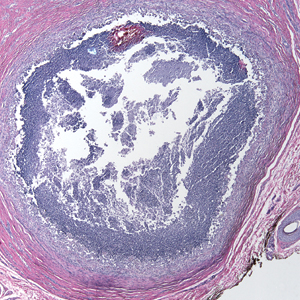
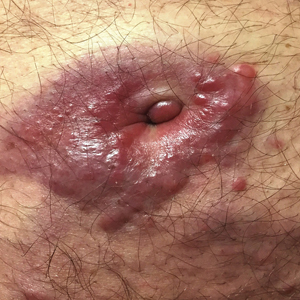
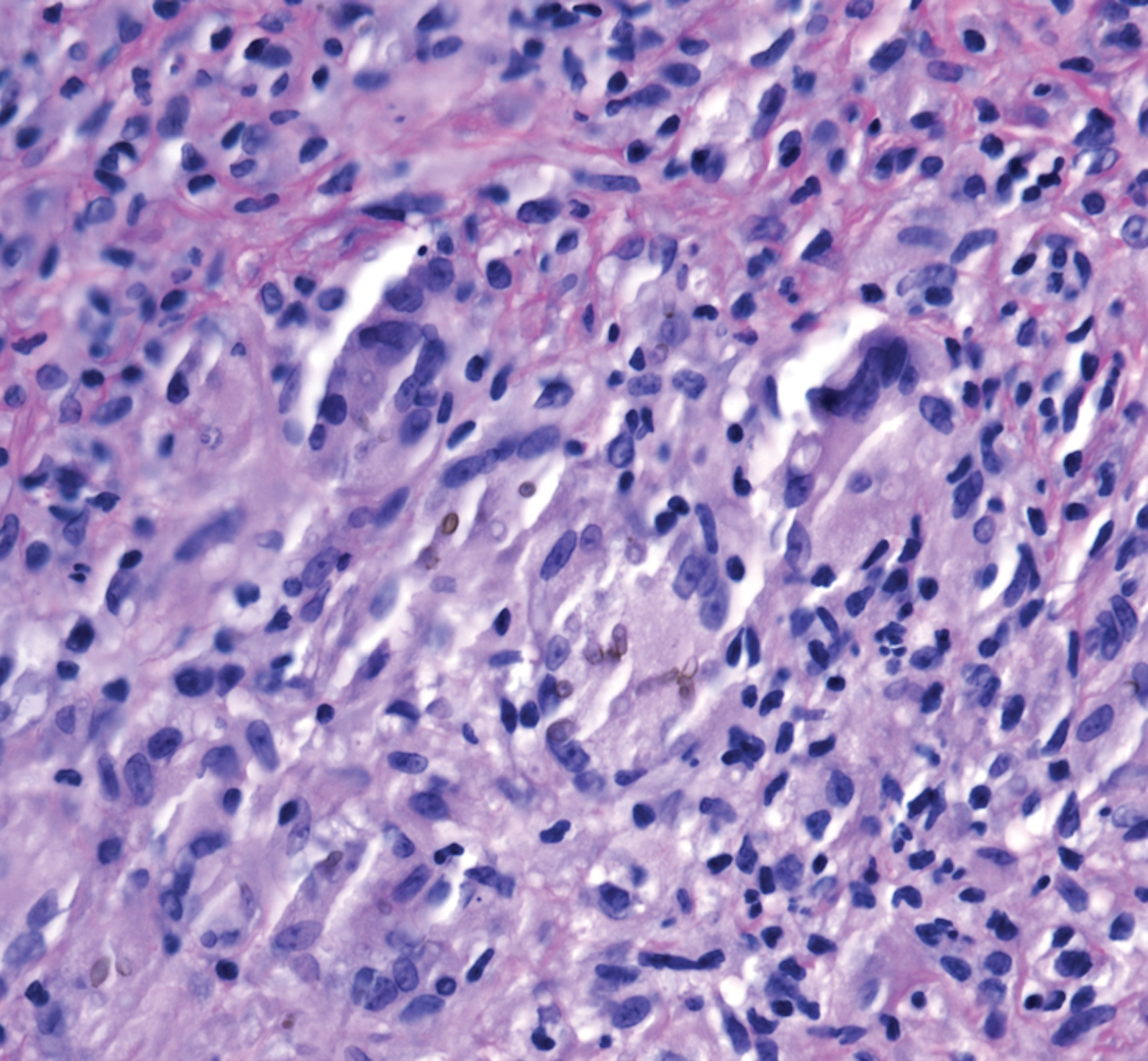
A 73-year-old man presented with a 2.5-cm, recurrent, fluctuant, multiloculated nodule on the left forearm. The lesion was nontender with occasional chalky, white to yellow discharge from multiple sinus tracts. He was otherwise well appearing without signs of systemic infection. He reported similar lesions in slightly different anatomic locations on the left forearm both 7 and 4 years prior to the current presentation. In both instances, the nodules were excised at an outside hospital without any additional treatment. Histopathology of the excised tissue from both prior occasions demonstrated brown septate hyphae surrounded by suppurative and granulomatous inflammation consistent with dematiaceous fungal infection of the dermis (Figures 1 and 2); the organisms were highlighted with periodic acid–Schiff stain.

