User login
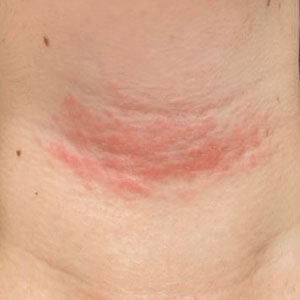
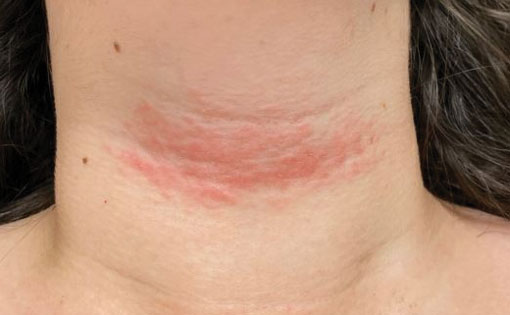
Solitary Pink Plaque on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
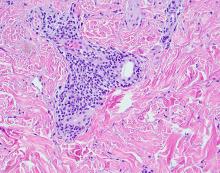
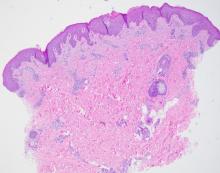
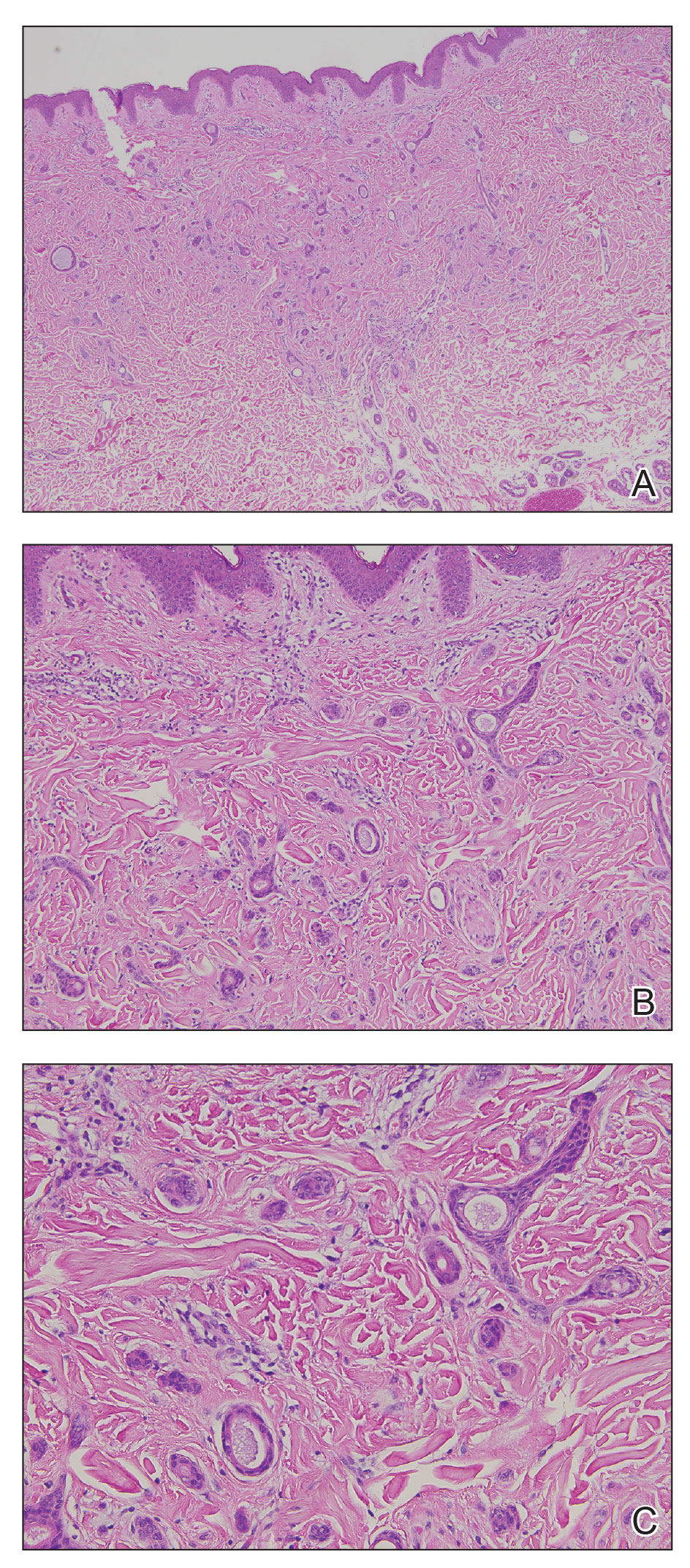
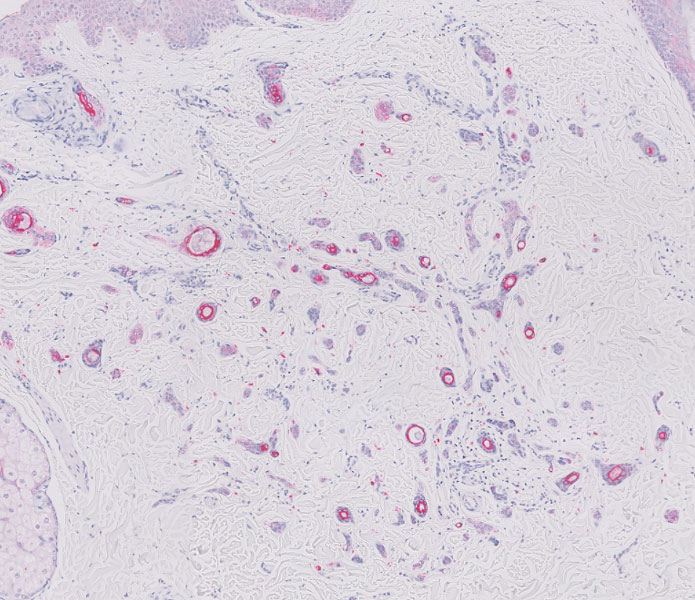
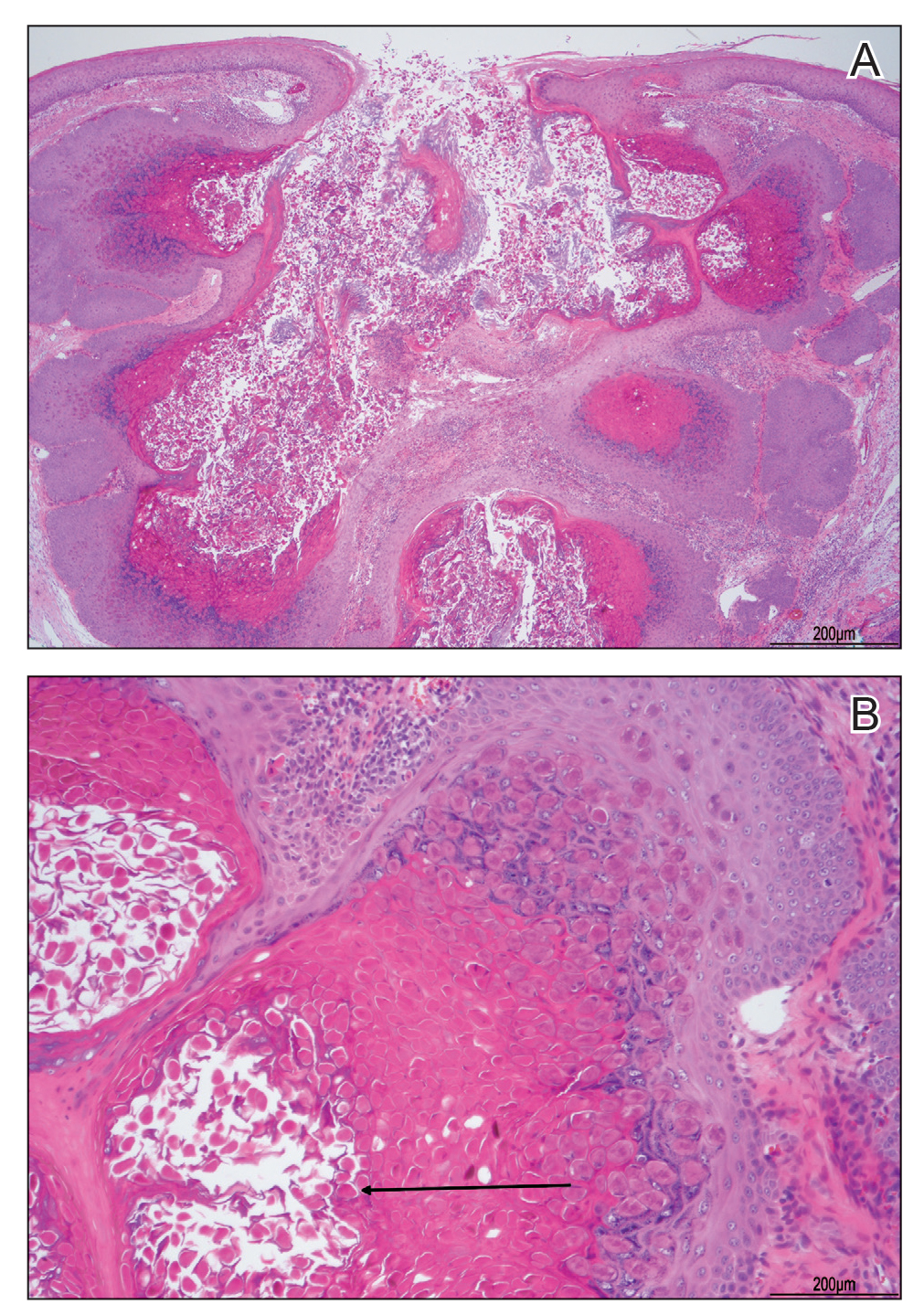
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.
Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6
Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
The Diagnosis: Plaque-type Syringoma
A biopsy demonstrated multiple basaloid islands of tumor cells in the reticular dermis with ductal differentiation, some with a commalike tail. The ducts were lined by 2 to 3 layers of small uniform cuboidal cells without atypia and contained inspissated secretions within the lumina of scattered ducts. There was an associated fibrotic collagenous stroma. There was no evidence of perineural invasion and no deep dermal or subcutaneous extension (Figure 1). Additional cytokeratin immunohistochemical staining highlighted the adnexal proliferation (Figure 2). A diagnosis of plaque-type syringoma (PTS) was made.

Syringomas are benign dermal sweat gland tumors that typically present as flesh-colored papules on the cheeks or periorbital area of young females. Plaque-type tumors as well as papulonodular, eruptive, disseminated, urticaria pigmentosa–like, lichen planus–like, or milialike syringomas also have been reported. Syringomas may be associated with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome, Nicolau-Balus syndrome, and both scarring and nonscarring alopecias.1 The clear cell variant of syringoma often is associated with diabetes mellitus.2 Kikuchi et al3 first described PTS in 1979. Plaque-type syringomas rarely are reported in the literature, and sites of involvement include the head and neck region, upper lip, chest, upper extremities, vulva, penis, and scrotum.4-6

Histologically, syringomatous lesions are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 to 3 layers of cuboidal epithelium. The ducts may be arranged in nests or strands of basaloid cells surrounded by a dense fibrotic stroma. Occasionally, the ducts will form a comma- or teardropshaped tail; however, this also may be observed in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE).7 Perineural invasion is absent in syringomas. Syringomas exhibit a lateral growth pattern that typically is limited to the upper half of the reticular dermis and spares the underlying subcutis, muscle, and bone. The growth pattern may be discontinuous with proliferations juxtaposed by normal-appearing skin.8 Syringomas usually express progesterone receptors and are known to proliferate at puberty, suggesting that these neoplasms are under hormonal control.9 Although syringomas are benign, various treatment options that may be pursued for cosmetic purposes include radiofrequency, staged excision, laser ablation, and oral isotretinoin.8,10 If only a superficial biopsy is obtained, syringomas may display features of other adnexal neoplasms, including microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC), DTE, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN).
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm first described by Goldstein et al11 in 1982 an indurated, ill-defined plaque or nodule on the face with a predilection for the upper and lower lip. Prior radiation therapy and immunosuppression are risk factors for the development of MAC.12 Histologically, the superficial portion displays small cornifying cysts interspersed with islands of basaloid cells and may mimic a syringoma. However, the deeper portions demonstrate ducts lined by a single layer of cells with a background of hyalinized and sclerotic stroma. The tumor cells may occupy the deep dermis and underlying subcutis, muscle, or bone and demonstrate an infiltrative growth pattern and perineural invasion. Treatment includes Mohs micrographic surgery.
Desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas most commonly present as solitary white to yellowish annular papules or plaques with a central dell located on sun-exposed areas of the face, cheeks, or chin. This benign neoplasm has a bimodal age distribution, primarily affecting females either in childhood or adulthood.13 Histologically, strands and nests of basaloid epithelial cells proliferate in a dense eosinophilic desmoplastic stroma. The basaloid islands are narrow and cordlike with growth parallel to the surface epidermis and do not dive deeply into the deep dermis or subcutis. Ductal differentiation with associated secretions typically is not seen in DTE.1 Calcifications and foreign body granulomatous infiltrates may be present. Merkel cells also are present in this tumor and may be highlighted by immunohistochemistry with cytokeratin 20.14 Rarely, desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas may transform into trichoblastic carcinomas. Treatment may consist of surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery.
Morpheaform BCC also is included in the clinical and histopathologic differential diagnosis of infiltrative basaloid neoplasms. It is one of the more aggressive variants of BCC. The use of immunohistochemical staining may aid in differentiating between these sclerosing adnexal neoplasms.15 For example, pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1) is a stem cell marker that is heavily expressed in DTE as a specific follicular bulge marker but is not present in a morpheaform BCC. This highlights the follicular nature of DTEs at the molecular level. BerEP4 is a monoclonal antibody that serves as an epithelial marker for 2 glycopolypeptides: 34 and 39 kDa. This antibody may demonstrate positivity in morpheaform BCC but does not stain cells of interest in MAC.
