User login
Let Lip Defect Size Drive Treatment
SAN DIEGO – Principles for lip repair are based on size and location of the defect, etiology of the lesions, and patient age and gender, said Dr. Michael A. Keefe.
Surgical goals of lip reconstruction are to cover the skin and oral lining, leave a semblance of a vermilion and an adequate stomal diameter, make sure sensation is intact, and ensure that the patient has a competent oral sphincter. "The vermilion is the most visible component of the lips, and it’s also the sensory unit of the lip," Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. The meeting was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
"Scars are very well hidden at the vermilion-cutaneous border. If you have to cross the vermilion-cutaneous junction, cross at 90 degrees."
Lower Lip
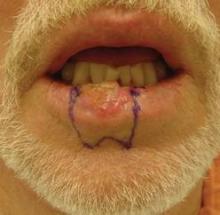
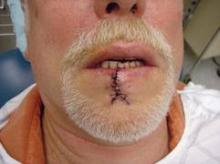
The lower vermilion is the most affected target of solar radiation injury. In cases of premalignant lesions such as actinic cheilitis or leukoplakia, Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said he often performs a total vermilionectomy (lip shave). This involves resection from the white roll to the contact area with opposite lip. "Primary closure is possible," he said. "You can get tension and dehiscence and flattening of the lip, but generally it heals up pretty well. An option for vermilion reconstruction of larger defects is the buccal mucosal advancement flap, which involves elevating the mucosa deep to salivary glands and superficial to the orbicularis oris muscle."
An advantage of treating the lower lip is that there is increased soft tissue laxity and there is no Cupid’s bow, philtrum, or nose, "so it’s nice that there are no dominant central structures," he said. "The downside is that you have to be mindful of the effect of gravity on the repair, so there is a greater need for tone to prevent drooling and incompetence."
He recommends a staged approach based on the extent of the defect and the age of the patient. For small defects (those less than one-third of the lip size) he uses primary closure. Options for medium defects (those that involve one-third to two-thirds of the lip size) include the Estlander flap, the Abbe flap, Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the stairstep repair, while the options for large defects (those that involve more than two-thirds of the lip size) include Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the free flap. "You have a lot of tools, depending on what you feel comfortable with," Dr. Keefe said.
Upper Lip
Cancerous tumors of the upper lip are less common, "but there are some unique structures to pay attention to, including the nose, columella, Cupid’s bow, and the philtrum," he said. "In men there’s a hair-bearing skin issue, but scars can be disguised in a mustache."
The aesthetic subunits to keep in mind, he continued, are the medial subunit, which is one-half of the philtrum, and the lateral subunit, which consists of the philtral column, the nostril sill, the alar base, and the nasolabial crease. Primary closure is used for upper lip defects that involve less than one-third of the lip size. "You can make some perialar crescentic skin excisions, which can help advance things," Dr. Keefe said.
For centrally located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, he often uses primary closure with perialar crescentic skin excisions. "If it’s greater than one-half of the lip size, you can add an Abbe flap," he said. "That’s nice because that recreates the philtrum area."
For medially located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, "you can use the Abbe flap if the commissure is not involved and the Estlander flap if the commissure is involved."
Options for cases with large defects and adequate cheek tissue, he said, include the reverse Karapandzic flap, the reverse fan flap, inverted Bernard Burow’s procedure, superiorly based cheek flaps, and the bilateral levator anguli oris flap combined with the Abbe flap. Options for cases with inadequate cheek tissue include the distal pedicle flap and the free flap.
Repair Risks
A lot of these patients have medical problems," he said. "When you do your first injection to resect the tumor or put the lip back together, make sure you don’t cause a myocardial infarction. Generally you should be comfortable with patients who have an INR [International Normalized Ratio] of 2.5 and below."
For patients with large cancerous tumors of the lip, be mindful of lymphatic drainage, because larger tumors have an increased risk of metastases, said Dr. Keefe. For tumors larger than 2 cm in length or 6 mm in spread, or if there is perineural spread, the patient should be referred for radiation therapy.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SAN DIEGO – Principles for lip repair are based on size and location of the defect, etiology of the lesions, and patient age and gender, said Dr. Michael A. Keefe.
