User login
Integrating intestinal ultrasound into inflammatory bowel disease training and practice in the United States
Evolving endpoints and treat-to-target strategies in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) incorporate a need for more frequent assessments of the disease, including objective measures of inflammation.1,2 Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is a noninvasive, well-tolerated,3 repeatable, point-of-care (POC) test that is highly sensitive and specific in detection of bowel inflammation, transmural healing,4,5 and response to therapy in both Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).6-8 As IUS is taking hold in the United States, there is a great need to teach the next generation of gastroenterologists about its value, how to incorporate it into clinical practice, and how to become appropriately trained and maintain competency.
Why incorporate IUS in the United States now?
As IBD management has evolved, so has the appreciation for the value of bedside IUS as a tool that addresses very real needs for the field. Unlike other parts of the world in which ultrasound skills are part of the training curriculum, this has not been the case in internal medicine and gastroenterology training in the United States. In addition, there have been no specific billing codes or clear renumeration processes outlined for IUS,9 nor have there been any local training opportunities. Because of these challenges, it was not until recently that several leaders in IBD in the United States championed the potential of this technology and incorporated it into IBD management. Subsequently, a number of gastroenterologists have been trained and are now leading the effort to disseminate this tool throughout the United States. A consequence of these efforts resulted in support from the Helmsley Charitable Trust (Helmsley) and the creation of the Intestinal Ultrasound Group of the United States and Canada to address the gaps unique to North America as well as to strengthen the quality of IUS research through collaborations across the continent.
What is IUS, and when is it performed?
IUS is a sonographic exam performed by a gastroenterology-trained professional who scans the abdominal wall (and perineum when the rectum and perineal disease is evaluated), using both a convex low-frequency probe and linear high-frequency probe to evaluate the small intestine, colon, and rectum. The bowel is composed of five layers with alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic layers: the mucosal-lumen interface (not a true part of the bowel wall), deep mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and serosa. (Figure)
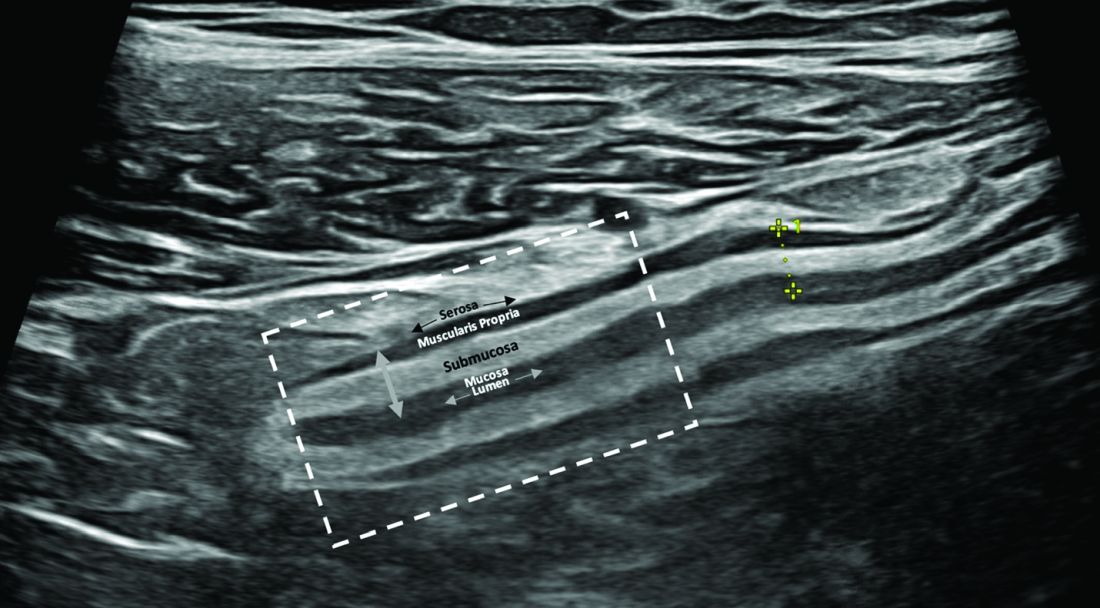
The most sensitive parameter for assessment of IBD activity is bowel wall thickness (≤ 3 mm in the small bowel and colon and ≤ 4 mm in the rectum are considered normal in adults).8,10 The second key parameter is the assessment of vascularization, in which presence of hyperemia suggests active disease.11 There are a number of indices to quantify hyperemia, with the most widely used being the Limberg score.12 Additional parameters include assessment of loss of the delineation of the bowel wall layers (loss of stratification signifies active inflammation), increased thickness of the submucosa,13 increased mesenteric fatty proliferation (with increased inflammation, mesenteric fat proliferation will appear as a hyperechoic area surrounding the bowel), lymphadenopathy, bowel strictures, and extramural complications such as fistulae and abscess. Shear wave elastography may be an effective way to differentiate severe fibrotic strictures, but this is an area that requires more investigation.14
IUS has been shown to be an excellent tool in not only assessing disease activity and disease complication (with higher sensitivity than the Harvey-Bradshaw Index, serum C-reactive protein),15 but, unique to IUS, can provide early prediction of response in moderate to severe active UC.6,7 This has also been shown with transperineal ultrasound in patients with UC, with the ability to predict response to therapy as early as 1 week from induction therapy.16 Furthermore, it can be used to assess transmural healing, which has been shown to be associated with improved outcomes in Crohn’s patient, such as lower rates of hospitalizations, surgery, medication escalation, and need for corticosteroids.17 IUS is associated with great patient satisfaction and greater understanding of disease-related symptoms when the patient sees the inflammation of the bowel. (Table)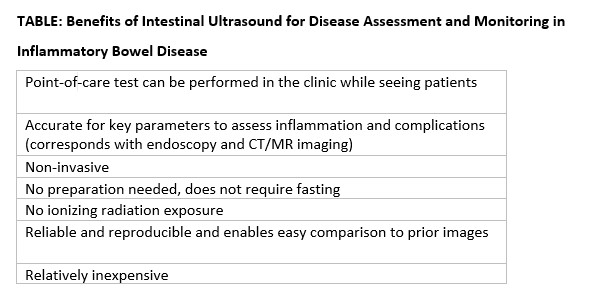
How can you get trained in IUS?
Training in IUS varies across the globe, from incorporation of IUS into the standard training curriculum to available training programs that can be followed and attended outside of medical training. In the United States, interested gastroenterologists can now be trained by becoming a member of the International Bowel Ultrasound Group (IBUS Group) and applying to the workshops now available. The IBUS Group has developed an IUS-specific training curriculum over the last 16 years, which is comprised of three modules: a 2-day hands-on workshop (Module 1) with final examination of theoretical competency, a preceptorship at an “expert center” with an experienced sonographer for a total of 4 weeks to complete 40 supervised IUS examinations (Module 2), and didactics and a final examination (Module 3). Also with support from Helmsley, the first Module 1 to be offered in the United States was hosted at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York in 2022, the second was hosted at the University of Chicago in March 2023, and the third is planned to take place at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles in March 2024.18 With the growing interest and demand for IUS training in the United States, U.S. experts are working to develop new training options that will be less time consuming, scalable, and still provide appropriate training and competency assessment.
How do you integrate IUS into your practice?
The keys to integrating IUS are a section chief or practice manager’s support of a trainee or faculty member for both funding of equipment and protected time for training and building of the program, as well as a permissive environment and collegial relationship with radiology. An ultrasound machine and additional transducers may range in price from $50,000-$120,000. Funding may be a limiting step for many, however. A detailed business plan is imperative to the success and investment of funds in an IUS program. With current billing practices in place that include ”limited abdominal ultrasound” (76705) and “Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen” (93975),19 reimbursement should include a technical fee, professional fee, and if in a hospital-based clinic, a facility fee. IUS pro-fee combined with technical fee is reimbursed at approximately 0.80 relative value units. When possible, the facility fee is included for approximately $800 per IUS visit. For billing and compliance with HIPAA, all billed IUS images must be stored in a durable and accessible format. It is recommended that the images and cine loops be digitally stored to the same or similar platform used by radiologists at the same institution. This requires early communication with the local information technology department for the connection of an ultrasound machine to the storage platform and/or electronic health record. Reporting results should be standardized with unique or otherwise available IUS templates, which also satisfy all billing components.9 The flow for incorporation of IUS into practice can be at the same time patients are seen during their visit, or alternatively, in a dedicated IUS clinic in which patients are referred by other providers and scheduled back to back.
Conclusions
In summary, the confluence of treat-to-target strategies in IBD, new treatment options in IBD, and successful efforts to translate IUS training and billing practices to the United States portends a great future for the field and for our patients.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Rubin, of the University of Chicago’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, are speakers for Samsung/Boston Imaging.
References
1. Turner D et al. Gastroenterology. Apr 2021;160(5):1570-83. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031
2. Hart AL and Rubin DT. Gastroenterology. Apr 2022;162(5):1367-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.013
3. Rajagopalan A et al. JGH Open. Apr 2020;4(2):267-72. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12268
4. Calabrese E et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Apr 2022;20(4):e711-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.030
5. Ripolles T et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Oct 2016;22(10):2465-73. doi10.1097/MIB.0000000000000882
6. Maaser C et al. Gut. Sep 2020;69(9):1629-36. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319451
7. Ilvemark J et al. J Crohns Colitis. Nov 23 2022;16(11):1725-34. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac083
8. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jun 2020;51(12):1373-83. doi: 10.1111/apt.15767
9. Dolinger MT et al. Guide to Intestinal Ultrasound Credentialing, Documentation, and Billing for Gastroenterologists in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023.
10. Maconi G et al. Ultraschall Med. Jun 2018;39(3):304-17. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-125329
11. Sasaki T et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Mar 2014;49(3):295-301. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2013.871744
12. Limberg B. Z Gastroenterol. Jun 1999;37(6):495-508.
13. Miyoshi J et al. J Gastroenterol. Feb 2022;57(2):82-9. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01847-3
14. Chen YJ et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Sep 15 2018;24(10):2183-90. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy115
15. Kucharzik T et al. Apr 2017;15(4):535-42e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.040
16. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. May 2022;55(10):1320-9. doi: 10.1111/apt.16817
17. Vaughan R et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jul 2022;56(1):84-94. doi: 10.1111/apt.16892
18. International Bowel Ultrasound Group. https://ibus-group.org/
19. American Medical Association. CPT (Current Procedural Terminology). https://www.ama-assn.org/amaone/cpt-current-procedural-terminology
Evolving endpoints and treat-to-target strategies in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) incorporate a need for more frequent assessments of the disease, including objective measures of inflammation.1,2 Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is a noninvasive, well-tolerated,3 repeatable, point-of-care (POC) test that is highly sensitive and specific in detection of bowel inflammation, transmural healing,4,5 and response to therapy in both Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).6-8 As IUS is taking hold in the United States, there is a great need to teach the next generation of gastroenterologists about its value, how to incorporate it into clinical practice, and how to become appropriately trained and maintain competency.
Why incorporate IUS in the United States now?
As IBD management has evolved, so has the appreciation for the value of bedside IUS as a tool that addresses very real needs for the field. Unlike other parts of the world in which ultrasound skills are part of the training curriculum, this has not been the case in internal medicine and gastroenterology training in the United States. In addition, there have been no specific billing codes or clear renumeration processes outlined for IUS,9 nor have there been any local training opportunities. Because of these challenges, it was not until recently that several leaders in IBD in the United States championed the potential of this technology and incorporated it into IBD management. Subsequently, a number of gastroenterologists have been trained and are now leading the effort to disseminate this tool throughout the United States. A consequence of these efforts resulted in support from the Helmsley Charitable Trust (Helmsley) and the creation of the Intestinal Ultrasound Group of the United States and Canada to address the gaps unique to North America as well as to strengthen the quality of IUS research through collaborations across the continent.
What is IUS, and when is it performed?
IUS is a sonographic exam performed by a gastroenterology-trained professional who scans the abdominal wall (and perineum when the rectum and perineal disease is evaluated), using both a convex low-frequency probe and linear high-frequency probe to evaluate the small intestine, colon, and rectum. The bowel is composed of five layers with alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic layers: the mucosal-lumen interface (not a true part of the bowel wall), deep mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and serosa. (Figure)

The most sensitive parameter for assessment of IBD activity is bowel wall thickness (≤ 3 mm in the small bowel and colon and ≤ 4 mm in the rectum are considered normal in adults).8,10 The second key parameter is the assessment of vascularization, in which presence of hyperemia suggests active disease.11 There are a number of indices to quantify hyperemia, with the most widely used being the Limberg score.12 Additional parameters include assessment of loss of the delineation of the bowel wall layers (loss of stratification signifies active inflammation), increased thickness of the submucosa,13 increased mesenteric fatty proliferation (with increased inflammation, mesenteric fat proliferation will appear as a hyperechoic area surrounding the bowel), lymphadenopathy, bowel strictures, and extramural complications such as fistulae and abscess. Shear wave elastography may be an effective way to differentiate severe fibrotic strictures, but this is an area that requires more investigation.14
IUS has been shown to be an excellent tool in not only assessing disease activity and disease complication (with higher sensitivity than the Harvey-Bradshaw Index, serum C-reactive protein),15 but, unique to IUS, can provide early prediction of response in moderate to severe active UC.6,7 This has also been shown with transperineal ultrasound in patients with UC, with the ability to predict response to therapy as early as 1 week from induction therapy.16 Furthermore, it can be used to assess transmural healing, which has been shown to be associated with improved outcomes in Crohn’s patient, such as lower rates of hospitalizations, surgery, medication escalation, and need for corticosteroids.17 IUS is associated with great patient satisfaction and greater understanding of disease-related symptoms when the patient sees the inflammation of the bowel. (Table)
How can you get trained in IUS?
Training in IUS varies across the globe, from incorporation of IUS into the standard training curriculum to available training programs that can be followed and attended outside of medical training. In the United States, interested gastroenterologists can now be trained by becoming a member of the International Bowel Ultrasound Group (IBUS Group) and applying to the workshops now available. The IBUS Group has developed an IUS-specific training curriculum over the last 16 years, which is comprised of three modules: a 2-day hands-on workshop (Module 1) with final examination of theoretical competency, a preceptorship at an “expert center” with an experienced sonographer for a total of 4 weeks to complete 40 supervised IUS examinations (Module 2), and didactics and a final examination (Module 3). Also with support from Helmsley, the first Module 1 to be offered in the United States was hosted at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York in 2022, the second was hosted at the University of Chicago in March 2023, and the third is planned to take place at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles in March 2024.18 With the growing interest and demand for IUS training in the United States, U.S. experts are working to develop new training options that will be less time consuming, scalable, and still provide appropriate training and competency assessment.
How do you integrate IUS into your practice?
The keys to integrating IUS are a section chief or practice manager’s support of a trainee or faculty member for both funding of equipment and protected time for training and building of the program, as well as a permissive environment and collegial relationship with radiology. An ultrasound machine and additional transducers may range in price from $50,000-$120,000. Funding may be a limiting step for many, however. A detailed business plan is imperative to the success and investment of funds in an IUS program. With current billing practices in place that include ”limited abdominal ultrasound” (76705) and “Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen” (93975),19 reimbursement should include a technical fee, professional fee, and if in a hospital-based clinic, a facility fee. IUS pro-fee combined with technical fee is reimbursed at approximately 0.80 relative value units. When possible, the facility fee is included for approximately $800 per IUS visit. For billing and compliance with HIPAA, all billed IUS images must be stored in a durable and accessible format. It is recommended that the images and cine loops be digitally stored to the same or similar platform used by radiologists at the same institution. This requires early communication with the local information technology department for the connection of an ultrasound machine to the storage platform and/or electronic health record. Reporting results should be standardized with unique or otherwise available IUS templates, which also satisfy all billing components.9 The flow for incorporation of IUS into practice can be at the same time patients are seen during their visit, or alternatively, in a dedicated IUS clinic in which patients are referred by other providers and scheduled back to back.
Conclusions
In summary, the confluence of treat-to-target strategies in IBD, new treatment options in IBD, and successful efforts to translate IUS training and billing practices to the United States portends a great future for the field and for our patients.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Rubin, of the University of Chicago’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, are speakers for Samsung/Boston Imaging.
References
1. Turner D et al. Gastroenterology. Apr 2021;160(5):1570-83. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031
2. Hart AL and Rubin DT. Gastroenterology. Apr 2022;162(5):1367-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.013
3. Rajagopalan A et al. JGH Open. Apr 2020;4(2):267-72. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12268
4. Calabrese E et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Apr 2022;20(4):e711-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.030
5. Ripolles T et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Oct 2016;22(10):2465-73. doi10.1097/MIB.0000000000000882
6. Maaser C et al. Gut. Sep 2020;69(9):1629-36. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319451
7. Ilvemark J et al. J Crohns Colitis. Nov 23 2022;16(11):1725-34. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac083
8. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jun 2020;51(12):1373-83. doi: 10.1111/apt.15767
9. Dolinger MT et al. Guide to Intestinal Ultrasound Credentialing, Documentation, and Billing for Gastroenterologists in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023.
10. Maconi G et al. Ultraschall Med. Jun 2018;39(3):304-17. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-125329
11. Sasaki T et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Mar 2014;49(3):295-301. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2013.871744
12. Limberg B. Z Gastroenterol. Jun 1999;37(6):495-508.
13. Miyoshi J et al. J Gastroenterol. Feb 2022;57(2):82-9. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01847-3
14. Chen YJ et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Sep 15 2018;24(10):2183-90. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy115
15. Kucharzik T et al. Apr 2017;15(4):535-42e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.040
16. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. May 2022;55(10):1320-9. doi: 10.1111/apt.16817
17. Vaughan R et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jul 2022;56(1):84-94. doi: 10.1111/apt.16892
18. International Bowel Ultrasound Group. https://ibus-group.org/
19. American Medical Association. CPT (Current Procedural Terminology). https://www.ama-assn.org/amaone/cpt-current-procedural-terminology
Evolving endpoints and treat-to-target strategies in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) incorporate a need for more frequent assessments of the disease, including objective measures of inflammation.1,2 Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is a noninvasive, well-tolerated,3 repeatable, point-of-care (POC) test that is highly sensitive and specific in detection of bowel inflammation, transmural healing,4,5 and response to therapy in both Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).6-8 As IUS is taking hold in the United States, there is a great need to teach the next generation of gastroenterologists about its value, how to incorporate it into clinical practice, and how to become appropriately trained and maintain competency.
Why incorporate IUS in the United States now?
As IBD management has evolved, so has the appreciation for the value of bedside IUS as a tool that addresses very real needs for the field. Unlike other parts of the world in which ultrasound skills are part of the training curriculum, this has not been the case in internal medicine and gastroenterology training in the United States. In addition, there have been no specific billing codes or clear renumeration processes outlined for IUS,9 nor have there been any local training opportunities. Because of these challenges, it was not until recently that several leaders in IBD in the United States championed the potential of this technology and incorporated it into IBD management. Subsequently, a number of gastroenterologists have been trained and are now leading the effort to disseminate this tool throughout the United States. A consequence of these efforts resulted in support from the Helmsley Charitable Trust (Helmsley) and the creation of the Intestinal Ultrasound Group of the United States and Canada to address the gaps unique to North America as well as to strengthen the quality of IUS research through collaborations across the continent.
What is IUS, and when is it performed?
IUS is a sonographic exam performed by a gastroenterology-trained professional who scans the abdominal wall (and perineum when the rectum and perineal disease is evaluated), using both a convex low-frequency probe and linear high-frequency probe to evaluate the small intestine, colon, and rectum. The bowel is composed of five layers with alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic layers: the mucosal-lumen interface (not a true part of the bowel wall), deep mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and serosa. (Figure)

The most sensitive parameter for assessment of IBD activity is bowel wall thickness (≤ 3 mm in the small bowel and colon and ≤ 4 mm in the rectum are considered normal in adults).8,10 The second key parameter is the assessment of vascularization, in which presence of hyperemia suggests active disease.11 There are a number of indices to quantify hyperemia, with the most widely used being the Limberg score.12 Additional parameters include assessment of loss of the delineation of the bowel wall layers (loss of stratification signifies active inflammation), increased thickness of the submucosa,13 increased mesenteric fatty proliferation (with increased inflammation, mesenteric fat proliferation will appear as a hyperechoic area surrounding the bowel), lymphadenopathy, bowel strictures, and extramural complications such as fistulae and abscess. Shear wave elastography may be an effective way to differentiate severe fibrotic strictures, but this is an area that requires more investigation.14
IUS has been shown to be an excellent tool in not only assessing disease activity and disease complication (with higher sensitivity than the Harvey-Bradshaw Index, serum C-reactive protein),15 but, unique to IUS, can provide early prediction of response in moderate to severe active UC.6,7 This has also been shown with transperineal ultrasound in patients with UC, with the ability to predict response to therapy as early as 1 week from induction therapy.16 Furthermore, it can be used to assess transmural healing, which has been shown to be associated with improved outcomes in Crohn’s patient, such as lower rates of hospitalizations, surgery, medication escalation, and need for corticosteroids.17 IUS is associated with great patient satisfaction and greater understanding of disease-related symptoms when the patient sees the inflammation of the bowel. (Table)
How can you get trained in IUS?
