User login
Five-day fever • elevated creatinine levels • kidney transplant 10 months prior • Dx?
THE CASE
On examination, the patient appeared to be in mild distress. His vital signs included: temperature 38.5°C, blood pressure 136/94 mm Hg, pulse 89 beats/min, and respiratory rate 18 breaths/min. Cardiopulmonary, abdominal, and genitourinary examinations were unremarkable. A well-healed scar was seen in the right lower quadrant at the site of the renal allograft and was nontender to palpation.
Laboratory values showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 4.3 × 109/L and an elevated creatinine of 1.16 mg/dL. Six months prior to presentation, his creatinine was 0.98 mg/dL. Blood cultures were obtained, and ceftriaxone (1 g) was given prior to obtaining a urine specimen. A urine dipstick revealed moderate leukocyte esterase, small blood, and 30 mg/dL of protein. Urine microscopy showed >50 WBCs per high power field (hpf), 6-10 red blood cells (RBCs), 30 mg/dL of protein, and an absence of bacteria.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient may be due to acute graft pyelonephritis (AGP) or acute renal allograft rejection. Initial assessment should be focused on empiric treatment for infection while also evaluating for the possibility of rejection.
Patients with AGP present with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of cystitis (frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria, suprapubic pain) along with upper urinary tract symptoms (fever, chills, pain at graft site). However, since the kidney graft is denervated, lack of tenderness over graft site does not rule out pyelonephritis.1
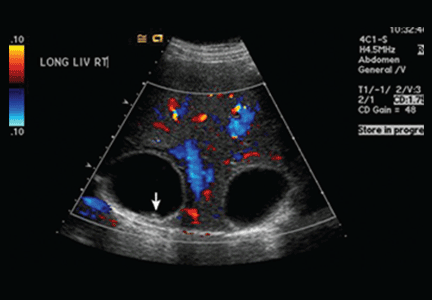
This patient was hospitalized and continued on ceftriaxone. Renal ultrasound showed an 11-cm transplanted kidney without hydronephrosis and normal Doppler flow at the anastomotic sites of the renal artery and vein. On hospital Day 2, his urine and blood cultures were negative, but ceftriaxone was continued since it had been given prior to obtaining urine culture. The patient’s tacrolimus level was slightly elevated at 15.6 mcg/L (therapeutic range: 5-15 mcg/L). He also tested negative for chlamydia and gonorrhea; a urine Wright stain was negative for eosinophils.
On hospital Day 4, the patient remained febrile, urinary symptoms persisted, and creatinine increased to 1.5 mg/dL. Tacrolimus was stopped and mycophenolate mofetil dosing was decreased to 500 mg PO bid, then 250 mg PO bid, and then stopped on hospital Day 5. Tacrolimus was reinitated on hospital Day 6 at 1 mg PO bid.
Continue to: Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen...
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis without contrast evaluating for a perinephric or renal abscess was negative. Antibiotic coverage was broadened to meropenem 1 g every 8 hours and vancomycin 1500 mg once, with levels to follow. Repeat urinalysis showed persistent pyuria and worsened hematuria and proteinuria. Urine protein to creatinine ratio was elevated at 1.3 mg/mg. Cystoscopy showed a normal urethra and multiple areas of erythema and edema in the bladder, which was consistent with cystitis.
Due to the lack of clinical improvement on broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, other urinary pathogens, including BK virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), fungi, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), were considered. Serum qualitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for BK virus and CMV were negative. Quantitative PCR for BK virus revealed presence of <500 copies/mL of BK virus. Quantiferon gold, urine MTB PCR, and urine fungal culture were negative.
The presence of worsening hematuria raised suspicion for hemorrhagic cystitis due to adenovirus. Urine adenovirus PCR confirmed the diagnosis of AGP due to adenovirus.
DISCUSSION
Acute graft pyelonephritis, also known as pyelonephritis of the renal allograft, can be categorized as early-onset (<6 months after transplant) or late onset (>6 months after transplant). Early-onset AGP is associated with bacteremia, pyelonephritis, and high rate of relapse,1-3 whereas late-onset AGP is associated with increased risk of graft loss.4
In a renal transplant patient, UTIs are usually caused by the same gram-negative bacteria that cause UTIs in patients without a transplant.5 Additionally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gram-positive bacteria such as those within the Enterococcus species should be considered. Candida albicans is the most common fungal cause and is associated with urinary obstruction.6
Continue to: Fungal culture...
Fungal culture, CMV PCR, and BK virus PCR should be considered in a patient who does not improve despite appropriate antibiotic coverage. Hematuria should raise concern for BK virus7 and adenovirus. BK virus should be considered when treating patients on high doses of immune suppression, as there is an association between this infection and graft failure.7 Rarely, MTB can cause AGP.8
Empiric antibiotic coverage includes broad-spectrum antibiotics against gram-negative enteric organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and gram-positive organisms, including Enterococcus species. Although optimal duration of antibiotics for AGP is unknown, most nephrologists treat graft pyelonephritis due to a bacterial etiology for 10 to 14 days.1 Complications include poor graft outcome and decreased long-term survival.
Adenovirus infection in a renal transplant patient is uncommon and typically presents with hemorrhagic cystitis. In rare cases, this infection can cause disseminated infection. Management is mostly supportive. Reduction of immunosuppression may be associated with viral clearance.9 Cidofovir and intravenous immune globulin may be considered for patients with life-threatening adenovirus infection10; however, there are no large trials that show a clear benefit for patients with AGP due to adenovirus.
Our patient’s urinary symptoms and fever resolved after 1 week of hospitalization with supportive measures and a reduction in immunosuppression, namely a reduction of the dosing of mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus. (Optimal changes in the dosing of immunosuppressive agents should be carried out under consultation with a transplant nephrologist.) However, our patient’s creatinine remained elevated at 1.5 mg/dL. Given the low suspicion for graft rejection, biopsy of the kidney transplant was not performed. He returned to the nephrology clinic 3 months later with an improved creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL.
THE TAKEAWAY
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient suggest either graft pyelonephritis or graft rejection. In addition to the usual gram-negative enteric organisms associated with pyelonephritis in a patient with native kidneys, clinicians should consider low-virulence gram-positive organisms, viruses, fungi, and mycobacteria as potential etiologies. The risks and benefits of reducing or discontinuing immunosuppressive medications in the setting of AGP should be discussed with a nephrologist.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pruthul Patel, MD, Los Angeles County + University of Southern California Medical Center, IRD Building, 2020 Zonal Ave, Rm. 115 Los Angeles, CA 90033; pruthulp@usc.edu
1. de Souza RM, Olsburgh J. Urinary tract infection in the renal transplant patient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008;4:252-264.
2. Schmaldienst S, Dittrich E, Hörl WH. Urinary tract infections after renal transplantation. Curr Opin Urol. 2002;12:125-130.
3. Brown PD. Urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2002;4:525-528.
4. Abbott KC, Swanson SJ, Richter ER, et al. Late urinary tract infection after renal transplantation in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:353-362.
5. Pellé F, Vimont S, Levy PP, et al. Acute pyelonephritis represents risk factor impairing long-term kidney graft function. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:899-907.
6. Alangaden GJ, Thyagarajan R, Gruber SA, et al. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:401-409.
7. Hirsch HH. Polyomavirus BK nephropathy: a (re-)emerging complication in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:25-30.
8. Wagener MM, Yu VL. Bacteremia in transplant recipients: a prospective study of demographics, etiologic agents, risk factors, and outcomes. Am J Infect Control. 1992;20:239-247.
9. Asim M, Chong-Lopez A, Nickeleit V. Adenovirus infection of a renal allograft. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:696-701.
10. Barraclough K, Oliver K, Playford EG, et al. Life-threatening adenovirus infection in a kidney transplant recipient. Clin Kidney J. 2010;3:388-392.
THE CASE
On examination, the patient appeared to be in mild distress. His vital signs included: temperature 38.5°C, blood pressure 136/94 mm Hg, pulse 89 beats/min, and respiratory rate 18 breaths/min. Cardiopulmonary, abdominal, and genitourinary examinations were unremarkable. A well-healed scar was seen in the right lower quadrant at the site of the renal allograft and was nontender to palpation.
Laboratory values showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 4.3 × 109/L and an elevated creatinine of 1.16 mg/dL. Six months prior to presentation, his creatinine was 0.98 mg/dL. Blood cultures were obtained, and ceftriaxone (1 g) was given prior to obtaining a urine specimen. A urine dipstick revealed moderate leukocyte esterase, small blood, and 30 mg/dL of protein. Urine microscopy showed >50 WBCs per high power field (hpf), 6-10 red blood cells (RBCs), 30 mg/dL of protein, and an absence of bacteria.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient may be due to acute graft pyelonephritis (AGP) or acute renal allograft rejection. Initial assessment should be focused on empiric treatment for infection while also evaluating for the possibility of rejection.
Patients with AGP present with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of cystitis (frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria, suprapubic pain) along with upper urinary tract symptoms (fever, chills, pain at graft site). However, since the kidney graft is denervated, lack of tenderness over graft site does not rule out pyelonephritis.1
This patient was hospitalized and continued on ceftriaxone. Renal ultrasound showed an 11-cm transplanted kidney without hydronephrosis and normal Doppler flow at the anastomotic sites of the renal artery and vein. On hospital Day 2, his urine and blood cultures were negative, but ceftriaxone was continued since it had been given prior to obtaining urine culture. The patient’s tacrolimus level was slightly elevated at 15.6 mcg/L (therapeutic range: 5-15 mcg/L). He also tested negative for chlamydia and gonorrhea; a urine Wright stain was negative for eosinophils.
On hospital Day 4, the patient remained febrile, urinary symptoms persisted, and creatinine increased to 1.5 mg/dL. Tacrolimus was stopped and mycophenolate mofetil dosing was decreased to 500 mg PO bid, then 250 mg PO bid, and then stopped on hospital Day 5. Tacrolimus was reinitated on hospital Day 6 at 1 mg PO bid.
Continue to: Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen...
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis without contrast evaluating for a perinephric or renal abscess was negative. Antibiotic coverage was broadened to meropenem 1 g every 8 hours and vancomycin 1500 mg once, with levels to follow. Repeat urinalysis showed persistent pyuria and worsened hematuria and proteinuria. Urine protein to creatinine ratio was elevated at 1.3 mg/mg. Cystoscopy showed a normal urethra and multiple areas of erythema and edema in the bladder, which was consistent with cystitis.
Due to the lack of clinical improvement on broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, other urinary pathogens, including BK virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), fungi, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), were considered. Serum qualitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for BK virus and CMV were negative. Quantitative PCR for BK virus revealed presence of <500 copies/mL of BK virus. Quantiferon gold, urine MTB PCR, and urine fungal culture were negative.
