User login
Virtual visits may cut no-show rate for follow-up HF appointment
PHILADELPHIA – For patients transitioning to home after a heart failure hospitalization, substituting in-person visits with virtual, video-based visits is feasible, safe, and may reduce appointment no-show rates, results of a randomized study suggest.
Connecting patients with clinicians over secure video cut no-show rates at 7 days post-discharge by about one-third, with no difference in risk of readmission, emergency department visits, or death, compared with the traditional in-person follow-up visit, investigator Eiran Z. Gorodeski, MD, MPH, reported here at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
While the video meet-up doesn’t allow for a physical exam, it’s still possible to collect history of what happened since hospital discharge, assess breathing, and complete other aspects of the follow-up visit, according to Dr. Gorodeski, director of advanced heart failure section at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center.
“The way we view use of virtual visits 7 days post-discharge is, in many ways, as a screening platform,” he said in a panel discussion. “If someone seems to be doing poorly, you can always invite them to come in, but most patients post discharge are not congested, and they’re doing quite well. Probably the more relevant issues are things like: Do they have their medications? Do they understand what their follow-up appointments are?”
During the virtual visit, patients are asked to hold their medication bottles up to the camera so the clinician can see what they are taking.
“Frequently, we are able to catch mistakes,” Dr. Gorodeski said. “Of note, most patients don’t bring their pill bottles to the clinic, so in some ways doing the virtual visit for that aspect was more valuable.”
Patients who opt for a virtual visit can do so from any smart phone, laptop, or desktop computer. Once logged in, they enter a virtual waiting room as the clinician receives a text notification to log in and begin the visit.
“It’s very efficient with time, and my questions were answered quickly,” said a patient in a short video Dr. Gorodeski played to illustrate the technology.
“I still feel the same connectivity with the patient,” a clinician in the video said.
There is currently no way to bill insurance companies for this type of visit, Dr. Gorodeski said when asked what initial barriers other institutions might have implementing a similar approach.
In the randomized, single-center clinical trial Dr. Gorodeski presented here at the HFSA meeting, called VIV-HF (Virtual Visits in Heart Failure Care Transitions), a total of 108 patients were randomized to the virtual visit (52 patients) or an in-person visit (56 patients).
The majority of patients (over 60%) had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, according to the reported study results.
No-show rates were 50% for the in-person visit, and 34.6% for the virtual visit, for a relative risk reduction of 31%. However, this difference did not reach statistical significance, likely because the study was underpowered, according to Dr. Gorodeski.
“This strategy may reduce postdischarge appointment no-show rates, and this needs to be studied further in larger and appropriately powered clinical trials,” he said in presenting the results.
The 7-day postdischarge outpatient clinic visit is recommended in guidelines and viewed as a way to increase care engagement while reducing risk of poor outcomes, according to VIV-HF investigators.
Support for the study came from the Hunnell Fund. Dr. Gorodeski reported being a consultant and advisor to Abbott.
cardnews@mdedge
SOURCE: Gorodeski EZ, et al. HFSA 2019. Late-Breaking Clinical Trials session.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients transitioning to home after a heart failure hospitalization, substituting in-person visits with virtual, video-based visits is feasible, safe, and may reduce appointment no-show rates, results of a randomized study suggest.
Connecting patients with clinicians over secure video cut no-show rates at 7 days post-discharge by about one-third, with no difference in risk of readmission, emergency department visits, or death, compared with the traditional in-person follow-up visit, investigator Eiran Z. Gorodeski, MD, MPH, reported here at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
While the video meet-up doesn’t allow for a physical exam, it’s still possible to collect history of what happened since hospital discharge, assess breathing, and complete other aspects of the follow-up visit, according to Dr. Gorodeski, director of advanced heart failure section at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center.
“The way we view use of virtual visits 7 days post-discharge is, in many ways, as a screening platform,” he said in a panel discussion. “If someone seems to be doing poorly, you can always invite them to come in, but most patients post discharge are not congested, and they’re doing quite well. Probably the more relevant issues are things like: Do they have their medications? Do they understand what their follow-up appointments are?”
During the virtual visit, patients are asked to hold their medication bottles up to the camera so the clinician can see what they are taking.
