User login
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas represent a group of lymphomas derived from B lymphocytes in various stages of differentiation. The skin can be the site of primary or secondary involvement of any of the B-cell lymphomas. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas present in the skin without evidence of extracutaneous disease at the time of diagnosis.1 The World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues recognizes 5 distinct primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma subtypes: primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma; primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma; primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), leg type; DLBCL, not otherwise specified; and intravascular DLBCL.1-3 The DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category includes less common provisional entities with insufficient evidence to be recognized as distinct diseases. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive DLBCL is a rare subtype in this group.4
This article reviews the different clinicopathologic subtypes of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. It also serves to help dermatologists recognize primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL as a rare and aggressive form of this disease.
Case Report
An 84-year-old white man presented with a pruritic eruption on the arms, legs, back, neck, and face of 5 months’ duration. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer that was successfully treated with radiation therapy 6 years prior. The patient denied any constitutional symptoms such as fever, chills, night sweats, or weight loss, and review of systems was negative. The patient was taking prednisone, which alleviated the pruritus, but the lesions persisted.
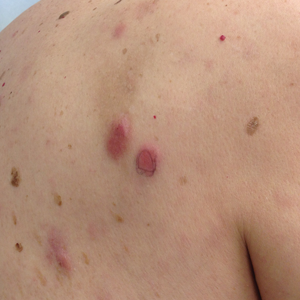
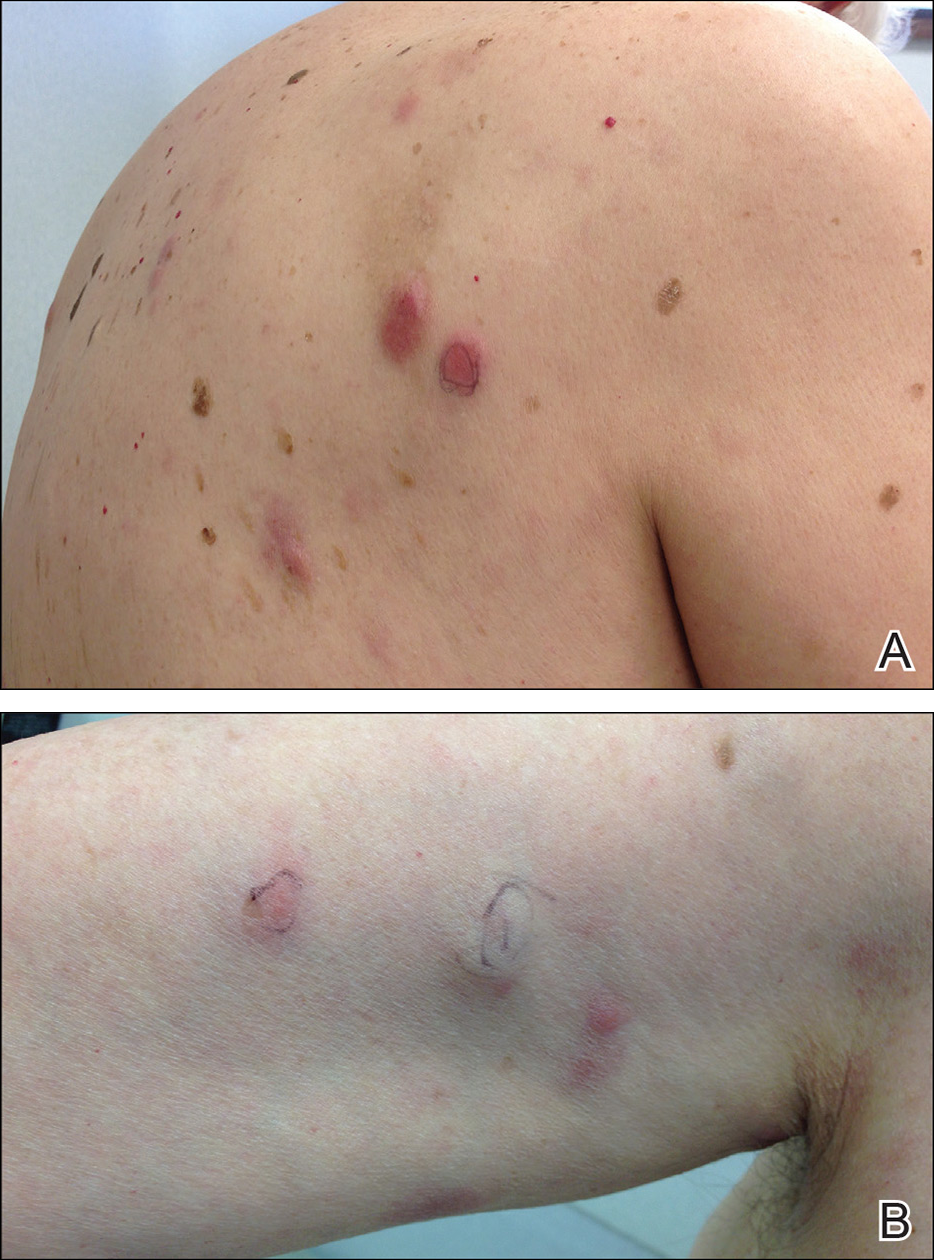
Physical examination revealed multiple pink to erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules involving the face, neck, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). No scale, crust, or ulceration was present. Palpation of the cervical, supraclavicular, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes was negative for lymphadenopathy.
