User login
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.
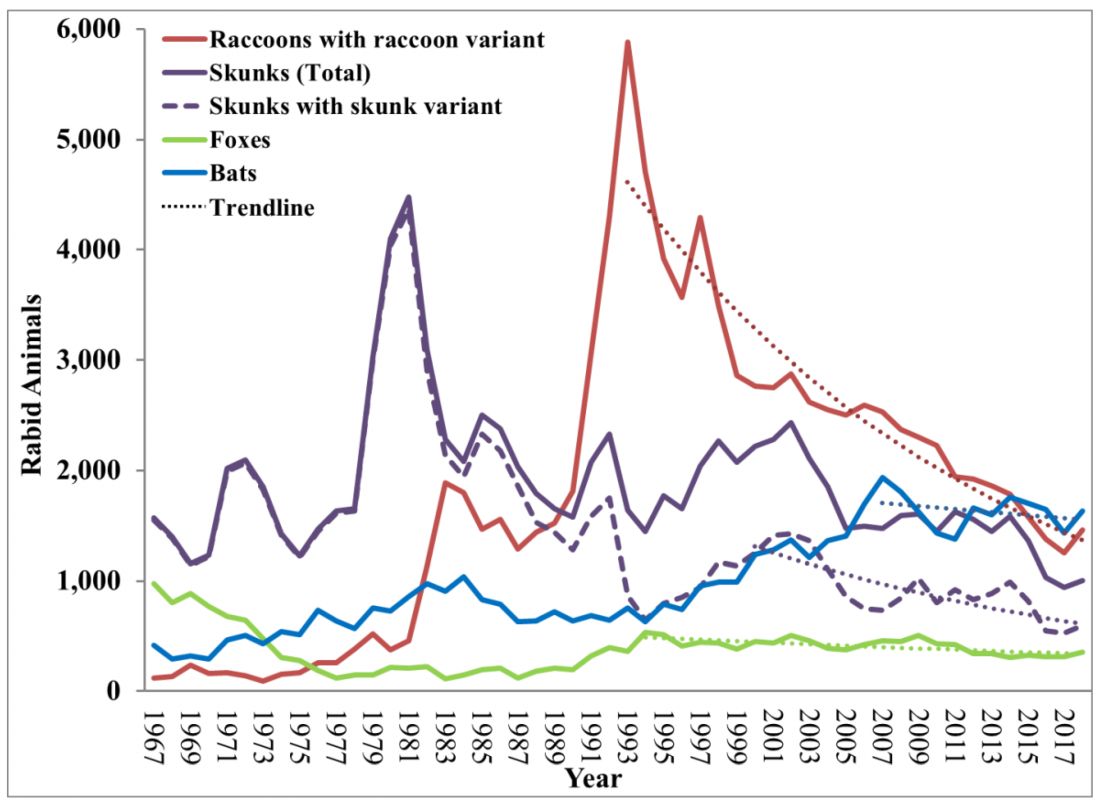
Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
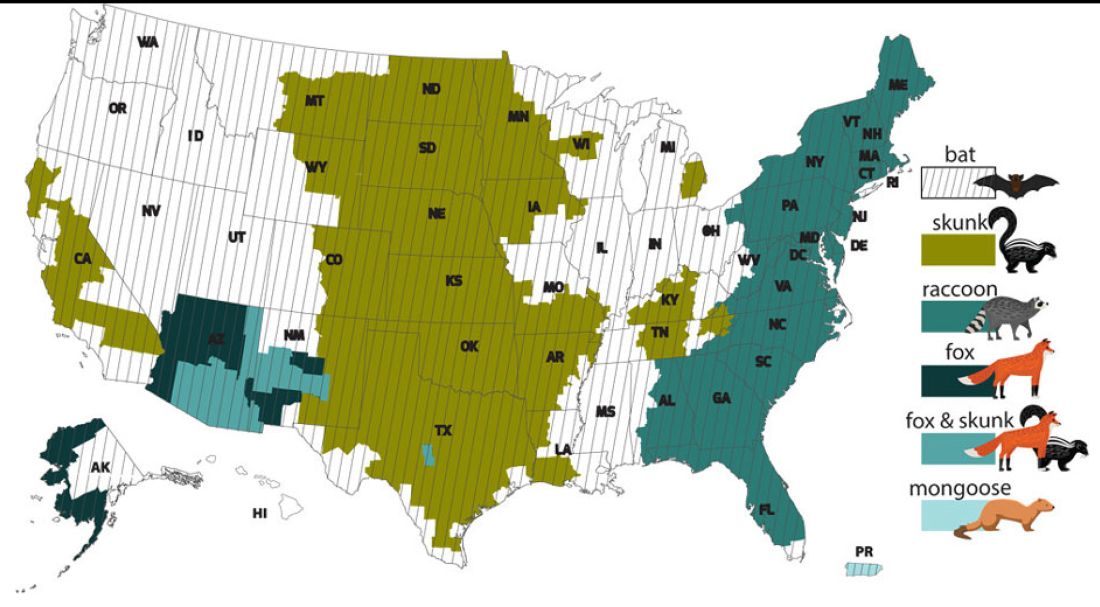
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.
You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.

Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.

You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.

Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.

You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