The presence of worsening hematuria raised suspicion for hemorrhagic cystitis due to adenovirus. Urine adenovirus PCR confirmed the diagnosis of AGP due to adenovirus.
DISCUSSION
Acute graft pyelonephritis, also known as pyelonephritis of the renal allograft, can be categorized as early-onset (<6 months after transplant) or late onset (>6 months after transplant). Early-onset AGP is associated with bacteremia, pyelonephritis, and high rate of relapse,1-3 whereas late-onset AGP is associated with increased risk of graft loss.4
In a renal transplant patient, UTIs are usually caused by the same gram-negative bacteria that cause UTIs in patients without a transplant.5 Additionally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gram-positive bacteria such as those within the Enterococcus species should be considered. Candida albicans is the most common fungal cause and is associated with urinary obstruction.6
Continue to: Fungal culture...
Fungal culture, CMV PCR, and BK virus PCR should be considered in a patient who does not improve despite appropriate antibiotic coverage. Hematuria should raise concern for BK virus7 and adenovirus. BK virus should be considered when treating patients on high doses of immune suppression, as there is an association between this infection and graft failure.7 Rarely, MTB can cause AGP.8
Empiric antibiotic coverage includes broad-spectrum antibiotics against gram-negative enteric organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and gram-positive organisms, including Enterococcus species. Although optimal duration of antibiotics for AGP is unknown, most nephrologists treat graft pyelonephritis due to a bacterial etiology for 10 to 14 days.1 Complications include poor graft outcome and decreased long-term survival.
Adenovirus infection in a renal transplant patient is uncommon and typically presents with hemorrhagic cystitis. In rare cases, this infection can cause disseminated infection. Management is mostly supportive. Reduction of immunosuppression may be associated with viral clearance.9 Cidofovir and intravenous immune globulin may be considered for patients with life-threatening adenovirus infection10; however, there are no large trials that show a clear benefit for patients with AGP due to adenovirus.
Our patient’s urinary symptoms and fever resolved after 1 week of hospitalization with supportive measures and a reduction in immunosuppression, namely a reduction of the dosing of mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus. (Optimal changes in the dosing of immunosuppressive agents should be carried out under consultation with a transplant nephrologist.) However, our patient’s creatinine remained elevated at 1.5 mg/dL. Given the low suspicion for graft rejection, biopsy of the kidney transplant was not performed. He returned to the nephrology clinic 3 months later with an improved creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL.
THE TAKEAWAY
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient suggest either graft pyelonephritis or graft rejection. In addition to the usual gram-negative enteric organisms associated with pyelonephritis in a patient with native kidneys, clinicians should consider low-virulence gram-positive organisms, viruses, fungi, and mycobacteria as potential etiologies. The risks and benefits of reducing or discontinuing immunosuppressive medications in the setting of AGP should be discussed with a nephrologist.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pruthul Patel, MD, Los Angeles County + University of Southern California Medical Center, IRD Building, 2020 Zonal Ave, Rm. 115 Los Angeles, CA 90033; pruthulp@usc.edu
THE CASE
On examination, the patient appeared to be in mild distress. His vital signs included: temperature 38.5°C, blood pressure 136/94 mm Hg, pulse 89 beats/min, and respiratory rate 18 breaths/min. Cardiopulmonary, abdominal, and genitourinary examinations were unremarkable. A well-healed scar was seen in the right lower quadrant at the site of the renal allograft and was nontender to palpation.
Laboratory values showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 4.3 × 109/L and an elevated creatinine of 1.16 mg/dL. Six months prior to presentation, his creatinine was 0.98 mg/dL. Blood cultures were obtained, and ceftriaxone (1 g) was given prior to obtaining a urine specimen. A urine dipstick revealed moderate leukocyte esterase, small blood, and 30 mg/dL of protein. Urine microscopy showed >50 WBCs per high power field (hpf), 6-10 red blood cells (RBCs), 30 mg/dL of protein, and an absence of bacteria.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient may be due to acute graft pyelonephritis (AGP) or acute renal allograft rejection. Initial assessment should be focused on empiric treatment for infection while also evaluating for the possibility of rejection.
Patients with AGP present with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of cystitis (frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria, suprapubic pain) along with upper urinary tract symptoms (fever, chills, pain at graft site). However, since the kidney graft is denervated, lack of tenderness over graft site does not rule out pyelonephritis.1
This patient was hospitalized and continued on ceftriaxone. Renal ultrasound showed an 11-cm transplanted kidney without hydronephrosis and normal Doppler flow at the anastomotic sites of the renal artery and vein. On hospital Day 2, his urine and blood cultures were negative, but ceftriaxone was continued since it had been given prior to obtaining urine culture. The patient’s tacrolimus level was slightly elevated at 15.6 mcg/L (therapeutic range: 5-15 mcg/L). He also tested negative for chlamydia and gonorrhea; a urine Wright stain was negative for eosinophils.
On hospital Day 4, the patient remained febrile, urinary symptoms persisted, and creatinine increased to 1.5 mg/dL. Tacrolimus was stopped and mycophenolate mofetil dosing was decreased to 500 mg PO bid, then 250 mg PO bid, and then stopped on hospital Day 5. Tacrolimus was reinitated on hospital Day 6 at 1 mg PO bid.
Continue to: Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen...
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis without contrast evaluating for a perinephric or renal abscess was negative. Antibiotic coverage was broadened to meropenem 1 g every 8 hours and vancomycin 1500 mg once, with levels to follow. Repeat urinalysis showed persistent pyuria and worsened hematuria and proteinuria. Urine protein to creatinine ratio was elevated at 1.3 mg/mg. Cystoscopy showed a normal urethra and multiple areas of erythema and edema in the bladder, which was consistent with cystitis.
Due to the lack of clinical improvement on broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, other urinary pathogens, including BK virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), fungi, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), were considered. Serum qualitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for BK virus and CMV were negative. Quantitative PCR for BK virus revealed presence of <500 copies/mL of BK virus. Quantiferon gold, urine MTB PCR, and urine fungal culture were negative.
The presence of worsening hematuria raised suspicion for hemorrhagic cystitis due to adenovirus. Urine adenovirus PCR confirmed the diagnosis of AGP due to adenovirus.
DISCUSSION
Acute graft pyelonephritis, also known as pyelonephritis of the renal allograft, can be categorized as early-onset (<6 months after transplant) or late onset (>6 months after transplant). Early-onset AGP is associated with bacteremia, pyelonephritis, and high rate of relapse,1-3 whereas late-onset AGP is associated with increased risk of graft loss.4
In a renal transplant patient, UTIs are usually caused by the same gram-negative bacteria that cause UTIs in patients without a transplant.5 Additionally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gram-positive bacteria such as those within the Enterococcus species should be considered. Candida albicans is the most common fungal cause and is associated with urinary obstruction.6
Continue to: Fungal culture...
Fungal culture, CMV PCR, and BK virus PCR should be considered in a patient who does not improve despite appropriate antibiotic coverage. Hematuria should raise concern for BK virus7 and adenovirus. BK virus should be considered when treating patients on high doses of immune suppression, as there is an association between this infection and graft failure.7 Rarely, MTB can cause AGP.8
Empiric antibiotic coverage includes broad-spectrum antibiotics against gram-negative enteric organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and gram-positive organisms, including Enterococcus species. Although optimal duration of antibiotics for AGP is unknown, most nephrologists treat graft pyelonephritis due to a bacterial etiology for 10 to 14 days.1 Complications include poor graft outcome and decreased long-term survival.
Adenovirus infection in a renal transplant patient is uncommon and typically presents with hemorrhagic cystitis. In rare cases, this infection can cause disseminated infection. Management is mostly supportive. Reduction of immunosuppression may be associated with viral clearance.9 Cidofovir and intravenous immune globulin may be considered for patients with life-threatening adenovirus infection10; however, there are no large trials that show a clear benefit for patients with AGP due to adenovirus.
Our patient’s urinary symptoms and fever resolved after 1 week of hospitalization with supportive measures and a reduction in immunosuppression, namely a reduction of the dosing of mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus. (Optimal changes in the dosing of immunosuppressive agents should be carried out under consultation with a transplant nephrologist.) However, our patient’s creatinine remained elevated at 1.5 mg/dL. Given the low suspicion for graft rejection, biopsy of the kidney transplant was not performed. He returned to the nephrology clinic 3 months later with an improved creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL.
THE TAKEAWAY
Fever and urinary symptoms in a renal transplant patient suggest either graft pyelonephritis or graft rejection. In addition to the usual gram-negative enteric organisms associated with pyelonephritis in a patient with native kidneys, clinicians should consider low-virulence gram-positive organisms, viruses, fungi, and mycobacteria as potential etiologies. The risks and benefits of reducing or discontinuing immunosuppressive medications in the setting of AGP should be discussed with a nephrologist.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pruthul Patel, MD, Los Angeles County + University of Southern California Medical Center, IRD Building, 2020 Zonal Ave, Rm. 115 Los Angeles, CA 90033; pruthulp@usc.edu
1. de Souza RM, Olsburgh J. Urinary tract infection in the renal transplant patient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008;4:252-264.
2. Schmaldienst S, Dittrich E, Hörl WH. Urinary tract infections after renal transplantation. Curr Opin Urol. 2002;12:125-130.
3. Brown PD. Urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2002;4:525-528.
4. Abbott KC, Swanson SJ, Richter ER, et al. Late urinary tract infection after renal transplantation in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:353-362.
5. Pellé F, Vimont S, Levy PP, et al. Acute pyelonephritis represents risk factor impairing long-term kidney graft function. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:899-907.
6. Alangaden GJ, Thyagarajan R, Gruber SA, et al. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:401-409.
7. Hirsch HH. Polyomavirus BK nephropathy: a (re-)emerging complication in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:25-30.
8. Wagener MM, Yu VL. Bacteremia in transplant recipients: a prospective study of demographics, etiologic agents, risk factors, and outcomes. Am J Infect Control. 1992;20:239-247.
9. Asim M, Chong-Lopez A, Nickeleit V. Adenovirus infection of a renal allograft. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:696-701.
10. Barraclough K, Oliver K, Playford EG, et al. Life-threatening adenovirus infection in a kidney transplant recipient. Clin Kidney J. 2010;3:388-392.
1. de Souza RM, Olsburgh J. Urinary tract infection in the renal transplant patient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008;4:252-264.
2. Schmaldienst S, Dittrich E, Hörl WH. Urinary tract infections after renal transplantation. Curr Opin Urol. 2002;12:125-130.
3. Brown PD. Urinary tract infections in renal transplant recipients. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2002;4:525-528.
4. Abbott KC, Swanson SJ, Richter ER, et al. Late urinary tract infection after renal transplantation in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:353-362.
