User login
First prospective study finds pregnancies with Sjögren’s to be largely safe
Women with Sjögren’s syndrome have pregnancy outcomes similar to those of the general population, according to the first study to prospectively track pregnancy outcomes among people with the autoimmune condition.
“Most early studies of pregnancy in rheumatic disease patients were retrospective and included only small numbers, making it difficult to know how generalizable the reported results were,” said Lisa Sammaritano, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, in an email interview with this news organization. She was not involved with the research.
Most of these previous studies suggested an increased risk of adverse outcomes, such as miscarriages, preterm deliveries, and small-for-gestational-age birth weight. But in addition to small patient numbers, retrospective studies “are subject to greater reporting bias, which may predispose patients with negative outcomes being more likely to be included because they were followed more closely,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“This prospective study has several advantages over the earlier retrospective reports: The same data were collected in the same way for all the patients, the patients were recruited at similar time points, and – due to the multicenter nature of the cohort – numbers are larger than in prior studies. All these factors make the results stronger and more generalizable to the Sjögren’s patients we see in our practices,” she added.
In the study, published May 8 in The Lancet Rheumatology, first author Grégoire Martin de Frémont, MD, of the rheumatology service at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University and colleagues used the GR2 registry, an observational database of pregnancies of women with systemic autoimmune diseases managed at 76 participating centers in France, to identify pregnant women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. To avoid bias, only women who entered the database before 18 weeks’ gestation were included. The final cohort included 106 pregnancies in 96 women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and 420 control pregnancies that were matched from the general population.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm delivery (< 37 weeks of gestation), intrauterine growth retardation, and low birth weight occurred in nine pregnancies (9%) in the Sjögren’s syndrome group and in 28 pregnancies in the control group (7%). Adverse pregnancy outcomes were not significantly associated with Sjögren’s syndrome (P = .52). Researchers found that there were more adverse pregnancy outcomes among women with Sjögren’s syndrome with antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies. Negative outcomes also increased among those with anti-RNP antibodies, but this association was not statistically significant.
“The main message – based on strong data from a well-designed study – is that patients with Sjögren’s overall do as well as the general population in terms of standard adverse pregnancy outcomes. The rate of flare of Sjögren’s disease was relatively low during the second and third trimesters, also reassuring,” Dr. Sammaritano said. She noted that the association between adverse pregnancy outcomes and aPL antibodies was not unexpected, given that they are a known risk factor.
The study authors recommend that patients with Sjögren’s syndrome be screened for aPL and anti-RNP antibodies prior to conception because of the potential increased risk for complications and that patients with positive screens be closely monitored during their pregnancy.
Dr. Sammaritano noted that there are other health problems to keep in mind. “It is important to remember that Sjögren’s patients – more than any other rheumatic disease patients – have the additional risk for neonatal lupus and complete heart block in their infant, since about two-thirds of Sjögren’s patients are positive for anti-Ro/SSA antibody,” she said. “This is a distinct issue related to the presence of this antibody alone and not specifically related to the underlying diagnosis. In clinical practice, positive anti-Ro/SSA antibody is often the main reason for counseling, monitoring, and even recommending therapy (hydroxychloroquine) in these patients.”
The study received funding from Lupus France, the France Association of Scleroderma, and the Association Gougerot Sjögren, among others. Dr. Sammaritano reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with Sjögren’s syndrome have pregnancy outcomes similar to those of the general population, according to the first study to prospectively track pregnancy outcomes among people with the autoimmune condition.
“Most early studies of pregnancy in rheumatic disease patients were retrospective and included only small numbers, making it difficult to know how generalizable the reported results were,” said Lisa Sammaritano, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, in an email interview with this news organization. She was not involved with the research.
Most of these previous studies suggested an increased risk of adverse outcomes, such as miscarriages, preterm deliveries, and small-for-gestational-age birth weight. But in addition to small patient numbers, retrospective studies “are subject to greater reporting bias, which may predispose patients with negative outcomes being more likely to be included because they were followed more closely,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“This prospective study has several advantages over the earlier retrospective reports: The same data were collected in the same way for all the patients, the patients were recruited at similar time points, and – due to the multicenter nature of the cohort – numbers are larger than in prior studies. All these factors make the results stronger and more generalizable to the Sjögren’s patients we see in our practices,” she added.
In the study, published May 8 in The Lancet Rheumatology, first author Grégoire Martin de Frémont, MD, of the rheumatology service at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University and colleagues used the GR2 registry, an observational database of pregnancies of women with systemic autoimmune diseases managed at 76 participating centers in France, to identify pregnant women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. To avoid bias, only women who entered the database before 18 weeks’ gestation were included. The final cohort included 106 pregnancies in 96 women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and 420 control pregnancies that were matched from the general population.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm delivery (< 37 weeks of gestation), intrauterine growth retardation, and low birth weight occurred in nine pregnancies (9%) in the Sjögren’s syndrome group and in 28 pregnancies in the control group (7%). Adverse pregnancy outcomes were not significantly associated with Sjögren’s syndrome (P = .52). Researchers found that there were more adverse pregnancy outcomes among women with Sjögren’s syndrome with antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies. Negative outcomes also increased among those with anti-RNP antibodies, but this association was not statistically significant.
“The main message – based on strong data from a well-designed study – is that patients with Sjögren’s overall do as well as the general population in terms of standard adverse pregnancy outcomes. The rate of flare of Sjögren’s disease was relatively low during the second and third trimesters, also reassuring,” Dr. Sammaritano said. She noted that the association between adverse pregnancy outcomes and aPL antibodies was not unexpected, given that they are a known risk factor.
The study authors recommend that patients with Sjögren’s syndrome be screened for aPL and anti-RNP antibodies prior to conception because of the potential increased risk for complications and that patients with positive screens be closely monitored during their pregnancy.
Dr. Sammaritano noted that there are other health problems to keep in mind. “It is important to remember that Sjögren’s patients – more than any other rheumatic disease patients – have the additional risk for neonatal lupus and complete heart block in their infant, since about two-thirds of Sjögren’s patients are positive for anti-Ro/SSA antibody,” she said. “This is a distinct issue related to the presence of this antibody alone and not specifically related to the underlying diagnosis. In clinical practice, positive anti-Ro/SSA antibody is often the main reason for counseling, monitoring, and even recommending therapy (hydroxychloroquine) in these patients.”
The study received funding from Lupus France, the France Association of Scleroderma, and the Association Gougerot Sjögren, among others. Dr. Sammaritano reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with Sjögren’s syndrome have pregnancy outcomes similar to those of the general population, according to the first study to prospectively track pregnancy outcomes among people with the autoimmune condition.
“Most early studies of pregnancy in rheumatic disease patients were retrospective and included only small numbers, making it difficult to know how generalizable the reported results were,” said Lisa Sammaritano, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, in an email interview with this news organization. She was not involved with the research.
Most of these previous studies suggested an increased risk of adverse outcomes, such as miscarriages, preterm deliveries, and small-for-gestational-age birth weight. But in addition to small patient numbers, retrospective studies “are subject to greater reporting bias, which may predispose patients with negative outcomes being more likely to be included because they were followed more closely,” Dr. Sammaritano said.
“This prospective study has several advantages over the earlier retrospective reports: The same data were collected in the same way for all the patients, the patients were recruited at similar time points, and – due to the multicenter nature of the cohort – numbers are larger than in prior studies. All these factors make the results stronger and more generalizable to the Sjögren’s patients we see in our practices,” she added.
In the study, published May 8 in The Lancet Rheumatology, first author Grégoire Martin de Frémont, MD, of the rheumatology service at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University and colleagues used the GR2 registry, an observational database of pregnancies of women with systemic autoimmune diseases managed at 76 participating centers in France, to identify pregnant women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. To avoid bias, only women who entered the database before 18 weeks’ gestation were included. The final cohort included 106 pregnancies in 96 women with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and 420 control pregnancies that were matched from the general population.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm delivery (< 37 weeks of gestation), intrauterine growth retardation, and low birth weight occurred in nine pregnancies (9%) in the Sjögren’s syndrome group and in 28 pregnancies in the control group (7%). Adverse pregnancy outcomes were not significantly associated with Sjögren’s syndrome (P = .52). Researchers found that there were more adverse pregnancy outcomes among women with Sjögren’s syndrome with antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies. Negative outcomes also increased among those with anti-RNP antibodies, but this association was not statistically significant.