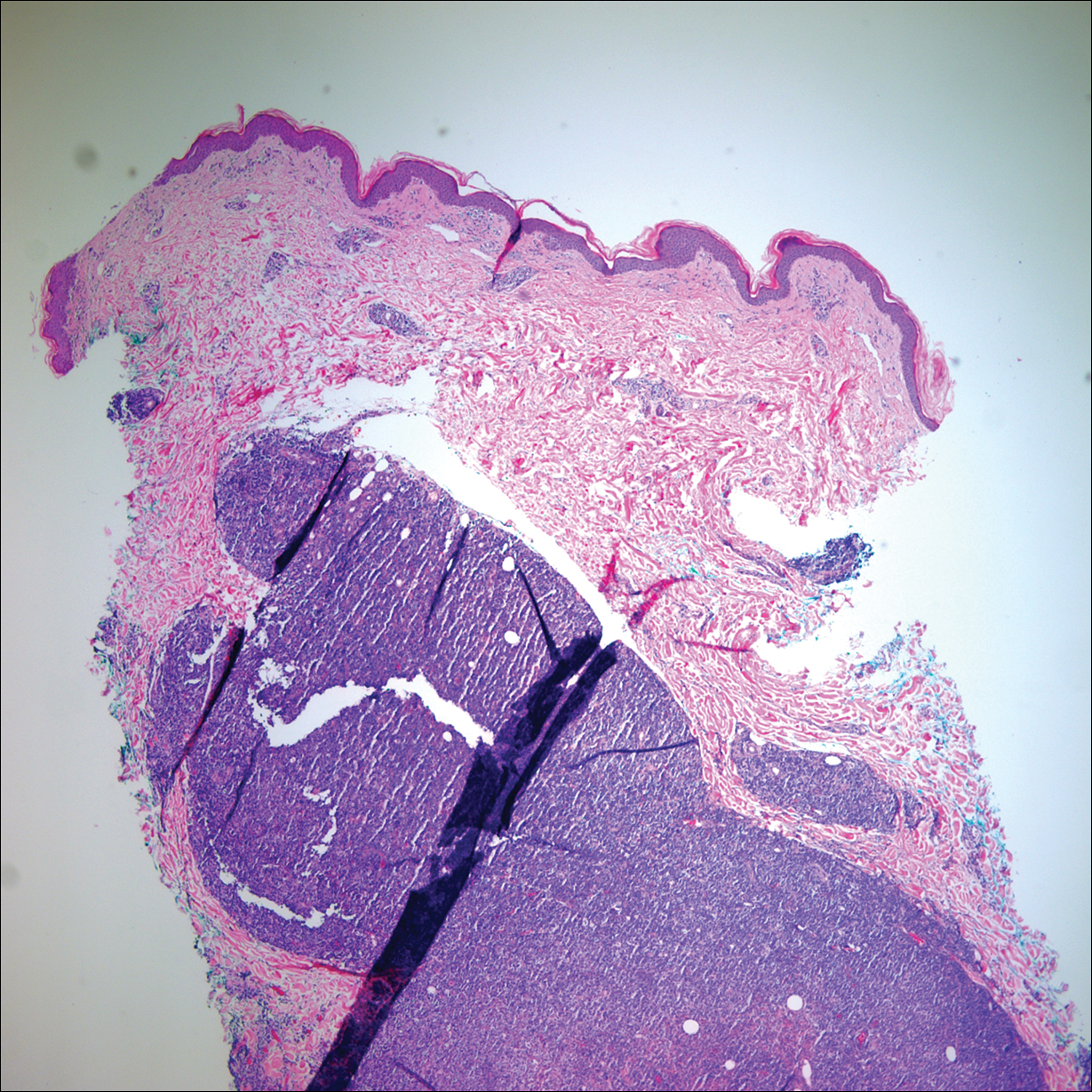
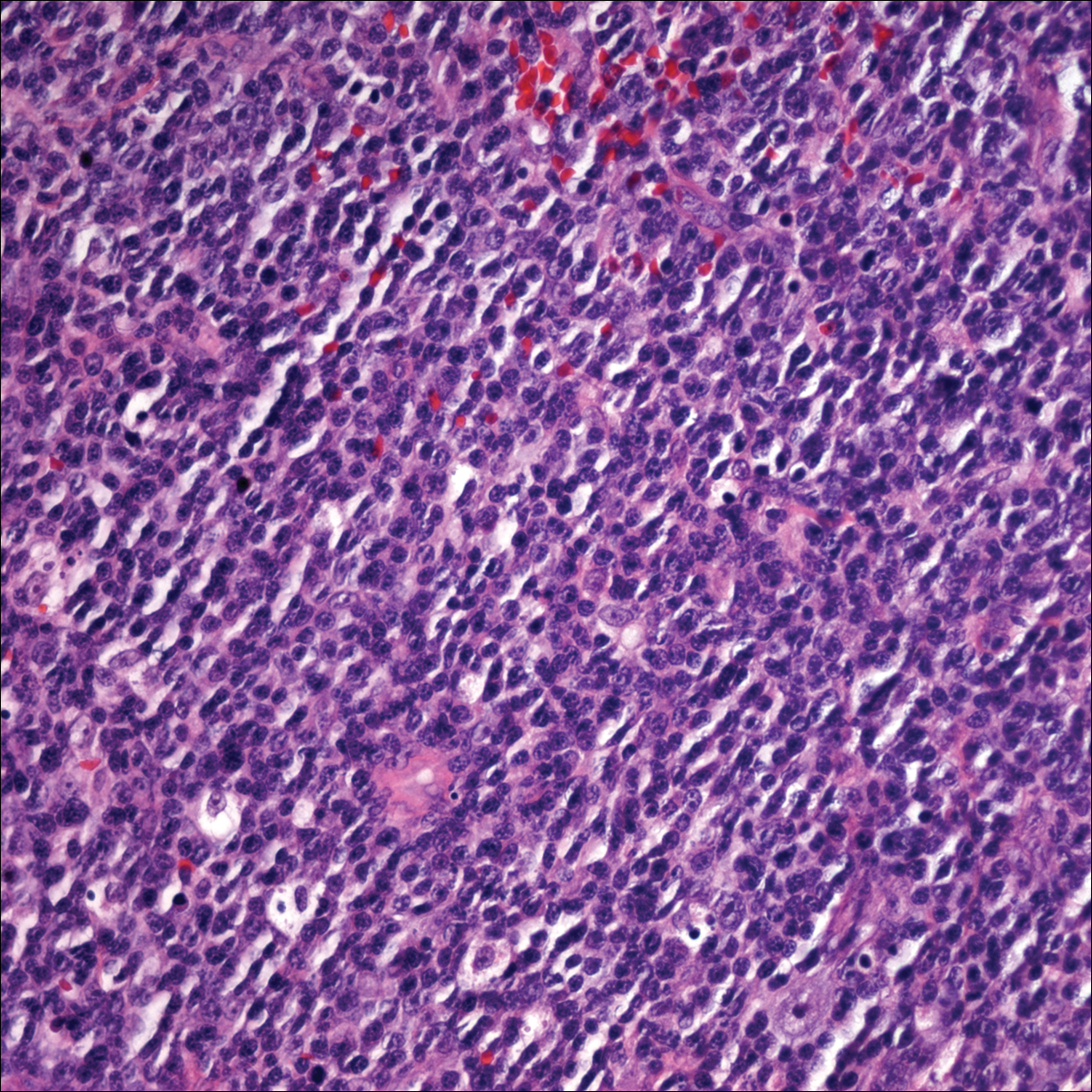
Punch biopsies of representative lesions on the upper back and right arm revealed diffuse and nodular infiltrates of large atypical lymphoid cells with scattered centroblasts and immunoblasts (Figures 2 and 3). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated CD79, MUM-1, and EBV-encoded RNA positivity among the neoplastic cells. The Ki-67 proliferative index was greater than 90%. The neoplastic cells were negative for CD5, CD10, CD20, CD21, CD30, CD56, CD123, CD138, PAX5, C-MYC, BCL-2, BCL-6, cyclin D1, TCL-1A, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
A peripheral blood smear did not show evidence of a B-cell lymphoproliferative process. A bone marrow biopsy was performed and did not show evidence of B-cell lymphoid neoplasia but did show reactive lymphoid aggregates composed of CD4+ and CD10+ T cells. Peripheral blood T-cell rearrangement and JAK2 were negative.