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus clinically presents with erythematous and warty papules in a linear distribution following the Blaschko lines. The papules often are reported to be intensely pruritic and usually are localized to one extremity.16 Although adultonset forms of ILVEN have been described,17 it most commonly is diagnosed in young children. Histologically, ILVEN consists of psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with alternating areas of parakeratosis and orthokeratosis with underlying agranulosis and hypergranulosis, respectively.18 The upper dermis contains a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. Treatment with laser therapy and surgical excision has led to both symptomatic and clinical improvement of ILVEN.16
Plaque-type syringomas are a rare variant of syringomas that clinically may mimic other common inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. An adequate biopsy is imperative to differentiate between adnexal neoplasms, as a small superficial biopsy of a syringoma may demonstrate features observed in other malignant or locally aggressive neoplasms. In our patient, the small ducts lined by cuboidal epithelium with no cellular atypia and no deep dermal growth or perineural invasion allowed for the diagnosis of PTS. Therapeutic options were reviewed with our patient, including oral isotretinoin, laser therapy, and staged excision. Ultimately, our patient elected not to pursue treatment, and she is being monitored clinically for any changes in appearance or symptoms.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma [published online November 12, 2007]. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Furue M, Hori Y, Nakabayashi Y. Clear-cell syringoma. association with diabetes mellitus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:131-138.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Okuda H, Tei N, Shimizu K, et al. Chondroid syringoma of the scrotum. Int J Urol. 2008;15:944-945.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaquetype syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:442-445.
- Mainitz M, Schmidt JB, Gebhart W. Response of multiple syringomas to isotretinoin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66:51-55.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Pujol RM, LeBoit PE, Su WP. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma with extensive sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:358-362.
- Rahman J, Tahir M, Arekemase H, et al. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: histopathologic and immunohistochemical criteria for differentiation of a rare benign hair follicle tumor from other cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cureus. 2020;12:E9703.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Sellheyer K, Nelson P, Kutzner H, et al. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:363-370.
- Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Gianfaldoni R, et al. A case of “inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus” (ILVEN) treated with CO2 laser ablation. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:454-457.
- Kawaguchi H, Takeuchi M, Ono H, et al. Adult onset of inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus [published online October 27, 1999]. J Dermatol. 1999;26:599-602.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA, Prenshaw KL, et al. The psoriasiform reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2021:99-120.
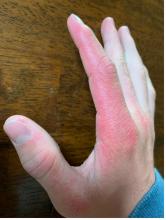
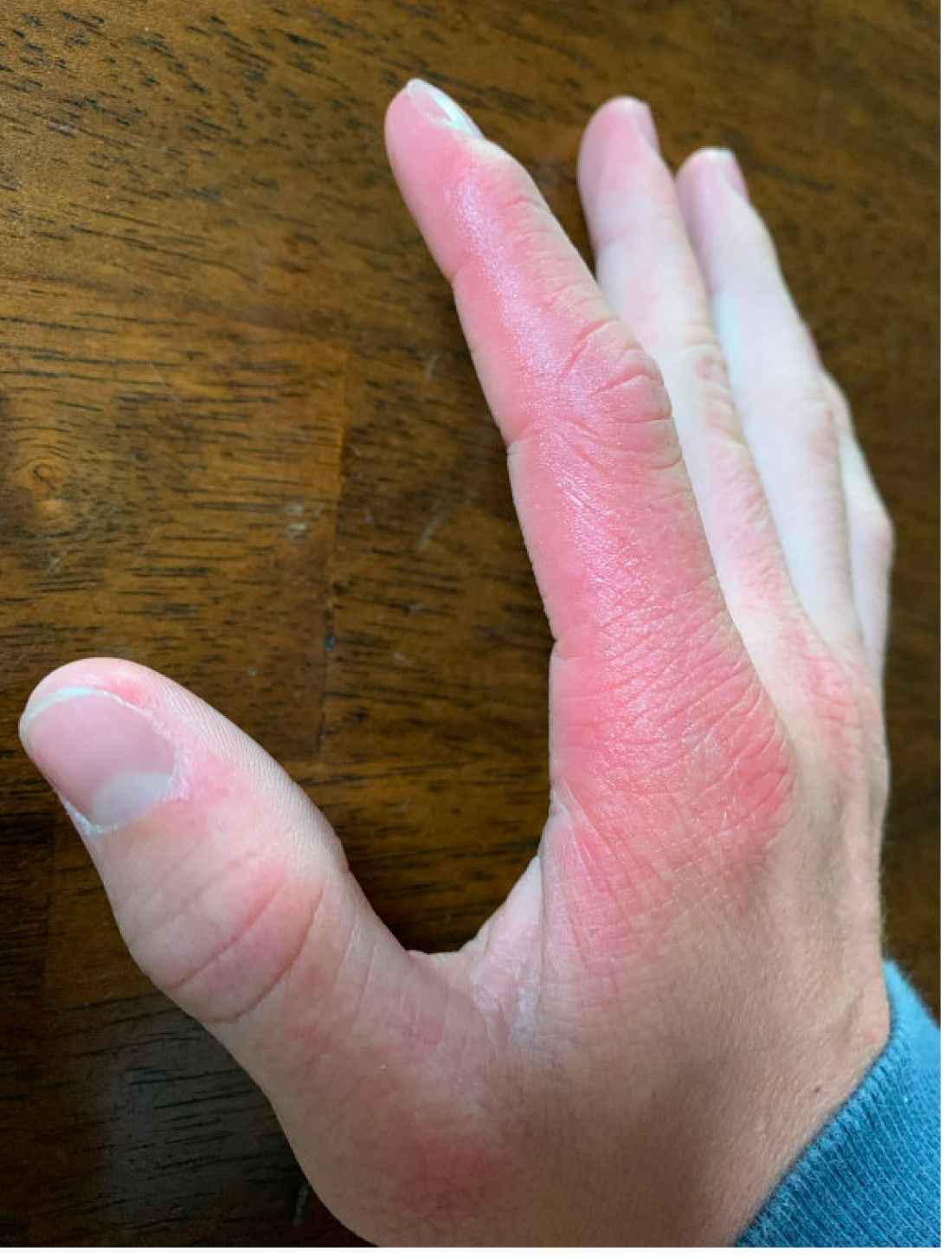
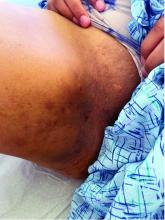
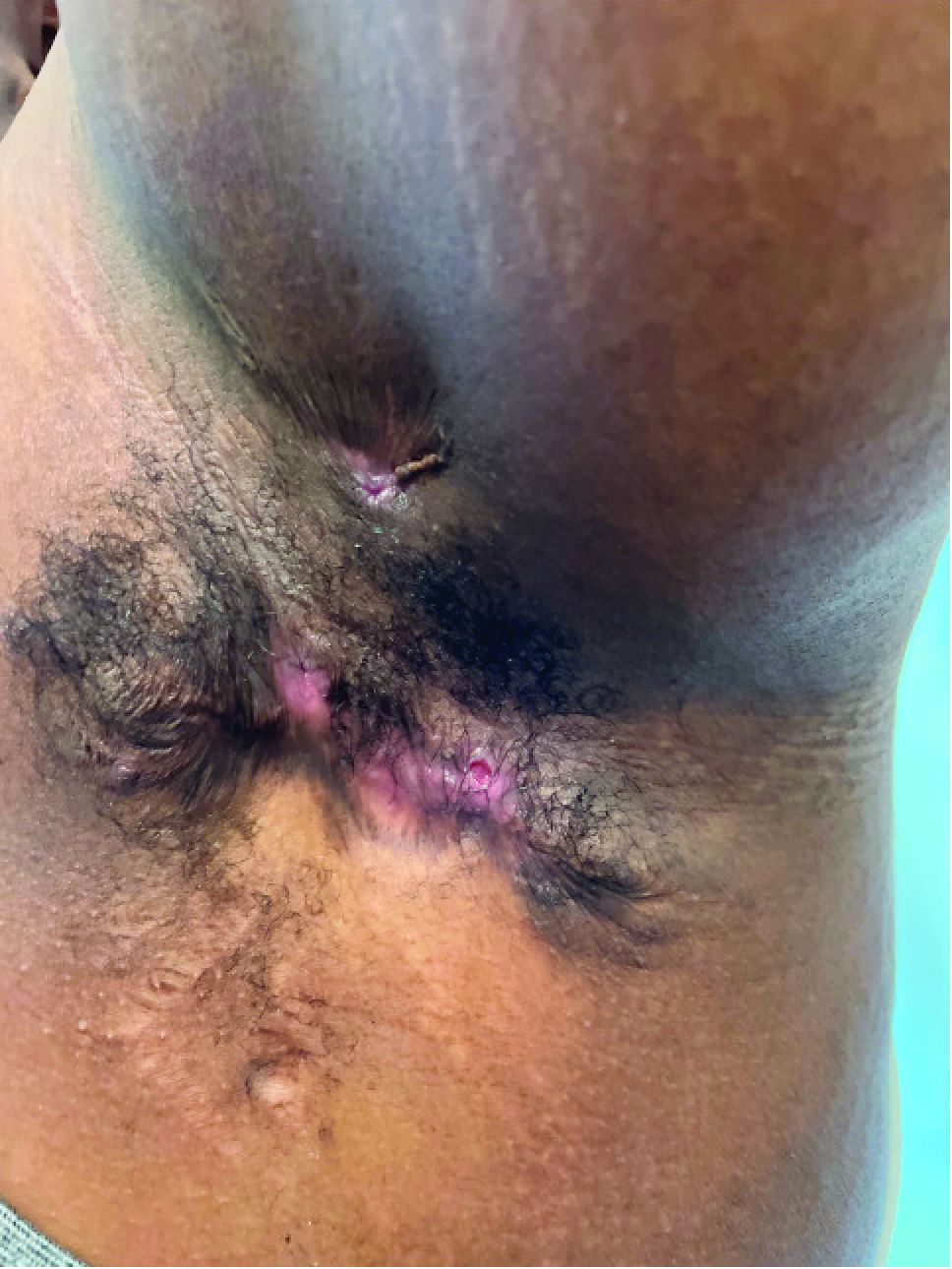
A 17-year-old adolescent girl presented with a solitary, 8-cm, pink plaque on the anterior aspect of the neck of 5 years’ duration. No similar skin findings were present elsewhere on the body. The rash was not painful or pruritic, and she denied prior trauma to the site. The patient previously had tried a salicylic acid bodywash as well as mupirocin cream 2% and mometasone ointment with no improvement. Her medical history was unremarkable, and she had no known allergies. There was no family history of a similar rash. Physical examination revealed no palpable subcutaneous lumps or masses and no lymphadenopathy of the head or neck. An incisional biopsy was performed.
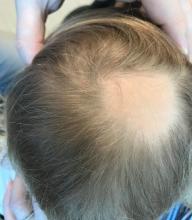
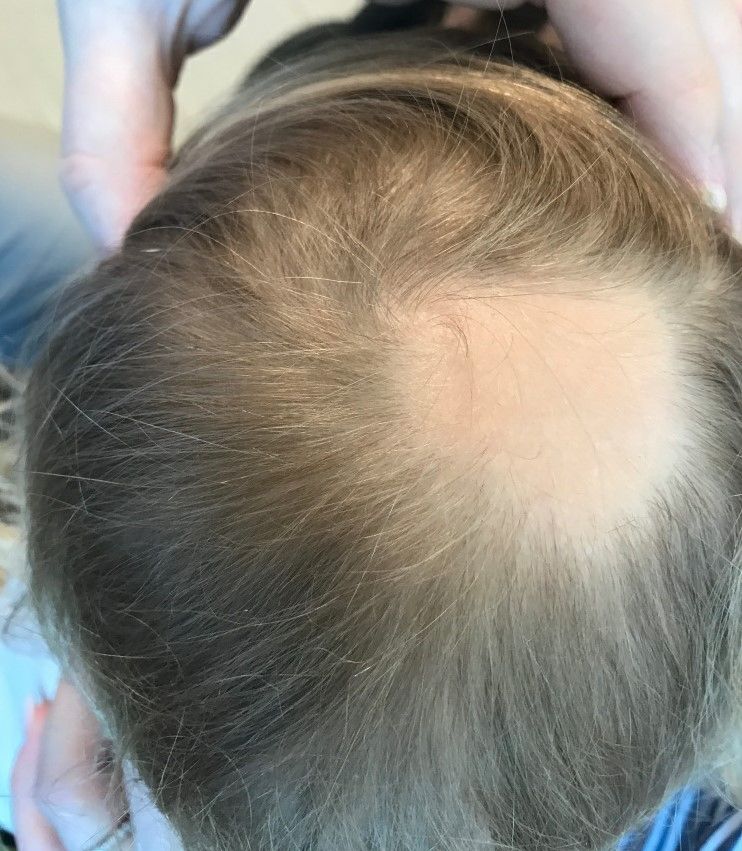
A toddler presents with patchy hair loss
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Examination findings of the scalp demonstrate a well-circumscribed alopecic patch on the vertex scalp without erythema or scale. Closer inspection of the patch with magnification or 'dermoscopy' reveals hair follicle ostia and hairs that are broader distally and narrower at their base. Nails and rest of the skin exam are unremarkable.
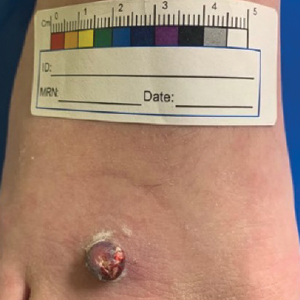
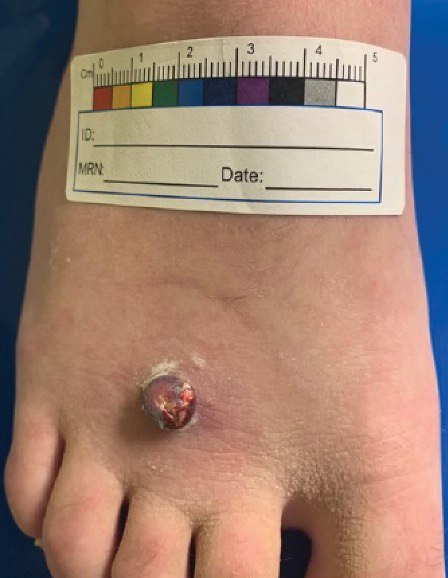
Erythematous Pedunculated Plaque on the Dorsal Aspect of the Foot
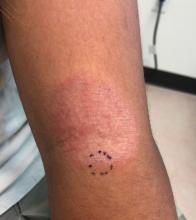
The Diagnosis: Molluscum Contagiosum
A tangential shave removal with electrocautery was performed. Histopathology demonstrated numerous eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (Figure), confirming a diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum (MC).