“The main message – based on strong data from a well-designed study – is that patients with Sjögren’s overall do as well as the general population in terms of standard adverse pregnancy outcomes. The rate of flare of Sjögren’s disease was relatively low during the second and third trimesters, also reassuring,” Dr. Sammaritano said. She noted that the association between adverse pregnancy outcomes and aPL antibodies was not unexpected, given that they are a known risk factor.
The study authors recommend that patients with Sjögren’s syndrome be screened for aPL and anti-RNP antibodies prior to conception because of the potential increased risk for complications and that patients with positive screens be closely monitored during their pregnancy.
Dr. Sammaritano noted that there are other health problems to keep in mind. “It is important to remember that Sjögren’s patients – more than any other rheumatic disease patients – have the additional risk for neonatal lupus and complete heart block in their infant, since about two-thirds of Sjögren’s patients are positive for anti-Ro/SSA antibody,” she said. “This is a distinct issue related to the presence of this antibody alone and not specifically related to the underlying diagnosis. In clinical practice, positive anti-Ro/SSA antibody is often the main reason for counseling, monitoring, and even recommending therapy (hydroxychloroquine) in these patients.”
The study received funding from Lupus France, the France Association of Scleroderma, and the Association Gougerot Sjögren, among others. Dr. Sammaritano reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
Investigational lupus drug cenerimod moves to phase 3 studies after equivocal phase 2 results
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A once-daily, oral dose of the investigational drug cenerimod, developed for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, has shown a greater response rate among individuals with more severe disease, according to data presented at an international congress on SLE.
Cenerimod is a potent, highly-selective sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) modulator with attenuated calcium signaling, which targets an important signaling molecule in immunity and cell migration, said rheumatologist Sandra Navarra, MD, of the University of Santo Tomas Hospital and St. Luke’s Medical Center in Manila, Philippines.
“It reduces the migration of T cells and B cells from the lymph nodes to the circulation into the tissues,” Dr. Navarra told the conference. S1P1 receptor modulators are already approved for treatment of multiple sclerosis, but cenerimod is the first to be explored for the treatment of lupus.
Dr. Navarra presented data from the international CARE study, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study involving 427 patients with moderate to severe SLE.
Patients had to have been diagnosed at least 6 months before screening, be on stable lupus medications, and have abnormal antinuclear or anti–double stranded DNA antibodies. They were randomized to either 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, or 4 mg of cenerimod daily or placebo for 12 months. At 6 months, the patients who had initially been randomized to 4 mg daily were rerandomized either to 2 mg daily or placebo.
While the study found that 4 mg of cenerimod was associated with a reduction in disease activity from baseline to month 6 on the modified Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2000 score (excluding leukopenia), compared with placebo (P = .029). However, the final result was not statistically significant after adjustment for the multiplicity of tests for the four doses against placebo.
But the researchers saw a greater response among individuals with higher levels of interferon type 1 gene expression at baseline, as well as those with higher anti-dsDNA and lower C4 levels, which “makes sense,” Dr. Navarra said in an interview, because those were the sicker patients with “more inflammatory, more active disease.”
The study did exclude patients with active lupus nephritis, severe active central nervous system lupus, or severe cardiovascular disorders.
Dr. Navarra said the findings are now factored into patient selection for two phase 3 trials, called OPUS-1 and OPUS-2, which are now underway. The OPUS trials have revised eligibility criteria, as well as a screening period of up to 60 days to ensure that only patients with true moderate to severe SLE are enrolled.
The drug was well tolerated, with the rate of adverse events similar across all study groups. The adverse events of particular interest – hypertension, infections and infestations, and eye disorders – were all mild and transient. There were a greater number of reports of hypertension among those taking 1-mg and 4-mg doses of cenerimod, but Dr. Navarra said monthly measurements of systolic or diastolic blood pressure didn’t show any change.
The study was funded by cenerimod manufacturer Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Navarra has financial relationships with Biogen, Astellas, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and GlaxoSmithKline.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A once-daily, oral dose of the investigational drug cenerimod, developed for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, has shown a greater response rate among individuals with more severe disease, according to data presented at an international congress on SLE.
Cenerimod is a potent, highly-selective sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) modulator with attenuated calcium signaling, which targets an important signaling molecule in immunity and cell migration, said rheumatologist Sandra Navarra, MD, of the University of Santo Tomas Hospital and St. Luke’s Medical Center in Manila, Philippines.
“It reduces the migration of T cells and B cells from the lymph nodes to the circulation into the tissues,” Dr. Navarra told the conference. S1P1 receptor modulators are already approved for treatment of multiple sclerosis, but cenerimod is the first to be explored for the treatment of lupus.
Dr. Navarra presented data from the international CARE study, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study involving 427 patients with moderate to severe SLE.
Patients had to have been diagnosed at least 6 months before screening, be on stable lupus medications, and have abnormal antinuclear or anti–double stranded DNA antibodies. They were randomized to either 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, or 4 mg of cenerimod daily or placebo for 12 months. At 6 months, the patients who had initially been randomized to 4 mg daily were rerandomized either to 2 mg daily or placebo.
While the study found that 4 mg of cenerimod was associated with a reduction in disease activity from baseline to month 6 on the modified Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2000 score (excluding leukopenia), compared with placebo (P = .029). However, the final result was not statistically significant after adjustment for the multiplicity of tests for the four doses against placebo.
But the researchers saw a greater response among individuals with higher levels of interferon type 1 gene expression at baseline, as well as those with higher anti-dsDNA and lower C4 levels, which “makes sense,” Dr. Navarra said in an interview, because those were the sicker patients with “more inflammatory, more active disease.”
The study did exclude patients with active lupus nephritis, severe active central nervous system lupus, or severe cardiovascular disorders.
Dr. Navarra said the findings are now factored into patient selection for two phase 3 trials, called OPUS-1 and OPUS-2, which are now underway. The OPUS trials have revised eligibility criteria, as well as a screening period of up to 60 days to ensure that only patients with true moderate to severe SLE are enrolled.
The drug was well tolerated, with the rate of adverse events similar across all study groups. The adverse events of particular interest – hypertension, infections and infestations, and eye disorders – were all mild and transient. There were a greater number of reports of hypertension among those taking 1-mg and 4-mg doses of cenerimod, but Dr. Navarra said monthly measurements of systolic or diastolic blood pressure didn’t show any change.
The study was funded by cenerimod manufacturer Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Navarra has financial relationships with Biogen, Astellas, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and GlaxoSmithKline.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A once-daily, oral dose of the investigational drug cenerimod, developed for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, has shown a greater response rate among individuals with more severe disease, according to data presented at an international congress on SLE.
Cenerimod is a potent, highly-selective sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) modulator with attenuated calcium signaling, which targets an important signaling molecule in immunity and cell migration, said rheumatologist Sandra Navarra, MD, of the University of Santo Tomas Hospital and St. Luke’s Medical Center in Manila, Philippines.
“It reduces the migration of T cells and B cells from the lymph nodes to the circulation into the tissues,” Dr. Navarra told the conference. S1P1 receptor modulators are already approved for treatment of multiple sclerosis, but cenerimod is the first to be explored for the treatment of lupus.
Dr. Navarra presented data from the international CARE study, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study involving 427 patients with moderate to severe SLE.
Patients had to have been diagnosed at least 6 months before screening, be on stable lupus medications, and have abnormal antinuclear or anti–double stranded DNA antibodies. They were randomized to either 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, or 4 mg of cenerimod daily or placebo for 12 months. At 6 months, the patients who had initially been randomized to 4 mg daily were rerandomized either to 2 mg daily or placebo.