The patient’s medical history was notable for advanced heart failure with an ejection fraction of 25% and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. He received an orthotopic kidney transplant 17 years prior to the current presentation. Medications included tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. He denied any trauma or notable exposures to vegetation, and his travel history was unremarkable. A review of systems was negative.
At the current presentation, a sterile fungal culture was performed and found positive for Exophiala species, while bacterial and mycobacterial cultures were negative. A diagnosis of phaeohyphomycosis was made, and he was scheduled for re-excision. Out of concern for interactions with his immunosuppressive regimen, he chose to forgo any systemic antifungal therapy. He died from hospital-acquired pneumonia and volume overload unresponsive to diuretics or dialysis.
Phaeohyphomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by several genera of dematiaceous fungi that are characterized by the presence of melaninlike cell wall pigments thought to locally hinder immune clearance by scavenging phagocyte-derived free radicals. These fungi are ubiquitous in soil and vegetation and usually penetrate the skin at sites of minor trauma.1 Phaeohyphomycosis typically affects immunosuppressed hosts, and its incidence among organ transplant recipients currently is 9%.2 The incidence in this population has been rising, however, as recent advances in immunosuppressive therapies have increased posttransplant survival.3
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis can present with nodules, cysts, tumors, and/or verrucous plaques, and the diagnosis almost always requires clinicopathologic correlation.3 Rapid diagnosis can be made when septate brown hyphae and/or yeast forms are observed on hematoxylin and eosin stain. Rarely, patients present with disseminated infection, characterized by fungemia; central nervous system involvement; and/or infection of multiple deep structures including the eyes, lungs, bones, and sinuses.4 The risk for dissemination from the skin likely is related to the culprit organism’s genus; Lomentospora, Cladophialophora, and Verruconis often are associated with dissemination, while Alternaria, Exophiala, and Fonsecaea typically remain confined to the skin and subcutis.5 Due to this difference and its potential to impact management, obtaining a tissue fungal culture is advisable when phaeohyphomycosis is suspected.
There is no standard treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. Regimens typically consist of excision and prolonged courses of azole therapy, though excision alone with close follow-up may be a reasonable alternative.6 The latter is a particularly important consideration when managing phaeohyphomycosis in organ transplant recipients, as azoles are known cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors that can affect serum levels of common immunosuppressive medications including calcineurin inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors.3 Local recurrence is common regardless of whether azole therapy is pursued,7 and dissemination of localized Exophiala infections is exceedingly rare.8 There is a strong argument to be made for our patient’s decision to forgo antifungal therapy.
This case underscores the difficulty inherent to eradicating local subcutaneous Exophiala phaeohyphomycosis while providing reassurance that with treatment, the risk of life-threatening complications is low. Obtaining tissue for both hematoxylin and eosin stain and sterile culture is crucial to ensuring prompt diagnosis and tailoring the optimal treatment and surveillance strategy to the culprit organism. To avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment, it is important for clinicians to consider phaeohyphomycosis in the differential diagnosis for recurrent nodulocystic lesions in immunosuppressed patients and to recognize that presentations may span many years.
- Bhardwaj S, Capoor MR, Kolte S, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala jeanselmei: an emerging pathogen in India—case report and review. Mycopathologia. 2016;181:279-284.
- Isa-Isa R, Garcia C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Tirico MCCP, Neto CF, Cruz LL, et al. Clinical spectrum of phaeohyphomycosis in solid organ transplant recipients. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:465-469.
- Revankar SG, Patterson JE, Sutton DA, et al. Disseminated phaeohyphomycosis: review of an emerging mycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:467-476.
- Revankar SG, Baddley JW, Chen SC-A, et al. A mycoses study group international prospective study of phaeohyphomycosis: an analysis of 99 proven/probable cases. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx200.
- Oberlin KE, Nichols AJ, Rosa R, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala infections in solid organ transplant recipients: case report and literature review [published online June 26, 2017]. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19. doi:10.1111/tid.12723.
- Shirbur S, Telkar S, Goudar B, et al. Recurrent phaeohyphomycosis: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:2015-2016.
- Li D-M, Li R-Y, de Hoog GS, et al. Fatal Exophiala infections in China, with a report of seven cases. Mycoses. 2011;54:E136-E142.
To the Editor:
A 73-year-old man presented with a 2.5-cm, recurrent, fluctuant, multiloculated nodule on the left forearm. The lesion was nontender with occasional chalky, white to yellow discharge from multiple sinus tracts. He was otherwise well appearing without signs of systemic infection. He reported similar lesions in slightly different anatomic locations on the left forearm both 7 and 4 years prior to the current presentation. In both instances, the nodules were excised at an outside hospital without any additional treatment. Histopathology of the excised tissue from both prior occasions demonstrated brown septate hyphae surrounded by suppurative and granulomatous inflammation consistent with dematiaceous fungal infection of the dermis (Figures 1 and 2); the organisms were highlighted with periodic acid–Schiff stain.


The patient’s medical history was notable for advanced heart failure with an ejection fraction of 25% and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. He received an orthotopic kidney transplant 17 years prior to the current presentation. Medications included tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. He denied any trauma or notable exposures to vegetation, and his travel history was unremarkable. A review of systems was negative.
