User login
More Than a Health Fair: Preventive Health Care During COVID-19 Vaccine Events
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
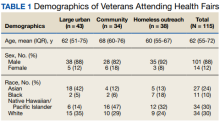
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
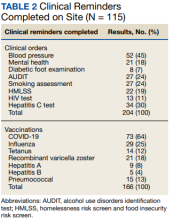
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
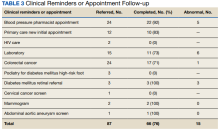
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
Is There a Relationship Between Facility Peer Review Findings and Quality in the Veterans Health Administration?
Hospital leaders report the most common aim of peer review (PR) is to improve quality and patient safety, thus it is a potentially powerful quality improvement (QI) driver.1 “When conducted systematically and credibly, peer review for quality management can result in both short-term and long-term improvements in patient care by revealing areas for improvement in the provision of care,” Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1190 states. “This ultimately contributes to organizational improvements.” At the same time, there are anecdotal concerns that PR may be used punitively and driven by case outcomes rather than by accepted best practices supporting QI.
Studies of the PR process suggest these concerns are valid. A key tenet of QI is standardization. PR is problematic in that regard; studies show poor interrater reliability for judgments on care, as well as hindsight bias—the fact that raters are strongly influenced by the outcome of care, not the process of care.2-5 There are concerns that case selection or review process when not standardized may be wielded as punitive too.6 In this study, we sought to identify the relationship between PR findings and subsequent institution quality metrics. If PR does lead to an improvement in quality, or if quality concerns are managed within the PR committee, it should be possible to identify a measurable relationship between the PR process and a facility’s subsequent quality measures.
A handful of studies describe the association between PR and quality of care. Itri and colleagues noted that random, not standardized PR in radiology does not achieve reductions in diagnostic error rate.7 However, adoption of just culture principles in PR resulted in a significant improvement in facility leaders’ self-reports of quality measures at surveyed institutions.8 The same author reported that increases in PR standardization and integration with performance improvement activities could explain up to 18% of objective quality measure variation.9
We sought to determine whether a specific aspect of the PR process, the PR committee judgment of quality of care by clinicians, was related to medical center quality in a cross-sectional study of 136 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) medical centers. The VHA is a good source of study because there are standardized PR processes and training for committee members and reviewers. Our hypothesis was that medical centers with a higher number of Level 2 (“most experienced and competent clinicians might have managed the case differently”) and Level 3 (“most experienced and competent providers would have managed the case differently”) PR findings would also have lower quality metric scores for processes and outcomes of care.
Methods
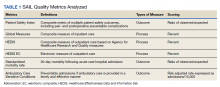
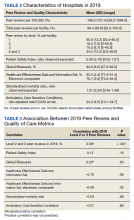
We used PR data from fiscal year 2018 and 2019. VHA PR data are available quarterly and are self-reported by each facility to the VHA Office of Clinical Risk Management. These data are broken down by facility. The following data, when available in both fiscal years 2018 and 2019, were used for this analysis: percent and number of PR that are ranked as level 1, 2, or 3; medical center group (MCG) acuity measure assigned by the VHA (1 is highest, 3 is lowest); and number of PR per 100,000 unique veteran encounters in 2019. Measures of facility quality are drawn from Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning (SAIL) data from 2019, which are available quarterly by facility and are rolling for 12 months. SAIL measures processes and outcomes of care. Table 1 indicates which measures are focused on outcomes vs quality processes.
SAS Version 9.2 was used to perform statistical analyses. We used Spearman correlation to estimate the PR and quality relationship.
Results
There were 136 facilities with 2 years of PR data available. The majority of these facilities (89) were highest complexity MCG 1 facilities; 19 were MCG 2, and 28 were MCG 3. Of 13,515 PRs, most of the 9555 PR findings were level 1 (70.7%). The between-facility range of level 2 and 3 findings was large, varying from 3.5% to nearly 70% in 2019 (Table 2). Findings were similar in 2018; facilities level 2 and 3 ratings ranged from 3.6% to 73.5% of all PR findings.
There was no correlation between most quality measures and facility PR findings (Table 3). The only exception was for Global Measures (GM90), an inpatient process of care measure. Unexpectedly, the correlation was positive—facilities with a higher percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings had better inpatient processes of care SAIL score. The strongest correlation was between 2018 and 2019 PR findings.