Surgical goals of lip reconstruction are to cover the skin and oral lining, leave a semblance of a vermilion and an adequate stomal diameter, make sure sensation is intact, and ensure that the patient has a competent oral sphincter. "The vermilion is the most visible component of the lips, and it’s also the sensory unit of the lip," Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. The meeting was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
"Scars are very well hidden at the vermilion-cutaneous border. If you have to cross the vermilion-cutaneous junction, cross at 90 degrees."
Lower Lip
The lower vermilion is the most affected target of solar radiation injury. In cases of premalignant lesions such as actinic cheilitis or leukoplakia, Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said he often performs a total vermilionectomy (lip shave). This involves resection from the white roll to the contact area with opposite lip. "Primary closure is possible," he said. "You can get tension and dehiscence and flattening of the lip, but generally it heals up pretty well. An option for vermilion reconstruction of larger defects is the buccal mucosal advancement flap, which involves elevating the mucosa deep to salivary glands and superficial to the orbicularis oris muscle."
An advantage of treating the lower lip is that there is increased soft tissue laxity and there is no Cupid’s bow, philtrum, or nose, "so it’s nice that there are no dominant central structures," he said. "The downside is that you have to be mindful of the effect of gravity on the repair, so there is a greater need for tone to prevent drooling and incompetence."
He recommends a staged approach based on the extent of the defect and the age of the patient. For small defects (those less than one-third of the lip size) he uses primary closure. Options for medium defects (those that involve one-third to two-thirds of the lip size) include the Estlander flap, the Abbe flap, Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the stairstep repair, while the options for large defects (those that involve more than two-thirds of the lip size) include Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the free flap. "You have a lot of tools, depending on what you feel comfortable with," Dr. Keefe said.
Upper Lip
Cancerous tumors of the upper lip are less common, "but there are some unique structures to pay attention to, including the nose, columella, Cupid’s bow, and the philtrum," he said. "In men there’s a hair-bearing skin issue, but scars can be disguised in a mustache."
The aesthetic subunits to keep in mind, he continued, are the medial subunit, which is one-half of the philtrum, and the lateral subunit, which consists of the philtral column, the nostril sill, the alar base, and the nasolabial crease. Primary closure is used for upper lip defects that involve less than one-third of the lip size. "You can make some perialar crescentic skin excisions, which can help advance things," Dr. Keefe said.
For centrally located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, he often uses primary closure with perialar crescentic skin excisions. "If it’s greater than one-half of the lip size, you can add an Abbe flap," he said. "That’s nice because that recreates the philtrum area."
For medially located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, "you can use the Abbe flap if the commissure is not involved and the Estlander flap if the commissure is involved."
Options for cases with large defects and adequate cheek tissue, he said, include the reverse Karapandzic flap, the reverse fan flap, inverted Bernard Burow’s procedure, superiorly based cheek flaps, and the bilateral levator anguli oris flap combined with the Abbe flap. Options for cases with inadequate cheek tissue include the distal pedicle flap and the free flap.
Repair Risks
A lot of these patients have medical problems," he said. "When you do your first injection to resect the tumor or put the lip back together, make sure you don’t cause a myocardial infarction. Generally you should be comfortable with patients who have an INR [International Normalized Ratio] of 2.5 and below."
For patients with large cancerous tumors of the lip, be mindful of lymphatic drainage, because larger tumors have an increased risk of metastases, said Dr. Keefe. For tumors larger than 2 cm in length or 6 mm in spread, or if there is perineural spread, the patient should be referred for radiation therapy.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SAN DIEGO – Principles for lip repair are based on size and location of the defect, etiology of the lesions, and patient age and gender, said Dr. Michael A. Keefe.
Surgical goals of lip reconstruction are to cover the skin and oral lining, leave a semblance of a vermilion and an adequate stomal diameter, make sure sensation is intact, and ensure that the patient has a competent oral sphincter. "The vermilion is the most visible component of the lips, and it’s also the sensory unit of the lip," Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. The meeting was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
"Scars are very well hidden at the vermilion-cutaneous border. If you have to cross the vermilion-cutaneous junction, cross at 90 degrees."
