User login
Possible biomarkers found for progression to liver cancer in chronic HCV infection
according to the results of a biochemical analysis of human blood samples performed by PhD student Paywast J. Jalal of the University of Sulaimani (Iraq) and colleagues.
Archived HCV-positive serum samples, including those from 31 patients who had developed HCC, were retrieved from the Trent HCV clinical cohort. They were compared with each other over time and against samples from HCV-infected individuals in the cohort who did not develop HCC. In addition, HCV-negative serum samples were obtained commercially and assessed identically. Circulating liver-expressed lectins, ficolin-2, ficolin-3, and MBL were all examined as potential biomarkers for the development of HCC, the authors wrote in Virology.
Binding of ficolin-3 to reference ligands was greater in chronic HCV infection, while ficolin-2 and MBL were significantly elevated in individuals who develop HCC, compared with HCV-infected individuals without HCC. Ficolin-2 and MBL were found to be elevated at 1 and 3 years prior to HCC diagnosis, respectively, suggesting they could be used as prognostic serum markers for the development of HCC.
“The strong evidence for an association between elevated MBL binding activity and the development of HCC is supportive for a larger prospective study of these biomarkers in HCV-induced liver cancer,” the researchers concluded.
This study was funded by a split-site PhD scholarship between the University of Sulaimani and the University of Nottingham (England). The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Jalal PJ et al. Virology. 2019;530:99-106.
according to the results of a biochemical analysis of human blood samples performed by PhD student Paywast J. Jalal of the University of Sulaimani (Iraq) and colleagues.
Archived HCV-positive serum samples, including those from 31 patients who had developed HCC, were retrieved from the Trent HCV clinical cohort. They were compared with each other over time and against samples from HCV-infected individuals in the cohort who did not develop HCC. In addition, HCV-negative serum samples were obtained commercially and assessed identically. Circulating liver-expressed lectins, ficolin-2, ficolin-3, and MBL were all examined as potential biomarkers for the development of HCC, the authors wrote in Virology.
Binding of ficolin-3 to reference ligands was greater in chronic HCV infection, while ficolin-2 and MBL were significantly elevated in individuals who develop HCC, compared with HCV-infected individuals without HCC. Ficolin-2 and MBL were found to be elevated at 1 and 3 years prior to HCC diagnosis, respectively, suggesting they could be used as prognostic serum markers for the development of HCC.
“The strong evidence for an association between elevated MBL binding activity and the development of HCC is supportive for a larger prospective study of these biomarkers in HCV-induced liver cancer,” the researchers concluded.
This study was funded by a split-site PhD scholarship between the University of Sulaimani and the University of Nottingham (England). The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Jalal PJ et al. Virology. 2019;530:99-106.
according to the results of a biochemical analysis of human blood samples performed by PhD student Paywast J. Jalal of the University of Sulaimani (Iraq) and colleagues.
Archived HCV-positive serum samples, including those from 31 patients who had developed HCC, were retrieved from the Trent HCV clinical cohort. They were compared with each other over time and against samples from HCV-infected individuals in the cohort who did not develop HCC. In addition, HCV-negative serum samples were obtained commercially and assessed identically. Circulating liver-expressed lectins, ficolin-2, ficolin-3, and MBL were all examined as potential biomarkers for the development of HCC, the authors wrote in Virology.
Binding of ficolin-3 to reference ligands was greater in chronic HCV infection, while ficolin-2 and MBL were significantly elevated in individuals who develop HCC, compared with HCV-infected individuals without HCC. Ficolin-2 and MBL were found to be elevated at 1 and 3 years prior to HCC diagnosis, respectively, suggesting they could be used as prognostic serum markers for the development of HCC.
“The strong evidence for an association between elevated MBL binding activity and the development of HCC is supportive for a larger prospective study of these biomarkers in HCV-induced liver cancer,” the researchers concluded.
This study was funded by a split-site PhD scholarship between the University of Sulaimani and the University of Nottingham (England). The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Jalal PJ et al. Virology. 2019;530:99-106.
FROM VIROLOGY
Caring for aging HIV-infected patients requires close attention to unrelated diseases
A substantial proportion of non–AIDS-defining cancers, and other noninfectious comorbid diseases, could be prevented with interventions on traditional risk factors in HIV-infected patients, according to the results of large database analysis published online in The Lancet HIV.
The researchers analyzed traditional and HIV-related risk factors for four validated noncommunicable disease outcomes (non–AIDS-defining cancers, myocardial infarction, end-stage liver disease, and end-stage renal disease) among participants of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), according to Keri N. Althoff, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and her colleagues on behalf of the NA-ACCORD.
The study comprised individuals with the assessed disease conditions from among more than 180,000 adults (aged 18 years or older) with HIV from more than 200 sites who had at least two care visits within 12 months. The researchers used a population attributable fraction (PAF) approach to quantify the proportion of noncommunicable diseases that could be eliminated if particular risk factors were not present. According to the researchers, PAF can be used to inform prioritization of interventions.
Dr. Althoff and her colleagues found that, for non–AIDS-defining cancer, the significant preventable or modifiable risk factors were smoking, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B infection.
For myocardial infarction, the significant factors were smoking, elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, stage 4 chronic kidney disease, a low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and hepatitis C infection.
For end-stage liver disease, the significant factors were low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of a clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B or C infection.
For end-stage renal disease, the significantly associated risk factors were elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis.
The most substantial PAF for each of the respective diseases was as follows: smoking for non–AIDS-related cancers (24%; 95% confidence interval, 13%-35%), elevated total cholesterol for myocardial infarction (44%; 95% CI, 30%-58%), and hepatitis C infection for end-stage liver disease (30%; 95% CI, 21%-39%). In addition, hypertension had the highest PAF for end-stage renal disease (39%; 95% CI, 26%-51%).
“Modifications to individual-level interventions and models of HIV care, and the implementation of structural and policy-level interventions that focus on prevention and modification of traditional risk factors are necessary to avoid noncommunicable diseases and preserve health among successfully antiretroviral-treated adults aging with HIV,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the NA-ACCORD. Dr. Althoff reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Althoff KN et al. The Lancet HIV. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30295-9.
A substantial proportion of non–AIDS-defining cancers, and other noninfectious comorbid diseases, could be prevented with interventions on traditional risk factors in HIV-infected patients, according to the results of large database analysis published online in The Lancet HIV.
The researchers analyzed traditional and HIV-related risk factors for four validated noncommunicable disease outcomes (non–AIDS-defining cancers, myocardial infarction, end-stage liver disease, and end-stage renal disease) among participants of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), according to Keri N. Althoff, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and her colleagues on behalf of the NA-ACCORD.
The study comprised individuals with the assessed disease conditions from among more than 180,000 adults (aged 18 years or older) with HIV from more than 200 sites who had at least two care visits within 12 months. The researchers used a population attributable fraction (PAF) approach to quantify the proportion of noncommunicable diseases that could be eliminated if particular risk factors were not present. According to the researchers, PAF can be used to inform prioritization of interventions.
Dr. Althoff and her colleagues found that, for non–AIDS-defining cancer, the significant preventable or modifiable risk factors were smoking, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B infection.
For myocardial infarction, the significant factors were smoking, elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, stage 4 chronic kidney disease, a low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and hepatitis C infection.
For end-stage liver disease, the significant factors were low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of a clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B or C infection.
For end-stage renal disease, the significantly associated risk factors were elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis.
The most substantial PAF for each of the respective diseases was as follows: smoking for non–AIDS-related cancers (24%; 95% confidence interval, 13%-35%), elevated total cholesterol for myocardial infarction (44%; 95% CI, 30%-58%), and hepatitis C infection for end-stage liver disease (30%; 95% CI, 21%-39%). In addition, hypertension had the highest PAF for end-stage renal disease (39%; 95% CI, 26%-51%).
“Modifications to individual-level interventions and models of HIV care, and the implementation of structural and policy-level interventions that focus on prevention and modification of traditional risk factors are necessary to avoid noncommunicable diseases and preserve health among successfully antiretroviral-treated adults aging with HIV,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the NA-ACCORD. Dr. Althoff reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Althoff KN et al. The Lancet HIV. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30295-9.
A substantial proportion of non–AIDS-defining cancers, and other noninfectious comorbid diseases, could be prevented with interventions on traditional risk factors in HIV-infected patients, according to the results of large database analysis published online in The Lancet HIV.