“Frequently, we are able to catch mistakes,” Dr. Gorodeski said. “Of note, most patients don’t bring their pill bottles to the clinic, so in some ways doing the virtual visit for that aspect was more valuable.”
Patients who opt for a virtual visit can do so from any smart phone, laptop, or desktop computer. Once logged in, they enter a virtual waiting room as the clinician receives a text notification to log in and begin the visit.
“It’s very efficient with time, and my questions were answered quickly,” said a patient in a short video Dr. Gorodeski played to illustrate the technology.
“I still feel the same connectivity with the patient,” a clinician in the video said.
There is currently no way to bill insurance companies for this type of visit, Dr. Gorodeski said when asked what initial barriers other institutions might have implementing a similar approach.
In the randomized, single-center clinical trial Dr. Gorodeski presented here at the HFSA meeting, called VIV-HF (Virtual Visits in Heart Failure Care Transitions), a total of 108 patients were randomized to the virtual visit (52 patients) or an in-person visit (56 patients).
The majority of patients (over 60%) had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, according to the reported study results.
No-show rates were 50% for the in-person visit, and 34.6% for the virtual visit, for a relative risk reduction of 31%. However, this difference did not reach statistical significance, likely because the study was underpowered, according to Dr. Gorodeski.
“This strategy may reduce postdischarge appointment no-show rates, and this needs to be studied further in larger and appropriately powered clinical trials,” he said in presenting the results.
The 7-day postdischarge outpatient clinic visit is recommended in guidelines and viewed as a way to increase care engagement while reducing risk of poor outcomes, according to VIV-HF investigators.
Support for the study came from the Hunnell Fund. Dr. Gorodeski reported being a consultant and advisor to Abbott.
cardnews@mdedge
SOURCE: Gorodeski EZ, et al. HFSA 2019. Late-Breaking Clinical Trials session.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients transitioning to home after a heart failure hospitalization, substituting in-person visits with virtual, video-based visits is feasible, safe, and may reduce appointment no-show rates, results of a randomized study suggest.
Connecting patients with clinicians over secure video cut no-show rates at 7 days post-discharge by about one-third, with no difference in risk of readmission, emergency department visits, or death, compared with the traditional in-person follow-up visit, investigator Eiran Z. Gorodeski, MD, MPH, reported here at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
While the video meet-up doesn’t allow for a physical exam, it’s still possible to collect history of what happened since hospital discharge, assess breathing, and complete other aspects of the follow-up visit, according to Dr. Gorodeski, director of advanced heart failure section at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center.
“The way we view use of virtual visits 7 days post-discharge is, in many ways, as a screening platform,” he said in a panel discussion. “If someone seems to be doing poorly, you can always invite them to come in, but most patients post discharge are not congested, and they’re doing quite well. Probably the more relevant issues are things like: Do they have their medications? Do they understand what their follow-up appointments are?”
During the virtual visit, patients are asked to hold their medication bottles up to the camera so the clinician can see what they are taking.
“Frequently, we are able to catch mistakes,” Dr. Gorodeski said. “Of note, most patients don’t bring their pill bottles to the clinic, so in some ways doing the virtual visit for that aspect was more valuable.”
Patients who opt for a virtual visit can do so from any smart phone, laptop, or desktop computer. Once logged in, they enter a virtual waiting room as the clinician receives a text notification to log in and begin the visit.
“It’s very efficient with time, and my questions were answered quickly,” said a patient in a short video Dr. Gorodeski played to illustrate the technology.
“I still feel the same connectivity with the patient,” a clinician in the video said.
There is currently no way to bill insurance companies for this type of visit, Dr. Gorodeski said when asked what initial barriers other institutions might have implementing a similar approach.
In the randomized, single-center clinical trial Dr. Gorodeski presented here at the HFSA meeting, called VIV-HF (Virtual Visits in Heart Failure Care Transitions), a total of 108 patients were randomized to the virtual visit (52 patients) or an in-person visit (56 patients).
The majority of patients (over 60%) had heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, according to the reported study results.
No-show rates were 50% for the in-person visit, and 34.6% for the virtual visit, for a relative risk reduction of 31%. However, this difference did not reach statistical significance, likely because the study was underpowered, according to Dr. Gorodeski.