At the current presentation, a sterile fungal culture was performed and found positive for Exophiala species, while bacterial and mycobacterial cultures were negative. A diagnosis of phaeohyphomycosis was made, and he was scheduled for re-excision. Out of concern for interactions with his immunosuppressive regimen, he chose to forgo any systemic antifungal therapy. He died from hospital-acquired pneumonia and volume overload unresponsive to diuretics or dialysis.
Phaeohyphomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by several genera of dematiaceous fungi that are characterized by the presence of melaninlike cell wall pigments thought to locally hinder immune clearance by scavenging phagocyte-derived free radicals. These fungi are ubiquitous in soil and vegetation and usually penetrate the skin at sites of minor trauma.1 Phaeohyphomycosis typically affects immunosuppressed hosts, and its incidence among organ transplant recipients currently is 9%.2 The incidence in this population has been rising, however, as recent advances in immunosuppressive therapies have increased posttransplant survival.3
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis can present with nodules, cysts, tumors, and/or verrucous plaques, and the diagnosis almost always requires clinicopathologic correlation.3 Rapid diagnosis can be made when septate brown hyphae and/or yeast forms are observed on hematoxylin and eosin stain. Rarely, patients present with disseminated infection, characterized by fungemia; central nervous system involvement; and/or infection of multiple deep structures including the eyes, lungs, bones, and sinuses.4 The risk for dissemination from the skin likely is related to the culprit organism’s genus; Lomentospora, Cladophialophora, and Verruconis often are associated with dissemination, while Alternaria, Exophiala, and Fonsecaea typically remain confined to the skin and subcutis.5 Due to this difference and its potential to impact management, obtaining a tissue fungal culture is advisable when phaeohyphomycosis is suspected.
There is no standard treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. Regimens typically consist of excision and prolonged courses of azole therapy, though excision alone with close follow-up may be a reasonable alternative.6 The latter is a particularly important consideration when managing phaeohyphomycosis in organ transplant recipients, as azoles are known cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors that can affect serum levels of common immunosuppressive medications including calcineurin inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors.3 Local recurrence is common regardless of whether azole therapy is pursued,7 and dissemination of localized Exophiala infections is exceedingly rare.8 There is a strong argument to be made for our patient’s decision to forgo antifungal therapy.
This case underscores the difficulty inherent to eradicating local subcutaneous Exophiala phaeohyphomycosis while providing reassurance that with treatment, the risk of life-threatening complications is low. Obtaining tissue for both hematoxylin and eosin stain and sterile culture is crucial to ensuring prompt diagnosis and tailoring the optimal treatment and surveillance strategy to the culprit organism. To avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment, it is important for clinicians to consider phaeohyphomycosis in the differential diagnosis for recurrent nodulocystic lesions in immunosuppressed patients and to recognize that presentations may span many years.
To the Editor:
A 73-year-old man presented with a 2.5-cm, recurrent, fluctuant, multiloculated nodule on the left forearm. The lesion was nontender with occasional chalky, white to yellow discharge from multiple sinus tracts. He was otherwise well appearing without signs of systemic infection. He reported similar lesions in slightly different anatomic locations on the left forearm both 7 and 4 years prior to the current presentation. In both instances, the nodules were excised at an outside hospital without any additional treatment. Histopathology of the excised tissue from both prior occasions demonstrated brown septate hyphae surrounded by suppurative and granulomatous inflammation consistent with dematiaceous fungal infection of the dermis (Figures 1 and 2); the organisms were highlighted with periodic acid–Schiff stain.


The patient’s medical history was notable for advanced heart failure with an ejection fraction of 25% and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. He received an orthotopic kidney transplant 17 years prior to the current presentation. Medications included tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. He denied any trauma or notable exposures to vegetation, and his travel history was unremarkable. A review of systems was negative.
At the current presentation, a sterile fungal culture was performed and found positive for Exophiala species, while bacterial and mycobacterial cultures were negative. A diagnosis of phaeohyphomycosis was made, and he was scheduled for re-excision. Out of concern for interactions with his immunosuppressive regimen, he chose to forgo any systemic antifungal therapy. He died from hospital-acquired pneumonia and volume overload unresponsive to diuretics or dialysis.
Phaeohyphomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by several genera of dematiaceous fungi that are characterized by the presence of melaninlike cell wall pigments thought to locally hinder immune clearance by scavenging phagocyte-derived free radicals. These fungi are ubiquitous in soil and vegetation and usually penetrate the skin at sites of minor trauma.1 Phaeohyphomycosis typically affects immunosuppressed hosts, and its incidence among organ transplant recipients currently is 9%.2 The incidence in this population has been rising, however, as recent advances in immunosuppressive therapies have increased posttransplant survival.3
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis can present with nodules, cysts, tumors, and/or verrucous plaques, and the diagnosis almost always requires clinicopathologic correlation.3 Rapid diagnosis can be made when septate brown hyphae and/or yeast forms are observed on hematoxylin and eosin stain. Rarely, patients present with disseminated infection, characterized by fungemia; central nervous system involvement; and/or infection of multiple deep structures including the eyes, lungs, bones, and sinuses.4 The risk for dissemination from the skin likely is related to the culprit organism’s genus; Lomentospora, Cladophialophora, and Verruconis often are associated with dissemination, while Alternaria, Exophiala, and Fonsecaea typically remain confined to the skin and subcutis.5 Due to this difference and its potential to impact management, obtaining a tissue fungal culture is advisable when phaeohyphomycosis is suspected.