The researchers analyzed traditional and HIV-related risk factors for four validated noncommunicable disease outcomes (non–AIDS-defining cancers, myocardial infarction, end-stage liver disease, and end-stage renal disease) among participants of the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD), according to Keri N. Althoff, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and her colleagues on behalf of the NA-ACCORD.
The study comprised individuals with the assessed disease conditions from among more than 180,000 adults (aged 18 years or older) with HIV from more than 200 sites who had at least two care visits within 12 months. The researchers used a population attributable fraction (PAF) approach to quantify the proportion of noncommunicable diseases that could be eliminated if particular risk factors were not present. According to the researchers, PAF can be used to inform prioritization of interventions.
Dr. Althoff and her colleagues found that, for non–AIDS-defining cancer, the significant preventable or modifiable risk factors were smoking, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B infection.
For myocardial infarction, the significant factors were smoking, elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, stage 4 chronic kidney disease, a low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and hepatitis C infection.
For end-stage liver disease, the significant factors were low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, a history of a clinical AIDS diagnosis, and hepatitis B or C infection.
For end-stage renal disease, the significantly associated risk factors were elevated total cholesterol, hypertension, diabetes, low CD4 cell count, detectable HIV RNA, and a history of clinical AIDS diagnosis.
The most substantial PAF for each of the respective diseases was as follows: smoking for non–AIDS-related cancers (24%; 95% confidence interval, 13%-35%), elevated total cholesterol for myocardial infarction (44%; 95% CI, 30%-58%), and hepatitis C infection for end-stage liver disease (30%; 95% CI, 21%-39%). In addition, hypertension had the highest PAF for end-stage renal disease (39%; 95% CI, 26%-51%).
“Modifications to individual-level interventions and models of HIV care, and the implementation of structural and policy-level interventions that focus on prevention and modification of traditional risk factors are necessary to avoid noncommunicable diseases and preserve health among successfully antiretroviral-treated adults aging with HIV,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the NA-ACCORD. Dr. Althoff reported having no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Althoff KN et al. The Lancet HIV. 2019 Jan 22. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30295-9.
FROM THE LANCET HIV
Heart failure outcomes are worse in select HIV-infected individuals
People living with HIV (PLHIV) who have a low CD4 count or detectable viral load (VL) have an increased 30-day heart failure (HF) readmission rate as well as increased cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, compared with uninfected controls, according to Raza M. Alvi, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues.
Overall, the 30-day HF hospital readmission rate was higher among PLHIV versus non-HIV–infected individuals (49% vs. 32%, P less than .001), according to the results of their cohort study of 2,308 individuals admitted to the hospital with decompensated HF.
PLHIV and the non-HIV control groups were both followed over 2 years with a median follow-up period of 19 months, the authors wrote in the American Heart Journal. Demographic make-up of the two groups was similar; in particular, there was no difference in blood pressure and heart rate between the PLHIV and non-HIV controls, suggesting that adherence with HF medications may be similar between groups. The cohorts differed primarily in that pulmonary artery systolic pressure was significantly higher (45 vs. 40 mm Hg; P less than .001) in the HIV group, as was cocaine use (36% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (13% vs. 7%; P less than .001).
The differing results between the two cohorts were primarily caused by the fact that, for PLHIV with HF, CD4 count and VL were risk factors for adverse outcomes among patients with all types of HF. (30-day HF readmission, cardiovascular [CV] mortality, and all-cause mortality), compared with those with CD4 count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3. In addition, a low CD4 count/high VL independently related to an increased 30-day HF readmission rate even after the researchers controlled for major traditional and nontraditional HF risk factors.
“Rates of 30-day HF readmission, CV mortality, and all-cause mortality are worse among individuals with a low CD4 count or nonsuppressed viral load,” the researchers concluded.
The National Institutes of Health sponsored the study. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Alvi RM et al. Am Heart J. 2019 Apr;210:39-48.
People living with HIV (PLHIV) who have a low CD4 count or detectable viral load (VL) have an increased 30-day heart failure (HF) readmission rate as well as increased cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, compared with uninfected controls, according to Raza M. Alvi, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues.
Overall, the 30-day HF hospital readmission rate was higher among PLHIV versus non-HIV–infected individuals (49% vs. 32%, P less than .001), according to the results of their cohort study of 2,308 individuals admitted to the hospital with decompensated HF.
PLHIV and the non-HIV control groups were both followed over 2 years with a median follow-up period of 19 months, the authors wrote in the American Heart Journal. Demographic make-up of the two groups was similar; in particular, there was no difference in blood pressure and heart rate between the PLHIV and non-HIV controls, suggesting that adherence with HF medications may be similar between groups. The cohorts differed primarily in that pulmonary artery systolic pressure was significantly higher (45 vs. 40 mm Hg; P less than .001) in the HIV group, as was cocaine use (36% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (13% vs. 7%; P less than .001).
The differing results between the two cohorts were primarily caused by the fact that, for PLHIV with HF, CD4 count and VL were risk factors for adverse outcomes among patients with all types of HF. (30-day HF readmission, cardiovascular [CV] mortality, and all-cause mortality), compared with those with CD4 count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3. In addition, a low CD4 count/high VL independently related to an increased 30-day HF readmission rate even after the researchers controlled for major traditional and nontraditional HF risk factors.
“Rates of 30-day HF readmission, CV mortality, and all-cause mortality are worse among individuals with a low CD4 count or nonsuppressed viral load,” the researchers concluded.
The National Institutes of Health sponsored the study. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Alvi RM et al. Am Heart J. 2019 Apr;210:39-48.
People living with HIV (PLHIV) who have a low CD4 count or detectable viral load (VL) have an increased 30-day heart failure (HF) readmission rate as well as increased cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, compared with uninfected controls, according to Raza M. Alvi, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, and his colleagues.
Overall, the 30-day HF hospital readmission rate was higher among PLHIV versus non-HIV–infected individuals (49% vs. 32%, P less than .001), according to the results of their cohort study of 2,308 individuals admitted to the hospital with decompensated HF.
PLHIV and the non-HIV control groups were both followed over 2 years with a median follow-up period of 19 months, the authors wrote in the American Heart Journal. Demographic make-up of the two groups was similar; in particular, there was no difference in blood pressure and heart rate between the PLHIV and non-HIV controls, suggesting that adherence with HF medications may be similar between groups. The cohorts differed primarily in that pulmonary artery systolic pressure was significantly higher (45 vs. 40 mm Hg; P less than .001) in the HIV group, as was cocaine use (36% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (13% vs. 7%; P less than .001).
The differing results between the two cohorts were primarily caused by the fact that, for PLHIV with HF, CD4 count and VL were risk factors for adverse outcomes among patients with all types of HF. (30-day HF readmission, cardiovascular [CV] mortality, and all-cause mortality), compared with those with CD4 count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3. In addition, a low CD4 count/high VL independently related to an increased 30-day HF readmission rate even after the researchers controlled for major traditional and nontraditional HF risk factors.
“Rates of 30-day HF readmission, CV mortality, and all-cause mortality are worse among individuals with a low CD4 count or nonsuppressed viral load,” the researchers concluded.
The National Institutes of Health sponsored the study. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Alvi RM et al. Am Heart J. 2019 Apr;210:39-48.
FROM THE AMERICAN HEART JOURNAL
Paclitaxel drug-coated balloons appear safe for PAD treatment
Mortality after the use of drug-coated balloons (DCB) for femoropopliteal peripheral arterial disease (PAD) was not correlated with paclitaxel exposure, according to the results of a meta-analysis of 5-year outcomes, according to a report published online.
“Paclitaxel DCBs are safe and effective to treat the symptoms of [Rutherford classification categories] 2-4 femoropopliteal PAD,” according to Peter A. Schneider, MD, of Hawaii Permanente Medical Group, Kaiser Foundation Hospital, Honolulu, and his coauthors.
Their study analyzed data pooled from five clinical trials NCT01175850, NCT01566461, NCT01947478, NCT02118532, and NCT01609296, comprising 1,980 patients from a variety of ethnic populations with Rutherford classification 2-4 disease.
Among these patients, 1,837 received DCB and 143 received uncoated percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA). The mean age of the overall cohort was 68.5 years; 68.4% of patients were men. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups. However, patients treated with a DCB were more likely to have critical limb ischemia, compared with PTA. DCB subjects were less likely to have hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus than were those treated with uncoated PTA. In addition, PTA patients who died were more likely to be active smokers than were DCB patients that died.
