User login
While many pediatric clinicians have not frequently managed newborns of mothers with reactive syphilis serology, increased adult syphilis may change that.1
Diagnosing/managing congenital syphilis is not always clear cut. A positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) titer in a newborn may not indicate congenital infection but merely may reflect transplacental, passively acquired maternal IgG from the mother’s current or previous infection rather than antibodies produced by the newborn. Because currently no IgM assay for syphilis is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for newborn testing, we must deal with IgG test results.
Often initial management decisions are needed while the infant’s status is evolving. The questions to answer to make final decisions include the following2:
- Was the mother actively infected with Treponema pallidum during pregnancy?
- If so, was the mother appropriately treated and when?
- Does the infant have any clinical, laboratory, or radiographic evidence of syphilis?
- How do the mother’s and infant’s nontreponemal serologic titers (NTT) compare at delivery using the same test?
Note: All infants assessed for congenital syphilis need a full evaluation for HIV.
Managing the infant of a mother with positive tests3,4
All such neonates need an examination for evidence of congenital syphilis. The clinical signs of congenital syphilis in neonates include nonimmune hydrops, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, rhinitis, skin rash, and pseudoparalysis of extremity. Also, consider dark-field examination or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of lesions (such as bullae) or secretions (nasal). If available, have the placenta examined histologically (silver stain) or by PCR (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–validated test). Skeletal radiographic surveys are more useful for stillborn than live born infants. (The complete algorithm can be found in Figure 3.10 of reference 4.)
Order a quantitative NTT, using the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test or RPR test on neonatal serum. Umbilical cord blood is not appropriate because of potential maternal blood contamination, which could give a false-positive result, or Wharton’s jelly, which could give a false-negative result. Use of treponemal-specific tests that are used for maternal diagnosis – such as T. pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA), T. pallidum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TP-EIA), fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test, or T. pallidum chemiluminescence immunoassay (TP-CIA) – on neonatal serum is not recommended because of difficulties in interpretation.
Diagnostic results allow designation of an infant into one of four CDC categories: proven/highly probable syphilis; possible syphilis; syphilis less likely; and syphilis unlikely. Treatment recommendations are based on these categories.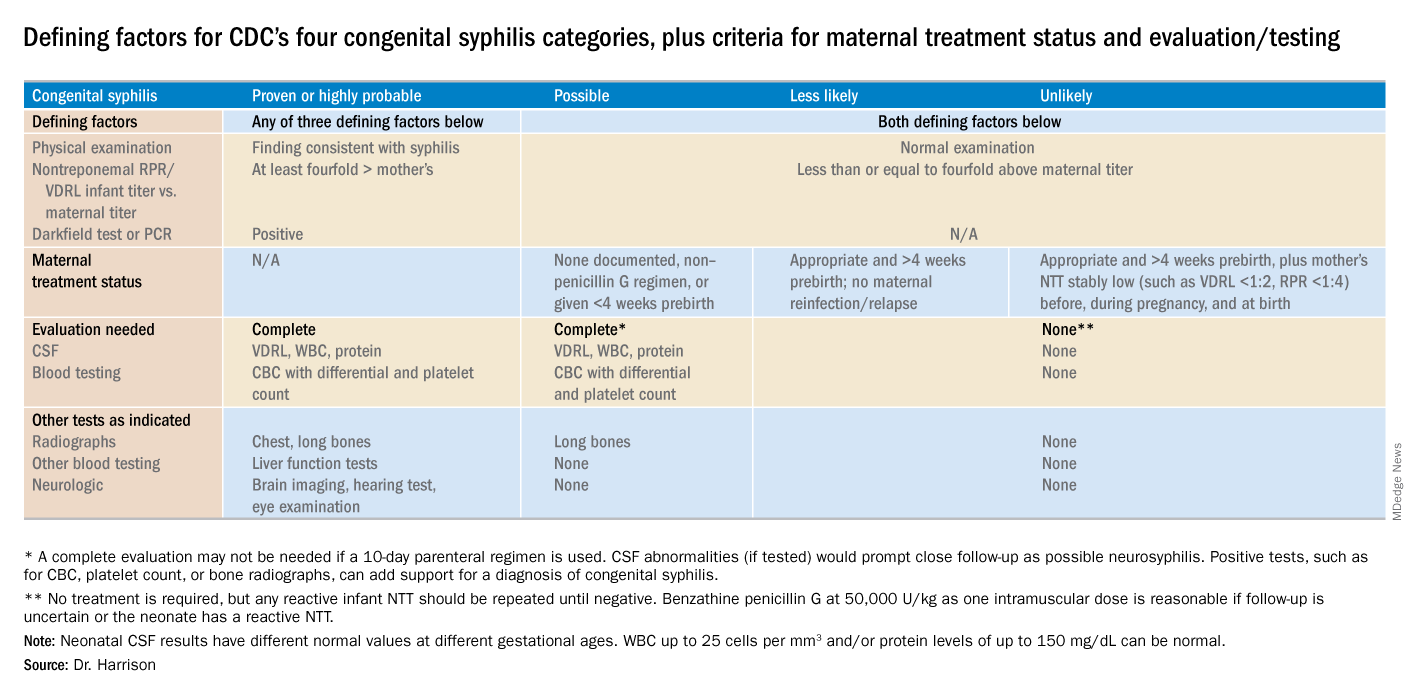
Proven or highly probable syphilis
There are two alternative recommended 10-day treatment regimens.
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 100,000-150,000 U/kg per day by IV at 50,000 U/kg per dose, given every 12 hours through 7 days of age or every 8 hours if greater than 7 days old.
