User login
Chronic pain disorders have reached epidemic levels in the United States, with the Institute of Medicine reporting more than 100 million Americans affected and health care costs more than $500 billion annually.1 Although many pain disorders are confined to the abdomen or pelvis (chronic pelvic pain, vulvodynia, irritable bowel syndrome, and bladder pain syndrome), others present with global symptoms (fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome). Women are more likely to be diagnosed with a chronic pain condition and more likely to seek treatment for chronic pain, including undergoing a surgical intervention. In fact, chronic pelvic pain alone affects upward of 20% of women in the United States, and, of the 400,000 hysterectomies performed each year (54.2%, abdominal; 16.7%, vaginal; and 16.8%, laparoscopic/robotic assisted), approximately 15% are for chronic pain.2
Neurobiology of pain
Perioperative pain control, specifically in women with preexisting pain disorders, can provide an additional challenge. Unlike acute pain, chronic pain (lasting more than 6 months) is associated with an amplified pain response of the central nervous system. This abnormal pain processing, known as centralization of pain, may result in a decrease of the inhibitory pain pathways and/or an increase of the amplification pathways, often augmenting the pain response of the original peripheral insult, specifically surgery. Because of these physiologic changes, a multimodal approach to perioperative pain should be offered, especially in women with preexisting pain. The approach ideally ought to target the different mechanisms of actions in both the peripheral and central nervous systems to provide an overall reduction in pain perception.
Preoperative visit
Perhaps the most underutilized opportunity to optimize postoperative pain is a proactive, preoperative approach. Preoperative education, including goal setting of postoperative pain expectations, has been associated with a significant reduction in postoperative opioid use, less preoperative anxiety, and a decreased length of surgical stay.3 While it is unknown exactly when this should be provided to the patient in the treatment course, it should occur prior to the day of surgery to allow for appropriate intervention.
The use of a shared decision-making model between the clinician and the chronic pain patient in the development of a pain management plan has been highly successful in improving pain outcomes in the outpatient setting.4 A similar method can be applied to the preoperative course as well. A detailed history (including the use of an opioid risk assessment tool) allows the clinician to identify patients at risk for opioid misuse and abuse. This is also an opportunity to review a plan for an opioid taper with the patient and the prescriber, if the postoperative plan includes opioid reduction/cessation. The preoperative visit may be an opportunity to adjust centrally acting medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants) before surgery or to reduce the dose or frequency of high-risk medications, such as benzodiazepines.
Perioperative strategy
One of the most impactful ways for us, as surgeons, to reduce tissue injury and decrease pain from surgery is by offering a minimally invasive approach. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery are well established, resulting in improved perioperative pain control, decreased blood loss, lower infection rates, decreased length of hospital stay, and a faster recovery, compared with laparotomy. Because patients with chronic pain disorders are at increased risk of greater acute postoperative pain and have an elevated risk for the development of chronic postsurgical pain, a minimally invasive surgical approach should be prioritized, when available.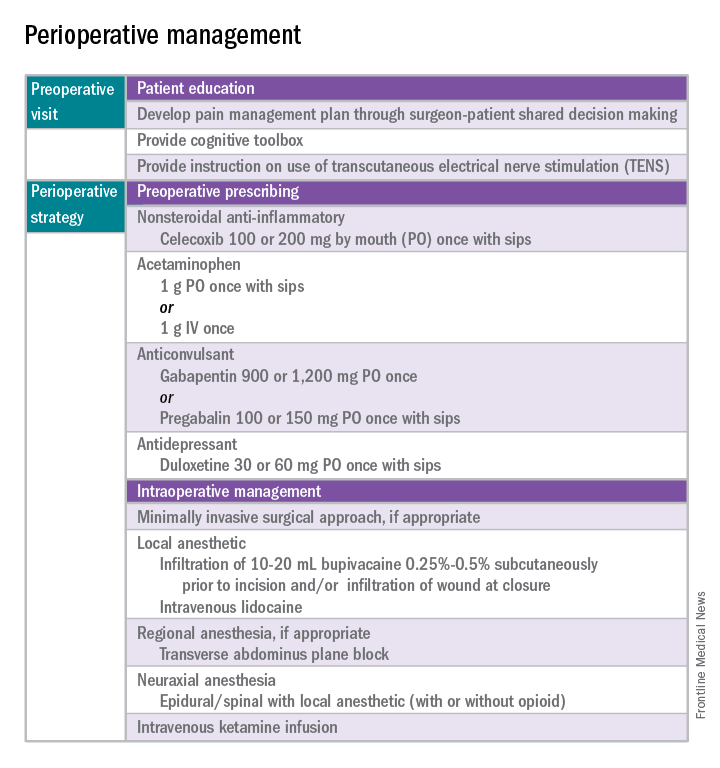
Perioperative multimodal drug therapy is associated with significant decreases in opioid consumption and reductions in acute postoperative pain.6 Recently, a multidisciplinary expert panel from the American Pain Society devised an evidence-based clinical practice guideline for postoperative pain.7 While there is no consensus as to the best regimen specific to gynecologic surgery, the general principles are similar across disciplines.