There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality between DCB and PTA through 5 years (9.3% vs 11.2%, respectively, P = .399).
A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis stratified paclitaxel dosage into three groups: low-dose, mid-dose, and upper-dose groups. Mean dosages for the three groups were 5,019, 10,008, and 19,978 mcg, respectively. The analysis showed no significant difference in mortality between groups, “demonstrating no direct impact of levels of nominal paclitaxel dose exposure at the index procedure and survival status in the DCB patients through 5 years (P = .700),” according to the authors.
Limitations of the study reported by the authors include the fact that pooling data from distinct trials has shortcomings. Some of data included had not yet undergone peer review, and PTA patients were included in only two randomized trials in a 2:1 ratio.
“The small numbers of PTA control patients (less than 10%) may not be representative of PTA patients in general and limits the strength of this analysis of mortality.” In addition, only patients with Rutherford classification 2-4 were included in these studies.
“Results from this independent patient-level meta-analysis show no difference in mortality between DCB and PTA at 5 years and no correlation between varying levels of paclitaxel exposure and mortality. ... Data transparency and additional analyses are needed to better understand how other factors influence long-term outcomes in this complex patient population,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by Medtronic, which provided the data for independent analysis to the Baim Institute for Clinical Research. Dr. Schneider is a member of the advisory board for Medtronic, Abbott, and Boston Scientific and is a consultant for Medtronic and other device companies. Coauthors had consulting, advisory board, or honoraria relationships with Medtronic and other device companies.
SOURCE: Schneider PA et al. JACC 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.013.
Mortality after the use of drug-coated balloons (DCB) for femoropopliteal peripheral arterial disease (PAD) was not correlated with paclitaxel exposure, according to the results of a meta-analysis of 5-year outcomes, according to a report published online.
“Paclitaxel DCBs are safe and effective to treat the symptoms of [Rutherford classification categories] 2-4 femoropopliteal PAD,” according to Peter A. Schneider, MD, of Hawaii Permanente Medical Group, Kaiser Foundation Hospital, Honolulu, and his coauthors.
Their study analyzed data pooled from five clinical trials NCT01175850, NCT01566461, NCT01947478, NCT02118532, and NCT01609296, comprising 1,980 patients from a variety of ethnic populations with Rutherford classification 2-4 disease.
Among these patients, 1,837 received DCB and 143 received uncoated percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA). The mean age of the overall cohort was 68.5 years; 68.4% of patients were men. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups. However, patients treated with a DCB were more likely to have critical limb ischemia, compared with PTA. DCB subjects were less likely to have hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus than were those treated with uncoated PTA. In addition, PTA patients who died were more likely to be active smokers than were DCB patients that died.
There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality between DCB and PTA through 5 years (9.3% vs 11.2%, respectively, P = .399).
A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis stratified paclitaxel dosage into three groups: low-dose, mid-dose, and upper-dose groups. Mean dosages for the three groups were 5,019, 10,008, and 19,978 mcg, respectively. The analysis showed no significant difference in mortality between groups, “demonstrating no direct impact of levels of nominal paclitaxel dose exposure at the index procedure and survival status in the DCB patients through 5 years (P = .700),” according to the authors.
Limitations of the study reported by the authors include the fact that pooling data from distinct trials has shortcomings. Some of data included had not yet undergone peer review, and PTA patients were included in only two randomized trials in a 2:1 ratio.
“The small numbers of PTA control patients (less than 10%) may not be representative of PTA patients in general and limits the strength of this analysis of mortality.” In addition, only patients with Rutherford classification 2-4 were included in these studies.
“Results from this independent patient-level meta-analysis show no difference in mortality between DCB and PTA at 5 years and no correlation between varying levels of paclitaxel exposure and mortality. ... Data transparency and additional analyses are needed to better understand how other factors influence long-term outcomes in this complex patient population,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by Medtronic, which provided the data for independent analysis to the Baim Institute for Clinical Research. Dr. Schneider is a member of the advisory board for Medtronic, Abbott, and Boston Scientific and is a consultant for Medtronic and other device companies. Coauthors had consulting, advisory board, or honoraria relationships with Medtronic and other device companies.
SOURCE: Schneider PA et al. JACC 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.013.
Mortality after the use of drug-coated balloons (DCB) for femoropopliteal peripheral arterial disease (PAD) was not correlated with paclitaxel exposure, according to the results of a meta-analysis of 5-year outcomes, according to a report published online.
“Paclitaxel DCBs are safe and effective to treat the symptoms of [Rutherford classification categories] 2-4 femoropopliteal PAD,” according to Peter A. Schneider, MD, of Hawaii Permanente Medical Group, Kaiser Foundation Hospital, Honolulu, and his coauthors.
Their study analyzed data pooled from five clinical trials NCT01175850, NCT01566461, NCT01947478, NCT02118532, and NCT01609296, comprising 1,980 patients from a variety of ethnic populations with Rutherford classification 2-4 disease.
Among these patients, 1,837 received DCB and 143 received uncoated percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA). The mean age of the overall cohort was 68.5 years; 68.4% of patients were men. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups. However, patients treated with a DCB were more likely to have critical limb ischemia, compared with PTA. DCB subjects were less likely to have hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus than were those treated with uncoated PTA. In addition, PTA patients who died were more likely to be active smokers than were DCB patients that died.
There was no statistically significant difference in all-cause mortality between DCB and PTA through 5 years (9.3% vs 11.2%, respectively, P = .399).
A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis stratified paclitaxel dosage into three groups: low-dose, mid-dose, and upper-dose groups. Mean dosages for the three groups were 5,019, 10,008, and 19,978 mcg, respectively. The analysis showed no significant difference in mortality between groups, “demonstrating no direct impact of levels of nominal paclitaxel dose exposure at the index procedure and survival status in the DCB patients through 5 years (P = .700),” according to the authors.
Limitations of the study reported by the authors include the fact that pooling data from distinct trials has shortcomings. Some of data included had not yet undergone peer review, and PTA patients were included in only two randomized trials in a 2:1 ratio.
“The small numbers of PTA control patients (less than 10%) may not be representative of PTA patients in general and limits the strength of this analysis of mortality.” In addition, only patients with Rutherford classification 2-4 were included in these studies.
“Results from this independent patient-level meta-analysis show no difference in mortality between DCB and PTA at 5 years and no correlation between varying levels of paclitaxel exposure and mortality. ... Data transparency and additional analyses are needed to better understand how other factors influence long-term outcomes in this complex patient population,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by Medtronic, which provided the data for independent analysis to the Baim Institute for Clinical Research. Dr. Schneider is a member of the advisory board for Medtronic, Abbott, and Boston Scientific and is a consultant for Medtronic and other device companies. Coauthors had consulting, advisory board, or honoraria relationships with Medtronic and other device companies.
SOURCE: Schneider PA et al. JACC 2019 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.013.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Baby boomers account for more than 74% of chronic HCV cases
The overall prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the United States was 1.19%, giving an estimate of 2,347,852 infected adults. Baby boomers had the highest prevalence at 2.23%, accounting for more than 74% of all chronic HCV cases, according to the results of a database analysis done by Kevin J. Moore, MD, of the University of Miami and his colleagues.
In the analysis, published in the Journal of Infection and Public Health, the researchers assessed data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for the years 1999-2012. They separated three age categories: baby boomers (BB), younger than BB (YG), and older than BB (OG). BBs showed an HCV prevalence over four times higher than YG or OG. BBs also had more significant predictors of positive HCV status than YGs or OGs.
In addition to the overall difference in incidence of HCV infection in boomers and nonboomers, they found that significant predictors of chronic HCV positivity among BBs were being male or non-Hispanic black, having a positive blood transfusion history, being a current or former smoker, and living below the poverty line.
The most significant risk factor for HCV positivity differed across age groups – being a current smoker in YG and BB and being non-Hispanic black in OG, the researchers noted.
“These results show that HCV infection continues to be a significant public health issue and warrants further attention given the aging BB population. Future studies should seek to further identify age-specific risk factors for HCV infection to optimize HCV screening and prevention programs through public health interventions,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Moore KJ et al. J Infect Public Health. 2019 Jan-Feb;12(1):32-6.
The overall prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the United States was 1.19%, giving an estimate of 2,347,852 infected adults. Baby boomers had the highest prevalence at 2.23%, accounting for more than 74% of all chronic HCV cases, according to the results of a database analysis done by Kevin J. Moore, MD, of the University of Miami and his colleagues.