While the study found that 4 mg of cenerimod was associated with a reduction in disease activity from baseline to month 6 on the modified Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2000 score (excluding leukopenia), compared with placebo (P = .029). However, the final result was not statistically significant after adjustment for the multiplicity of tests for the four doses against placebo.
But the researchers saw a greater response among individuals with higher levels of interferon type 1 gene expression at baseline, as well as those with higher anti-dsDNA and lower C4 levels, which “makes sense,” Dr. Navarra said in an interview, because those were the sicker patients with “more inflammatory, more active disease.”
The study did exclude patients with active lupus nephritis, severe active central nervous system lupus, or severe cardiovascular disorders.
Dr. Navarra said the findings are now factored into patient selection for two phase 3 trials, called OPUS-1 and OPUS-2, which are now underway. The OPUS trials have revised eligibility criteria, as well as a screening period of up to 60 days to ensure that only patients with true moderate to severe SLE are enrolled.
The drug was well tolerated, with the rate of adverse events similar across all study groups. The adverse events of particular interest – hypertension, infections and infestations, and eye disorders – were all mild and transient. There were a greater number of reports of hypertension among those taking 1-mg and 4-mg doses of cenerimod, but Dr. Navarra said monthly measurements of systolic or diastolic blood pressure didn’t show any change.
The study was funded by cenerimod manufacturer Idorsia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Navarra has financial relationships with Biogen, Astellas, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and GlaxoSmithKline.
AT LUPUS 2023
Severe hydroxychloroquine nonadherence linked to worse SLE outcomes
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Regular testing of hydroxychloroquine levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus – especially those who are experiencing a disease flare – could help to identify patients who are not taking their treatment and are at risk of worse outcomes.
Data presented at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus showed that 7.3% of patients with SLE are severely nonadherent to their medication and have a higher risk of flare, early damage, and mortality.
Rheumatologist Nathalie Costedoat-Chalumeau, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine at Cochin Hospital, Paris, presented data from 660 patients enrolled in the international longitudinal SLICC Inception Cohort, who had all been on hydroxychloroquine therapy for at least 3 months at baseline.
Patients’ serum hydroxychloroquine levels were measured at baseline and follow-up, and severe nonadherence was defined as below 106 ng/mL for those on 400 mg/day or 53 ng/mL for those on 200 mg/day.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said that those thresholds were chosen based on earlier work that analyzed the blood concentration of hydroxychloroquine in a group of patients and identified a group with very low concentrations corresponding to severe nonadherence.
“Since then, it has been reproduced by others with the same threshold,” she said. “When you have very low levels of hydroxychloroquine in their blood, you know that your patients don’t take their treatment.”
In the present study, the 7.3% of patients who met the criteria for severe nonadherence had a significant 3.3-fold higher risk of disease flare within a year of enrollment than did those who were adherent. They also had significantly higher mortality at 5 years after enrollment.
While the study didn’t show a significant difference in the level of damage at 5 years – defined as a worsening of their SLICC damage index – Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said they saw significantly greater damage occurring at 1, 2, and 3 years after enrollment among those who were severely nonadherent.
The challenge with recognizing these nonadherent patients is that they have no obvious differences at baseline from those who are adherent, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said. The rates of nonadherence were similar regardless of what dose the patient was on, their ethnicity, gender, education level, or other demographic variables.
“I believe strongly that there is a benefit of testing hydroxychloroquine levels in the blood or serum to detect severe nonadherence,” she said.
At Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau’s clinic, patients’ hydroxychloroquine levels are tested at every clinic visit, she said in an interview, and especially if they are experiencing a disease flare. “We want to know if the flare is because the patient is not taking the treatment or if it’s because the treatment is not effective, which is very different in terms of management,” she said. She recommended waiting at least 1 month after patients start treatment before measuring their hydroxychloroquine levels.
As to why some patients choose to stop taking their medication, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said sometimes it was because patients were worried about side effects, but others were also unclear about why they needed to keep taking hydroxychloroquine.
“They think steroids are effective because when they take it they are better, but they don’t see the effect of hydroxychloroquine,” she said. “You have to explain that it doesn’t work the same.”
Commenting on the findings, session chair Joan Merrill, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said the data show that severe nonadherence does have prognostic significance. “Many patients with SLE have low-grade disease or inflammation in the blood vessels that may not be clinically apparent and which hydroxychloroquine can help, so it might be wise to routinely get blood levels,” she said.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau reported no relevant financial relationships apart from unrestricted institutional research grants from UCB and Roche.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Regular testing of hydroxychloroquine levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus – especially those who are experiencing a disease flare – could help to identify patients who are not taking their treatment and are at risk of worse outcomes.
Data presented at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus showed that 7.3% of patients with SLE are severely nonadherent to their medication and have a higher risk of flare, early damage, and mortality.
Rheumatologist Nathalie Costedoat-Chalumeau, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine at Cochin Hospital, Paris, presented data from 660 patients enrolled in the international longitudinal SLICC Inception Cohort, who had all been on hydroxychloroquine therapy for at least 3 months at baseline.
Patients’ serum hydroxychloroquine levels were measured at baseline and follow-up, and severe nonadherence was defined as below 106 ng/mL for those on 400 mg/day or 53 ng/mL for those on 200 mg/day.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said that those thresholds were chosen based on earlier work that analyzed the blood concentration of hydroxychloroquine in a group of patients and identified a group with very low concentrations corresponding to severe nonadherence.
“Since then, it has been reproduced by others with the same threshold,” she said. “When you have very low levels of hydroxychloroquine in their blood, you know that your patients don’t take their treatment.”
In the present study, the 7.3% of patients who met the criteria for severe nonadherence had a significant 3.3-fold higher risk of disease flare within a year of enrollment than did those who were adherent. They also had significantly higher mortality at 5 years after enrollment.
While the study didn’t show a significant difference in the level of damage at 5 years – defined as a worsening of their SLICC damage index – Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said they saw significantly greater damage occurring at 1, 2, and 3 years after enrollment among those who were severely nonadherent.
The challenge with recognizing these nonadherent patients is that they have no obvious differences at baseline from those who are adherent, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said. The rates of nonadherence were similar regardless of what dose the patient was on, their ethnicity, gender, education level, or other demographic variables.
“I believe strongly that there is a benefit of testing hydroxychloroquine levels in the blood or serum to detect severe nonadherence,” she said.
At Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau’s clinic, patients’ hydroxychloroquine levels are tested at every clinic visit, she said in an interview, and especially if they are experiencing a disease flare. “We want to know if the flare is because the patient is not taking the treatment or if it’s because the treatment is not effective, which is very different in terms of management,” she said. She recommended waiting at least 1 month after patients start treatment before measuring their hydroxychloroquine levels.
As to why some patients choose to stop taking their medication, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said sometimes it was because patients were worried about side effects, but others were also unclear about why they needed to keep taking hydroxychloroquine.
“They think steroids are effective because when they take it they are better, but they don’t see the effect of hydroxychloroquine,” she said. “You have to explain that it doesn’t work the same.”
Commenting on the findings, session chair Joan Merrill, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said the data show that severe nonadherence does have prognostic significance. “Many patients with SLE have low-grade disease or inflammation in the blood vessels that may not be clinically apparent and which hydroxychloroquine can help, so it might be wise to routinely get blood levels,” she said.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau reported no relevant financial relationships apart from unrestricted institutional research grants from UCB and Roche.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Regular testing of hydroxychloroquine levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus – especially those who are experiencing a disease flare – could help to identify patients who are not taking their treatment and are at risk of worse outcomes.
Data presented at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus showed that 7.3% of patients with SLE are severely nonadherent to their medication and have a higher risk of flare, early damage, and mortality.
Rheumatologist Nathalie Costedoat-Chalumeau, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine at Cochin Hospital, Paris, presented data from 660 patients enrolled in the international longitudinal SLICC Inception Cohort, who had all been on hydroxychloroquine therapy for at least 3 months at baseline.