Based on clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL. The patient was started on CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy for treatment of this aggressive cutaneous lymphoma, which initially resulted in clinical improvement of the lesions and complete involution of the subcutaneous nodules. After the sixth cycle of CHOP, he developed faintly erythematous indurated papules on the upper arms, chest, and back. Biopsy confirmed recurrence of the EBV-positive cutaneous lymphoma, and he started salvage chemotherapy with gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and rituximab every 2 weeks; however, 4 months later (9 months after the initial presentation) he died from complications of the disease.
Comment
Etiology
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL, also called EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly, was initially described in 2003 by Oyama et al5 and was included as a provisional entity in the 2008 World Health Organization classification system as a rare subtype of the DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category.2 It is defined as an EBV-positive monoclonal large B-cell proliferation that occurs in immunocompetent patients older than 50 years.6 Epstein-Barr virus is a human herpesvirus that demonstrates tropism for lymphocytes and survives in human hosts by establishing latency in B cells. Under normal immune conditions, the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells is prevented by cytotoxic T cells.7 It is important to recognize that patients with EBV-positive DLBCL do not have a known immunodeficiency state; therefore, it has been postulated that EBV-positive DLBCL might be caused by age-related senescence of the immune system.4,8
Epidemiology and Clinical Features
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL is more common in Asian countries than in Western countries, and there is a slight male predominance.6 A majority of patients present with extranodal disease at the time of diagnosis, and the skin is the most common extranodal site of involvement.6,9 Rare cases of primary cutaneous involvement also have been described.7,9,10 Cutaneous manifestations include erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules. Other sites of extranodal involvement include the lungs, oral cavity, pharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and bone marrow.8,9 However, EBV-positive DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma and prognosis is poor irrespective of the primary site of involvement.
Histopathology
Two morphologic subtypes can be seen on histology. The polymorphic pattern is characterized by a broad range of B-cell maturation with admixed reactive cells (eg, lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells). The monomorphic or large-cell pattern is characterized by monotonous sheets of large transformed B cells.4,11 Many cases show both histologic patterns, and these morphologic variants do not impart any clinical or prognostic significance. Regardless of the histologic subtype, the neoplastic cells express pan B-cell antigens (eg, CD19, CD20, CD79a, PAX5), as well as MUM-1, BCL-2, and EBV-encoded RNA.4 Cases with plasmablastic features, as in our patient, may show weak or absent CD20 staining.12 Detection of EBV by in situ hybridization is required for the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Workup for a suspected cutaneous lymphoma should include a complete history and physical examination; laboratory studies; and relevant imaging evaluation such as computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with or without whole-body positron emission tomography. A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate also should be performed in all cutaneous lymphomas with intermediate to aggressive clinical behavior. Accurate staging evaluation is integral to confirm the absence of extracutaneous involvement and to provide prognostic and anatomic information for the appropriate selection of treatment.13
Prognosis and Management
Primary cutaneous lymphomas tend to have different clinical behaviors and prognoses compared to histologically similar systemic lymphomas; therefore, different therapeutic strategies are warranted.14 Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL has an aggressive clinical course with a median survival of 2 years.8 Patients with EBV-positive DLBCL have a poorer overall survival and treatment response when compared to patients with EBV-negative DLBCLs.4 Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas with indolent behavior, such as primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma, can be treated with surgical excision, radiation therapy, or observation.15 No standard treatment exists for EBV-positive DLBCL, but R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone), which is the standard treatment of primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type, may provide a survival benefit.13,15 Further studies are required to determine optimal treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Although rare, EBV-positive DLBCL is an important entity to consider when evaluating a patient with a suspected primary cutaneous lymphoma. Workup to rule out an underlying systemic lymphoma with relevant laboratory evaluation, imaging studies, and bone marrow biopsy is critical. Prognosis is poor and treatment is difficult, as standard treatment protocols have yet to be determined.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Nakmura S, Jaffe ES, Swerdlow SH. EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2008:243-244.