In the analysis, published in the Journal of Infection and Public Health, the researchers assessed data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for the years 1999-2012. They separated three age categories: baby boomers (BB), younger than BB (YG), and older than BB (OG). BBs showed an HCV prevalence over four times higher than YG or OG. BBs also had more significant predictors of positive HCV status than YGs or OGs.
In addition to the overall difference in incidence of HCV infection in boomers and nonboomers, they found that significant predictors of chronic HCV positivity among BBs were being male or non-Hispanic black, having a positive blood transfusion history, being a current or former smoker, and living below the poverty line.
The most significant risk factor for HCV positivity differed across age groups – being a current smoker in YG and BB and being non-Hispanic black in OG, the researchers noted.
“These results show that HCV infection continues to be a significant public health issue and warrants further attention given the aging BB population. Future studies should seek to further identify age-specific risk factors for HCV infection to optimize HCV screening and prevention programs through public health interventions,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Moore KJ et al. J Infect Public Health. 2019 Jan-Feb;12(1):32-6.
The overall prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the United States was 1.19%, giving an estimate of 2,347,852 infected adults. Baby boomers had the highest prevalence at 2.23%, accounting for more than 74% of all chronic HCV cases, according to the results of a database analysis done by Kevin J. Moore, MD, of the University of Miami and his colleagues.
In the analysis, published in the Journal of Infection and Public Health, the researchers assessed data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for the years 1999-2012. They separated three age categories: baby boomers (BB), younger than BB (YG), and older than BB (OG). BBs showed an HCV prevalence over four times higher than YG or OG. BBs also had more significant predictors of positive HCV status than YGs or OGs.
In addition to the overall difference in incidence of HCV infection in boomers and nonboomers, they found that significant predictors of chronic HCV positivity among BBs were being male or non-Hispanic black, having a positive blood transfusion history, being a current or former smoker, and living below the poverty line.
The most significant risk factor for HCV positivity differed across age groups – being a current smoker in YG and BB and being non-Hispanic black in OG, the researchers noted.
“These results show that HCV infection continues to be a significant public health issue and warrants further attention given the aging BB population. Future studies should seek to further identify age-specific risk factors for HCV infection to optimize HCV screening and prevention programs through public health interventions,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Moore KJ et al. J Infect Public Health. 2019 Jan-Feb;12(1):32-6.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INFECTION AND PUBLIC HEALTH
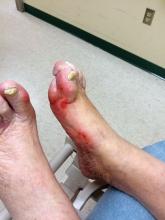
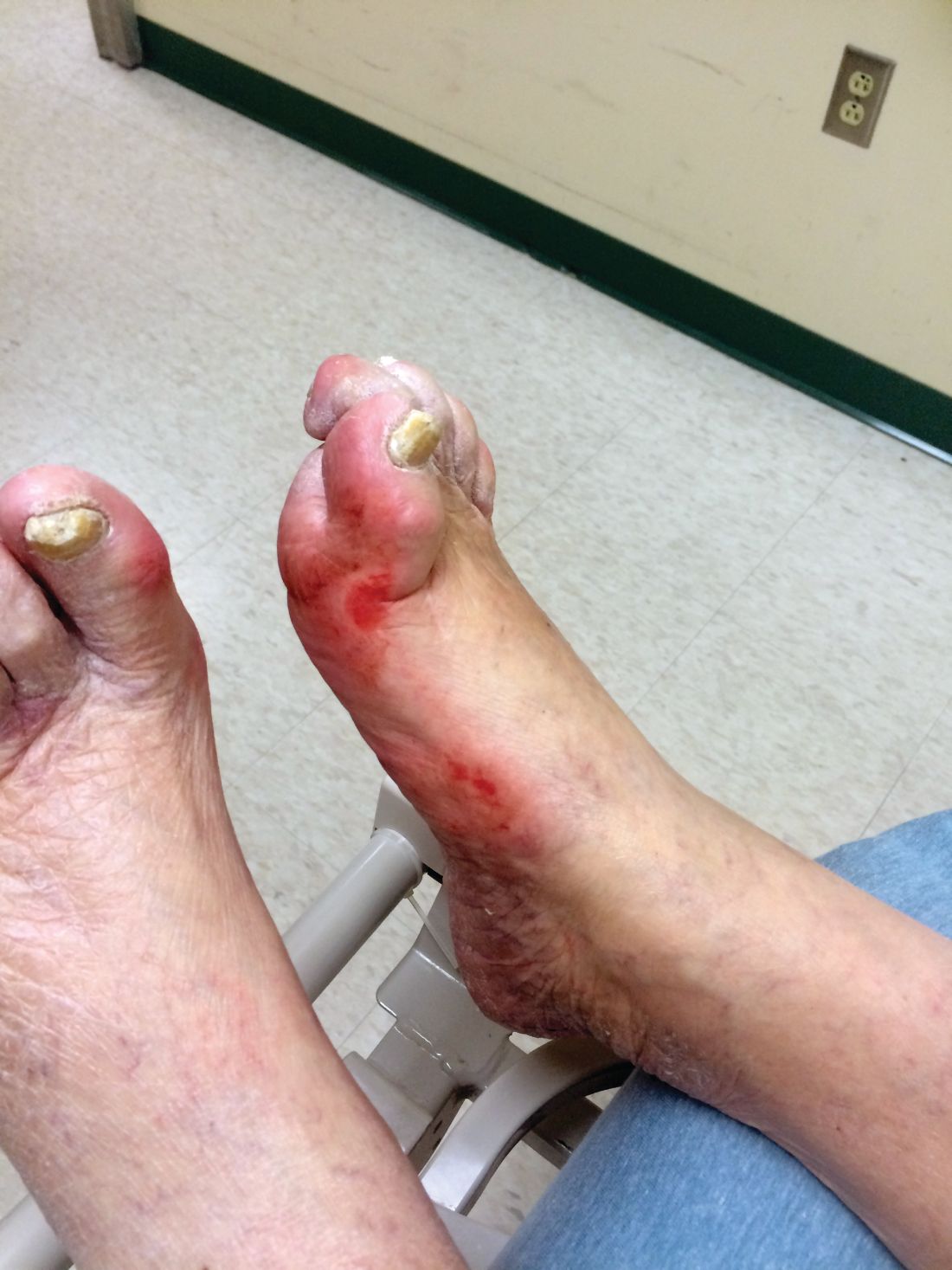
Diabetic kidney disease, retinopathy associated with PAD in patients with foot ulcers
Patients with diabetic foot ulcers have a high incidence of associated chronic vascular disease, including kidney disease, retinopathy, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). In addition, according to a study reported by Magdy H. Megallaa, MD, and colleagues at Alexandria (Egypt) University.
Their cross-sectional study, published in Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, comprised 180 type 2 diabetic patients (aged 30-70 years) with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) who attended an outpatient clinic between July and December 2017.
The prevalence of diabetic kidney disease and diabetic retinopathy was 86.1% and 90.0%, respectively, with 86.7% of patients having neuropathic DFUs, 11.1% having ischemic DFUs, and 2.2% having neuroischemic DFUs. The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and PAD was 82% and 20%, respectively.
Using albuminuria as a measure of diabetic kidney disease, the researchers found that 86.1% of the patients had albuminuria and that there was a statistically significant association between albuminuria and the patient’s vibration reception threshold (VPT), a measure of diabetic neuropathy (P less than .001), and the ankle brachial index (ABI), a measure of PAD (P less than .031).
In addition, there was a statistically significant association between diabetic retinopathy and VPT (P less than .008) and between diabetic retinopathy and ABI (P less than .001).
“Albuminuria, diabetic retinopathy and peripheral neuropathy are very common among those patients and strongly associated with risk factors of diabetic foot ulceration,” the researchers concluded.
They reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Megallaa MH et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Mar-Apr;13(2):1287-92.
Patients with diabetic foot ulcers have a high incidence of associated chronic vascular disease, including kidney disease, retinopathy, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). In addition, according to a study reported by Magdy H. Megallaa, MD, and colleagues at Alexandria (Egypt) University.
Their cross-sectional study, published in Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, comprised 180 type 2 diabetic patients (aged 30-70 years) with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) who attended an outpatient clinic between July and December 2017.
The prevalence of diabetic kidney disease and diabetic retinopathy was 86.1% and 90.0%, respectively, with 86.7% of patients having neuropathic DFUs, 11.1% having ischemic DFUs, and 2.2% having neuroischemic DFUs. The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and PAD was 82% and 20%, respectively.