Lower Lip
The lower vermilion is the most affected target of solar radiation injury. In cases of premalignant lesions such as actinic cheilitis or leukoplakia, Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said he often performs a total vermilionectomy (lip shave). This involves resection from the white roll to the contact area with opposite lip. "Primary closure is possible," he said. "You can get tension and dehiscence and flattening of the lip, but generally it heals up pretty well. An option for vermilion reconstruction of larger defects is the buccal mucosal advancement flap, which involves elevating the mucosa deep to salivary glands and superficial to the orbicularis oris muscle."
An advantage of treating the lower lip is that there is increased soft tissue laxity and there is no Cupid’s bow, philtrum, or nose, "so it’s nice that there are no dominant central structures," he said. "The downside is that you have to be mindful of the effect of gravity on the repair, so there is a greater need for tone to prevent drooling and incompetence."
He recommends a staged approach based on the extent of the defect and the age of the patient. For small defects (those less than one-third of the lip size) he uses primary closure. Options for medium defects (those that involve one-third to two-thirds of the lip size) include the Estlander flap, the Abbe flap, Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the stairstep repair, while the options for large defects (those that involve more than two-thirds of the lip size) include Bernard Burow’s procedure, the Karapandzic flap, and the free flap. "You have a lot of tools, depending on what you feel comfortable with," Dr. Keefe said.
Upper Lip
Cancerous tumors of the upper lip are less common, "but there are some unique structures to pay attention to, including the nose, columella, Cupid’s bow, and the philtrum," he said. "In men there’s a hair-bearing skin issue, but scars can be disguised in a mustache."
The aesthetic subunits to keep in mind, he continued, are the medial subunit, which is one-half of the philtrum, and the lateral subunit, which consists of the philtral column, the nostril sill, the alar base, and the nasolabial crease. Primary closure is used for upper lip defects that involve less than one-third of the lip size. "You can make some perialar crescentic skin excisions, which can help advance things," Dr. Keefe said.
For centrally located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, he often uses primary closure with perialar crescentic skin excisions. "If it’s greater than one-half of the lip size, you can add an Abbe flap," he said. "That’s nice because that recreates the philtrum area."
For medially located medium-sized defects of the upper lip, "you can use the Abbe flap if the commissure is not involved and the Estlander flap if the commissure is involved."
Options for cases with large defects and adequate cheek tissue, he said, include the reverse Karapandzic flap, the reverse fan flap, inverted Bernard Burow’s procedure, superiorly based cheek flaps, and the bilateral levator anguli oris flap combined with the Abbe flap. Options for cases with inadequate cheek tissue include the distal pedicle flap and the free flap.
Repair Risks
A lot of these patients have medical problems," he said. "When you do your first injection to resect the tumor or put the lip back together, make sure you don’t cause a myocardial infarction. Generally you should be comfortable with patients who have an INR [International Normalized Ratio] of 2.5 and below."
For patients with large cancerous tumors of the lip, be mindful of lymphatic drainage, because larger tumors have an increased risk of metastases, said Dr. Keefe. For tumors larger than 2 cm in length or 6 mm in spread, or if there is perineural spread, the patient should be referred for radiation therapy.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
AT A MEETING ON SUPERFICIAL ANATOMY AND CUTANEOUS SURGERY
Skin Flaps Remedy Defects of the Ear
SAN DIEGO – In the clinical experience of Dr. Michael A. Keefe, 70%-80% of ear defects from auricular cancer treatment can be easily remedied with skin flaps.
The most common locations of auricular cancer are the helix, the posterior auricle skin, and the antihelix, Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery.
"More than 70% of lesions are smaller than 3 cm in size, and auricular lesions make up an estimated 8% of all skin cancers," said Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. "The defects are unique, and the underlying cartilage structure makes it all the more interesting."
And challenging – defects may be located on the skin of the ear only, on the lateral side, or on the posterior side, or they may involve a combination of skin and cartilage. Healing by secondary intention is effective for concave defects, but the size of the defect drives the reconstruction options. "If there is no perichondrium, punch holes through cartilage with a 2-3 mm punch to allow granulation tissue to grow through, and then use a skin graft or allow it to heal with secondary intention," he said. "Keep the area moist with antibiotic ointment."
Options for reconstruction of defects in the middle one-third of the ear include primary closure, full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs), the helical advancement flap, and the retroauricular composite advancement flap, while options for defects in the lower one-third of the ear include primary closure and the preauricular tubed flap. Options for reconstruction of defects in the upper one-third of the ear include primary closure, FTSGs, the helical advancement flap, the retroauricular and preauricular tubed flaps, and constructing an autogenous cartilage framework with FTSGs.