- Kempf W, Sander CA. Classification of cutaneous lymphomas—an update. Histopathology. 2010;56:57-70.
- Castillo JJ, Beltran BE, Miranda RN, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: what we know so far. Oncologist. 2011;16:87-96.
- Oyama T, Ichimura K, Suzuki R, et al. Senile EBV+ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: a clinicopathologic study of 22 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:16-26.
- Ok CY, Papathomas TG, Medeiros LJ, et al. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood. 2013;122:328-340.
- Tokuda Y, Fukushima M, Nakazawa K, et al. A case of primary Epstein-Barr virus-associated cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma unassociated with iatrogenic or endogenous immune dysregulation. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:666-671.
- Oyama T, Yamamoto K, Asano N, et al. Age-related EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders constitute a distinct clinicopathologic group: a study of 96 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5124-5132.
- Eminger LA, Hall LD, Hesterman KS, et al. Epstein-Barr virus: dermatologic associations and implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:21-34.
- Martin B, Whittaker S, Morris S, et al. A case of primary cutaneous senile EBV-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:190-193.
- Gibson SE, Hsi ED. Epstein-Barr virus-positive B-cell lymphoma of the elderly at a United States tertiary medical center: an uncommon aggressive lymphoma with a nongerminal center B-cell phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:653-661.
- Castillo JJ, Bibas M, Miranda RN. The biology and treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood. 2015;125:2323-2330.
- Kim YH, Willemze R, Pimpinelli N, et al. TNM classification system for primary cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood. 2007;110:479-484.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-329.e13; quiz 341-342.
- Suárez AL, Querfeld C, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part II. therapy and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:343.e1-343.e11; quiz 355-356.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas represent a group of lymphomas derived from B lymphocytes in various stages of differentiation. The skin can be the site of primary or secondary involvement of any of the B-cell lymphomas. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas present in the skin without evidence of extracutaneous disease at the time of diagnosis.1 The World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues recognizes 5 distinct primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma subtypes: primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma; primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma; primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), leg type; DLBCL, not otherwise specified; and intravascular DLBCL.1-3 The DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category includes less common provisional entities with insufficient evidence to be recognized as distinct diseases. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive DLBCL is a rare subtype in this group.4
This article reviews the different clinicopathologic subtypes of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. It also serves to help dermatologists recognize primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL as a rare and aggressive form of this disease.
Case Report
An 84-year-old white man presented with a pruritic eruption on the arms, legs, back, neck, and face of 5 months’ duration. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer that was successfully treated with radiation therapy 6 years prior. The patient denied any constitutional symptoms such as fever, chills, night sweats, or weight loss, and review of systems was negative. The patient was taking prednisone, which alleviated the pruritus, but the lesions persisted.
Physical examination revealed multiple pink to erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules involving the face, neck, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). No scale, crust, or ulceration was present. Palpation of the cervical, supraclavicular, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes was negative for lymphadenopathy.

Punch biopsies of representative lesions on the upper back and right arm revealed diffuse and nodular infiltrates of large atypical lymphoid cells with scattered centroblasts and immunoblasts (Figures 2 and 3). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated CD79, MUM-1, and EBV-encoded RNA positivity among the neoplastic cells. The Ki-67 proliferative index was greater than 90%. The neoplastic cells were negative for CD5, CD10, CD20, CD21, CD30, CD56, CD123, CD138, PAX5, C-MYC, BCL-2, BCL-6, cyclin D1, TCL-1A, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase


A peripheral blood smear did not show evidence of a B-cell lymphoproliferative process. A bone marrow biopsy was performed and did not show evidence of B-cell lymphoid neoplasia but did show reactive lymphoid aggregates composed of CD4+ and CD10+ T cells. Peripheral blood T-cell rearrangement and JAK2 were negative.
Based on clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL. The patient was started on CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy for treatment of this aggressive cutaneous lymphoma, which initially resulted in clinical improvement of the lesions and complete involution of the subcutaneous nodules. After the sixth cycle of CHOP, he developed faintly erythematous indurated papules on the upper arms, chest, and back. Biopsy confirmed recurrence of the EBV-positive cutaneous lymphoma, and he started salvage chemotherapy with gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and rituximab every 2 weeks; however, 4 months later (9 months after the initial presentation) he died from complications of the disease.