Discussion
We hypothesized that a high percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings would be negatively associated with objective facility measures of care processes in SAIL but we did not see this association. The only quality measure associated with PR findings was GM90, a score of inpatient care processes. However, the association was positive, with better performance associated with more level 2 and 3 PR findings.
The best predictor of the proportion of a facility’s PR findings is the previous year’s PR findings. With an R = 0.59, the previous year findings explain about 35% of the variability in level assignment. Our analysis may describe a new bias in PR, in which committees consistently assign either low or high proportions of level 2 and 3 findings. This correlation could be due to individual PR committee culture or composition, but it does not relate to objective quality measures.
Strengths
For this study we use objective measures of PR processes, the assignment of levels of care.
Limitations
Facilities self-report PR outcomes, so there could be errors in reporting. In addition, this study was cross sectional and not longitudinal and it is possible that change in quality measures over time are correlated with PR findings. Future studies using the VHA PR and SAIL data could evaluate whether changes over time, and perhaps in response to level 2 and 3 findings, would be a more sensitive indicator of the impact of the PR process on quality metrics. Future studies could incorporate the relationship between findings from the All Employee Survey, which is conducted annually, such as psychologic safety, as well as the distance the facility has gone on the high reliability organization journey, with PR findings and SAIL metrics. Finally, PR is focused on the practice of an individual clinician, while SAIL quality metrics reflect facility performance. Interventions possibly stay at the clinician level and do not drive subsequent QI processes.
What does this mean for PR? Since the early 1990s, there have been exhortations from experts to improve PR, by adopting a QI model, or for a deeper integration of PR and QI.1,2,10 Just culture tools, which include QI, are promoted as a means to improve PR.8,11,12 Other studies show PR remains problematic in terms of standardization, incorporation of best practices, redesigning systems of care, or demonstrable improvements to facility safety and care quality.1,4,6,8 Several publications have described interventions to improve PR. Deyo-Svedson discussed a program with standardized training and triggers, much like VHA.13 Itri and colleagues standardized PR in radiology to target areas of known diagnostic error, as well as use the issues assessed in PR to perform QI and education. One example of a successful QI effort involved changing the radiology reporting template to make sure areas that are prone to diagnostic error are addressed.7
Conclusions
Since 35% of PR level variance is correlated with prior year’s results, PR committees should look at increased standardization in reviews and findings. We endorse a strong focus on standardization, application of just culture tools to case reviews, and tighter linkage between process and outcome metrics measured by SAIL and PR case finding. Studies should be performed to pilot interventions to improve the linkage between PR and quality, so that greater and faster gains can be made in quality processes and, leading from this, outcomes. Additionally, future research should investigate why some facilities consistently choose higher or lower PR ratings.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. George “Web” Ross for his helpful edits.
1. Edwards MT. In pursuit of quality and safety: an 8-year study of clinical peer review best practices in US hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018;30(8):602-607. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzy069
2. Dans PE. Clinical peer Review: burnishing a tarnished icon. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118(7):566-568. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-118-7-199304010-00014
3. Goldman RL. The reliability of peer assessments of quality of care. JAMA. 1992;267(7):958-960. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480070074034
4. Swaroop R. Disrupting physician clinical practice peer review. Perm J. 2019;23:18-207. doi:10.7812/TPP/18-207
5. Caplan RA, Posner KL, Cheney FW. Effect of outcome on physician judgments of appropriateness of care. JAMA. 1991;265(15):1957–1960. doi:10.1001/jama.1991.03460150061024
6. Vyas D, Hozain AE. Clinical peer review in the United States: history, legal development and subsequent abuse. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(21):6357-6363. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6357
7. Itri JN, Donithan A, Patel SH. Random versus nonrandom peer review: a case for more meaningful peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(7):1045-1052. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.054
8. Edwards MT. An assessment of the impact of just culture on quality and safety in US hospitals. Am J Med Qual. 2018; 33(5):502-508. doi:10.1177/1062860618768057
9. Edwards MT. The objective impact of clinical peer review on hospital quality and safety. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26(2);110-119. doi:10.1177/1062860610380732
10. Berwick DM. Peer review and quality management: are they compatible?. QRB Qual Rev Bull. 1990;16(7):246-251. doi:10.1016/s0097-5990(16)30377-3
11. Volkar JK, Phrampus P, English D, et al. Institution of just culture physician peer review in an academic medical center. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(7):e689-e693. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000449
12. Burns J, Miller T, Weiss JM, Erdfarb A, Silber D, Goldberg-Stein S. Just culture: practical implementation for radiologist peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(3):384-388. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.10.021
13. Deyo-Svendsen ME, Phillips MR, Albright JK, et al. A systematic approach to clinical peer review in a critical access hospital. Qual Manag Health Care. 2016;25(4):213-218. doi:10.1097/QMH.0000000000000113
Hospital leaders report the most common aim of peer review (PR) is to improve quality and patient safety, thus it is a potentially powerful quality improvement (QI) driver.1 “When conducted systematically and credibly, peer review for quality management can result in both short-term and long-term improvements in patient care by revealing areas for improvement in the provision of care,” Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1190 states. “This ultimately contributes to organizational improvements.” At the same time, there are anecdotal concerns that PR may be used punitively and driven by case outcomes rather than by accepted best practices supporting QI.