5. Pellé F, Vimont S, Levy PP, et al. Acute pyelonephritis represents risk factor impairing long-term kidney graft function. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:899-907.
6. Alangaden GJ, Thyagarajan R, Gruber SA, et al. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:401-409.
7. Hirsch HH. Polyomavirus BK nephropathy: a (re-)emerging complication in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:25-30.
8. Wagener MM, Yu VL. Bacteremia in transplant recipients: a prospective study of demographics, etiologic agents, risk factors, and outcomes. Am J Infect Control. 1992;20:239-247.
9. Asim M, Chong-Lopez A, Nickeleit V. Adenovirus infection of a renal allograft. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:696-701.
10. Barraclough K, Oliver K, Playford EG, et al. Life-threatening adenovirus infection in a kidney transplant recipient. Clin Kidney J. 2010;3:388-392.
A 20-year-old woman with fatigue and palpitations
A 20-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with fatigue and the sudden onset of palpitations. She reports no history of significant illness or surgery. She says she is not currently taking prescription or over-the-counter medications. She does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs.
Her weight is 52 kg (115 lb), her height is 170 cm (67 in), and her body mass index (BMI) is 18 kg/m2. Vital signs: temperature 35.7°C (96.4°F), blood pressure 92/48 mm Hg, heart rate 73 bpm, respiratory rate 5 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation 98% on room air.
She appears tired but is alert, conversant, and cooperative. Her skin is normal, and dentition is fair. Her pulse is regular, and respirations are slow. The abdomen is soft, non-tender, and flat. Strength is 4 on a scale of 5 in all extremities. Deep-tendon reflexes are 2+ and symmetric.
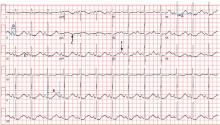
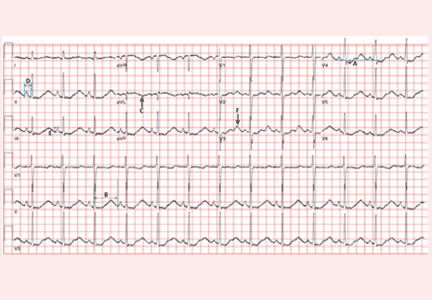
Electrocardiography (Figure 1) in the emergency department shows ST-segment depression, a prolonged corrected QT interval of 665 msec, T-wave inversion, PR prolongation, increased P-wave amplitude, and U waves.
1. Which electrolyte abnormality is associated with this electrocardiographic picture?
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is the likely cause of these findings. The finding of U waves is considered significant when they are inverted, merged with the T wave, or have an amplitude greater than the T wave.1 U waves are best seen in the precordial leads. When severe, hypokalemia can lead to potentially fatal arrhythmias such as high-grade atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.2
Hyperkalemia is associated with peaked T waves, a prolonged PR interval, decreased P wave amplitude, and a widened QRS complex.2 When acute and severe, hyperkalemia is associated with ventricular arrhythmia.
Hypocalcemia is associated with a prolonged QT interval and ventricular dysrhythmia, but not U waves.2
Hypercalcemia is associated with bradydysrhythmia, as well as with a shortened QT interval.2
LABORATORY TESTING
Laboratory testing shows the following:
- Sodium 126 mmol/L (reference range 135–145)
- Potassium 1.5 mmol/L (3.5–5.1)
- Chloride 58 mmol/L (100–110)
- Bicarbonate 62 mmol/L (20–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dL (7–18)
- Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL (0.5–1.0)
- Glucose 106 mg/dL (70–110)
- Ionized calcium 4.4 mg/dL (4.5–5.3)
- Magnesium 1.8 mg/dL (1.7–2.3)
- Phosphorus 4.1 mg/dL (2.5–4.5)
- Venous blood gases pH 7.56 (7.35–7.45), Pco2 69 mm Hg (35–45).
POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS
Ninety-eight percent of potassium is intracellular and only 2% is extracellular.3 The main cellular stores are myocytes and hepatocytes. Patients with decreased muscle mass may be at a higher risk of hypokalemia as a result of decreased skeletal muscle stores.4
The acute development of hypokalemia occurs from transcellular shifts. Alkalosis, insulin secretion, and beta-adrenergic stimulation promote the intracellular uptake of potassium. The major hormonal regulator of potassium excretion is aldosterone, which is stimulated by renal hypoperfusion and promotes potassium-ion secretion in the distal convoluted tubule.
Chronic hypokalemia develops in patients with ongoing renal or gastrointestinal potassium loss. If the cause of potassium loss is not elucidated by the history, the physical, and a review of medications, then one of two things is possible: either the patient has renal tubular disease affecting acid-base and potassium regulation, causing excessive mineralocorticoid secretion, which is associated with an abnormal response to aldosterone; or the patient is not being forthcoming in the history.
2. Which is the most likely cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Vomiting
- Liddle syndrome
- Bartter syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Diuretic use
Her laboratory tests reveal hypokalemia and hyponatremic-hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis with compensatory respiratory acidosis. In metabolic alkalosis, the expected respiratory compensation is an increase of 0.7 mm Hg in Pco2 for each 1-mEq/L increase in bicarbonate. Therefore, the expected Pco2 is 67, close to the patient’s actual value of 69.
Protracted vomiting with loss of gastric acid juices could be a cause of the metabolic disturbances in this young woman, although she did not mention vomiting during the history.
Liddle syndrome, or pseudoaldosteronism, is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by altered renal epithelial sodium channels, excessive sodium retention, and resultant hypertension. Hypokalemia and alkalosis are seen in Liddle syndrome, but the absence of hypertension in our patient makes Liddle syndrome unlikely.
Bartter syndrome is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder of the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending loop of Henle, resulting in impaired reabsorption of chloride and sodium. Bartter syndrome mimics chronic loop-diuretic use and is associated with hypercalciuria. Bartter syndrome is possible in this patient; however, patients with Bartter syndrome are usually diagnosed in infancy or childhood and have evidence of growth impairment.
Gitelman syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter. Although Gitelman syndrome is more common than Bartter syndrome and presents at older ages, it is not usually associated with such profound metabolic alkalosis. Gitelman syndrome mimics chronic use of thiazide diuretics and is associated with hypocalciuria.
Diuretic use could also cause the metabolic disturbances described; however, the patient denied taking diuretics.
The most common cause of hypokalemia in clinical practice is diuretic use.4 In this young woman with unexplained hypokalemia, the most likely cause is either undisclosed self-induced vomiting or diuretic abuse. The degree of metabolic alkalosis suggests vomiting, since metabolic alkalosis this severe is usually seen only with protracted vomiting. Bartter and Gitelman syndromes are included in the differential diagnosis, but they are much less common than hypokalemia associated with diuretics or self-induced vomiting.5
3. Which test could help elucidate the cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Ratio of plasma aldosterone to rennin
- Urine chloride
- Ratio of urinary potassium to creatinine
- Urinary anion gap and urinary pH
APPROACH TO HYPOKALEMIA
Determining the cause of hypokalemia starts with a thorough history and physical examination. The history should focus on drugs such as diuretics and laxatives. Women should be asked about their menstrual history since irregular periods may suggest an eating disorder. The physical examination should focus on signs that suggest self-induced vomiting, such as dry skin, dental erosions, enlarged parotid glands, and calluses or scars on the knuckles.
Patients with an unclear cause of hypokalemia after a thorough history and physical examination can be categorized into one of three groups based on blood pressure and acid-base status:
- Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis.
Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
The blood pressure provides an important clue in the evaluation of hypokalemia. The combination of hypertension, hypokalemia, and alkalosis should raise concern for hyperaldosteronism or pseudoaldosteronism. Primary hyperaldosteronism from an adrenal adenoma (Conn syndrome) is characterized by a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of greater than 20.6,7 In contrast, patients with secondary hyperaldosteronism due to renovascular disease have a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of less than 10. Patients with pseudoaldosteronism have low aldosterone and renin levels and hypertension. Since our patient has a normal blood pressure, testing the plasma aldosterone and renin levels would not help determine the cause of her hypokalemia.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
Patients with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and normal plasma anion gap acidosis either have renal tubular acidosis or have lost potassium because of diarrhea or laxative abuse. In a patient who denies taking laxatives or denies a history of diarrhea, checking the urinary anion gap and urinary pH may help differentiate the cause of acidosis and hypokalemia.
The urinary anion gap, calculated by the equation sodium + potassium − chloride, is an indirect estimate of hydrogen excretion in the form of ammonium ion8; the normal value is 0 to 10 mEq/L. A negative value represents increased hydrogen excretion in response to systemic acidosis from gastrointestinal or renal loss of bicarbonate (proximal renal tubular acidosis). A urinary pH greater than 5.5 in the setting of systemic acidosis suggests impaired ability of the kidneys to acidify urine and raises the possibility of renal tubular acidosis.
This patient has metabolic alkalosis, so calculation of the urinary anion gap would not be helpful.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis
Patients such as ours, with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and alkalosis, have been vomiting, have used diuretics, or have an inherited renal tubulopathy such as Bartter or Gitelman syndrome. Usually, differentiating Bartter and Gitelman syndromes from chronic vomiting or diuretic use is done with the history and physical examination. However, in patients with a questionable history and a lack of findings on physical examination, checking the urinary chloride, potassium, calcium, and creatinine may be helpful.
A urinary potassium-creatinine ratio greater than 15 suggests renal loss, whereas a ratio less than 15 suggests extrarenal loss.9
Patients who are taking a diuretic or who have Bartter or Gitelman syndrome have a high urinary chloride concentration, ie, greater than 20 mmol/L, whereas patients with hypokalemia and alkalosis from chronic vomiting tend to have a concentration less than 10 mmol/L.10
Table 1 summarizes an approach to the evaluation of unexplained hypokalemia based on blood pressure and acid-base status.
A HIDDEN HISTORY
On further questioning, the patient admits to an 8-year history of daily self-induced vomiting in an attempt to lose weight, in addition to multiple hospitalizations for hypokalemia and a previous diagnosis of an eating disorder.
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF HYPOKALEMIA
The initial management of hypokalemia should focus on life-threatening emergencies. While patients with potassium levels greater than 3 mmol/L are usually asymptomatic, those with levels below 3 mmol/L present with muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis.4 An acute drop in serum potassium to less than 2 mmol/L is associated with respiratory muscle weakness and ventricular arrhythmias.4 If the patient has cardiac symptoms or hypoventilation due to respiratory muscle weakness, continuous monitoring in the intensive care unit and aggressive therapy are warranted.