Patients’ serum hydroxychloroquine levels were measured at baseline and follow-up, and severe nonadherence was defined as below 106 ng/mL for those on 400 mg/day or 53 ng/mL for those on 200 mg/day.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said that those thresholds were chosen based on earlier work that analyzed the blood concentration of hydroxychloroquine in a group of patients and identified a group with very low concentrations corresponding to severe nonadherence.
“Since then, it has been reproduced by others with the same threshold,” she said. “When you have very low levels of hydroxychloroquine in their blood, you know that your patients don’t take their treatment.”
In the present study, the 7.3% of patients who met the criteria for severe nonadherence had a significant 3.3-fold higher risk of disease flare within a year of enrollment than did those who were adherent. They also had significantly higher mortality at 5 years after enrollment.
While the study didn’t show a significant difference in the level of damage at 5 years – defined as a worsening of their SLICC damage index – Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said they saw significantly greater damage occurring at 1, 2, and 3 years after enrollment among those who were severely nonadherent.
The challenge with recognizing these nonadherent patients is that they have no obvious differences at baseline from those who are adherent, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said. The rates of nonadherence were similar regardless of what dose the patient was on, their ethnicity, gender, education level, or other demographic variables.
“I believe strongly that there is a benefit of testing hydroxychloroquine levels in the blood or serum to detect severe nonadherence,” she said.
At Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau’s clinic, patients’ hydroxychloroquine levels are tested at every clinic visit, she said in an interview, and especially if they are experiencing a disease flare. “We want to know if the flare is because the patient is not taking the treatment or if it’s because the treatment is not effective, which is very different in terms of management,” she said. She recommended waiting at least 1 month after patients start treatment before measuring their hydroxychloroquine levels.
As to why some patients choose to stop taking their medication, Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau said sometimes it was because patients were worried about side effects, but others were also unclear about why they needed to keep taking hydroxychloroquine.
“They think steroids are effective because when they take it they are better, but they don’t see the effect of hydroxychloroquine,” she said. “You have to explain that it doesn’t work the same.”
Commenting on the findings, session chair Joan Merrill, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said the data show that severe nonadherence does have prognostic significance. “Many patients with SLE have low-grade disease or inflammation in the blood vessels that may not be clinically apparent and which hydroxychloroquine can help, so it might be wise to routinely get blood levels,” she said.
Dr. Costedoat-Chalumeau reported no relevant financial relationships apart from unrestricted institutional research grants from UCB and Roche.
AT LUPUS 2023
Lupus landmark study aims for personalized medicine goals
A new prospective, observational study from the Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) aims to enroll 3,500 patients in an effort to accelerate the development of personalized treatments for individuals living with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
The LRA on May 23 announced the launch of the Lupus Landmark Study (LLS). The study will be conducted in partnership with Lupus Therapeutics, the clinical research affiliate of the LRA.
The study will be a key feature of the Lupus Nexus, a unique combination of lupus patient registry, biorepository, and portal for data sharing and analysis.
“The aim of the Lupus Nexus is to transform lupus research and drug development through unprecedented information exchange capabilities,” according to the LRA press release.
“SLE is a debilitating autoimmune disease that disproportionately impacts women and people from minority groups, but the cause of lupus is unknown, and no single laboratory test can definitively identify lupus,” lead investigator S. Sam Lim, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Nevertheless, early detection and treatment can often lessen the progression and severity of the disease. Although there are numerous contributing factors to the lag in research discoveries and new treatments for patients with lupus, limited access to standardized, high-quality biological samples and natural history data provides a significant roadblock to advancing lupus research,” Dr. Lim said.
“Existing registry and biorepository resources in the lupus field are largely siloed, mostly limited to relatively small or discrete patient populations, and frequently not designed for broad sharing across all stakeholders of the research community,” Dr. Lim said. The LRA and its affiliate Lupus Therapeutics are committed to developing Lupus Nexus, a first-of-its-kind registry and biorepository, to serve as a collaborative research platform for lupus and a leading source of prospective, longitudinal patient data and biological samples for the research community, Dr. Lim added.
“The Lupus Landmark Study will form the foundation of this registry and biorepository and will provide a critical resource to enable the understanding of lupus heterogeneity at the molecular level,” Dr. Lim said. The molecular data can be linked to clinical phenotypes, he explained, “while providing an opportunity to better understand the holistic experience of patients with lupus, thus helping patients address the daily life challenges they face.”
The Lupus Accelerating Breakthroughs Consortium (Lupus ABC) was announced earlier this spring by the LRA. It represents a collaboration between the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the lupus community to improve and accelerate the development of safer and more effective treatments for people with lupus, Dr. Lim said. “Data and other results from the LLS will inform this collaboration,” he said.
“The LLS will provide greater insight into the pathogenesis and evolution of the condition, providing much needed information and guidance to clinicians so that the disease can be detected and treated earlier and with better precision,” Dr. Lim said. “The partnership with patients will ensure that advances will not only be meaningful to clinicians but their patients and caregivers as well,” he added.
Individuals living with lupus were essential to the development of the Lupus Nexus, and patients will continue to be engaged through participation in the LLS, which will not only generate data to promote patient-centered treatments but will also give participants more insight into their health data, according to the LRA press release.
The clinical coordinating center and biorepository elements of the Lupus Nexus will be managed by Embleema and Azenta Life Sciences, respectively, according the LRA.
Biomarker analysis will be conducted by DxTerity Diagnostics via the company’s proprietary DxCollection MicroCollection Device and Modular Immune Profile platform.
The LLS is scheduled to begin enrolling patients through select academic medical centers in the Lupus Therapeutics Lupus Clinical Investigators Network later in 2023, with an expanded roll-out in 2024, according to the press release. More information about the Lupus Landmark Study is available from Lupus Nexus at LupusNexus@lupusresearch.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new prospective, observational study from the Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) aims to enroll 3,500 patients in an effort to accelerate the development of personalized treatments for individuals living with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
The LRA on May 23 announced the launch of the Lupus Landmark Study (LLS). The study will be conducted in partnership with Lupus Therapeutics, the clinical research affiliate of the LRA.
The study will be a key feature of the Lupus Nexus, a unique combination of lupus patient registry, biorepository, and portal for data sharing and analysis.
“The aim of the Lupus Nexus is to transform lupus research and drug development through unprecedented information exchange capabilities,” according to the LRA press release.
“SLE is a debilitating autoimmune disease that disproportionately impacts women and people from minority groups, but the cause of lupus is unknown, and no single laboratory test can definitively identify lupus,” lead investigator S. Sam Lim, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Nevertheless, early detection and treatment can often lessen the progression and severity of the disease. Although there are numerous contributing factors to the lag in research discoveries and new treatments for patients with lupus, limited access to standardized, high-quality biological samples and natural history data provides a significant roadblock to advancing lupus research,” Dr. Lim said.
“Existing registry and biorepository resources in the lupus field are largely siloed, mostly limited to relatively small or discrete patient populations, and frequently not designed for broad sharing across all stakeholders of the research community,” Dr. Lim said. The LRA and its affiliate Lupus Therapeutics are committed to developing Lupus Nexus, a first-of-its-kind registry and biorepository, to serve as a collaborative research platform for lupus and a leading source of prospective, longitudinal patient data and biological samples for the research community, Dr. Lim added.
“The Lupus Landmark Study will form the foundation of this registry and biorepository and will provide a critical resource to enable the understanding of lupus heterogeneity at the molecular level,” Dr. Lim said. The molecular data can be linked to clinical phenotypes, he explained, “while providing an opportunity to better understand the holistic experience of patients with lupus, thus helping patients address the daily life challenges they face.”
The Lupus Accelerating Breakthroughs Consortium (Lupus ABC) was announced earlier this spring by the LRA. It represents a collaboration between the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the lupus community to improve and accelerate the development of safer and more effective treatments for people with lupus, Dr. Lim said. “Data and other results from the LLS will inform this collaboration,” he said.