Training in IUS varies across the globe, from incorporation of IUS into the standard training curriculum to available training programs that can be followed and attended outside of medical training. In the United States, interested gastroenterologists can now be trained by becoming a member of the International Bowel Ultrasound Group (IBUS Group) and applying to the workshops now available. The IBUS Group has developed an IUS-specific training curriculum over the last 16 years, which is comprised of three modules: a 2-day hands-on workshop (Module 1) with final examination of theoretical competency, a preceptorship at an “expert center” with an experienced sonographer for a total of 4 weeks to complete 40 supervised IUS examinations (Module 2), and didactics and a final examination (Module 3). Also with support from Helmsley, the first Module 1 to be offered in the United States was hosted at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York in 2022, the second was hosted at the University of Chicago in March 2023, and the third is planned to take place at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles in March 2024.18 With the growing interest and demand for IUS training in the United States, U.S. experts are working to develop new training options that will be less time consuming, scalable, and still provide appropriate training and competency assessment.
How do you integrate IUS into your practice?
The keys to integrating IUS are a section chief or practice manager’s support of a trainee or faculty member for both funding of equipment and protected time for training and building of the program, as well as a permissive environment and collegial relationship with radiology. An ultrasound machine and additional transducers may range in price from $50,000-$120,000. Funding may be a limiting step for many, however. A detailed business plan is imperative to the success and investment of funds in an IUS program. With current billing practices in place that include ”limited abdominal ultrasound” (76705) and “Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen” (93975),19 reimbursement should include a technical fee, professional fee, and if in a hospital-based clinic, a facility fee. IUS pro-fee combined with technical fee is reimbursed at approximately 0.80 relative value units. When possible, the facility fee is included for approximately $800 per IUS visit. For billing and compliance with HIPAA, all billed IUS images must be stored in a durable and accessible format. It is recommended that the images and cine loops be digitally stored to the same or similar platform used by radiologists at the same institution. This requires early communication with the local information technology department for the connection of an ultrasound machine to the storage platform and/or electronic health record. Reporting results should be standardized with unique or otherwise available IUS templates, which also satisfy all billing components.9 The flow for incorporation of IUS into practice can be at the same time patients are seen during their visit, or alternatively, in a dedicated IUS clinic in which patients are referred by other providers and scheduled back to back.
Conclusions
In summary, the confluence of treat-to-target strategies in IBD, new treatment options in IBD, and successful efforts to translate IUS training and billing practices to the United States portends a great future for the field and for our patients.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Rubin, of the University of Chicago’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, are speakers for Samsung/Boston Imaging.
References
1. Turner D et al. Gastroenterology. Apr 2021;160(5):1570-83. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031
2. Hart AL and Rubin DT. Gastroenterology. Apr 2022;162(5):1367-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.013
3. Rajagopalan A et al. JGH Open. Apr 2020;4(2):267-72. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12268
4. Calabrese E et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Apr 2022;20(4):e711-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.030
5. Ripolles T et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Oct 2016;22(10):2465-73. doi10.1097/MIB.0000000000000882
6. Maaser C et al. Gut. Sep 2020;69(9):1629-36. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319451
7. Ilvemark J et al. J Crohns Colitis. Nov 23 2022;16(11):1725-34. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac083
8. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jun 2020;51(12):1373-83. doi: 10.1111/apt.15767
9. Dolinger MT et al. Guide to Intestinal Ultrasound Credentialing, Documentation, and Billing for Gastroenterologists in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023.
10. Maconi G et al. Ultraschall Med. Jun 2018;39(3):304-17. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-125329
11. Sasaki T et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Mar 2014;49(3):295-301. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2013.871744
12. Limberg B. Z Gastroenterol. Jun 1999;37(6):495-508.
13. Miyoshi J et al. J Gastroenterol. Feb 2022;57(2):82-9. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01847-3
14. Chen YJ et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Sep 15 2018;24(10):2183-90. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy115
15. Kucharzik T et al. Apr 2017;15(4):535-42e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.040
16. Sagami S et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. May 2022;55(10):1320-9. doi: 10.1111/apt.16817
17. Vaughan R et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Jul 2022;56(1):84-94. doi: 10.1111/apt.16892
18. International Bowel Ultrasound Group. https://ibus-group.org/
19. American Medical Association. CPT (Current Procedural Terminology). https://www.ama-assn.org/amaone/cpt-current-procedural-terminology
Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related gastrointestinal adverse events
Introduction
The field of cancer immunotherapy has exploded in recent years, with new therapies showing promising results for effective treatment of various cancer types. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) work by blocking checkpoint proteins that prevent breakdown of tumor cells by T-lymphocytes. Checkpoint proteins exist to prevent autoimmunity and destruction of healthy cells, but may allow tumor cells to grow unchallenged. Three checkpoint proteins – cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein–4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell-death protein–1 (PD-1), and programmed cell-death protein ligand–1 (PDL-1) – are therapeutic targets for current ICIs.1
ICIs are used to treat various cancer types (e.g., lung, renal-cell, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma). Immune-related adverse events (irAE) are frequently seen with ICI use, ranging from 15% to 90%, and can occur at any point during, or even after, treatment.2
Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related gastrointestinal adverse reactions
GI adverse reactions are the second most common irAE, occurring in about 35%-50% of all reported irAEs.3 Anti-CTLA-4 medications have the highest association with GI irAE. The most common GI symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal pain, urgency, and nausea/vomiting. GI involvement can occur along the entirety of the GI tract – from the oral cavity to the colorectum. These are usually seen within 6-8 weeks of starting treatment, but can occur as early as 1 week after initiation or as late as 12 months after the last dose.2 Although colitis is the most common area of luminal inflammation, aphthous ulcers, esophagitis, gastritis, and enteritis can be seen. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies have the highest associated rate of diarrhea (33%-50%) and colitis (7%-22%) of all ICIs.4 Computed tomography (CT) may show colonic wall thickening or fat stranding, indicating inflammation. Endoscopically, the colon can appear grossly normal or demonstrate erythema, erosions, ulcerations, and/or loss of vascular pattern.5 Inflammation can be patchy or continuous. Typical histology shows increased lamina propria cellularity, neutrophilic infiltration (intraepithelial or crypt abscesses), and increased crypt apoptosis.6
The liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and biliary tract can also be affected by irAE. The liver is most commonly involved (i.e. 5% of irAE), manifesting as asymptomatic liver chemistry elevation, particularly aminotransferases. This can progress to acute symptomatic hepatitis with jaundice, fever, or malaise, and rarely to fulminant hepatitis. ICI-associated hepatitis appears histologically similar to autoimmune hepatitis, with pan-lobular hepatitis and infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes seen on liver biopsy.7 Less commonly, pancreatic toxicity can occur (<2% of irAE), seen with anti-CTLA-4 therapy.8 While this typically results in asymptomatic lipase or amylase elevations (2.7%), acute pancreatitis (AP) can occur(1.9%). ICI-associated AP presents with classic symptoms and imaging changes, but can also manifest with exocrine or endocrine pancreatic insufficiency. An increase in rates of acute acalculous cholecystitis has been reported in patients receiving ICIs compared to patients receiving non-ICI chemotherapy.9 There are also rare reports of ICI-associated secondary sclerosing cholangitis.
Management
Evaluation and management of GI irAEs are guided by severity, based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grading classification (Table 1).10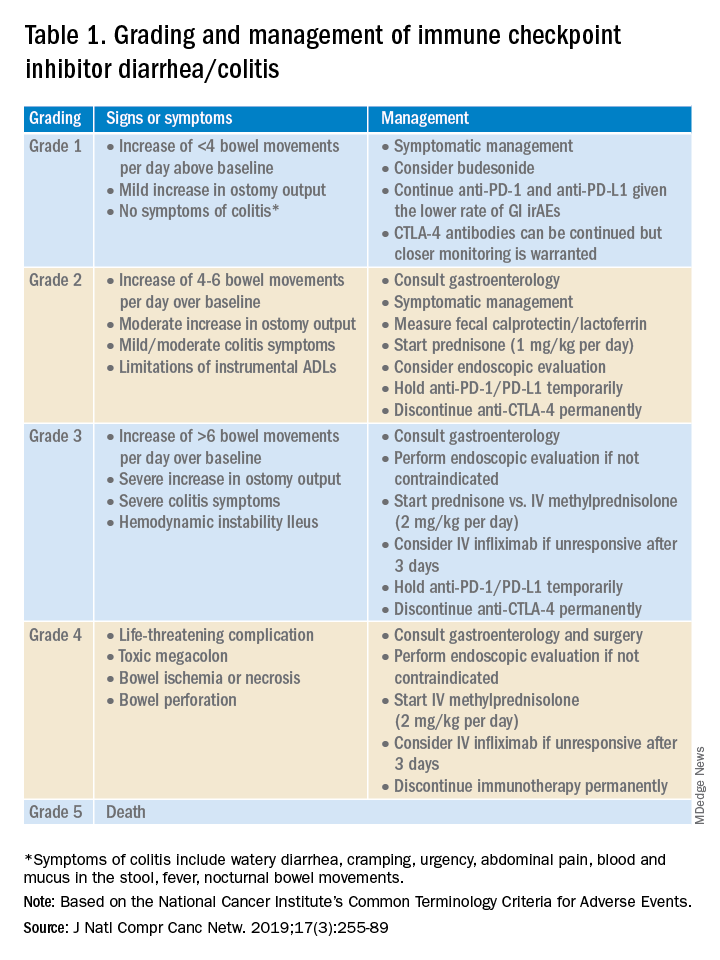
A thorough history of GI and systemic symptoms should be obtained and compared to baseline bowel habits. Patients with mild symptoms should undergo studies to assess alternate etiologies for their symptoms. Bacterial stool cultures and testing for C. difficile should be performed. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, fecal lactoferrin, and calprotectin can help assess the degree of intestinal inflammation and can be used to risk-stratify or assess treatment response. CT scans can assess for colitis and associated complications, including abdominal abscess, toxic megacolon, and bowel perforation.
Patients unresponsive to initial treatment for grade I irAE, with hematochezia, or with at least grade 2 diarrhea, should undergo GI consultation and endoscopic evaluation. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is the test of choice, as 95% of patients will have left-sided colonic inflammation.11 Patients with at least grade 3 diarrhea should be hospitalized for treatment. In cases of failed methylprednisolone and when infliximab is ineffective or contraindicated, vedolizumab is suggested, although evidence is limited.12
Patients responsive to systemic corticosteroids (complete resolution or improvement to grade 1) can continue a tapered regimen over 4-6 weeks. There is conflicting evidence on the effect that corticosteroids have on ICI-related antitumor response rates. While some studies report no change in antitumor response rates or survival, others report reduced overall survival.13 Regardless, given its unfavorable side-effect profile, steroids should be used only for short periods of time.
PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies can be restarted after symptoms have resolved or improved to grade 1, having finished the corticosteroid taper. CTLA-4 antibodies should be discontinued permanently in the setting of grade 3 toxicity. All ICIs should be discontinued permanently in grade 4 toxicity.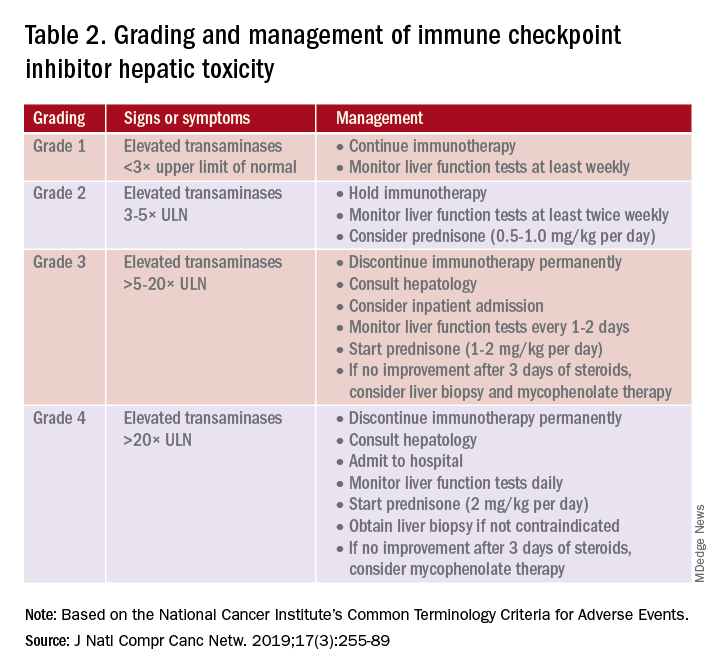
A grading system also exists for ICI-associated hepatitis (Table 2) and AP (Table 3). Patients with elevated aminotransferases greater than 2x upper limit of normal (ULN) should have alternative etiologies excluded. A thorough medication reconciliation, including over-the-counter and nonpharmaceutical supplements, should be performed. All potentially-hepatotoxic drugs and substances (including alcohol) should be discontinued. Viral hepatitis serology (A,B,C), Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus also should be performed. Additional tests, including prothrombin time and albumin, can help assess for liver synthetic dysfunction. Abdominal ultrasound or CT can assist in excluding biliary obstruction or metastatic disease. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) can be considered for further evaluation of biliary obstruction in patients with hyperbilirubinemia and normal ultrasound.14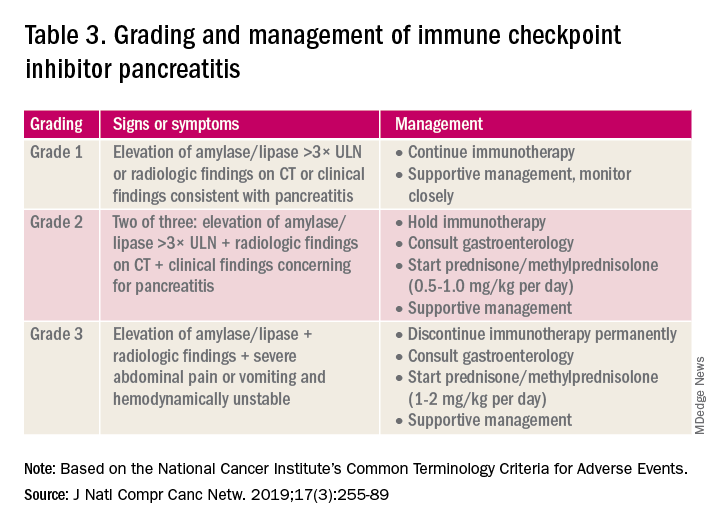
Table 2 reviews the grading system and management of ICI-associated hepatitis. Patients with grade 3 and above should be hospitalized for treatment. As with the management of colitis, patients responding to corticosteroids should be tapered off over 4-6 weeks. In steroid-refractory cases or if there is no improvement after 3 days, mycophenolate mofetil is used. Other immunomodulators such as azathioprine and tacrolimus also can be considered, although evidence is limited.15 ICI-associated cholangitis presenting with elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase is approached similarly to ICI-associated hepatitis. Abnormal findings of biliary obstruction or sclerosing cholangitis should be further evaluated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Mild asymptomatic elevation in lipase and amylase <3x ULN can be managed with observation and ICIs can be safely continued. Symptomatic patients should have a diagnostic workup for other etiologies. As with hepatitis, a thorough history including alcohol intake and a medication reconciliation should be performed. In the absence of other etiologies, grade 2 ICI-associated AP is managed by holding immunotherapy, administering steroids, and managing AP with fluid resuscitation and analgesia.
Conclusions
Therapy with ICI is a rapidly expanding and changing field. Side effects of ICIs can affect nearly every organ system, and thus management should involve a multidisciplinary team of oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and other specialists. Given that GI adverse effects are the second most commonly affected system, all gastroenterologists and hepatologists should be knowledgeable about the spectrum of GI adverse events, as well as with the respective clinical presentations, diagnostics, and management of these events.
Dr. Kwon is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of California Irvine, Orange. Dr. Kröner is with the division of advanced endoscopy, Riverside Health System, Newport News, Va. The authors certify that they have no financial arrangements (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interests, patent-licensing arrangements, research support, honoraria, etc.) with a company whose product figures prominently in this manuscript or with a company making a competing product. Funding: None.
References
1. Webster RM. The immune checkpoint inhibitors: where are we now? Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery. 2014;13(12):883.
2. Thompson JA et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2020: Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3):230-41.
3. Bertrand A et al. Immune related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015 Sep 4;13:211.
4. Gupta A et al. Systematic review: Colitis associated with anti‐CTLA‐4 therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(4):406-17.
5. Verschuren EC et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic characteristics of ipilimumab-associated colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(6):836-42.
6. Foppen MHG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition–related colitis: Symptoms, endoscopic features, histology and response to management. ESMO Open. 2018;3(1):e000278.
7. Sanjeevaiah A et al. Approach and management of checkpoint inhibitor–related immune hepatitis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018;9(1):220.
8. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced pancreatic injury. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Feb 6;7(1):31.
9. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Case series of cancer patients who developed cholecystitis related to immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 3;7(1):118.
10. Thompson JA et al. Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(3):255-89.
11. Marthey L et al. Cancer immunotherapy with anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies induces an inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(4):395-401.
12. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Outcomes of vedolizumab therapy in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis: A multicenter study. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Dec 5;6(1):142.
13. Das S and Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Nov 15;7(1):306.
14. Reddy HG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated colitis and hepatitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):180.
15. Reynolds K et al. Diagnosis and management of hepatitis in patients on checkpoint blockade. Oncologist. 2018;23(9):991-7.
Introduction
The field of cancer immunotherapy has exploded in recent years, with new therapies showing promising results for effective treatment of various cancer types. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) work by blocking checkpoint proteins that prevent breakdown of tumor cells by T-lymphocytes. Checkpoint proteins exist to prevent autoimmunity and destruction of healthy cells, but may allow tumor cells to grow unchallenged. Three checkpoint proteins – cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein–4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell-death protein–1 (PD-1), and programmed cell-death protein ligand–1 (PDL-1) – are therapeutic targets for current ICIs.1
ICIs are used to treat various cancer types (e.g., lung, renal-cell, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma). Immune-related adverse events (irAE) are frequently seen with ICI use, ranging from 15% to 90%, and can occur at any point during, or even after, treatment.2
Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related gastrointestinal adverse reactions
GI adverse reactions are the second most common irAE, occurring in about 35%-50% of all reported irAEs.3 Anti-CTLA-4 medications have the highest association with GI irAE. The most common GI symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal pain, urgency, and nausea/vomiting. GI involvement can occur along the entirety of the GI tract – from the oral cavity to the colorectum. These are usually seen within 6-8 weeks of starting treatment, but can occur as early as 1 week after initiation or as late as 12 months after the last dose.2 Although colitis is the most common area of luminal inflammation, aphthous ulcers, esophagitis, gastritis, and enteritis can be seen. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies have the highest associated rate of diarrhea (33%-50%) and colitis (7%-22%) of all ICIs.4 Computed tomography (CT) may show colonic wall thickening or fat stranding, indicating inflammation. Endoscopically, the colon can appear grossly normal or demonstrate erythema, erosions, ulcerations, and/or loss of vascular pattern.5 Inflammation can be patchy or continuous. Typical histology shows increased lamina propria cellularity, neutrophilic infiltration (intraepithelial or crypt abscesses), and increased crypt apoptosis.6
The liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and biliary tract can also be affected by irAE. The liver is most commonly involved (i.e. 5% of irAE), manifesting as asymptomatic liver chemistry elevation, particularly aminotransferases. This can progress to acute symptomatic hepatitis with jaundice, fever, or malaise, and rarely to fulminant hepatitis. ICI-associated hepatitis appears histologically similar to autoimmune hepatitis, with pan-lobular hepatitis and infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes seen on liver biopsy.7 Less commonly, pancreatic toxicity can occur (<2% of irAE), seen with anti-CTLA-4 therapy.8 While this typically results in asymptomatic lipase or amylase elevations (2.7%), acute pancreatitis (AP) can occur(1.9%). ICI-associated AP presents with classic symptoms and imaging changes, but can also manifest with exocrine or endocrine pancreatic insufficiency. An increase in rates of acute acalculous cholecystitis has been reported in patients receiving ICIs compared to patients receiving non-ICI chemotherapy.9 There are also rare reports of ICI-associated secondary sclerosing cholangitis.
Management
Evaluation and management of GI irAEs are guided by severity, based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grading classification (Table 1).10
A thorough history of GI and systemic symptoms should be obtained and compared to baseline bowel habits. Patients with mild symptoms should undergo studies to assess alternate etiologies for their symptoms. Bacterial stool cultures and testing for C. difficile should be performed. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, fecal lactoferrin, and calprotectin can help assess the degree of intestinal inflammation and can be used to risk-stratify or assess treatment response. CT scans can assess for colitis and associated complications, including abdominal abscess, toxic megacolon, and bowel perforation.
Patients unresponsive to initial treatment for grade I irAE, with hematochezia, or with at least grade 2 diarrhea, should undergo GI consultation and endoscopic evaluation. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is the test of choice, as 95% of patients will have left-sided colonic inflammation.11 Patients with at least grade 3 diarrhea should be hospitalized for treatment. In cases of failed methylprednisolone and when infliximab is ineffective or contraindicated, vedolizumab is suggested, although evidence is limited.12
Patients responsive to systemic corticosteroids (complete resolution or improvement to grade 1) can continue a tapered regimen over 4-6 weeks. There is conflicting evidence on the effect that corticosteroids have on ICI-related antitumor response rates. While some studies report no change in antitumor response rates or survival, others report reduced overall survival.13 Regardless, given its unfavorable side-effect profile, steroids should be used only for short periods of time.
PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies can be restarted after symptoms have resolved or improved to grade 1, having finished the corticosteroid taper. CTLA-4 antibodies should be discontinued permanently in the setting of grade 3 toxicity. All ICIs should be discontinued permanently in grade 4 toxicity.
A grading system also exists for ICI-associated hepatitis (Table 2) and AP (Table 3). Patients with elevated aminotransferases greater than 2x upper limit of normal (ULN) should have alternative etiologies excluded. A thorough medication reconciliation, including over-the-counter and nonpharmaceutical supplements, should be performed. All potentially-hepatotoxic drugs and substances (including alcohol) should be discontinued. Viral hepatitis serology (A,B,C), Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus also should be performed. Additional tests, including prothrombin time and albumin, can help assess for liver synthetic dysfunction. Abdominal ultrasound or CT can assist in excluding biliary obstruction or metastatic disease. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) can be considered for further evaluation of biliary obstruction in patients with hyperbilirubinemia and normal ultrasound.14
Table 2 reviews the grading system and management of ICI-associated hepatitis. Patients with grade 3 and above should be hospitalized for treatment. As with the management of colitis, patients responding to corticosteroids should be tapered off over 4-6 weeks. In steroid-refractory cases or if there is no improvement after 3 days, mycophenolate mofetil is used. Other immunomodulators such as azathioprine and tacrolimus also can be considered, although evidence is limited.15 ICI-associated cholangitis presenting with elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase is approached similarly to ICI-associated hepatitis. Abnormal findings of biliary obstruction or sclerosing cholangitis should be further evaluated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Mild asymptomatic elevation in lipase and amylase <3x ULN can be managed with observation and ICIs can be safely continued. Symptomatic patients should have a diagnostic workup for other etiologies. As with hepatitis, a thorough history including alcohol intake and a medication reconciliation should be performed. In the absence of other etiologies, grade 2 ICI-associated AP is managed by holding immunotherapy, administering steroids, and managing AP with fluid resuscitation and analgesia.
Conclusions
Therapy with ICI is a rapidly expanding and changing field. Side effects of ICIs can affect nearly every organ system, and thus management should involve a multidisciplinary team of oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and other specialists. Given that GI adverse effects are the second most commonly affected system, all gastroenterologists and hepatologists should be knowledgeable about the spectrum of GI adverse events, as well as with the respective clinical presentations, diagnostics, and management of these events.
Dr. Kwon is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of California Irvine, Orange. Dr. Kröner is with the division of advanced endoscopy, Riverside Health System, Newport News, Va. The authors certify that they have no financial arrangements (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interests, patent-licensing arrangements, research support, honoraria, etc.) with a company whose product figures prominently in this manuscript or with a company making a competing product. Funding: None.
References
1. Webster RM. The immune checkpoint inhibitors: where are we now? Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery. 2014;13(12):883.
2. Thompson JA et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2020: Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3):230-41.
3. Bertrand A et al. Immune related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015 Sep 4;13:211.
4. Gupta A et al. Systematic review: Colitis associated with anti‐CTLA‐4 therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(4):406-17.
5. Verschuren EC et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic characteristics of ipilimumab-associated colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(6):836-42.
6. Foppen MHG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition–related colitis: Symptoms, endoscopic features, histology and response to management. ESMO Open. 2018;3(1):e000278.
7. Sanjeevaiah A et al. Approach and management of checkpoint inhibitor–related immune hepatitis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018;9(1):220.
8. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced pancreatic injury. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Feb 6;7(1):31.
9. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Case series of cancer patients who developed cholecystitis related to immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 3;7(1):118.
10. Thompson JA et al. Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(3):255-89.
11. Marthey L et al. Cancer immunotherapy with anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies induces an inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(4):395-401.
12. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Outcomes of vedolizumab therapy in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis: A multicenter study. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Dec 5;6(1):142.
13. Das S and Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Nov 15;7(1):306.
14. Reddy HG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated colitis and hepatitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):180.
15. Reynolds K et al. Diagnosis and management of hepatitis in patients on checkpoint blockade. Oncologist. 2018;23(9):991-7.
Introduction
The field of cancer immunotherapy has exploded in recent years, with new therapies showing promising results for effective treatment of various cancer types. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) work by blocking checkpoint proteins that prevent breakdown of tumor cells by T-lymphocytes. Checkpoint proteins exist to prevent autoimmunity and destruction of healthy cells, but may allow tumor cells to grow unchallenged. Three checkpoint proteins – cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein–4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell-death protein–1 (PD-1), and programmed cell-death protein ligand–1 (PDL-1) – are therapeutic targets for current ICIs.1
ICIs are used to treat various cancer types (e.g., lung, renal-cell, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma). Immune-related adverse events (irAE) are frequently seen with ICI use, ranging from 15% to 90%, and can occur at any point during, or even after, treatment.2
Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related gastrointestinal adverse reactions
GI adverse reactions are the second most common irAE, occurring in about 35%-50% of all reported irAEs.3 Anti-CTLA-4 medications have the highest association with GI irAE. The most common GI symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal pain, urgency, and nausea/vomiting. GI involvement can occur along the entirety of the GI tract – from the oral cavity to the colorectum. These are usually seen within 6-8 weeks of starting treatment, but can occur as early as 1 week after initiation or as late as 12 months after the last dose.2 Although colitis is the most common area of luminal inflammation, aphthous ulcers, esophagitis, gastritis, and enteritis can be seen. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies have the highest associated rate of diarrhea (33%-50%) and colitis (7%-22%) of all ICIs.4 Computed tomography (CT) may show colonic wall thickening or fat stranding, indicating inflammation. Endoscopically, the colon can appear grossly normal or demonstrate erythema, erosions, ulcerations, and/or loss of vascular pattern.5 Inflammation can be patchy or continuous. Typical histology shows increased lamina propria cellularity, neutrophilic infiltration (intraepithelial or crypt abscesses), and increased crypt apoptosis.6
The liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and biliary tract can also be affected by irAE. The liver is most commonly involved (i.e. 5% of irAE), manifesting as asymptomatic liver chemistry elevation, particularly aminotransferases. This can progress to acute symptomatic hepatitis with jaundice, fever, or malaise, and rarely to fulminant hepatitis. ICI-associated hepatitis appears histologically similar to autoimmune hepatitis, with pan-lobular hepatitis and infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes seen on liver biopsy.7 Less commonly, pancreatic toxicity can occur (<2% of irAE), seen with anti-CTLA-4 therapy.8 While this typically results in asymptomatic lipase or amylase elevations (2.7%), acute pancreatitis (AP) can occur(1.9%). ICI-associated AP presents with classic symptoms and imaging changes, but can also manifest with exocrine or endocrine pancreatic insufficiency. An increase in rates of acute acalculous cholecystitis has been reported in patients receiving ICIs compared to patients receiving non-ICI chemotherapy.9 There are also rare reports of ICI-associated secondary sclerosing cholangitis.
Management
Evaluation and management of GI irAEs are guided by severity, based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grading classification (Table 1).10
A thorough history of GI and systemic symptoms should be obtained and compared to baseline bowel habits. Patients with mild symptoms should undergo studies to assess alternate etiologies for their symptoms. Bacterial stool cultures and testing for C. difficile should be performed. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, fecal lactoferrin, and calprotectin can help assess the degree of intestinal inflammation and can be used to risk-stratify or assess treatment response. CT scans can assess for colitis and associated complications, including abdominal abscess, toxic megacolon, and bowel perforation.
Patients unresponsive to initial treatment for grade I irAE, with hematochezia, or with at least grade 2 diarrhea, should undergo GI consultation and endoscopic evaluation. Flexible sigmoidoscopy is the test of choice, as 95% of patients will have left-sided colonic inflammation.11 Patients with at least grade 3 diarrhea should be hospitalized for treatment. In cases of failed methylprednisolone and when infliximab is ineffective or contraindicated, vedolizumab is suggested, although evidence is limited.12
Patients responsive to systemic corticosteroids (complete resolution or improvement to grade 1) can continue a tapered regimen over 4-6 weeks. There is conflicting evidence on the effect that corticosteroids have on ICI-related antitumor response rates. While some studies report no change in antitumor response rates or survival, others report reduced overall survival.13 Regardless, given its unfavorable side-effect profile, steroids should be used only for short periods of time.
PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies can be restarted after symptoms have resolved or improved to grade 1, having finished the corticosteroid taper. CTLA-4 antibodies should be discontinued permanently in the setting of grade 3 toxicity. All ICIs should be discontinued permanently in grade 4 toxicity.
A grading system also exists for ICI-associated hepatitis (Table 2) and AP (Table 3). Patients with elevated aminotransferases greater than 2x upper limit of normal (ULN) should have alternative etiologies excluded. A thorough medication reconciliation, including over-the-counter and nonpharmaceutical supplements, should be performed. All potentially-hepatotoxic drugs and substances (including alcohol) should be discontinued. Viral hepatitis serology (A,B,C), Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus also should be performed. Additional tests, including prothrombin time and albumin, can help assess for liver synthetic dysfunction. Abdominal ultrasound or CT can assist in excluding biliary obstruction or metastatic disease. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) can be considered for further evaluation of biliary obstruction in patients with hyperbilirubinemia and normal ultrasound.14
Table 2 reviews the grading system and management of ICI-associated hepatitis. Patients with grade 3 and above should be hospitalized for treatment. As with the management of colitis, patients responding to corticosteroids should be tapered off over 4-6 weeks. In steroid-refractory cases or if there is no improvement after 3 days, mycophenolate mofetil is used. Other immunomodulators such as azathioprine and tacrolimus also can be considered, although evidence is limited.15 ICI-associated cholangitis presenting with elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase is approached similarly to ICI-associated hepatitis. Abnormal findings of biliary obstruction or sclerosing cholangitis should be further evaluated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Mild asymptomatic elevation in lipase and amylase <3x ULN can be managed with observation and ICIs can be safely continued. Symptomatic patients should have a diagnostic workup for other etiologies. As with hepatitis, a thorough history including alcohol intake and a medication reconciliation should be performed. In the absence of other etiologies, grade 2 ICI-associated AP is managed by holding immunotherapy, administering steroids, and managing AP with fluid resuscitation and analgesia.
Conclusions
Therapy with ICI is a rapidly expanding and changing field. Side effects of ICIs can affect nearly every organ system, and thus management should involve a multidisciplinary team of oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and other specialists. Given that GI adverse effects are the second most commonly affected system, all gastroenterologists and hepatologists should be knowledgeable about the spectrum of GI adverse events, as well as with the respective clinical presentations, diagnostics, and management of these events.
Dr. Kwon is with the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of California Irvine, Orange. Dr. Kröner is with the division of advanced endoscopy, Riverside Health System, Newport News, Va. The authors certify that they have no financial arrangements (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interests, patent-licensing arrangements, research support, honoraria, etc.) with a company whose product figures prominently in this manuscript or with a company making a competing product. Funding: None.
References
1. Webster RM. The immune checkpoint inhibitors: where are we now? Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery. 2014;13(12):883.
2. Thompson JA et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2020: Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3):230-41.
3. Bertrand A et al. Immune related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015 Sep 4;13:211.
4. Gupta A et al. Systematic review: Colitis associated with anti‐CTLA‐4 therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(4):406-17.
5. Verschuren EC et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic characteristics of ipilimumab-associated colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(6):836-42.
6. Foppen MHG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition–related colitis: Symptoms, endoscopic features, histology and response to management. ESMO Open. 2018;3(1):e000278.
7. Sanjeevaiah A et al. Approach and management of checkpoint inhibitor–related immune hepatitis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018;9(1):220.
8. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced pancreatic injury. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Feb 6;7(1):31.
9. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Case series of cancer patients who developed cholecystitis related to immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 3;7(1):118.
10. Thompson JA et al. Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(3):255-89.
11. Marthey L et al. Cancer immunotherapy with anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies induces an inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(4):395-401.
12. Abu-Sbeih H et al. Outcomes of vedolizumab therapy in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–induced colitis: A multicenter study. J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Dec 5;6(1):142.
13. Das S and Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Nov 15;7(1):306.
14. Reddy HG et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated colitis and hepatitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):180.
15. Reynolds K et al. Diagnosis and management of hepatitis in patients on checkpoint blockade. Oncologist. 2018;23(9):991-7.
Lean and clean: Minimally invasive endoscopic and pharmacologic approaches to obesity
Obesity currently affects more than 40% of the U.S. population. It is the second-leading preventable cause of mortality behind smoking with an estimated 300,000 deaths per year.1,2 Weight loss can reduce the risk of metabolic comorbidities such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. However, 5%-10% total body weight loss (TBWL) is required for risk reduction.3 Sustained weight loss involves dietary alterations and physical activity, although it is difficult to maintain long term with lifestyle changes alone. Less than 10% of Americans with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 will achieve 5% TBWL each year, and nearly 80% of people will regain the weight within 5 years, a phenomenon known as “weight cycling.”4,5 Not only can these weight fluctuations make future weight-loss efforts more difficult, but they can also negatively impact cardiometabolic health in the long term.5 Thus, additional therapies are typically needed in conjunction with lifestyle interventions to treat obesity.
Current guidelines recommend bariatric surgery for patients unable to achieve or maintain weight loss through lifestyle changes.6 Surgeries like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy lead to improvements in morbidity and mortality from metabolic diseases but are often only approved for select patients with a BMI of at least 40 or at least 35 with obesity-related comorbidities.7 These restrictions exclude patients at lower BMIs who may have early metabolic disease. Furthermore, only a small proportion of eligible patients are referred or willing to undergo surgery because of access issues, socioeconomic barriers, and concerns about adverse events.8,9 Endoscopic bariatric therapy and antiobesity medications (AOMs) have blossomed because of the need for other less-invasive options to stimulate weight loss.
Minimally invasive and noninvasive therapies in obesity
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies
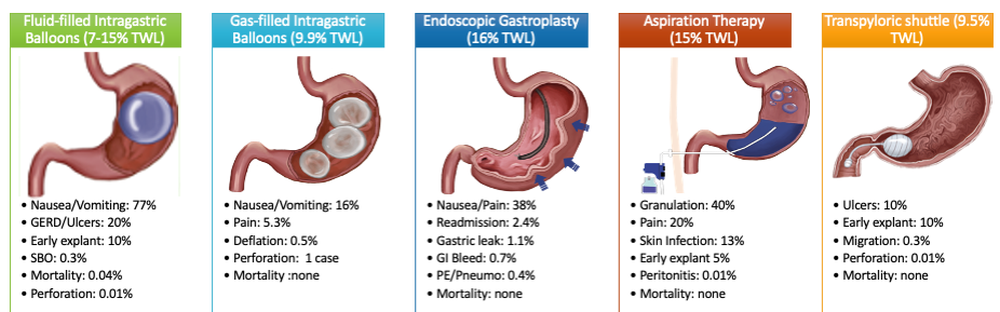
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) are used for the treatment of obesity in patients with a BMI of 30 kg/m2, a cohort that may be ineligible for bariatric surgery.10,11 EBMTs involve three categories: space-occupying devices (intragastric balloons [IGBs], transpyloric shuttle [TPS]), aspiration therapy, and gastric remodeling (endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty [ESG]).21,13 Presently, TPS and aspiration therapy are not commercially available in the United States. There are three types of IGB approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and Apollo ESGTM recently received de novo marketing authorization for the treatment of obesity. TBWL with EBMTs is promising at 12 months post procedure. Ranges include 7%-12% TBWL for IGBs and 15%-19% for ESG, with low rates of serious adverse events (AEs).13-18 Weight loss often reaches or exceeds the 10% TBWL needed to improve or completely reverse metabolic complications.
Obesity pharmacotherapy
Multiple professional societies support the use of obesity pharmacotherapy as an effective adjunct to lifestyle interventions.19 AOMs are classified as peripherally-acting to prevent nutrition absorption (e.g. orlistat), centrally acting to suppress appetite and/or cravings (e.g., phentermine/topiramate or naltrexone/bupropion), or incretin mimetics such as glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists (e.g., liraglutide, semaglutide).20 With the exception of orlistat, most agents have some effects on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite.21 Obesity medications tend to lead to a minimum weight loss of 3-10 kg after 12 months of treatment, and newer medications have even greater efficacy.22 Despite these results, discontinuation rates of the popular GLP-1 agonists can be as high as 47.7% and 70.1% at 12 and 24 months, respectively, because of the high cost of medications, gastrointestinal side effects, and poor tolerance.23,24
An ongoing challenge for patients is maintaining weight loss following cessation of pharmacotherapy when weight loss goals have been achieved. In this context, the combination of obesity pharmacotherapy and EBMTs can be utilized for long-term weight loss and weight maintenance given the chronic, relapsing, and complex nature of obesity.25
Advantages of less-invasive therapies in obesity management
The advantages of both pharmacologic and endoscopic weight-loss therapies are numerous. Pharmacotherapies are noninvasive, and their multiple mechanisms allow for combined use to synergistically promote weight reduction.26,27 Medications can be used in both the short- and long-term management of obesity, allowing for flexibility in use for patients pending fluctuations in weight. Furthermore, medications can improve markers of cardiovascular health including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and glycemic control.28
As minimally invasive therapies, EBMTs have less morbidity and mortality, compared with bariatric surgeries.29 The most common side effects of IGBs or ESG include abdominal pain, nausea, and worsening of acid reflux symptoms, which can be medically managed unlike some of the AEs associated with surgery, such as bowel obstruction, anastomotic dehiscence, fistulization, and postoperative infections.30 Long-term AEs from surgery also include malabsorption, nutritional deficiencies, cholelithiasis, and anastomotic stenosis.31 Even with improvement in surgical techniques, the rate of perioperative and postoperative mortality in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is estimated to be 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively, compared with only 0.08% with IGBs.30,32
In addition, EBMTs are also more cost effective than surgery, as they are often same-day outpatient procedures, leading to decreased length of stay (LOS) for patients. In ongoing research conducted by Sharaiha and colleagues, it was found that patients undergoing ESG had an average LOS of only 0.13 days, compared with 3.09 days for laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and 1.68 for laparoscopic gastric banding. The cost for ESG was approximately $12,000, compared with $15,000-$22,000 for laparoscopic bariatric surgeries.33 With their availability to patients with lower BMIs and their less-invasive nature, EBMTs and pharmacotherapy can be utilized on the spectrum of obesity care as bridge therapies both before and after surgery.
Our clinical approach
In 2015, the first Veterans Affairs hospital-based endoscopic bariatric program was established at the VA New York Harbor Healthcare System utilizing IGBs and weight loss pharmacotherapy in conjunction with the VA MOVE! Program to treat obesity and metabolic comorbidities in veterans. Since then, EBMTs have expanded to include ESG and novel medications. Our treatment algorithm accounts for the chronic nature of obesity, the risk of weight regain after any intervention, and the need for longitudinal patient care.
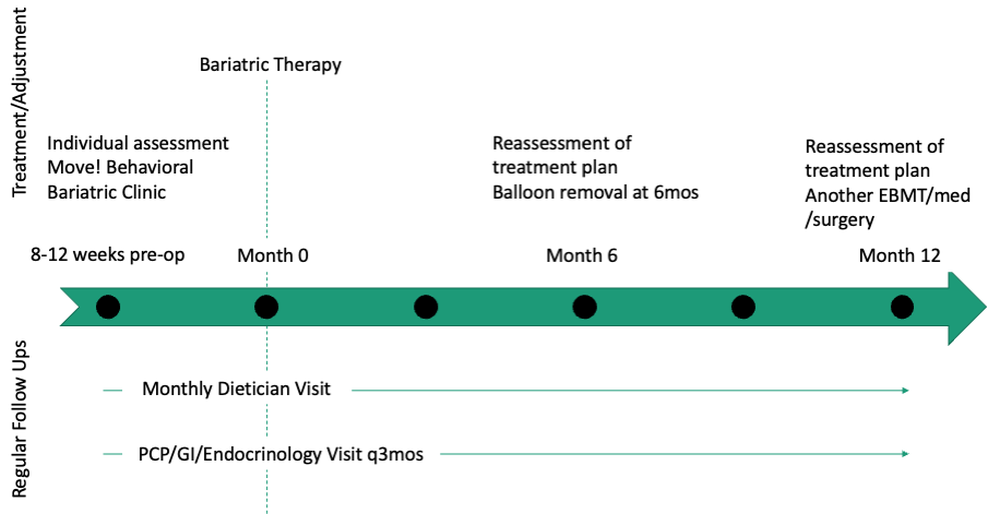
Patients undergo work-up by a multidisciplinary team (MD team) with a nutritionist, psychologist, primary care physician, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist to determine the optimal treatment plan (Fig. 1).29
Patients are required to attend multiple information sessions, where all weight-loss methods are presented, including surgery, bariatric endoscopy, and pharmacotherapy. Other specialists also help manage comorbid conditions. Prior to selecting an initial intervention, patients undergo intensive lifestyle and behavioral therapy (Fig. 2 and 3). Depending on the selected therapy, initial treatment lasts between 3 and 12 months with ongoing support from the MD team.
If patients do not achieve their targeted weight loss after initial treatment, a new strategy is selected. This includes a different EBMT such as ESG, alternate pharmacotherapy, or surgery until the weight and health goals of the patient are achieved and sustained (Fig. 3). From the start, patients are informed that our program is a long-term intervention and that active participation in the MOVE! Program, as well as follow-up with the MD team are keys to success. EBMTs and medications are presented as effective tools that only work to enhance the effects of lifestyle changes.