Molluscum contagiosum is a common poxvirus infection that is transmitted through fomites, contact, or self-inoculation.1 This infection most frequently occurs in school-aged children younger than 8 years1-3; peak incidence is 6 years of age.2,3 The worldwide estimated prevalence in children is 5.1% to 11.5%.1,3 In children cohabitating with others infected by MC, approximately 40% of households experienced a spread of infection; the risk of transmission is not associated with greater number of lesions.4 In adults, infection most commonly occurs in the setting of immunodeficiency or as a sexually transmitted infection in immunocompetent patients.3 Molluscum contagiosum infection classically presents as 1- to 3-mm, flesh- or white-colored, dome-shaped, smooth papules with central umbilication.1 Lesions often occur in clusters or lines, indicating local spread. The trunk, extremities, and face are areas that frequently are involved.2,3
Atypical presentations of MC infection can occur, as demonstrated by our case. Involvement of hair follicles by the infection can result in follicular induction.1,5 Secondary infection can mimic abscess formation.1 Inflamed MC lesions demonstrating the “beginning of the end” sign often are mistaken for primary infection, which is thought to be an inflammatory immune response to the virus.6 Lesions located on the eye or eyelid can present as unilateral conjunctivitis, conjunctival or corneal nodules, eyelid abscesses, or chalazions.1 Giant MC is a nodular variant of this infection measuring larger than 1 cm in size that can present similar to epidermoid cysts, condyloma acuminatum, or verruca vulgaris.1,7 Other reported mimicked conditions include basal cell carcinoma, trichoepithelioma, appendageal tumors, keratoacanthoma, foreign body granulomas, nevus sebaceous, or ecthyma.1,3 Molluscum contagiosum also has been reported to present as large ulcerative growths.8 In immunocompromised patients, deep fungal infection is another mimicker.1 Lesions on the plantar surfaces of the feet often are misdiagnosed as plantar verruca and present with pain during ambulation.9
The diagnosis of MC is clinical, with additional diagnostic tools reserved for more challenging situations.1 In cases with atypical presentations, dermoscopy may aid diagnosis through visualization of orifices and vascular patterns including crown, radial, and punctiform vessels.10 Biopsy or fine-needle aspiration also can be utilized as a diagnostic tool. Histopathology often reveals pathognomonic intracytoplasmic inclusions or Henderson-Paterson bodies.8,10 The appearance of MC can mimic other conditions that should be included in the differential diagnosis. Pyogenic granuloma often presents as a benign red papule that may grow rapidly and become pedunculated, sometimes with bleeding and crusting, though histology reveals groups of proliferating capillaries.11 More than half of amelanotic melanomas present in the papulonodular form as vascular or ulcerated nodules, and others may appear as erythematous macules. Diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma is made through histologic examination, which reveals atypical melanocytes in nests or cords, in conjunction with immunohistochemical stains such as S-100.12 Spitz nevi often appear as round, dome-shaped papules that most commonly are red, pink, or fleshcolored. They appear histologically similar to melanoma with nests of atypical melanocytes and nuclear atypia.13
A variety of treatment modalities can be used for MC including cantharidin, curettage, and cryotherapy.14 Imiquimod no longer is recommended due to a lack of demonstrated superiority over placebo in recent studies as well as its adverse effects.3 Topical retinoids have been recommended; however, their use frequently is limited by local irritation.3,14 Cantharidin is the most frequently utilized treatment by pediatric dermatologists. Most health care providers report subjective satisfaction with its results and efficacy, though some side effects may occur including discomfort and temporary changes in pigmentation. Treatment for MC is not required, as the condition is self-limiting.14 Therapy often is reserved for those with extensive disease, complications from lesions, cosmetic or psychological concerns, or genital involvement given the potential for sexual transmission.3 Time to resolution without treatment varies and is more prolonged in immunocompromised patients. Mean time to resolution in immunocompetent hosts has been reported as 13.3 months, but most infections are noted to clear within 2 to 4 years.1,4 Although resolution without treatment occurs, transmission to others and negative impact on quality of life (QOL) can occur and support the need for treatment. Greater impact on QOL was observed in females, those with more lesions, and patients with a longer duration of symptoms. Moderate impact on QOL was reported in 28% of patients (n=301), and severe effects were reported in 11%.4
In conclusion, MC is a common, benign, treatable cutaneous viral infection that often presents as small, flesh-colored papules in children. Its appearance can mimic a variety of other conditions. In cases with abnormal presentations, definitive diagnosis with pathology can be important to differentiate MC from more dangerous etiologies that may require further treatment.
- Brown J, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, et al. Childhood molluscum contagiosum. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:93-99. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2006.02737.x
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.035
- Robinson G, Townsend S, Jahnke MN. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on clinical presentation, diagnosis, risk, prevention, and treatment. Curr Derm Rep. 2020;9:83-92.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71053-9
- Davey J, Biswas A. Follicular induction in a case of molluscum contagiosum: possible link with secondary anetoderma-like changes? Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E19-E21. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31828bc7c7
- Butala N, Siegfried E, Weissler A. Molluscum BOTE sign: a predictor of imminent resolution. Pediatrics. 2013;131:E1650-E1653. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-2933
- Uzuncakmak TK, Kuru BC, Zemheri EI, et al. Isolated giant molluscum contagiosum mimicking epidermoid cyst. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:71-73. doi:10.5826/dpc.0603a15
- Singh S, Swain M, Shukla S, et al. An unusual presentation of giant molluscum contagiosum diagnosed on cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2018;46:794-796. doi:10.1002/dc.23964
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA. Plantar molluscum contagiosum: a case report of molluscum contagiosum occurring on the sole of the foot and a review of the world literature. Cutis. 2012;90:35-41.
- Megalla M, Bronsnick T, Noor O, et al. Dermoscopic, confocal microscopic, and histologic characteristics of an atypical presentation of molluscum contagiosum. Ann Clin Pathol. 2014;2:1038.
- Patrice SJ, Wiss K, Mulliken JB. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma): a clinicopathologic study of 178 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:267-276. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1991.tb00931.x
- Gong H-Z, Zheng H-Y, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2019;29:221-230. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571
- Casso EM, Grin-Jorgensen CM, Grant-Kels JM. Spitz nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27(6 pt 1):901-913. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70286-o
- Coloe J, Morrell DS. Cantharidin use among pediatric dermatologists in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:405-408.
The Diagnosis: Molluscum Contagiosum
A tangential shave removal with electrocautery was performed. Histopathology demonstrated numerous eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (Figure), confirming a diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum (MC).

Molluscum contagiosum is a common poxvirus infection that is transmitted through fomites, contact, or self-inoculation.1 This infection most frequently occurs in school-aged children younger than 8 years1-3; peak incidence is 6 years of age.2,3 The worldwide estimated prevalence in children is 5.1% to 11.5%.1,3 In children cohabitating with others infected by MC, approximately 40% of households experienced a spread of infection; the risk of transmission is not associated with greater number of lesions.4 In adults, infection most commonly occurs in the setting of immunodeficiency or as a sexually transmitted infection in immunocompetent patients.3 Molluscum contagiosum infection classically presents as 1- to 3-mm, flesh- or white-colored, dome-shaped, smooth papules with central umbilication.1 Lesions often occur in clusters or lines, indicating local spread. The trunk, extremities, and face are areas that frequently are involved.2,3
Atypical presentations of MC infection can occur, as demonstrated by our case. Involvement of hair follicles by the infection can result in follicular induction.1,5 Secondary infection can mimic abscess formation.1 Inflamed MC lesions demonstrating the “beginning of the end” sign often are mistaken for primary infection, which is thought to be an inflammatory immune response to the virus.6 Lesions located on the eye or eyelid can present as unilateral conjunctivitis, conjunctival or corneal nodules, eyelid abscesses, or chalazions.1 Giant MC is a nodular variant of this infection measuring larger than 1 cm in size that can present similar to epidermoid cysts, condyloma acuminatum, or verruca vulgaris.1,7 Other reported mimicked conditions include basal cell carcinoma, trichoepithelioma, appendageal tumors, keratoacanthoma, foreign body granulomas, nevus sebaceous, or ecthyma.1,3 Molluscum contagiosum also has been reported to present as large ulcerative growths.8 In immunocompromised patients, deep fungal infection is another mimicker.1 Lesions on the plantar surfaces of the feet often are misdiagnosed as plantar verruca and present with pain during ambulation.9
The diagnosis of MC is clinical, with additional diagnostic tools reserved for more challenging situations.1 In cases with atypical presentations, dermoscopy may aid diagnosis through visualization of orifices and vascular patterns including crown, radial, and punctiform vessels.10 Biopsy or fine-needle aspiration also can be utilized as a diagnostic tool. Histopathology often reveals pathognomonic intracytoplasmic inclusions or Henderson-Paterson bodies.8,10 The appearance of MC can mimic other conditions that should be included in the differential diagnosis. Pyogenic granuloma often presents as a benign red papule that may grow rapidly and become pedunculated, sometimes with bleeding and crusting, though histology reveals groups of proliferating capillaries.11 More than half of amelanotic melanomas present in the papulonodular form as vascular or ulcerated nodules, and others may appear as erythematous macules. Diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma is made through histologic examination, which reveals atypical melanocytes in nests or cords, in conjunction with immunohistochemical stains such as S-100.12 Spitz nevi often appear as round, dome-shaped papules that most commonly are red, pink, or fleshcolored. They appear histologically similar to melanoma with nests of atypical melanocytes and nuclear atypia.13
A variety of treatment modalities can be used for MC including cantharidin, curettage, and cryotherapy.14 Imiquimod no longer is recommended due to a lack of demonstrated superiority over placebo in recent studies as well as its adverse effects.3 Topical retinoids have been recommended; however, their use frequently is limited by local irritation.3,14 Cantharidin is the most frequently utilized treatment by pediatric dermatologists. Most health care providers report subjective satisfaction with its results and efficacy, though some side effects may occur including discomfort and temporary changes in pigmentation. Treatment for MC is not required, as the condition is self-limiting.14 Therapy often is reserved for those with extensive disease, complications from lesions, cosmetic or psychological concerns, or genital involvement given the potential for sexual transmission.3 Time to resolution without treatment varies and is more prolonged in immunocompromised patients. Mean time to resolution in immunocompetent hosts has been reported as 13.3 months, but most infections are noted to clear within 2 to 4 years.1,4 Although resolution without treatment occurs, transmission to others and negative impact on quality of life (QOL) can occur and support the need for treatment. Greater impact on QOL was observed in females, those with more lesions, and patients with a longer duration of symptoms. Moderate impact on QOL was reported in 28% of patients (n=301), and severe effects were reported in 11%.4
In conclusion, MC is a common, benign, treatable cutaneous viral infection that often presents as small, flesh-colored papules in children. Its appearance can mimic a variety of other conditions. In cases with abnormal presentations, definitive diagnosis with pathology can be important to differentiate MC from more dangerous etiologies that may require further treatment.
The Diagnosis: Molluscum Contagiosum
A tangential shave removal with electrocautery was performed. Histopathology demonstrated numerous eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (Figure), confirming a diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum (MC).

Molluscum contagiosum is a common poxvirus infection that is transmitted through fomites, contact, or self-inoculation.1 This infection most frequently occurs in school-aged children younger than 8 years1-3; peak incidence is 6 years of age.2,3 The worldwide estimated prevalence in children is 5.1% to 11.5%.1,3 In children cohabitating with others infected by MC, approximately 40% of households experienced a spread of infection; the risk of transmission is not associated with greater number of lesions.4 In adults, infection most commonly occurs in the setting of immunodeficiency or as a sexually transmitted infection in immunocompetent patients.3 Molluscum contagiosum infection classically presents as 1- to 3-mm, flesh- or white-colored, dome-shaped, smooth papules with central umbilication.1 Lesions often occur in clusters or lines, indicating local spread. The trunk, extremities, and face are areas that frequently are involved.2,3
Atypical presentations of MC infection can occur, as demonstrated by our case. Involvement of hair follicles by the infection can result in follicular induction.1,5 Secondary infection can mimic abscess formation.1 Inflamed MC lesions demonstrating the “beginning of the end” sign often are mistaken for primary infection, which is thought to be an inflammatory immune response to the virus.6 Lesions located on the eye or eyelid can present as unilateral conjunctivitis, conjunctival or corneal nodules, eyelid abscesses, or chalazions.1 Giant MC is a nodular variant of this infection measuring larger than 1 cm in size that can present similar to epidermoid cysts, condyloma acuminatum, or verruca vulgaris.1,7 Other reported mimicked conditions include basal cell carcinoma, trichoepithelioma, appendageal tumors, keratoacanthoma, foreign body granulomas, nevus sebaceous, or ecthyma.1,3 Molluscum contagiosum also has been reported to present as large ulcerative growths.8 In immunocompromised patients, deep fungal infection is another mimicker.1 Lesions on the plantar surfaces of the feet often are misdiagnosed as plantar verruca and present with pain during ambulation.9
The diagnosis of MC is clinical, with additional diagnostic tools reserved for more challenging situations.1 In cases with atypical presentations, dermoscopy may aid diagnosis through visualization of orifices and vascular patterns including crown, radial, and punctiform vessels.10 Biopsy or fine-needle aspiration also can be utilized as a diagnostic tool. Histopathology often reveals pathognomonic intracytoplasmic inclusions or Henderson-Paterson bodies.8,10 The appearance of MC can mimic other conditions that should be included in the differential diagnosis. Pyogenic granuloma often presents as a benign red papule that may grow rapidly and become pedunculated, sometimes with bleeding and crusting, though histology reveals groups of proliferating capillaries.11 More than half of amelanotic melanomas present in the papulonodular form as vascular or ulcerated nodules, and others may appear as erythematous macules. Diagnosis of amelanotic melanoma is made through histologic examination, which reveals atypical melanocytes in nests or cords, in conjunction with immunohistochemical stains such as S-100.12 Spitz nevi often appear as round, dome-shaped papules that most commonly are red, pink, or fleshcolored. They appear histologically similar to melanoma with nests of atypical melanocytes and nuclear atypia.13
A variety of treatment modalities can be used for MC including cantharidin, curettage, and cryotherapy.14 Imiquimod no longer is recommended due to a lack of demonstrated superiority over placebo in recent studies as well as its adverse effects.3 Topical retinoids have been recommended; however, their use frequently is limited by local irritation.3,14 Cantharidin is the most frequently utilized treatment by pediatric dermatologists. Most health care providers report subjective satisfaction with its results and efficacy, though some side effects may occur including discomfort and temporary changes in pigmentation. Treatment for MC is not required, as the condition is self-limiting.14 Therapy often is reserved for those with extensive disease, complications from lesions, cosmetic or psychological concerns, or genital involvement given the potential for sexual transmission.3 Time to resolution without treatment varies and is more prolonged in immunocompromised patients. Mean time to resolution in immunocompetent hosts has been reported as 13.3 months, but most infections are noted to clear within 2 to 4 years.1,4 Although resolution without treatment occurs, transmission to others and negative impact on quality of life (QOL) can occur and support the need for treatment. Greater impact on QOL was observed in females, those with more lesions, and patients with a longer duration of symptoms. Moderate impact on QOL was reported in 28% of patients (n=301), and severe effects were reported in 11%.4
In conclusion, MC is a common, benign, treatable cutaneous viral infection that often presents as small, flesh-colored papules in children. Its appearance can mimic a variety of other conditions. In cases with abnormal presentations, definitive diagnosis with pathology can be important to differentiate MC from more dangerous etiologies that may require further treatment.