4. Which potassium formulation is most appropriate for the treatment of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Potassium chloride
- Potassium phosphate
- Potassium acetate
Oral potassium is preferable in patients with a serum potassium above 2.5 mmol/L.4,11 Potassium phosphate should be used when supplementation with both potassium and phosphorus is needed. Potassium acetate should be reserved for patients with acidosis and hypokalemia. Otherwise, potassium chloride is typically preferred.4,12 It comes in liquid and tablet forms. Liquid forms have an unpleasant taste, whereas tablets are usually well tolerated. No more than 20 to 40 mEq of potassium chloride tablets should be given at a time, since higher doses are associated with gastrointestinal mucosal injury.12
Potassium chloride is particularly preferred in patients with metabolic alkalosis, since increased chloride intake and delivery to the distal tubule increases the expression of pendrin, a luminal chloride and bicarbonate exchanger in the cortical collecting duct.13 With metabolic alkalosis, increased excretion of bicarbonate occurs through up-regulation of pendrin. Potassium depletion down-regulates pendrin.13 Additionally, correction of metabolic alkalosis increases serum potassium by movement of potassium from the intracellular to the extracellular space.
Intravenous potassium should be reserved for patients with severe hypokalemia (< 2.5 mmol/L) or significant arrhythmias.11 Oral and intravenous potassium can safely be given simultaneously.11 The intravenous rate should not exceed more than 10 to 20 mEq of potassium chloride per hour unless the patient has a life-threatening arrhythmia, respiratory failure, or severe hypokalemia.14,15 In life-threatening situations, a femoral line should be placed, and potassium should be given as rapidly as 20 mEq over 15 to 20 minutes.14 Cannulation of the subclavian and internal jugular veins should be avoided in severe hypokalemia since mechanical irritation from guidewire placement can provoke ventricular arrhythmias.14
During intravenous administration of potassium, laboratory monitoring after every 20 mEq of potassium chloride is advised because of the possibility of rebound hyperkalemia. In patients with severe hypokalemia, avoidance of factors that can worsen intracellular shift of potassium is also important. Avoid dextrose-containing fluids to prevent insulin-induced shifting of potassium into cells. Restore intravascular volume to blunt hypovolemia-induced renin and aldosterone secretion. If a patient presents with severe hypokalemia and acidosis, correct the hypokalemia before the acidosis to avoid intracellular shift of potassium.
OUR PATIENT’S MANAGEMENT AND FOLLOW-UP PLAN
Given the severity of our patient’s hypokalemia and her complaint of palpitations, she was admitted to the hospital for monitoring. She required 180 mEq of intravenous potassium chloride and 140 mEq of oral potassium chloride during the first 24 hours in order to achieve a serum potassium level above 3 mmol/L. Electrocardiographic U waves resolved once the level was above 2 mmol/L, and ST depressions resolved once it was above 3 mmol/L. The QT interval normalized after 24 hours of hospitalization.
On discharge, she was prescribed oral potassium chloride 40 mEq daily and magnesium sulfate 400 mg twice daily, with plans for a followup visit with her outpatient therapy team, which includes a psychiatrist, a social worker, and her primary care provider. She declined a referral for inpatient therapy but agreed to a goal of decreasing the frequency of induced vomiting and outpatient visits. She was also educated on how and when to access emergency medical care.16
- Rautaharju PM, Surawicz B, Gettes LS, et al; American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; American College of Cardiology Foundation; Heart Rhythm Society. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part IV: the ST segment, T and U waves, and the QT Interval: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society. Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 53:982–991.
- Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC. Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities. J Emerg Med 2004; 27:153–160.
- Unwin RJ, Luft FC, Shirley DG. Pathophysiology and management of hypokalemia: a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011; 7:75–84.
- Gennari FJ. Hypokalemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 339:451–458.
- Mehler PS. Clinical practice. Bulimia nervosa. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:875–881.
- Tzanela M, Effraimidis G, Vassiliadi D, et al. The aldosterone to renin ratio in the evaluation of patients with incidentally detected adrenal masses. Endocrine 2007; 32:136–142.
- Diederich S, Mai K, Bähr V, Helffrich S, Pfeiffer A, Perschel FH. The simultaneous measurement of plasma-aldosterone- and -renin-concentration allows rapid classification of all disorders of the renin-aldosterone system. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2007; 115:433–438.
- Goldstein MB, Bear R, Richardson RM, Marsden PA, Halperin ML. The urine anion gap: a clinically useful index of ammonium excretion. Am J Med Sci 1986; 292:198–202.
- Groeneveld JH, Sijpkens YW, Lin SH, Davids MR, Halperin ML. An approach to the patient with severe hypokalaemia: the potassium quiz. QJM 2005; 98:305–316.
- Galla JH. Metabolic alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11:369–375.
- Asmar A, Mohandas R, Wingo CS. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of a patient with hypokalemia. Am J Kidney Dis 2012; 60:492–497.
- Cohn JN, Kowey PR, Whelton PK, Prisant LM. New guidelines for potassium replacement in clinical practice: a contemporary review by the National Council on Potassium in Clinical Practice. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160:2429–2436.
- Luke RG, Galla JH. It is chloride depletion alkalosis, not contraction alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23:204–207.
- Kruse JA, Carlson RW. Rapid correction of hypokalemia using concentrated intravenous potassium chloride infusions. Arch Intern Med 1990; 150:613–617.
- Weiner ID, Wingo CS. Hypokalemia—consequences, causes, and correction. J Am Soc Nephrol 1997; 8:1179–1188.
- AED Medical Care Standards Task Force. Eating disorders: Critical Points for Early Recognition and Medical Risk Management in the Care of Individuals with Eating Disorders. AED Report 2012. www.aedweb.org/web/downloads/Guide-English.pdf. Accessed April 4, 2014.
A 20-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with fatigue and the sudden onset of palpitations. She reports no history of significant illness or surgery. She says she is not currently taking prescription or over-the-counter medications. She does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs.
Her weight is 52 kg (115 lb), her height is 170 cm (67 in), and her body mass index (BMI) is 18 kg/m2. Vital signs: temperature 35.7°C (96.4°F), blood pressure 92/48 mm Hg, heart rate 73 bpm, respiratory rate 5 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation 98% on room air.
She appears tired but is alert, conversant, and cooperative. Her skin is normal, and dentition is fair. Her pulse is regular, and respirations are slow. The abdomen is soft, non-tender, and flat. Strength is 4 on a scale of 5 in all extremities. Deep-tendon reflexes are 2+ and symmetric.
Electrocardiography (Figure 1) in the emergency department shows ST-segment depression, a prolonged corrected QT interval of 665 msec, T-wave inversion, PR prolongation, increased P-wave amplitude, and U waves.
1. Which electrolyte abnormality is associated with this electrocardiographic picture?
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is the likely cause of these findings. The finding of U waves is considered significant when they are inverted, merged with the T wave, or have an amplitude greater than the T wave.1 U waves are best seen in the precordial leads. When severe, hypokalemia can lead to potentially fatal arrhythmias such as high-grade atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.2
Hyperkalemia is associated with peaked T waves, a prolonged PR interval, decreased P wave amplitude, and a widened QRS complex.2 When acute and severe, hyperkalemia is associated with ventricular arrhythmia.
Hypocalcemia is associated with a prolonged QT interval and ventricular dysrhythmia, but not U waves.2
Hypercalcemia is associated with bradydysrhythmia, as well as with a shortened QT interval.2
LABORATORY TESTING
Laboratory testing shows the following:
- Sodium 126 mmol/L (reference range 135–145)
- Potassium 1.5 mmol/L (3.5–5.1)
- Chloride 58 mmol/L (100–110)
- Bicarbonate 62 mmol/L (20–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dL (7–18)
- Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL (0.5–1.0)
- Glucose 106 mg/dL (70–110)
- Ionized calcium 4.4 mg/dL (4.5–5.3)
- Magnesium 1.8 mg/dL (1.7–2.3)
- Phosphorus 4.1 mg/dL (2.5–4.5)
- Venous blood gases pH 7.56 (7.35–7.45), Pco2 69 mm Hg (35–45).
POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS
Ninety-eight percent of potassium is intracellular and only 2% is extracellular.3 The main cellular stores are myocytes and hepatocytes. Patients with decreased muscle mass may be at a higher risk of hypokalemia as a result of decreased skeletal muscle stores.4
The acute development of hypokalemia occurs from transcellular shifts. Alkalosis, insulin secretion, and beta-adrenergic stimulation promote the intracellular uptake of potassium. The major hormonal regulator of potassium excretion is aldosterone, which is stimulated by renal hypoperfusion and promotes potassium-ion secretion in the distal convoluted tubule.
Chronic hypokalemia develops in patients with ongoing renal or gastrointestinal potassium loss. If the cause of potassium loss is not elucidated by the history, the physical, and a review of medications, then one of two things is possible: either the patient has renal tubular disease affecting acid-base and potassium regulation, causing excessive mineralocorticoid secretion, which is associated with an abnormal response to aldosterone; or the patient is not being forthcoming in the history.
2. Which is the most likely cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Vomiting
- Liddle syndrome
- Bartter syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Diuretic use
Her laboratory tests reveal hypokalemia and hyponatremic-hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis with compensatory respiratory acidosis. In metabolic alkalosis, the expected respiratory compensation is an increase of 0.7 mm Hg in Pco2 for each 1-mEq/L increase in bicarbonate. Therefore, the expected Pco2 is 67, close to the patient’s actual value of 69.
Protracted vomiting with loss of gastric acid juices could be a cause of the metabolic disturbances in this young woman, although she did not mention vomiting during the history.
Liddle syndrome, or pseudoaldosteronism, is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by altered renal epithelial sodium channels, excessive sodium retention, and resultant hypertension. Hypokalemia and alkalosis are seen in Liddle syndrome, but the absence of hypertension in our patient makes Liddle syndrome unlikely.
Bartter syndrome is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder of the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending loop of Henle, resulting in impaired reabsorption of chloride and sodium. Bartter syndrome mimics chronic loop-diuretic use and is associated with hypercalciuria. Bartter syndrome is possible in this patient; however, patients with Bartter syndrome are usually diagnosed in infancy or childhood and have evidence of growth impairment.
Gitelman syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter. Although Gitelman syndrome is more common than Bartter syndrome and presents at older ages, it is not usually associated with such profound metabolic alkalosis. Gitelman syndrome mimics chronic use of thiazide diuretics and is associated with hypocalciuria.
Diuretic use could also cause the metabolic disturbances described; however, the patient denied taking diuretics.
The most common cause of hypokalemia in clinical practice is diuretic use.4 In this young woman with unexplained hypokalemia, the most likely cause is either undisclosed self-induced vomiting or diuretic abuse. The degree of metabolic alkalosis suggests vomiting, since metabolic alkalosis this severe is usually seen only with protracted vomiting. Bartter and Gitelman syndromes are included in the differential diagnosis, but they are much less common than hypokalemia associated with diuretics or self-induced vomiting.5
3. Which test could help elucidate the cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Ratio of plasma aldosterone to rennin
- Urine chloride
- Ratio of urinary potassium to creatinine
- Urinary anion gap and urinary pH
APPROACH TO HYPOKALEMIA
Determining the cause of hypokalemia starts with a thorough history and physical examination. The history should focus on drugs such as diuretics and laxatives. Women should be asked about their menstrual history since irregular periods may suggest an eating disorder. The physical examination should focus on signs that suggest self-induced vomiting, such as dry skin, dental erosions, enlarged parotid glands, and calluses or scars on the knuckles.