“The LLS will provide greater insight into the pathogenesis and evolution of the condition, providing much needed information and guidance to clinicians so that the disease can be detected and treated earlier and with better precision,” Dr. Lim said. “The partnership with patients will ensure that advances will not only be meaningful to clinicians but their patients and caregivers as well,” he added.
Individuals living with lupus were essential to the development of the Lupus Nexus, and patients will continue to be engaged through participation in the LLS, which will not only generate data to promote patient-centered treatments but will also give participants more insight into their health data, according to the LRA press release.
The clinical coordinating center and biorepository elements of the Lupus Nexus will be managed by Embleema and Azenta Life Sciences, respectively, according the LRA.
Biomarker analysis will be conducted by DxTerity Diagnostics via the company’s proprietary DxCollection MicroCollection Device and Modular Immune Profile platform.
The LLS is scheduled to begin enrolling patients through select academic medical centers in the Lupus Therapeutics Lupus Clinical Investigators Network later in 2023, with an expanded roll-out in 2024, according to the press release. More information about the Lupus Landmark Study is available from Lupus Nexus at LupusNexus@lupusresearch.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new prospective, observational study from the Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) aims to enroll 3,500 patients in an effort to accelerate the development of personalized treatments for individuals living with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
The LRA on May 23 announced the launch of the Lupus Landmark Study (LLS). The study will be conducted in partnership with Lupus Therapeutics, the clinical research affiliate of the LRA.
The study will be a key feature of the Lupus Nexus, a unique combination of lupus patient registry, biorepository, and portal for data sharing and analysis.
“The aim of the Lupus Nexus is to transform lupus research and drug development through unprecedented information exchange capabilities,” according to the LRA press release.
“SLE is a debilitating autoimmune disease that disproportionately impacts women and people from minority groups, but the cause of lupus is unknown, and no single laboratory test can definitively identify lupus,” lead investigator S. Sam Lim, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Nevertheless, early detection and treatment can often lessen the progression and severity of the disease. Although there are numerous contributing factors to the lag in research discoveries and new treatments for patients with lupus, limited access to standardized, high-quality biological samples and natural history data provides a significant roadblock to advancing lupus research,” Dr. Lim said.
“Existing registry and biorepository resources in the lupus field are largely siloed, mostly limited to relatively small or discrete patient populations, and frequently not designed for broad sharing across all stakeholders of the research community,” Dr. Lim said. The LRA and its affiliate Lupus Therapeutics are committed to developing Lupus Nexus, a first-of-its-kind registry and biorepository, to serve as a collaborative research platform for lupus and a leading source of prospective, longitudinal patient data and biological samples for the research community, Dr. Lim added.
“The Lupus Landmark Study will form the foundation of this registry and biorepository and will provide a critical resource to enable the understanding of lupus heterogeneity at the molecular level,” Dr. Lim said. The molecular data can be linked to clinical phenotypes, he explained, “while providing an opportunity to better understand the holistic experience of patients with lupus, thus helping patients address the daily life challenges they face.”
The Lupus Accelerating Breakthroughs Consortium (Lupus ABC) was announced earlier this spring by the LRA. It represents a collaboration between the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the lupus community to improve and accelerate the development of safer and more effective treatments for people with lupus, Dr. Lim said. “Data and other results from the LLS will inform this collaboration,” he said.
“The LLS will provide greater insight into the pathogenesis and evolution of the condition, providing much needed information and guidance to clinicians so that the disease can be detected and treated earlier and with better precision,” Dr. Lim said. “The partnership with patients will ensure that advances will not only be meaningful to clinicians but their patients and caregivers as well,” he added.
Individuals living with lupus were essential to the development of the Lupus Nexus, and patients will continue to be engaged through participation in the LLS, which will not only generate data to promote patient-centered treatments but will also give participants more insight into their health data, according to the LRA press release.
The clinical coordinating center and biorepository elements of the Lupus Nexus will be managed by Embleema and Azenta Life Sciences, respectively, according the LRA.
Biomarker analysis will be conducted by DxTerity Diagnostics via the company’s proprietary DxCollection MicroCollection Device and Modular Immune Profile platform.
The LLS is scheduled to begin enrolling patients through select academic medical centers in the Lupus Therapeutics Lupus Clinical Investigators Network later in 2023, with an expanded roll-out in 2024, according to the press release. More information about the Lupus Landmark Study is available from Lupus Nexus at LupusNexus@lupusresearch.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early remission in lupus nephritis can still progress to advanced CKD
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Nearly 8% of people with lupus nephritis who achieve complete remission of disease within 1 year of starting treatment will still go on to develop advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatologist Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and codirector of the Lupus Clinic at Toronto Western Hospital, showed data from the Lupus Clinic’s prospective longitudinal cohort study in 273 patients with confirmed lupus nephritis who achieved complete remission within 12 months of baseline.
Remission was defined as less than 0.5 g proteinuria over 24 hours, inactive urinary sediment, and serum creatinine less than 120% of baseline.
Of this group, 21 (7.7%) progressed to advanced CKD during follow-up, which ranged from 0.7 to 31.7 years with a median of 5.8 years, after enrollment.
Patients who had experienced at least one flare during their first 5 years were around 4.5 times more likely to progress to advanced CKD than were those who did not experience a flare.
While the study excluded patients who already had advanced CKD, the analysis found those with evidence of impaired kidney function at baseline also had more than a fourfold higher risk of developing advanced CKD.
Other significant risk factors for progression were having low complement C3 levels at baseline and having had a longer duration of disease before enrollment.
“Those patients already have abnormal renal function, so the message is that patients who are already in trouble, you’ve got to watch them very carefully,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
The study also looked at whether there was a difference between patients who developed advanced CKD earlier – before the median of 5.8 years – or later. While the numbers were small, Dr. Gladman said patients who progressed earlier tended to be older and were more likely to be on antihypertensive treatment and have lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and a lower Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2K, compared with those who progressed later. Some patients also were noncompliant and/or experienced concomitant infections; four had moderate to severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
“We conclude that such patients should be monitored closely despite early remission, and we also highlight the importance of maintenance therapy, which should be communicated to the patients to prevent noncompliance and subsequent flare,” Dr. Gladman told the conference.
Dr. Gladman said her clinic told patients from the very beginning of their treatment that they would need to be seen at 2- to 6-month intervals, regardless of how well their disease was doing.
Commenting on the presentation, rheumatologist Mandana Nikpour MD, PhD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne, said the findings showed the importance of keeping a close eye on patients with lupus nephritis, even if their disease appears to be in remission.
“If you’ve had nephritis, and you go into remission, you may already have a degree of damage in your kidneys,” said Dr. Nikpour, also from the University of Melbourne. “If there’s a degree of uncontrolled hypertension, or if a patient is noncompliant with their treatment, and there’s a degree of grumbling disease activity, that can all conspire and add up to result in long-term kidney damage and loss of renal function.”
Dr. Gladman has received grants or research support from, or has consulted for, Amgen, AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Gilead.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Nearly 8% of people with lupus nephritis who achieve complete remission of disease within 1 year of starting treatment will still go on to develop advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatologist Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and codirector of the Lupus Clinic at Toronto Western Hospital, showed data from the Lupus Clinic’s prospective longitudinal cohort study in 273 patients with confirmed lupus nephritis who achieved complete remission within 12 months of baseline.
Remission was defined as less than 0.5 g proteinuria over 24 hours, inactive urinary sediment, and serum creatinine less than 120% of baseline.
Of this group, 21 (7.7%) progressed to advanced CKD during follow-up, which ranged from 0.7 to 31.7 years with a median of 5.8 years, after enrollment.
Patients who had experienced at least one flare during their first 5 years were around 4.5 times more likely to progress to advanced CKD than were those who did not experience a flare.
While the study excluded patients who already had advanced CKD, the analysis found those with evidence of impaired kidney function at baseline also had more than a fourfold higher risk of developing advanced CKD.