- Brown J, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, et al. Childhood molluscum contagiosum. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:93-99. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2006.02737.x
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.035
- Robinson G, Townsend S, Jahnke MN. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on clinical presentation, diagnosis, risk, prevention, and treatment. Curr Derm Rep. 2020;9:83-92.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71053-9
- Davey J, Biswas A. Follicular induction in a case of molluscum contagiosum: possible link with secondary anetoderma-like changes? Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E19-E21. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31828bc7c7
- Butala N, Siegfried E, Weissler A. Molluscum BOTE sign: a predictor of imminent resolution. Pediatrics. 2013;131:E1650-E1653. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-2933
- Uzuncakmak TK, Kuru BC, Zemheri EI, et al. Isolated giant molluscum contagiosum mimicking epidermoid cyst. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:71-73. doi:10.5826/dpc.0603a15
- Singh S, Swain M, Shukla S, et al. An unusual presentation of giant molluscum contagiosum diagnosed on cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2018;46:794-796. doi:10.1002/dc.23964
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA. Plantar molluscum contagiosum: a case report of molluscum contagiosum occurring on the sole of the foot and a review of the world literature. Cutis. 2012;90:35-41.
- Megalla M, Bronsnick T, Noor O, et al. Dermoscopic, confocal microscopic, and histologic characteristics of an atypical presentation of molluscum contagiosum. Ann Clin Pathol. 2014;2:1038.
- Patrice SJ, Wiss K, Mulliken JB. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma): a clinicopathologic study of 178 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:267-276. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1991.tb00931.x
- Gong H-Z, Zheng H-Y, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2019;29:221-230. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571
- Casso EM, Grin-Jorgensen CM, Grant-Kels JM. Spitz nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27(6 pt 1):901-913. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70286-o
- Coloe J, Morrell DS. Cantharidin use among pediatric dermatologists in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:405-408.
- Brown J, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, et al. Childhood molluscum contagiosum. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:93-99. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2006.02737.x
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.035
- Robinson G, Townsend S, Jahnke MN. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on clinical presentation, diagnosis, risk, prevention, and treatment. Curr Derm Rep. 2020;9:83-92.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)71053-9
- Davey J, Biswas A. Follicular induction in a case of molluscum contagiosum: possible link with secondary anetoderma-like changes? Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E19-E21. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31828bc7c7
- Butala N, Siegfried E, Weissler A. Molluscum BOTE sign: a predictor of imminent resolution. Pediatrics. 2013;131:E1650-E1653. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-2933
- Uzuncakmak TK, Kuru BC, Zemheri EI, et al. Isolated giant molluscum contagiosum mimicking epidermoid cyst. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:71-73. doi:10.5826/dpc.0603a15
- Singh S, Swain M, Shukla S, et al. An unusual presentation of giant molluscum contagiosum diagnosed on cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2018;46:794-796. doi:10.1002/dc.23964
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA. Plantar molluscum contagiosum: a case report of molluscum contagiosum occurring on the sole of the foot and a review of the world literature. Cutis. 2012;90:35-41.
- Megalla M, Bronsnick T, Noor O, et al. Dermoscopic, confocal microscopic, and histologic characteristics of an atypical presentation of molluscum contagiosum. Ann Clin Pathol. 2014;2:1038.
- Patrice SJ, Wiss K, Mulliken JB. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma): a clinicopathologic study of 178 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:267-276. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1991.tb00931.x
- Gong H-Z, Zheng H-Y, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2019;29:221-230. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571
- Casso EM, Grin-Jorgensen CM, Grant-Kels JM. Spitz nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27(6 pt 1):901-913. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(92)70286-o
- Coloe J, Morrell DS. Cantharidin use among pediatric dermatologists in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:405-408.
A 13-year-old adolescent girl presented for evaluation of a lesion on the dorsal aspect of the right foot of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of acne vulgaris and seasonal allergic rhinitis. She previously had noticed a persistent, small, flesh-colored bump of unknown chronicity in the same location, which had been diagnosed as a skin tag at an outside clinic. She denied any prior treatment in this area. Approximately a week prior to presentation, the lesion became painful, larger, and darkened in color before draining yellowish fluid. Due to concern for superinfection, the patient was prescribed cephalexin by her pediatrician. Dermatologic examination revealed a 1-cm, violaceous, pedunculated plaque with hemorrhagic crust on the dorsal aspect of the right foot with surrounding erythema and tenderness.
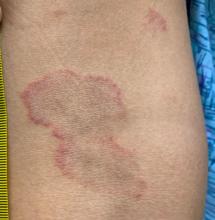
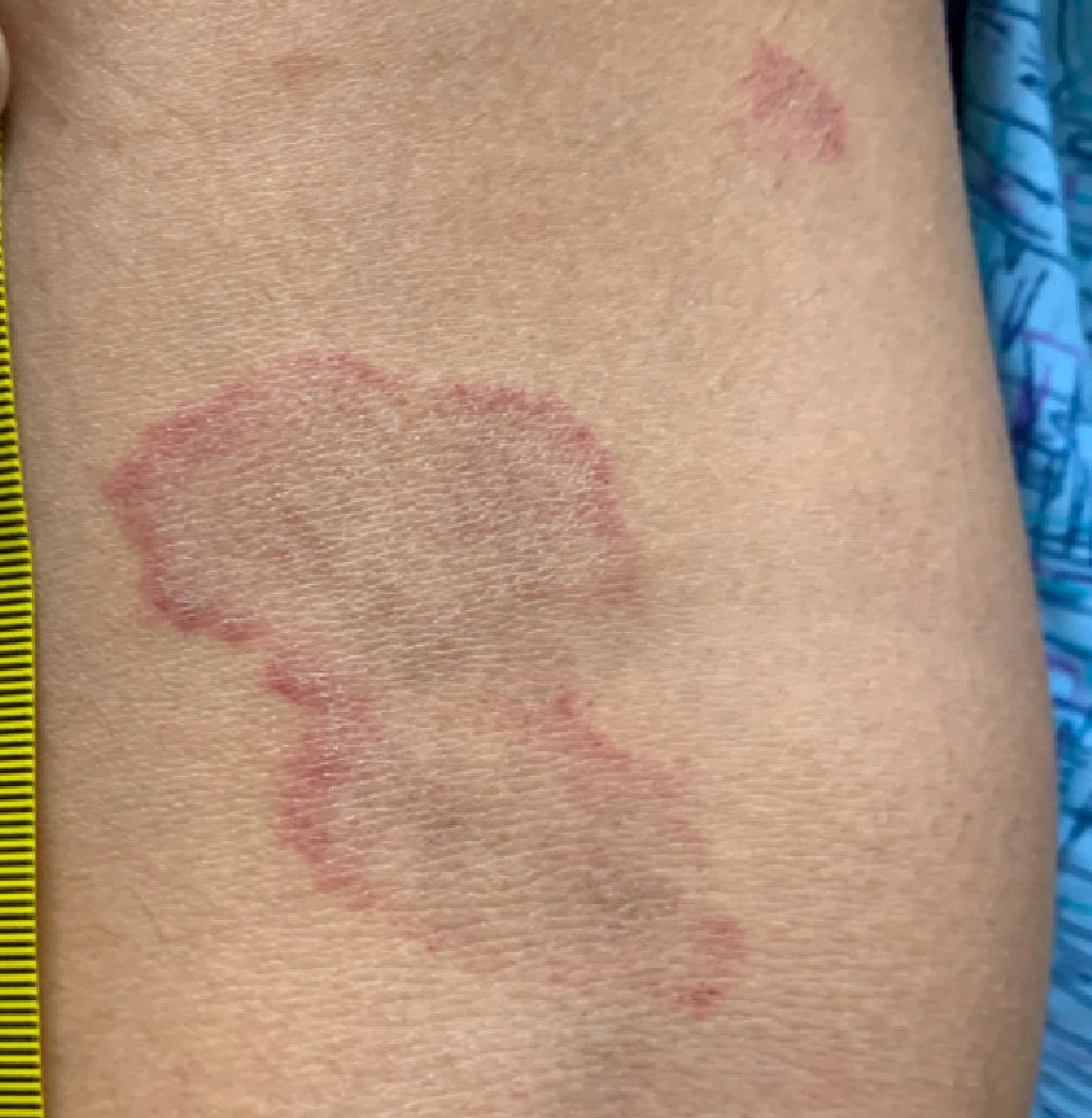
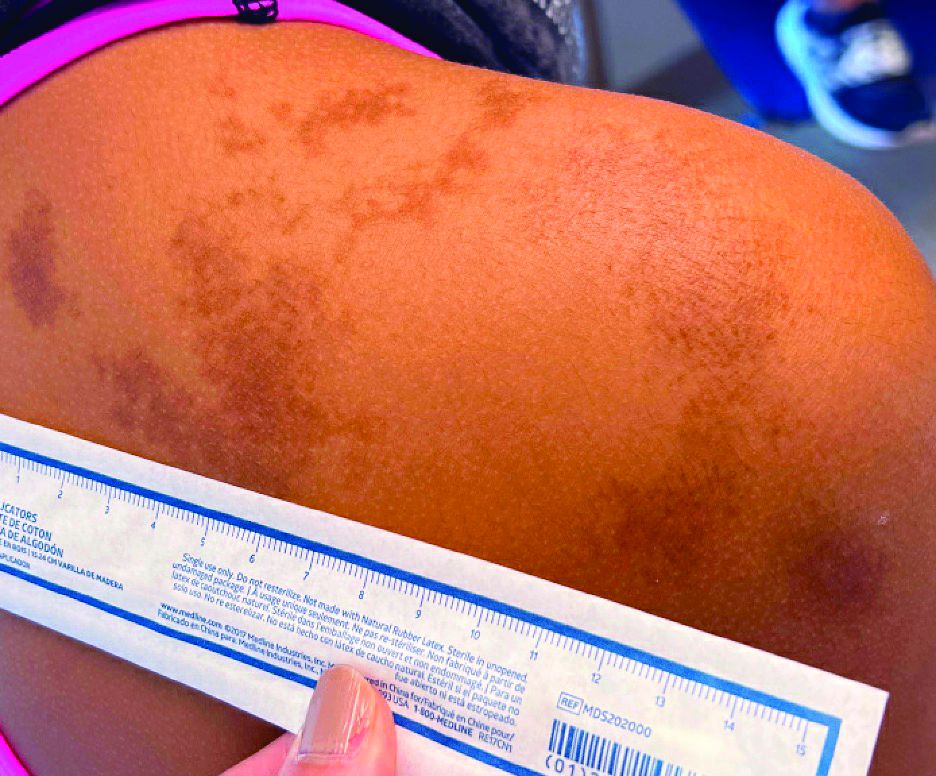
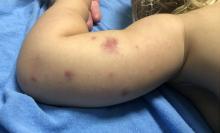
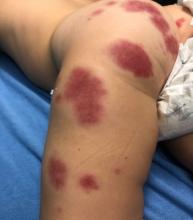
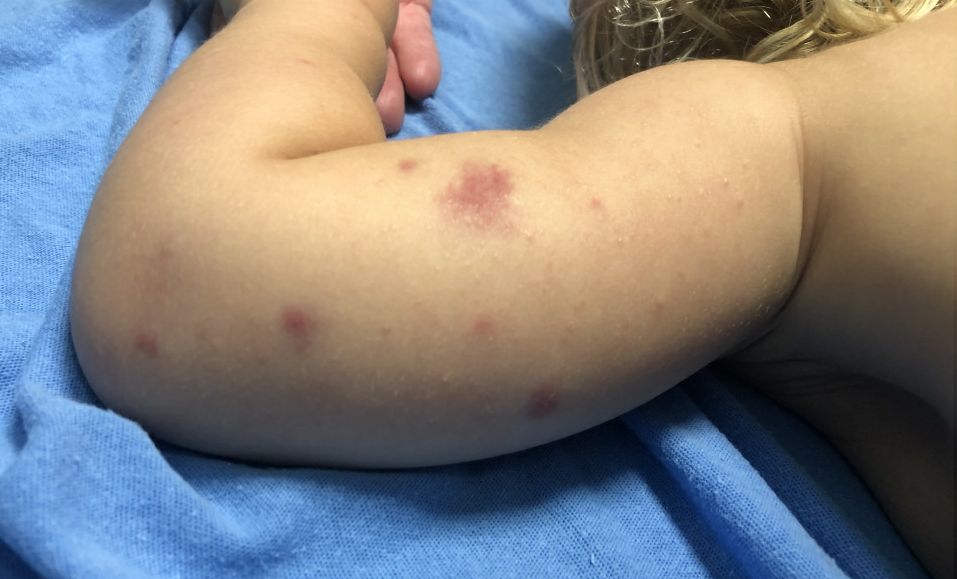
Adolescent female with rash on the arms and posterior legs
Erythema annulare centrifugum
A thorough body examination failed to reveal any other rashes or lesions suggestive of a fungal infection. A blood count and urinalysis were within normal limits. She had no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly. A potassium hydroxide analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements. Punch biopsy of the skin on the left arm revealed focal intermittent parakeratosis, mildly acanthotic and spongiotic epidermis, and a tight superficial perivascular chronic dermatitis consisting of lymphocytes and histiocytes (Figures). Given these findings, a diagnosis of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) was rendered.