Dr. Keefe said that most small helical rim defects limited to the skin can be closed primarily. "There might be slight rim asymmetry [after closure]," he said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic. "Some patients might not care [about this], but you have to advise them of that," he added.
A bilobed advancement flap is another option for helical rim defects limited to the skin. This flap "works well for cutaneous defects 2 cm or smaller in the helical rim or the posterior auricle," he said. "The other thing you can do with these bilobed flaps is advance them over the edge to correct helical rim defects."
The banner flap is another effective flap for helical rim defects, especially those located on the superior helix. It does not replace cartilage, but it conceals the incision well. For small composite helix and anterior defects, Dr. Keefe favors the chondrocutaneous advancement flap.
He said that he favors using FTSGs on the anterior surface of the helix for skin defects whenever possible. "You can use a composite skin graft as well, especially to replace cartilage or skin defects that are smaller than 1 cm in size," he said. "A FTSG is easy to harvest and has minimal contraction. Common donor sites include the preauricular, postauricular, supraclavicular, and clavicular regions. Make sure you trim off the fat." For posterior surface defects, the bilobe or advancement flaps work well.
Grafts must be placed on tissue with an adequate blood supply. Effective grafts establish imbibition in the first 24 hours, inosculation within 48-72 hours, and restoration of circulation within 4-7 days.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SAN DIEGO – In the clinical experience of Dr. Michael A. Keefe, 70%-80% of ear defects from auricular cancer treatment can be easily remedied with skin flaps.
The most common locations of auricular cancer are the helix, the posterior auricle skin, and the antihelix, Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery.
"More than 70% of lesions are smaller than 3 cm in size, and auricular lesions make up an estimated 8% of all skin cancers," said Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. "The defects are unique, and the underlying cartilage structure makes it all the more interesting."
And challenging – defects may be located on the skin of the ear only, on the lateral side, or on the posterior side, or they may involve a combination of skin and cartilage. Healing by secondary intention is effective for concave defects, but the size of the defect drives the reconstruction options. "If there is no perichondrium, punch holes through cartilage with a 2-3 mm punch to allow granulation tissue to grow through, and then use a skin graft or allow it to heal with secondary intention," he said. "Keep the area moist with antibiotic ointment."
Options for reconstruction of defects in the middle one-third of the ear include primary closure, full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs), the helical advancement flap, and the retroauricular composite advancement flap, while options for defects in the lower one-third of the ear include primary closure and the preauricular tubed flap. Options for reconstruction of defects in the upper one-third of the ear include primary closure, FTSGs, the helical advancement flap, the retroauricular and preauricular tubed flaps, and constructing an autogenous cartilage framework with FTSGs.
Dr. Keefe said that most small helical rim defects limited to the skin can be closed primarily. "There might be slight rim asymmetry [after closure]," he said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic. "Some patients might not care [about this], but you have to advise them of that," he added.
A bilobed advancement flap is another option for helical rim defects limited to the skin. This flap "works well for cutaneous defects 2 cm or smaller in the helical rim or the posterior auricle," he said. "The other thing you can do with these bilobed flaps is advance them over the edge to correct helical rim defects."
The banner flap is another effective flap for helical rim defects, especially those located on the superior helix. It does not replace cartilage, but it conceals the incision well. For small composite helix and anterior defects, Dr. Keefe favors the chondrocutaneous advancement flap.
He said that he favors using FTSGs on the anterior surface of the helix for skin defects whenever possible. "You can use a composite skin graft as well, especially to replace cartilage or skin defects that are smaller than 1 cm in size," he said. "A FTSG is easy to harvest and has minimal contraction. Common donor sites include the preauricular, postauricular, supraclavicular, and clavicular regions. Make sure you trim off the fat." For posterior surface defects, the bilobe or advancement flaps work well.
Grafts must be placed on tissue with an adequate blood supply. Effective grafts establish imbibition in the first 24 hours, inosculation within 48-72 hours, and restoration of circulation within 4-7 days.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SAN DIEGO – In the clinical experience of Dr. Michael A. Keefe, 70%-80% of ear defects from auricular cancer treatment can be easily remedied with skin flaps.