“This strategy may reduce postdischarge appointment no-show rates, and this needs to be studied further in larger and appropriately powered clinical trials,” he said in presenting the results.
The 7-day postdischarge outpatient clinic visit is recommended in guidelines and viewed as a way to increase care engagement while reducing risk of poor outcomes, according to VIV-HF investigators.
Support for the study came from the Hunnell Fund. Dr. Gorodeski reported being a consultant and advisor to Abbott.
cardnews@mdedge
SOURCE: Gorodeski EZ, et al. HFSA 2019. Late-Breaking Clinical Trials session.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Patiromer allows more CKD patients to continue on spironolactone
PHILADELPHIA – Among patients with chronic kidney disease with resistant hypertension, coadministration of patiromer enables more patients to stay on spironolactone, Bryan Williams, MD, of University College London, said at the scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
Having the potassium-binding polymer on board allowed for more persistent use of spironolactone, both in the subgroup of patients with heart failure, and those without, he said in a late-breaking clinical trials session.
In the international, phase 2 AMBER (Spironolactone With Patiromer in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease) trial, 295 patients with chronic kidney disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate from 25 to 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) were randomly assigned to treatment with spironolactone either placebo (148) or patiromer (147).
, for a significant between-group difference of 19.5% (P less than .0001). In addition, blood pressure lowering was significantly greater in the patiromer (–11.7 mm Hg) than in the placebo (–10.8 mm Hg) group. Results of the AMBER trial were published concurrently with Dr. Williams’ presentation (Lancet 2019 Sep 15; doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32135-X).
While spironolactone is a “highly effective” drug, studies supporting guideline recommendations for its use in resistant hypertension have largely excluded patients with advanced chronic kidney disease because of increased risk of developing spironolactone-induced hyperkalemia, Dr. Williams told attendees. It remains unclear, however, whether coadministration of patiromer will improve long-term outcomes. Also, many placebo-treated patients in AMBER were able to continue on spironolactone without the help of patiromer, prompting one attendee to question whether there was a smarter way to target the drug, rather than treating all patients up front.
“I don’t think it’s going to be easy to say, ‘this patient’s going to respond, and this patient’s not going to respond,’ ” Dr. Williams said in response, “but at least we have an opportunity to try now in a group of patients who simply may be denied treatment because of a perception that it is difficult to use spironolactone in them.”
That perception is actually not unreasonable, he added, given that 66% of patients in the placebo group in AMBER developed hyperkalemia, suggesting that spironolactone is “not an easy drug to use” in chronic kidney disease patients.
John Teerlink, MD, of the San Francisco VA Medical Center, said the AMBER study is “another building block” in a series of developments of enabling therapies.
“I think it’s a great message for all of us to begin thinking about other therapies we can use to help modify our use of these potential life-saving therapies,” he said in a panel discussion of the results.
Patiromer’s impact on longer-term outcomes is the focus of DIAMOND, a phase 3, randomized, placebo controlled trial that is currently recruiting. DIAMOND will determine whether giving patiromer to patients who developed hyperkalemia on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors decreases cardiovascular deaths and hospitalizations, by virtue of enabling continued RAAS inhibitor use.
Funding for AMBER came from Relypsa, which markets patiromer (Veltassa). Dr. Williams reported consulting for Relypsa during the conduct of the study, along with disclosures outside the scope of the AMBER study (Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Novartis, Servier, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Vascular Dynamics).
SOURCE: Williams B. HFSA 2019.
PHILADELPHIA – Among patients with chronic kidney disease with resistant hypertension, coadministration of patiromer enables more patients to stay on spironolactone, Bryan Williams, MD, of University College London, said at the scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
Having the potassium-binding polymer on board allowed for more persistent use of spironolactone, both in the subgroup of patients with heart failure, and those without, he said in a late-breaking clinical trials session.
In the international, phase 2 AMBER (Spironolactone With Patiromer in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease) trial, 295 patients with chronic kidney disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate from 25 to 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) were randomly assigned to treatment with spironolactone either placebo (148) or patiromer (147).