EAC is a rare, reactive skin rash characterized by redness (erythema) and ring-shaped lesions (annulare) that slowly spread from the center (centrifugum). The lesions present with a characteristic trailing scale on the inner border of the erythematous ring. Lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and commonly involve the trunk, buttocks, hips, and upper legs. It is important to note that its duration is highly variable, ranging from weeks to decades, with most cases persisting for 9 months. EAC typically affects young or middle-aged adults but can occur at any age.
Although the etiology of EAC is unknown, it is believed to be a hypersensitivity reaction to a foreign antigen. Cutaneous fungal infections are commonly reported as triggers as well as other viral infections, medications, malignancy, underlying systemic disease, and certain foods. Treatment depends on the underlying condition and removing the implicated agent. However, most cases of EAC are idiopathic and self-limiting. It is possible that our patient’s prior history of tinea capitis could have triggered the skin lesions suggestive of EAC, but interestingly, these lesions did not go away after the fungal infection was cleared and have continued to recur. For patients with refractory lesions or treatment of patients without an identifiable cause, the use of oral antimicrobials has been proposed. Medications such as azithromycin, erythromycin, fluconazole, and metronidazole have been reported to be helpful in some patients with refractory EAC. Our patient wanted to continue topical treatment with betamethasone as needed and may consider antimicrobial therapy if the lesions continue to recur.
Tinea corporis refers to a superficial fungal infection of the skin. It may present as one or more asymmetrical, annular, pruritic plaques with a raised scaly leading edge rather than the trailing scale seen with EAC. Diagnosis is made by KOH examination of skin scrapings. Common risk factors include close contact with an infected person or animal, warm, moist environments, sharing personal items, and prolonged use of systemic corticosteroids. Our patient’s KOH analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements.
Erythema marginatum is a rare skin rash commonly seen with acute rheumatic fever secondary to streptococcal infection. It presents as annular erythematous lesions on the trunk and proximal extremities that are exacerbated by heat. It is often associated with active carditis related to rheumatic fever. This self-limited rash usually resolves in 2-3 days. Our patient was asymptomatic without involvement of other organs.
Like EAC, granuloma annulare is a benign chronic skin condition that presents with ring-shaped lesions. Its etiology is unknown, and lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic. Localized granuloma annulare typically presents as reddish-brown papules or plaques on the fingers, hands, elbows, dorsal feet, or ankles. The distinguishing feature of granuloma annulare from other annular lesions is its absence of scale.
Urticaria multiforme is an allergic hypersensitivity reaction commonly linked to viral infections, medications, and immunizations. Clinical features include blanchable annular/polycyclic lesions with a central purplish or dusky hue. Diagnostic pearls include the presence of pruritus, dermatographism, and individual lesions that resolve within 24 hours, all of which were not found in our patient’s case.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Matiz have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Paller A and Mancini AJ. Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A Textbook of Skin Disorders of Childhood and Adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
2. McDaniel B and Cook C. “Erythema annulare centrifugum” 2021 Aug 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan. PMID: 29494101.
3. Leung AK e al. Drugs Context. 2020 Jul 20;9:5-6.
4. Majmundar VD and Nagalli S. “Erythema marginatum” 2022 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
5. Piette EW and Rosenbach M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):467-79.
6. Barros M et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Jan 28;14(1):e241011.
Erythema annulare centrifugum
A thorough body examination failed to reveal any other rashes or lesions suggestive of a fungal infection. A blood count and urinalysis were within normal limits. She had no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly. A potassium hydroxide analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements. Punch biopsy of the skin on the left arm revealed focal intermittent parakeratosis, mildly acanthotic and spongiotic epidermis, and a tight superficial perivascular chronic dermatitis consisting of lymphocytes and histiocytes (Figures). Given these findings, a diagnosis of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) was rendered.
EAC is a rare, reactive skin rash characterized by redness (erythema) and ring-shaped lesions (annulare) that slowly spread from the center (centrifugum). The lesions present with a characteristic trailing scale on the inner border of the erythematous ring. Lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and commonly involve the trunk, buttocks, hips, and upper legs. It is important to note that its duration is highly variable, ranging from weeks to decades, with most cases persisting for 9 months. EAC typically affects young or middle-aged adults but can occur at any age.
Although the etiology of EAC is unknown, it is believed to be a hypersensitivity reaction to a foreign antigen. Cutaneous fungal infections are commonly reported as triggers as well as other viral infections, medications, malignancy, underlying systemic disease, and certain foods. Treatment depends on the underlying condition and removing the implicated agent. However, most cases of EAC are idiopathic and self-limiting. It is possible that our patient’s prior history of tinea capitis could have triggered the skin lesions suggestive of EAC, but interestingly, these lesions did not go away after the fungal infection was cleared and have continued to recur. For patients with refractory lesions or treatment of patients without an identifiable cause, the use of oral antimicrobials has been proposed. Medications such as azithromycin, erythromycin, fluconazole, and metronidazole have been reported to be helpful in some patients with refractory EAC. Our patient wanted to continue topical treatment with betamethasone as needed and may consider antimicrobial therapy if the lesions continue to recur.
Tinea corporis refers to a superficial fungal infection of the skin. It may present as one or more asymmetrical, annular, pruritic plaques with a raised scaly leading edge rather than the trailing scale seen with EAC. Diagnosis is made by KOH examination of skin scrapings. Common risk factors include close contact with an infected person or animal, warm, moist environments, sharing personal items, and prolonged use of systemic corticosteroids. Our patient’s KOH analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements.
Erythema marginatum is a rare skin rash commonly seen with acute rheumatic fever secondary to streptococcal infection. It presents as annular erythematous lesions on the trunk and proximal extremities that are exacerbated by heat. It is often associated with active carditis related to rheumatic fever. This self-limited rash usually resolves in 2-3 days. Our patient was asymptomatic without involvement of other organs.
Like EAC, granuloma annulare is a benign chronic skin condition that presents with ring-shaped lesions. Its etiology is unknown, and lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic. Localized granuloma annulare typically presents as reddish-brown papules or plaques on the fingers, hands, elbows, dorsal feet, or ankles. The distinguishing feature of granuloma annulare from other annular lesions is its absence of scale.
Urticaria multiforme is an allergic hypersensitivity reaction commonly linked to viral infections, medications, and immunizations. Clinical features include blanchable annular/polycyclic lesions with a central purplish or dusky hue. Diagnostic pearls include the presence of pruritus, dermatographism, and individual lesions that resolve within 24 hours, all of which were not found in our patient’s case.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Matiz have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Paller A and Mancini AJ. Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A Textbook of Skin Disorders of Childhood and Adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
2. McDaniel B and Cook C. “Erythema annulare centrifugum” 2021 Aug 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan. PMID: 29494101.
3. Leung AK e al. Drugs Context. 2020 Jul 20;9:5-6.
4. Majmundar VD and Nagalli S. “Erythema marginatum” 2022 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
5. Piette EW and Rosenbach M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):467-79.
6. Barros M et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Jan 28;14(1):e241011.
Erythema annulare centrifugum
A thorough body examination failed to reveal any other rashes or lesions suggestive of a fungal infection. A blood count and urinalysis were within normal limits. She had no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly. A potassium hydroxide analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements. Punch biopsy of the skin on the left arm revealed focal intermittent parakeratosis, mildly acanthotic and spongiotic epidermis, and a tight superficial perivascular chronic dermatitis consisting of lymphocytes and histiocytes (Figures). Given these findings, a diagnosis of erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) was rendered.
EAC is a rare, reactive skin rash characterized by redness (erythema) and ring-shaped lesions (annulare) that slowly spread from the center (centrifugum). The lesions present with a characteristic trailing scale on the inner border of the erythematous ring. Lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic and commonly involve the trunk, buttocks, hips, and upper legs. It is important to note that its duration is highly variable, ranging from weeks to decades, with most cases persisting for 9 months. EAC typically affects young or middle-aged adults but can occur at any age.
Although the etiology of EAC is unknown, it is believed to be a hypersensitivity reaction to a foreign antigen. Cutaneous fungal infections are commonly reported as triggers as well as other viral infections, medications, malignancy, underlying systemic disease, and certain foods. Treatment depends on the underlying condition and removing the implicated agent. However, most cases of EAC are idiopathic and self-limiting. It is possible that our patient’s prior history of tinea capitis could have triggered the skin lesions suggestive of EAC, but interestingly, these lesions did not go away after the fungal infection was cleared and have continued to recur. For patients with refractory lesions or treatment of patients without an identifiable cause, the use of oral antimicrobials has been proposed. Medications such as azithromycin, erythromycin, fluconazole, and metronidazole have been reported to be helpful in some patients with refractory EAC. Our patient wanted to continue topical treatment with betamethasone as needed and may consider antimicrobial therapy if the lesions continue to recur.
Tinea corporis refers to a superficial fungal infection of the skin. It may present as one or more asymmetrical, annular, pruritic plaques with a raised scaly leading edge rather than the trailing scale seen with EAC. Diagnosis is made by KOH examination of skin scrapings. Common risk factors include close contact with an infected person or animal, warm, moist environments, sharing personal items, and prolonged use of systemic corticosteroids. Our patient’s KOH analysis of skin scrapings was negative for fungal elements.
Erythema marginatum is a rare skin rash commonly seen with acute rheumatic fever secondary to streptococcal infection. It presents as annular erythematous lesions on the trunk and proximal extremities that are exacerbated by heat. It is often associated with active carditis related to rheumatic fever. This self-limited rash usually resolves in 2-3 days. Our patient was asymptomatic without involvement of other organs.
Like EAC, granuloma annulare is a benign chronic skin condition that presents with ring-shaped lesions. Its etiology is unknown, and lesions may be asymptomatic or mildly pruritic. Localized granuloma annulare typically presents as reddish-brown papules or plaques on the fingers, hands, elbows, dorsal feet, or ankles. The distinguishing feature of granuloma annulare from other annular lesions is its absence of scale.
Urticaria multiforme is an allergic hypersensitivity reaction commonly linked to viral infections, medications, and immunizations. Clinical features include blanchable annular/polycyclic lesions with a central purplish or dusky hue. Diagnostic pearls include the presence of pruritus, dermatographism, and individual lesions that resolve within 24 hours, all of which were not found in our patient’s case.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Matiz have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Paller A and Mancini AJ. Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A Textbook of Skin Disorders of Childhood and Adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
2. McDaniel B and Cook C. “Erythema annulare centrifugum” 2021 Aug 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan. PMID: 29494101.
3. Leung AK e al. Drugs Context. 2020 Jul 20;9:5-6.
4. Majmundar VD and Nagalli S. “Erythema marginatum” 2022 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
5. Piette EW and Rosenbach M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):467-79.
6. Barros M et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Jan 28;14(1):e241011.
A review of systems was noncontributory. She was not taking any other medications or vitamin supplements. There were no pets at home and no other affected family members. Physical exam was notable for scattered, pink, annular plaques with central clearing, faint brownish pigmentation, and fine scale.
A 7-year-old with red bumps on her nose
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
The finding of individual, 1- to 4-mm firm, red papules depicted in the image are consistent with facial angiofibromas, which are most commonly seen in pediatric patients as a manifestation of tuberous sclerosis (TSC). Angiofibromas, previously called adenoma sebaceum, a misnomer, are seen in TSC as smooth papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques that typically involve the malar region of the face. These lesions usually develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne. The number of lesions tend to increase with age, though there is no significant risk of malignant transformation. Ultraviolet-induced DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of facial angiofibromas, so sun protection is called for.1 Patients may seek treatment to minimize deformity and the stigma of angiofibromas. Recently, the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor sirolimus (rapamycin) topical gel received Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of facial angiofibromas associated with TSC in patients age at least 6 years.2
The presence of angiofibromas should prompt consideration of TSC and as such, a thorough family history, medical history, and full-body skin examination. TSC is a rare autosomal-dominant genetic disorder, caused by a pathogenic variant in either the TSC1 or TSC2 gene. This neurocutaneous disorder is characterized by the development of multiple benign hamartomas across many organ systems including the brain, eyes, heart, lung, liver, kidney, and skin. The phenotypic expression of TSC is highly variable. Besides angiofibromas, some other characteristic dermatological findings in TSC include periungual fibromas, hypopigmented macules usually elliptical in shape (known as ash-leaf spots), and irregularly shaped elevated flesh-colored fibrous tissue most often found over the lower back (known as shagreen patches).3
What is on the differential?
Agminated spitz nevi refers to multiple spitz nevi in a localized area. Spitz nevi present as a well-circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papules, most commonly located on the face or lower extremities.4 The finding of agminated spitz nevi is very rare and less likely for this patient given the concomitant skin findings of dental pitting, renal cysts, and cortical tubers.
Juvenile xanthogranulomas are benign,proliferations of histiocytic cells that present as reddish or yellowish-to-brown papules, plaques, or nodules that typically develop in young children around the age of 1. With time, juvenile xanthogranulomas may flatten and become more yellow.
Basal cell carcinomas present as dome-shaped lesions with centralized erosions on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are remarkably uncommon in children but are occasionally seen in basal cell nevus syndrome (also known as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or Gorlin syndrome). Affected patients may have other findings such as developmental anomalies, bifid ribs, palmar and plantar pitting, odontogenic keratocysts, and/or medulloblastomas.5
Flat warts commonly occur in children and occur by direct skin contact with human papillomavirus. Of the various types of warts, flat warts are smaller and tend to be smooth on top. The diagnosis of cutaneous warts is based on clinical appearance, showing thrombosed capillaries underneath the overlying hyperkeratotic debris. Our patient’s history of having a common wart on her hands raises suspicion for inoculation onto her face, but the morphology, distribution, and lack of response to tretinoin makes this diagnosis much less likely.