B. Procaine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in one dose each day.
More than 1 day of missed therapy requires restarting a new 10-day course. Use of other antimicrobial agents (such as ampicillin) is not validated, so any empiric ampicillin initially given for possible sepsis does not count toward the 10-day penicillin regimen. If nonpenicillin drugs must be used, close serologic follow-up must occur to ensure adequacy of response to therapy.
Possible syphilis
There are three alternative regimens, the same two as in proven/highly probable syphilis (above) plus a single-dose option
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G, as described above.
B. Procaine penicillin G, as described above.
C. Benzathine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in a single dose.
Note: To be eligible for regimen C, an infant must have a complete evaluation that is normal (cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] examination, long-bone radiographs, and complete blood count with platelet count) and follow-up must be assured. Exception: Neonates born to mothers with untreated early syphilis at the time of delivery are at increased risk for congenital syphilis, and the 10-day course of penicillin G may be considered even if the complete evaluation is normal and follow-up is certain.
Less likely syphilis
One antibiotic regimen is available, but no treatment also may be an option.
A. Benzathine penicillin G as described above.
B. If mother’s NTT has decreased at least fourfold after appropriate early syphilis therapy or remained stably low, which indicates latent syphilis (VDRL less than 1:2; RPR less than 1:4), no treatment is an option but requires repeat serology every 2-3 months until infant is 6 months old.
Unlikely syphilis
No treatment is recommended unless follow-up is uncertain, in which case it is appropriate to give the infant benzathine penicillin G as described above.
Infant with positive NTT at birth
All neonates with reactive NTT need careful follow-up examinations and repeat NTT every 2-3 months until nonreactive. NTT in infants who are not treated because of less likely or unlikely syphilis status should drop by 3 months and be nonreactive by 6 months; this indicates NTT was passively transferred maternal IgG. If NTT remains reactive at 6 months, the infant is likely infected and needs treatment. Persistent NTT at 6-12 months in treated neonates should trigger repeat CSF examination and infectious diseases consultation about a possible repeat of the 10-day penicillin G regimen. If the mother was seroreactive, but the newborn’s NTT was negative at birth, testing of the infant’s NTT needs repeating at 3 months to exclude the possibility that the congenital syphilis was incubating when prior testing occurred at birth. Note: Treponemal-specific tests are not useful in assessing treatment because detectable maternal IgG treponemal antibody can persist at least 15 months.
Neonates with abnormal CSF at birth
Repeat cerebrospinal fluid evaluation every 6 months until results normalize. Persistently reactive CSF VDRL or abnormal CSF indexes not caused by another known cause requires retreatment for possible neurosyphilis, as well as consultation with an expert.