, for a significant between-group difference of 19.5% (P less than .0001). In addition, blood pressure lowering was significantly greater in the patiromer (–11.7 mm Hg) than in the placebo (–10.8 mm Hg) group. Results of the AMBER trial were published concurrently with Dr. Williams’ presentation (Lancet 2019 Sep 15; doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32135-X).
While spironolactone is a “highly effective” drug, studies supporting guideline recommendations for its use in resistant hypertension have largely excluded patients with advanced chronic kidney disease because of increased risk of developing spironolactone-induced hyperkalemia, Dr. Williams told attendees. It remains unclear, however, whether coadministration of patiromer will improve long-term outcomes. Also, many placebo-treated patients in AMBER were able to continue on spironolactone without the help of patiromer, prompting one attendee to question whether there was a smarter way to target the drug, rather than treating all patients up front.
“I don’t think it’s going to be easy to say, ‘this patient’s going to respond, and this patient’s not going to respond,’ ” Dr. Williams said in response, “but at least we have an opportunity to try now in a group of patients who simply may be denied treatment because of a perception that it is difficult to use spironolactone in them.”
That perception is actually not unreasonable, he added, given that 66% of patients in the placebo group in AMBER developed hyperkalemia, suggesting that spironolactone is “not an easy drug to use” in chronic kidney disease patients.
John Teerlink, MD, of the San Francisco VA Medical Center, said the AMBER study is “another building block” in a series of developments of enabling therapies.
“I think it’s a great message for all of us to begin thinking about other therapies we can use to help modify our use of these potential life-saving therapies,” he said in a panel discussion of the results.
Patiromer’s impact on longer-term outcomes is the focus of DIAMOND, a phase 3, randomized, placebo controlled trial that is currently recruiting. DIAMOND will determine whether giving patiromer to patients who developed hyperkalemia on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors decreases cardiovascular deaths and hospitalizations, by virtue of enabling continued RAAS inhibitor use.
Funding for AMBER came from Relypsa, which markets patiromer (Veltassa). Dr. Williams reported consulting for Relypsa during the conduct of the study, along with disclosures outside the scope of the AMBER study (Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Novartis, Servier, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Vascular Dynamics).
SOURCE: Williams B. HFSA 2019.
PHILADELPHIA – Among patients with chronic kidney disease with resistant hypertension, coadministration of patiromer enables more patients to stay on spironolactone, Bryan Williams, MD, of University College London, said at the scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
Having the potassium-binding polymer on board allowed for more persistent use of spironolactone, both in the subgroup of patients with heart failure, and those without, he said in a late-breaking clinical trials session.
In the international, phase 2 AMBER (Spironolactone With Patiromer in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease) trial, 295 patients with chronic kidney disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate from 25 to 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) were randomly assigned to treatment with spironolactone either placebo (148) or patiromer (147).
, for a significant between-group difference of 19.5% (P less than .0001). In addition, blood pressure lowering was significantly greater in the patiromer (–11.7 mm Hg) than in the placebo (–10.8 mm Hg) group. Results of the AMBER trial were published concurrently with Dr. Williams’ presentation (Lancet 2019 Sep 15; doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32135-X).
While spironolactone is a “highly effective” drug, studies supporting guideline recommendations for its use in resistant hypertension have largely excluded patients with advanced chronic kidney disease because of increased risk of developing spironolactone-induced hyperkalemia, Dr. Williams told attendees. It remains unclear, however, whether coadministration of patiromer will improve long-term outcomes. Also, many placebo-treated patients in AMBER were able to continue on spironolactone without the help of patiromer, prompting one attendee to question whether there was a smarter way to target the drug, rather than treating all patients up front.
“I don’t think it’s going to be easy to say, ‘this patient’s going to respond, and this patient’s not going to respond,’ ” Dr. Williams said in response, “but at least we have an opportunity to try now in a group of patients who simply may be denied treatment because of a perception that it is difficult to use spironolactone in them.”
That perception is actually not unreasonable, he added, given that 66% of patients in the placebo group in AMBER developed hyperkalemia, suggesting that spironolactone is “not an easy drug to use” in chronic kidney disease patients.