Our multidisciplinary approach provides flexibility for patients to trial different options depending on their progress. Research on long-term outcomes with weight loss and metabolic parameters is ongoing, though early results are promising. Thus far, we have observed that patients undergoing a combination therapy of EBMTs and AOMs have greater weight loss than patients on a single therapeutic approach with either EBMT or AOMs alone.34 Racial and socioeconomic disparities in referrals to bariatric surgery are yet another barrier for patients to access weight reduction and improvement in cardiovascular health.35 EBMTs and pharmacotherapy are no longer just on the horizon; they are here as accessible, effective, and long-term treatments for all patients with obesity. More expansive insurance coverage is needed for EBMTs and AOMs in order to prevent progression of obesity-related comorbidities, reduce high costs, and ensure more equitable access to these effective therapies.
Dr. Young and Dr. Zenger are resident physicians in the department of internal medicine at New York University. Dr. Holzwanger is an advanced endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Dr. Popov is director of bariatric endoscopy at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System, and assistant professor of medicine at New York University. Dr. Popov reported relationships with Obalon, Microtech, and Spatz, but the remaining authors reported no competing interests.
References
1. Ward ZJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(25):2440-50.
2. Stein CJ and Colditz GA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2522-5.
3. Ryan DH and Yockey SR. Curr Obes Rep. 2017;6(2):187-94.
4. Fildes A et al. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(9):e54-9.
5. Rhee E-J. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017;26(4):237-42.
6. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines OEP. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22 Suppl 2:S5-39.
7. Adams TD et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):93-6.
8. Wharton S et al. Clin Obes. 2016;6(2):154-60.
9. Iuzzolino E and Kim Y. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14(4):310-20.
10. Goyal D, Watson RR. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016;18(6):26.
11. Ali MR et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(3):462-467.
12. Turkeltaub JA, Edmundowicz SA. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):187-201.
13. Reja D et al. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:21.
14. Force ABET et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-38e5.
15. Thompson CC et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(3):447-57.
16. Nystrom M et al. Obes Surg. 2018;28(7):1860-8.
17. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(8):1423-4.
18. Sharaiha RZ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-10.
19. Apovian CM et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-62.
20. Son JW and Kim S. Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):802-18.
21. Holst JJ. Int J Obes (Lond). Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(9):1161-8.
22. Joo JK and Lee KS. J Menopausal Med. 2014;20(3):90-6.
23. Weiss T et al. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2020;14:2337-45.
24. Sikirica MV et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017;10:403-12.
25. Kahan S et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;22(3):154-8.
26. Bhat SP and Sharma A. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(8):983-93.
27. Pendse J et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29(2):308-16.
28. Rucker D et al. BMJ. 2007;335(7631):1194-9.
29. Jirapinyo P and Thompson CC. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(5):619-30.
30. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(5):1073-86.
31. Schulman AR and Thompson CC. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(11):1640-55.
32. Ma IT and Madura JA, 2nd. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 2015;11(8):526-35.
33. Sharaiha RZ. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty as a nonsurgical weight loss alternative. Digestive Disease Week, oral presentation. 2017.
34. Young S et al. Long-term efficacy of a multidisciplinary minimally invasive approach to weight management compared to single endoscopic therapy: A cohort study. P0865. American College of Gastroenterology Meeting, Abstract P0865. 2021.
35. Johnson-Mann C et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(4):615-20.
Obesity currently affects more than 40% of the U.S. population. It is the second-leading preventable cause of mortality behind smoking with an estimated 300,000 deaths per year.1,2 Weight loss can reduce the risk of metabolic comorbidities such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. However, 5%-10% total body weight loss (TBWL) is required for risk reduction.3 Sustained weight loss involves dietary alterations and physical activity, although it is difficult to maintain long term with lifestyle changes alone. Less than 10% of Americans with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 will achieve 5% TBWL each year, and nearly 80% of people will regain the weight within 5 years, a phenomenon known as “weight cycling.”4,5 Not only can these weight fluctuations make future weight-loss efforts more difficult, but they can also negatively impact cardiometabolic health in the long term.5 Thus, additional therapies are typically needed in conjunction with lifestyle interventions to treat obesity.
Current guidelines recommend bariatric surgery for patients unable to achieve or maintain weight loss through lifestyle changes.6 Surgeries like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy lead to improvements in morbidity and mortality from metabolic diseases but are often only approved for select patients with a BMI of at least 40 or at least 35 with obesity-related comorbidities.7 These restrictions exclude patients at lower BMIs who may have early metabolic disease. Furthermore, only a small proportion of eligible patients are referred or willing to undergo surgery because of access issues, socioeconomic barriers, and concerns about adverse events.8,9 Endoscopic bariatric therapy and antiobesity medications (AOMs) have blossomed because of the need for other less-invasive options to stimulate weight loss.
Minimally invasive and noninvasive therapies in obesity
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) are used for the treatment of obesity in patients with a BMI of 30 kg/m2, a cohort that may be ineligible for bariatric surgery.10,11 EBMTs involve three categories: space-occupying devices (intragastric balloons [IGBs], transpyloric shuttle [TPS]), aspiration therapy, and gastric remodeling (endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty [ESG]).21,13 Presently, TPS and aspiration therapy are not commercially available in the United States. There are three types of IGB approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and Apollo ESGTM recently received de novo marketing authorization for the treatment of obesity. TBWL with EBMTs is promising at 12 months post procedure. Ranges include 7%-12% TBWL for IGBs and 15%-19% for ESG, with low rates of serious adverse events (AEs).13-18 Weight loss often reaches or exceeds the 10% TBWL needed to improve or completely reverse metabolic complications.
Obesity pharmacotherapy
Multiple professional societies support the use of obesity pharmacotherapy as an effective adjunct to lifestyle interventions.19 AOMs are classified as peripherally-acting to prevent nutrition absorption (e.g. orlistat), centrally acting to suppress appetite and/or cravings (e.g., phentermine/topiramate or naltrexone/bupropion), or incretin mimetics such as glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists (e.g., liraglutide, semaglutide).20 With the exception of orlistat, most agents have some effects on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite.21 Obesity medications tend to lead to a minimum weight loss of 3-10 kg after 12 months of treatment, and newer medications have even greater efficacy.22 Despite these results, discontinuation rates of the popular GLP-1 agonists can be as high as 47.7% and 70.1% at 12 and 24 months, respectively, because of the high cost of medications, gastrointestinal side effects, and poor tolerance.23,24
An ongoing challenge for patients is maintaining weight loss following cessation of pharmacotherapy when weight loss goals have been achieved. In this context, the combination of obesity pharmacotherapy and EBMTs can be utilized for long-term weight loss and weight maintenance given the chronic, relapsing, and complex nature of obesity.25
Advantages of less-invasive therapies in obesity management
The advantages of both pharmacologic and endoscopic weight-loss therapies are numerous. Pharmacotherapies are noninvasive, and their multiple mechanisms allow for combined use to synergistically promote weight reduction.26,27 Medications can be used in both the short- and long-term management of obesity, allowing for flexibility in use for patients pending fluctuations in weight. Furthermore, medications can improve markers of cardiovascular health including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and glycemic control.28
As minimally invasive therapies, EBMTs have less morbidity and mortality, compared with bariatric surgeries.29 The most common side effects of IGBs or ESG include abdominal pain, nausea, and worsening of acid reflux symptoms, which can be medically managed unlike some of the AEs associated with surgery, such as bowel obstruction, anastomotic dehiscence, fistulization, and postoperative infections.30 Long-term AEs from surgery also include malabsorption, nutritional deficiencies, cholelithiasis, and anastomotic stenosis.31 Even with improvement in surgical techniques, the rate of perioperative and postoperative mortality in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is estimated to be 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively, compared with only 0.08% with IGBs.30,32
In addition, EBMTs are also more cost effective than surgery, as they are often same-day outpatient procedures, leading to decreased length of stay (LOS) for patients. In ongoing research conducted by Sharaiha and colleagues, it was found that patients undergoing ESG had an average LOS of only 0.13 days, compared with 3.09 days for laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and 1.68 for laparoscopic gastric banding. The cost for ESG was approximately $12,000, compared with $15,000-$22,000 for laparoscopic bariatric surgeries.33 With their availability to patients with lower BMIs and their less-invasive nature, EBMTs and pharmacotherapy can be utilized on the spectrum of obesity care as bridge therapies both before and after surgery.
Our clinical approach
In 2015, the first Veterans Affairs hospital-based endoscopic bariatric program was established at the VA New York Harbor Healthcare System utilizing IGBs and weight loss pharmacotherapy in conjunction with the VA MOVE! Program to treat obesity and metabolic comorbidities in veterans. Since then, EBMTs have expanded to include ESG and novel medications. Our treatment algorithm accounts for the chronic nature of obesity, the risk of weight regain after any intervention, and the need for longitudinal patient care.
Patients undergo work-up by a multidisciplinary team (MD team) with a nutritionist, psychologist, primary care physician, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist to determine the optimal treatment plan (Fig. 1).29

Patients are required to attend multiple information sessions, where all weight-loss methods are presented, including surgery, bariatric endoscopy, and pharmacotherapy. Other specialists also help manage comorbid conditions. Prior to selecting an initial intervention, patients undergo intensive lifestyle and behavioral therapy (Fig. 2 and 3). Depending on the selected therapy, initial treatment lasts between 3 and 12 months with ongoing support from the MD team.

If patients do not achieve their targeted weight loss after initial treatment, a new strategy is selected. This includes a different EBMT such as ESG, alternate pharmacotherapy, or surgery until the weight and health goals of the patient are achieved and sustained (Fig. 3). From the start, patients are informed that our program is a long-term intervention and that active participation in the MOVE! Program, as well as follow-up with the MD team are keys to success. EBMTs and medications are presented as effective tools that only work to enhance the effects of lifestyle changes.

Our multidisciplinary approach provides flexibility for patients to trial different options depending on their progress. Research on long-term outcomes with weight loss and metabolic parameters is ongoing, though early results are promising. Thus far, we have observed that patients undergoing a combination therapy of EBMTs and AOMs have greater weight loss than patients on a single therapeutic approach with either EBMT or AOMs alone.34 Racial and socioeconomic disparities in referrals to bariatric surgery are yet another barrier for patients to access weight reduction and improvement in cardiovascular health.35 EBMTs and pharmacotherapy are no longer just on the horizon; they are here as accessible, effective, and long-term treatments for all patients with obesity. More expansive insurance coverage is needed for EBMTs and AOMs in order to prevent progression of obesity-related comorbidities, reduce high costs, and ensure more equitable access to these effective therapies.
Dr. Young and Dr. Zenger are resident physicians in the department of internal medicine at New York University. Dr. Holzwanger is an advanced endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Dr. Popov is director of bariatric endoscopy at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System, and assistant professor of medicine at New York University. Dr. Popov reported relationships with Obalon, Microtech, and Spatz, but the remaining authors reported no competing interests.
References
1. Ward ZJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(25):2440-50.
2. Stein CJ and Colditz GA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2522-5.
3. Ryan DH and Yockey SR. Curr Obes Rep. 2017;6(2):187-94.
4. Fildes A et al. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(9):e54-9.
5. Rhee E-J. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017;26(4):237-42.
6. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines OEP. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22 Suppl 2:S5-39.
7. Adams TD et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):93-6.
8. Wharton S et al. Clin Obes. 2016;6(2):154-60.
9. Iuzzolino E and Kim Y. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14(4):310-20.
10. Goyal D, Watson RR. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016;18(6):26.
11. Ali MR et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(3):462-467.
12. Turkeltaub JA, Edmundowicz SA. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):187-201.
13. Reja D et al. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:21.
14. Force ABET et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-38e5.
15. Thompson CC et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(3):447-57.
16. Nystrom M et al. Obes Surg. 2018;28(7):1860-8.
17. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(8):1423-4.
18. Sharaiha RZ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-10.
19. Apovian CM et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-62.
20. Son JW and Kim S. Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):802-18.
21. Holst JJ. Int J Obes (Lond). Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(9):1161-8.
22. Joo JK and Lee KS. J Menopausal Med. 2014;20(3):90-6.
23. Weiss T et al. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2020;14:2337-45.
24. Sikirica MV et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017;10:403-12.
25. Kahan S et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;22(3):154-8.
26. Bhat SP and Sharma A. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(8):983-93.
27. Pendse J et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29(2):308-16.
28. Rucker D et al. BMJ. 2007;335(7631):1194-9.
29. Jirapinyo P and Thompson CC. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(5):619-30.
30. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(5):1073-86.
31. Schulman AR and Thompson CC. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(11):1640-55.
32. Ma IT and Madura JA, 2nd. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 2015;11(8):526-35.
33. Sharaiha RZ. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty as a nonsurgical weight loss alternative. Digestive Disease Week, oral presentation. 2017.
34. Young S et al. Long-term efficacy of a multidisciplinary minimally invasive approach to weight management compared to single endoscopic therapy: A cohort study. P0865. American College of Gastroenterology Meeting, Abstract P0865. 2021.
35. Johnson-Mann C et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(4):615-20.
Obesity currently affects more than 40% of the U.S. population. It is the second-leading preventable cause of mortality behind smoking with an estimated 300,000 deaths per year.1,2 Weight loss can reduce the risk of metabolic comorbidities such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. However, 5%-10% total body weight loss (TBWL) is required for risk reduction.3 Sustained weight loss involves dietary alterations and physical activity, although it is difficult to maintain long term with lifestyle changes alone. Less than 10% of Americans with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 will achieve 5% TBWL each year, and nearly 80% of people will regain the weight within 5 years, a phenomenon known as “weight cycling.”4,5 Not only can these weight fluctuations make future weight-loss efforts more difficult, but they can also negatively impact cardiometabolic health in the long term.5 Thus, additional therapies are typically needed in conjunction with lifestyle interventions to treat obesity.
Current guidelines recommend bariatric surgery for patients unable to achieve or maintain weight loss through lifestyle changes.6 Surgeries like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy lead to improvements in morbidity and mortality from metabolic diseases but are often only approved for select patients with a BMI of at least 40 or at least 35 with obesity-related comorbidities.7 These restrictions exclude patients at lower BMIs who may have early metabolic disease. Furthermore, only a small proportion of eligible patients are referred or willing to undergo surgery because of access issues, socioeconomic barriers, and concerns about adverse events.8,9 Endoscopic bariatric therapy and antiobesity medications (AOMs) have blossomed because of the need for other less-invasive options to stimulate weight loss.
Minimally invasive and noninvasive therapies in obesity
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) are used for the treatment of obesity in patients with a BMI of 30 kg/m2, a cohort that may be ineligible for bariatric surgery.10,11 EBMTs involve three categories: space-occupying devices (intragastric balloons [IGBs], transpyloric shuttle [TPS]), aspiration therapy, and gastric remodeling (endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty [ESG]).21,13 Presently, TPS and aspiration therapy are not commercially available in the United States. There are three types of IGB approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and Apollo ESGTM recently received de novo marketing authorization for the treatment of obesity. TBWL with EBMTs is promising at 12 months post procedure. Ranges include 7%-12% TBWL for IGBs and 15%-19% for ESG, with low rates of serious adverse events (AEs).13-18 Weight loss often reaches or exceeds the 10% TBWL needed to improve or completely reverse metabolic complications.
Obesity pharmacotherapy
Multiple professional societies support the use of obesity pharmacotherapy as an effective adjunct to lifestyle interventions.19 AOMs are classified as peripherally-acting to prevent nutrition absorption (e.g. orlistat), centrally acting to suppress appetite and/or cravings (e.g., phentermine/topiramate or naltrexone/bupropion), or incretin mimetics such as glucagonlike peptide–1 agonists (e.g., liraglutide, semaglutide).20 With the exception of orlistat, most agents have some effects on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite.21 Obesity medications tend to lead to a minimum weight loss of 3-10 kg after 12 months of treatment, and newer medications have even greater efficacy.22 Despite these results, discontinuation rates of the popular GLP-1 agonists can be as high as 47.7% and 70.1% at 12 and 24 months, respectively, because of the high cost of medications, gastrointestinal side effects, and poor tolerance.23,24
An ongoing challenge for patients is maintaining weight loss following cessation of pharmacotherapy when weight loss goals have been achieved. In this context, the combination of obesity pharmacotherapy and EBMTs can be utilized for long-term weight loss and weight maintenance given the chronic, relapsing, and complex nature of obesity.25
Advantages of less-invasive therapies in obesity management
The advantages of both pharmacologic and endoscopic weight-loss therapies are numerous. Pharmacotherapies are noninvasive, and their multiple mechanisms allow for combined use to synergistically promote weight reduction.26,27 Medications can be used in both the short- and long-term management of obesity, allowing for flexibility in use for patients pending fluctuations in weight. Furthermore, medications can improve markers of cardiovascular health including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and glycemic control.28
As minimally invasive therapies, EBMTs have less morbidity and mortality, compared with bariatric surgeries.29 The most common side effects of IGBs or ESG include abdominal pain, nausea, and worsening of acid reflux symptoms, which can be medically managed unlike some of the AEs associated with surgery, such as bowel obstruction, anastomotic dehiscence, fistulization, and postoperative infections.30 Long-term AEs from surgery also include malabsorption, nutritional deficiencies, cholelithiasis, and anastomotic stenosis.31 Even with improvement in surgical techniques, the rate of perioperative and postoperative mortality in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is estimated to be 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively, compared with only 0.08% with IGBs.30,32
In addition, EBMTs are also more cost effective than surgery, as they are often same-day outpatient procedures, leading to decreased length of stay (LOS) for patients. In ongoing research conducted by Sharaiha and colleagues, it was found that patients undergoing ESG had an average LOS of only 0.13 days, compared with 3.09 days for laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and 1.68 for laparoscopic gastric banding. The cost for ESG was approximately $12,000, compared with $15,000-$22,000 for laparoscopic bariatric surgeries.33 With their availability to patients with lower BMIs and their less-invasive nature, EBMTs and pharmacotherapy can be utilized on the spectrum of obesity care as bridge therapies both before and after surgery.
Our clinical approach
In 2015, the first Veterans Affairs hospital-based endoscopic bariatric program was established at the VA New York Harbor Healthcare System utilizing IGBs and weight loss pharmacotherapy in conjunction with the VA MOVE! Program to treat obesity and metabolic comorbidities in veterans. Since then, EBMTs have expanded to include ESG and novel medications. Our treatment algorithm accounts for the chronic nature of obesity, the risk of weight regain after any intervention, and the need for longitudinal patient care.
Patients undergo work-up by a multidisciplinary team (MD team) with a nutritionist, psychologist, primary care physician, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist to determine the optimal treatment plan (Fig. 1).29

Patients are required to attend multiple information sessions, where all weight-loss methods are presented, including surgery, bariatric endoscopy, and pharmacotherapy. Other specialists also help manage comorbid conditions. Prior to selecting an initial intervention, patients undergo intensive lifestyle and behavioral therapy (Fig. 2 and 3). Depending on the selected therapy, initial treatment lasts between 3 and 12 months with ongoing support from the MD team.

If patients do not achieve their targeted weight loss after initial treatment, a new strategy is selected. This includes a different EBMT such as ESG, alternate pharmacotherapy, or surgery until the weight and health goals of the patient are achieved and sustained (Fig. 3). From the start, patients are informed that our program is a long-term intervention and that active participation in the MOVE! Program, as well as follow-up with the MD team are keys to success. EBMTs and medications are presented as effective tools that only work to enhance the effects of lifestyle changes.

Our multidisciplinary approach provides flexibility for patients to trial different options depending on their progress. Research on long-term outcomes with weight loss and metabolic parameters is ongoing, though early results are promising. Thus far, we have observed that patients undergoing a combination therapy of EBMTs and AOMs have greater weight loss than patients on a single therapeutic approach with either EBMT or AOMs alone.34 Racial and socioeconomic disparities in referrals to bariatric surgery are yet another barrier for patients to access weight reduction and improvement in cardiovascular health.35 EBMTs and pharmacotherapy are no longer just on the horizon; they are here as accessible, effective, and long-term treatments for all patients with obesity. More expansive insurance coverage is needed for EBMTs and AOMs in order to prevent progression of obesity-related comorbidities, reduce high costs, and ensure more equitable access to these effective therapies.
Dr. Young and Dr. Zenger are resident physicians in the department of internal medicine at New York University. Dr. Holzwanger is an advanced endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Dr. Popov is director of bariatric endoscopy at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System, and assistant professor of medicine at New York University. Dr. Popov reported relationships with Obalon, Microtech, and Spatz, but the remaining authors reported no competing interests.
References
1. Ward ZJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(25):2440-50.
2. Stein CJ and Colditz GA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2522-5.
3. Ryan DH and Yockey SR. Curr Obes Rep. 2017;6(2):187-94.
4. Fildes A et al. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(9):e54-9.
5. Rhee E-J. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017;26(4):237-42.
6. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines OEP. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22 Suppl 2:S5-39.
7. Adams TD et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):93-6.
8. Wharton S et al. Clin Obes. 2016;6(2):154-60.
9. Iuzzolino E and Kim Y. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14(4):310-20.
10. Goyal D, Watson RR. Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016;18(6):26.
11. Ali MR et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(3):462-467.
12. Turkeltaub JA, Edmundowicz SA. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019;17(2):187-201.
13. Reja D et al. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:21.
14. Force ABET et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-38e5.
15. Thompson CC et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(3):447-57.
16. Nystrom M et al. Obes Surg. 2018;28(7):1860-8.
17. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(8):1423-4.