Patients with an unclear cause of hypokalemia after a thorough history and physical examination can be categorized into one of three groups based on blood pressure and acid-base status:
- Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis.
Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
The blood pressure provides an important clue in the evaluation of hypokalemia. The combination of hypertension, hypokalemia, and alkalosis should raise concern for hyperaldosteronism or pseudoaldosteronism. Primary hyperaldosteronism from an adrenal adenoma (Conn syndrome) is characterized by a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of greater than 20.6,7 In contrast, patients with secondary hyperaldosteronism due to renovascular disease have a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of less than 10. Patients with pseudoaldosteronism have low aldosterone and renin levels and hypertension. Since our patient has a normal blood pressure, testing the plasma aldosterone and renin levels would not help determine the cause of her hypokalemia.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
Patients with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and normal plasma anion gap acidosis either have renal tubular acidosis or have lost potassium because of diarrhea or laxative abuse. In a patient who denies taking laxatives or denies a history of diarrhea, checking the urinary anion gap and urinary pH may help differentiate the cause of acidosis and hypokalemia.
The urinary anion gap, calculated by the equation sodium + potassium − chloride, is an indirect estimate of hydrogen excretion in the form of ammonium ion8; the normal value is 0 to 10 mEq/L. A negative value represents increased hydrogen excretion in response to systemic acidosis from gastrointestinal or renal loss of bicarbonate (proximal renal tubular acidosis). A urinary pH greater than 5.5 in the setting of systemic acidosis suggests impaired ability of the kidneys to acidify urine and raises the possibility of renal tubular acidosis.
This patient has metabolic alkalosis, so calculation of the urinary anion gap would not be helpful.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis
Patients such as ours, with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and alkalosis, have been vomiting, have used diuretics, or have an inherited renal tubulopathy such as Bartter or Gitelman syndrome. Usually, differentiating Bartter and Gitelman syndromes from chronic vomiting or diuretic use is done with the history and physical examination. However, in patients with a questionable history and a lack of findings on physical examination, checking the urinary chloride, potassium, calcium, and creatinine may be helpful.
A urinary potassium-creatinine ratio greater than 15 suggests renal loss, whereas a ratio less than 15 suggests extrarenal loss.9
Patients who are taking a diuretic or who have Bartter or Gitelman syndrome have a high urinary chloride concentration, ie, greater than 20 mmol/L, whereas patients with hypokalemia and alkalosis from chronic vomiting tend to have a concentration less than 10 mmol/L.10
Table 1 summarizes an approach to the evaluation of unexplained hypokalemia based on blood pressure and acid-base status.
A HIDDEN HISTORY
On further questioning, the patient admits to an 8-year history of daily self-induced vomiting in an attempt to lose weight, in addition to multiple hospitalizations for hypokalemia and a previous diagnosis of an eating disorder.
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF HYPOKALEMIA
The initial management of hypokalemia should focus on life-threatening emergencies. While patients with potassium levels greater than 3 mmol/L are usually asymptomatic, those with levels below 3 mmol/L present with muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis.4 An acute drop in serum potassium to less than 2 mmol/L is associated with respiratory muscle weakness and ventricular arrhythmias.4 If the patient has cardiac symptoms or hypoventilation due to respiratory muscle weakness, continuous monitoring in the intensive care unit and aggressive therapy are warranted.
4. Which potassium formulation is most appropriate for the treatment of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Potassium chloride
- Potassium phosphate
- Potassium acetate
Oral potassium is preferable in patients with a serum potassium above 2.5 mmol/L.4,11 Potassium phosphate should be used when supplementation with both potassium and phosphorus is needed. Potassium acetate should be reserved for patients with acidosis and hypokalemia. Otherwise, potassium chloride is typically preferred.4,12 It comes in liquid and tablet forms. Liquid forms have an unpleasant taste, whereas tablets are usually well tolerated. No more than 20 to 40 mEq of potassium chloride tablets should be given at a time, since higher doses are associated with gastrointestinal mucosal injury.12
Potassium chloride is particularly preferred in patients with metabolic alkalosis, since increased chloride intake and delivery to the distal tubule increases the expression of pendrin, a luminal chloride and bicarbonate exchanger in the cortical collecting duct.13 With metabolic alkalosis, increased excretion of bicarbonate occurs through up-regulation of pendrin. Potassium depletion down-regulates pendrin.13 Additionally, correction of metabolic alkalosis increases serum potassium by movement of potassium from the intracellular to the extracellular space.
Intravenous potassium should be reserved for patients with severe hypokalemia (< 2.5 mmol/L) or significant arrhythmias.11 Oral and intravenous potassium can safely be given simultaneously.11 The intravenous rate should not exceed more than 10 to 20 mEq of potassium chloride per hour unless the patient has a life-threatening arrhythmia, respiratory failure, or severe hypokalemia.14,15 In life-threatening situations, a femoral line should be placed, and potassium should be given as rapidly as 20 mEq over 15 to 20 minutes.14 Cannulation of the subclavian and internal jugular veins should be avoided in severe hypokalemia since mechanical irritation from guidewire placement can provoke ventricular arrhythmias.14
During intravenous administration of potassium, laboratory monitoring after every 20 mEq of potassium chloride is advised because of the possibility of rebound hyperkalemia. In patients with severe hypokalemia, avoidance of factors that can worsen intracellular shift of potassium is also important. Avoid dextrose-containing fluids to prevent insulin-induced shifting of potassium into cells. Restore intravascular volume to blunt hypovolemia-induced renin and aldosterone secretion. If a patient presents with severe hypokalemia and acidosis, correct the hypokalemia before the acidosis to avoid intracellular shift of potassium.
OUR PATIENT’S MANAGEMENT AND FOLLOW-UP PLAN
Given the severity of our patient’s hypokalemia and her complaint of palpitations, she was admitted to the hospital for monitoring. She required 180 mEq of intravenous potassium chloride and 140 mEq of oral potassium chloride during the first 24 hours in order to achieve a serum potassium level above 3 mmol/L. Electrocardiographic U waves resolved once the level was above 2 mmol/L, and ST depressions resolved once it was above 3 mmol/L. The QT interval normalized after 24 hours of hospitalization.
On discharge, she was prescribed oral potassium chloride 40 mEq daily and magnesium sulfate 400 mg twice daily, with plans for a followup visit with her outpatient therapy team, which includes a psychiatrist, a social worker, and her primary care provider. She declined a referral for inpatient therapy but agreed to a goal of decreasing the frequency of induced vomiting and outpatient visits. She was also educated on how and when to access emergency medical care.16
A 20-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with fatigue and the sudden onset of palpitations. She reports no history of significant illness or surgery. She says she is not currently taking prescription or over-the-counter medications. She does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs.
Her weight is 52 kg (115 lb), her height is 170 cm (67 in), and her body mass index (BMI) is 18 kg/m2. Vital signs: temperature 35.7°C (96.4°F), blood pressure 92/48 mm Hg, heart rate 73 bpm, respiratory rate 5 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation 98% on room air.
She appears tired but is alert, conversant, and cooperative. Her skin is normal, and dentition is fair. Her pulse is regular, and respirations are slow. The abdomen is soft, non-tender, and flat. Strength is 4 on a scale of 5 in all extremities. Deep-tendon reflexes are 2+ and symmetric.
Electrocardiography (Figure 1) in the emergency department shows ST-segment depression, a prolonged corrected QT interval of 665 msec, T-wave inversion, PR prolongation, increased P-wave amplitude, and U waves.
1. Which electrolyte abnormality is associated with this electrocardiographic picture?
- Hypercalcemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is the likely cause of these findings. The finding of U waves is considered significant when they are inverted, merged with the T wave, or have an amplitude greater than the T wave.1 U waves are best seen in the precordial leads. When severe, hypokalemia can lead to potentially fatal arrhythmias such as high-grade atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.2
Hyperkalemia is associated with peaked T waves, a prolonged PR interval, decreased P wave amplitude, and a widened QRS complex.2 When acute and severe, hyperkalemia is associated with ventricular arrhythmia.
Hypocalcemia is associated with a prolonged QT interval and ventricular dysrhythmia, but not U waves.2
Hypercalcemia is associated with bradydysrhythmia, as well as with a shortened QT interval.2
LABORATORY TESTING
Laboratory testing shows the following:
- Sodium 126 mmol/L (reference range 135–145)
- Potassium 1.5 mmol/L (3.5–5.1)
- Chloride 58 mmol/L (100–110)
- Bicarbonate 62 mmol/L (20–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dL (7–18)
- Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL (0.5–1.0)
- Glucose 106 mg/dL (70–110)
- Ionized calcium 4.4 mg/dL (4.5–5.3)
- Magnesium 1.8 mg/dL (1.7–2.3)
- Phosphorus 4.1 mg/dL (2.5–4.5)
- Venous blood gases pH 7.56 (7.35–7.45), Pco2 69 mm Hg (35–45).
POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS
Ninety-eight percent of potassium is intracellular and only 2% is extracellular.3 The main cellular stores are myocytes and hepatocytes. Patients with decreased muscle mass may be at a higher risk of hypokalemia as a result of decreased skeletal muscle stores.4
The acute development of hypokalemia occurs from transcellular shifts. Alkalosis, insulin secretion, and beta-adrenergic stimulation promote the intracellular uptake of potassium. The major hormonal regulator of potassium excretion is aldosterone, which is stimulated by renal hypoperfusion and promotes potassium-ion secretion in the distal convoluted tubule.
Chronic hypokalemia develops in patients with ongoing renal or gastrointestinal potassium loss. If the cause of potassium loss is not elucidated by the history, the physical, and a review of medications, then one of two things is possible: either the patient has renal tubular disease affecting acid-base and potassium regulation, causing excessive mineralocorticoid secretion, which is associated with an abnormal response to aldosterone; or the patient is not being forthcoming in the history.
2. Which is the most likely cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Vomiting
- Liddle syndrome
- Bartter syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Diuretic use
Her laboratory tests reveal hypokalemia and hyponatremic-hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis with compensatory respiratory acidosis. In metabolic alkalosis, the expected respiratory compensation is an increase of 0.7 mm Hg in Pco2 for each 1-mEq/L increase in bicarbonate. Therefore, the expected Pco2 is 67, close to the patient’s actual value of 69.