Summary
NTT are the essential test for newborns and some degree of laboratory or imaging work up often are needed. Consider consulting an expert in infectious diseases and/or perinatology if the gray areas do not readily become clear. Treatment of the correct patients with the right drug for the right duration remains the goal, as usual.
Dr. Harrison is a professor of pediatrics at University of Missouri-Kansas City and Director of Research Affairs in the pediatric infectious diseases division at Children’s Mercy Hospital – Kansas City. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. MMWR. 2015 Nov 13;64(44);1241-5.
2. “Congenital Syphilis,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
3. “Syphilis During Pregnancy,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
4. Syphilis – Section 3: Summaries of Infectious Diseases. Red Book Online. 2018.
While many pediatric clinicians have not frequently managed newborns of mothers with reactive syphilis serology, increased adult syphilis may change that.1
Diagnosing/managing congenital syphilis is not always clear cut. A positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) titer in a newborn may not indicate congenital infection but merely may reflect transplacental, passively acquired maternal IgG from the mother’s current or previous infection rather than antibodies produced by the newborn. Because currently no IgM assay for syphilis is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for newborn testing, we must deal with IgG test results.
Often initial management decisions are needed while the infant’s status is evolving. The questions to answer to make final decisions include the following2:
- Was the mother actively infected with Treponema pallidum during pregnancy?
- If so, was the mother appropriately treated and when?
- Does the infant have any clinical, laboratory, or radiographic evidence of syphilis?
- How do the mother’s and infant’s nontreponemal serologic titers (NTT) compare at delivery using the same test?
Note: All infants assessed for congenital syphilis need a full evaluation for HIV.
Managing the infant of a mother with positive tests3,4
All such neonates need an examination for evidence of congenital syphilis. The clinical signs of congenital syphilis in neonates include nonimmune hydrops, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, rhinitis, skin rash, and pseudoparalysis of extremity. Also, consider dark-field examination or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of lesions (such as bullae) or secretions (nasal). If available, have the placenta examined histologically (silver stain) or by PCR (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–validated test). Skeletal radiographic surveys are more useful for stillborn than live born infants. (The complete algorithm can be found in Figure 3.10 of reference 4.)
Order a quantitative NTT, using the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test or RPR test on neonatal serum. Umbilical cord blood is not appropriate because of potential maternal blood contamination, which could give a false-positive result, or Wharton’s jelly, which could give a false-negative result. Use of treponemal-specific tests that are used for maternal diagnosis – such as T. pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA), T. pallidum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TP-EIA), fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test, or T. pallidum chemiluminescence immunoassay (TP-CIA) – on neonatal serum is not recommended because of difficulties in interpretation.
Diagnostic results allow designation of an infant into one of four CDC categories: proven/highly probable syphilis; possible syphilis; syphilis less likely; and syphilis unlikely. Treatment recommendations are based on these categories.
Proven or highly probable syphilis
There are two alternative recommended 10-day treatment regimens.
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 100,000-150,000 U/kg per day by IV at 50,000 U/kg per dose, given every 12 hours through 7 days of age or every 8 hours if greater than 7 days old.
B. Procaine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in one dose each day.
More than 1 day of missed therapy requires restarting a new 10-day course. Use of other antimicrobial agents (such as ampicillin) is not validated, so any empiric ampicillin initially given for possible sepsis does not count toward the 10-day penicillin regimen. If nonpenicillin drugs must be used, close serologic follow-up must occur to ensure adequacy of response to therapy.
Possible syphilis
There are three alternative regimens, the same two as in proven/highly probable syphilis (above) plus a single-dose option
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G, as described above.
B. Procaine penicillin G, as described above.
C. Benzathine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in a single dose.
Note: To be eligible for regimen C, an infant must have a complete evaluation that is normal (cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] examination, long-bone radiographs, and complete blood count with platelet count) and follow-up must be assured. Exception: Neonates born to mothers with untreated early syphilis at the time of delivery are at increased risk for congenital syphilis, and the 10-day course of penicillin G may be considered even if the complete evaluation is normal and follow-up is certain.