Studies of the PR process suggest these concerns are valid. A key tenet of QI is standardization. PR is problematic in that regard; studies show poor interrater reliability for judgments on care, as well as hindsight bias—the fact that raters are strongly influenced by the outcome of care, not the process of care.2-5 There are concerns that case selection or review process when not standardized may be wielded as punitive too.6 In this study, we sought to identify the relationship between PR findings and subsequent institution quality metrics. If PR does lead to an improvement in quality, or if quality concerns are managed within the PR committee, it should be possible to identify a measurable relationship between the PR process and a facility’s subsequent quality measures.
A handful of studies describe the association between PR and quality of care. Itri and colleagues noted that random, not standardized PR in radiology does not achieve reductions in diagnostic error rate.7 However, adoption of just culture principles in PR resulted in a significant improvement in facility leaders’ self-reports of quality measures at surveyed institutions.8 The same author reported that increases in PR standardization and integration with performance improvement activities could explain up to 18% of objective quality measure variation.9
We sought to determine whether a specific aspect of the PR process, the PR committee judgment of quality of care by clinicians, was related to medical center quality in a cross-sectional study of 136 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) medical centers. The VHA is a good source of study because there are standardized PR processes and training for committee members and reviewers. Our hypothesis was that medical centers with a higher number of Level 2 (“most experienced and competent clinicians might have managed the case differently”) and Level 3 (“most experienced and competent providers would have managed the case differently”) PR findings would also have lower quality metric scores for processes and outcomes of care.
Methods
We used PR data from fiscal year 2018 and 2019. VHA PR data are available quarterly and are self-reported by each facility to the VHA Office of Clinical Risk Management. These data are broken down by facility. The following data, when available in both fiscal years 2018 and 2019, were used for this analysis: percent and number of PR that are ranked as level 1, 2, or 3; medical center group (MCG) acuity measure assigned by the VHA (1 is highest, 3 is lowest); and number of PR per 100,000 unique veteran encounters in 2019. Measures of facility quality are drawn from Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning (SAIL) data from 2019, which are available quarterly by facility and are rolling for 12 months. SAIL measures processes and outcomes of care. Table 1 indicates which measures are focused on outcomes vs quality processes.
SAS Version 9.2 was used to perform statistical analyses. We used Spearman correlation to estimate the PR and quality relationship.
Results
There were 136 facilities with 2 years of PR data available. The majority of these facilities (89) were highest complexity MCG 1 facilities; 19 were MCG 2, and 28 were MCG 3. Of 13,515 PRs, most of the 9555 PR findings were level 1 (70.7%). The between-facility range of level 2 and 3 findings was large, varying from 3.5% to nearly 70% in 2019 (Table 2). Findings were similar in 2018; facilities level 2 and 3 ratings ranged from 3.6% to 73.5% of all PR findings.
There was no correlation between most quality measures and facility PR findings (Table 3). The only exception was for Global Measures (GM90), an inpatient process of care measure. Unexpectedly, the correlation was positive—facilities with a higher percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings had better inpatient processes of care SAIL score. The strongest correlation was between 2018 and 2019 PR findings.
Discussion
We hypothesized that a high percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings would be negatively associated with objective facility measures of care processes in SAIL but we did not see this association. The only quality measure associated with PR findings was GM90, a score of inpatient care processes. However, the association was positive, with better performance associated with more level 2 and 3 PR findings.