18. Sharaiha RZ et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-10.
19. Apovian CM et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342-62.
20. Son JW and Kim S. Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):802-18.
21. Holst JJ. Int J Obes (Lond). Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(9):1161-8.
22. Joo JK and Lee KS. J Menopausal Med. 2014;20(3):90-6.
23. Weiss T et al. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2020;14:2337-45.
24. Sikirica MV et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017;10:403-12.
25. Kahan S et al. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;22(3):154-8.
26. Bhat SP and Sharma A. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(8):983-93.
27. Pendse J et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021;29(2):308-16.
28. Rucker D et al. BMJ. 2007;335(7631):1194-9.
29. Jirapinyo P and Thompson CC. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(5):619-30.
30. Abu Dayyeh BK et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(5):1073-86.
31. Schulman AR and Thompson CC. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(11):1640-55.
32. Ma IT and Madura JA, 2nd. Gastroenterol Hepatol (NY). 2015;11(8):526-35.
33. Sharaiha RZ. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty as a nonsurgical weight loss alternative. Digestive Disease Week, oral presentation. 2017.
34. Young S et al. Long-term efficacy of a multidisciplinary minimally invasive approach to weight management compared to single endoscopic therapy: A cohort study. P0865. American College of Gastroenterology Meeting, Abstract P0865. 2021.
35. Johnson-Mann C et al. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15(4):615-20.
Endoscopic management of duodenal and ampullary adenomas
Duodenal polyps are a relatively rare entity with a reported incidence of 0.3%-4.6%.1 There are three major types of duodenal adenomas: sporadic, nonampullary duodenal adenomas (SNDAs), adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, and ampullary adenomas. It is important to distinguish between the different types of duodenal polyps as the management may differ depending on the etiology.
SNDAs constitute <10% of all duodenal polyps, most commonly located in the second portion of the duodenum, and up to 85% have been shown to have malignant transformation over time.2 Most of the studies of SNDAs are small series, and there are no consensus guidelines for management. Villous features increase malignancy risk, thus resection of SNDAs is advised.3-7 It has also been shown that 72% of patients with SNDAs also have colon polyps,8 and therefore these patients should be up to date on colonoscopy screening.
Ampullary adenomas are less common, but up to half may be associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), and some may be surveyed.9 However, those that are larger than 10 mm or have villous features may raise concern for malignancy with up to half harboring small foci of adenocarcinoma.10,11 These require ERCP with ampullectomy. For the purposes of this paper, we will focus on endoscopic resection of SNDAs and ampullary adenomas.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of duodenal polyps can be technically challenging. There are considerations specific to the duodenum: thin muscle layer, increased motility, and significant vascular supply including two major arterial supplies – the gastroduodenal artery from the celiac branch and the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery from the superior mesenteric artery. These factors may explain higher reported rates of perforation and bleeding compared to colon EMR.
After a detailed inspection is performed to define the duodenal polyp in terms of size, location, and position relative to the ampulla, a submucosal injection is performed using a dye solution. Once adequate lift is achieved, the lesion is resected using stiff monofilament snares. If possible, resection sites are closed with hemostatic clips, although their utility in preventing delayed complications may be less than that in the colon because of increased motility causing them to become dislodged more easily. We avoid using snares larger than 2 cm given increased risk of perforation. Intraprocedural bleeding may be controlled with coagulation graspers on soft coagulation setting; using a bipolar electrocoagulation therapy or argon plasma coagulation is avoided, as these have been shown to increase rates of complications. Figure 1 provides examples of duodenal adenomas that have been resected.
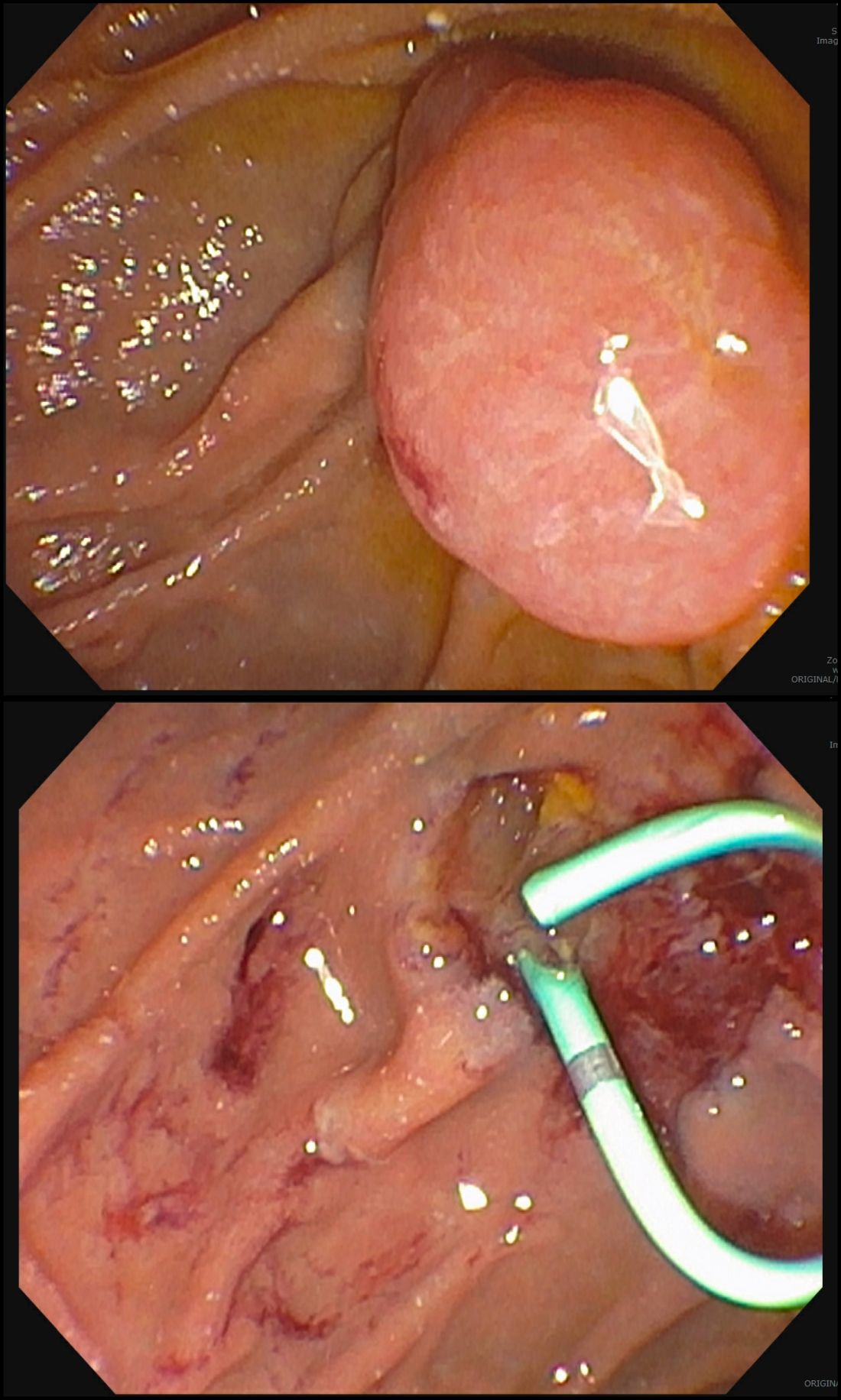
The ampullectomy technique is slightly different from duodenal EMRs and carries the additional risk of pancreatitis.12,13 In our opinion, there is low utility for submucosal injection unless there is a laterally spreading component onto the duodenal wall, as injection of the ampulla itself does not lift well and simply distorts views. Typically, both the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct are injected with contrast, and we typically perform a biliary sphincterotomy prior to ampullectomy. Based on endoscopist preference, one can also leave a guide wire in the pancreatic duct (PD) and pass the snare over it to perform resection to maintain access for a subsequent stent placement. This technique has the advantage of never losing pancreatic duct access, which can occur after resection from edema or bleeding and allows easy PD stent placement. The snare should be opened in a line corresponding to the long axis of the mound with the snare tip anchored above the apex of the papilla and snare opened and drawn down over the papilla. After resection, the PD must be stented to minimize pancreatitis risk.14 Figure 2 shows an ampullary adenoma pre and post EMR, with a PD stent.
Recurrence of duodenal adenomas, both SNDAs and ampullary, can be quite high, with reports up to 39%.15-18 Risk factors include histology and size, but interestingly were not shown to be associated with en-bloc resection.15,19 On the other hand, intraprocedural bleeding also occurs in up to 43% of patients and is associated with size, number of resections, and procedure time.20 Per 2015 ASGE Standards of Practice, duodenal lesions warrant short follow-up at 3- to 6-month intervals given high recurrence rates, then at 6- to 12-month intervals for 2-5 years thereafter.21
When a duodenal polyp is detected, it is important to determine which type of adenoma it is to guide management. There are various techniques utilized to perform duodenal EMR and ampullectomy with some highlighted in this article. It is important to understand how to recognize, prevent, and manage associated adverse events, as well as to have a surveillance plan given the risk of recurrence.
Dr. Kim has no disclosures. Dr. Siddiqui has financial relationships with Boston Scientific (research support, consulting fees, speaking honoraria); Cook, Medtronic, ConMed (consulting fees, speaking honoraria); and Pinnacle Biologic, Ovesco (speaking honoraria).
Dr. Kim is a GI fellow, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago. Dr. Siddiqui is a professor of medicine and the director of the Center for Endoscopic Research and Therapeutics (CERT), section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago.
References
1. Jepsen JM et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Jun 1994;29(6):483-7.
2. Sellner F. Cancer. 1990 Aug 15;66(4):702-15.
3. Witteman BJ et al. Neth J Med. 1993 Feb;42(1-2):5-11.
4. Reddy RR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun;3(2):139-47.
5. Sakorafas GH et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000 Apr;35(4):337-44.
6. Galandiuk S et al. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):234-9.
7. Farnell MB et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Jan-Feb;4(1):13-21, discussion 22-3.
8. Apel D et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004 Sep;60(3):397-9.
9. Kashiwagi H et al. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1582.
10. Clary BM et al. Surgery. 2000 Jun;127(6):628-33.
11. Posner S et al. Surgery. 2000 Oct;128(4):694-701.
12. Harewood GC et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005 Sep;62(3):367-70.
13. Chini P et al. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011 Dec 16;3(12):241-7.
14. Chang WI et al. Gut Liver. May 2014;8(3):306-12.
15. Hoibian S et al. Ann Gastroenterol. 2021;34(2):169-176. doi: 10.20524/aog.2021.0581.
16. Kakushima N et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12501-8.
17. Lienert A and Bagshaw PF. ANZ J Surg. 2007 May;77(5):371-3.
18. Singh A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):700-8.
19. Tomizawa Y and Ginsberg GG. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 May;87(5):1270-8.
20. Klein A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):688-96.
21. Chathadi KV et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Nov;82(5):773-81.
Duodenal polyps are a relatively rare entity with a reported incidence of 0.3%-4.6%.1 There are three major types of duodenal adenomas: sporadic, nonampullary duodenal adenomas (SNDAs), adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, and ampullary adenomas. It is important to distinguish between the different types of duodenal polyps as the management may differ depending on the etiology.
SNDAs constitute <10% of all duodenal polyps, most commonly located in the second portion of the duodenum, and up to 85% have been shown to have malignant transformation over time.2 Most of the studies of SNDAs are small series, and there are no consensus guidelines for management. Villous features increase malignancy risk, thus resection of SNDAs is advised.3-7 It has also been shown that 72% of patients with SNDAs also have colon polyps,8 and therefore these patients should be up to date on colonoscopy screening.
Ampullary adenomas are less common, but up to half may be associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), and some may be surveyed.9 However, those that are larger than 10 mm or have villous features may raise concern for malignancy with up to half harboring small foci of adenocarcinoma.10,11 These require ERCP with ampullectomy. For the purposes of this paper, we will focus on endoscopic resection of SNDAs and ampullary adenomas.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of duodenal polyps can be technically challenging. There are considerations specific to the duodenum: thin muscle layer, increased motility, and significant vascular supply including two major arterial supplies – the gastroduodenal artery from the celiac branch and the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery from the superior mesenteric artery. These factors may explain higher reported rates of perforation and bleeding compared to colon EMR.
After a detailed inspection is performed to define the duodenal polyp in terms of size, location, and position relative to the ampulla, a submucosal injection is performed using a dye solution. Once adequate lift is achieved, the lesion is resected using stiff monofilament snares. If possible, resection sites are closed with hemostatic clips, although their utility in preventing delayed complications may be less than that in the colon because of increased motility causing them to become dislodged more easily. We avoid using snares larger than 2 cm given increased risk of perforation. Intraprocedural bleeding may be controlled with coagulation graspers on soft coagulation setting; using a bipolar electrocoagulation therapy or argon plasma coagulation is avoided, as these have been shown to increase rates of complications. Figure 1 provides examples of duodenal adenomas that have been resected.

The ampullectomy technique is slightly different from duodenal EMRs and carries the additional risk of pancreatitis.12,13 In our opinion, there is low utility for submucosal injection unless there is a laterally spreading component onto the duodenal wall, as injection of the ampulla itself does not lift well and simply distorts views. Typically, both the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct are injected with contrast, and we typically perform a biliary sphincterotomy prior to ampullectomy. Based on endoscopist preference, one can also leave a guide wire in the pancreatic duct (PD) and pass the snare over it to perform resection to maintain access for a subsequent stent placement. This technique has the advantage of never losing pancreatic duct access, which can occur after resection from edema or bleeding and allows easy PD stent placement. The snare should be opened in a line corresponding to the long axis of the mound with the snare tip anchored above the apex of the papilla and snare opened and drawn down over the papilla. After resection, the PD must be stented to minimize pancreatitis risk.14 Figure 2 shows an ampullary adenoma pre and post EMR, with a PD stent.
Recurrence of duodenal adenomas, both SNDAs and ampullary, can be quite high, with reports up to 39%.15-18 Risk factors include histology and size, but interestingly were not shown to be associated with en-bloc resection.15,19 On the other hand, intraprocedural bleeding also occurs in up to 43% of patients and is associated with size, number of resections, and procedure time.20 Per 2015 ASGE Standards of Practice, duodenal lesions warrant short follow-up at 3- to 6-month intervals given high recurrence rates, then at 6- to 12-month intervals for 2-5 years thereafter.21
When a duodenal polyp is detected, it is important to determine which type of adenoma it is to guide management. There are various techniques utilized to perform duodenal EMR and ampullectomy with some highlighted in this article. It is important to understand how to recognize, prevent, and manage associated adverse events, as well as to have a surveillance plan given the risk of recurrence.
Dr. Kim has no disclosures. Dr. Siddiqui has financial relationships with Boston Scientific (research support, consulting fees, speaking honoraria); Cook, Medtronic, ConMed (consulting fees, speaking honoraria); and Pinnacle Biologic, Ovesco (speaking honoraria).
Dr. Kim is a GI fellow, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago. Dr. Siddiqui is a professor of medicine and the director of the Center for Endoscopic Research and Therapeutics (CERT), section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago.
References
1. Jepsen JM et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Jun 1994;29(6):483-7.
2. Sellner F. Cancer. 1990 Aug 15;66(4):702-15.
3. Witteman BJ et al. Neth J Med. 1993 Feb;42(1-2):5-11.
4. Reddy RR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun;3(2):139-47.
5. Sakorafas GH et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000 Apr;35(4):337-44.
6. Galandiuk S et al. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):234-9.
7. Farnell MB et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Jan-Feb;4(1):13-21, discussion 22-3.
8. Apel D et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004 Sep;60(3):397-9.
9. Kashiwagi H et al. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1582.
10. Clary BM et al. Surgery. 2000 Jun;127(6):628-33.
11. Posner S et al. Surgery. 2000 Oct;128(4):694-701.
12. Harewood GC et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005 Sep;62(3):367-70.
13. Chini P et al. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011 Dec 16;3(12):241-7.
14. Chang WI et al. Gut Liver. May 2014;8(3):306-12.
15. Hoibian S et al. Ann Gastroenterol. 2021;34(2):169-176. doi: 10.20524/aog.2021.0581.
16. Kakushima N et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12501-8.
17. Lienert A and Bagshaw PF. ANZ J Surg. 2007 May;77(5):371-3.
18. Singh A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):700-8.
19. Tomizawa Y and Ginsberg GG. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 May;87(5):1270-8.
20. Klein A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):688-96.
21. Chathadi KV et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Nov;82(5):773-81.
Duodenal polyps are a relatively rare entity with a reported incidence of 0.3%-4.6%.1 There are three major types of duodenal adenomas: sporadic, nonampullary duodenal adenomas (SNDAs), adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome, and ampullary adenomas. It is important to distinguish between the different types of duodenal polyps as the management may differ depending on the etiology.
SNDAs constitute <10% of all duodenal polyps, most commonly located in the second portion of the duodenum, and up to 85% have been shown to have malignant transformation over time.2 Most of the studies of SNDAs are small series, and there are no consensus guidelines for management. Villous features increase malignancy risk, thus resection of SNDAs is advised.3-7 It has also been shown that 72% of patients with SNDAs also have colon polyps,8 and therefore these patients should be up to date on colonoscopy screening.
Ampullary adenomas are less common, but up to half may be associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), and some may be surveyed.9 However, those that are larger than 10 mm or have villous features may raise concern for malignancy with up to half harboring small foci of adenocarcinoma.10,11 These require ERCP with ampullectomy. For the purposes of this paper, we will focus on endoscopic resection of SNDAs and ampullary adenomas.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of duodenal polyps can be technically challenging. There are considerations specific to the duodenum: thin muscle layer, increased motility, and significant vascular supply including two major arterial supplies – the gastroduodenal artery from the celiac branch and the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery from the superior mesenteric artery. These factors may explain higher reported rates of perforation and bleeding compared to colon EMR.
After a detailed inspection is performed to define the duodenal polyp in terms of size, location, and position relative to the ampulla, a submucosal injection is performed using a dye solution. Once adequate lift is achieved, the lesion is resected using stiff monofilament snares. If possible, resection sites are closed with hemostatic clips, although their utility in preventing delayed complications may be less than that in the colon because of increased motility causing them to become dislodged more easily. We avoid using snares larger than 2 cm given increased risk of perforation. Intraprocedural bleeding may be controlled with coagulation graspers on soft coagulation setting; using a bipolar electrocoagulation therapy or argon plasma coagulation is avoided, as these have been shown to increase rates of complications. Figure 1 provides examples of duodenal adenomas that have been resected.

The ampullectomy technique is slightly different from duodenal EMRs and carries the additional risk of pancreatitis.12,13 In our opinion, there is low utility for submucosal injection unless there is a laterally spreading component onto the duodenal wall, as injection of the ampulla itself does not lift well and simply distorts views. Typically, both the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct are injected with contrast, and we typically perform a biliary sphincterotomy prior to ampullectomy. Based on endoscopist preference, one can also leave a guide wire in the pancreatic duct (PD) and pass the snare over it to perform resection to maintain access for a subsequent stent placement. This technique has the advantage of never losing pancreatic duct access, which can occur after resection from edema or bleeding and allows easy PD stent placement. The snare should be opened in a line corresponding to the long axis of the mound with the snare tip anchored above the apex of the papilla and snare opened and drawn down over the papilla. After resection, the PD must be stented to minimize pancreatitis risk.14 Figure 2 shows an ampullary adenoma pre and post EMR, with a PD stent.
Recurrence of duodenal adenomas, both SNDAs and ampullary, can be quite high, with reports up to 39%.15-18 Risk factors include histology and size, but interestingly were not shown to be associated with en-bloc resection.15,19 On the other hand, intraprocedural bleeding also occurs in up to 43% of patients and is associated with size, number of resections, and procedure time.20 Per 2015 ASGE Standards of Practice, duodenal lesions warrant short follow-up at 3- to 6-month intervals given high recurrence rates, then at 6- to 12-month intervals for 2-5 years thereafter.21
When a duodenal polyp is detected, it is important to determine which type of adenoma it is to guide management. There are various techniques utilized to perform duodenal EMR and ampullectomy with some highlighted in this article. It is important to understand how to recognize, prevent, and manage associated adverse events, as well as to have a surveillance plan given the risk of recurrence.
Dr. Kim has no disclosures. Dr. Siddiqui has financial relationships with Boston Scientific (research support, consulting fees, speaking honoraria); Cook, Medtronic, ConMed (consulting fees, speaking honoraria); and Pinnacle Biologic, Ovesco (speaking honoraria).
Dr. Kim is a GI fellow, section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago. Dr. Siddiqui is a professor of medicine and the director of the Center for Endoscopic Research and Therapeutics (CERT), section of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition, department of internal medicine, University of Chicago.
