User login
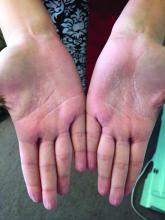
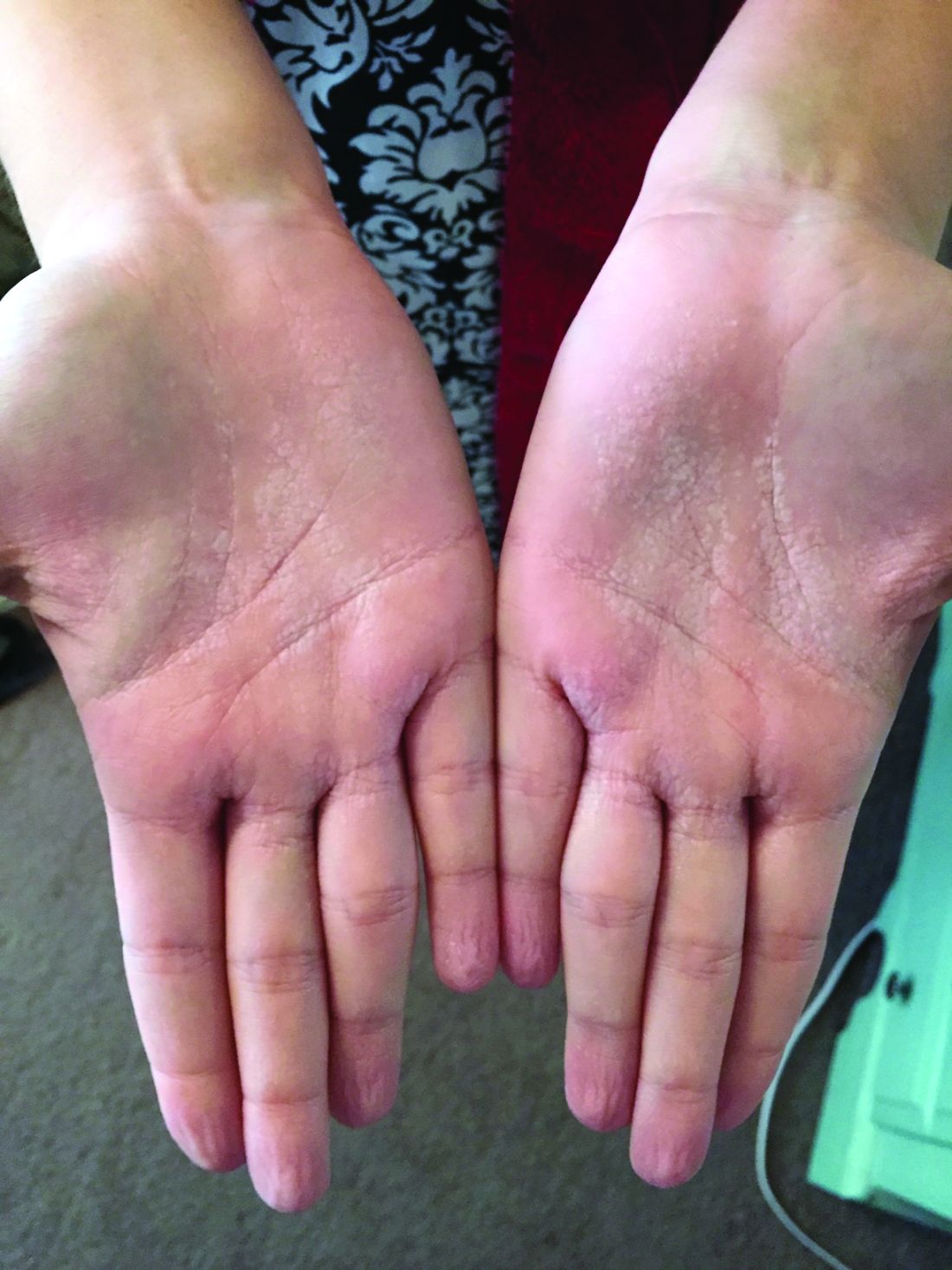
This eruption can be accompanied by a mild burning or tingling sensation, which will subside with the rest of the symptoms in minutes to hours after drying.1
AWP is most frequently associated with cystic fibrosis (CF).2 It can be observed in up to 80% of CF patients and is considered a clinical sign of the disease. AWP can be present in CF carriers to a lesser extent,2,4 and has also been associated with focal hyperhidrosis, atopic dermatitis, Raynaud phenomenon, and COX-2 inhibitor use.5
While a definitive cause is unknown, it is thought that AWP is caused by dysregulation of sweat glands in the palms through increased expression of aquaporin, a protein crucial in the transport of water between cells.3
AWP is quite rare and benign in nature. However, because of its strong association with CF, genetic screening should be considered in asymptomatic patients. Our patient had been screened in the past and is not a CF carrier. Often, the itching or burning associated with CF is mild and easily controlled. The patient was placed on low dose isotretinoin for treatment of her acne. Interestingly, the patient claimed her eruption no longer appeared after starting isotretinoin therapy. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of AWP resolving with isotretinoin use.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Birk, University of Texas, Austin, Texas; and Dr. Mamelak, Sanova Dermatology, in Austin. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Katz M, Ramot Y. CMAJ. 2015 Dec 8;187(18):E515.