Protracted vomiting with loss of gastric acid juices could be a cause of the metabolic disturbances in this young woman, although she did not mention vomiting during the history.
Liddle syndrome, or pseudoaldosteronism, is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by altered renal epithelial sodium channels, excessive sodium retention, and resultant hypertension. Hypokalemia and alkalosis are seen in Liddle syndrome, but the absence of hypertension in our patient makes Liddle syndrome unlikely.
Bartter syndrome is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder of the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending loop of Henle, resulting in impaired reabsorption of chloride and sodium. Bartter syndrome mimics chronic loop-diuretic use and is associated with hypercalciuria. Bartter syndrome is possible in this patient; however, patients with Bartter syndrome are usually diagnosed in infancy or childhood and have evidence of growth impairment.
Gitelman syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter. Although Gitelman syndrome is more common than Bartter syndrome and presents at older ages, it is not usually associated with such profound metabolic alkalosis. Gitelman syndrome mimics chronic use of thiazide diuretics and is associated with hypocalciuria.
Diuretic use could also cause the metabolic disturbances described; however, the patient denied taking diuretics.
The most common cause of hypokalemia in clinical practice is diuretic use.4 In this young woman with unexplained hypokalemia, the most likely cause is either undisclosed self-induced vomiting or diuretic abuse. The degree of metabolic alkalosis suggests vomiting, since metabolic alkalosis this severe is usually seen only with protracted vomiting. Bartter and Gitelman syndromes are included in the differential diagnosis, but they are much less common than hypokalemia associated with diuretics or self-induced vomiting.5
3. Which test could help elucidate the cause of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Ratio of plasma aldosterone to rennin
- Urine chloride
- Ratio of urinary potassium to creatinine
- Urinary anion gap and urinary pH
APPROACH TO HYPOKALEMIA
Determining the cause of hypokalemia starts with a thorough history and physical examination. The history should focus on drugs such as diuretics and laxatives. Women should be asked about their menstrual history since irregular periods may suggest an eating disorder. The physical examination should focus on signs that suggest self-induced vomiting, such as dry skin, dental erosions, enlarged parotid glands, and calluses or scars on the knuckles.
Patients with an unclear cause of hypokalemia after a thorough history and physical examination can be categorized into one of three groups based on blood pressure and acid-base status:
- Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
- Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis.
Hypokalemia, hypertension, metabolic alkalosis
The blood pressure provides an important clue in the evaluation of hypokalemia. The combination of hypertension, hypokalemia, and alkalosis should raise concern for hyperaldosteronism or pseudoaldosteronism. Primary hyperaldosteronism from an adrenal adenoma (Conn syndrome) is characterized by a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of greater than 20.6,7 In contrast, patients with secondary hyperaldosteronism due to renovascular disease have a plasma aldosterone-renin ratio of less than 10. Patients with pseudoaldosteronism have low aldosterone and renin levels and hypertension. Since our patient has a normal blood pressure, testing the plasma aldosterone and renin levels would not help determine the cause of her hypokalemia.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic acidosis
Patients with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and normal plasma anion gap acidosis either have renal tubular acidosis or have lost potassium because of diarrhea or laxative abuse. In a patient who denies taking laxatives or denies a history of diarrhea, checking the urinary anion gap and urinary pH may help differentiate the cause of acidosis and hypokalemia.
The urinary anion gap, calculated by the equation sodium + potassium − chloride, is an indirect estimate of hydrogen excretion in the form of ammonium ion8; the normal value is 0 to 10 mEq/L. A negative value represents increased hydrogen excretion in response to systemic acidosis from gastrointestinal or renal loss of bicarbonate (proximal renal tubular acidosis). A urinary pH greater than 5.5 in the setting of systemic acidosis suggests impaired ability of the kidneys to acidify urine and raises the possibility of renal tubular acidosis.
This patient has metabolic alkalosis, so calculation of the urinary anion gap would not be helpful.
Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, metabolic alkalosis
Patients such as ours, with normal blood pressure, hypokalemia, and alkalosis, have been vomiting, have used diuretics, or have an inherited renal tubulopathy such as Bartter or Gitelman syndrome. Usually, differentiating Bartter and Gitelman syndromes from chronic vomiting or diuretic use is done with the history and physical examination. However, in patients with a questionable history and a lack of findings on physical examination, checking the urinary chloride, potassium, calcium, and creatinine may be helpful.
A urinary potassium-creatinine ratio greater than 15 suggests renal loss, whereas a ratio less than 15 suggests extrarenal loss.9
Patients who are taking a diuretic or who have Bartter or Gitelman syndrome have a high urinary chloride concentration, ie, greater than 20 mmol/L, whereas patients with hypokalemia and alkalosis from chronic vomiting tend to have a concentration less than 10 mmol/L.10
Table 1 summarizes an approach to the evaluation of unexplained hypokalemia based on blood pressure and acid-base status.
A HIDDEN HISTORY
On further questioning, the patient admits to an 8-year history of daily self-induced vomiting in an attempt to lose weight, in addition to multiple hospitalizations for hypokalemia and a previous diagnosis of an eating disorder.
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF HYPOKALEMIA
The initial management of hypokalemia should focus on life-threatening emergencies. While patients with potassium levels greater than 3 mmol/L are usually asymptomatic, those with levels below 3 mmol/L present with muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis.4 An acute drop in serum potassium to less than 2 mmol/L is associated with respiratory muscle weakness and ventricular arrhythmias.4 If the patient has cardiac symptoms or hypoventilation due to respiratory muscle weakness, continuous monitoring in the intensive care unit and aggressive therapy are warranted.
4. Which potassium formulation is most appropriate for the treatment of hypokalemia in this patient?
- Potassium chloride
- Potassium phosphate
- Potassium acetate
Oral potassium is preferable in patients with a serum potassium above 2.5 mmol/L.4,11 Potassium phosphate should be used when supplementation with both potassium and phosphorus is needed. Potassium acetate should be reserved for patients with acidosis and hypokalemia. Otherwise, potassium chloride is typically preferred.4,12 It comes in liquid and tablet forms. Liquid forms have an unpleasant taste, whereas tablets are usually well tolerated. No more than 20 to 40 mEq of potassium chloride tablets should be given at a time, since higher doses are associated with gastrointestinal mucosal injury.12
Potassium chloride is particularly preferred in patients with metabolic alkalosis, since increased chloride intake and delivery to the distal tubule increases the expression of pendrin, a luminal chloride and bicarbonate exchanger in the cortical collecting duct.13 With metabolic alkalosis, increased excretion of bicarbonate occurs through up-regulation of pendrin. Potassium depletion down-regulates pendrin.13 Additionally, correction of metabolic alkalosis increases serum potassium by movement of potassium from the intracellular to the extracellular space.
Intravenous potassium should be reserved for patients with severe hypokalemia (< 2.5 mmol/L) or significant arrhythmias.11 Oral and intravenous potassium can safely be given simultaneously.11 The intravenous rate should not exceed more than 10 to 20 mEq of potassium chloride per hour unless the patient has a life-threatening arrhythmia, respiratory failure, or severe hypokalemia.14,15 In life-threatening situations, a femoral line should be placed, and potassium should be given as rapidly as 20 mEq over 15 to 20 minutes.14 Cannulation of the subclavian and internal jugular veins should be avoided in severe hypokalemia since mechanical irritation from guidewire placement can provoke ventricular arrhythmias.14
During intravenous administration of potassium, laboratory monitoring after every 20 mEq of potassium chloride is advised because of the possibility of rebound hyperkalemia. In patients with severe hypokalemia, avoidance of factors that can worsen intracellular shift of potassium is also important. Avoid dextrose-containing fluids to prevent insulin-induced shifting of potassium into cells. Restore intravascular volume to blunt hypovolemia-induced renin and aldosterone secretion. If a patient presents with severe hypokalemia and acidosis, correct the hypokalemia before the acidosis to avoid intracellular shift of potassium.
OUR PATIENT’S MANAGEMENT AND FOLLOW-UP PLAN
Given the severity of our patient’s hypokalemia and her complaint of palpitations, she was admitted to the hospital for monitoring. She required 180 mEq of intravenous potassium chloride and 140 mEq of oral potassium chloride during the first 24 hours in order to achieve a serum potassium level above 3 mmol/L. Electrocardiographic U waves resolved once the level was above 2 mmol/L, and ST depressions resolved once it was above 3 mmol/L. The QT interval normalized after 24 hours of hospitalization.
On discharge, she was prescribed oral potassium chloride 40 mEq daily and magnesium sulfate 400 mg twice daily, with plans for a followup visit with her outpatient therapy team, which includes a psychiatrist, a social worker, and her primary care provider. She declined a referral for inpatient therapy but agreed to a goal of decreasing the frequency of induced vomiting and outpatient visits. She was also educated on how and when to access emergency medical care.16
- Rautaharju PM, Surawicz B, Gettes LS, et al; American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; American College of Cardiology Foundation; Heart Rhythm Society. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part IV: the ST segment, T and U waves, and the QT Interval: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society. Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 53:982–991.
- Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC. Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities. J Emerg Med 2004; 27:153–160.
- Unwin RJ, Luft FC, Shirley DG. Pathophysiology and management of hypokalemia: a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011; 7:75–84.
- Gennari FJ. Hypokalemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 339:451–458.
- Mehler PS. Clinical practice. Bulimia nervosa. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:875–881.
- Tzanela M, Effraimidis G, Vassiliadi D, et al. The aldosterone to renin ratio in the evaluation of patients with incidentally detected adrenal masses. Endocrine 2007; 32:136–142.
- Diederich S, Mai K, Bähr V, Helffrich S, Pfeiffer A, Perschel FH. The simultaneous measurement of plasma-aldosterone- and -renin-concentration allows rapid classification of all disorders of the renin-aldosterone system. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2007; 115:433–438.
- Goldstein MB, Bear R, Richardson RM, Marsden PA, Halperin ML. The urine anion gap: a clinically useful index of ammonium excretion. Am J Med Sci 1986; 292:198–202.
- Groeneveld JH, Sijpkens YW, Lin SH, Davids MR, Halperin ML. An approach to the patient with severe hypokalaemia: the potassium quiz. QJM 2005; 98:305–316.
- Galla JH. Metabolic alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11:369–375.
- Asmar A, Mohandas R, Wingo CS. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of a patient with hypokalemia. Am J Kidney Dis 2012; 60:492–497.
- Cohn JN, Kowey PR, Whelton PK, Prisant LM. New guidelines for potassium replacement in clinical practice: a contemporary review by the National Council on Potassium in Clinical Practice. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160:2429–2436.
- Luke RG, Galla JH. It is chloride depletion alkalosis, not contraction alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23:204–207.
- Kruse JA, Carlson RW. Rapid correction of hypokalemia using concentrated intravenous potassium chloride infusions. Arch Intern Med 1990; 150:613–617.