The most common locations of auricular cancer are the helix, the posterior auricle skin, and the antihelix, Dr. Keefe said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery.
"More than 70% of lesions are smaller than 3 cm in size, and auricular lesions make up an estimated 8% of all skin cancers," said Dr. Keefe, a plastic surgeon with the division of head and neck surgery at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego. "The defects are unique, and the underlying cartilage structure makes it all the more interesting."
And challenging – defects may be located on the skin of the ear only, on the lateral side, or on the posterior side, or they may involve a combination of skin and cartilage. Healing by secondary intention is effective for concave defects, but the size of the defect drives the reconstruction options. "If there is no perichondrium, punch holes through cartilage with a 2-3 mm punch to allow granulation tissue to grow through, and then use a skin graft or allow it to heal with secondary intention," he said. "Keep the area moist with antibiotic ointment."
Options for reconstruction of defects in the middle one-third of the ear include primary closure, full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs), the helical advancement flap, and the retroauricular composite advancement flap, while options for defects in the lower one-third of the ear include primary closure and the preauricular tubed flap. Options for reconstruction of defects in the upper one-third of the ear include primary closure, FTSGs, the helical advancement flap, the retroauricular and preauricular tubed flaps, and constructing an autogenous cartilage framework with FTSGs.
Dr. Keefe said that most small helical rim defects limited to the skin can be closed primarily. "There might be slight rim asymmetry [after closure]," he said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic. "Some patients might not care [about this], but you have to advise them of that," he added.
A bilobed advancement flap is another option for helical rim defects limited to the skin. This flap "works well for cutaneous defects 2 cm or smaller in the helical rim or the posterior auricle," he said. "The other thing you can do with these bilobed flaps is advance them over the edge to correct helical rim defects."
The banner flap is another effective flap for helical rim defects, especially those located on the superior helix. It does not replace cartilage, but it conceals the incision well. For small composite helix and anterior defects, Dr. Keefe favors the chondrocutaneous advancement flap.
He said that he favors using FTSGs on the anterior surface of the helix for skin defects whenever possible. "You can use a composite skin graft as well, especially to replace cartilage or skin defects that are smaller than 1 cm in size," he said. "A FTSG is easy to harvest and has minimal contraction. Common donor sites include the preauricular, postauricular, supraclavicular, and clavicular regions. Make sure you trim off the fat." For posterior surface defects, the bilobe or advancement flaps work well.
Grafts must be placed on tissue with an adequate blood supply. Effective grafts establish imbibition in the first 24 hours, inosculation within 48-72 hours, and restoration of circulation within 4-7 days.
Dr. Keefe said that he had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SUPERFICIAL ANATOMY AND CUTANEOUS SURGERY
Early Scar Treatment Is 'Critical'
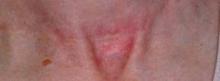
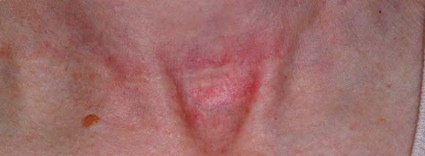
SAN DIEGO – The future of treating hypertrophic and keloidal scars will involve earlier intervention with new and existing technologies – even at the genesis of scar formation, said Dr. E. Victor Ross.
"I think you’re going to see a lot more in the future about scars, not just in the laser area, but also in the biologic arena, because we’re learning more about the way scars behave," Dr. Ross said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. "Some physicians are treating scars as early as the time of Mohs surgery, for example, by applying the PDL [pulsed-dye laser] at the time of suture placement. That’s perhaps a bit extreme, but I think you are going to see newer technologies and drugs used synergistically to give us a better fighting chance to prevent and treat scars."
Dr. Ross of Scripps Clinic Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Center in Carmel Valley, Calif., said that there is a lack of consensus regarding how the two main types of scars hypertrophic and keloidal – are defined. Historically, "we’ve said that hypertrophic scars don’t go beyond the boundary of where the scar tissue was, and keloidal scars go around the perimeter of where the scar boundaries were," he noted. "If the scar is red, even if it’s longstanding, I tend to call it a hypertrophic scar. If it tends to be more flesh colored, and aged like a fine wine, I tend to call it a keloidal scar. The critical thing with these scars is how long it takes the wound to heal. If an open wound takes more than 3-4 weeks to heal, often it will be hypertrophic."