Disease workup and course
Our patient’s physical exam revealed dental pits but no evidence of hypopigmented macules, shagreen patches, or periungual lesions. Ultrasound of the kidney displayed renal cortical cysts and brain MRI showed cortical tubers, confirming extracutaneous TSC involvement. Over time, our patient developed angiofibromas on the forehead and was ultimately started on topical sirolimus, which led to marked improvement within months.
Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, also in San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. They have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Tyburczy ME et al. Hum Molec Genet. 2014;23(8):2023-9.
2. Food & Drug Administration. New drug application (NDA) approval for Hyftor (sirolimus topical gel). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2022/213478Orig1s000ltr.pdf.
3. Webb DW et al. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135(1):1-5.
4. Ricci F et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27(1):59-62.
5. Evans DG and Farndon PA. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, in “GeneReviews®.” Seattle: University of Washington, 2002.
A 7-year-old female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks.
A 7-year-old, previously healthy female presented with a bump on the bridge of her nose that was present for 10 months, with subsequent development of multiple papules on the nose and cheeks. She has no significant medical history aside from a wart on her hand that was recently frozen with liquid nitrogen and resolved. She denied pruritus, bumps, or skin changes elsewhere on the body. The patient was prescribed tretinoin 0.1% cream applied nightly for several months without response.
Blistering Lesions in a Newborn
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa
Our patient was found to have epidermolysis bullosa (EB), a rare genetic disease in which the superficial layers of the skin separate to form vesicles or bullae due to a mutation in the keratin 14 gene, KRT14. Separation of the skin occurs due to cleavage of various proteins that connect the epidermis to the dermis. A genetic mutation in KRT14, one of the more common genetic mutations associated with EB, results in cleavage at the basal epidermal protein keratin 14. The skin of individuals with EB typically is fragile and cannot tolerate friction or manipulation due to the risk for new bullae formation.1 Epidermolysis bullosa is rare, affecting approximately 20 children per 1 million births in the United States, and is not commonly seen by most general adult dermatologists.2
In our patient, the differential diagnoses included staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), herpes simplex virus (HSV), and bullous pemphigoid (BP). Symptoms of SSSS can range from mild and localized to full-body exfoliation of the skin. Although SSSS can resemble other bullous disorders, its etiology arises from the Staphylococcus exotoxin targeting desmoglein in the stratum granulosum— the layer of the epidermis between the stratum corneum and stratum spinosum.3 Lesions start on the face, neck, and body folds, which was consistent with our patient’s presentation. However, bullae continued to develop in our patient despite antibiotic therapy, which reduced the likelihood of SSSS. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis develops rapidly and often involves the mucosa, which our patient initially did not have. In children, SJS/TEN can develop secondary to infection, whereas in adults it more commonly is associated with medication administration.4 Although the mother tested negative for HSV, the infant was started on acyclovir, which ultimately was discontinued due to low clinical suspicion. The clinical presentation of HSV (ie, clustered vesicles) was not consistent with our patient’s presentation. Bullous pemphigoid is a subepithelial blistering disease seen in older adults. Tense, fluidfilled blisters primarily are seen on the trunk and flexures. Although infantile BP can occur, it usually does not present in the neonatal period but rather at approximately 3 to 5 months of age.5
High clinical suspicion for EB due to the common characteristics of bullae location and formation following skin manipulation led to genetic testing in our patient. Mild forms of EB simplex typically appear on the upper and lower extremities with sparing of the trunk. In more severe cases of EB simplex, truncal and mucosal involvement may occur.6 In our case, the infant had a classic distribution of arm and leg blisters with truncal sparing. Epidermolysis bullosa may not be diagnosed in the neonatal period because of its similarities to other more common diseases, such as HSV or bullous impetigo, or other genetic blistering diseases, such as epidermolytic ichthyosis and incontinentia pigmenti.6
Epidermolysis bullosa can be inherited in an autosomal-dominant or autosomal-recessive fashion or with de novo mutations and is classified based on the location of cleavage in the skin. The 4 classical subtypes— simplex, junctional, dystrophic, and Kindler—have now been further subclassified. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (intraepidermal split) is now separated into basal and suprabasal, with further subclassification including the distribution of blisters (generalized or localized) and the severity of cutaneous or extracutaneous involvement.7
In our case, the infant was found to have intraepidermal EB (simplex) due to a KRT14 mutation (missense mutation).6 KRT14 (17q21.2) and KRT5 (12q13.3) are the 2 most common mutations causing cleavage at the basal intraepidermal layer. Thickening of the palms, soles, and nails can be seen; however, blisters heal well without scarring, as seen in our patient. Junctional EB due to cleavage at the intralamina lucida often involves mutations in laminin 332, plectin, and α6β4 integrin. Infants with junctional EB often die from severe infection, dehydration, or malnutrition due to mucosal involvement. Dystrophic EB occurs due to a collagen VII mutation in the dermis, leading to blisters at the sublamina densa and more severe symptoms in the recessive form.7
Newborn management for infants with EB differs from normal newborn care due to increased skin fragility with physical manipulation. Minimal skin manipulation and proper wound care are essential from the first day of life. For new bullae formation, bullae should be ruptured with a needle at the base of the blister and drained. The remaining skin overlying the wound should remain in place as a natural wound barrier. Patients with EB should not have tape or adhesive bandages applied directly to the skin. Instead, nonadhesive dressings can be placed directly on wounds and covered in soft wraps circumferentially. Dressings can be taped together without involving the skin. The cost for supplies for families to manage bullae is expensive. Fortunately, there are resources available for supplies and support for families, including the EB Research Partnership (https://www.ebresearch.org/) and DEBRA of America (https://www.debra.org/).
Currently, there is no cure for EB. Current treatment involves wound care, prevention, and symptomatic relief. Prevention includes avoiding activities that may result in increased friction of the skin and ensuring careful manipulation. Children with EB may have pain or itching from their blisters, which can be treated with oral acetaminophen or ibuprofen and diphenhydramine, respectively. Other complications of EB include anemia, dehydration, constipation, infection, and malnutrition. In more severe forms of EB, complications including eye problems, mucosal strictures, and skin cancer may occur.8 Future treatment directions include gene therapy, bone marrow transplantation, protein replacement therapies, and cell-based therapies. Prognosis for infants with EB due to KRT14 mutation is good, as it is a milder subtype of EB with a full life expectancy and improvement of blistering skin with age. The most at-risk time for early death is during infancy due to increased risk for infection.8 In this case, our patient showed full healing with no scar formation, which suggested a reassuring prognosis.
- Fine JD, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Eady RAJ, et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:1103-1126.
- Wolff K, Johnson RA, Saavedra AP, et al. Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2017:94-99.
- Ross A, Shoff HW. Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020:1-20.
- Alerhand S, Cassella C, Koyfman A. Steven-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in the pediatric population. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016;32:472-476.
- Schwieger-Briel A, Moellmann C, Mattulat B, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in infants: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:185.
- Gonzalez ME. Evaluation and treatment of the newborn with epidermolysis bullosa. Semin Perinatol. 2013;37:32-39.
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627.
- Watkins J. Diagnosis, treatment and management of epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Nurs. 2016;25:428-431.
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa
Our patient was found to have epidermolysis bullosa (EB), a rare genetic disease in which the superficial layers of the skin separate to form vesicles or bullae due to a mutation in the keratin 14 gene, KRT14. Separation of the skin occurs due to cleavage of various proteins that connect the epidermis to the dermis. A genetic mutation in KRT14, one of the more common genetic mutations associated with EB, results in cleavage at the basal epidermal protein keratin 14. The skin of individuals with EB typically is fragile and cannot tolerate friction or manipulation due to the risk for new bullae formation.1 Epidermolysis bullosa is rare, affecting approximately 20 children per 1 million births in the United States, and is not commonly seen by most general adult dermatologists.2
In our patient, the differential diagnoses included staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), herpes simplex virus (HSV), and bullous pemphigoid (BP). Symptoms of SSSS can range from mild and localized to full-body exfoliation of the skin. Although SSSS can resemble other bullous disorders, its etiology arises from the Staphylococcus exotoxin targeting desmoglein in the stratum granulosum— the layer of the epidermis between the stratum corneum and stratum spinosum.3 Lesions start on the face, neck, and body folds, which was consistent with our patient’s presentation. However, bullae continued to develop in our patient despite antibiotic therapy, which reduced the likelihood of SSSS. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis develops rapidly and often involves the mucosa, which our patient initially did not have. In children, SJS/TEN can develop secondary to infection, whereas in adults it more commonly is associated with medication administration.4 Although the mother tested negative for HSV, the infant was started on acyclovir, which ultimately was discontinued due to low clinical suspicion. The clinical presentation of HSV (ie, clustered vesicles) was not consistent with our patient’s presentation. Bullous pemphigoid is a subepithelial blistering disease seen in older adults. Tense, fluidfilled blisters primarily are seen on the trunk and flexures. Although infantile BP can occur, it usually does not present in the neonatal period but rather at approximately 3 to 5 months of age.5
High clinical suspicion for EB due to the common characteristics of bullae location and formation following skin manipulation led to genetic testing in our patient. Mild forms of EB simplex typically appear on the upper and lower extremities with sparing of the trunk. In more severe cases of EB simplex, truncal and mucosal involvement may occur.6 In our case, the infant had a classic distribution of arm and leg blisters with truncal sparing. Epidermolysis bullosa may not be diagnosed in the neonatal period because of its similarities to other more common diseases, such as HSV or bullous impetigo, or other genetic blistering diseases, such as epidermolytic ichthyosis and incontinentia pigmenti.6
Epidermolysis bullosa can be inherited in an autosomal-dominant or autosomal-recessive fashion or with de novo mutations and is classified based on the location of cleavage in the skin. The 4 classical subtypes— simplex, junctional, dystrophic, and Kindler—have now been further subclassified. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (intraepidermal split) is now separated into basal and suprabasal, with further subclassification including the distribution of blisters (generalized or localized) and the severity of cutaneous or extracutaneous involvement.7
In our case, the infant was found to have intraepidermal EB (simplex) due to a KRT14 mutation (missense mutation).6 KRT14 (17q21.2) and KRT5 (12q13.3) are the 2 most common mutations causing cleavage at the basal intraepidermal layer. Thickening of the palms, soles, and nails can be seen; however, blisters heal well without scarring, as seen in our patient. Junctional EB due to cleavage at the intralamina lucida often involves mutations in laminin 332, plectin, and α6β4 integrin. Infants with junctional EB often die from severe infection, dehydration, or malnutrition due to mucosal involvement. Dystrophic EB occurs due to a collagen VII mutation in the dermis, leading to blisters at the sublamina densa and more severe symptoms in the recessive form.7
Newborn management for infants with EB differs from normal newborn care due to increased skin fragility with physical manipulation. Minimal skin manipulation and proper wound care are essential from the first day of life. For new bullae formation, bullae should be ruptured with a needle at the base of the blister and drained. The remaining skin overlying the wound should remain in place as a natural wound barrier. Patients with EB should not have tape or adhesive bandages applied directly to the skin. Instead, nonadhesive dressings can be placed directly on wounds and covered in soft wraps circumferentially. Dressings can be taped together without involving the skin. The cost for supplies for families to manage bullae is expensive. Fortunately, there are resources available for supplies and support for families, including the EB Research Partnership (https://www.ebresearch.org/) and DEBRA of America (https://www.debra.org/).
Currently, there is no cure for EB. Current treatment involves wound care, prevention, and symptomatic relief. Prevention includes avoiding activities that may result in increased friction of the skin and ensuring careful manipulation. Children with EB may have pain or itching from their blisters, which can be treated with oral acetaminophen or ibuprofen and diphenhydramine, respectively. Other complications of EB include anemia, dehydration, constipation, infection, and malnutrition. In more severe forms of EB, complications including eye problems, mucosal strictures, and skin cancer may occur.8 Future treatment directions include gene therapy, bone marrow transplantation, protein replacement therapies, and cell-based therapies. Prognosis for infants with EB due to KRT14 mutation is good, as it is a milder subtype of EB with a full life expectancy and improvement of blistering skin with age. The most at-risk time for early death is during infancy due to increased risk for infection.8 In this case, our patient showed full healing with no scar formation, which suggested a reassuring prognosis.