Other significant risk factors for progression were having low complement C3 levels at baseline and having had a longer duration of disease before enrollment.
“Those patients already have abnormal renal function, so the message is that patients who are already in trouble, you’ve got to watch them very carefully,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
The study also looked at whether there was a difference between patients who developed advanced CKD earlier – before the median of 5.8 years – or later. While the numbers were small, Dr. Gladman said patients who progressed earlier tended to be older and were more likely to be on antihypertensive treatment and have lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and a lower Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2K, compared with those who progressed later. Some patients also were noncompliant and/or experienced concomitant infections; four had moderate to severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
“We conclude that such patients should be monitored closely despite early remission, and we also highlight the importance of maintenance therapy, which should be communicated to the patients to prevent noncompliance and subsequent flare,” Dr. Gladman told the conference.
Dr. Gladman said her clinic told patients from the very beginning of their treatment that they would need to be seen at 2- to 6-month intervals, regardless of how well their disease was doing.
Commenting on the presentation, rheumatologist Mandana Nikpour MD, PhD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne, said the findings showed the importance of keeping a close eye on patients with lupus nephritis, even if their disease appears to be in remission.
“If you’ve had nephritis, and you go into remission, you may already have a degree of damage in your kidneys,” said Dr. Nikpour, also from the University of Melbourne. “If there’s a degree of uncontrolled hypertension, or if a patient is noncompliant with their treatment, and there’s a degree of grumbling disease activity, that can all conspire and add up to result in long-term kidney damage and loss of renal function.”
Dr. Gladman has received grants or research support from, or has consulted for, Amgen, AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Gilead.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – Nearly 8% of people with lupus nephritis who achieve complete remission of disease within 1 year of starting treatment will still go on to develop advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatologist Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and codirector of the Lupus Clinic at Toronto Western Hospital, showed data from the Lupus Clinic’s prospective longitudinal cohort study in 273 patients with confirmed lupus nephritis who achieved complete remission within 12 months of baseline.
Remission was defined as less than 0.5 g proteinuria over 24 hours, inactive urinary sediment, and serum creatinine less than 120% of baseline.
Of this group, 21 (7.7%) progressed to advanced CKD during follow-up, which ranged from 0.7 to 31.7 years with a median of 5.8 years, after enrollment.
Patients who had experienced at least one flare during their first 5 years were around 4.5 times more likely to progress to advanced CKD than were those who did not experience a flare.
While the study excluded patients who already had advanced CKD, the analysis found those with evidence of impaired kidney function at baseline also had more than a fourfold higher risk of developing advanced CKD.
Other significant risk factors for progression were having low complement C3 levels at baseline and having had a longer duration of disease before enrollment.
“Those patients already have abnormal renal function, so the message is that patients who are already in trouble, you’ve got to watch them very carefully,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
The study also looked at whether there was a difference between patients who developed advanced CKD earlier – before the median of 5.8 years – or later. While the numbers were small, Dr. Gladman said patients who progressed earlier tended to be older and were more likely to be on antihypertensive treatment and have lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and a lower Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index–2K, compared with those who progressed later. Some patients also were noncompliant and/or experienced concomitant infections; four had moderate to severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
“We conclude that such patients should be monitored closely despite early remission, and we also highlight the importance of maintenance therapy, which should be communicated to the patients to prevent noncompliance and subsequent flare,” Dr. Gladman told the conference.
Dr. Gladman said her clinic told patients from the very beginning of their treatment that they would need to be seen at 2- to 6-month intervals, regardless of how well their disease was doing.
Commenting on the presentation, rheumatologist Mandana Nikpour MD, PhD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne, said the findings showed the importance of keeping a close eye on patients with lupus nephritis, even if their disease appears to be in remission.
“If you’ve had nephritis, and you go into remission, you may already have a degree of damage in your kidneys,” said Dr. Nikpour, also from the University of Melbourne. “If there’s a degree of uncontrolled hypertension, or if a patient is noncompliant with their treatment, and there’s a degree of grumbling disease activity, that can all conspire and add up to result in long-term kidney damage and loss of renal function.”
Dr. Gladman has received grants or research support from, or has consulted for, Amgen, AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Gilead.
AT LUPUS 2023
Biomarkers for measuring lupus nephritis treatment response gain ground
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A panel of urinary biomarkers may do better than measuring proteinuria in predicting which patients with lupus nephritis are going to respond to treatment, according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Physician-scientist Andrea Fava, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, presented data from a study using urine proteomics to identify biomarkers present in the urine of patients with lupus nephritis at 3 months after starting treatment that were linked to better outcomes from that treatment at 1 year.
While proteinuria is the standard measure used to guide decisions about whether to do a kidney biopsy and how to treat lupus nephritis, it doesn’t always correlate with what’s actually going on inside the kidney in terms of histology and inflammation, Dr. Fava said.
He pointed to an earlier study in which researchers did kidney biopsies 6 months after patients with lupus nephritis started treatment with mycophenolate. This suggested that around half of patients who showed a clinical response to treatment – defined as proteinuria below 500 mg/day – still had significant histologic disease activity. Another study suggested that this elevated histologic disease activity is associated with a risk of flare, which can result in significant nephron loss. On the flip side, nearly two-thirds of patients in complete histologic remission still had elevated proteinuria.
Unfortunately, it’s not possible or practical to biopsy patients on a regular basis, Dr. Fava said. “So we need better biomarkers, and to do so, we need better knowledge of the pathophysiology because if we have biomarkers that reflect tissue biology in real-time, that may surely guide personalized treatments,” he said at the congress.
Dr. Fava and colleagues enrolled 225 patients with SLE who were undergoing kidney biopsy and 10 healthy controls and used proteomics to quantify the urinary levels of around 1,200 proteins at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months after initiating treatment.
The team then analyzed these data to look for protein signatures that correlated with histologic phenotypes – particularly the amount of inflammation in the kidney – and clinical features such as response to treatment.
They found several protein biomarkers that appeared to be linked to histologic activity in the kidney, including interleukin (IL)-16, CD163, and neutrophil granule proteins.
Initially, the team looked at baseline levels of these proteins to see if they predicted who responded to treatment, but found no difference between responders and nonresponders.
However, when they looked at levels at 3 months after treatment, a pattern emerged. “We found that in patients who were not responding, there were no changes after 3 months of treatment in the urine proteome,” Dr. Fava said. Among those who did respond to treatment, the levels of these proteins – IL-16, CD163, galectin-1, and CD206 – decreased significantly.
“So the proteins that are linked to renal activity decrease only in responders, suggesting that effective immunosuppression is effective in reducing intrarenal inflammation, which eventually results in low proteinuria at 1 year.”
The decline in these biomarkers persisted at 1 year, and the study suggested it was a better predictor of which patients would respond to treatment at 1 year than proteinuria.
Dr. Fava said in an interview that better biomarkers could revolutionize the treatment and management of lupus nephritis.
“First of all, it can shift the management strategy from treatment to prevention, because at the very beginning we can nip it in the bud maybe with very gentle treatment,” he said. Different panels of urine biomarkers could identify patients at risk of treatment failure, and also help patients to taper off their immunosuppressive therapy without an increased risk of flare. “If we have a way to tell us there’s still inflammation that needs treatment, that could change the way we do it,” he said.
He acknowledged there are significant challenges to developing these biomarkers for clinical use; one is the decision of how to define disease activity without relying on proteinuria as a measure. “Why do I want a biomarker that can predict another biomarker?” he said.
Another presentation during the same session, by Huihua Ding, MD, of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, China, reported on the use of urinary L-selectin to assess renal disease activity and response to treatment in a multiethnic cohort.
This study, involving 474 patients with SLE with or without renal involvement in the United States and China, found levels of urinary L-selectin were elevated only in patients with active lupus nephritis and showed patterns that correlated with renal histologic characteristics.