Using albuminuria as a measure of diabetic kidney disease, the researchers found that 86.1% of the patients had albuminuria and that there was a statistically significant association between albuminuria and the patient’s vibration reception threshold (VPT), a measure of diabetic neuropathy (P less than .001), and the ankle brachial index (ABI), a measure of PAD (P less than .031).
In addition, there was a statistically significant association between diabetic retinopathy and VPT (P less than .008) and between diabetic retinopathy and ABI (P less than .001).
“Albuminuria, diabetic retinopathy and peripheral neuropathy are very common among those patients and strongly associated with risk factors of diabetic foot ulceration,” the researchers concluded.
They reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Megallaa MH et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Mar-Apr;13(2):1287-92.
Patients with diabetic foot ulcers have a high incidence of associated chronic vascular disease, including kidney disease, retinopathy, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). In addition, according to a study reported by Magdy H. Megallaa, MD, and colleagues at Alexandria (Egypt) University.
Their cross-sectional study, published in Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, comprised 180 type 2 diabetic patients (aged 30-70 years) with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) who attended an outpatient clinic between July and December 2017.
The prevalence of diabetic kidney disease and diabetic retinopathy was 86.1% and 90.0%, respectively, with 86.7% of patients having neuropathic DFUs, 11.1% having ischemic DFUs, and 2.2% having neuroischemic DFUs. The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and PAD was 82% and 20%, respectively.
Using albuminuria as a measure of diabetic kidney disease, the researchers found that 86.1% of the patients had albuminuria and that there was a statistically significant association between albuminuria and the patient’s vibration reception threshold (VPT), a measure of diabetic neuropathy (P less than .001), and the ankle brachial index (ABI), a measure of PAD (P less than .031).
In addition, there was a statistically significant association between diabetic retinopathy and VPT (P less than .008) and between diabetic retinopathy and ABI (P less than .001).
“Albuminuria, diabetic retinopathy and peripheral neuropathy are very common among those patients and strongly associated with risk factors of diabetic foot ulceration,” the researchers concluded.
They reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Megallaa MH et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Mar-Apr;13(2):1287-92.
FROM DIABETES & METABOLIC SYNDROME: CLINICAL RESEARCH & REVIEWS
PAD tied to higher prevalence of LV diastolic dysfunction
Patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD) were also more likely to have left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, according to a study published in the Journal of Cardiology.
The study enrolled 1,121 patients with preserved left ventricular (LV) systolic function. The mean age was 68 years and 56% of patients were men. A total of 200 patients (17.8%) had PAD; 33.0% of these had no symptoms, 54.5% had intermittent symptoms, and 12.5% had critical ischemia, according to Koji Yanaka, MD, and colleagues at the Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that PAD was an independent predictor of LV diastolic dysfunction (adjusted odds ratio, 1.77; P = .01).
“The prevalence of LV diastolic dysfunction was higher in patients with PAD than those without PAD. These findings suggest that patients with PAD should be evaluated not only for LV systolic but also diastolic function in echocardiography,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Yanaka K et al. J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 18. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.01.011.
Patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD) were also more likely to have left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, according to a study published in the Journal of Cardiology.
The study enrolled 1,121 patients with preserved left ventricular (LV) systolic function. The mean age was 68 years and 56% of patients were men. A total of 200 patients (17.8%) had PAD; 33.0% of these had no symptoms, 54.5% had intermittent symptoms, and 12.5% had critical ischemia, according to Koji Yanaka, MD, and colleagues at the Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that PAD was an independent predictor of LV diastolic dysfunction (adjusted odds ratio, 1.77; P = .01).
“The prevalence of LV diastolic dysfunction was higher in patients with PAD than those without PAD. These findings suggest that patients with PAD should be evaluated not only for LV systolic but also diastolic function in echocardiography,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Yanaka K et al. J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 18. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.01.011.
Patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD) were also more likely to have left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, according to a study published in the Journal of Cardiology.
The study enrolled 1,121 patients with preserved left ventricular (LV) systolic function. The mean age was 68 years and 56% of patients were men. A total of 200 patients (17.8%) had PAD; 33.0% of these had no symptoms, 54.5% had intermittent symptoms, and 12.5% had critical ischemia, according to Koji Yanaka, MD, and colleagues at the Hyogo College of Medicine, Nishinomiya, Japan.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that PAD was an independent predictor of LV diastolic dysfunction (adjusted odds ratio, 1.77; P = .01).
“The prevalence of LV diastolic dysfunction was higher in patients with PAD than those without PAD. These findings suggest that patients with PAD should be evaluated not only for LV systolic but also diastolic function in echocardiography,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Yanaka K et al. J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 18. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.01.011.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY
HCV-infected patients in the ED should be tested for advanced liver fibrosis
More than one-third of hepatitis C virus-infected patients in the emergency department (ED) were found to have advanced liver fibrosis and higher mortality, according to the results of a retrospective study of 113 known patients with HCV at a single institution.
As part of an ongoing HCV linkage-to-care (LTC) program, HCV-infected ED patients were retrospectively identified. Components of FIB-4 (a noninvasive serum fibrosis index, which includes age, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and platelet count), were abstracted. Patients with an FIB-4 greater than 3.25 were classified with advanced fibrosis and characterized with regard to downstream outcomes at 1 year after enrollment.
The 1-year outcomes after the ED encounter for the 113 patients showed 38 with and 75 patients without advanced fibrosis. Among these, 72 (96%) and 34 (89.5%), respectively, agreed to be linked to HCV care. Ten patients of the total number of patients died within the 1-year follow-up. For those HCV-infected patients with advanced liver fibrosis compared to those without, all-cause mortality was more than fourfold higher, (18.4% [7 patients] vs. 4.0% [3 patients], P = .030), according to Yu-Hsiang Hsieh, PhD, associate professor of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and his colleagues (Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90).
“Given the substantial burden of HCV-related illness in urban ED patients nationally, and the recognized fact that EDs are often the only point of contact with the health care system for many of these patients, we propose incorporating FIB-4 based rapid assessment into ED-based HCV screening and LTC programs in order to prioritize LTC for patients with advanced liver fibrosis, as well as routine ED clinical practice,” the researchers concluded.
They reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Yu-Hsiang Hsieh Y-H, Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90.
More than one-third of hepatitis C virus-infected patients in the emergency department (ED) were found to have advanced liver fibrosis and higher mortality, according to the results of a retrospective study of 113 known patients with HCV at a single institution.
As part of an ongoing HCV linkage-to-care (LTC) program, HCV-infected ED patients were retrospectively identified. Components of FIB-4 (a noninvasive serum fibrosis index, which includes age, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and platelet count), were abstracted. Patients with an FIB-4 greater than 3.25 were classified with advanced fibrosis and characterized with regard to downstream outcomes at 1 year after enrollment.
The 1-year outcomes after the ED encounter for the 113 patients showed 38 with and 75 patients without advanced fibrosis. Among these, 72 (96%) and 34 (89.5%), respectively, agreed to be linked to HCV care. Ten patients of the total number of patients died within the 1-year follow-up. For those HCV-infected patients with advanced liver fibrosis compared to those without, all-cause mortality was more than fourfold higher, (18.4% [7 patients] vs. 4.0% [3 patients], P = .030), according to Yu-Hsiang Hsieh, PhD, associate professor of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and his colleagues (Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90).
“Given the substantial burden of HCV-related illness in urban ED patients nationally, and the recognized fact that EDs are often the only point of contact with the health care system for many of these patients, we propose incorporating FIB-4 based rapid assessment into ED-based HCV screening and LTC programs in order to prioritize LTC for patients with advanced liver fibrosis, as well as routine ED clinical practice,” the researchers concluded.
They reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Yu-Hsiang Hsieh Y-H, Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90.
More than one-third of hepatitis C virus-infected patients in the emergency department (ED) were found to have advanced liver fibrosis and higher mortality, according to the results of a retrospective study of 113 known patients with HCV at a single institution.
As part of an ongoing HCV linkage-to-care (LTC) program, HCV-infected ED patients were retrospectively identified. Components of FIB-4 (a noninvasive serum fibrosis index, which includes age, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and platelet count), were abstracted. Patients with an FIB-4 greater than 3.25 were classified with advanced fibrosis and characterized with regard to downstream outcomes at 1 year after enrollment.