There is no standard treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. Regimens typically consist of excision and prolonged courses of azole therapy, though excision alone with close follow-up may be a reasonable alternative.6 The latter is a particularly important consideration when managing phaeohyphomycosis in organ transplant recipients, as azoles are known cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors that can affect serum levels of common immunosuppressive medications including calcineurin inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors.3 Local recurrence is common regardless of whether azole therapy is pursued,7 and dissemination of localized Exophiala infections is exceedingly rare.8 There is a strong argument to be made for our patient’s decision to forgo antifungal therapy.
This case underscores the difficulty inherent to eradicating local subcutaneous Exophiala phaeohyphomycosis while providing reassurance that with treatment, the risk of life-threatening complications is low. Obtaining tissue for both hematoxylin and eosin stain and sterile culture is crucial to ensuring prompt diagnosis and tailoring the optimal treatment and surveillance strategy to the culprit organism. To avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment, it is important for clinicians to consider phaeohyphomycosis in the differential diagnosis for recurrent nodulocystic lesions in immunosuppressed patients and to recognize that presentations may span many years.
- Bhardwaj S, Capoor MR, Kolte S, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala jeanselmei: an emerging pathogen in India—case report and review. Mycopathologia. 2016;181:279-284.
- Isa-Isa R, Garcia C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Tirico MCCP, Neto CF, Cruz LL, et al. Clinical spectrum of phaeohyphomycosis in solid organ transplant recipients. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:465-469.
- Revankar SG, Patterson JE, Sutton DA, et al. Disseminated phaeohyphomycosis: review of an emerging mycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:467-476.
- Revankar SG, Baddley JW, Chen SC-A, et al. A mycoses study group international prospective study of phaeohyphomycosis: an analysis of 99 proven/probable cases. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx200.
- Oberlin KE, Nichols AJ, Rosa R, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala infections in solid organ transplant recipients: case report and literature review [published online June 26, 2017]. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19. doi:10.1111/tid.12723.
- Shirbur S, Telkar S, Goudar B, et al. Recurrent phaeohyphomycosis: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:2015-2016.
- Li D-M, Li R-Y, de Hoog GS, et al. Fatal Exophiala infections in China, with a report of seven cases. Mycoses. 2011;54:E136-E142.
- Bhardwaj S, Capoor MR, Kolte S, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala jeanselmei: an emerging pathogen in India—case report and review. Mycopathologia. 2016;181:279-284.
- Isa-Isa R, Garcia C, Isa M, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (mycotic cyst). Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:425-431.
- Tirico MCCP, Neto CF, Cruz LL, et al. Clinical spectrum of phaeohyphomycosis in solid organ transplant recipients. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:465-469.
- Revankar SG, Patterson JE, Sutton DA, et al. Disseminated phaeohyphomycosis: review of an emerging mycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:467-476.
- Revankar SG, Baddley JW, Chen SC-A, et al. A mycoses study group international prospective study of phaeohyphomycosis: an analysis of 99 proven/probable cases. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx200.
- Oberlin KE, Nichols AJ, Rosa R, et al. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala infections in solid organ transplant recipients: case report and literature review [published online June 26, 2017]. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19. doi:10.1111/tid.12723.
- Shirbur S, Telkar S, Goudar B, et al. Recurrent phaeohyphomycosis: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:2015-2016.
- Li D-M, Li R-Y, de Hoog GS, et al. Fatal Exophiala infections in China, with a report of seven cases. Mycoses. 2011;54:E136-E142.
Practice Points
- Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection with dematiaceous fungi that most commonly affects immunosuppressed patients.
- Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis may present with nodulocystic lesions that recur over the course of years.
- Tissue fungal culture should be obtained when the diagnosis is suspected, as the risk for dissemination is related to the culprit organism.
- Surgical excision with close follow-up may be an appropriate management strategy for patients on immunosuppressive medications to avoid interactions with azole therapy.
Violaceous Plaques and Papulonodules on the Umbilicus
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Deposits Of Myeloma
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a rare skin manifestation of multiple myeloma that typically occur in less than 5% of patients.1,2 The lesions represent monoclonal proliferations of plasma cells and arise from direct extension of a neoplastic mass or less commonly from hematogenous or lymphatic spread. This secondary cutaneous involvement by plasma cell myeloma has been referred to in the literature as metastatic or extramedullary cutaneous plasmacytoma.1,2 This condition must be distinguished from cutaneous plasma cell infiltrates without underlying bone marrow involvement, classified by the World Health Organization as primary cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and previously referred to as primary cutaneous plasmacytoma.3
Clinically, cutaneous deposits of myeloma manifest as erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules with a smooth surface and firm consistency.1,2 The lesions typically occur on the trunk and less commonly on the head, neck, arms, and legs. In a review of 83 cases of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma and primary cutaneous plasmacytoma in multiple myeloma, Kato et al4 found that 52% (43/83) of cases occurred in IgG myelomas and 23% (19/83) in IgA myelomas.