Clinical rheumatologist Eric F. Morand, MD, PhD, and head of the School of Clinical Sciences at Monash University in Melbourne said one challenge with using urinary biomarkers was that it was not yet clear what these biomarkers reveal about the kidney. “It will be important to see whether this proteomic data actually link to renal outcomes,” Dr. Morand said in an interview. “I think predicting the response to treatment should be based around GFR [glomerular filtration rate] preservation, and I don’t think I’ve seen data yet that the urine biomarkers are going to tell us how to do that better.”
Dr. Morand is optimistic that urine biomarkers will one day be able to achieve that, but he stressed the importance of having urine biomarker tests available in the field at low cost. “You’re going to be doing the tests repeatedly, so therefore, you’re probably going to need to come down to a smaller list of proteins that you measure.”
Dr. Fava reported receiving support from Sanofi and Annexion Bio.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A panel of urinary biomarkers may do better than measuring proteinuria in predicting which patients with lupus nephritis are going to respond to treatment, according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Physician-scientist Andrea Fava, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, presented data from a study using urine proteomics to identify biomarkers present in the urine of patients with lupus nephritis at 3 months after starting treatment that were linked to better outcomes from that treatment at 1 year.
While proteinuria is the standard measure used to guide decisions about whether to do a kidney biopsy and how to treat lupus nephritis, it doesn’t always correlate with what’s actually going on inside the kidney in terms of histology and inflammation, Dr. Fava said.
He pointed to an earlier study in which researchers did kidney biopsies 6 months after patients with lupus nephritis started treatment with mycophenolate. This suggested that around half of patients who showed a clinical response to treatment – defined as proteinuria below 500 mg/day – still had significant histologic disease activity. Another study suggested that this elevated histologic disease activity is associated with a risk of flare, which can result in significant nephron loss. On the flip side, nearly two-thirds of patients in complete histologic remission still had elevated proteinuria.
Unfortunately, it’s not possible or practical to biopsy patients on a regular basis, Dr. Fava said. “So we need better biomarkers, and to do so, we need better knowledge of the pathophysiology because if we have biomarkers that reflect tissue biology in real-time, that may surely guide personalized treatments,” he said at the congress.
Dr. Fava and colleagues enrolled 225 patients with SLE who were undergoing kidney biopsy and 10 healthy controls and used proteomics to quantify the urinary levels of around 1,200 proteins at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months after initiating treatment.
The team then analyzed these data to look for protein signatures that correlated with histologic phenotypes – particularly the amount of inflammation in the kidney – and clinical features such as response to treatment.
They found several protein biomarkers that appeared to be linked to histologic activity in the kidney, including interleukin (IL)-16, CD163, and neutrophil granule proteins.
Initially, the team looked at baseline levels of these proteins to see if they predicted who responded to treatment, but found no difference between responders and nonresponders.
However, when they looked at levels at 3 months after treatment, a pattern emerged. “We found that in patients who were not responding, there were no changes after 3 months of treatment in the urine proteome,” Dr. Fava said. Among those who did respond to treatment, the levels of these proteins – IL-16, CD163, galectin-1, and CD206 – decreased significantly.
“So the proteins that are linked to renal activity decrease only in responders, suggesting that effective immunosuppression is effective in reducing intrarenal inflammation, which eventually results in low proteinuria at 1 year.”
The decline in these biomarkers persisted at 1 year, and the study suggested it was a better predictor of which patients would respond to treatment at 1 year than proteinuria.
Dr. Fava said in an interview that better biomarkers could revolutionize the treatment and management of lupus nephritis.
“First of all, it can shift the management strategy from treatment to prevention, because at the very beginning we can nip it in the bud maybe with very gentle treatment,” he said. Different panels of urine biomarkers could identify patients at risk of treatment failure, and also help patients to taper off their immunosuppressive therapy without an increased risk of flare. “If we have a way to tell us there’s still inflammation that needs treatment, that could change the way we do it,” he said.
He acknowledged there are significant challenges to developing these biomarkers for clinical use; one is the decision of how to define disease activity without relying on proteinuria as a measure. “Why do I want a biomarker that can predict another biomarker?” he said.
Another presentation during the same session, by Huihua Ding, MD, of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, China, reported on the use of urinary L-selectin to assess renal disease activity and response to treatment in a multiethnic cohort.
This study, involving 474 patients with SLE with or without renal involvement in the United States and China, found levels of urinary L-selectin were elevated only in patients with active lupus nephritis and showed patterns that correlated with renal histologic characteristics.
Clinical rheumatologist Eric F. Morand, MD, PhD, and head of the School of Clinical Sciences at Monash University in Melbourne said one challenge with using urinary biomarkers was that it was not yet clear what these biomarkers reveal about the kidney. “It will be important to see whether this proteomic data actually link to renal outcomes,” Dr. Morand said in an interview. “I think predicting the response to treatment should be based around GFR [glomerular filtration rate] preservation, and I don’t think I’ve seen data yet that the urine biomarkers are going to tell us how to do that better.”
Dr. Morand is optimistic that urine biomarkers will one day be able to achieve that, but he stressed the importance of having urine biomarker tests available in the field at low cost. “You’re going to be doing the tests repeatedly, so therefore, you’re probably going to need to come down to a smaller list of proteins that you measure.”
Dr. Fava reported receiving support from Sanofi and Annexion Bio.
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA – A panel of urinary biomarkers may do better than measuring proteinuria in predicting which patients with lupus nephritis are going to respond to treatment, according to a presentation at an international congress on systemic lupus erythematosus.
Physician-scientist Andrea Fava, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, presented data from a study using urine proteomics to identify biomarkers present in the urine of patients with lupus nephritis at 3 months after starting treatment that were linked to better outcomes from that treatment at 1 year.
While proteinuria is the standard measure used to guide decisions about whether to do a kidney biopsy and how to treat lupus nephritis, it doesn’t always correlate with what’s actually going on inside the kidney in terms of histology and inflammation, Dr. Fava said.
He pointed to an earlier study in which researchers did kidney biopsies 6 months after patients with lupus nephritis started treatment with mycophenolate. This suggested that around half of patients who showed a clinical response to treatment – defined as proteinuria below 500 mg/day – still had significant histologic disease activity. Another study suggested that this elevated histologic disease activity is associated with a risk of flare, which can result in significant nephron loss. On the flip side, nearly two-thirds of patients in complete histologic remission still had elevated proteinuria.
Unfortunately, it’s not possible or practical to biopsy patients on a regular basis, Dr. Fava said. “So we need better biomarkers, and to do so, we need better knowledge of the pathophysiology because if we have biomarkers that reflect tissue biology in real-time, that may surely guide personalized treatments,” he said at the congress.
Dr. Fava and colleagues enrolled 225 patients with SLE who were undergoing kidney biopsy and 10 healthy controls and used proteomics to quantify the urinary levels of around 1,200 proteins at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months after initiating treatment.
The team then analyzed these data to look for protein signatures that correlated with histologic phenotypes – particularly the amount of inflammation in the kidney – and clinical features such as response to treatment.
They found several protein biomarkers that appeared to be linked to histologic activity in the kidney, including interleukin (IL)-16, CD163, and neutrophil granule proteins.
Initially, the team looked at baseline levels of these proteins to see if they predicted who responded to treatment, but found no difference between responders and nonresponders.
However, when they looked at levels at 3 months after treatment, a pattern emerged. “We found that in patients who were not responding, there were no changes after 3 months of treatment in the urine proteome,” Dr. Fava said. Among those who did respond to treatment, the levels of these proteins – IL-16, CD163, galectin-1, and CD206 – decreased significantly.
“So the proteins that are linked to renal activity decrease only in responders, suggesting that effective immunosuppression is effective in reducing intrarenal inflammation, which eventually results in low proteinuria at 1 year.”
The decline in these biomarkers persisted at 1 year, and the study suggested it was a better predictor of which patients would respond to treatment at 1 year than proteinuria.
Dr. Fava said in an interview that better biomarkers could revolutionize the treatment and management of lupus nephritis.