The 1-year outcomes after the ED encounter for the 113 patients showed 38 with and 75 patients without advanced fibrosis. Among these, 72 (96%) and 34 (89.5%), respectively, agreed to be linked to HCV care. Ten patients of the total number of patients died within the 1-year follow-up. For those HCV-infected patients with advanced liver fibrosis compared to those without, all-cause mortality was more than fourfold higher, (18.4% [7 patients] vs. 4.0% [3 patients], P = .030), according to Yu-Hsiang Hsieh, PhD, associate professor of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and his colleagues (Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90).
“Given the substantial burden of HCV-related illness in urban ED patients nationally, and the recognized fact that EDs are often the only point of contact with the health care system for many of these patients, we propose incorporating FIB-4 based rapid assessment into ED-based HCV screening and LTC programs in order to prioritize LTC for patients with advanced liver fibrosis, as well as routine ED clinical practice,” the researchers concluded.
They reported having no conflicts.
SOURCE: Yu-Hsiang Hsieh Y-H, Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37[2]:286-90.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Possible mechanism for fluoroquinolone-induced aortopathy uncovered
A new study finds that patients taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics may be at higher risk of aortopathy in part because of human aortic myofibroblast–mediated extracellular matrix (ECM) dysregulation.
“Emerging evidence supports pharmacologic-associated aortopathy in patients receiving fluoroquinolone [FQ] antibiotics,” said first author David G. Guzzardi, PhD, and his colleagues, citing previous research showing that, “compared with patients receiving amoxicillin antibiotics, those receiving FQ have a 66% higher risk of aneurysm or dissection within a 2-month period after commencing FQ use.”
Based upon such data, the Food and Drug Administration issued a December 2018 warning about the increased risk of ruptures or tears in the aorta with fluoroquinolone antibiotics in certain patients, updating their May 2017 warning regarding “disabling and potentially permanent side effects of the tendons, muscles, joints, nerves, and central nervous system that can occur together in the same patient,” upon exposure to this class of antibiotics. Earlier in 2018, the FDA had reinforced their safety information about serious and potentially fatal low blood sugar levels and mental health side effects with fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues at the University of Calgary (Alta.) performed a study to attempt to determine the possible cellular mechanisms for the observed aortopathy. In their study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues isolated human aortic myofibroblasts from nine patients with aortopathy who were undergoing elective ascending aortic resection.
Following exposure of cells to FQ, the researchers assessed secreted matrix metalloproteinases relative to tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs). In addition, they examined ECM degradation by using a three-dimensional gelatin-fluorescein isothiocyanate fluorescence microgel assay. Aortic cellular collagen type I expression following FQ exposure was determined by immunoblotting and immunofluorescent staining. Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues also looked at cell apoptosis, necrosis, and metabolic viability using two versions of vital staining.
They found that FQ exposure significantly decreased aortic cell TIMP-1 (P less than .004) and TIMP-2 (P less than .0004) protein expression, compared with controls, and the ratio of matrix metalloproteinase 9/TIMP-2 was increased (P less than .01). This suggests an increased capacity for ECM degradation after FQ exposure, according to the researchers.
In addition, FQ exposure attenuated collagen type I expression as assessed by immunoblotting (P less than .002) and immunofluorescence (P less than .02).
“FQ induces human aortic myofibroblast–mediated ECM dysregulation by decreasing TIMP expression and preventing compensatory collagen deposition. These data provide novel insights into the mechanisms that may underlie the clinical association of FQ exposure and increased risk of acute aortic events in the community. Our data suggest cautious use of FQ in selected patient populations with preexistent aortopathy and connective tissue disorders,” the researchers concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, while warning that these are preliminary observations based upon a small number of patients with aortopathy, Ari A. Mennander, MD, PhD, of Tampere (Finland) University, wrote that, “for the first time, the wild theory of fluoroquinolone-associated aortopathy has a molecular hint that is based on collagen degeneration and progression of aortic disease. ... This theory is in line with previous observations revealing antifibrotic activity and decreased collagen-1 protein expression with fluoroquinolones. The enigmatic puzzle of the progression of some aortic events may alarmingly be iatrogenic, and the clinician may wisely consider a prudent use of fluoroquinolones in patients with aortic dilatation.”
The authors and commentators reported that they had no commercial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Guzzardi DG et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:109-19.
The issue of fluoroquinolones is certainly of concern. I wonder how many of my patients who have suffered a ruptured aneurysm were on one of these drugs? In the last few years, Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin) were commonly used by our family practice and internal medicine colleagues for almost all outpatient infections. It was so common that even my wife, who is not a physician, would request Cipro whenever she had a sneeze. We would also bring large bottles of Cipro every time we went traveling to some exotic destination, reassuring ourselves that the only “runs” we would have would be in the airport trying to catch a flight. A cousin of mine, prescribed Levaquin by a well-meaning physician while he was cruising the Nile River, ruptured his Achilles tendon.
Russell H. Samson, MD, FACS, DFSVS , is a clinical professor of surgery at Florida State University, Sarasota, a senior surgeon at Sarasota Vascular Specialists, and President of the Mote Vascular Foundation.
The issue of fluoroquinolones is certainly of concern. I wonder how many of my patients who have suffered a ruptured aneurysm were on one of these drugs? In the last few years, Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin) were commonly used by our family practice and internal medicine colleagues for almost all outpatient infections. It was so common that even my wife, who is not a physician, would request Cipro whenever she had a sneeze. We would also bring large bottles of Cipro every time we went traveling to some exotic destination, reassuring ourselves that the only “runs” we would have would be in the airport trying to catch a flight. A cousin of mine, prescribed Levaquin by a well-meaning physician while he was cruising the Nile River, ruptured his Achilles tendon.
Russell H. Samson, MD, FACS, DFSVS , is a clinical professor of surgery at Florida State University, Sarasota, a senior surgeon at Sarasota Vascular Specialists, and President of the Mote Vascular Foundation.
The issue of fluoroquinolones is certainly of concern. I wonder how many of my patients who have suffered a ruptured aneurysm were on one of these drugs? In the last few years, Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin) were commonly used by our family practice and internal medicine colleagues for almost all outpatient infections. It was so common that even my wife, who is not a physician, would request Cipro whenever she had a sneeze. We would also bring large bottles of Cipro every time we went traveling to some exotic destination, reassuring ourselves that the only “runs” we would have would be in the airport trying to catch a flight. A cousin of mine, prescribed Levaquin by a well-meaning physician while he was cruising the Nile River, ruptured his Achilles tendon.
Russell H. Samson, MD, FACS, DFSVS , is a clinical professor of surgery at Florida State University, Sarasota, a senior surgeon at Sarasota Vascular Specialists, and President of the Mote Vascular Foundation.
A new study finds that patients taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics may be at higher risk of aortopathy in part because of human aortic myofibroblast–mediated extracellular matrix (ECM) dysregulation.
“Emerging evidence supports pharmacologic-associated aortopathy in patients receiving fluoroquinolone [FQ] antibiotics,” said first author David G. Guzzardi, PhD, and his colleagues, citing previous research showing that, “compared with patients receiving amoxicillin antibiotics, those receiving FQ have a 66% higher risk of aneurysm or dissection within a 2-month period after commencing FQ use.”
Based upon such data, the Food and Drug Administration issued a December 2018 warning about the increased risk of ruptures or tears in the aorta with fluoroquinolone antibiotics in certain patients, updating their May 2017 warning regarding “disabling and potentially permanent side effects of the tendons, muscles, joints, nerves, and central nervous system that can occur together in the same patient,” upon exposure to this class of antibiotics. Earlier in 2018, the FDA had reinforced their safety information about serious and potentially fatal low blood sugar levels and mental health side effects with fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues at the University of Calgary (Alta.) performed a study to attempt to determine the possible cellular mechanisms for the observed aortopathy. In their study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues isolated human aortic myofibroblasts from nine patients with aortopathy who were undergoing elective ascending aortic resection.
Following exposure of cells to FQ, the researchers assessed secreted matrix metalloproteinases relative to tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs). In addition, they examined ECM degradation by using a three-dimensional gelatin-fluorescein isothiocyanate fluorescence microgel assay. Aortic cellular collagen type I expression following FQ exposure was determined by immunoblotting and immunofluorescent staining. Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues also looked at cell apoptosis, necrosis, and metabolic viability using two versions of vital staining.