- Weiner ID, Wingo CS. Hypokalemia—consequences, causes, and correction. J Am Soc Nephrol 1997; 8:1179–1188.
- AED Medical Care Standards Task Force. Eating disorders: Critical Points for Early Recognition and Medical Risk Management in the Care of Individuals with Eating Disorders. AED Report 2012. www.aedweb.org/web/downloads/Guide-English.pdf. Accessed April 4, 2014.
- Rautaharju PM, Surawicz B, Gettes LS, et al; American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; American College of Cardiology Foundation; Heart Rhythm Society. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part IV: the ST segment, T and U waves, and the QT Interval: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society. Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 53:982–991.
- Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC. Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities. J Emerg Med 2004; 27:153–160.
- Unwin RJ, Luft FC, Shirley DG. Pathophysiology and management of hypokalemia: a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011; 7:75–84.
- Gennari FJ. Hypokalemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 339:451–458.
- Mehler PS. Clinical practice. Bulimia nervosa. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:875–881.
- Tzanela M, Effraimidis G, Vassiliadi D, et al. The aldosterone to renin ratio in the evaluation of patients with incidentally detected adrenal masses. Endocrine 2007; 32:136–142.
- Diederich S, Mai K, Bähr V, Helffrich S, Pfeiffer A, Perschel FH. The simultaneous measurement of plasma-aldosterone- and -renin-concentration allows rapid classification of all disorders of the renin-aldosterone system. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2007; 115:433–438.
- Goldstein MB, Bear R, Richardson RM, Marsden PA, Halperin ML. The urine anion gap: a clinically useful index of ammonium excretion. Am J Med Sci 1986; 292:198–202.
- Groeneveld JH, Sijpkens YW, Lin SH, Davids MR, Halperin ML. An approach to the patient with severe hypokalaemia: the potassium quiz. QJM 2005; 98:305–316.
- Galla JH. Metabolic alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11:369–375.
- Asmar A, Mohandas R, Wingo CS. A physiologic-based approach to the treatment of a patient with hypokalemia. Am J Kidney Dis 2012; 60:492–497.
- Cohn JN, Kowey PR, Whelton PK, Prisant LM. New guidelines for potassium replacement in clinical practice: a contemporary review by the National Council on Potassium in Clinical Practice. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160:2429–2436.
- Luke RG, Galla JH. It is chloride depletion alkalosis, not contraction alkalosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23:204–207.
- Kruse JA, Carlson RW. Rapid correction of hypokalemia using concentrated intravenous potassium chloride infusions. Arch Intern Med 1990; 150:613–617.
- Weiner ID, Wingo CS. Hypokalemia—consequences, causes, and correction. J Am Soc Nephrol 1997; 8:1179–1188.
- AED Medical Care Standards Task Force. Eating disorders: Critical Points for Early Recognition and Medical Risk Management in the Care of Individuals with Eating Disorders. AED Report 2012. www.aedweb.org/web/downloads/Guide-English.pdf. Accessed April 4, 2014.
An 18-year-old woman with hepatic cysts
An 18-year-old woman presents with 3 days of epigastric abdominal pain, with no fever or constitutional symptoms. She was born in the United States and reports yearly trips since age 3 to her family’s farm in a rural area of Mexico, where she is exposed to dogs and horses.
Ultrasonography reveals two large hepatic cysts measuring 5.8 × 6.8 × 5.4 cm and 5.3 × 4.9 × 7 cm, with thickened walls and internal debris (Figure 1). The debris moves to dependent areas when the patient is asked to move onto her side.
Laboratory values at the time of presentation are as follows:
- White blood cell count 11.9 × 109/L (reference range 4.5–11.0), with 20% eosinophils
- Alkaline phosphatase 116 U/L (30–100)
- Total protein 7.3 g/dL (6.0–8.0)
- Albumin 4.3 g/dL (3.5–5.0)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 19 U/L (10–40)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 18 U/L (5–40)
- Total bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL (0.3–1.2)
- Direct bilirubin 0.1 mg/dL (0.1–0.3)
- Echinococcus antibody (IgG) testing is positive.
CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS
The two clinically relevant species of Echinococcus that cause human infection are E granulosus (in cystic echinococcosis) and E multilocularis (in alveolar echinococcosis). Based on clinical and radiographic findings, hepatic hydatid disease from cystic echinococcosis can usually be differentiated from the alveolar form.
E granulosus is a parasitic tapeworm that requires an intermediate host (sheep, goats, cows) and a definite host (dogs, foxes, and related species) for its life cycle. Humans become infected when they ingest food contaminated with feces that contain the eggs of the tapeworm or when they handle carnivorous animals, usually dogs, and accidentally ingest the tapeworm eggs. Once ingested, the egg releases an oncosphere that penetrates the intestinal wall, enters the circulation, and develops into a cyst, most often in the liver and the lungs.1 Human-to-human transmission does not occur.2
Hydatid cysts grow slowly, at a rate of 1 to 50 mm per year,3 so most patients remain asymptomatic for several years. Symptoms occur when a cyst ruptures or impinges on structures.3 Fever and constitutional symptoms usually occur only if there is rupture or bacterial superinfection of the cyst. Tests of liver function tend to be normal unless a cyst obstructs biliary flow. Eosinophilia occurs in 25% of patients.1 Eosinophilia along with the abrupt onset of abdominal pain suggests cyst rupture.
Making the diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by characteristic ultrasonographic findings and by serologic testing. Antibody assays for Echinococcus include indirect hemagglutination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and latex agglutination. However, these serologic antibody assays for immunoglobulin G cross-react to different echinococcal species as well as to other helminthic infections. Specific serologic studies such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for E multilocularis are available to confirm the species of Echinococcus but are only used to distinguish cystic echinococcosis from alveolar echinococcosis.
Treatment options
Treatment options include surgery, percutaneous procedures, drug therapy, and observation.
Currently, there is no clear consensus on treatment. To guide treatment decisions, the World Health Organization Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis (WHO-IWGE) recommends management of hepatic hydatid cysts based on classification, size, symptoms, location, and available resources.3
Two percutaneous treatments are aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration to destroy the germinal matrix, and percutaneous therapy to destroy the endocyst. Percutaneous aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration is increasingly used as the first-line treatment for single or easily accessible cysts and for patients who cannot undergo surgery. Surgery is considered for multiple cysts, large cysts, and cysts not easily accessible with a percutaneous technique.3 Complication rates and length of hospital stay with percutaneous aspiration are lower than with surgery.4 Observation is recommended for small, asymptomatic, inactive cysts.
Leakage of cyst contents during surgical or percutaneous intervention or spontaneous rupture can cause a recurrence,5 and anaphylaxis is a potential complication of cyst rupture.1 For this reason, giving oral albendazole (Albenza) is recommended before any intervention. Sterilization of the cyst contents with a protoscolicidal agent (20% NaCl) before evacuation of cyst contents is also standard practice.
The rate of cyst recurrence is 16.2% with open surgery and 3.5% with percutaneous intervention.6 A higher incidence of recurrence in patients who undergo surgical cystectomy likely reflects the more complicated and active nature of the cysts in patients who undergo surgery.6
Albendazole is the drug of choice for hepatic hydatid disease.3 The optimal duration of treatment is unclear but should be guided by a combination of clinical response, medication side effects, serologic titers, and imaging. The most common adverse effects of albendazole are hepatotoxicity, abdominal pain, and nausea.
OUR PATIENT’S DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
In our patient, ultrasonography confirmed the diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis by the finding of active anechoic cysts with echogenic internal debris and with a well-delineated cyst wall. The WHO-IWGE classification was CE1, ie, active anechoic cysts with internal echogenic debris.
Our patient underwent surgical rather than percutaneous cystectomy because of concern about possible cyst leakage, since she had presented with the acute onset of pain and eosinophilia. We were also concerned about the subdiaphragmatic location of the larger cyst, which could have been difficult to reach percutaneously.
Open total pericystectomy involved opening the cyst cavity, sterilizing the contents with 20% NaCl, evacuating the cyst contents, and removing the cyst tissue. Two large cysts were excised and sent for histologic examination, which confirmed E granulosus. Percutaneous aspiration was necessary 4 months later because of a recurrence, and albendazole 400 mg twice daily was continued for another 5 months. Ultrasonography 3 years later showed no evidence of echinococcal cysts, and her antibody titers remain undetectable.
- McManus DP, Gray DJ, Zhang W, Yang Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012; 344:e3866.
- McManus DP, Zhang W, Li J, Bartley PB. Echinococcosis. Lancet 2003; 362:1295–1304.
- Brunetti E, Kern P, Vuitton DA; Writing Panel for the WHO-IWGE. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop 2010; 114:1–16.
- Khuroo MS, Wani NA, Javid G, et al. Percutaneous drainage compared with surgery for hepatic hydatid cysts. N Engl J Med 1997; 337:881–887.
- Kayaalp C, Sengul N, Akoglu M. Importance of cyst content in hydatid liver surgery. Arch Surg 2002; 137:159–163.
- Yagci G, Ustunsoz B, Kaymakcioglu N, et al. Results of surgical, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: 10 years experience with 355 patients. World J Surg 2005; 29:1670–1679.
An 18-year-old woman presents with 3 days of epigastric abdominal pain, with no fever or constitutional symptoms. She was born in the United States and reports yearly trips since age 3 to her family’s farm in a rural area of Mexico, where she is exposed to dogs and horses.
Ultrasonography reveals two large hepatic cysts measuring 5.8 × 6.8 × 5.4 cm and 5.3 × 4.9 × 7 cm, with thickened walls and internal debris (Figure 1). The debris moves to dependent areas when the patient is asked to move onto her side.
Laboratory values at the time of presentation are as follows:
- White blood cell count 11.9 × 109/L (reference range 4.5–11.0), with 20% eosinophils
- Alkaline phosphatase 116 U/L (30–100)
- Total protein 7.3 g/dL (6.0–8.0)
- Albumin 4.3 g/dL (3.5–5.0)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 19 U/L (10–40)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 18 U/L (5–40)
- Total bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL (0.3–1.2)
- Direct bilirubin 0.1 mg/dL (0.1–0.3)
- Echinococcus antibody (IgG) testing is positive.
CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS
The two clinically relevant species of Echinococcus that cause human infection are E granulosus (in cystic echinococcosis) and E multilocularis (in alveolar echinococcosis). Based on clinical and radiographic findings, hepatic hydatid disease from cystic echinococcosis can usually be differentiated from the alveolar form.