The best predictor of the proportion of a facility’s PR findings is the previous year’s PR findings. With an R = 0.59, the previous year findings explain about 35% of the variability in level assignment. Our analysis may describe a new bias in PR, in which committees consistently assign either low or high proportions of level 2 and 3 findings. This correlation could be due to individual PR committee culture or composition, but it does not relate to objective quality measures.
Strengths
For this study we use objective measures of PR processes, the assignment of levels of care.
Limitations
Facilities self-report PR outcomes, so there could be errors in reporting. In addition, this study was cross sectional and not longitudinal and it is possible that change in quality measures over time are correlated with PR findings. Future studies using the VHA PR and SAIL data could evaluate whether changes over time, and perhaps in response to level 2 and 3 findings, would be a more sensitive indicator of the impact of the PR process on quality metrics. Future studies could incorporate the relationship between findings from the All Employee Survey, which is conducted annually, such as psychologic safety, as well as the distance the facility has gone on the high reliability organization journey, with PR findings and SAIL metrics. Finally, PR is focused on the practice of an individual clinician, while SAIL quality metrics reflect facility performance. Interventions possibly stay at the clinician level and do not drive subsequent QI processes.
What does this mean for PR? Since the early 1990s, there have been exhortations from experts to improve PR, by adopting a QI model, or for a deeper integration of PR and QI.1,2,10 Just culture tools, which include QI, are promoted as a means to improve PR.8,11,12 Other studies show PR remains problematic in terms of standardization, incorporation of best practices, redesigning systems of care, or demonstrable improvements to facility safety and care quality.1,4,6,8 Several publications have described interventions to improve PR. Deyo-Svedson discussed a program with standardized training and triggers, much like VHA.13 Itri and colleagues standardized PR in radiology to target areas of known diagnostic error, as well as use the issues assessed in PR to perform QI and education. One example of a successful QI effort involved changing the radiology reporting template to make sure areas that are prone to diagnostic error are addressed.7
Conclusions
Since 35% of PR level variance is correlated with prior year’s results, PR committees should look at increased standardization in reviews and findings. We endorse a strong focus on standardization, application of just culture tools to case reviews, and tighter linkage between process and outcome metrics measured by SAIL and PR case finding. Studies should be performed to pilot interventions to improve the linkage between PR and quality, so that greater and faster gains can be made in quality processes and, leading from this, outcomes. Additionally, future research should investigate why some facilities consistently choose higher or lower PR ratings.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. George “Web” Ross for his helpful edits.
Hospital leaders report the most common aim of peer review (PR) is to improve quality and patient safety, thus it is a potentially powerful quality improvement (QI) driver.1 “When conducted systematically and credibly, peer review for quality management can result in both short-term and long-term improvements in patient care by revealing areas for improvement in the provision of care,” Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1190 states. “This ultimately contributes to organizational improvements.” At the same time, there are anecdotal concerns that PR may be used punitively and driven by case outcomes rather than by accepted best practices supporting QI.
Studies of the PR process suggest these concerns are valid. A key tenet of QI is standardization. PR is problematic in that regard; studies show poor interrater reliability for judgments on care, as well as hindsight bias—the fact that raters are strongly influenced by the outcome of care, not the process of care.2-5 There are concerns that case selection or review process when not standardized may be wielded as punitive too.6 In this study, we sought to identify the relationship between PR findings and subsequent institution quality metrics. If PR does lead to an improvement in quality, or if quality concerns are managed within the PR committee, it should be possible to identify a measurable relationship between the PR process and a facility’s subsequent quality measures.
A handful of studies describe the association between PR and quality of care. Itri and colleagues noted that random, not standardized PR in radiology does not achieve reductions in diagnostic error rate.7 However, adoption of just culture principles in PR resulted in a significant improvement in facility leaders’ self-reports of quality measures at surveyed institutions.8 The same author reported that increases in PR standardization and integration with performance improvement activities could explain up to 18% of objective quality measure variation.9
We sought to determine whether a specific aspect of the PR process, the PR committee judgment of quality of care by clinicians, was related to medical center quality in a cross-sectional study of 136 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) medical centers. The VHA is a good source of study because there are standardized PR processes and training for committee members and reviewers. Our hypothesis was that medical centers with a higher number of Level 2 (“most experienced and competent clinicians might have managed the case differently”) and Level 3 (“most experienced and competent providers would have managed the case differently”) PR findings would also have lower quality metric scores for processes and outcomes of care.