References
1. Jepsen JM et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. Jun 1994;29(6):483-7.
2. Sellner F. Cancer. 1990 Aug 15;66(4):702-15.
3. Witteman BJ et al. Neth J Med. 1993 Feb;42(1-2):5-11.
4. Reddy RR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1981 Jun;3(2):139-47.
5. Sakorafas GH et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000 Apr;35(4):337-44.
6. Galandiuk S et al. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):234-9.
7. Farnell MB et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Jan-Feb;4(1):13-21, discussion 22-3.
8. Apel D et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004 Sep;60(3):397-9.
9. Kashiwagi H et al. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1582.
10. Clary BM et al. Surgery. 2000 Jun;127(6):628-33.
11. Posner S et al. Surgery. 2000 Oct;128(4):694-701.
12. Harewood GC et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005 Sep;62(3):367-70.
13. Chini P et al. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011 Dec 16;3(12):241-7.
14. Chang WI et al. Gut Liver. May 2014;8(3):306-12.
15. Hoibian S et al. Ann Gastroenterol. 2021;34(2):169-176. doi: 10.20524/aog.2021.0581.
16. Kakushima N et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12501-8.
17. Lienert A and Bagshaw PF. ANZ J Surg. 2007 May;77(5):371-3.
18. Singh A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):700-8.
19. Tomizawa Y and Ginsberg GG. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 May;87(5):1270-8.
20. Klein A et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Oct;84(4):688-96.
21. Chathadi KV et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Nov;82(5):773-81.
Integrating psychogastroenterology into GI care
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.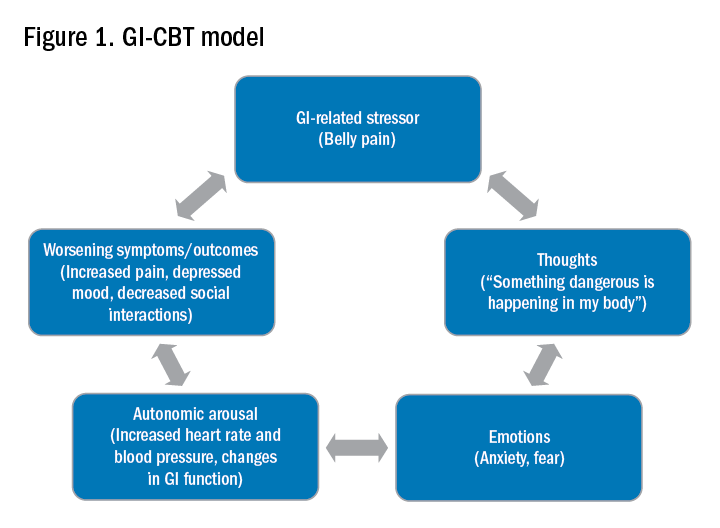
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
An update on COVID-19 vaccine recommendations for patients with IBD
In December 2019, cases of pulmonary infection secondary to a novel coronavirus, known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, were first identified in the city of Wuhan, China.
The clinical disease caused by the virus, COVID-19, has resulted in a worldwide pandemic that has portended significant morbidity and mortality throughout the United States. Three highly efficacious COVID-19 vaccines have received emergency use authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration to help prevent COVID-19, all of which are effective at preventing severe COVID-19.1-3 The Pfizer vaccine was given full FDA approval on Aug. 23, 2021.4
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are commonly treated with immune-modifying therapies that may increase their risk for serious and opportunistic infections. As such, there was concern at the beginning of the pandemic that patients with IBD may be at increased risk of contracting COVID-19 and/or developing severe disease (that is, ICU-level care, mechanical ventilation, and/or death). There is evidence that the incidence of COVID-19 in the IBD population is similar to that of the general population.5-7 Furthermore, most patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe disease, including those on biologic therapies. Several studies demonstrated that those on corticosteroids are at increased risk of severe COVID-19, while those on other immune-modifying therapies such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNFs) are not at increased risk.5,7-10 Patients with IBD with other well-known risk factors for severe disease include comorbidities such as diabetes and obesity.
It is known that patients with IBD on certain immune-modifying therapies such as anti-TNFs, especially those on combination therapy, may have a blunted immune response to certain vaccines.11 Neither patients with IBD nor patients on immunosuppressive therapy were included in phase 3 clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccine development, contributing to uncertainty regarding the safety and efficacy in our patient population. The risk of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination in the IBD population has been found to be similar to that of the general population.12 It has also been reported that those who have had reactions to injectable therapies in the past may safely be vaccinated against COVID-19.13,14 With regard to vaccine efficacy, initial studies, including ICARUS, PREVENT-COVID, and CORALE-IBD, have demonstrated that patients with IBD do indeed mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine, including those on immune-modifying therapies.15-17 Nonhumoral aspects of immunity, such as cell-mediated immunity, have not yet been thoroughly evaluated. In addition, the risk of breakthrough COVID-19 infection after vaccination is low in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapy.14-18 While initial studies are reassuring that the vast majority of patients with IBD are able to mount a vaccine response, future studies are needed to determine the effects of immune-modifying therapy on sustained antibody concentrations and other correlates of immunity.
For those who received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, on Aug. 12, 2021, the FDA amended their EUA to allow for an additional dose in the initial vaccination series for certain immunocompromised individuals, specifically solid organ transplant recipients or those with conditions that make them equally immunocompromised.19 Based on evidence suggesting that certain solid organ transplant recipients do not mount an immune response after completing a two-dose series, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which advises the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on how to use vaccines, recommended that moderate to severely immunocompromised individuals should complete a three-dose series, with the third dose being given at least 28 days after the second dose.20 This recommendation included those on high-dose corticosteroids defined as oral prednisone at least 20 mg/day, anti-TNFs and biosimilars, and antimetabolites such as azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and methotrexate.
It is worth noting that the role of the ACIP here was to consider the available evidence supporting the use of an additional dose and then make recommendations on which conditions may qualify; the ACIP was not able to provide recommendations for every disease state. At the time of writing this article, no recommendations have been made with regards to an additional dose of the Janssen vaccine. Likewise, in response to the ACIP recommendations, the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommended an additional dose for patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies.21,22
Less than one week after the EUA amendment for an additional dose, the Department of Health & Human Services announced that booster shots would likely become available to the general population as early as the week of Sept. 20, 2021 and starting 8 months after an individual’s second dose.23 Here, it is worth noting that an additional dose is distinct from a booster. An additional dose (or third dose here) refers to the initial vaccination series and is given when the standard schedule is thought to be insufficient in a certain patient population. In contrast, a booster dose is administered when the initial and sufficient immunity gained from a primary vaccination series has likely dissipated. The HHS acknowledged that boosters would likely be needed for those who received the Janssen vaccine but noted that further data and recommendations would be forthcoming.
To summarize, COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective in the IBD population, and patients should be vaccinated at the earliest opportunity regardless of concurrent therapies. For those that received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, the ACIP recommended an additional dose in the initial vaccination series to be given at least 28 days after the second dose for those that are immunosuppressed. This recommendation was largely based off of transplant data. Reassuringly, the available data demonstrates a humoral immune response to a two-dose vaccination series in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies. The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommends that patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapy receive an additional dose (i.e., a three-dose series), which should be from the same manufacturer as the first two doses. In addition, at press time, HHS indicated that there will be a movement toward a booster dose for the general population in late September, which would also apply to patients with IBD. The ACIP has yet to comment on this change at the time of preparing this article, but the announcement indicated that a booster could be given “8 months after an individual’s second dose.” It is unclear how those who may receive a three-dose vaccination series will factor in, but it is possible that they would be eligible for a booster 8 months after their most recent dose. Gastroenterologists should also be aware that there is no role for serologic testing in the clinical setting because it has not been validated for such purposes and is primarily used in the research setting. Finally, it is paramount to emphasize that patients with IBD have historically had lower vaccination rates than the general population,24 and we must take an active role in ensuring that our patients are immunized by addressing their concerns, communicating the risks of COVID-19 and the benefits of vaccination, providing information on how to get vaccinated, and strongly recommending vaccination.
The following list also summarizes the recommendations:
- Patients with IBD should be vaccinated against COVID-19 regardless of concurrent therapies.
- Patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe COVID-19.
- Patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies, mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine.
- Patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies, who received either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, should receive a three-dose vaccination series, with the third dose at least 28 days after the second dose.
- Patients with IBD on biologic therapy can receive the third dose of the vaccine at any time point and should not interrupt biologic therapy.
- Boosters are likely to become available to the general public in September and would be given at least 8 months after an individual’s second dose.
- Recommendations regarding boosters for those who received a three-dose vaccination series are forthcoming.
- Recommendations regarding boosters and additional doses for those that received the Janssen vaccine are forthcoming.
- Gastroenterologists should take an active role in ensuring that their patients are vaccinated.
Dr. Schell is a second-year graduate student in the division of internal medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Caldera is an associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Schell has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Caldera has received research support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi. He has been a consultant for Takeda, Arena Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Celgene.
References
1. Sadoff J et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(23):2187-201.
2. Baden LR et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):403-16.
3. Polack FP et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-15.
4. Johnson K et al. U.S. FDA aims to give full approval to Pfizer vaccine on Monday – NYT. Reuters. 2021 Aug 20. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/us-fda-aims-give-full-nod-pfizers-covid-19-vaccine-monday-new-york-times-2021-08-20/.
5. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct;9(11):3533.
6. Monteleone G and Ardizzone S. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep;14(9):1334-6.
7. Papa A et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(10):1722-4.
8. Derikx LAAP et al. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2021 Apr 6;15(4):529-39.
9. Brenner EJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(2):481-91.
10. Ungaro RC et al. Gut. 2021;70(4):725-32.
11. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26(4):593-602.
12. Botwin GJ et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001342.
13. Squire JD et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021 Jul 27;27(8):1358-60.
14. Hadi YB et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.014.
15. Wong S-Y et al. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:715-8.
16. Kappelman MD et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.016.
17. Pozdnyakova V et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.014.
18. Ben-Tov A et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.076.
19. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Vaccine Dose for Certain Immunocompromised Individuals. FDA News Release. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-vaccine-dose-certain-immunocompromised.
20. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines for Moderately to Severely Immunocompromised People. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/immuno.html.
21. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 31;9(11):3533.
22. Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. COVID-19 Vaccines: Position Statements. IBD & Coronavirus. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 20. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/coronavirus/vaccine-position-statements.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Joint Statement from HHS Public Health and Medical Experts on COVID-19 Booster Shots. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s0818-covid-19-booster-shots.html.
24. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(1):123-133.
In December 2019, cases of pulmonary infection secondary to a novel coronavirus, known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, were first identified in the city of Wuhan, China.
The clinical disease caused by the virus, COVID-19, has resulted in a worldwide pandemic that has portended significant morbidity and mortality throughout the United States. Three highly efficacious COVID-19 vaccines have received emergency use authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration to help prevent COVID-19, all of which are effective at preventing severe COVID-19.1-3 The Pfizer vaccine was given full FDA approval on Aug. 23, 2021.4
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are commonly treated with immune-modifying therapies that may increase their risk for serious and opportunistic infections. As such, there was concern at the beginning of the pandemic that patients with IBD may be at increased risk of contracting COVID-19 and/or developing severe disease (that is, ICU-level care, mechanical ventilation, and/or death). There is evidence that the incidence of COVID-19 in the IBD population is similar to that of the general population.5-7 Furthermore, most patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe disease, including those on biologic therapies. Several studies demonstrated that those on corticosteroids are at increased risk of severe COVID-19, while those on other immune-modifying therapies such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNFs) are not at increased risk.5,7-10 Patients with IBD with other well-known risk factors for severe disease include comorbidities such as diabetes and obesity.
It is known that patients with IBD on certain immune-modifying therapies such as anti-TNFs, especially those on combination therapy, may have a blunted immune response to certain vaccines.11 Neither patients with IBD nor patients on immunosuppressive therapy were included in phase 3 clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccine development, contributing to uncertainty regarding the safety and efficacy in our patient population. The risk of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination in the IBD population has been found to be similar to that of the general population.12 It has also been reported that those who have had reactions to injectable therapies in the past may safely be vaccinated against COVID-19.13,14 With regard to vaccine efficacy, initial studies, including ICARUS, PREVENT-COVID, and CORALE-IBD, have demonstrated that patients with IBD do indeed mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine, including those on immune-modifying therapies.15-17 Nonhumoral aspects of immunity, such as cell-mediated immunity, have not yet been thoroughly evaluated. In addition, the risk of breakthrough COVID-19 infection after vaccination is low in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapy.14-18 While initial studies are reassuring that the vast majority of patients with IBD are able to mount a vaccine response, future studies are needed to determine the effects of immune-modifying therapy on sustained antibody concentrations and other correlates of immunity.
For those who received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, on Aug. 12, 2021, the FDA amended their EUA to allow for an additional dose in the initial vaccination series for certain immunocompromised individuals, specifically solid organ transplant recipients or those with conditions that make them equally immunocompromised.19 Based on evidence suggesting that certain solid organ transplant recipients do not mount an immune response after completing a two-dose series, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which advises the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on how to use vaccines, recommended that moderate to severely immunocompromised individuals should complete a three-dose series, with the third dose being given at least 28 days after the second dose.20 This recommendation included those on high-dose corticosteroids defined as oral prednisone at least 20 mg/day, anti-TNFs and biosimilars, and antimetabolites such as azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and methotrexate.
It is worth noting that the role of the ACIP here was to consider the available evidence supporting the use of an additional dose and then make recommendations on which conditions may qualify; the ACIP was not able to provide recommendations for every disease state. At the time of writing this article, no recommendations have been made with regards to an additional dose of the Janssen vaccine. Likewise, in response to the ACIP recommendations, the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommended an additional dose for patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies.21,22
Less than one week after the EUA amendment for an additional dose, the Department of Health & Human Services announced that booster shots would likely become available to the general population as early as the week of Sept. 20, 2021 and starting 8 months after an individual’s second dose.23 Here, it is worth noting that an additional dose is distinct from a booster. An additional dose (or third dose here) refers to the initial vaccination series and is given when the standard schedule is thought to be insufficient in a certain patient population. In contrast, a booster dose is administered when the initial and sufficient immunity gained from a primary vaccination series has likely dissipated. The HHS acknowledged that boosters would likely be needed for those who received the Janssen vaccine but noted that further data and recommendations would be forthcoming.
To summarize, COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective in the IBD population, and patients should be vaccinated at the earliest opportunity regardless of concurrent therapies. For those that received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, the ACIP recommended an additional dose in the initial vaccination series to be given at least 28 days after the second dose for those that are immunosuppressed. This recommendation was largely based off of transplant data. Reassuringly, the available data demonstrates a humoral immune response to a two-dose vaccination series in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies. The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommends that patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapy receive an additional dose (i.e., a three-dose series), which should be from the same manufacturer as the first two doses. In addition, at press time, HHS indicated that there will be a movement toward a booster dose for the general population in late September, which would also apply to patients with IBD. The ACIP has yet to comment on this change at the time of preparing this article, but the announcement indicated that a booster could be given “8 months after an individual’s second dose.” It is unclear how those who may receive a three-dose vaccination series will factor in, but it is possible that they would be eligible for a booster 8 months after their most recent dose. Gastroenterologists should also be aware that there is no role for serologic testing in the clinical setting because it has not been validated for such purposes and is primarily used in the research setting. Finally, it is paramount to emphasize that patients with IBD have historically had lower vaccination rates than the general population,24 and we must take an active role in ensuring that our patients are immunized by addressing their concerns, communicating the risks of COVID-19 and the benefits of vaccination, providing information on how to get vaccinated, and strongly recommending vaccination.
The following list also summarizes the recommendations:
- Patients with IBD should be vaccinated against COVID-19 regardless of concurrent therapies.
- Patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe COVID-19.
- Patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies, mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine.
- Patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies, who received either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, should receive a three-dose vaccination series, with the third dose at least 28 days after the second dose.
- Patients with IBD on biologic therapy can receive the third dose of the vaccine at any time point and should not interrupt biologic therapy.
- Boosters are likely to become available to the general public in September and would be given at least 8 months after an individual’s second dose.
- Recommendations regarding boosters for those who received a three-dose vaccination series are forthcoming.
- Recommendations regarding boosters and additional doses for those that received the Janssen vaccine are forthcoming.
- Gastroenterologists should take an active role in ensuring that their patients are vaccinated.
Dr. Schell is a second-year graduate student in the division of internal medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Caldera is an associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Schell has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Caldera has received research support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi. He has been a consultant for Takeda, Arena Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Celgene.
References
1. Sadoff J et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(23):2187-201.
2. Baden LR et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):403-16.
3. Polack FP et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-15.
4. Johnson K et al. U.S. FDA aims to give full approval to Pfizer vaccine on Monday – NYT. Reuters. 2021 Aug 20. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/us-fda-aims-give-full-nod-pfizers-covid-19-vaccine-monday-new-york-times-2021-08-20/.
5. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct;9(11):3533.
6. Monteleone G and Ardizzone S. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep;14(9):1334-6.
7. Papa A et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(10):1722-4.
8. Derikx LAAP et al. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2021 Apr 6;15(4):529-39.
9. Brenner EJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(2):481-91.
10. Ungaro RC et al. Gut. 2021;70(4):725-32.
11. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26(4):593-602.
12. Botwin GJ et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001342.
13. Squire JD et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021 Jul 27;27(8):1358-60.
14. Hadi YB et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.014.
15. Wong S-Y et al. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:715-8.
16. Kappelman MD et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.016.
17. Pozdnyakova V et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.014.
18. Ben-Tov A et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.076.
19. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Vaccine Dose for Certain Immunocompromised Individuals. FDA News Release. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-vaccine-dose-certain-immunocompromised.
20. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines for Moderately to Severely Immunocompromised People. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/immuno.html.
21. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 31;9(11):3533.
22. Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. COVID-19 Vaccines: Position Statements. IBD & Coronavirus. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 20. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/coronavirus/vaccine-position-statements.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Joint Statement from HHS Public Health and Medical Experts on COVID-19 Booster Shots. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s0818-covid-19-booster-shots.html.
24. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(1):123-133.
In December 2019, cases of pulmonary infection secondary to a novel coronavirus, known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, were first identified in the city of Wuhan, China.
The clinical disease caused by the virus, COVID-19, has resulted in a worldwide pandemic that has portended significant morbidity and mortality throughout the United States. Three highly efficacious COVID-19 vaccines have received emergency use authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration to help prevent COVID-19, all of which are effective at preventing severe COVID-19.1-3 The Pfizer vaccine was given full FDA approval on Aug. 23, 2021.4
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are commonly treated with immune-modifying therapies that may increase their risk for serious and opportunistic infections. As such, there was concern at the beginning of the pandemic that patients with IBD may be at increased risk of contracting COVID-19 and/or developing severe disease (that is, ICU-level care, mechanical ventilation, and/or death). There is evidence that the incidence of COVID-19 in the IBD population is similar to that of the general population.5-7 Furthermore, most patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe disease, including those on biologic therapies. Several studies demonstrated that those on corticosteroids are at increased risk of severe COVID-19, while those on other immune-modifying therapies such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNFs) are not at increased risk.5,7-10 Patients with IBD with other well-known risk factors for severe disease include comorbidities such as diabetes and obesity.
It is known that patients with IBD on certain immune-modifying therapies such as anti-TNFs, especially those on combination therapy, may have a blunted immune response to certain vaccines.11 Neither patients with IBD nor patients on immunosuppressive therapy were included in phase 3 clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccine development, contributing to uncertainty regarding the safety and efficacy in our patient population. The risk of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination in the IBD population has been found to be similar to that of the general population.12 It has also been reported that those who have had reactions to injectable therapies in the past may safely be vaccinated against COVID-19.13,14 With regard to vaccine efficacy, initial studies, including ICARUS, PREVENT-COVID, and CORALE-IBD, have demonstrated that patients with IBD do indeed mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine, including those on immune-modifying therapies.15-17 Nonhumoral aspects of immunity, such as cell-mediated immunity, have not yet been thoroughly evaluated. In addition, the risk of breakthrough COVID-19 infection after vaccination is low in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapy.14-18 While initial studies are reassuring that the vast majority of patients with IBD are able to mount a vaccine response, future studies are needed to determine the effects of immune-modifying therapy on sustained antibody concentrations and other correlates of immunity.
For those who received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, on Aug. 12, 2021, the FDA amended their EUA to allow for an additional dose in the initial vaccination series for certain immunocompromised individuals, specifically solid organ transplant recipients or those with conditions that make them equally immunocompromised.19 Based on evidence suggesting that certain solid organ transplant recipients do not mount an immune response after completing a two-dose series, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which advises the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on how to use vaccines, recommended that moderate to severely immunocompromised individuals should complete a three-dose series, with the third dose being given at least 28 days after the second dose.20 This recommendation included those on high-dose corticosteroids defined as oral prednisone at least 20 mg/day, anti-TNFs and biosimilars, and antimetabolites such as azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and methotrexate.
It is worth noting that the role of the ACIP here was to consider the available evidence supporting the use of an additional dose and then make recommendations on which conditions may qualify; the ACIP was not able to provide recommendations for every disease state. At the time of writing this article, no recommendations have been made with regards to an additional dose of the Janssen vaccine. Likewise, in response to the ACIP recommendations, the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommended an additional dose for patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies.21,22
Less than one week after the EUA amendment for an additional dose, the Department of Health & Human Services announced that booster shots would likely become available to the general population as early as the week of Sept. 20, 2021 and starting 8 months after an individual’s second dose.23 Here, it is worth noting that an additional dose is distinct from a booster. An additional dose (or third dose here) refers to the initial vaccination series and is given when the standard schedule is thought to be insufficient in a certain patient population. In contrast, a booster dose is administered when the initial and sufficient immunity gained from a primary vaccination series has likely dissipated. The HHS acknowledged that boosters would likely be needed for those who received the Janssen vaccine but noted that further data and recommendations would be forthcoming.