E granulosus is a parasitic tapeworm that requires an intermediate host (sheep, goats, cows) and a definite host (dogs, foxes, and related species) for its life cycle. Humans become infected when they ingest food contaminated with feces that contain the eggs of the tapeworm or when they handle carnivorous animals, usually dogs, and accidentally ingest the tapeworm eggs. Once ingested, the egg releases an oncosphere that penetrates the intestinal wall, enters the circulation, and develops into a cyst, most often in the liver and the lungs.1 Human-to-human transmission does not occur.2
Hydatid cysts grow slowly, at a rate of 1 to 50 mm per year,3 so most patients remain asymptomatic for several years. Symptoms occur when a cyst ruptures or impinges on structures.3 Fever and constitutional symptoms usually occur only if there is rupture or bacterial superinfection of the cyst. Tests of liver function tend to be normal unless a cyst obstructs biliary flow. Eosinophilia occurs in 25% of patients.1 Eosinophilia along with the abrupt onset of abdominal pain suggests cyst rupture.
Making the diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by characteristic ultrasonographic findings and by serologic testing. Antibody assays for Echinococcus include indirect hemagglutination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and latex agglutination. However, these serologic antibody assays for immunoglobulin G cross-react to different echinococcal species as well as to other helminthic infections. Specific serologic studies such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for E multilocularis are available to confirm the species of Echinococcus but are only used to distinguish cystic echinococcosis from alveolar echinococcosis.
Treatment options
Treatment options include surgery, percutaneous procedures, drug therapy, and observation.
Currently, there is no clear consensus on treatment. To guide treatment decisions, the World Health Organization Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis (WHO-IWGE) recommends management of hepatic hydatid cysts based on classification, size, symptoms, location, and available resources.3
Two percutaneous treatments are aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration to destroy the germinal matrix, and percutaneous therapy to destroy the endocyst. Percutaneous aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration is increasingly used as the first-line treatment for single or easily accessible cysts and for patients who cannot undergo surgery. Surgery is considered for multiple cysts, large cysts, and cysts not easily accessible with a percutaneous technique.3 Complication rates and length of hospital stay with percutaneous aspiration are lower than with surgery.4 Observation is recommended for small, asymptomatic, inactive cysts.
Leakage of cyst contents during surgical or percutaneous intervention or spontaneous rupture can cause a recurrence,5 and anaphylaxis is a potential complication of cyst rupture.1 For this reason, giving oral albendazole (Albenza) is recommended before any intervention. Sterilization of the cyst contents with a protoscolicidal agent (20% NaCl) before evacuation of cyst contents is also standard practice.
The rate of cyst recurrence is 16.2% with open surgery and 3.5% with percutaneous intervention.6 A higher incidence of recurrence in patients who undergo surgical cystectomy likely reflects the more complicated and active nature of the cysts in patients who undergo surgery.6
Albendazole is the drug of choice for hepatic hydatid disease.3 The optimal duration of treatment is unclear but should be guided by a combination of clinical response, medication side effects, serologic titers, and imaging. The most common adverse effects of albendazole are hepatotoxicity, abdominal pain, and nausea.
OUR PATIENT’S DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
In our patient, ultrasonography confirmed the diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis by the finding of active anechoic cysts with echogenic internal debris and with a well-delineated cyst wall. The WHO-IWGE classification was CE1, ie, active anechoic cysts with internal echogenic debris.
Our patient underwent surgical rather than percutaneous cystectomy because of concern about possible cyst leakage, since she had presented with the acute onset of pain and eosinophilia. We were also concerned about the subdiaphragmatic location of the larger cyst, which could have been difficult to reach percutaneously.
Open total pericystectomy involved opening the cyst cavity, sterilizing the contents with 20% NaCl, evacuating the cyst contents, and removing the cyst tissue. Two large cysts were excised and sent for histologic examination, which confirmed E granulosus. Percutaneous aspiration was necessary 4 months later because of a recurrence, and albendazole 400 mg twice daily was continued for another 5 months. Ultrasonography 3 years later showed no evidence of echinococcal cysts, and her antibody titers remain undetectable.
An 18-year-old woman presents with 3 days of epigastric abdominal pain, with no fever or constitutional symptoms. She was born in the United States and reports yearly trips since age 3 to her family’s farm in a rural area of Mexico, where she is exposed to dogs and horses.
Ultrasonography reveals two large hepatic cysts measuring 5.8 × 6.8 × 5.4 cm and 5.3 × 4.9 × 7 cm, with thickened walls and internal debris (Figure 1). The debris moves to dependent areas when the patient is asked to move onto her side.
Laboratory values at the time of presentation are as follows:
- White blood cell count 11.9 × 109/L (reference range 4.5–11.0), with 20% eosinophils
- Alkaline phosphatase 116 U/L (30–100)
- Total protein 7.3 g/dL (6.0–8.0)
- Albumin 4.3 g/dL (3.5–5.0)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 19 U/L (10–40)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 18 U/L (5–40)
- Total bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL (0.3–1.2)
- Direct bilirubin 0.1 mg/dL (0.1–0.3)
- Echinococcus antibody (IgG) testing is positive.
CYSTIC ECHINOCOCCOSIS
The two clinically relevant species of Echinococcus that cause human infection are E granulosus (in cystic echinococcosis) and E multilocularis (in alveolar echinococcosis). Based on clinical and radiographic findings, hepatic hydatid disease from cystic echinococcosis can usually be differentiated from the alveolar form.
E granulosus is a parasitic tapeworm that requires an intermediate host (sheep, goats, cows) and a definite host (dogs, foxes, and related species) for its life cycle. Humans become infected when they ingest food contaminated with feces that contain the eggs of the tapeworm or when they handle carnivorous animals, usually dogs, and accidentally ingest the tapeworm eggs. Once ingested, the egg releases an oncosphere that penetrates the intestinal wall, enters the circulation, and develops into a cyst, most often in the liver and the lungs.1 Human-to-human transmission does not occur.2
Hydatid cysts grow slowly, at a rate of 1 to 50 mm per year,3 so most patients remain asymptomatic for several years. Symptoms occur when a cyst ruptures or impinges on structures.3 Fever and constitutional symptoms usually occur only if there is rupture or bacterial superinfection of the cyst. Tests of liver function tend to be normal unless a cyst obstructs biliary flow. Eosinophilia occurs in 25% of patients.1 Eosinophilia along with the abrupt onset of abdominal pain suggests cyst rupture.
Making the diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by characteristic ultrasonographic findings and by serologic testing. Antibody assays for Echinococcus include indirect hemagglutination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and latex agglutination. However, these serologic antibody assays for immunoglobulin G cross-react to different echinococcal species as well as to other helminthic infections. Specific serologic studies such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for E multilocularis are available to confirm the species of Echinococcus but are only used to distinguish cystic echinococcosis from alveolar echinococcosis.
Treatment options
Treatment options include surgery, percutaneous procedures, drug therapy, and observation.
Currently, there is no clear consensus on treatment. To guide treatment decisions, the World Health Organization Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis (WHO-IWGE) recommends management of hepatic hydatid cysts based on classification, size, symptoms, location, and available resources.3
Two percutaneous treatments are aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration to destroy the germinal matrix, and percutaneous therapy to destroy the endocyst. Percutaneous aspiration, injection, and re-aspiration is increasingly used as the first-line treatment for single or easily accessible cysts and for patients who cannot undergo surgery. Surgery is considered for multiple cysts, large cysts, and cysts not easily accessible with a percutaneous technique.3 Complication rates and length of hospital stay with percutaneous aspiration are lower than with surgery.4 Observation is recommended for small, asymptomatic, inactive cysts.
Leakage of cyst contents during surgical or percutaneous intervention or spontaneous rupture can cause a recurrence,5 and anaphylaxis is a potential complication of cyst rupture.1 For this reason, giving oral albendazole (Albenza) is recommended before any intervention. Sterilization of the cyst contents with a protoscolicidal agent (20% NaCl) before evacuation of cyst contents is also standard practice.
The rate of cyst recurrence is 16.2% with open surgery and 3.5% with percutaneous intervention.6 A higher incidence of recurrence in patients who undergo surgical cystectomy likely reflects the more complicated and active nature of the cysts in patients who undergo surgery.6
Albendazole is the drug of choice for hepatic hydatid disease.3 The optimal duration of treatment is unclear but should be guided by a combination of clinical response, medication side effects, serologic titers, and imaging. The most common adverse effects of albendazole are hepatotoxicity, abdominal pain, and nausea.
OUR PATIENT’S DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
In our patient, ultrasonography confirmed the diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis by the finding of active anechoic cysts with echogenic internal debris and with a well-delineated cyst wall. The WHO-IWGE classification was CE1, ie, active anechoic cysts with internal echogenic debris.
Our patient underwent surgical rather than percutaneous cystectomy because of concern about possible cyst leakage, since she had presented with the acute onset of pain and eosinophilia. We were also concerned about the subdiaphragmatic location of the larger cyst, which could have been difficult to reach percutaneously.
Open total pericystectomy involved opening the cyst cavity, sterilizing the contents with 20% NaCl, evacuating the cyst contents, and removing the cyst tissue. Two large cysts were excised and sent for histologic examination, which confirmed E granulosus. Percutaneous aspiration was necessary 4 months later because of a recurrence, and albendazole 400 mg twice daily was continued for another 5 months. Ultrasonography 3 years later showed no evidence of echinococcal cysts, and her antibody titers remain undetectable.
- McManus DP, Gray DJ, Zhang W, Yang Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012; 344:e3866.
- McManus DP, Zhang W, Li J, Bartley PB. Echinococcosis. Lancet 2003; 362:1295–1304.
- Brunetti E, Kern P, Vuitton DA; Writing Panel for the WHO-IWGE. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop 2010; 114:1–16.
- Khuroo MS, Wani NA, Javid G, et al. Percutaneous drainage compared with surgery for hepatic hydatid cysts. N Engl J Med 1997; 337:881–887.
- Kayaalp C, Sengul N, Akoglu M. Importance of cyst content in hydatid liver surgery. Arch Surg 2002; 137:159–163.
- Yagci G, Ustunsoz B, Kaymakcioglu N, et al. Results of surgical, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: 10 years experience with 355 patients. World J Surg 2005; 29:1670–1679.
- McManus DP, Gray DJ, Zhang W, Yang Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012; 344:e3866.
- McManus DP, Zhang W, Li J, Bartley PB. Echinococcosis. Lancet 2003; 362:1295–1304.
- Brunetti E, Kern P, Vuitton DA; Writing Panel for the WHO-IWGE. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop 2010; 114:1–16.
- Khuroo MS, Wani NA, Javid G, et al. Percutaneous drainage compared with surgery for hepatic hydatid cysts. N Engl J Med 1997; 337:881–887.
- Kayaalp C, Sengul N, Akoglu M. Importance of cyst content in hydatid liver surgery. Arch Surg 2002; 137:159–163.
- Yagci G, Ustunsoz B, Kaymakcioglu N, et al. Results of surgical, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: 10 years experience with 355 patients. World J Surg 2005; 29:1670–1679.