Existing therapies that are commonly used to treat scars include intralesional steroids, intralesional 5-fluorouracil, oral antihistamines, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, lasers, hydrogel sheeting, and compression. "The critical thing is to treat relatively early; you have to use all the weapons that are available to you," Dr. Ross said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
He said that when treating scars, a modifiable approach should be taken. "You want to modify the scar. After it’s formed, you want to rehabilitate the scar and make it more like the skin around it."
When using intralesional steroids, Dr. Ross prefers to use very low volumes with a very high concentration of Kenalog, "typically 40 mg/mL in tiny amounts with a 3-gauge, half-inch needle," he said. "You want to keep the needle tip relatively superficial. If the steroid floats into the scar too easily you’re probably too deep or under the scar."
He favors using fractional lasers for scars whenever possible. These devices "create microscopic wounds in the skin," he said. "It turns out that if you fractionate a wound, the reservoirs of normal, undamaged skin act as ‘seeds’ to make the wounds heal quickly. I like to use purpuric settings with the pulsed-dye laser. They tend to give you better results than other settings."
For scars that form after thyroid surgery, Dr. Ross likes to use a PDL or IPL (intense pulsed light) to reduce the redness, followed by a nonablative fractional laser. With that tandem approach "you can almost make the scar go away, which is a complete rehabilitation of the scar," he said.
Innovative scar therapies include topical mitomycin C, which has worked well for postoperative keloids; oral and topical tamoxifen, which helps in the formation of fibroblasts; and oral methotrexate, which has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment and prevention of keloids. Imiquimod has also been used, "but I’m not a believer in it," Dr. Ross said. "We’ve tried it several times and we found that it irritated the skin most of the time. Retinoids are good and bad. They decrease fibroblast activity but also decrease collagenase."
Dr. Ross disclosed that he is a consultant for Cutera, Palomar Medical Technologies, and Lumenis. He has also received research support from Palomar, Sciton, and Syneron Medical.
SAN DIEGO – The future of treating hypertrophic and keloidal scars will involve earlier intervention with new and existing technologies – even at the genesis of scar formation, said Dr. E. Victor Ross.
"I think you’re going to see a lot more in the future about scars, not just in the laser area, but also in the biologic arena, because we’re learning more about the way scars behave," Dr. Ross said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. "Some physicians are treating scars as early as the time of Mohs surgery, for example, by applying the PDL [pulsed-dye laser] at the time of suture placement. That’s perhaps a bit extreme, but I think you are going to see newer technologies and drugs used synergistically to give us a better fighting chance to prevent and treat scars."
Dr. Ross of Scripps Clinic Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Center in Carmel Valley, Calif., said that there is a lack of consensus regarding how the two main types of scars hypertrophic and keloidal – are defined. Historically, "we’ve said that hypertrophic scars don’t go beyond the boundary of where the scar tissue was, and keloidal scars go around the perimeter of where the scar boundaries were," he noted. "If the scar is red, even if it’s longstanding, I tend to call it a hypertrophic scar. If it tends to be more flesh colored, and aged like a fine wine, I tend to call it a keloidal scar. The critical thing with these scars is how long it takes the wound to heal. If an open wound takes more than 3-4 weeks to heal, often it will be hypertrophic."
Existing therapies that are commonly used to treat scars include intralesional steroids, intralesional 5-fluorouracil, oral antihistamines, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, lasers, hydrogel sheeting, and compression. "The critical thing is to treat relatively early; you have to use all the weapons that are available to you," Dr. Ross said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
He said that when treating scars, a modifiable approach should be taken. "You want to modify the scar. After it’s formed, you want to rehabilitate the scar and make it more like the skin around it."
When using intralesional steroids, Dr. Ross prefers to use very low volumes with a very high concentration of Kenalog, "typically 40 mg/mL in tiny amounts with a 3-gauge, half-inch needle," he said. "You want to keep the needle tip relatively superficial. If the steroid floats into the scar too easily you’re probably too deep or under the scar."
He favors using fractional lasers for scars whenever possible. These devices "create microscopic wounds in the skin," he said. "It turns out that if you fractionate a wound, the reservoirs of normal, undamaged skin act as ‘seeds’ to make the wounds heal quickly. I like to use purpuric settings with the pulsed-dye laser. They tend to give you better results than other settings."