2. Tolland JP et al. Dermatology. 2010;221(4):326-30.
3. Kabashima K et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Aug;59(2 Suppl 1):S28-32.
4. Gild R et al. Br J Dermatol. 2010 Nov;163(5):1082-4.
5. Glatz M and Muellegger RR. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203929.
This eruption can be accompanied by a mild burning or tingling sensation, which will subside with the rest of the symptoms in minutes to hours after drying.1
AWP is most frequently associated with cystic fibrosis (CF).2 It can be observed in up to 80% of CF patients and is considered a clinical sign of the disease. AWP can be present in CF carriers to a lesser extent,2,4 and has also been associated with focal hyperhidrosis, atopic dermatitis, Raynaud phenomenon, and COX-2 inhibitor use.5
While a definitive cause is unknown, it is thought that AWP is caused by dysregulation of sweat glands in the palms through increased expression of aquaporin, a protein crucial in the transport of water between cells.3
AWP is quite rare and benign in nature. However, because of its strong association with CF, genetic screening should be considered in asymptomatic patients. Our patient had been screened in the past and is not a CF carrier. Often, the itching or burning associated with CF is mild and easily controlled. The patient was placed on low dose isotretinoin for treatment of her acne. Interestingly, the patient claimed her eruption no longer appeared after starting isotretinoin therapy. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of AWP resolving with isotretinoin use.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Birk, University of Texas, Austin, Texas; and Dr. Mamelak, Sanova Dermatology, in Austin. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Katz M, Ramot Y. CMAJ. 2015 Dec 8;187(18):E515.
2. Tolland JP et al. Dermatology. 2010;221(4):326-30.
3. Kabashima K et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Aug;59(2 Suppl 1):S28-32.
4. Gild R et al. Br J Dermatol. 2010 Nov;163(5):1082-4.
5. Glatz M and Muellegger RR. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203929.
This eruption can be accompanied by a mild burning or tingling sensation, which will subside with the rest of the symptoms in minutes to hours after drying.1
AWP is most frequently associated with cystic fibrosis (CF).2 It can be observed in up to 80% of CF patients and is considered a clinical sign of the disease. AWP can be present in CF carriers to a lesser extent,2,4 and has also been associated with focal hyperhidrosis, atopic dermatitis, Raynaud phenomenon, and COX-2 inhibitor use.5
While a definitive cause is unknown, it is thought that AWP is caused by dysregulation of sweat glands in the palms through increased expression of aquaporin, a protein crucial in the transport of water between cells.3
AWP is quite rare and benign in nature. However, because of its strong association with CF, genetic screening should be considered in asymptomatic patients. Our patient had been screened in the past and is not a CF carrier. Often, the itching or burning associated with CF is mild and easily controlled. The patient was placed on low dose isotretinoin for treatment of her acne. Interestingly, the patient claimed her eruption no longer appeared after starting isotretinoin therapy. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of AWP resolving with isotretinoin use.
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Birk, University of Texas, Austin, Texas; and Dr. Mamelak, Sanova Dermatology, in Austin. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Katz M, Ramot Y. CMAJ. 2015 Dec 8;187(18):E515.
2. Tolland JP et al. Dermatology. 2010;221(4):326-30.
3. Kabashima K et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Aug;59(2 Suppl 1):S28-32.
4. Gild R et al. Br J Dermatol. 2010 Nov;163(5):1082-4.
5. Glatz M and Muellegger RR. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203929.