Methods
We used PR data from fiscal year 2018 and 2019. VHA PR data are available quarterly and are self-reported by each facility to the VHA Office of Clinical Risk Management. These data are broken down by facility. The following data, when available in both fiscal years 2018 and 2019, were used for this analysis: percent and number of PR that are ranked as level 1, 2, or 3; medical center group (MCG) acuity measure assigned by the VHA (1 is highest, 3 is lowest); and number of PR per 100,000 unique veteran encounters in 2019. Measures of facility quality are drawn from Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning (SAIL) data from 2019, which are available quarterly by facility and are rolling for 12 months. SAIL measures processes and outcomes of care. Table 1 indicates which measures are focused on outcomes vs quality processes.
SAS Version 9.2 was used to perform statistical analyses. We used Spearman correlation to estimate the PR and quality relationship.
Results
There were 136 facilities with 2 years of PR data available. The majority of these facilities (89) were highest complexity MCG 1 facilities; 19 were MCG 2, and 28 were MCG 3. Of 13,515 PRs, most of the 9555 PR findings were level 1 (70.7%). The between-facility range of level 2 and 3 findings was large, varying from 3.5% to nearly 70% in 2019 (Table 2). Findings were similar in 2018; facilities level 2 and 3 ratings ranged from 3.6% to 73.5% of all PR findings.
There was no correlation between most quality measures and facility PR findings (Table 3). The only exception was for Global Measures (GM90), an inpatient process of care measure. Unexpectedly, the correlation was positive—facilities with a higher percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings had better inpatient processes of care SAIL score. The strongest correlation was between 2018 and 2019 PR findings.
Discussion
We hypothesized that a high percentage of level 2 and 3 PR findings would be negatively associated with objective facility measures of care processes in SAIL but we did not see this association. The only quality measure associated with PR findings was GM90, a score of inpatient care processes. However, the association was positive, with better performance associated with more level 2 and 3 PR findings.
The best predictor of the proportion of a facility’s PR findings is the previous year’s PR findings. With an R = 0.59, the previous year findings explain about 35% of the variability in level assignment. Our analysis may describe a new bias in PR, in which committees consistently assign either low or high proportions of level 2 and 3 findings. This correlation could be due to individual PR committee culture or composition, but it does not relate to objective quality measures.
Strengths
For this study we use objective measures of PR processes, the assignment of levels of care.
Limitations
Facilities self-report PR outcomes, so there could be errors in reporting. In addition, this study was cross sectional and not longitudinal and it is possible that change in quality measures over time are correlated with PR findings. Future studies using the VHA PR and SAIL data could evaluate whether changes over time, and perhaps in response to level 2 and 3 findings, would be a more sensitive indicator of the impact of the PR process on quality metrics. Future studies could incorporate the relationship between findings from the All Employee Survey, which is conducted annually, such as psychologic safety, as well as the distance the facility has gone on the high reliability organization journey, with PR findings and SAIL metrics. Finally, PR is focused on the practice of an individual clinician, while SAIL quality metrics reflect facility performance. Interventions possibly stay at the clinician level and do not drive subsequent QI processes.
What does this mean for PR? Since the early 1990s, there have been exhortations from experts to improve PR, by adopting a QI model, or for a deeper integration of PR and QI.1,2,10 Just culture tools, which include QI, are promoted as a means to improve PR.8,11,12 Other studies show PR remains problematic in terms of standardization, incorporation of best practices, redesigning systems of care, or demonstrable improvements to facility safety and care quality.1,4,6,8 Several publications have described interventions to improve PR. Deyo-Svedson discussed a program with standardized training and triggers, much like VHA.13 Itri and colleagues standardized PR in radiology to target areas of known diagnostic error, as well as use the issues assessed in PR to perform QI and education. One example of a successful QI effort involved changing the radiology reporting template to make sure areas that are prone to diagnostic error are addressed.7
Conclusions
Since 35% of PR level variance is correlated with prior year’s results, PR committees should look at increased standardization in reviews and findings. We endorse a strong focus on standardization, application of just culture tools to case reviews, and tighter linkage between process and outcome metrics measured by SAIL and PR case finding. Studies should be performed to pilot interventions to improve the linkage between PR and quality, so that greater and faster gains can be made in quality processes and, leading from this, outcomes. Additionally, future research should investigate why some facilities consistently choose higher or lower PR ratings.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. George “Web” Ross for his helpful edits.