For scars that form after thyroid surgery, Dr. Ross likes to use a PDL or IPL (intense pulsed light) to reduce the redness, followed by a nonablative fractional laser. With that tandem approach "you can almost make the scar go away, which is a complete rehabilitation of the scar," he said.
Innovative scar therapies include topical mitomycin C, which has worked well for postoperative keloids; oral and topical tamoxifen, which helps in the formation of fibroblasts; and oral methotrexate, which has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment and prevention of keloids. Imiquimod has also been used, "but I’m not a believer in it," Dr. Ross said. "We’ve tried it several times and we found that it irritated the skin most of the time. Retinoids are good and bad. They decrease fibroblast activity but also decrease collagenase."
Dr. Ross disclosed that he is a consultant for Cutera, Palomar Medical Technologies, and Lumenis. He has also received research support from Palomar, Sciton, and Syneron Medical.
SAN DIEGO – The future of treating hypertrophic and keloidal scars will involve earlier intervention with new and existing technologies – even at the genesis of scar formation, said Dr. E. Victor Ross.
"I think you’re going to see a lot more in the future about scars, not just in the laser area, but also in the biologic arena, because we’re learning more about the way scars behave," Dr. Ross said at a meeting on superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery. "Some physicians are treating scars as early as the time of Mohs surgery, for example, by applying the PDL [pulsed-dye laser] at the time of suture placement. That’s perhaps a bit extreme, but I think you are going to see newer technologies and drugs used synergistically to give us a better fighting chance to prevent and treat scars."
Dr. Ross of Scripps Clinic Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Center in Carmel Valley, Calif., said that there is a lack of consensus regarding how the two main types of scars hypertrophic and keloidal – are defined. Historically, "we’ve said that hypertrophic scars don’t go beyond the boundary of where the scar tissue was, and keloidal scars go around the perimeter of where the scar boundaries were," he noted. "If the scar is red, even if it’s longstanding, I tend to call it a hypertrophic scar. If it tends to be more flesh colored, and aged like a fine wine, I tend to call it a keloidal scar. The critical thing with these scars is how long it takes the wound to heal. If an open wound takes more than 3-4 weeks to heal, often it will be hypertrophic."
Existing therapies that are commonly used to treat scars include intralesional steroids, intralesional 5-fluorouracil, oral antihistamines, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, lasers, hydrogel sheeting, and compression. "The critical thing is to treat relatively early; you have to use all the weapons that are available to you," Dr. Ross said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the Scripps Clinic.
He said that when treating scars, a modifiable approach should be taken. "You want to modify the scar. After it’s formed, you want to rehabilitate the scar and make it more like the skin around it."
When using intralesional steroids, Dr. Ross prefers to use very low volumes with a very high concentration of Kenalog, "typically 40 mg/mL in tiny amounts with a 3-gauge, half-inch needle," he said. "You want to keep the needle tip relatively superficial. If the steroid floats into the scar too easily you’re probably too deep or under the scar."
He favors using fractional lasers for scars whenever possible. These devices "create microscopic wounds in the skin," he said. "It turns out that if you fractionate a wound, the reservoirs of normal, undamaged skin act as ‘seeds’ to make the wounds heal quickly. I like to use purpuric settings with the pulsed-dye laser. They tend to give you better results than other settings."
For scars that form after thyroid surgery, Dr. Ross likes to use a PDL or IPL (intense pulsed light) to reduce the redness, followed by a nonablative fractional laser. With that tandem approach "you can almost make the scar go away, which is a complete rehabilitation of the scar," he said.
Innovative scar therapies include topical mitomycin C, which has worked well for postoperative keloids; oral and topical tamoxifen, which helps in the formation of fibroblasts; and oral methotrexate, which has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment and prevention of keloids. Imiquimod has also been used, "but I’m not a believer in it," Dr. Ross said. "We’ve tried it several times and we found that it irritated the skin most of the time. Retinoids are good and bad. They decrease fibroblast activity but also decrease collagenase."
Dr. Ross disclosed that he is a consultant for Cutera, Palomar Medical Technologies, and Lumenis. He has also received research support from Palomar, Sciton, and Syneron Medical.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SUPERFICIAL ANATOMY AND CUTANEOUS SURGERY