They found that FQ exposure significantly decreased aortic cell TIMP-1 (P less than .004) and TIMP-2 (P less than .0004) protein expression, compared with controls, and the ratio of matrix metalloproteinase 9/TIMP-2 was increased (P less than .01). This suggests an increased capacity for ECM degradation after FQ exposure, according to the researchers.
In addition, FQ exposure attenuated collagen type I expression as assessed by immunoblotting (P less than .002) and immunofluorescence (P less than .02).
“FQ induces human aortic myofibroblast–mediated ECM dysregulation by decreasing TIMP expression and preventing compensatory collagen deposition. These data provide novel insights into the mechanisms that may underlie the clinical association of FQ exposure and increased risk of acute aortic events in the community. Our data suggest cautious use of FQ in selected patient populations with preexistent aortopathy and connective tissue disorders,” the researchers concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, while warning that these are preliminary observations based upon a small number of patients with aortopathy, Ari A. Mennander, MD, PhD, of Tampere (Finland) University, wrote that, “for the first time, the wild theory of fluoroquinolone-associated aortopathy has a molecular hint that is based on collagen degeneration and progression of aortic disease. ... This theory is in line with previous observations revealing antifibrotic activity and decreased collagen-1 protein expression with fluoroquinolones. The enigmatic puzzle of the progression of some aortic events may alarmingly be iatrogenic, and the clinician may wisely consider a prudent use of fluoroquinolones in patients with aortic dilatation.”
The authors and commentators reported that they had no commercial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Guzzardi DG et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:109-19.
A new study finds that patients taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics may be at higher risk of aortopathy in part because of human aortic myofibroblast–mediated extracellular matrix (ECM) dysregulation.
“Emerging evidence supports pharmacologic-associated aortopathy in patients receiving fluoroquinolone [FQ] antibiotics,” said first author David G. Guzzardi, PhD, and his colleagues, citing previous research showing that, “compared with patients receiving amoxicillin antibiotics, those receiving FQ have a 66% higher risk of aneurysm or dissection within a 2-month period after commencing FQ use.”
Based upon such data, the Food and Drug Administration issued a December 2018 warning about the increased risk of ruptures or tears in the aorta with fluoroquinolone antibiotics in certain patients, updating their May 2017 warning regarding “disabling and potentially permanent side effects of the tendons, muscles, joints, nerves, and central nervous system that can occur together in the same patient,” upon exposure to this class of antibiotics. Earlier in 2018, the FDA had reinforced their safety information about serious and potentially fatal low blood sugar levels and mental health side effects with fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues at the University of Calgary (Alta.) performed a study to attempt to determine the possible cellular mechanisms for the observed aortopathy. In their study published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues isolated human aortic myofibroblasts from nine patients with aortopathy who were undergoing elective ascending aortic resection.
Following exposure of cells to FQ, the researchers assessed secreted matrix metalloproteinases relative to tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs). In addition, they examined ECM degradation by using a three-dimensional gelatin-fluorescein isothiocyanate fluorescence microgel assay. Aortic cellular collagen type I expression following FQ exposure was determined by immunoblotting and immunofluorescent staining. Dr. Guzzardi and his colleagues also looked at cell apoptosis, necrosis, and metabolic viability using two versions of vital staining.
They found that FQ exposure significantly decreased aortic cell TIMP-1 (P less than .004) and TIMP-2 (P less than .0004) protein expression, compared with controls, and the ratio of matrix metalloproteinase 9/TIMP-2 was increased (P less than .01). This suggests an increased capacity for ECM degradation after FQ exposure, according to the researchers.
In addition, FQ exposure attenuated collagen type I expression as assessed by immunoblotting (P less than .002) and immunofluorescence (P less than .02).
“FQ induces human aortic myofibroblast–mediated ECM dysregulation by decreasing TIMP expression and preventing compensatory collagen deposition. These data provide novel insights into the mechanisms that may underlie the clinical association of FQ exposure and increased risk of acute aortic events in the community. Our data suggest cautious use of FQ in selected patient populations with preexistent aortopathy and connective tissue disorders,” the researchers concluded.
In an accompanying editorial, while warning that these are preliminary observations based upon a small number of patients with aortopathy, Ari A. Mennander, MD, PhD, of Tampere (Finland) University, wrote that, “for the first time, the wild theory of fluoroquinolone-associated aortopathy has a molecular hint that is based on collagen degeneration and progression of aortic disease. ... This theory is in line with previous observations revealing antifibrotic activity and decreased collagen-1 protein expression with fluoroquinolones. The enigmatic puzzle of the progression of some aortic events may alarmingly be iatrogenic, and the clinician may wisely consider a prudent use of fluoroquinolones in patients with aortic dilatation.”
The authors and commentators reported that they had no commercial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Guzzardi DG et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157:109-19.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Adult HIV patients should receive standard vaccinations, with caveats
Patients infected with HIV have an increased risk of mortality and morbidity from diseases that are preventable with vaccines. Undervaccination of these patients poses a major concern, according to a literature review of the vaccine response in the adult patient with HIV published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Despite the fact that data are limited, patients infected with HIV are advised to receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, according to Firas El Chaer, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and his colleague.
HIV patients are of particular concern regarding vaccination, because, despite the use of retroviral therapy, CD4+ T-lymphocytes in individuals infected with HIV remain lower than in those without HIV. In addition, HIV causes an inappropriate response to B-cell stimulation, which results in suboptimal primary and secondary response to vaccination, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Despite this and initial concerns about vaccine safety in this population, it is now recommended that adult patients infected with HIV receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, they stated.
Inactivated or subunit vaccines
Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine is not recommended under current guidelines for individuals older than age 18 with HIV infection, unless they have a clinical indication.
Vaccination against hepatitis A virus is recommended for HIV-infected patients who are hepatitis A virus seronegative and have chronic liver disease, men who have sex with men, intravenous drug users, and travelers to endemic regions. However, research has shown that the immunogenicity of the vaccine is lower in patients with HIV than in uninfected individuals. It was found that the CD4 count at the time of vaccination, not the CD4 low point, was the major predictor of the immune response.
Patients coinfected with HIV and hepatitis B virus have an 8-fold and 19-fold increase in mortality, respectively, compared with either virus monoinfection. Although vaccination is recommended, the optimal hepatitis B virus vaccination schedule in patients with HIV remains controversial, according to the authors. They indicated that new strategies to improve hepatitis B virus vaccine immunogenicity for those infected with HIV are needed.
Individuals infected with HIV have been found to have a higher risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The safety and immunogenicity results and prospect of benefits has led to a consensus on the benefit of vaccinating HIV-infected patients who meet the HPV vaccine age criteria, the authors indicated.
With regard to standard flu vaccinations: “An annual inactivated influenza vaccine is recommended during the influenza season for all adult individuals with HIV; however, a live attenuated influenza vaccine is contraindicated in this population,” according to the review.
Patients with HIV have a more than 10-fold increased risk of invasive meningococcal disease, compared with the general population, with the risk being particularly higher in those individuals with CD4 counts less than 200 cells/mm3 and in men who have sex with men in cities with meningococcal outbreaks. For these reasons, the “quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV regardless of their CD4 count, with 2-dose primary series at least 2 months apart and with a booster every 5 years.”
Pneumonia is known to be especially dangerous in the HIV-infected population. With regard to pneumonia vaccination, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV, regardless of their CD4 cell counts. According to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague, it should be followed by the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at least 8 weeks later as a prime-boost regimen, preferably when CD4 counts are greater than 200 cells/mm3 and in patients receiving ART.
“Tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccines are recommended once for all individuals infected with HIV, regardless of the CD4 count, with a tetanus toxoid and diphtheria toxoid booster every 10 years,” according to the review.
Live vaccines
Live vaccines are a concerning issue for HIV-infected adults and recommendations for use are generally tied to the CD4 T-cell count. The measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine seems to be safe in patients infected with HIV with a CD4 count greater than 200 cells/mm3, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Similarly, patients with HIV with CD4 counts greater than 200 cells/mm3 and no evidence of documented immunity to varicella should receive the varicella vaccine.
In contrast, the live, attenuated varicella zoster virus vaccine is not recommended for patients infected with HIV, and it is contraindicated if CD4 count is less than 200 cells/mm3. Recently, a herpes zoster subunit vaccine (HZ/su) was tested in a phase 1/2a randomized, placebo-controlled study and was found to be safe and immunogenic regardless of CD4 count, although it has not yet been given a specific recommendation for immunocompromised patients.
“With the widespread use of ART resulting in better HIV control, ,” the authors concluded.