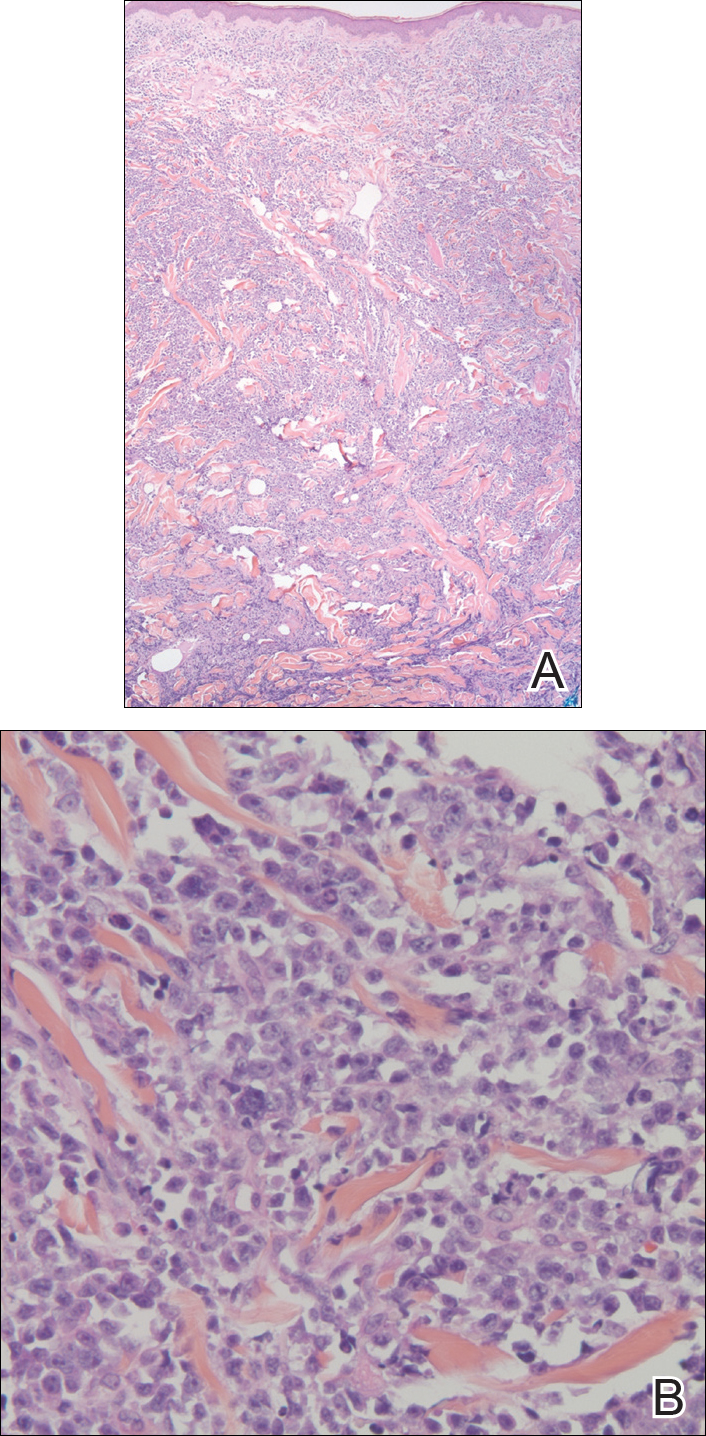
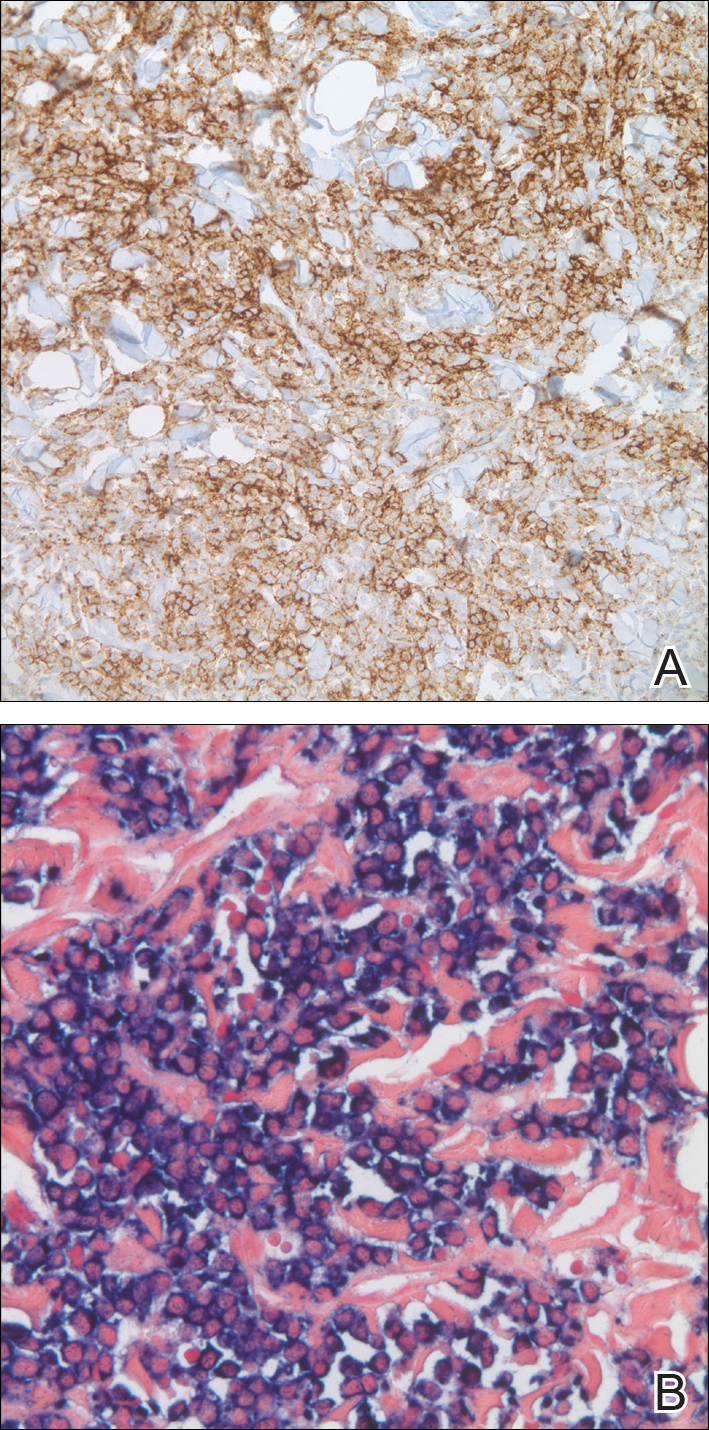
In our patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy of an umbilical plaque demonstrated a dense infiltrate of atypical plasmacytoid cells through the full thickness of the dermis with nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, and frequent mitoses (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for IgA λ light chain (Figure 2A) and CD138 (Figure 2B) and was negative for CD20, which was consistent with the patient's known plasma cell myeloma. Positron emission tomography revealed progression of underlying disease compared to prior studies with hypermetabolic mediastinal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic side wall lymphadenopathy, as well as extensive hypermetabolic soft tissue masses with involvement of the periumbilical region.
The differential diagnosis for violaceous periumbilical plaques includes cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary) or T-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary), cutaneous metastases from solid organ or hematologic malignancies (eg, Sister Mary Joseph nodule), AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma (plum-colored plaques that may be extensive), and cutaneous endometriosis (umbilical nodules that may develop in women after surgical excision of endometrial tissue).
The mainstay of therapy for secondary cutaneous involvement of plasma cell myeloma includes treatment with chemotherapy and local radiotherapy.1,2,5 After the diagnosis of cutaneous deposits of myeloma was made in our patient, he was treated with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide with dexamethasone, and local radiotherapy to symptomatic bony lesions; however, he was unresponsive to therapy and the disease progressed with numerous extramedullary lesions of the mediastinum, gastrointestinal tract, and retroperitoneum 2 months later. The patient developed hydronephrosis from external renal compression necessitating nephrostomy tube and malignant pleural effusions requiring intubation. He experienced rapid clinical decline and died 3 months after the initial presentation due to multiorgan failure.
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a sign of underlying disease progression in plasma cell myeloma and often herald a fulminant course (eg, death within 12 months of presentation), as seen in our patient.5 Clinicians should be aware of this rare manifestation of plasma cell myeloma and pursue aggressive therapy given the poor prognostic nature of these cutaneous findings.
- Jorizzo JL, Gammon WR, Briggaman RA. Cutaneous plasmacytomas: a review and presentation of an unusual case. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:59-66.