John Teerlink, MD, of the San Francisco VA Medical Center, said the AMBER study is “another building block” in a series of developments of enabling therapies.
“I think it’s a great message for all of us to begin thinking about other therapies we can use to help modify our use of these potential life-saving therapies,” he said in a panel discussion of the results.
Patiromer’s impact on longer-term outcomes is the focus of DIAMOND, a phase 3, randomized, placebo controlled trial that is currently recruiting. DIAMOND will determine whether giving patiromer to patients who developed hyperkalemia on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors decreases cardiovascular deaths and hospitalizations, by virtue of enabling continued RAAS inhibitor use.
Funding for AMBER came from Relypsa, which markets patiromer (Veltassa). Dr. Williams reported consulting for Relypsa during the conduct of the study, along with disclosures outside the scope of the AMBER study (Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Novartis, Servier, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Vascular Dynamics).
SOURCE: Williams B. HFSA 2019.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Treatment guided by remote readings works when used as intended
PHILADELPHIA – A heart failure management strategy guided by home lung fluid measurements from the remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) system can significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations, as long as the technology is used as intended.
A ReDS-directed management strategy did not significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) in the traditional intent-to-treat analysis of the randomized, controlled SMILE trial, William T. Abraham, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
However, use of the Food and Drug Administration–cleared thoracic fluid status monitoring system to guide treatment changes did cut such hospitalizations by 58% in a modified intent-to-treat population that excluded patients who failed to take daily measurements at home and who didn’t receive modified treatment despite actionable readings, Dr. Abraham reported in an oral presentation.
“These observations may support an adherence-based approach to the utilization and reimbursement of ReDS-guided management in recently discharged ADHF patients,” he said.
The ReDS system consists of a device that, within about 90 seconds, provides a measurement of lung fluid via a focused electromagnetic radar beam that passes through the right lung, Dr. Abraham said. Clinicians access data from measurements patients initiate at home through a secure, cloud-based system, and then initiate changes to heart failure management as warranted based on a ReDS-specific treatment algorithm, Dr. Abraham said.
The postmarketing SMILE study of the ReDS system was stopped early because of an administrative decision by the sponsor, according to Dr. Abraham. However, 268 patients enrolled at 43 U.S. sites continued to the end of the study, with an average follow-up of about 6 months, while readmissions were collected and adjudicated by an independent clinical events committee.
A total of 135 patients were randomized to a ReDS-based management strategy, while 133 were randomized to standard of care, the investigator said.
Most of the medication changes made in response to ReDS measurements were increased diuretics because of high lung fluid volume measurements, or decreased diuretics in response to low measurements, though some changes in vasodilator medications were also made, Dr. Abraham said.
The ReDS-directed management approach yielded a “highly nonsignificant” 19% reduction in recurrent or cumulative heart failure readmissions (P = .36); by contrast, after removing nonadherent, noncompliant cases, there were 11 hospitalizations in 91 treatment patients, compared with 43 hospitalizations in 133 control patients, yielding a hazard ratio of 0.42 (95% CI, 0.22-0.82; P = .01).
“This comes back to the adage that, if you don’t use it, you can’t improve clinical outcomes,” he said, explaining that this study’s modified intent-to-treat population was defined by excluding patients who took no ReDS measurements for more than 20 consecutive days; or by clinicians who received at least eight notifications of out-of-range ReDS values yet didn’t implement the ReDS treatment algorithm.
There were no adverse events reported as being definitely related to the use of the device, and five adverse events reported as possibly related to the device, Dr. Abraham said.
SMILE was sponsored by Sensible Medical Innovations. Dr. Abraham reported disclosures (consultant/advisory board) related to Sensible Medical Innovations, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Victorious Medical, V-Wave Medical, and others.
PHILADELPHIA – A heart failure management strategy guided by home lung fluid measurements from the remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) system can significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations, as long as the technology is used as intended.
A ReDS-directed management strategy did not significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) in the traditional intent-to-treat analysis of the randomized, controlled SMILE trial, William T. Abraham, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
However, use of the Food and Drug Administration–cleared thoracic fluid status monitoring system to guide treatment changes did cut such hospitalizations by 58% in a modified intent-to-treat population that excluded patients who failed to take daily measurements at home and who didn’t receive modified treatment despite actionable readings, Dr. Abraham reported in an oral presentation.