To summarize, COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective in the IBD population, and patients should be vaccinated at the earliest opportunity regardless of concurrent therapies. For those that received the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, the ACIP recommended an additional dose in the initial vaccination series to be given at least 28 days after the second dose for those that are immunosuppressed. This recommendation was largely based off of transplant data. Reassuringly, the available data demonstrates a humoral immune response to a two-dose vaccination series in patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies. The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation recommends that patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapy receive an additional dose (i.e., a three-dose series), which should be from the same manufacturer as the first two doses. In addition, at press time, HHS indicated that there will be a movement toward a booster dose for the general population in late September, which would also apply to patients with IBD. The ACIP has yet to comment on this change at the time of preparing this article, but the announcement indicated that a booster could be given “8 months after an individual’s second dose.” It is unclear how those who may receive a three-dose vaccination series will factor in, but it is possible that they would be eligible for a booster 8 months after their most recent dose. Gastroenterologists should also be aware that there is no role for serologic testing in the clinical setting because it has not been validated for such purposes and is primarily used in the research setting. Finally, it is paramount to emphasize that patients with IBD have historically had lower vaccination rates than the general population,24 and we must take an active role in ensuring that our patients are immunized by addressing their concerns, communicating the risks of COVID-19 and the benefits of vaccination, providing information on how to get vaccinated, and strongly recommending vaccination.
The following list also summarizes the recommendations:
- Patients with IBD should be vaccinated against COVID-19 regardless of concurrent therapies.
- Patients with IBD are not at increased risk of severe COVID-19.
- Patients with IBD, including those on immune-modifying therapies, mount a humoral immune response to the vaccine.
- Patients with IBD on immune-modifying therapies, who received either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine, should receive a three-dose vaccination series, with the third dose at least 28 days after the second dose.
- Patients with IBD on biologic therapy can receive the third dose of the vaccine at any time point and should not interrupt biologic therapy.
- Boosters are likely to become available to the general public in September and would be given at least 8 months after an individual’s second dose.
- Recommendations regarding boosters for those who received a three-dose vaccination series are forthcoming.
- Recommendations regarding boosters and additional doses for those that received the Janssen vaccine are forthcoming.
- Gastroenterologists should take an active role in ensuring that their patients are vaccinated.
Dr. Schell is a second-year graduate student in the division of internal medicine at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Caldera is an associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Dr. Schell has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Caldera has received research support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi. He has been a consultant for Takeda, Arena Pharmaceuticals, GSK, and Celgene.
References
1. Sadoff J et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(23):2187-201.
2. Baden LR et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(5):403-16.
3. Polack FP et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-15.
4. Johnson K et al. U.S. FDA aims to give full approval to Pfizer vaccine on Monday – NYT. Reuters. 2021 Aug 20. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/us-fda-aims-give-full-nod-pfizers-covid-19-vaccine-monday-new-york-times-2021-08-20/.
5. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct;9(11):3533.
6. Monteleone G and Ardizzone S. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep;14(9):1334-6.
7. Papa A et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(10):1722-4.
8. Derikx LAAP et al. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2021 Apr 6;15(4):529-39.
9. Brenner EJ et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(2):481-91.
10. Ungaro RC et al. Gut. 2021;70(4):725-32.
11. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26(4):593-602.
12. Botwin GJ et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001342.
13. Squire JD et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021 Jul 27;27(8):1358-60.
14. Hadi YB et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.014.
15. Wong S-Y et al. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:715-8.
16. Kappelman MD et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.016.
17. Pozdnyakova V et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.014.
18. Ben-Tov A et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.076.
19. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Vaccine Dose for Certain Immunocompromised Individuals. FDA News Release. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-vaccine-dose-certain-immunocompromised.
20. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines for Moderately to Severely Immunocompromised People. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 18. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/immuno.html.
21. Allocca M et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 31;9(11):3533.
22. Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. COVID-19 Vaccines: Position Statements. IBD & Coronavirus. 2021. Accessed 2021 Aug 20. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/coronavirus/vaccine-position-statements.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Joint Statement from HHS Public Health and Medical Experts on COVID-19 Booster Shots. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s0818-covid-19-booster-shots.html.
24. Caldera F et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(1):123-133.
Addressing an unmet need in IBD patients: Treatment of acute abdominal pain
In the acute care setting, providers of care for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients are often faced with the dilemma of providing effective abdominal pain management in a population that has worse outcomes with both opioid and NSAID therapy. There is increased mortality associated with opioid use and risk of disease relapse with NSAID use in IBD patients.1,2 Due to this, patients often feel that their pain is inadequately addressed.3,4 There are multiple sources of abdominal pain in IBD, and understanding the mechanisms and presentations can help identify effective treatments. We will review pharmacologic and supportive therapies to optimize pain management in IBD.
Common pain presentations in IBD
Visceral pain is a dull, poorly localized, cramping pain from intestinal distension. It is associated with inflammation, dysmotility, obstruction, and visceral hypersensitivity. Somatic and parietal pain is sharp, intense, and often localizable. Somatic pain originates from surrounding skin or muscles, and parietal pain arises from irritation of the peritoneum.5 We will review two common pain presentations in IBD.
Case 1: Mr. A is a 32-year-old male with stricturing small bowel Crohn’s disease s/p small bowel resection, who presents to the ED with 3 days of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. C-reactive protein is elevated to 6.8 mg/dL (normal 0.0 – 0.6 mg/dL), and CT is consistent with active small bowel inflammation, intraabdominal abscess at the anastomosis, and associated partial small bowel obstruction. He describes a sharp, intense abdominal pain with cramping. His exam is significant for diffuse abdominal tenderness and distension.
Case 2: Ms. B is a 28-year-old female with ulcerative colitis on mesalamine monotherapy who presents to the hospital for rectal bleeding and cramping abdominal pain. After 3 days of IV steroids her rectal bleeding has resolved, and CRP has normalized. However, she continues to have dull, cramping abdominal pain. Ibuprofen has improved this pain in the past.
Mr. A is having somatic pain from inflammation, abscess, and partial bowel obstruction. He also has visceral pain from luminal distension proximal to the obstruction. Ms. B is having visceral pain despite resolution of inflammation, which may be from postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity.
Etiologies of pain
It’s best to group pain etiologies into inflammatory and noninflammatory causes. Inflammatory pain can be secondary to infection, such as abscess or enteric infection, active bowel inflammation, or disease complications (that is, enteric fistula). It is important to recognize that patients with active inflammation may also have noninflammatory pain. These include small bowel obstruction, strictures, adhesions, narcotic bowel syndrome, bacterial overgrowth, and visceral hypersensitivity. See figure 1.
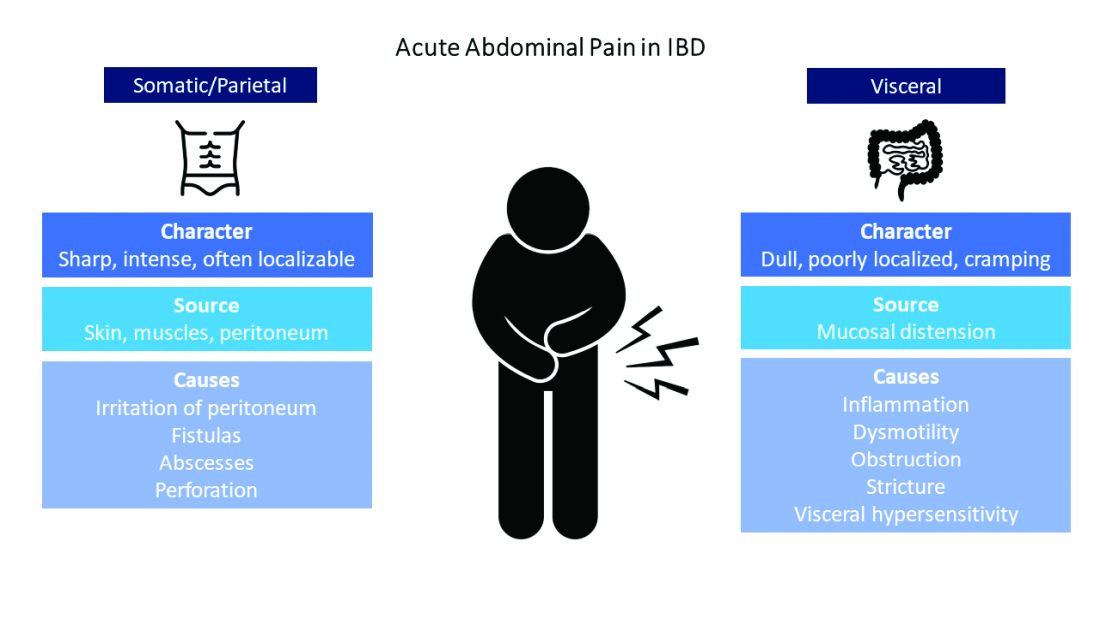
The brain-gut connection matters
Abdominal pain in IBD patients starts from painful stimuli in the gut. In addition to direct pain pathways, multiple areas of the brain modulate perception of pain.6 Patients with psychiatric comorbidities have increased perception of abdominal pain.7 In fact, high perceived stress is associated with disease relapse.8 Treatment of psychiatric disorders improves these symptoms with lasting effects.9 Addressing psychological and psychosocial needs is essential to successful pain management with long-term effect on quality of life and pain perception in IBD patients.
What are my options?
When IBD patients present with acute abdominal pain, it is important to directly address their pain as one of your primary concerns and provide them with a management plan. While this seems obvious, it is not routinely done.3-4
Next, it is important to identify the cause, whether it be infection, obstruction, active inflammation, or functional abdominal pain. In the case of active disease, in addition to steroids and optimization of IBD therapies, acetaminophen and antispasmodics can be used for initial pain management. Supportive therapies include sleep hygiene, physical activity, and psychotherapy. If initial treatments are unsuccessful in the acute setting, and presentation is consistent with somatic pain, it may be necessary to escalate to tramadol, opioid, or NSAID therapy. For visceral pain, a neuromodulator, such as a tricyclic antidepressant or gabapentin, may have greater effect. Bupropion, SNRIs, and SSRIs are options; however, they may not be effective in the acute setting. More recent focus in the IBD community has questioned the role of cannabinoids on pain in IBD patients. Cannabis has been shown in a few small studies to provide pain relief in IBD patients with active inflammation.10-11 In patients with mechanical causes for pain, management of obstruction is an important part of the treatment plan.
Let’s talk about opioids in IBD patients
Chronic narcotic use in IBD is associated with worse outcomes. So when is it okay to use opioid therapies in IBD patients? Postoperative patients, patients with severe perianal disease, or those who fail alternative pain management strategies may require opioid medications. The association with mortality and opioids in IBD is with patients who require moderate to heavy use, which is defined as being prescribed opioids more than once a year. Opioid use in IBD patients is also associated with increased risk of readmissions and poor surgical outcomes.12-13 Tramadol does not have increased mortality risk.1 If selecting opioid therapy in managing pain in IBD, it is important to define the course of therapy, with a clear goal of discontinuation after the acute episode. Opioids should be used in tandem with alternative strategies. Patients should be counseled on the synergistic effect of acetaminophen with opioids, which may allow lower effective doses of opioids.
What about NSAID use in IBD patients?
NSAIDs have negative effects in the gastrointestinal tract due to inhibition of protective prostaglandins. They also alter the gut microbiome, although clinical implications of this are unknown.14 A small study showed that IBD patients who used NSAIDs had increased risk of disease relapse.2 Symptoms of relapse would present within 2-9 days of exposure; however, most had resolution of symptoms within 2-11 days of discontinuation.2 Follow-up studies have not reliably found that NSAIDs are associated with disease relapse.8 and thus NSAIDs may be used sparingly if needed in the acute setting.
Case Review: How do we approach Mr. A and Ms. B?
Mr. A presented with a partial small bowel obstruction and abscess. His pain presentation was consistent with both visceral and somatic pain etiologies. In addition to treating active inflammation and infection, bowel rest, acetaminophen, and antispasmodics can be initiated for pain control. Concomitantly, gabapentin, TCA, or SNRI can be initiated for neurobiological pain but may have limited benefit in the acute hospitalized setting. Social work may identify needs that affect pain perception and assist in addressing those needs. If abdominal pain persists, tramadol or hydrocodone-acetaminophen can be considered.
Ms. B presented with disease relapse, but despite improving inflammatory markers she had continued cramping abdominal pain, which can be consistent with visceral hypersensitivity. Antispasmodic and neuromodulating agents, such as a TCA, could be effective. We can recommend discontinuation of chronic ibuprofen due to risk of intestinal inflammation. Patients may inquire about adjuvant cannabis in pain management. While cannabis can be considered, further research is needed to recommend its regular use.
Conclusion
Acute abdominal pain management in IBD can be challenging for providers when typical options are limited in this population. Addressing inflammatory, mechanical, neurobiological, and psychological influences is vital to appropriately address pain. Having a structured plan for pain management in IBD can improve outcomes by decreasing recurrent hospitalizations and use of opioids.15 Figure 2 presents an overview.
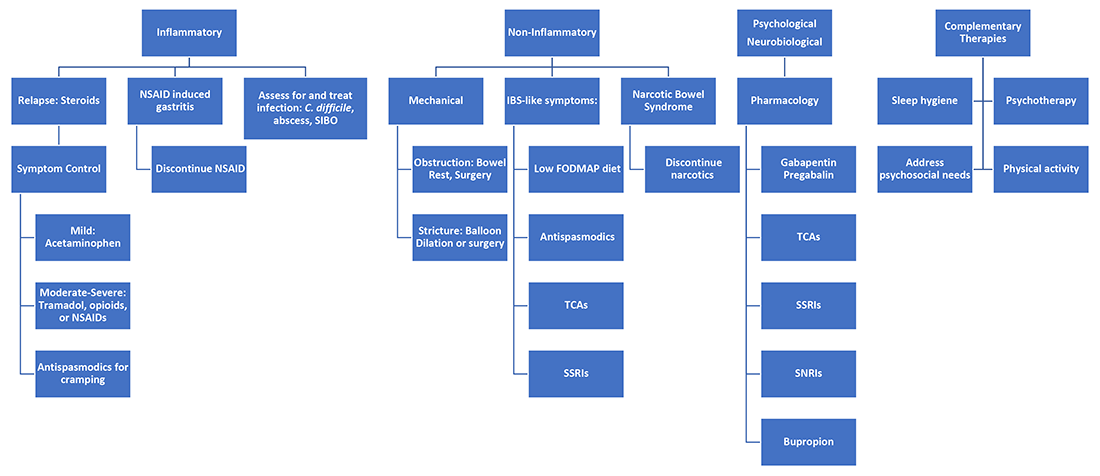
Dr. Ahmed is a second-year internal medicine resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Kinnucan is with the department of internal medicine and the division of gastroenterology and hepatology and is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, both at the University of Michigan. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Burr NE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;16(4):534-41.e6.
2. Takeuchi K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Feb;4(2):196-202.
3. Bernhofer EI et al. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2017 May/Jun;40(3):200-7.
4. Zeitz J et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0156666.
5. Srinath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014 Dec;20(12):2433-49.
6. Docherty MJ et al. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011 Sep;7(9):592-601.
7. Elsenbruch S et al. Gut. 2010 Apr;59(4):489-95.
8. Bernstein CN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep;105(9):1994-2002.
9. Palsson OS and Whitehead WE. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;11(3):208-16; quiz e22-3.
10. Swaminath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019 Mar; 25(3):427-35.
11. Naftali T et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1276-80.e1.
12. Sultan K and Swaminath A. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep 16;14(9):1188-89.
13. Hirsch A et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015 Oct;19(10):1852-61.
14. Rogers MAM and Aronoff DM. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(2):178.e1-178.e9.
15. Kaimakliotis P et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Jun;36(6):1193-200.
In the acute care setting, providers of care for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients are often faced with the dilemma of providing effective abdominal pain management in a population that has worse outcomes with both opioid and NSAID therapy. There is increased mortality associated with opioid use and risk of disease relapse with NSAID use in IBD patients.1,2 Due to this, patients often feel that their pain is inadequately addressed.3,4 There are multiple sources of abdominal pain in IBD, and understanding the mechanisms and presentations can help identify effective treatments. We will review pharmacologic and supportive therapies to optimize pain management in IBD.
Common pain presentations in IBD
Visceral pain is a dull, poorly localized, cramping pain from intestinal distension. It is associated with inflammation, dysmotility, obstruction, and visceral hypersensitivity. Somatic and parietal pain is sharp, intense, and often localizable. Somatic pain originates from surrounding skin or muscles, and parietal pain arises from irritation of the peritoneum.5 We will review two common pain presentations in IBD.
Case 1: Mr. A is a 32-year-old male with stricturing small bowel Crohn’s disease s/p small bowel resection, who presents to the ED with 3 days of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. C-reactive protein is elevated to 6.8 mg/dL (normal 0.0 – 0.6 mg/dL), and CT is consistent with active small bowel inflammation, intraabdominal abscess at the anastomosis, and associated partial small bowel obstruction. He describes a sharp, intense abdominal pain with cramping. His exam is significant for diffuse abdominal tenderness and distension.
Case 2: Ms. B is a 28-year-old female with ulcerative colitis on mesalamine monotherapy who presents to the hospital for rectal bleeding and cramping abdominal pain. After 3 days of IV steroids her rectal bleeding has resolved, and CRP has normalized. However, she continues to have dull, cramping abdominal pain. Ibuprofen has improved this pain in the past.
Mr. A is having somatic pain from inflammation, abscess, and partial bowel obstruction. He also has visceral pain from luminal distension proximal to the obstruction. Ms. B is having visceral pain despite resolution of inflammation, which may be from postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity.
Etiologies of pain
It’s best to group pain etiologies into inflammatory and noninflammatory causes. Inflammatory pain can be secondary to infection, such as abscess or enteric infection, active bowel inflammation, or disease complications (that is, enteric fistula). It is important to recognize that patients with active inflammation may also have noninflammatory pain. These include small bowel obstruction, strictures, adhesions, narcotic bowel syndrome, bacterial overgrowth, and visceral hypersensitivity. See figure 1.

The brain-gut connection matters
Abdominal pain in IBD patients starts from painful stimuli in the gut. In addition to direct pain pathways, multiple areas of the brain modulate perception of pain.6 Patients with psychiatric comorbidities have increased perception of abdominal pain.7 In fact, high perceived stress is associated with disease relapse.8 Treatment of psychiatric disorders improves these symptoms with lasting effects.9 Addressing psychological and psychosocial needs is essential to successful pain management with long-term effect on quality of life and pain perception in IBD patients.
What are my options?
When IBD patients present with acute abdominal pain, it is important to directly address their pain as one of your primary concerns and provide them with a management plan. While this seems obvious, it is not routinely done.3-4
Next, it is important to identify the cause, whether it be infection, obstruction, active inflammation, or functional abdominal pain. In the case of active disease, in addition to steroids and optimization of IBD therapies, acetaminophen and antispasmodics can be used for initial pain management. Supportive therapies include sleep hygiene, physical activity, and psychotherapy. If initial treatments are unsuccessful in the acute setting, and presentation is consistent with somatic pain, it may be necessary to escalate to tramadol, opioid, or NSAID therapy. For visceral pain, a neuromodulator, such as a tricyclic antidepressant or gabapentin, may have greater effect. Bupropion, SNRIs, and SSRIs are options; however, they may not be effective in the acute setting. More recent focus in the IBD community has questioned the role of cannabinoids on pain in IBD patients. Cannabis has been shown in a few small studies to provide pain relief in IBD patients with active inflammation.10-11 In patients with mechanical causes for pain, management of obstruction is an important part of the treatment plan.
Let’s talk about opioids in IBD patients
Chronic narcotic use in IBD is associated with worse outcomes. So when is it okay to use opioid therapies in IBD patients? Postoperative patients, patients with severe perianal disease, or those who fail alternative pain management strategies may require opioid medications. The association with mortality and opioids in IBD is with patients who require moderate to heavy use, which is defined as being prescribed opioids more than once a year. Opioid use in IBD patients is also associated with increased risk of readmissions and poor surgical outcomes.12-13 Tramadol does not have increased mortality risk.1 If selecting opioid therapy in managing pain in IBD, it is important to define the course of therapy, with a clear goal of discontinuation after the acute episode. Opioids should be used in tandem with alternative strategies. Patients should be counseled on the synergistic effect of acetaminophen with opioids, which may allow lower effective doses of opioids.
What about NSAID use in IBD patients?
NSAIDs have negative effects in the gastrointestinal tract due to inhibition of protective prostaglandins. They also alter the gut microbiome, although clinical implications of this are unknown.14 A small study showed that IBD patients who used NSAIDs had increased risk of disease relapse.2 Symptoms of relapse would present within 2-9 days of exposure; however, most had resolution of symptoms within 2-11 days of discontinuation.2 Follow-up studies have not reliably found that NSAIDs are associated with disease relapse.8 and thus NSAIDs may be used sparingly if needed in the acute setting.
Case Review: How do we approach Mr. A and Ms. B?