- Bayer-Garner IB, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in multiple myeloma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:497-507.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Kato N, Kimura K, Yasukawa K, et al. Metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma: a case report associated with IgA lambda multiple myeloma and a review of the literature of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytomas associated with multiple myeloma and primary cutaneous plasmacytomas. J Dermatol. 1999;26:587-594.
- Sanal SM, Yaylaci M, Mangold KA, et al. Extensive extramedullary disease in myeloma. an uncommon variant with features of poor prognosis and dedifferentiation. Cancer. 1996;77:1298-1302.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Deposits Of Myeloma
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a rare skin manifestation of multiple myeloma that typically occur in less than 5% of patients.1,2 The lesions represent monoclonal proliferations of plasma cells and arise from direct extension of a neoplastic mass or less commonly from hematogenous or lymphatic spread. This secondary cutaneous involvement by plasma cell myeloma has been referred to in the literature as metastatic or extramedullary cutaneous plasmacytoma.1,2 This condition must be distinguished from cutaneous plasma cell infiltrates without underlying bone marrow involvement, classified by the World Health Organization as primary cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and previously referred to as primary cutaneous plasmacytoma.3
Clinically, cutaneous deposits of myeloma manifest as erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules with a smooth surface and firm consistency.1,2 The lesions typically occur on the trunk and less commonly on the head, neck, arms, and legs. In a review of 83 cases of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma and primary cutaneous plasmacytoma in multiple myeloma, Kato et al4 found that 52% (43/83) of cases occurred in IgG myelomas and 23% (19/83) in IgA myelomas.
In our patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy of an umbilical plaque demonstrated a dense infiltrate of atypical plasmacytoid cells through the full thickness of the dermis with nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, and frequent mitoses (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for IgA λ light chain (Figure 2A) and CD138 (Figure 2B) and was negative for CD20, which was consistent with the patient's known plasma cell myeloma. Positron emission tomography revealed progression of underlying disease compared to prior studies with hypermetabolic mediastinal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic side wall lymphadenopathy, as well as extensive hypermetabolic soft tissue masses with involvement of the periumbilical region.