Comment
Etiology
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL, also called EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly, was initially described in 2003 by Oyama et al5 and was included as a provisional entity in the 2008 World Health Organization classification system as a rare subtype of the DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category.2 It is defined as an EBV-positive monoclonal large B-cell proliferation that occurs in immunocompetent patients older than 50 years.6 Epstein-Barr virus is a human herpesvirus that demonstrates tropism for lymphocytes and survives in human hosts by establishing latency in B cells. Under normal immune conditions, the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells is prevented by cytotoxic T cells.7 It is important to recognize that patients with EBV-positive DLBCL do not have a known immunodeficiency state; therefore, it has been postulated that EBV-positive DLBCL might be caused by age-related senescence of the immune system.4,8
Epidemiology and Clinical Features
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL is more common in Asian countries than in Western countries, and there is a slight male predominance.6 A majority of patients present with extranodal disease at the time of diagnosis, and the skin is the most common extranodal site of involvement.6,9 Rare cases of primary cutaneous involvement also have been described.7,9,10 Cutaneous manifestations include erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules. Other sites of extranodal involvement include the lungs, oral cavity, pharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and bone marrow.8,9 However, EBV-positive DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma and prognosis is poor irrespective of the primary site of involvement.
Histopathology
Two morphologic subtypes can be seen on histology. The polymorphic pattern is characterized by a broad range of B-cell maturation with admixed reactive cells (eg, lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells). The monomorphic or large-cell pattern is characterized by monotonous sheets of large transformed B cells.4,11 Many cases show both histologic patterns, and these morphologic variants do not impart any clinical or prognostic significance. Regardless of the histologic subtype, the neoplastic cells express pan B-cell antigens (eg, CD19, CD20, CD79a, PAX5), as well as MUM-1, BCL-2, and EBV-encoded RNA.4 Cases with plasmablastic features, as in our patient, may show weak or absent CD20 staining.12 Detection of EBV by in situ hybridization is required for the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Workup for a suspected cutaneous lymphoma should include a complete history and physical examination; laboratory studies; and relevant imaging evaluation such as computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with or without whole-body positron emission tomography. A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate also should be performed in all cutaneous lymphomas with intermediate to aggressive clinical behavior. Accurate staging evaluation is integral to confirm the absence of extracutaneous involvement and to provide prognostic and anatomic information for the appropriate selection of treatment.13
Prognosis and Management
Primary cutaneous lymphomas tend to have different clinical behaviors and prognoses compared to histologically similar systemic lymphomas; therefore, different therapeutic strategies are warranted.14 Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL has an aggressive clinical course with a median survival of 2 years.8 Patients with EBV-positive DLBCL have a poorer overall survival and treatment response when compared to patients with EBV-negative DLBCLs.4 Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas with indolent behavior, such as primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma, can be treated with surgical excision, radiation therapy, or observation.15 No standard treatment exists for EBV-positive DLBCL, but R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone), which is the standard treatment of primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type, may provide a survival benefit.13,15 Further studies are required to determine optimal treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Although rare, EBV-positive DLBCL is an important entity to consider when evaluating a patient with a suspected primary cutaneous lymphoma. Workup to rule out an underlying systemic lymphoma with relevant laboratory evaluation, imaging studies, and bone marrow biopsy is critical. Prognosis is poor and treatment is difficult, as standard treatment protocols have yet to be determined.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas represent a group of lymphomas derived from B lymphocytes in various stages of differentiation. The skin can be the site of primary or secondary involvement of any of the B-cell lymphomas. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas present in the skin without evidence of extracutaneous disease at the time of diagnosis.1 The World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues recognizes 5 distinct primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma subtypes: primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma; primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma; primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), leg type; DLBCL, not otherwise specified; and intravascular DLBCL.1-3 The DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category includes less common provisional entities with insufficient evidence to be recognized as distinct diseases. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive DLBCL is a rare subtype in this group.4
This article reviews the different clinicopathologic subtypes of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma. It also serves to help dermatologists recognize primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL as a rare and aggressive form of this disease.
Case Report
An 84-year-old white man presented with a pruritic eruption on the arms, legs, back, neck, and face of 5 months’ duration. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer that was successfully treated with radiation therapy 6 years prior. The patient denied any constitutional symptoms such as fever, chills, night sweats, or weight loss, and review of systems was negative. The patient was taking prednisone, which alleviated the pruritus, but the lesions persisted.