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa
Our patient was found to have epidermolysis bullosa (EB), a rare genetic disease in which the superficial layers of the skin separate to form vesicles or bullae due to a mutation in the keratin 14 gene, KRT14. Separation of the skin occurs due to cleavage of various proteins that connect the epidermis to the dermis. A genetic mutation in KRT14, one of the more common genetic mutations associated with EB, results in cleavage at the basal epidermal protein keratin 14. The skin of individuals with EB typically is fragile and cannot tolerate friction or manipulation due to the risk for new bullae formation.1 Epidermolysis bullosa is rare, affecting approximately 20 children per 1 million births in the United States, and is not commonly seen by most general adult dermatologists.2
In our patient, the differential diagnoses included staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), herpes simplex virus (HSV), and bullous pemphigoid (BP). Symptoms of SSSS can range from mild and localized to full-body exfoliation of the skin. Although SSSS can resemble other bullous disorders, its etiology arises from the Staphylococcus exotoxin targeting desmoglein in the stratum granulosum— the layer of the epidermis between the stratum corneum and stratum spinosum.3 Lesions start on the face, neck, and body folds, which was consistent with our patient’s presentation. However, bullae continued to develop in our patient despite antibiotic therapy, which reduced the likelihood of SSSS. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis develops rapidly and often involves the mucosa, which our patient initially did not have. In children, SJS/TEN can develop secondary to infection, whereas in adults it more commonly is associated with medication administration.4 Although the mother tested negative for HSV, the infant was started on acyclovir, which ultimately was discontinued due to low clinical suspicion. The clinical presentation of HSV (ie, clustered vesicles) was not consistent with our patient’s presentation. Bullous pemphigoid is a subepithelial blistering disease seen in older adults. Tense, fluidfilled blisters primarily are seen on the trunk and flexures. Although infantile BP can occur, it usually does not present in the neonatal period but rather at approximately 3 to 5 months of age.5
High clinical suspicion for EB due to the common characteristics of bullae location and formation following skin manipulation led to genetic testing in our patient. Mild forms of EB simplex typically appear on the upper and lower extremities with sparing of the trunk. In more severe cases of EB simplex, truncal and mucosal involvement may occur.6 In our case, the infant had a classic distribution of arm and leg blisters with truncal sparing. Epidermolysis bullosa may not be diagnosed in the neonatal period because of its similarities to other more common diseases, such as HSV or bullous impetigo, or other genetic blistering diseases, such as epidermolytic ichthyosis and incontinentia pigmenti.6
Epidermolysis bullosa can be inherited in an autosomal-dominant or autosomal-recessive fashion or with de novo mutations and is classified based on the location of cleavage in the skin. The 4 classical subtypes— simplex, junctional, dystrophic, and Kindler—have now been further subclassified. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (intraepidermal split) is now separated into basal and suprabasal, with further subclassification including the distribution of blisters (generalized or localized) and the severity of cutaneous or extracutaneous involvement.7
In our case, the infant was found to have intraepidermal EB (simplex) due to a KRT14 mutation (missense mutation).6 KRT14 (17q21.2) and KRT5 (12q13.3) are the 2 most common mutations causing cleavage at the basal intraepidermal layer. Thickening of the palms, soles, and nails can be seen; however, blisters heal well without scarring, as seen in our patient. Junctional EB due to cleavage at the intralamina lucida often involves mutations in laminin 332, plectin, and α6β4 integrin. Infants with junctional EB often die from severe infection, dehydration, or malnutrition due to mucosal involvement. Dystrophic EB occurs due to a collagen VII mutation in the dermis, leading to blisters at the sublamina densa and more severe symptoms in the recessive form.7
Newborn management for infants with EB differs from normal newborn care due to increased skin fragility with physical manipulation. Minimal skin manipulation and proper wound care are essential from the first day of life. For new bullae formation, bullae should be ruptured with a needle at the base of the blister and drained. The remaining skin overlying the wound should remain in place as a natural wound barrier. Patients with EB should not have tape or adhesive bandages applied directly to the skin. Instead, nonadhesive dressings can be placed directly on wounds and covered in soft wraps circumferentially. Dressings can be taped together without involving the skin. The cost for supplies for families to manage bullae is expensive. Fortunately, there are resources available for supplies and support for families, including the EB Research Partnership (https://www.ebresearch.org/) and DEBRA of America (https://www.debra.org/).
Currently, there is no cure for EB. Current treatment involves wound care, prevention, and symptomatic relief. Prevention includes avoiding activities that may result in increased friction of the skin and ensuring careful manipulation. Children with EB may have pain or itching from their blisters, which can be treated with oral acetaminophen or ibuprofen and diphenhydramine, respectively. Other complications of EB include anemia, dehydration, constipation, infection, and malnutrition. In more severe forms of EB, complications including eye problems, mucosal strictures, and skin cancer may occur.8 Future treatment directions include gene therapy, bone marrow transplantation, protein replacement therapies, and cell-based therapies. Prognosis for infants with EB due to KRT14 mutation is good, as it is a milder subtype of EB with a full life expectancy and improvement of blistering skin with age. The most at-risk time for early death is during infancy due to increased risk for infection.8 In this case, our patient showed full healing with no scar formation, which suggested a reassuring prognosis.
- Fine JD, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Eady RAJ, et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:1103-1126.
- Wolff K, Johnson RA, Saavedra AP, et al. Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2017:94-99.
- Ross A, Shoff HW. Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020:1-20.
- Alerhand S, Cassella C, Koyfman A. Steven-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in the pediatric population. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016;32:472-476.
- Schwieger-Briel A, Moellmann C, Mattulat B, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in infants: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:185.
- Gonzalez ME. Evaluation and treatment of the newborn with epidermolysis bullosa. Semin Perinatol. 2013;37:32-39.
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627.
- Watkins J. Diagnosis, treatment and management of epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Nurs. 2016;25:428-431.
- Fine JD, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Eady RAJ, et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:1103-1126.
- Wolff K, Johnson RA, Saavedra AP, et al. Hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2017:94-99.
- Ross A, Shoff HW. Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020:1-20.
- Alerhand S, Cassella C, Koyfman A. Steven-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in the pediatric population. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016;32:472-476.
- Schwieger-Briel A, Moellmann C, Mattulat B, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in infants: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:185.
- Gonzalez ME. Evaluation and treatment of the newborn with epidermolysis bullosa. Semin Perinatol. 2013;37:32-39.
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627.
- Watkins J. Diagnosis, treatment and management of epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Nurs. 2016;25:428-431.
A 4-day-old infant boy presented with blisters on the skin. He was born at 36 weeks’ gestation by cesarean delivery to a nulliparous mother who received appropriate prenatal care. On day 2 of life, the patient developed bullae with breakdown of the skin on the bilateral heels and on the skin surrounding intravenous injection sites. Similar blisters subsequently developed on the fingers (top), thighs, groin, and toes (bottom), sparing the oral mucosa and trunk. He remained afebrile and stable and was started on ampicillin, gentamicin, and acyclovir with continued development of blisters. Two weeks later he developed painful ulcers on the tongue that bled upon scraping.
A 14-year-old male presents to clinic with a new-onset rash of the hands
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
He reported no hiking or gardening, no new topical products such as new sunscreens or lotions, and no new medications. The patient had a history of acne, for which he used over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide wash, adapalene gel, and an oral antibiotic for 3 months. His review of systems was negative for fevers, chills, muscle weakness, mouth sores, or joint pain and no prior rashes following sun exposure.
On physical exam he presented with pink plaques with thin vesicles on the dorsum of the hands that were more noticeable on the lateral aspect of both the first and second fingers (Figures 1 and 2). His nails also had a yellow discoloration.
An 11-year-old female presented with skin discoloration on her back
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
A 19-month-old vaccinated female with 2 days of rash
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is a leukocytoclastic vasculitis that typically affects children between 4 months and 2 years of age.1 Etiology is unknown but the majority of cases are preceded by infections, vaccinations, or certain medications.2
AHEI is a self-limited disease that runs a benign course with spontaneous resolution within days to 3 weeks.3 Classic presentation involves acute onset of fever, purpura, ecchymosis, and inflammatory edema. Edema is often the first sign, and may involve the face, ears, scrotum, or extremities. Hemorrhagic lesions may vary in size but often coalesce and present in a distinctive “cockade” or rosette pattern with scalloped borders. Systemic manifestations are rare, but renal and joint involvement may occur.4 Despite the dramatic and sometimes extensive appearance of the dermatologic manifestations, patients with AHEI are usually not in significant distress.
Diagnosis is clinical, but skin biopsy may show leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the superficial small vessels with infiltrations of neutrophils, extravasation of red blood cells, and fibrinoid necrosis.5 In most cases, immunofluorescence is negative for perivascular IgA deposition. Treatment is symptomatic as the disease resolves spontaneously. Recurrence is uncommon but may occur, and usually occurs early.
What is on the differential?
Kawasaki disease. Similar to AHEI, patients with Kawasaki disease also may present with facial and extremity edema. However, patients with Kawasaki disease appear sicker, have associated lymphadenopathy, conjunctivitis, and fever longer than 5 days. The lack of elevated inflammatory markers, acute-onset, classic dermatologic lesions, and nontoxic appearance in our patient rule out Kawasaki disease and make AHEI more likely.
IgA vasculitis/Henoch-Schönlein purpura. The distinction between AHEI and Henoch-Schönlein purpura is among the most challenging. AHEI commonly afflicts younger children ranging from 4 months to 2 years, whereas Henoch-Schönlein purpura occurs in older children from 3 to 6 years of age. Visceral involvement is rare in AHEI, but frequently presents in Henoch-Schönlein purpura with gastrointestinal and renal complications. Although our patient had both mild renal involvement and a distribution primarily on the buttocks and lower limbs, similar to the classic distribution of Henoch-Schönlein purpura, the younger age and lack of gastrointestinal and arthritic manifestations make AHEI more likely.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, also known as papulovesicular acrodermatitis of childhood, mainly affects children between the ages of 6 months and 12 years. Like AHEI, Gianotti-Crosti is a self-limiting condition likely triggered by viral infection or immunization. However, Gianotti-Crosti is characterized by a papular rash that may last for several weeks. Neither AHEI nor Gianotti-Crosti are pruritic, but patients with Gianotti-Crosti tend to have either inguinal or axillary lymphadenopathy. Our patient’s large, coalescing dusky red patches and edematous plaques without lymphadenopathy are more consistent with AHEI.
Erythema multiforme. Erythema multiforme is an acute, immune-mediated condition characterized by distinctive target-like lesions on the skin often accompanied by erosions or bullae. Unlike AHEI, erythema multiforme can involve the oral, genital, and/or ocular mucosae. Erythema multiforme is rare before the age of 4 years. Although the targetoid or annular purpuric configuration of erythema multiforme may present similarly to AHEI in some cases, the young age of our patient and the lack of mucosal involvement make AHEI more likely.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Kleinman has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Savino F et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30(6):e149-e152.
2. Carboni E et al. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771. 2019 Oct 17.
3. Fiore E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(4):684-95.
4. Watanabe T and Sato Y. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22(11):1979-81.
5. Cunha DF et al. Autops Case Rep. 2015;5(3):37-41.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is a leukocytoclastic vasculitis that typically affects children between 4 months and 2 years of age.1 Etiology is unknown but the majority of cases are preceded by infections, vaccinations, or certain medications.2
AHEI is a self-limited disease that runs a benign course with spontaneous resolution within days to 3 weeks.3 Classic presentation involves acute onset of fever, purpura, ecchymosis, and inflammatory edema. Edema is often the first sign, and may involve the face, ears, scrotum, or extremities. Hemorrhagic lesions may vary in size but often coalesce and present in a distinctive “cockade” or rosette pattern with scalloped borders. Systemic manifestations are rare, but renal and joint involvement may occur.4 Despite the dramatic and sometimes extensive appearance of the dermatologic manifestations, patients with AHEI are usually not in significant distress.
Diagnosis is clinical, but skin biopsy may show leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the superficial small vessels with infiltrations of neutrophils, extravasation of red blood cells, and fibrinoid necrosis.5 In most cases, immunofluorescence is negative for perivascular IgA deposition. Treatment is symptomatic as the disease resolves spontaneously. Recurrence is uncommon but may occur, and usually occurs early.
What is on the differential?
Kawasaki disease. Similar to AHEI, patients with Kawasaki disease also may present with facial and extremity edema. However, patients with Kawasaki disease appear sicker, have associated lymphadenopathy, conjunctivitis, and fever longer than 5 days. The lack of elevated inflammatory markers, acute-onset, classic dermatologic lesions, and nontoxic appearance in our patient rule out Kawasaki disease and make AHEI more likely.
IgA vasculitis/Henoch-Schönlein purpura. The distinction between AHEI and Henoch-Schönlein purpura is among the most challenging. AHEI commonly afflicts younger children ranging from 4 months to 2 years, whereas Henoch-Schönlein purpura occurs in older children from 3 to 6 years of age. Visceral involvement is rare in AHEI, but frequently presents in Henoch-Schönlein purpura with gastrointestinal and renal complications. Although our patient had both mild renal involvement and a distribution primarily on the buttocks and lower limbs, similar to the classic distribution of Henoch-Schönlein purpura, the younger age and lack of gastrointestinal and arthritic manifestations make AHEI more likely.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, also known as papulovesicular acrodermatitis of childhood, mainly affects children between the ages of 6 months and 12 years. Like AHEI, Gianotti-Crosti is a self-limiting condition likely triggered by viral infection or immunization. However, Gianotti-Crosti is characterized by a papular rash that may last for several weeks. Neither AHEI nor Gianotti-Crosti are pruritic, but patients with Gianotti-Crosti tend to have either inguinal or axillary lymphadenopathy. Our patient’s large, coalescing dusky red patches and edematous plaques without lymphadenopathy are more consistent with AHEI.
Erythema multiforme. Erythema multiforme is an acute, immune-mediated condition characterized by distinctive target-like lesions on the skin often accompanied by erosions or bullae. Unlike AHEI, erythema multiforme can involve the oral, genital, and/or ocular mucosae. Erythema multiforme is rare before the age of 4 years. Although the targetoid or annular purpuric configuration of erythema multiforme may present similarly to AHEI in some cases, the young age of our patient and the lack of mucosal involvement make AHEI more likely.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Kleinman has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Savino F et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30(6):e149-e152.
2. Carboni E et al. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771. 2019 Oct 17.
3. Fiore E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(4):684-95.
4. Watanabe T and Sato Y. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22(11):1979-81.
5. Cunha DF et al. Autops Case Rep. 2015;5(3):37-41.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is a leukocytoclastic vasculitis that typically affects children between 4 months and 2 years of age.1 Etiology is unknown but the majority of cases are preceded by infections, vaccinations, or certain medications.2
AHEI is a self-limited disease that runs a benign course with spontaneous resolution within days to 3 weeks.3 Classic presentation involves acute onset of fever, purpura, ecchymosis, and inflammatory edema. Edema is often the first sign, and may involve the face, ears, scrotum, or extremities. Hemorrhagic lesions may vary in size but often coalesce and present in a distinctive “cockade” or rosette pattern with scalloped borders. Systemic manifestations are rare, but renal and joint involvement may occur.4 Despite the dramatic and sometimes extensive appearance of the dermatologic manifestations, patients with AHEI are usually not in significant distress.
Diagnosis is clinical, but skin biopsy may show leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the superficial small vessels with infiltrations of neutrophils, extravasation of red blood cells, and fibrinoid necrosis.5 In most cases, immunofluorescence is negative for perivascular IgA deposition. Treatment is symptomatic as the disease resolves spontaneously. Recurrence is uncommon but may occur, and usually occurs early.
What is on the differential?