The study was not sponsored. Dr. El Chaer and his colleague reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: El Chaer F et al. Am J Med. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.12.011.
Patients infected with HIV have an increased risk of mortality and morbidity from diseases that are preventable with vaccines. Undervaccination of these patients poses a major concern, according to a literature review of the vaccine response in the adult patient with HIV published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Despite the fact that data are limited, patients infected with HIV are advised to receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, according to Firas El Chaer, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and his colleague.
HIV patients are of particular concern regarding vaccination, because, despite the use of retroviral therapy, CD4+ T-lymphocytes in individuals infected with HIV remain lower than in those without HIV. In addition, HIV causes an inappropriate response to B-cell stimulation, which results in suboptimal primary and secondary response to vaccination, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Despite this and initial concerns about vaccine safety in this population, it is now recommended that adult patients infected with HIV receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, they stated.
Inactivated or subunit vaccines
Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine is not recommended under current guidelines for individuals older than age 18 with HIV infection, unless they have a clinical indication.
Vaccination against hepatitis A virus is recommended for HIV-infected patients who are hepatitis A virus seronegative and have chronic liver disease, men who have sex with men, intravenous drug users, and travelers to endemic regions. However, research has shown that the immunogenicity of the vaccine is lower in patients with HIV than in uninfected individuals. It was found that the CD4 count at the time of vaccination, not the CD4 low point, was the major predictor of the immune response.
Patients coinfected with HIV and hepatitis B virus have an 8-fold and 19-fold increase in mortality, respectively, compared with either virus monoinfection. Although vaccination is recommended, the optimal hepatitis B virus vaccination schedule in patients with HIV remains controversial, according to the authors. They indicated that new strategies to improve hepatitis B virus vaccine immunogenicity for those infected with HIV are needed.
Individuals infected with HIV have been found to have a higher risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The safety and immunogenicity results and prospect of benefits has led to a consensus on the benefit of vaccinating HIV-infected patients who meet the HPV vaccine age criteria, the authors indicated.
With regard to standard flu vaccinations: “An annual inactivated influenza vaccine is recommended during the influenza season for all adult individuals with HIV; however, a live attenuated influenza vaccine is contraindicated in this population,” according to the review.
Patients with HIV have a more than 10-fold increased risk of invasive meningococcal disease, compared with the general population, with the risk being particularly higher in those individuals with CD4 counts less than 200 cells/mm3 and in men who have sex with men in cities with meningococcal outbreaks. For these reasons, the “quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV regardless of their CD4 count, with 2-dose primary series at least 2 months apart and with a booster every 5 years.”
Pneumonia is known to be especially dangerous in the HIV-infected population. With regard to pneumonia vaccination, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV, regardless of their CD4 cell counts. According to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague, it should be followed by the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at least 8 weeks later as a prime-boost regimen, preferably when CD4 counts are greater than 200 cells/mm3 and in patients receiving ART.
“Tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccines are recommended once for all individuals infected with HIV, regardless of the CD4 count, with a tetanus toxoid and diphtheria toxoid booster every 10 years,” according to the review.
Live vaccines
Live vaccines are a concerning issue for HIV-infected adults and recommendations for use are generally tied to the CD4 T-cell count. The measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine seems to be safe in patients infected with HIV with a CD4 count greater than 200 cells/mm3, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Similarly, patients with HIV with CD4 counts greater than 200 cells/mm3 and no evidence of documented immunity to varicella should receive the varicella vaccine.
In contrast, the live, attenuated varicella zoster virus vaccine is not recommended for patients infected with HIV, and it is contraindicated if CD4 count is less than 200 cells/mm3. Recently, a herpes zoster subunit vaccine (HZ/su) was tested in a phase 1/2a randomized, placebo-controlled study and was found to be safe and immunogenic regardless of CD4 count, although it has not yet been given a specific recommendation for immunocompromised patients.
“With the widespread use of ART resulting in better HIV control, ,” the authors concluded.
The study was not sponsored. Dr. El Chaer and his colleague reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: El Chaer F et al. Am J Med. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.12.011.
Patients infected with HIV have an increased risk of mortality and morbidity from diseases that are preventable with vaccines. Undervaccination of these patients poses a major concern, according to a literature review of the vaccine response in the adult patient with HIV published in The American Journal of Medicine.
Despite the fact that data are limited, patients infected with HIV are advised to receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, according to Firas El Chaer, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and his colleague.
HIV patients are of particular concern regarding vaccination, because, despite the use of retroviral therapy, CD4+ T-lymphocytes in individuals infected with HIV remain lower than in those without HIV. In addition, HIV causes an inappropriate response to B-cell stimulation, which results in suboptimal primary and secondary response to vaccination, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Despite this and initial concerns about vaccine safety in this population, it is now recommended that adult patients infected with HIV receive their age-specific and risk group−based vaccines, they stated.
Inactivated or subunit vaccines
Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine is not recommended under current guidelines for individuals older than age 18 with HIV infection, unless they have a clinical indication.
Vaccination against hepatitis A virus is recommended for HIV-infected patients who are hepatitis A virus seronegative and have chronic liver disease, men who have sex with men, intravenous drug users, and travelers to endemic regions. However, research has shown that the immunogenicity of the vaccine is lower in patients with HIV than in uninfected individuals. It was found that the CD4 count at the time of vaccination, not the CD4 low point, was the major predictor of the immune response.
Patients coinfected with HIV and hepatitis B virus have an 8-fold and 19-fold increase in mortality, respectively, compared with either virus monoinfection. Although vaccination is recommended, the optimal hepatitis B virus vaccination schedule in patients with HIV remains controversial, according to the authors. They indicated that new strategies to improve hepatitis B virus vaccine immunogenicity for those infected with HIV are needed.
Individuals infected with HIV have been found to have a higher risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The safety and immunogenicity results and prospect of benefits has led to a consensus on the benefit of vaccinating HIV-infected patients who meet the HPV vaccine age criteria, the authors indicated.
With regard to standard flu vaccinations: “An annual inactivated influenza vaccine is recommended during the influenza season for all adult individuals with HIV; however, a live attenuated influenza vaccine is contraindicated in this population,” according to the review.
Patients with HIV have a more than 10-fold increased risk of invasive meningococcal disease, compared with the general population, with the risk being particularly higher in those individuals with CD4 counts less than 200 cells/mm3 and in men who have sex with men in cities with meningococcal outbreaks. For these reasons, the “quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV regardless of their CD4 count, with 2-dose primary series at least 2 months apart and with a booster every 5 years.”
Pneumonia is known to be especially dangerous in the HIV-infected population. With regard to pneumonia vaccination, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is recommended for all patients with HIV, regardless of their CD4 cell counts. According to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague, it should be followed by the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at least 8 weeks later as a prime-boost regimen, preferably when CD4 counts are greater than 200 cells/mm3 and in patients receiving ART.
“Tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccines are recommended once for all individuals infected with HIV, regardless of the CD4 count, with a tetanus toxoid and diphtheria toxoid booster every 10 years,” according to the review.
Live vaccines
Live vaccines are a concerning issue for HIV-infected adults and recommendations for use are generally tied to the CD4 T-cell count. The measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine seems to be safe in patients infected with HIV with a CD4 count greater than 200 cells/mm3, according to Dr. El Chaer and his colleague. Similarly, patients with HIV with CD4 counts greater than 200 cells/mm3 and no evidence of documented immunity to varicella should receive the varicella vaccine.
In contrast, the live, attenuated varicella zoster virus vaccine is not recommended for patients infected with HIV, and it is contraindicated if CD4 count is less than 200 cells/mm3. Recently, a herpes zoster subunit vaccine (HZ/su) was tested in a phase 1/2a randomized, placebo-controlled study and was found to be safe and immunogenic regardless of CD4 count, although it has not yet been given a specific recommendation for immunocompromised patients.
“With the widespread use of ART resulting in better HIV control, ,” the authors concluded.
The study was not sponsored. Dr. El Chaer and his colleague reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: El Chaer F et al. Am J Med. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.12.011.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Undervaccination is too common among HIV-infected patients.
Major finding: Data on vaccine effectiveness in HIV patients are limited, but do not contraindicate the need for vaccination.
Study details: Literature review of immunogenicity and vaccine efficacy in HIV-infected adults.
Disclosures: The study was unsponsored and the authors reported they had no conflicts.
Source: El Chaer F et al. Am J Med. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.12.011.