Physical examination revealed multiple pink to erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules involving the face, neck, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1). No scale, crust, or ulceration was present. Palpation of the cervical, supraclavicular, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes was negative for lymphadenopathy.

Punch biopsies of representative lesions on the upper back and right arm revealed diffuse and nodular infiltrates of large atypical lymphoid cells with scattered centroblasts and immunoblasts (Figures 2 and 3). Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated CD79, MUM-1, and EBV-encoded RNA positivity among the neoplastic cells. The Ki-67 proliferative index was greater than 90%. The neoplastic cells were negative for CD5, CD10, CD20, CD21, CD30, CD56, CD123, CD138, PAX5, C-MYC, BCL-2, BCL-6, cyclin D1, TCL-1A, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase


A peripheral blood smear did not show evidence of a B-cell lymphoproliferative process. A bone marrow biopsy was performed and did not show evidence of B-cell lymphoid neoplasia but did show reactive lymphoid aggregates composed of CD4+ and CD10+ T cells. Peripheral blood T-cell rearrangement and JAK2 were negative.
Based on clinical and histologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with primary cutaneous EBV-positive DLBCL. The patient was started on CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy for treatment of this aggressive cutaneous lymphoma, which initially resulted in clinical improvement of the lesions and complete involution of the subcutaneous nodules. After the sixth cycle of CHOP, he developed faintly erythematous indurated papules on the upper arms, chest, and back. Biopsy confirmed recurrence of the EBV-positive cutaneous lymphoma, and he started salvage chemotherapy with gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and rituximab every 2 weeks; however, 4 months later (9 months after the initial presentation) he died from complications of the disease.
Comment
Etiology
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL, also called EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly, was initially described in 2003 by Oyama et al5 and was included as a provisional entity in the 2008 World Health Organization classification system as a rare subtype of the DLBCL, not otherwise specified, category.2 It is defined as an EBV-positive monoclonal large B-cell proliferation that occurs in immunocompetent patients older than 50 years.6 Epstein-Barr virus is a human herpesvirus that demonstrates tropism for lymphocytes and survives in human hosts by establishing latency in B cells. Under normal immune conditions, the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells is prevented by cytotoxic T cells.7 It is important to recognize that patients with EBV-positive DLBCL do not have a known immunodeficiency state; therefore, it has been postulated that EBV-positive DLBCL might be caused by age-related senescence of the immune system.4,8
Epidemiology and Clinical Features
Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL is more common in Asian countries than in Western countries, and there is a slight male predominance.6 A majority of patients present with extranodal disease at the time of diagnosis, and the skin is the most common extranodal site of involvement.6,9 Rare cases of primary cutaneous involvement also have been described.7,9,10 Cutaneous manifestations include erythematous papules and subcutaneous nodules. Other sites of extranodal involvement include the lungs, oral cavity, pharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and bone marrow.8,9 However, EBV-positive DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma and prognosis is poor irrespective of the primary site of involvement.
Histopathology
Two morphologic subtypes can be seen on histology. The polymorphic pattern is characterized by a broad range of B-cell maturation with admixed reactive cells (eg, lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells). The monomorphic or large-cell pattern is characterized by monotonous sheets of large transformed B cells.4,11 Many cases show both histologic patterns, and these morphologic variants do not impart any clinical or prognostic significance. Regardless of the histologic subtype, the neoplastic cells express pan B-cell antigens (eg, CD19, CD20, CD79a, PAX5), as well as MUM-1, BCL-2, and EBV-encoded RNA.4 Cases with plasmablastic features, as in our patient, may show weak or absent CD20 staining.12 Detection of EBV by in situ hybridization is required for the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Workup for a suspected cutaneous lymphoma should include a complete history and physical examination; laboratory studies; and relevant imaging evaluation such as computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with or without whole-body positron emission tomography. A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate also should be performed in all cutaneous lymphomas with intermediate to aggressive clinical behavior. Accurate staging evaluation is integral to confirm the absence of extracutaneous involvement and to provide prognostic and anatomic information for the appropriate selection of treatment.13
Prognosis and Management
Primary cutaneous lymphomas tend to have different clinical behaviors and prognoses compared to histologically similar systemic lymphomas; therefore, different therapeutic strategies are warranted.14 Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL has an aggressive clinical course with a median survival of 2 years.8 Patients with EBV-positive DLBCL have a poorer overall survival and treatment response when compared to patients with EBV-negative DLBCLs.4 Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas with indolent behavior, such as primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma, can be treated with surgical excision, radiation therapy, or observation.15 No standard treatment exists for EBV-positive DLBCL, but R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone), which is the standard treatment of primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type, may provide a survival benefit.13,15 Further studies are required to determine optimal treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Although rare, EBV-positive DLBCL is an important entity to consider when evaluating a patient with a suspected primary cutaneous lymphoma. Workup to rule out an underlying systemic lymphoma with relevant laboratory evaluation, imaging studies, and bone marrow biopsy is critical. Prognosis is poor and treatment is difficult, as standard treatment protocols have yet to be determined.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Nakmura S, Jaffe ES, Swerdlow SH. EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2008:243-244.