Kawasaki disease. Similar to AHEI, patients with Kawasaki disease also may present with facial and extremity edema. However, patients with Kawasaki disease appear sicker, have associated lymphadenopathy, conjunctivitis, and fever longer than 5 days. The lack of elevated inflammatory markers, acute-onset, classic dermatologic lesions, and nontoxic appearance in our patient rule out Kawasaki disease and make AHEI more likely.
IgA vasculitis/Henoch-Schönlein purpura. The distinction between AHEI and Henoch-Schönlein purpura is among the most challenging. AHEI commonly afflicts younger children ranging from 4 months to 2 years, whereas Henoch-Schönlein purpura occurs in older children from 3 to 6 years of age. Visceral involvement is rare in AHEI, but frequently presents in Henoch-Schönlein purpura with gastrointestinal and renal complications. Although our patient had both mild renal involvement and a distribution primarily on the buttocks and lower limbs, similar to the classic distribution of Henoch-Schönlein purpura, the younger age and lack of gastrointestinal and arthritic manifestations make AHEI more likely.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, also known as papulovesicular acrodermatitis of childhood, mainly affects children between the ages of 6 months and 12 years. Like AHEI, Gianotti-Crosti is a self-limiting condition likely triggered by viral infection or immunization. However, Gianotti-Crosti is characterized by a papular rash that may last for several weeks. Neither AHEI nor Gianotti-Crosti are pruritic, but patients with Gianotti-Crosti tend to have either inguinal or axillary lymphadenopathy. Our patient’s large, coalescing dusky red patches and edematous plaques without lymphadenopathy are more consistent with AHEI.
Erythema multiforme. Erythema multiforme is an acute, immune-mediated condition characterized by distinctive target-like lesions on the skin often accompanied by erosions or bullae. Unlike AHEI, erythema multiforme can involve the oral, genital, and/or ocular mucosae. Erythema multiforme is rare before the age of 4 years. Although the targetoid or annular purpuric configuration of erythema multiforme may present similarly to AHEI in some cases, the young age of our patient and the lack of mucosal involvement make AHEI more likely.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Kleinman has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Savino F et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30(6):e149-e152.
2. Carboni E et al. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771. 2019 Oct 17.
3. Fiore E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59(4):684-95.
4. Watanabe T and Sato Y. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22(11):1979-81.
5. Cunha DF et al. Autops Case Rep. 2015;5(3):37-41.
What is the diagnosis?
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is becoming more recognized in children. It has a variable presentation, most commonly presenting as painful, recurrent cysts, abscesses, nodules, and/or pustules in classic locations with associated scarring and sinus tract formation.
The majority of patients present with bilateral lesions found most commonly in the axillae and inguinal folds.1 There are myriad other potential sites of involvement including the inframammary folds, inner thighs, buttocks, and groin.1 Diagnosis is made based on history and physical exam. There is a standard severity classification scheme called the Hurley score, which stratifies disease severity based on the presence of sinus tracts and extent of disease.1 HS is associated with comorbid conditions such as obesity, overweight, acne, and inflammatory bowel and joint disease.2 This painful, persistent condition is well documented to have a negative impact on quality of life in adult patients, and similar impairment has been found in pediatric patients.3,4
HS may be increasing in pediatric and adolescent patients, with recent studies showing onset coinciding most commonly with the onset of puberty.1,2 There is often a period of several years between symptom onset and diagnosis.1 A recent editorial highlighted the disparities that exist in HS, with disease more common in Black children and limited information about disease prevalence in Hispanic children.5
What’s the treatment plan?
HS is a difficult disease to treat, with few patients achieving remission and a significant proportion of patients with treatment-refractory disease.1 There are limited studies of HS treatment in pediatric patients. Topical and systemic antibiotic therapy are mainstays of HS treatment, with tetracyclines and a combination of clindamycin plus rifampin commonly used in adults and children alike. Topical therapies including topical antibiotics and antibacterial solutions are frequently used as adjunctive therapy.6 Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor receptor blocker, has been Food and Drug Administration approved for HS for ages 12 and up and is currently the only FDA-approved medication for HS in pediatric patients. Our patient was started on 100 mg doxycycline twice daily, with short-dose topical corticosteroids for symptom management of the most inflamed lesions.
What’s on the differential?
Acne conglobata
Acne conglobata is an uncommon, severe variant of acne vulgaris which arise in patients with a history of acne vulgaris and presents with comedones, cysts, abscesses, and scarring with possible drainage of pus. Lesions can present diffusely on the face, back, and body, including in the axillae, groin, and buttocks, and as such can be confused with HS.7
However, in contrast with HS, patients with acne conglobata will also develop disease in non–apocrine gland–bearing skin. This patient’s lack of preceding acne and restriction of lesions to the axillae, inguinal folds, and buttocks makes acne conglobata less likely.
Epidermal inclusion cyst
Epidermal inclusion cyst (EIC) is a common cutaneous cyst, presenting as a well-circumscribed nodule(s) with a central punctum. If not excised, lesions can sometimes become infected and painful.8 In contrast with HS, EIC presents only uncommonly as multiple lesions arising in different areas, and spontaneous drainage is uncommon. Our patient’s development of multiple draining lesions makes this diagnosis unlikely.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is a common bacterial infection of the skin, presenting with inflammatory nodules or pustules centered around the hair follicle. Lesions may commonly present at sites of skin trauma and are found most frequently on the extremities.9 Though furunculosis lesions may drain pus and can coalesce to form larger “carbuncles,” our patient’s presence of significant scarring and lack of extremity involvement makes HS more likely.
Recurrent MRSA abscesses
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft-tissue infections are not uncommon in the pediatric population, with presentation of infection ranging from cellulitis to fluid-containing abscesses.10 Recurrent abscesses may be seen in MRSA infection, however in this patient the presence of draining, scarring lesions in multiple locations typical for HS over time is more consistent with a diagnosis of HS.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Appiah have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Liy-Wong C et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):385-91.
2. Choi E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(1):140-7.
3. Machado MO et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(8):939-45.
4. McAndrew R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(3):829-30.
5. Kirby JS and Zaenglein AL. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):379-80.
6. Alikhan A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(1):91-101.
7. Greydanus DE et al. Dis Mon. 2021;67(4):101103.
8. Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal Inclusion Cyst, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
9. Atanaskova N and Tomecki KJ. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(3):479-87.
10. Papastefan ST et al. J Surg Res. 2019;242:70-7.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is becoming more recognized in children. It has a variable presentation, most commonly presenting as painful, recurrent cysts, abscesses, nodules, and/or pustules in classic locations with associated scarring and sinus tract formation.
The majority of patients present with bilateral lesions found most commonly in the axillae and inguinal folds.1 There are myriad other potential sites of involvement including the inframammary folds, inner thighs, buttocks, and groin.1 Diagnosis is made based on history and physical exam. There is a standard severity classification scheme called the Hurley score, which stratifies disease severity based on the presence of sinus tracts and extent of disease.1 HS is associated with comorbid conditions such as obesity, overweight, acne, and inflammatory bowel and joint disease.2 This painful, persistent condition is well documented to have a negative impact on quality of life in adult patients, and similar impairment has been found in pediatric patients.3,4
HS may be increasing in pediatric and adolescent patients, with recent studies showing onset coinciding most commonly with the onset of puberty.1,2 There is often a period of several years between symptom onset and diagnosis.1 A recent editorial highlighted the disparities that exist in HS, with disease more common in Black children and limited information about disease prevalence in Hispanic children.5
What’s the treatment plan?
HS is a difficult disease to treat, with few patients achieving remission and a significant proportion of patients with treatment-refractory disease.1 There are limited studies of HS treatment in pediatric patients. Topical and systemic antibiotic therapy are mainstays of HS treatment, with tetracyclines and a combination of clindamycin plus rifampin commonly used in adults and children alike. Topical therapies including topical antibiotics and antibacterial solutions are frequently used as adjunctive therapy.6 Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor receptor blocker, has been Food and Drug Administration approved for HS for ages 12 and up and is currently the only FDA-approved medication for HS in pediatric patients. Our patient was started on 100 mg doxycycline twice daily, with short-dose topical corticosteroids for symptom management of the most inflamed lesions.
What’s on the differential?
Acne conglobata
Acne conglobata is an uncommon, severe variant of acne vulgaris which arise in patients with a history of acne vulgaris and presents with comedones, cysts, abscesses, and scarring with possible drainage of pus. Lesions can present diffusely on the face, back, and body, including in the axillae, groin, and buttocks, and as such can be confused with HS.7
However, in contrast with HS, patients with acne conglobata will also develop disease in non–apocrine gland–bearing skin. This patient’s lack of preceding acne and restriction of lesions to the axillae, inguinal folds, and buttocks makes acne conglobata less likely.
Epidermal inclusion cyst
Epidermal inclusion cyst (EIC) is a common cutaneous cyst, presenting as a well-circumscribed nodule(s) with a central punctum. If not excised, lesions can sometimes become infected and painful.8 In contrast with HS, EIC presents only uncommonly as multiple lesions arising in different areas, and spontaneous drainage is uncommon. Our patient’s development of multiple draining lesions makes this diagnosis unlikely.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is a common bacterial infection of the skin, presenting with inflammatory nodules or pustules centered around the hair follicle. Lesions may commonly present at sites of skin trauma and are found most frequently on the extremities.9 Though furunculosis lesions may drain pus and can coalesce to form larger “carbuncles,” our patient’s presence of significant scarring and lack of extremity involvement makes HS more likely.
Recurrent MRSA abscesses
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft-tissue infections are not uncommon in the pediatric population, with presentation of infection ranging from cellulitis to fluid-containing abscesses.10 Recurrent abscesses may be seen in MRSA infection, however in this patient the presence of draining, scarring lesions in multiple locations typical for HS over time is more consistent with a diagnosis of HS.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Appiah have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Liy-Wong C et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):385-91.
2. Choi E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(1):140-7.
3. Machado MO et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(8):939-45.
4. McAndrew R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(3):829-30.
5. Kirby JS and Zaenglein AL. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):379-80.
6. Alikhan A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(1):91-101.
7. Greydanus DE et al. Dis Mon. 2021;67(4):101103.
8. Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal Inclusion Cyst, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
9. Atanaskova N and Tomecki KJ. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(3):479-87.
10. Papastefan ST et al. J Surg Res. 2019;242:70-7.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is becoming more recognized in children. It has a variable presentation, most commonly presenting as painful, recurrent cysts, abscesses, nodules, and/or pustules in classic locations with associated scarring and sinus tract formation.
The majority of patients present with bilateral lesions found most commonly in the axillae and inguinal folds.1 There are myriad other potential sites of involvement including the inframammary folds, inner thighs, buttocks, and groin.1 Diagnosis is made based on history and physical exam. There is a standard severity classification scheme called the Hurley score, which stratifies disease severity based on the presence of sinus tracts and extent of disease.1 HS is associated with comorbid conditions such as obesity, overweight, acne, and inflammatory bowel and joint disease.2 This painful, persistent condition is well documented to have a negative impact on quality of life in adult patients, and similar impairment has been found in pediatric patients.3,4
HS may be increasing in pediatric and adolescent patients, with recent studies showing onset coinciding most commonly with the onset of puberty.1,2 There is often a period of several years between symptom onset and diagnosis.1 A recent editorial highlighted the disparities that exist in HS, with disease more common in Black children and limited information about disease prevalence in Hispanic children.5
What’s the treatment plan?
HS is a difficult disease to treat, with few patients achieving remission and a significant proportion of patients with treatment-refractory disease.1 There are limited studies of HS treatment in pediatric patients. Topical and systemic antibiotic therapy are mainstays of HS treatment, with tetracyclines and a combination of clindamycin plus rifampin commonly used in adults and children alike. Topical therapies including topical antibiotics and antibacterial solutions are frequently used as adjunctive therapy.6 Adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor receptor blocker, has been Food and Drug Administration approved for HS for ages 12 and up and is currently the only FDA-approved medication for HS in pediatric patients. Our patient was started on 100 mg doxycycline twice daily, with short-dose topical corticosteroids for symptom management of the most inflamed lesions.
What’s on the differential?
Acne conglobata
Acne conglobata is an uncommon, severe variant of acne vulgaris which arise in patients with a history of acne vulgaris and presents with comedones, cysts, abscesses, and scarring with possible drainage of pus. Lesions can present diffusely on the face, back, and body, including in the axillae, groin, and buttocks, and as such can be confused with HS.7
However, in contrast with HS, patients with acne conglobata will also develop disease in non–apocrine gland–bearing skin. This patient’s lack of preceding acne and restriction of lesions to the axillae, inguinal folds, and buttocks makes acne conglobata less likely.
Epidermal inclusion cyst
Epidermal inclusion cyst (EIC) is a common cutaneous cyst, presenting as a well-circumscribed nodule(s) with a central punctum. If not excised, lesions can sometimes become infected and painful.8 In contrast with HS, EIC presents only uncommonly as multiple lesions arising in different areas, and spontaneous drainage is uncommon. Our patient’s development of multiple draining lesions makes this diagnosis unlikely.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is a common bacterial infection of the skin, presenting with inflammatory nodules or pustules centered around the hair follicle. Lesions may commonly present at sites of skin trauma and are found most frequently on the extremities.9 Though furunculosis lesions may drain pus and can coalesce to form larger “carbuncles,” our patient’s presence of significant scarring and lack of extremity involvement makes HS more likely.
Recurrent MRSA abscesses
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft-tissue infections are not uncommon in the pediatric population, with presentation of infection ranging from cellulitis to fluid-containing abscesses.10 Recurrent abscesses may be seen in MRSA infection, however in this patient the presence of draining, scarring lesions in multiple locations typical for HS over time is more consistent with a diagnosis of HS.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Appiah have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Liy-Wong C et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):385-91.
2. Choi E et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(1):140-7.
3. Machado MO et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(8):939-45.
4. McAndrew R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(3):829-30.
5. Kirby JS and Zaenglein AL. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):379-80.
6. Alikhan A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(1):91-101.
7. Greydanus DE et al. Dis Mon. 2021;67(4):101103.
8. Weir CB, St. Hilaire NJ. Epidermal Inclusion Cyst, in “StatPearls.” Treasure Island, Fla: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
9. Atanaskova N and Tomecki KJ. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(3):479-87.
10. Papastefan ST et al. J Surg Res. 2019;242:70-7.