The differential diagnosis for violaceous periumbilical plaques includes cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary) or T-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary), cutaneous metastases from solid organ or hematologic malignancies (eg, Sister Mary Joseph nodule), AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma (plum-colored plaques that may be extensive), and cutaneous endometriosis (umbilical nodules that may develop in women after surgical excision of endometrial tissue).
The mainstay of therapy for secondary cutaneous involvement of plasma cell myeloma includes treatment with chemotherapy and local radiotherapy.1,2,5 After the diagnosis of cutaneous deposits of myeloma was made in our patient, he was treated with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide with dexamethasone, and local radiotherapy to symptomatic bony lesions; however, he was unresponsive to therapy and the disease progressed with numerous extramedullary lesions of the mediastinum, gastrointestinal tract, and retroperitoneum 2 months later. The patient developed hydronephrosis from external renal compression necessitating nephrostomy tube and malignant pleural effusions requiring intubation. He experienced rapid clinical decline and died 3 months after the initial presentation due to multiorgan failure.
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a sign of underlying disease progression in plasma cell myeloma and often herald a fulminant course (eg, death within 12 months of presentation), as seen in our patient.5 Clinicians should be aware of this rare manifestation of plasma cell myeloma and pursue aggressive therapy given the poor prognostic nature of these cutaneous findings.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Deposits Of Myeloma
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a rare skin manifestation of multiple myeloma that typically occur in less than 5% of patients.1,2 The lesions represent monoclonal proliferations of plasma cells and arise from direct extension of a neoplastic mass or less commonly from hematogenous or lymphatic spread. This secondary cutaneous involvement by plasma cell myeloma has been referred to in the literature as metastatic or extramedullary cutaneous plasmacytoma.1,2 This condition must be distinguished from cutaneous plasma cell infiltrates without underlying bone marrow involvement, classified by the World Health Organization as primary cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and previously referred to as primary cutaneous plasmacytoma.3
Clinically, cutaneous deposits of myeloma manifest as erythematous to violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules with a smooth surface and firm consistency.1,2 The lesions typically occur on the trunk and less commonly on the head, neck, arms, and legs. In a review of 83 cases of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma and primary cutaneous plasmacytoma in multiple myeloma, Kato et al4 found that 52% (43/83) of cases occurred in IgG myelomas and 23% (19/83) in IgA myelomas.
In our patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy of an umbilical plaque demonstrated a dense infiltrate of atypical plasmacytoid cells through the full thickness of the dermis with nuclear pleomorphism, prominent nucleoli, and frequent mitoses (Figure 1). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for IgA λ light chain (Figure 2A) and CD138 (Figure 2B) and was negative for CD20, which was consistent with the patient's known plasma cell myeloma. Positron emission tomography revealed progression of underlying disease compared to prior studies with hypermetabolic mediastinal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic side wall lymphadenopathy, as well as extensive hypermetabolic soft tissue masses with involvement of the periumbilical region.


The differential diagnosis for violaceous periumbilical plaques includes cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary) or T-cell lymphoma (primary or secondary), cutaneous metastases from solid organ or hematologic malignancies (eg, Sister Mary Joseph nodule), AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma (plum-colored plaques that may be extensive), and cutaneous endometriosis (umbilical nodules that may develop in women after surgical excision of endometrial tissue).
The mainstay of therapy for secondary cutaneous involvement of plasma cell myeloma includes treatment with chemotherapy and local radiotherapy.1,2,5 After the diagnosis of cutaneous deposits of myeloma was made in our patient, he was treated with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide with dexamethasone, and local radiotherapy to symptomatic bony lesions; however, he was unresponsive to therapy and the disease progressed with numerous extramedullary lesions of the mediastinum, gastrointestinal tract, and retroperitoneum 2 months later. The patient developed hydronephrosis from external renal compression necessitating nephrostomy tube and malignant pleural effusions requiring intubation. He experienced rapid clinical decline and died 3 months after the initial presentation due to multiorgan failure.
Cutaneous deposits of myeloma are a sign of underlying disease progression in plasma cell myeloma and often herald a fulminant course (eg, death within 12 months of presentation), as seen in our patient.5 Clinicians should be aware of this rare manifestation of plasma cell myeloma and pursue aggressive therapy given the poor prognostic nature of these cutaneous findings.
- Jorizzo JL, Gammon WR, Briggaman RA. Cutaneous plasmacytomas: a review and presentation of an unusual case. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:59-66.
- Bayer-Garner IB, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in multiple myeloma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:497-507.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Kato N, Kimura K, Yasukawa K, et al. Metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma: a case report associated with IgA lambda multiple myeloma and a review of the literature of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytomas associated with multiple myeloma and primary cutaneous plasmacytomas. J Dermatol. 1999;26:587-594.
- Sanal SM, Yaylaci M, Mangold KA, et al. Extensive extramedullary disease in myeloma. an uncommon variant with features of poor prognosis and dedifferentiation. Cancer. 1996;77:1298-1302.
- Jorizzo JL, Gammon WR, Briggaman RA. Cutaneous plasmacytomas: a review and presentation of an unusual case. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:59-66.