“These observations may support an adherence-based approach to the utilization and reimbursement of ReDS-guided management in recently discharged ADHF patients,” he said.
The ReDS system consists of a device that, within about 90 seconds, provides a measurement of lung fluid via a focused electromagnetic radar beam that passes through the right lung, Dr. Abraham said. Clinicians access data from measurements patients initiate at home through a secure, cloud-based system, and then initiate changes to heart failure management as warranted based on a ReDS-specific treatment algorithm, Dr. Abraham said.
The postmarketing SMILE study of the ReDS system was stopped early because of an administrative decision by the sponsor, according to Dr. Abraham. However, 268 patients enrolled at 43 U.S. sites continued to the end of the study, with an average follow-up of about 6 months, while readmissions were collected and adjudicated by an independent clinical events committee.
A total of 135 patients were randomized to a ReDS-based management strategy, while 133 were randomized to standard of care, the investigator said.
Most of the medication changes made in response to ReDS measurements were increased diuretics because of high lung fluid volume measurements, or decreased diuretics in response to low measurements, though some changes in vasodilator medications were also made, Dr. Abraham said.
The ReDS-directed management approach yielded a “highly nonsignificant” 19% reduction in recurrent or cumulative heart failure readmissions (P = .36); by contrast, after removing nonadherent, noncompliant cases, there were 11 hospitalizations in 91 treatment patients, compared with 43 hospitalizations in 133 control patients, yielding a hazard ratio of 0.42 (95% CI, 0.22-0.82; P = .01).
“This comes back to the adage that, if you don’t use it, you can’t improve clinical outcomes,” he said, explaining that this study’s modified intent-to-treat population was defined by excluding patients who took no ReDS measurements for more than 20 consecutive days; or by clinicians who received at least eight notifications of out-of-range ReDS values yet didn’t implement the ReDS treatment algorithm.
There were no adverse events reported as being definitely related to the use of the device, and five adverse events reported as possibly related to the device, Dr. Abraham said.
SMILE was sponsored by Sensible Medical Innovations. Dr. Abraham reported disclosures (consultant/advisory board) related to Sensible Medical Innovations, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Victorious Medical, V-Wave Medical, and others.
PHILADELPHIA – A heart failure management strategy guided by home lung fluid measurements from the remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) system can significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations, as long as the technology is used as intended.
A ReDS-directed management strategy did not significantly reduce recurrent hospitalizations for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) in the traditional intent-to-treat analysis of the randomized, controlled SMILE trial, William T. Abraham, MD, of the Ohio State University, Columbus, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
However, use of the Food and Drug Administration–cleared thoracic fluid status monitoring system to guide treatment changes did cut such hospitalizations by 58% in a modified intent-to-treat population that excluded patients who failed to take daily measurements at home and who didn’t receive modified treatment despite actionable readings, Dr. Abraham reported in an oral presentation.
“These observations may support an adherence-based approach to the utilization and reimbursement of ReDS-guided management in recently discharged ADHF patients,” he said.
The ReDS system consists of a device that, within about 90 seconds, provides a measurement of lung fluid via a focused electromagnetic radar beam that passes through the right lung, Dr. Abraham said. Clinicians access data from measurements patients initiate at home through a secure, cloud-based system, and then initiate changes to heart failure management as warranted based on a ReDS-specific treatment algorithm, Dr. Abraham said.
The postmarketing SMILE study of the ReDS system was stopped early because of an administrative decision by the sponsor, according to Dr. Abraham. However, 268 patients enrolled at 43 U.S. sites continued to the end of the study, with an average follow-up of about 6 months, while readmissions were collected and adjudicated by an independent clinical events committee.
A total of 135 patients were randomized to a ReDS-based management strategy, while 133 were randomized to standard of care, the investigator said.
Most of the medication changes made in response to ReDS measurements were increased diuretics because of high lung fluid volume measurements, or decreased diuretics in response to low measurements, though some changes in vasodilator medications were also made, Dr. Abraham said.
The ReDS-directed management approach yielded a “highly nonsignificant” 19% reduction in recurrent or cumulative heart failure readmissions (P = .36); by contrast, after removing nonadherent, noncompliant cases, there were 11 hospitalizations in 91 treatment patients, compared with 43 hospitalizations in 133 control patients, yielding a hazard ratio of 0.42 (95% CI, 0.22-0.82; P = .01).
“This comes back to the adage that, if you don’t use it, you can’t improve clinical outcomes,” he said, explaining that this study’s modified intent-to-treat population was defined by excluding patients who took no ReDS measurements for more than 20 consecutive days; or by clinicians who received at least eight notifications of out-of-range ReDS values yet didn’t implement the ReDS treatment algorithm.
There were no adverse events reported as being definitely related to the use of the device, and five adverse events reported as possibly related to the device, Dr. Abraham said.
SMILE was sponsored by Sensible Medical Innovations. Dr. Abraham reported disclosures (consultant/advisory board) related to Sensible Medical Innovations, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Victorious Medical, V-Wave Medical, and others.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Cardiotoxicity after checkpoint inhibitor treatment seen early, linked to elevated biomarkers
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
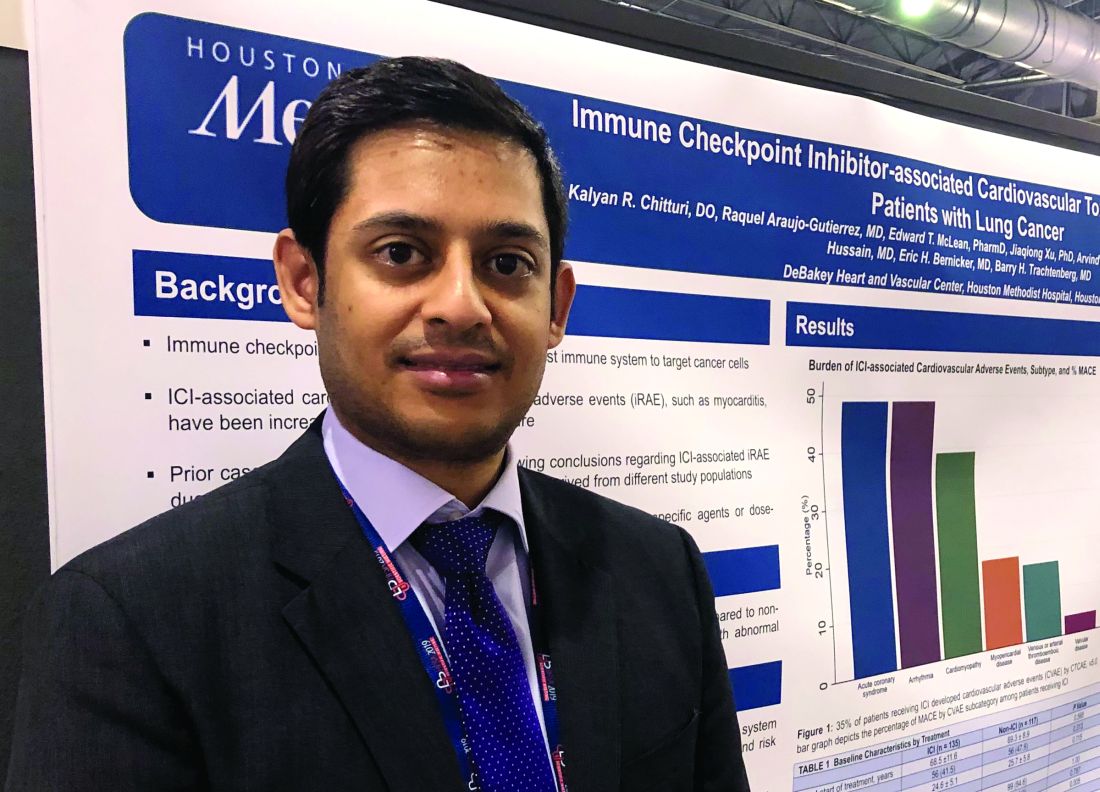
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Machine learning–derived risk score predicts heart failure risk in diabetes patients
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Milrinone beats dobutamine in extending survival in HF
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019