The postoperative period
Opioid-tolerant patients may experience greater pain during the first 24 hours postoperatively and require an increase in opioids, compared with opioid-naive patients.8 In the event that a postoperative patient does not respond as expected to the usual course, that patient should be evaluated for barriers to routine postoperative care, such as a surgical complication, opioid tolerance, or psychological distress. Surgeons should be aggressive with pain management immediately after surgery, even in the opioid-tolerant patient, and make short-term adjustments as needed based on the pain response. These patients will require pain medications beyond their baseline dose. Additionally, if an opioid taper is not planned in a chronic opioid user, work with the patient and the long-term opioid prescriber in restarting baseline opioid therapy outside of the acute surgical window. 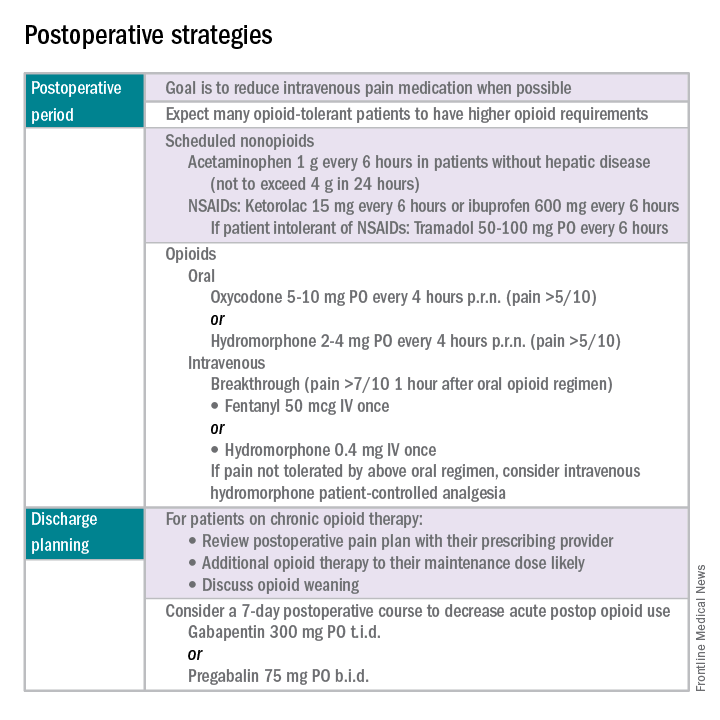
References
1. Institute of Medicine. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Aug;122(2 Pt 1):233-41.
3. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 16;270:825-7.
4. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1999 Jul;18(1):38-48.
5. Pain. 2010 Dec;151(3):694-702.
6. Anesthesiology. 2005 Dec;103(6):1296-304.
7. J Pain. 2016 Feb;17(2):131-57.
8. Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Dec;28(12):1453-60.
Dr. Carey is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and specializes in the medical and surgical management of pelvic pain disorders. Dr. Rossi is an assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at UNC–Chapel Hill. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Chronic pain disorders have reached epidemic levels in the United States, with the Institute of Medicine reporting more than 100 million Americans affected and health care costs more than $500 billion annually.1 Although many pain disorders are confined to the abdomen or pelvis (chronic pelvic pain, vulvodynia, irritable bowel syndrome, and bladder pain syndrome), others present with global symptoms (fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome). Women are more likely to be diagnosed with a chronic pain condition and more likely to seek treatment for chronic pain, including undergoing a surgical intervention. In fact, chronic pelvic pain alone affects upward of 20% of women in the United States, and, of the 400,000 hysterectomies performed each year (54.2%, abdominal; 16.7%, vaginal; and 16.8%, laparoscopic/robotic assisted), approximately 15% are for chronic pain.2
Neurobiology of pain
Perioperative pain control, specifically in women with preexisting pain disorders, can provide an additional challenge. Unlike acute pain, chronic pain (lasting more than 6 months) is associated with an amplified pain response of the central nervous system. This abnormal pain processing, known as centralization of pain, may result in a decrease of the inhibitory pain pathways and/or an increase of the amplification pathways, often augmenting the pain response of the original peripheral insult, specifically surgery. Because of these physiologic changes, a multimodal approach to perioperative pain should be offered, especially in women with preexisting pain. The approach ideally ought to target the different mechanisms of actions in both the peripheral and central nervous systems to provide an overall reduction in pain perception.
Preoperative visit
Perhaps the most underutilized opportunity to optimize postoperative pain is a proactive, preoperative approach. Preoperative education, including goal setting of postoperative pain expectations, has been associated with a significant reduction in postoperative opioid use, less preoperative anxiety, and a decreased length of surgical stay.3 While it is unknown exactly when this should be provided to the patient in the treatment course, it should occur prior to the day of surgery to allow for appropriate intervention.
The use of a shared decision-making model between the clinician and the chronic pain patient in the development of a pain management plan has been highly successful in improving pain outcomes in the outpatient setting.4 A similar method can be applied to the preoperative course as well. A detailed history (including the use of an opioid risk assessment tool) allows the clinician to identify patients at risk for opioid misuse and abuse. This is also an opportunity to review a plan for an opioid taper with the patient and the prescriber, if the postoperative plan includes opioid reduction/cessation. The preoperative visit may be an opportunity to adjust centrally acting medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants) before surgery or to reduce the dose or frequency of high-risk medications, such as benzodiazepines.
Perioperative strategy
One of the most impactful ways for us, as surgeons, to reduce tissue injury and decrease pain from surgery is by offering a minimally invasive approach. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery are well established, resulting in improved perioperative pain control, decreased blood loss, lower infection rates, decreased length of hospital stay, and a faster recovery, compared with laparotomy. Because patients with chronic pain disorders are at increased risk of greater acute postoperative pain and have an elevated risk for the development of chronic postsurgical pain, a minimally invasive surgical approach should be prioritized, when available.
Perioperative multimodal drug therapy is associated with significant decreases in opioid consumption and reductions in acute postoperative pain.6 Recently, a multidisciplinary expert panel from the American Pain Society devised an evidence-based clinical practice guideline for postoperative pain.7 While there is no consensus as to the best regimen specific to gynecologic surgery, the general principles are similar across disciplines.
The postoperative period
Opioid-tolerant patients may experience greater pain during the first 24 hours postoperatively and require an increase in opioids, compared with opioid-naive patients.8 In the event that a postoperative patient does not respond as expected to the usual course, that patient should be evaluated for barriers to routine postoperative care, such as a surgical complication, opioid tolerance, or psychological distress. Surgeons should be aggressive with pain management immediately after surgery, even in the opioid-tolerant patient, and make short-term adjustments as needed based on the pain response. These patients will require pain medications beyond their baseline dose. Additionally, if an opioid taper is not planned in a chronic opioid user, work with the patient and the long-term opioid prescriber in restarting baseline opioid therapy outside of the acute surgical window. 
References
1. Institute of Medicine. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Aug;122(2 Pt 1):233-41.
3. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 16;270:825-7.
4. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1999 Jul;18(1):38-48.
5. Pain. 2010 Dec;151(3):694-702.
6. Anesthesiology. 2005 Dec;103(6):1296-304.
7. J Pain. 2016 Feb;17(2):131-57.
8. Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Dec;28(12):1453-60.
Dr. Carey is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and specializes in the medical and surgical management of pelvic pain disorders. Dr. Rossi is an assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at UNC–Chapel Hill. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Chronic pain disorders have reached epidemic levels in the United States, with the Institute of Medicine reporting more than 100 million Americans affected and health care costs more than $500 billion annually.1 Although many pain disorders are confined to the abdomen or pelvis (chronic pelvic pain, vulvodynia, irritable bowel syndrome, and bladder pain syndrome), others present with global symptoms (fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome). Women are more likely to be diagnosed with a chronic pain condition and more likely to seek treatment for chronic pain, including undergoing a surgical intervention. In fact, chronic pelvic pain alone affects upward of 20% of women in the United States, and, of the 400,000 hysterectomies performed each year (54.2%, abdominal; 16.7%, vaginal; and 16.8%, laparoscopic/robotic assisted), approximately 15% are for chronic pain.2
Neurobiology of pain
Perioperative pain control, specifically in women with preexisting pain disorders, can provide an additional challenge. Unlike acute pain, chronic pain (lasting more than 6 months) is associated with an amplified pain response of the central nervous system. This abnormal pain processing, known as centralization of pain, may result in a decrease of the inhibitory pain pathways and/or an increase of the amplification pathways, often augmenting the pain response of the original peripheral insult, specifically surgery. Because of these physiologic changes, a multimodal approach to perioperative pain should be offered, especially in women with preexisting pain. The approach ideally ought to target the different mechanisms of actions in both the peripheral and central nervous systems to provide an overall reduction in pain perception.
Preoperative visit
Perhaps the most underutilized opportunity to optimize postoperative pain is a proactive, preoperative approach. Preoperative education, including goal setting of postoperative pain expectations, has been associated with a significant reduction in postoperative opioid use, less preoperative anxiety, and a decreased length of surgical stay.3 While it is unknown exactly when this should be provided to the patient in the treatment course, it should occur prior to the day of surgery to allow for appropriate intervention.
The use of a shared decision-making model between the clinician and the chronic pain patient in the development of a pain management plan has been highly successful in improving pain outcomes in the outpatient setting.4 A similar method can be applied to the preoperative course as well. A detailed history (including the use of an opioid risk assessment tool) allows the clinician to identify patients at risk for opioid misuse and abuse. This is also an opportunity to review a plan for an opioid taper with the patient and the prescriber, if the postoperative plan includes opioid reduction/cessation. The preoperative visit may be an opportunity to adjust centrally acting medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants) before surgery or to reduce the dose or frequency of high-risk medications, such as benzodiazepines.
Perioperative strategy
One of the most impactful ways for us, as surgeons, to reduce tissue injury and decrease pain from surgery is by offering a minimally invasive approach. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery are well established, resulting in improved perioperative pain control, decreased blood loss, lower infection rates, decreased length of hospital stay, and a faster recovery, compared with laparotomy. Because patients with chronic pain disorders are at increased risk of greater acute postoperative pain and have an elevated risk for the development of chronic postsurgical pain, a minimally invasive surgical approach should be prioritized, when available.
Perioperative multimodal drug therapy is associated with significant decreases in opioid consumption and reductions in acute postoperative pain.6 Recently, a multidisciplinary expert panel from the American Pain Society devised an evidence-based clinical practice guideline for postoperative pain.7 While there is no consensus as to the best regimen specific to gynecologic surgery, the general principles are similar across disciplines.
The postoperative period
Opioid-tolerant patients may experience greater pain during the first 24 hours postoperatively and require an increase in opioids, compared with opioid-naive patients.8 In the event that a postoperative patient does not respond as expected to the usual course, that patient should be evaluated for barriers to routine postoperative care, such as a surgical complication, opioid tolerance, or psychological distress. Surgeons should be aggressive with pain management immediately after surgery, even in the opioid-tolerant patient, and make short-term adjustments as needed based on the pain response. These patients will require pain medications beyond their baseline dose. Additionally, if an opioid taper is not planned in a chronic opioid user, work with the patient and the long-term opioid prescriber in restarting baseline opioid therapy outside of the acute surgical window. 
References
1. Institute of Medicine. Relieving Pain in America: A Blueprint for Transforming Prevention, Care, Education, and Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Aug;122(2 Pt 1):233-41.
3. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 16;270:825-7.
4. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1999 Jul;18(1):38-48.
5. Pain. 2010 Dec;151(3):694-702.
6. Anesthesiology. 2005 Dec;103(6):1296-304.
7. J Pain. 2016 Feb;17(2):131-57.
8. Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Dec;28(12):1453-60.
Dr. Carey is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and specializes in the medical and surgical management of pelvic pain disorders. Dr. Rossi is an assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at UNC–Chapel Hill. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures.