1. Edwards MT. In pursuit of quality and safety: an 8-year study of clinical peer review best practices in US hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018;30(8):602-607. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzy069
2. Dans PE. Clinical peer Review: burnishing a tarnished icon. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118(7):566-568. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-118-7-199304010-00014
3. Goldman RL. The reliability of peer assessments of quality of care. JAMA. 1992;267(7):958-960. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480070074034
4. Swaroop R. Disrupting physician clinical practice peer review. Perm J. 2019;23:18-207. doi:10.7812/TPP/18-207
5. Caplan RA, Posner KL, Cheney FW. Effect of outcome on physician judgments of appropriateness of care. JAMA. 1991;265(15):1957–1960. doi:10.1001/jama.1991.03460150061024
6. Vyas D, Hozain AE. Clinical peer review in the United States: history, legal development and subsequent abuse. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(21):6357-6363. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6357
7. Itri JN, Donithan A, Patel SH. Random versus nonrandom peer review: a case for more meaningful peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(7):1045-1052. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.054
8. Edwards MT. An assessment of the impact of just culture on quality and safety in US hospitals. Am J Med Qual. 2018; 33(5):502-508. doi:10.1177/1062860618768057
9. Edwards MT. The objective impact of clinical peer review on hospital quality and safety. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26(2);110-119. doi:10.1177/1062860610380732
10. Berwick DM. Peer review and quality management: are they compatible?. QRB Qual Rev Bull. 1990;16(7):246-251. doi:10.1016/s0097-5990(16)30377-3
11. Volkar JK, Phrampus P, English D, et al. Institution of just culture physician peer review in an academic medical center. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(7):e689-e693. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000449
12. Burns J, Miller T, Weiss JM, Erdfarb A, Silber D, Goldberg-Stein S. Just culture: practical implementation for radiologist peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(3):384-388. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.10.021
13. Deyo-Svendsen ME, Phillips MR, Albright JK, et al. A systematic approach to clinical peer review in a critical access hospital. Qual Manag Health Care. 2016;25(4):213-218. doi:10.1097/QMH.0000000000000113
1. Edwards MT. In pursuit of quality and safety: an 8-year study of clinical peer review best practices in US hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018;30(8):602-607. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzy069
2. Dans PE. Clinical peer Review: burnishing a tarnished icon. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118(7):566-568. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-118-7-199304010-00014
3. Goldman RL. The reliability of peer assessments of quality of care. JAMA. 1992;267(7):958-960. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480070074034
4. Swaroop R. Disrupting physician clinical practice peer review. Perm J. 2019;23:18-207. doi:10.7812/TPP/18-207
5. Caplan RA, Posner KL, Cheney FW. Effect of outcome on physician judgments of appropriateness of care. JAMA. 1991;265(15):1957–1960. doi:10.1001/jama.1991.03460150061024
6. Vyas D, Hozain AE. Clinical peer review in the United States: history, legal development and subsequent abuse. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(21):6357-6363. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6357
7. Itri JN, Donithan A, Patel SH. Random versus nonrandom peer review: a case for more meaningful peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(7):1045-1052. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.054
8. Edwards MT. An assessment of the impact of just culture on quality and safety in US hospitals. Am J Med Qual. 2018; 33(5):502-508. doi:10.1177/1062860618768057
9. Edwards MT. The objective impact of clinical peer review on hospital quality and safety. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26(2);110-119. doi:10.1177/1062860610380732
10. Berwick DM. Peer review and quality management: are they compatible?. QRB Qual Rev Bull. 1990;16(7):246-251. doi:10.1016/s0097-5990(16)30377-3
11. Volkar JK, Phrampus P, English D, et al. Institution of just culture physician peer review in an academic medical center. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(7):e689-e693. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000449
12. Burns J, Miller T, Weiss JM, Erdfarb A, Silber D, Goldberg-Stein S. Just culture: practical implementation for radiologist peer review. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(3):384-388. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.10.021
13. Deyo-Svendsen ME, Phillips MR, Albright JK, et al. A systematic approach to clinical peer review in a critical access hospital. Qual Manag Health Care. 2016;25(4):213-218. doi:10.1097/QMH.0000000000000113