“First of all, it can shift the management strategy from treatment to prevention, because at the very beginning we can nip it in the bud maybe with very gentle treatment,” he said. Different panels of urine biomarkers could identify patients at risk of treatment failure, and also help patients to taper off their immunosuppressive therapy without an increased risk of flare. “If we have a way to tell us there’s still inflammation that needs treatment, that could change the way we do it,” he said.
He acknowledged there are significant challenges to developing these biomarkers for clinical use; one is the decision of how to define disease activity without relying on proteinuria as a measure. “Why do I want a biomarker that can predict another biomarker?” he said.
Another presentation during the same session, by Huihua Ding, MD, of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in Shanghai, China, reported on the use of urinary L-selectin to assess renal disease activity and response to treatment in a multiethnic cohort.
This study, involving 474 patients with SLE with or without renal involvement in the United States and China, found levels of urinary L-selectin were elevated only in patients with active lupus nephritis and showed patterns that correlated with renal histologic characteristics.
Clinical rheumatologist Eric F. Morand, MD, PhD, and head of the School of Clinical Sciences at Monash University in Melbourne said one challenge with using urinary biomarkers was that it was not yet clear what these biomarkers reveal about the kidney. “It will be important to see whether this proteomic data actually link to renal outcomes,” Dr. Morand said in an interview. “I think predicting the response to treatment should be based around GFR [glomerular filtration rate] preservation, and I don’t think I’ve seen data yet that the urine biomarkers are going to tell us how to do that better.”
Dr. Morand is optimistic that urine biomarkers will one day be able to achieve that, but he stressed the importance of having urine biomarker tests available in the field at low cost. “You’re going to be doing the tests repeatedly, so therefore, you’re probably going to need to come down to a smaller list of proteins that you measure.”
Dr. Fava reported receiving support from Sanofi and Annexion Bio.
AT LUPUS 2023
Cutaneous vasculitis curtails quality of life
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
, and its measurement with an organ-specific instrument may catch important disease outcomes better than a generic health-related quality of life index, according to survey responses from participants in the Vasculitis Patient-Powered Research Network (VPPRN).
Although cutaneous vasculitis often causes itching, pain, and ulceration, the impact of the disease on specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes has not been systematically assessed, wrote Sarah Mann, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers used the VPPRN to conduct an online survey of adults aged 18 years and older with cutaneous manifestations of vasculitis. The survey was conducted between January 2020 and August 2021.
The primary outcomes of HRQOL were determined using two validated measures. One measured skin-related HRQOL (the Effects of Skin Disease on Quality-of-Life Survey [Skindex-29]), and the other measured general health and well-being (36-Item Short Form Health Survey [SF-36]).
The final analysis included 190 survey responses. The mean age of the respondents was 50.5 years, 84.1% were female, and approximately two-thirds reported a duration of vasculitis of at least 5 years. Respondents’ vasculitides included cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (14%), IgA vasculitis (6.5%), urticarial vasculitis (8.4%), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (17.6%), microscopic polyangiitis (10.3%), eosinophilic vasculitis (15%), polyarteritis nodosa (3.7%), and other vasculitis types (24.2%).
On the Skindex-29 domains, severely or very severely diminished HRQOL was reported by 77.6% of respondents for emotions, 78.5% for symptoms, 60.7% for functioning, and 75.7% for overall HRQOL.
On the SF-36, the HRQOL was below average on six of eight domains, and approximately half of the patients had summative physical component scores (56%) and mental component scores (52%) below 50.
The HRQOL outcomes of cutaneous vasculitis were worse on the Skindex-29 than the SF-36, the researchers noted. “This discordance may reflect the value of disease or organ-specific measures, which may be able to capture important outcomes of disease even when generic measures do not,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential lack of generalizability to broader populations of vasculitis patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the underrepresentation of male patients and the lack of a disease-specific patient-reported outcome measure, they said.
In addition, “Because half of patients reported having disease which was in remission or mildly active, the study findings may underestimate the true role of active cutaneous vasculitis on HRQOL,” the researchers said.
More studies are needed to assess how HRQOL measures respond to disease treatment and control, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, the results suggest that cutaneous vasculitis has a significant effect on patients’ perception of their health, as well as on their well-being and symptoms, they said.
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Mann had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including GlaxoSmithKline.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
IVIG shows no impact on VTE risk in dermatomyositis patients
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
Use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) had no apparent effect on the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults with dermatomyositis (DM), based on data from more than 400 individuals.
DM has been associated with an increased risk of VTE in previous studies, wrote Elizabeth T. Rotrosen, of Boston University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Although IVIG is often effective for DM patients with recalcitrant disease, it carries a boxed warning for increased thrombosis risk; however, the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in DM has not been well examined, the researchers said.
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, the researchers identified 458 adults with DM based on the European Alliance of Associations for Reumatology/American College of Rheumatology criteria. The mean age of the participants was 51.8 years, 76% were female, and 82% were White. Of these, 178 were treated with IVIG and 280 were not. The mean duration of IVIG treatment was 32.9 months. The researchers used the chi square test to test for independence between binary variables, the Pearson chi square test to test for independence between categorical variables, and the unpaired t test to compare continuous variables in their statistical analysis.
A total of 23 patients experienced DM-associated VTEs; 6 in the IVIG group and 17 in the non-IVIG group (3.4% vs. 5.7%, P = .20), a nonsignificant difference. The patients in the IVIG group who experienced a DM-associated VTE all underwent IVIG treatment within 4 weeks before the event.
The most common risk factors for VTE in both the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were malignant neoplasm (66.7% and 58.8%, respectively), followed by immobilization (16.7% and 35.3%, respectively) and tobacco use (16.7% and 23.5%, respectively).
“Notably, 5 of the IVIG-treated patients with DM who experienced a VTE also had at least 1 additional underlying risk factor for VTE, including 4 with malignant neoplasm,” the researchers wrote.
A total of 76 patients had cancer-associated DM, including 12 treated with IVIG and 64 not treated with IVIG. Of these, 14 experienced a VTE (4 IVIG patients and 10 non-IVIG patients).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and small number of VTEs. Prospective studies are needed for better assessment of the VTE risk in patients with DM treated with IVIG, the researchers noted. However, the study is the largest known to explore the association between IVIG use and VTE risk in patients with DM, they said, and the results suggest that clinicians may continue IVIG use in these patients with considerations of risks and benefits on an individual basis.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Rotrosen had no financial conflicts to disclose. Two coauthors reported financial relationships with Pfizer unrelated to this study.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Low disease state for childhood lupus approaches validation
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT BSR 2023
Study shifts burden of IgG4-related disease to women
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.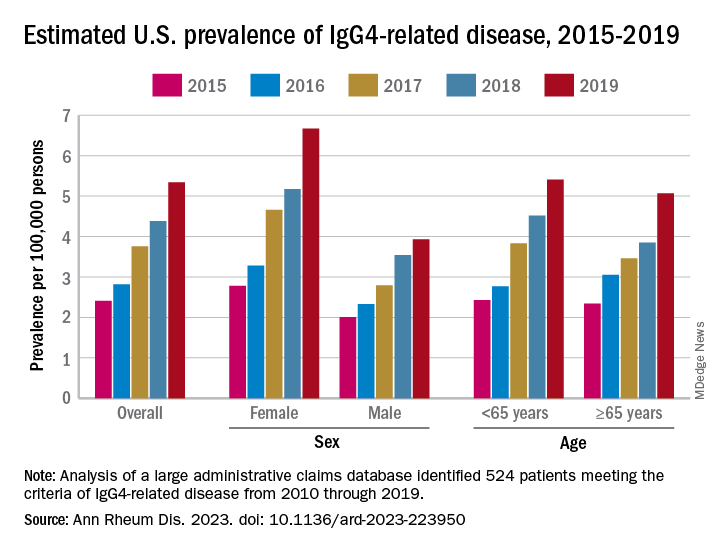
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES