User login
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
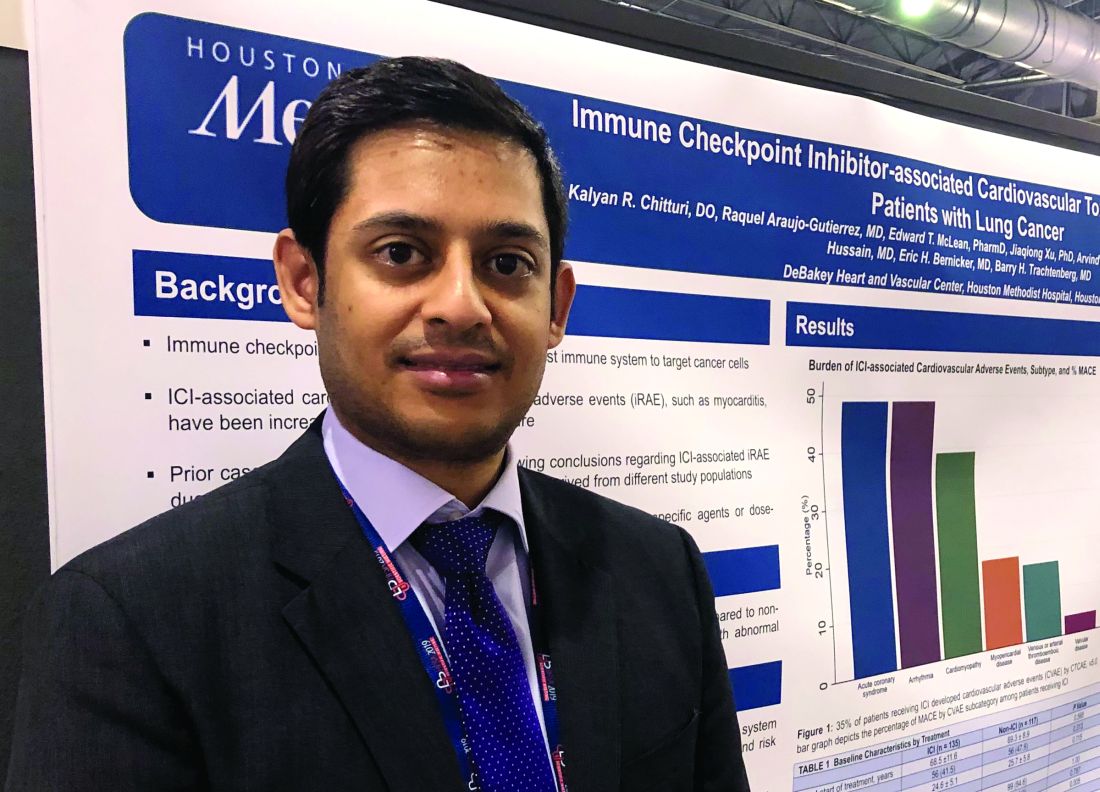
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
PHILADELPHIA – , and occurred more frequently in patients with elevated biomarkers, in a retrospective cohort study reported at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The findings support monitoring of cardiac biomarkers in the initial phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment to identify patient at high cardiac risk, according to Kalyan R. Chitturi, DO, a resident physician with the DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center, Houston Methodist Hospital, who presented the results.
“It’s the early period that warrants the closest monitoring, as within the first 30-40 days, there’s higher risk,” Dr. Chitturi said in an interview. “When there was a biomarker elevation, it markedly increased the risk of MACE, warranting a closer vigilance during that time period.”
The retrospective study conducted by Dr. Chitturi and colleagues included a total of 252 patients with lung cancer who had been treated at one of seven different sites in Houston Methodist Cancer Center between Aug. 1, 2015, and Aug. 1, 2018.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors did not significantly increase the risk of MACE, compared with other lung cancer therapies, with incidences of 13.3% and 10.3%, respectively (P = .632), the investigators found.
However, MACE did occur earlier in the checkpoint inhibitor group, at a median time to event of 40 days, compared with 118 days in the patients not treated with checkpoint inhibitors, they found.
Risk of MACE with checkpoint inhibitor treatment was increased in patients with elevated troponin (hazard ratio, 2.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.18-5.21; P = .017) or elevated brain natriuretic peptide (HR, 5.77; 95% CI, 2.70-12.35; P less than .001), according to multivariate logistic regression analysis results.
These results suggest biomarkers such as cardiac troponin and brain natriuretic peptide are warranted to monitor patients in the early phase of checkpoint inhibitor treatment, according to Dr. Chitturi. “In the cost-benefit ratio of often-lethal MACE, it’s well worth it to collect these,” he said in the interview.
The results corroborate findings from some other recent studies, he noted. These include a recent study that linked elevated serum troponin to myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 24;71[16]:1755-64).
Dr. Chitturi and coauthors reported no disclosures related to their presentation at the HFSA meeting.
SOURCE: Chitturi KR et al. HFSA 2019, Abstract 127.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019