Less likely syphilis
One antibiotic regimen is available, but no treatment also may be an option.
A. Benzathine penicillin G as described above.
B. If mother’s NTT has decreased at least fourfold after appropriate early syphilis therapy or remained stably low, which indicates latent syphilis (VDRL less than 1:2; RPR less than 1:4), no treatment is an option but requires repeat serology every 2-3 months until infant is 6 months old.
Unlikely syphilis
No treatment is recommended unless follow-up is uncertain, in which case it is appropriate to give the infant benzathine penicillin G as described above.
Infant with positive NTT at birth
All neonates with reactive NTT need careful follow-up examinations and repeat NTT every 2-3 months until nonreactive. NTT in infants who are not treated because of less likely or unlikely syphilis status should drop by 3 months and be nonreactive by 6 months; this indicates NTT was passively transferred maternal IgG. If NTT remains reactive at 6 months, the infant is likely infected and needs treatment. Persistent NTT at 6-12 months in treated neonates should trigger repeat CSF examination and infectious diseases consultation about a possible repeat of the 10-day penicillin G regimen. If the mother was seroreactive, but the newborn’s NTT was negative at birth, testing of the infant’s NTT needs repeating at 3 months to exclude the possibility that the congenital syphilis was incubating when prior testing occurred at birth. Note: Treponemal-specific tests are not useful in assessing treatment because detectable maternal IgG treponemal antibody can persist at least 15 months.
Neonates with abnormal CSF at birth
Repeat cerebrospinal fluid evaluation every 6 months until results normalize. Persistently reactive CSF VDRL or abnormal CSF indexes not caused by another known cause requires retreatment for possible neurosyphilis, as well as consultation with an expert.
Summary
NTT are the essential test for newborns and some degree of laboratory or imaging work up often are needed. Consider consulting an expert in infectious diseases and/or perinatology if the gray areas do not readily become clear. Treatment of the correct patients with the right drug for the right duration remains the goal, as usual.
Dr. Harrison is a professor of pediatrics at University of Missouri-Kansas City and Director of Research Affairs in the pediatric infectious diseases division at Children’s Mercy Hospital – Kansas City. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. MMWR. 2015 Nov 13;64(44);1241-5.
2. “Congenital Syphilis,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
3. “Syphilis During Pregnancy,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
4. Syphilis – Section 3: Summaries of Infectious Diseases. Red Book Online. 2018.
While many pediatric clinicians have not frequently managed newborns of mothers with reactive syphilis serology, increased adult syphilis may change that.1
Diagnosing/managing congenital syphilis is not always clear cut. A positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) titer in a newborn may not indicate congenital infection but merely may reflect transplacental, passively acquired maternal IgG from the mother’s current or previous infection rather than antibodies produced by the newborn. Because currently no IgM assay for syphilis is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for newborn testing, we must deal with IgG test results.
Often initial management decisions are needed while the infant’s status is evolving. The questions to answer to make final decisions include the following2:
- Was the mother actively infected with Treponema pallidum during pregnancy?
- If so, was the mother appropriately treated and when?
- Does the infant have any clinical, laboratory, or radiographic evidence of syphilis?
- How do the mother’s and infant’s nontreponemal serologic titers (NTT) compare at delivery using the same test?
Note: All infants assessed for congenital syphilis need a full evaluation for HIV.
Managing the infant of a mother with positive tests3,4
All such neonates need an examination for evidence of congenital syphilis. The clinical signs of congenital syphilis in neonates include nonimmune hydrops, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, rhinitis, skin rash, and pseudoparalysis of extremity. Also, consider dark-field examination or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of lesions (such as bullae) or secretions (nasal). If available, have the placenta examined histologically (silver stain) or by PCR (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–validated test). Skeletal radiographic surveys are more useful for stillborn than live born infants. (The complete algorithm can be found in Figure 3.10 of reference 4.)
Order a quantitative NTT, using the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test or RPR test on neonatal serum. Umbilical cord blood is not appropriate because of potential maternal blood contamination, which could give a false-positive result, or Wharton’s jelly, which could give a false-negative result. Use of treponemal-specific tests that are used for maternal diagnosis – such as T. pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA), T. pallidum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TP-EIA), fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test, or T. pallidum chemiluminescence immunoassay (TP-CIA) – on neonatal serum is not recommended because of difficulties in interpretation.