Mr. A presented with a partial small bowel obstruction and abscess. His pain presentation was consistent with both visceral and somatic pain etiologies. In addition to treating active inflammation and infection, bowel rest, acetaminophen, and antispasmodics can be initiated for pain control. Concomitantly, gabapentin, TCA, or SNRI can be initiated for neurobiological pain but may have limited benefit in the acute hospitalized setting. Social work may identify needs that affect pain perception and assist in addressing those needs. If abdominal pain persists, tramadol or hydrocodone-acetaminophen can be considered.
Ms. B presented with disease relapse, but despite improving inflammatory markers she had continued cramping abdominal pain, which can be consistent with visceral hypersensitivity. Antispasmodic and neuromodulating agents, such as a TCA, could be effective. We can recommend discontinuation of chronic ibuprofen due to risk of intestinal inflammation. Patients may inquire about adjuvant cannabis in pain management. While cannabis can be considered, further research is needed to recommend its regular use.
Conclusion
Acute abdominal pain management in IBD can be challenging for providers when typical options are limited in this population. Addressing inflammatory, mechanical, neurobiological, and psychological influences is vital to appropriately address pain. Having a structured plan for pain management in IBD can improve outcomes by decreasing recurrent hospitalizations and use of opioids.15 Figure 2 presents an overview.

Dr. Ahmed is a second-year internal medicine resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Kinnucan is with the department of internal medicine and the division of gastroenterology and hepatology and is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, both at the University of Michigan. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Burr NE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;16(4):534-41.e6.
2. Takeuchi K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Feb;4(2):196-202.
3. Bernhofer EI et al. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2017 May/Jun;40(3):200-7.
4. Zeitz J et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0156666.
5. Srinath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014 Dec;20(12):2433-49.
6. Docherty MJ et al. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011 Sep;7(9):592-601.
7. Elsenbruch S et al. Gut. 2010 Apr;59(4):489-95.
8. Bernstein CN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep;105(9):1994-2002.
9. Palsson OS and Whitehead WE. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;11(3):208-16; quiz e22-3.
10. Swaminath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019 Mar; 25(3):427-35.
11. Naftali T et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1276-80.e1.
12. Sultan K and Swaminath A. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep 16;14(9):1188-89.
13. Hirsch A et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015 Oct;19(10):1852-61.
14. Rogers MAM and Aronoff DM. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(2):178.e1-178.e9.
15. Kaimakliotis P et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Jun;36(6):1193-200.
In the acute care setting, providers of care for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients are often faced with the dilemma of providing effective abdominal pain management in a population that has worse outcomes with both opioid and NSAID therapy. There is increased mortality associated with opioid use and risk of disease relapse with NSAID use in IBD patients.1,2 Due to this, patients often feel that their pain is inadequately addressed.3,4 There are multiple sources of abdominal pain in IBD, and understanding the mechanisms and presentations can help identify effective treatments. We will review pharmacologic and supportive therapies to optimize pain management in IBD.
Common pain presentations in IBD
Visceral pain is a dull, poorly localized, cramping pain from intestinal distension. It is associated with inflammation, dysmotility, obstruction, and visceral hypersensitivity. Somatic and parietal pain is sharp, intense, and often localizable. Somatic pain originates from surrounding skin or muscles, and parietal pain arises from irritation of the peritoneum.5 We will review two common pain presentations in IBD.
Case 1: Mr. A is a 32-year-old male with stricturing small bowel Crohn’s disease s/p small bowel resection, who presents to the ED with 3 days of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. C-reactive protein is elevated to 6.8 mg/dL (normal 0.0 – 0.6 mg/dL), and CT is consistent with active small bowel inflammation, intraabdominal abscess at the anastomosis, and associated partial small bowel obstruction. He describes a sharp, intense abdominal pain with cramping. His exam is significant for diffuse abdominal tenderness and distension.
Case 2: Ms. B is a 28-year-old female with ulcerative colitis on mesalamine monotherapy who presents to the hospital for rectal bleeding and cramping abdominal pain. After 3 days of IV steroids her rectal bleeding has resolved, and CRP has normalized. However, she continues to have dull, cramping abdominal pain. Ibuprofen has improved this pain in the past.
Mr. A is having somatic pain from inflammation, abscess, and partial bowel obstruction. He also has visceral pain from luminal distension proximal to the obstruction. Ms. B is having visceral pain despite resolution of inflammation, which may be from postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity.
Etiologies of pain
It’s best to group pain etiologies into inflammatory and noninflammatory causes. Inflammatory pain can be secondary to infection, such as abscess or enteric infection, active bowel inflammation, or disease complications (that is, enteric fistula). It is important to recognize that patients with active inflammation may also have noninflammatory pain. These include small bowel obstruction, strictures, adhesions, narcotic bowel syndrome, bacterial overgrowth, and visceral hypersensitivity. See figure 1.

The brain-gut connection matters
Abdominal pain in IBD patients starts from painful stimuli in the gut. In addition to direct pain pathways, multiple areas of the brain modulate perception of pain.6 Patients with psychiatric comorbidities have increased perception of abdominal pain.7 In fact, high perceived stress is associated with disease relapse.8 Treatment of psychiatric disorders improves these symptoms with lasting effects.9 Addressing psychological and psychosocial needs is essential to successful pain management with long-term effect on quality of life and pain perception in IBD patients.
What are my options?
When IBD patients present with acute abdominal pain, it is important to directly address their pain as one of your primary concerns and provide them with a management plan. While this seems obvious, it is not routinely done.3-4
Next, it is important to identify the cause, whether it be infection, obstruction, active inflammation, or functional abdominal pain. In the case of active disease, in addition to steroids and optimization of IBD therapies, acetaminophen and antispasmodics can be used for initial pain management. Supportive therapies include sleep hygiene, physical activity, and psychotherapy. If initial treatments are unsuccessful in the acute setting, and presentation is consistent with somatic pain, it may be necessary to escalate to tramadol, opioid, or NSAID therapy. For visceral pain, a neuromodulator, such as a tricyclic antidepressant or gabapentin, may have greater effect. Bupropion, SNRIs, and SSRIs are options; however, they may not be effective in the acute setting. More recent focus in the IBD community has questioned the role of cannabinoids on pain in IBD patients. Cannabis has been shown in a few small studies to provide pain relief in IBD patients with active inflammation.10-11 In patients with mechanical causes for pain, management of obstruction is an important part of the treatment plan.
Let’s talk about opioids in IBD patients
Chronic narcotic use in IBD is associated with worse outcomes. So when is it okay to use opioid therapies in IBD patients? Postoperative patients, patients with severe perianal disease, or those who fail alternative pain management strategies may require opioid medications. The association with mortality and opioids in IBD is with patients who require moderate to heavy use, which is defined as being prescribed opioids more than once a year. Opioid use in IBD patients is also associated with increased risk of readmissions and poor surgical outcomes.12-13 Tramadol does not have increased mortality risk.1 If selecting opioid therapy in managing pain in IBD, it is important to define the course of therapy, with a clear goal of discontinuation after the acute episode. Opioids should be used in tandem with alternative strategies. Patients should be counseled on the synergistic effect of acetaminophen with opioids, which may allow lower effective doses of opioids.
What about NSAID use in IBD patients?
NSAIDs have negative effects in the gastrointestinal tract due to inhibition of protective prostaglandins. They also alter the gut microbiome, although clinical implications of this are unknown.14 A small study showed that IBD patients who used NSAIDs had increased risk of disease relapse.2 Symptoms of relapse would present within 2-9 days of exposure; however, most had resolution of symptoms within 2-11 days of discontinuation.2 Follow-up studies have not reliably found that NSAIDs are associated with disease relapse.8 and thus NSAIDs may be used sparingly if needed in the acute setting.
Case Review: How do we approach Mr. A and Ms. B?
Mr. A presented with a partial small bowel obstruction and abscess. His pain presentation was consistent with both visceral and somatic pain etiologies. In addition to treating active inflammation and infection, bowel rest, acetaminophen, and antispasmodics can be initiated for pain control. Concomitantly, gabapentin, TCA, or SNRI can be initiated for neurobiological pain but may have limited benefit in the acute hospitalized setting. Social work may identify needs that affect pain perception and assist in addressing those needs. If abdominal pain persists, tramadol or hydrocodone-acetaminophen can be considered.
Ms. B presented with disease relapse, but despite improving inflammatory markers she had continued cramping abdominal pain, which can be consistent with visceral hypersensitivity. Antispasmodic and neuromodulating agents, such as a TCA, could be effective. We can recommend discontinuation of chronic ibuprofen due to risk of intestinal inflammation. Patients may inquire about adjuvant cannabis in pain management. While cannabis can be considered, further research is needed to recommend its regular use.
Conclusion
Acute abdominal pain management in IBD can be challenging for providers when typical options are limited in this population. Addressing inflammatory, mechanical, neurobiological, and psychological influences is vital to appropriately address pain. Having a structured plan for pain management in IBD can improve outcomes by decreasing recurrent hospitalizations and use of opioids.15 Figure 2 presents an overview.

Dr. Ahmed is a second-year internal medicine resident at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Kinnucan is with the department of internal medicine and the division of gastroenterology and hepatology and is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, both at the University of Michigan. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Burr NE et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;16(4):534-41.e6.
2. Takeuchi K et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Feb;4(2):196-202.
3. Bernhofer EI et al. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2017 May/Jun;40(3):200-7.
4. Zeitz J et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jun 22;11(6):e0156666.
5. Srinath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014 Dec;20(12):2433-49.
6. Docherty MJ et al. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011 Sep;7(9):592-601.
7. Elsenbruch S et al. Gut. 2010 Apr;59(4):489-95.
8. Bernstein CN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep;105(9):1994-2002.
9. Palsson OS and Whitehead WE. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;11(3):208-16; quiz e22-3.
10. Swaminath A et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019 Mar; 25(3):427-35.
11. Naftali T et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1276-80.e1.
12. Sultan K and Swaminath A. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Sep 16;14(9):1188-89.
13. Hirsch A et al. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015 Oct;19(10):1852-61.
14. Rogers MAM and Aronoff DM. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(2):178.e1-178.e9.
15. Kaimakliotis P et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Jun;36(6):1193-200.
When to not go with your gut: Modern approaches to abdominal wall pain
Abdominal pain is a commonly seen presenting concern in gastroenterology clinics. Establishing a diagnosis effectively and efficiently can be challenging given the broad differential. Abdominal wall pain is an often-overlooked diagnosis but accounts for up to 30% of cases of chronic abdominal pain1 and up to 10% of patients with chronic idiopathic abdominal pain seen in gastroenterology practices.2 Trigger point injection in the office can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
The prevalence of chronic abdominal wall pain is highest in the fifth and sixth decades, and it is four times more likely to occur in women than in men. Common comorbid conditions include obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and fibromyalgia.3 Abdominal wall pain is often sharp or burning due to somatic innervation of the abdominal wall supplied by the anterior branches of thoracic intercostal nerves (T7 to T11). Abdominal wall pain may originate from entrapment of these nerves.2 Potential causes of entrapment include disruption of insulating fat, localized edema and distension, and scar tissue or fibrosis from prior surgical procedures.3 Symptoms are typically exacerbated with any actions or activities that engage the abdominal wall such as twisting or turning, and pain often improves with rest.
The classic physical exam finding for abdominal wall pain is a positive Carnett sign. This is determined via palpation of the point of maximal tenderness. First, this is done with a single finger while the patient’s abdominal wall is relaxed. The same point is then palpated again while the patient engages their abdominal muscles, most commonly while the patient to performs a “sit up” or lifts their legs off the exam table. Exacerbation of pain with these maneuvers indicates a positive test and suggests the abdominal wall as the underlying etiology.
While performing the maneuver for determining Carnett sign is a simple test in the traditional office visit, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a burgeoning proportion of telehealth visits, limiting the physician’s ability to perform a direct physical exam. Fortunately, the maneuvers required when testing for Carnett sign are simple enough that a clinician can guide a patient step-by-step on how to perform the test. Ideally, if a family member or friend is available to serve as the clinician’s hands, the test can be performed with ease while directly visualizing proper technique. Sample videos of how the test is performed are readily available on the Internet for patients to view (the authors suggest screening the video yourself before providing a link to patients). The sensitivity and specificity of Carnett sign are very high (>70%) and even better when there is no apparent hernia.1
Management
Trigger point injections with local anesthetic can be both diagnostic and therapeutic in patients with abdominal wall pain. An immediate reduction of pain by at least 50% with injection at the site of maximal tenderness strongly supports the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.1 Patients should first be thoroughly counseled on potential side effects of local corticosteroid injection to include risk of infection, bleeding, pain, skin hypopigmentation, or thinning and fat atrophy. Repeat injections are rarely needed, and any additional injection should be performed after at least 3 months. Additional adjunct therapies include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, topical therapies such as lidocaine, and neuroleptic agents such as gabapentin.4 One previously described trigger point injection technique, involves a mix of triamcinolone and lidocaine injected at the point of maximal tenderness.5 This technique is easy to perform in clinic and has minimal risks.
Conclusion
Abdominal wall pain is a common, yet often-overlooked, condition that can be diagnosed with a good clinical history and physical exam. A simple in-office trigger point injection can confirm the diagnosis and offer durable relief for most patients. A shift to virtual medicine does not need to a barrier to diagnosis, particularly in the attentive patient.
Dr. Park is a fellow in the gastroenterology service in the Department of Internal Medicine at Naval Medical Center San Diego and an assistant professor in the department of medicine of the Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md. Dr. Singla is a gastroenterologist at Capital Digestive Care in Silver Spring, Md., and an associate professor in the department of medicine at the Uniformed Services University. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Glissen Brown JR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(10):828-35.
2. Srinivasan R, Greenbaum DS. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(4):824-30.
3. Kambox AK et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(1):139-44.
4. Scheltinga MR, Roumen RM. Hernia. 2018;22(3):507-16.
5. Singla M, Laczek JT. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115(5):645-7.
Abdominal pain is a commonly seen presenting concern in gastroenterology clinics. Establishing a diagnosis effectively and efficiently can be challenging given the broad differential. Abdominal wall pain is an often-overlooked diagnosis but accounts for up to 30% of cases of chronic abdominal pain1 and up to 10% of patients with chronic idiopathic abdominal pain seen in gastroenterology practices.2 Trigger point injection in the office can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
The prevalence of chronic abdominal wall pain is highest in the fifth and sixth decades, and it is four times more likely to occur in women than in men. Common comorbid conditions include obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and fibromyalgia.3 Abdominal wall pain is often sharp or burning due to somatic innervation of the abdominal wall supplied by the anterior branches of thoracic intercostal nerves (T7 to T11). Abdominal wall pain may originate from entrapment of these nerves.2 Potential causes of entrapment include disruption of insulating fat, localized edema and distension, and scar tissue or fibrosis from prior surgical procedures.3 Symptoms are typically exacerbated with any actions or activities that engage the abdominal wall such as twisting or turning, and pain often improves with rest.
The classic physical exam finding for abdominal wall pain is a positive Carnett sign. This is determined via palpation of the point of maximal tenderness. First, this is done with a single finger while the patient’s abdominal wall is relaxed. The same point is then palpated again while the patient engages their abdominal muscles, most commonly while the patient to performs a “sit up” or lifts their legs off the exam table. Exacerbation of pain with these maneuvers indicates a positive test and suggests the abdominal wall as the underlying etiology.
While performing the maneuver for determining Carnett sign is a simple test in the traditional office visit, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a burgeoning proportion of telehealth visits, limiting the physician’s ability to perform a direct physical exam. Fortunately, the maneuvers required when testing for Carnett sign are simple enough that a clinician can guide a patient step-by-step on how to perform the test. Ideally, if a family member or friend is available to serve as the clinician’s hands, the test can be performed with ease while directly visualizing proper technique. Sample videos of how the test is performed are readily available on the Internet for patients to view (the authors suggest screening the video yourself before providing a link to patients). The sensitivity and specificity of Carnett sign are very high (>70%) and even better when there is no apparent hernia.1
Management
Trigger point injections with local anesthetic can be both diagnostic and therapeutic in patients with abdominal wall pain. An immediate reduction of pain by at least 50% with injection at the site of maximal tenderness strongly supports the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.1 Patients should first be thoroughly counseled on potential side effects of local corticosteroid injection to include risk of infection, bleeding, pain, skin hypopigmentation, or thinning and fat atrophy. Repeat injections are rarely needed, and any additional injection should be performed after at least 3 months. Additional adjunct therapies include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, topical therapies such as lidocaine, and neuroleptic agents such as gabapentin.4 One previously described trigger point injection technique, involves a mix of triamcinolone and lidocaine injected at the point of maximal tenderness.5 This technique is easy to perform in clinic and has minimal risks.
Conclusion
Abdominal wall pain is a common, yet often-overlooked, condition that can be diagnosed with a good clinical history and physical exam. A simple in-office trigger point injection can confirm the diagnosis and offer durable relief for most patients. A shift to virtual medicine does not need to a barrier to diagnosis, particularly in the attentive patient.
Dr. Park is a fellow in the gastroenterology service in the Department of Internal Medicine at Naval Medical Center San Diego and an assistant professor in the department of medicine of the Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md. Dr. Singla is a gastroenterologist at Capital Digestive Care in Silver Spring, Md., and an associate professor in the department of medicine at the Uniformed Services University. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Glissen Brown JR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(10):828-35.
2. Srinivasan R, Greenbaum DS. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(4):824-30.
3. Kambox AK et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(1):139-44.
4. Scheltinga MR, Roumen RM. Hernia. 2018;22(3):507-16.
5. Singla M, Laczek JT. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115(5):645-7.
Abdominal pain is a commonly seen presenting concern in gastroenterology clinics. Establishing a diagnosis effectively and efficiently can be challenging given the broad differential. Abdominal wall pain is an often-overlooked diagnosis but accounts for up to 30% of cases of chronic abdominal pain1 and up to 10% of patients with chronic idiopathic abdominal pain seen in gastroenterology practices.2 Trigger point injection in the office can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
The prevalence of chronic abdominal wall pain is highest in the fifth and sixth decades, and it is four times more likely to occur in women than in men. Common comorbid conditions include obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and fibromyalgia.3 Abdominal wall pain is often sharp or burning due to somatic innervation of the abdominal wall supplied by the anterior branches of thoracic intercostal nerves (T7 to T11). Abdominal wall pain may originate from entrapment of these nerves.2 Potential causes of entrapment include disruption of insulating fat, localized edema and distension, and scar tissue or fibrosis from prior surgical procedures.3 Symptoms are typically exacerbated with any actions or activities that engage the abdominal wall such as twisting or turning, and pain often improves with rest.
The classic physical exam finding for abdominal wall pain is a positive Carnett sign. This is determined via palpation of the point of maximal tenderness. First, this is done with a single finger while the patient’s abdominal wall is relaxed. The same point is then palpated again while the patient engages their abdominal muscles, most commonly while the patient to performs a “sit up” or lifts their legs off the exam table. Exacerbation of pain with these maneuvers indicates a positive test and suggests the abdominal wall as the underlying etiology.
While performing the maneuver for determining Carnett sign is a simple test in the traditional office visit, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a burgeoning proportion of telehealth visits, limiting the physician’s ability to perform a direct physical exam. Fortunately, the maneuvers required when testing for Carnett sign are simple enough that a clinician can guide a patient step-by-step on how to perform the test. Ideally, if a family member or friend is available to serve as the clinician’s hands, the test can be performed with ease while directly visualizing proper technique. Sample videos of how the test is performed are readily available on the Internet for patients to view (the authors suggest screening the video yourself before providing a link to patients). The sensitivity and specificity of Carnett sign are very high (>70%) and even better when there is no apparent hernia.1
Management
Trigger point injections with local anesthetic can be both diagnostic and therapeutic in patients with abdominal wall pain. An immediate reduction of pain by at least 50% with injection at the site of maximal tenderness strongly supports the diagnosis of abdominal wall pain.1 Patients should first be thoroughly counseled on potential side effects of local corticosteroid injection to include risk of infection, bleeding, pain, skin hypopigmentation, or thinning and fat atrophy. Repeat injections are rarely needed, and any additional injection should be performed after at least 3 months. Additional adjunct therapies include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, topical therapies such as lidocaine, and neuroleptic agents such as gabapentin.4 One previously described trigger point injection technique, involves a mix of triamcinolone and lidocaine injected at the point of maximal tenderness.5 This technique is easy to perform in clinic and has minimal risks.
Conclusion
Abdominal wall pain is a common, yet often-overlooked, condition that can be diagnosed with a good clinical history and physical exam. A simple in-office trigger point injection can confirm the diagnosis and offer durable relief for most patients. A shift to virtual medicine does not need to a barrier to diagnosis, particularly in the attentive patient.
Dr. Park is a fellow in the gastroenterology service in the Department of Internal Medicine at Naval Medical Center San Diego and an assistant professor in the department of medicine of the Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md. Dr. Singla is a gastroenterologist at Capital Digestive Care in Silver Spring, Md., and an associate professor in the department of medicine at the Uniformed Services University. The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Glissen Brown JR et al. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(10):828-35.
2. Srinivasan R, Greenbaum DS. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(4):824-30.
3. Kambox AK et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(1):139-44.
4. Scheltinga MR, Roumen RM. Hernia. 2018;22(3):507-16.
5. Singla M, Laczek JT. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;115(5):645-7.
Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.


