- Kempf W, Sander CA. Classification of cutaneous lymphomas—an update. Histopathology. 2010;56:57-70.
- Castillo JJ, Beltran BE, Miranda RN, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: what we know so far. Oncologist. 2011;16:87-96.
- Oyama T, Ichimura K, Suzuki R, et al. Senile EBV+ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: a clinicopathologic study of 22 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:16-26.
- Ok CY, Papathomas TG, Medeiros LJ, et al. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood. 2013;122:328-340.
- Tokuda Y, Fukushima M, Nakazawa K, et al. A case of primary Epstein-Barr virus-associated cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma unassociated with iatrogenic or endogenous immune dysregulation. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:666-671.
- Oyama T, Yamamoto K, Asano N, et al. Age-related EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders constitute a distinct clinicopathologic group: a study of 96 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5124-5132.
- Eminger LA, Hall LD, Hesterman KS, et al. Epstein-Barr virus: dermatologic associations and implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:21-34.
- Martin B, Whittaker S, Morris S, et al. A case of primary cutaneous senile EBV-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:190-193.
- Gibson SE, Hsi ED. Epstein-Barr virus-positive B-cell lymphoma of the elderly at a United States tertiary medical center: an uncommon aggressive lymphoma with a nongerminal center B-cell phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:653-661.
- Castillo JJ, Bibas M, Miranda RN. The biology and treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood. 2015;125:2323-2330.
- Kim YH, Willemze R, Pimpinelli N, et al. TNM classification system for primary cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood. 2007;110:479-484.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-329.e13; quiz 341-342.
- Suárez AL, Querfeld C, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part II. therapy and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:343.e1-343.e11; quiz 355-356.
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Nakmura S, Jaffe ES, Swerdlow SH. EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2008:243-244.
- Kempf W, Sander CA. Classification of cutaneous lymphomas—an update. Histopathology. 2010;56:57-70.
- Castillo JJ, Beltran BE, Miranda RN, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: what we know so far. Oncologist. 2011;16:87-96.
- Oyama T, Ichimura K, Suzuki R, et al. Senile EBV+ B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: a clinicopathologic study of 22 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:16-26.
- Ok CY, Papathomas TG, Medeiros LJ, et al. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood. 2013;122:328-340.
- Tokuda Y, Fukushima M, Nakazawa K, et al. A case of primary Epstein-Barr virus-associated cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma unassociated with iatrogenic or endogenous immune dysregulation. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:666-671.
- Oyama T, Yamamoto K, Asano N, et al. Age-related EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders constitute a distinct clinicopathologic group: a study of 96 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5124-5132.
- Eminger LA, Hall LD, Hesterman KS, et al. Epstein-Barr virus: dermatologic associations and implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:21-34.
- Martin B, Whittaker S, Morris S, et al. A case of primary cutaneous senile EBV-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:190-193.
- Gibson SE, Hsi ED. Epstein-Barr virus-positive B-cell lymphoma of the elderly at a United States tertiary medical center: an uncommon aggressive lymphoma with a nongerminal center B-cell phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:653-661.
- Castillo JJ, Bibas M, Miranda RN. The biology and treatment of plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood. 2015;125:2323-2330.
- Kim YH, Willemze R, Pimpinelli N, et al. TNM classification system for primary cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood. 2007;110:479-484.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-329.e13; quiz 341-342.
- Suárez AL, Querfeld C, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part II. therapy and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:343.e1-343.e11; quiz 355-356.
Practice Points
- Primary cutaneous lymphomas are malignant lymphomas confined to the skin.
- Complete staging workup is necessary to rule out secondary involvement of the skin from a nodal lymphoma.
- Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is a rare and aggressive primary cutaneous lymphoma.