Diagnostic results allow designation of an infant into one of four CDC categories: proven/highly probable syphilis; possible syphilis; syphilis less likely; and syphilis unlikely. Treatment recommendations are based on these categories.
Proven or highly probable syphilis
There are two alternative recommended 10-day treatment regimens.
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 100,000-150,000 U/kg per day by IV at 50,000 U/kg per dose, given every 12 hours through 7 days of age or every 8 hours if greater than 7 days old.
B. Procaine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in one dose each day.
More than 1 day of missed therapy requires restarting a new 10-day course. Use of other antimicrobial agents (such as ampicillin) is not validated, so any empiric ampicillin initially given for possible sepsis does not count toward the 10-day penicillin regimen. If nonpenicillin drugs must be used, close serologic follow-up must occur to ensure adequacy of response to therapy.
Possible syphilis
There are three alternative regimens, the same two as in proven/highly probable syphilis (above) plus a single-dose option
A. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G, as described above.
B. Procaine penicillin G, as described above.
C. Benzathine penicillin G at 50,000 U/kg per dose intramuscularly in a single dose.
Note: To be eligible for regimen C, an infant must have a complete evaluation that is normal (cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] examination, long-bone radiographs, and complete blood count with platelet count) and follow-up must be assured. Exception: Neonates born to mothers with untreated early syphilis at the time of delivery are at increased risk for congenital syphilis, and the 10-day course of penicillin G may be considered even if the complete evaluation is normal and follow-up is certain.
Less likely syphilis
One antibiotic regimen is available, but no treatment also may be an option.
A. Benzathine penicillin G as described above.
B. If mother’s NTT has decreased at least fourfold after appropriate early syphilis therapy or remained stably low, which indicates latent syphilis (VDRL less than 1:2; RPR less than 1:4), no treatment is an option but requires repeat serology every 2-3 months until infant is 6 months old.
Unlikely syphilis
No treatment is recommended unless follow-up is uncertain, in which case it is appropriate to give the infant benzathine penicillin G as described above.
Infant with positive NTT at birth
All neonates with reactive NTT need careful follow-up examinations and repeat NTT every 2-3 months until nonreactive. NTT in infants who are not treated because of less likely or unlikely syphilis status should drop by 3 months and be nonreactive by 6 months; this indicates NTT was passively transferred maternal IgG. If NTT remains reactive at 6 months, the infant is likely infected and needs treatment. Persistent NTT at 6-12 months in treated neonates should trigger repeat CSF examination and infectious diseases consultation about a possible repeat of the 10-day penicillin G regimen. If the mother was seroreactive, but the newborn’s NTT was negative at birth, testing of the infant’s NTT needs repeating at 3 months to exclude the possibility that the congenital syphilis was incubating when prior testing occurred at birth. Note: Treponemal-specific tests are not useful in assessing treatment because detectable maternal IgG treponemal antibody can persist at least 15 months.
Neonates with abnormal CSF at birth
Repeat cerebrospinal fluid evaluation every 6 months until results normalize. Persistently reactive CSF VDRL or abnormal CSF indexes not caused by another known cause requires retreatment for possible neurosyphilis, as well as consultation with an expert.
Summary
NTT are the essential test for newborns and some degree of laboratory or imaging work up often are needed. Consider consulting an expert in infectious diseases and/or perinatology if the gray areas do not readily become clear. Treatment of the correct patients with the right drug for the right duration remains the goal, as usual.
Dr. Harrison is a professor of pediatrics at University of Missouri-Kansas City and Director of Research Affairs in the pediatric infectious diseases division at Children’s Mercy Hospital – Kansas City. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. MMWR. 2015 Nov 13;64(44);1241-5.
2. “Congenital Syphilis,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
3. “Syphilis During Pregnancy,” 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines.
4. Syphilis – Section 3: Summaries of Infectious Diseases. Red Book Online. 2018.