- Bayer-Garner IB, Smoller BR. The spectrum of cutaneous disease in multiple myeloma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:497-507.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Kato N, Kimura K, Yasukawa K, et al. Metastatic cutaneous plasmacytoma: a case report associated with IgA lambda multiple myeloma and a review of the literature of metastatic cutaneous plasmacytomas associated with multiple myeloma and primary cutaneous plasmacytomas. J Dermatol. 1999;26:587-594.
- Sanal SM, Yaylaci M, Mangold KA, et al. Extensive extramedullary disease in myeloma. an uncommon variant with features of poor prognosis and dedifferentiation. Cancer. 1996;77:1298-1302.
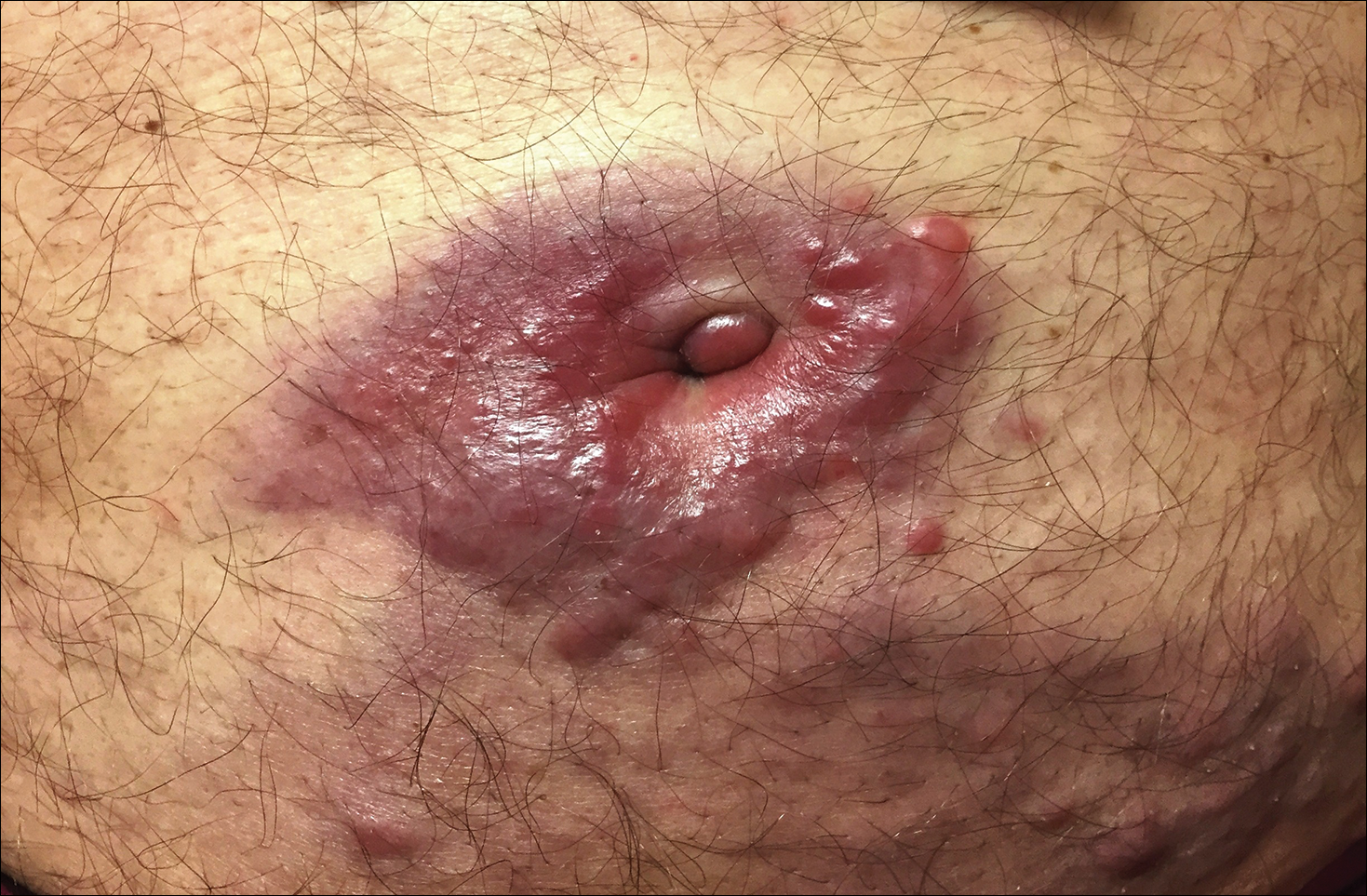
A 75-year-old man presented for evaluation of lesions on the umbilicus and lower abdomen that had developed over the past 4 weeks and were asymptomatic. His medical history was notable for plasma cell myeloma (stage III, IgA λ light chain restricted), deep vein thrombosis, and a 30-year history of smoking (20 packs per year). On physical examination, violaceous plaques and papulonodules were noted on the umbilicus. The lesions had a firm consistency and smooth surface without epidermal change. Violaceous papulonodules and subcutaneous plaques were noted on the lower abdomen. The lesions were nontender to palpation. Bilateral edema of the legs also was noted. The remainder of the skin was normal and there was no cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymphadenopathy.