User login
The American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) has decided to trade the phrase “maintenance of certification” (MOC) for “continuing board certification,” a seemingly minor change that has an important backstory. This is the story of how the physician community flexed its collective muscle and how the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) helped broker an important détente and pathway in a highly contentious issue.
Founded in 1933 as a nonprofit organization dedicated to maintaining high uniform standards among physicians, the ABMS and many of its specialty boards have found themselves, for more than a decade, under heavy fire from physicians (especially family physicians, internists, and surgeons), their 24 subspecialties, and the state medical societies representing them.
The ObGyn experience with the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG), however, is better for a number of reasons. Historically, ABOG and ACOG have worked closely together, which is an anomaly among boards as many boards have an arms-length or even an antagonistic relationship with their specialty society.
The discussion below outlines physician concerns with the ABMS and related boards and describes efforts to address and rebuild the continuing board certification process.
Direct and indirect costs
Physicians are very concerned with the costs involved in MOC. Measurable costs include testing fees, while indirect costs include time, stress, travel to test centers, and threats to livelihood for failing a high-stakes examination. Physicians want the high-stakes exam eliminated.
Relevance to practice
Physicians often feel that the MOC has little relevance to their practice, which fuels a sense of resentment toward boards that they believe are dominated by physicians who no longer practice. Subspecialists feel farther away from general practice and the base exams. Generalists feel that the exams miss the points of their daily practice.
Lack of data to show improved quality of care
Physicians want to know that the MOC is worth their time, effort, and money because it improves patient care. To date, however, empirical or clinical data on patient outcomes are absent or ambiguous; most studies lack high-level data or do not investigate the MOC requirements. Physicians want to know what the best MOC practices are, what improves care, and that practices that make no difference will be discarded. In addition, they want timely knowledge alerts when evidence changes.
Relationship to licensing, employment, privileging, credentialing, and reimbursement
Hospitals, insurers, and states increasingly—and inappropriately—use board certification as the primary (sometimes only) default measure of a physician’s fitness for patient care. Physicians without board certification often are denied hospital privileges, inclusion in insurance panels, and even medical licenses. This changes certification from a voluntary physician self-improvement exercise into a can’t-earn-a-living-without-it cudgel.
Variation
Boards vary significantly in their MOC requirements and costs. The importance of an equal standard across all boards is a clear theme among physician concerns.
Role and authority of the ABMS and related boards
Many physicians are frustrated with the perceived autocratic nature of their boards—boards that lack transparency, do not solicit or allow input from practicing physicians, and are unresponsive to physician concerns.
According to Susan Ramin, MD, ABOG Associate Executive Director, ABOG is leading in a number of these areas, including:
- rapidly disseminating clinical information on emerging topics, such as Zika virus infection and opioid misuse
- offering physician choice of testing categories
- exempting high scorers from the secured written exam, which saved physicians a total of $881,000 in exam fees
- crediting physicians for what they already are doing, including serving on maternal mortality review committees, participating in registries, and participating in the Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health (AIM)
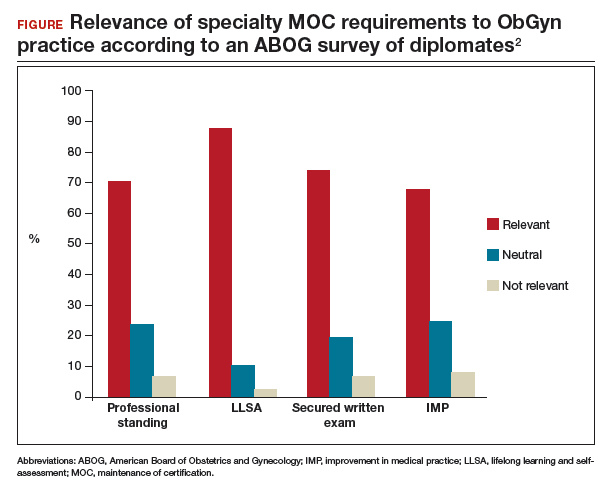
- providing Lifelong Learning and Self-Assessment (LLSA) articles that, according to 90% of diplomates surveyed, are beneficial to their clinical practice (FIGURE).1,2
Our colleague physicians are not so lucky. In a 2015 New England Journal of Medicine Perspective, one physician called out the American Board of Internal Medicine as “a private, self-appointed certifying organization,” a not-for-profit organization that has “grown into a $55-million-per-year business.”3 He concluded that “many physicians are waking up to the fact that our profession is increasingly controlled by people not directly involved in patient care who have lost contact with the realities of day-to-day clinical practice.”3
State and society responses to MOC requirements
Frustration with an inability to resolve these concerns has grown steadily, bubbling over into state governments. The American Medical Association developed “model state legislation intended to prohibit hospitals, health care insurers, and state boards of medicine and osteopathic medicine from requiring participation in MOC processes as a condition of credentialing, privileging, insurance panel participation, licensure, or licensure renewal.”4
Some states are proposing or have enacted legislation that prohibits the use of MOC as a criterion for licensure, privileging, employment, reimbursement, and/or insurance panel participation. Eight states (Arizona, Georgia, Kentucky, Maryland, Maine, Missouri, Oklahoma, Tennessee) have enacted laws to prohibit the use of MOC for initial and renewal licensure decisions. Many states are actively considering MOC-related legislation, including Alaska, Florida, Iowa, Indiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Legislation is not the only outlet for physician frustration. Some medical specialty societies are considering dropping board certification as a membership requirement; physicians are exploring developing alternative boards; and some physicians are defying the board certification requirement altogether, with thousands signing anti-MOC petitions.
ACOG asserts importance of maintaining self-regulation
While other specialties are actively advocating state legislation, ACOG and ABOG have worked together to oppose state legislation, believing that physician self-regulation is paramount. In fact, in 2017, ACOG and ABOG issued a joint statement urging state lawmakers to “not interfere with our decades of successful self-regulation and to realize that each medical society has its own experience with its MOC program.”5
Negotiations lead to new initiative
This brings us to an interesting situation. ACOG’s Executive Vice President and CEO Hal Lawrence III, MD, was tapped (in his position as Chair of the Specialty Society CEO Consortium) to represent physician specialties in negotiations and discussions with the boards, which were represented by Lois Nora, MD, JD, President and CEO of the ABMS, and state medical societies, represented by Donald Palmisano Jr, JD, Executive Director and CEO of the Medical Association of Georgia. Many state medical societies, boards, and physician specialty organizations participated in these meetings.
Throughout months of debate, Dr. Lawrence urged his colleagues to stay at the table and do the hard work of reaching an agreement, rather than ask politicians to solve medicine’s problems. This approach was leveraged by the serious efforts and threats of state legislation, which brought the boards to the table. In August 2017, 41 state medical societies and 33 national medical specialty societies wrote to Dr. Nora expressing their concerns that “professional self-regulation is under attack. Concerns regarding the usefulness of the high-stakes exam, the exorbitant costs of the MOC process, and the lack of transparent communication from the certifying boards have led to damaging the MOC brand, and creating state-based attacks on the MOC process.”6
In December 2017, Dr. Lawrence and Mr. Palmisano led a meeting of principals from the national medical specialty societies and state medical societies with leaders of ABMS and 8 specialty boards, including ABOG, an opportunity to secure meaningful change. Dr. Lawrence began by stressing that the interests of physicians and patients would be best served by all parties coming together and collaborating on a meaningful solution, to repair trust and preserve physician self-regulation.
Dr. Ramin presented ABOG’s approach to continuous certification, lifelong learning, and self-assessment. The American Board of Urology and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology indicated that they were basing important changes in their MOC process on ABOG’s work, including using 5 modules (1 general and 4 specific to the physician’s practice) and multiple open-book mini-exams based on selected journal articles as an alternative to the 10-year MOC exam.
The Vision Initiative. At that meeting and others, the ABMS and other boards heard physicians’ candid and sometimes blunt concerns. Dr. Nora spoke to the recently announced Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future program, also known as the “Vision Initiative,” a process designed to fundamentally rebuild the continuing certification process with input and guidance from practicing physicians. Physician response seemed uniform: Seeing is believing.
Importantly, all participants at the December meeting agreed to work together to rebuild trust and ensure professionalism and professional self-regulation, reflected in this Statement of Shared Purpose:
ABMS certifying boards and national medical specialty societies will collaborate to resolve differences in the process of ongoing certification and to fulfill the principles of professional self-regulation, achieving appropriate standardization, and assuring that ongoing certification is relevant to the practices of physicians without undue burden. Furthermore, the boards and societies, and their organizations (ABMS and CMSS [Council of Medical Specialty Societies]), will undertake necessary changes in a timely manner, and will commit to ongoing communication with state medical associations to solicit their input.4
Two ObGyns participating in the Vision Initiative are Haywood Brown, MD, ACOG’s Immediate Past President, and George Wendel, MD, ABOG’s Executive Director. The Vision Initiative is composed of 3 parts. Part 1, Organization, is complete. The committee is currently working on part 2, Envisioning the Future, an information-gathering component that includes physician surveys, hearings, open solicited input, and identifying new and better approaches. After the final report is delivered to the ABMS in February 2019, part 3, Implementation, will begin.
The Vision Initiative offers physicians an important opportunity to help shape the future of continuing education and certification. ObGyns and other physicians should consider reviewing and commenting on the draft report, due in November, during the public comment period. Visit https://visioninitiative.org for more information and to sign up for email updates.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology. From pilot to permanent: ABOG's program offering an innovative pathway integrating lifelong learning and self-assessment and external assessment is approved. https://www.abog.org/new/ABOG_PilotToPermanent.aspx. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Ramin S. American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology MOC program. PowerPoint presentation; December 4, 2017.
- Teirstein PS. Boarded to death--why maintenance of certification is bad for doctors and patients. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(2):106-108.
- AMA Council on Medical Education. Executive summary. 2017. https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/default/files/media-browser/public/council-on-med-ed/a18-cme-02.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG-ABOG joint statement: political interference in physician maintenance of skills threatens women's health care. https://www.acog.org/-/media/Departments/State-Legislative-Activities/2017ACOG-ABMS-MOC-Statement.pdf?dmc=1&ts=20180706T1615538746. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Letter to Lois Nora, MD, JD. August 18, 2017. https://www.mainemed.com/sites/default/files/content/MOC%20Letter%20082117.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.
The American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) has decided to trade the phrase “maintenance of certification” (MOC) for “continuing board certification,” a seemingly minor change that has an important backstory. This is the story of how the physician community flexed its collective muscle and how the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) helped broker an important détente and pathway in a highly contentious issue.
Founded in 1933 as a nonprofit organization dedicated to maintaining high uniform standards among physicians, the ABMS and many of its specialty boards have found themselves, for more than a decade, under heavy fire from physicians (especially family physicians, internists, and surgeons), their 24 subspecialties, and the state medical societies representing them.
The ObGyn experience with the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG), however, is better for a number of reasons. Historically, ABOG and ACOG have worked closely together, which is an anomaly among boards as many boards have an arms-length or even an antagonistic relationship with their specialty society.
The discussion below outlines physician concerns with the ABMS and related boards and describes efforts to address and rebuild the continuing board certification process.
Direct and indirect costs
Physicians are very concerned with the costs involved in MOC. Measurable costs include testing fees, while indirect costs include time, stress, travel to test centers, and threats to livelihood for failing a high-stakes examination. Physicians want the high-stakes exam eliminated.
Relevance to practice
Physicians often feel that the MOC has little relevance to their practice, which fuels a sense of resentment toward boards that they believe are dominated by physicians who no longer practice. Subspecialists feel farther away from general practice and the base exams. Generalists feel that the exams miss the points of their daily practice.
Lack of data to show improved quality of care
Physicians want to know that the MOC is worth their time, effort, and money because it improves patient care. To date, however, empirical or clinical data on patient outcomes are absent or ambiguous; most studies lack high-level data or do not investigate the MOC requirements. Physicians want to know what the best MOC practices are, what improves care, and that practices that make no difference will be discarded. In addition, they want timely knowledge alerts when evidence changes.
Relationship to licensing, employment, privileging, credentialing, and reimbursement
Hospitals, insurers, and states increasingly—and inappropriately—use board certification as the primary (sometimes only) default measure of a physician’s fitness for patient care. Physicians without board certification often are denied hospital privileges, inclusion in insurance panels, and even medical licenses. This changes certification from a voluntary physician self-improvement exercise into a can’t-earn-a-living-without-it cudgel.
Variation
Boards vary significantly in their MOC requirements and costs. The importance of an equal standard across all boards is a clear theme among physician concerns.
Role and authority of the ABMS and related boards
Many physicians are frustrated with the perceived autocratic nature of their boards—boards that lack transparency, do not solicit or allow input from practicing physicians, and are unresponsive to physician concerns.
According to Susan Ramin, MD, ABOG Associate Executive Director, ABOG is leading in a number of these areas, including:
- rapidly disseminating clinical information on emerging topics, such as Zika virus infection and opioid misuse
- offering physician choice of testing categories
- exempting high scorers from the secured written exam, which saved physicians a total of $881,000 in exam fees
- crediting physicians for what they already are doing, including serving on maternal mortality review committees, participating in registries, and participating in the Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health (AIM)
- providing Lifelong Learning and Self-Assessment (LLSA) articles that, according to 90% of diplomates surveyed, are beneficial to their clinical practice (FIGURE).1,2
Our colleague physicians are not so lucky. In a 2015 New England Journal of Medicine Perspective, one physician called out the American Board of Internal Medicine as “a private, self-appointed certifying organization,” a not-for-profit organization that has “grown into a $55-million-per-year business.”3 He concluded that “many physicians are waking up to the fact that our profession is increasingly controlled by people not directly involved in patient care who have lost contact with the realities of day-to-day clinical practice.”3
State and society responses to MOC requirements
Frustration with an inability to resolve these concerns has grown steadily, bubbling over into state governments. The American Medical Association developed “model state legislation intended to prohibit hospitals, health care insurers, and state boards of medicine and osteopathic medicine from requiring participation in MOC processes as a condition of credentialing, privileging, insurance panel participation, licensure, or licensure renewal.”4
Some states are proposing or have enacted legislation that prohibits the use of MOC as a criterion for licensure, privileging, employment, reimbursement, and/or insurance panel participation. Eight states (Arizona, Georgia, Kentucky, Maryland, Maine, Missouri, Oklahoma, Tennessee) have enacted laws to prohibit the use of MOC for initial and renewal licensure decisions. Many states are actively considering MOC-related legislation, including Alaska, Florida, Iowa, Indiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Legislation is not the only outlet for physician frustration. Some medical specialty societies are considering dropping board certification as a membership requirement; physicians are exploring developing alternative boards; and some physicians are defying the board certification requirement altogether, with thousands signing anti-MOC petitions.
ACOG asserts importance of maintaining self-regulation
While other specialties are actively advocating state legislation, ACOG and ABOG have worked together to oppose state legislation, believing that physician self-regulation is paramount. In fact, in 2017, ACOG and ABOG issued a joint statement urging state lawmakers to “not interfere with our decades of successful self-regulation and to realize that each medical society has its own experience with its MOC program.”5
Negotiations lead to new initiative
This brings us to an interesting situation. ACOG’s Executive Vice President and CEO Hal Lawrence III, MD, was tapped (in his position as Chair of the Specialty Society CEO Consortium) to represent physician specialties in negotiations and discussions with the boards, which were represented by Lois Nora, MD, JD, President and CEO of the ABMS, and state medical societies, represented by Donald Palmisano Jr, JD, Executive Director and CEO of the Medical Association of Georgia. Many state medical societies, boards, and physician specialty organizations participated in these meetings.
Throughout months of debate, Dr. Lawrence urged his colleagues to stay at the table and do the hard work of reaching an agreement, rather than ask politicians to solve medicine’s problems. This approach was leveraged by the serious efforts and threats of state legislation, which brought the boards to the table. In August 2017, 41 state medical societies and 33 national medical specialty societies wrote to Dr. Nora expressing their concerns that “professional self-regulation is under attack. Concerns regarding the usefulness of the high-stakes exam, the exorbitant costs of the MOC process, and the lack of transparent communication from the certifying boards have led to damaging the MOC brand, and creating state-based attacks on the MOC process.”6
In December 2017, Dr. Lawrence and Mr. Palmisano led a meeting of principals from the national medical specialty societies and state medical societies with leaders of ABMS and 8 specialty boards, including ABOG, an opportunity to secure meaningful change. Dr. Lawrence began by stressing that the interests of physicians and patients would be best served by all parties coming together and collaborating on a meaningful solution, to repair trust and preserve physician self-regulation.
Dr. Ramin presented ABOG’s approach to continuous certification, lifelong learning, and self-assessment. The American Board of Urology and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology indicated that they were basing important changes in their MOC process on ABOG’s work, including using 5 modules (1 general and 4 specific to the physician’s practice) and multiple open-book mini-exams based on selected journal articles as an alternative to the 10-year MOC exam.
The Vision Initiative. At that meeting and others, the ABMS and other boards heard physicians’ candid and sometimes blunt concerns. Dr. Nora spoke to the recently announced Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future program, also known as the “Vision Initiative,” a process designed to fundamentally rebuild the continuing certification process with input and guidance from practicing physicians. Physician response seemed uniform: Seeing is believing.
Importantly, all participants at the December meeting agreed to work together to rebuild trust and ensure professionalism and professional self-regulation, reflected in this Statement of Shared Purpose:
ABMS certifying boards and national medical specialty societies will collaborate to resolve differences in the process of ongoing certification and to fulfill the principles of professional self-regulation, achieving appropriate standardization, and assuring that ongoing certification is relevant to the practices of physicians without undue burden. Furthermore, the boards and societies, and their organizations (ABMS and CMSS [Council of Medical Specialty Societies]), will undertake necessary changes in a timely manner, and will commit to ongoing communication with state medical associations to solicit their input.4
Two ObGyns participating in the Vision Initiative are Haywood Brown, MD, ACOG’s Immediate Past President, and George Wendel, MD, ABOG’s Executive Director. The Vision Initiative is composed of 3 parts. Part 1, Organization, is complete. The committee is currently working on part 2, Envisioning the Future, an information-gathering component that includes physician surveys, hearings, open solicited input, and identifying new and better approaches. After the final report is delivered to the ABMS in February 2019, part 3, Implementation, will begin.
The Vision Initiative offers physicians an important opportunity to help shape the future of continuing education and certification. ObGyns and other physicians should consider reviewing and commenting on the draft report, due in November, during the public comment period. Visit https://visioninitiative.org for more information and to sign up for email updates.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
The American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) has decided to trade the phrase “maintenance of certification” (MOC) for “continuing board certification,” a seemingly minor change that has an important backstory. This is the story of how the physician community flexed its collective muscle and how the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) helped broker an important détente and pathway in a highly contentious issue.
Founded in 1933 as a nonprofit organization dedicated to maintaining high uniform standards among physicians, the ABMS and many of its specialty boards have found themselves, for more than a decade, under heavy fire from physicians (especially family physicians, internists, and surgeons), their 24 subspecialties, and the state medical societies representing them.
The ObGyn experience with the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG), however, is better for a number of reasons. Historically, ABOG and ACOG have worked closely together, which is an anomaly among boards as many boards have an arms-length or even an antagonistic relationship with their specialty society.
The discussion below outlines physician concerns with the ABMS and related boards and describes efforts to address and rebuild the continuing board certification process.
Direct and indirect costs
Physicians are very concerned with the costs involved in MOC. Measurable costs include testing fees, while indirect costs include time, stress, travel to test centers, and threats to livelihood for failing a high-stakes examination. Physicians want the high-stakes exam eliminated.
Relevance to practice
Physicians often feel that the MOC has little relevance to their practice, which fuels a sense of resentment toward boards that they believe are dominated by physicians who no longer practice. Subspecialists feel farther away from general practice and the base exams. Generalists feel that the exams miss the points of their daily practice.
Lack of data to show improved quality of care
Physicians want to know that the MOC is worth their time, effort, and money because it improves patient care. To date, however, empirical or clinical data on patient outcomes are absent or ambiguous; most studies lack high-level data or do not investigate the MOC requirements. Physicians want to know what the best MOC practices are, what improves care, and that practices that make no difference will be discarded. In addition, they want timely knowledge alerts when evidence changes.
Relationship to licensing, employment, privileging, credentialing, and reimbursement
Hospitals, insurers, and states increasingly—and inappropriately—use board certification as the primary (sometimes only) default measure of a physician’s fitness for patient care. Physicians without board certification often are denied hospital privileges, inclusion in insurance panels, and even medical licenses. This changes certification from a voluntary physician self-improvement exercise into a can’t-earn-a-living-without-it cudgel.
Variation
Boards vary significantly in their MOC requirements and costs. The importance of an equal standard across all boards is a clear theme among physician concerns.
Role and authority of the ABMS and related boards
Many physicians are frustrated with the perceived autocratic nature of their boards—boards that lack transparency, do not solicit or allow input from practicing physicians, and are unresponsive to physician concerns.
According to Susan Ramin, MD, ABOG Associate Executive Director, ABOG is leading in a number of these areas, including:
- rapidly disseminating clinical information on emerging topics, such as Zika virus infection and opioid misuse
- offering physician choice of testing categories
- exempting high scorers from the secured written exam, which saved physicians a total of $881,000 in exam fees
- crediting physicians for what they already are doing, including serving on maternal mortality review committees, participating in registries, and participating in the Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health (AIM)
- providing Lifelong Learning and Self-Assessment (LLSA) articles that, according to 90% of diplomates surveyed, are beneficial to their clinical practice (FIGURE).1,2
Our colleague physicians are not so lucky. In a 2015 New England Journal of Medicine Perspective, one physician called out the American Board of Internal Medicine as “a private, self-appointed certifying organization,” a not-for-profit organization that has “grown into a $55-million-per-year business.”3 He concluded that “many physicians are waking up to the fact that our profession is increasingly controlled by people not directly involved in patient care who have lost contact with the realities of day-to-day clinical practice.”3
State and society responses to MOC requirements
Frustration with an inability to resolve these concerns has grown steadily, bubbling over into state governments. The American Medical Association developed “model state legislation intended to prohibit hospitals, health care insurers, and state boards of medicine and osteopathic medicine from requiring participation in MOC processes as a condition of credentialing, privileging, insurance panel participation, licensure, or licensure renewal.”4
Some states are proposing or have enacted legislation that prohibits the use of MOC as a criterion for licensure, privileging, employment, reimbursement, and/or insurance panel participation. Eight states (Arizona, Georgia, Kentucky, Maryland, Maine, Missouri, Oklahoma, Tennessee) have enacted laws to prohibit the use of MOC for initial and renewal licensure decisions. Many states are actively considering MOC-related legislation, including Alaska, Florida, Iowa, Indiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Tennessee, Utah, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Legislation is not the only outlet for physician frustration. Some medical specialty societies are considering dropping board certification as a membership requirement; physicians are exploring developing alternative boards; and some physicians are defying the board certification requirement altogether, with thousands signing anti-MOC petitions.
ACOG asserts importance of maintaining self-regulation
While other specialties are actively advocating state legislation, ACOG and ABOG have worked together to oppose state legislation, believing that physician self-regulation is paramount. In fact, in 2017, ACOG and ABOG issued a joint statement urging state lawmakers to “not interfere with our decades of successful self-regulation and to realize that each medical society has its own experience with its MOC program.”5
Negotiations lead to new initiative
This brings us to an interesting situation. ACOG’s Executive Vice President and CEO Hal Lawrence III, MD, was tapped (in his position as Chair of the Specialty Society CEO Consortium) to represent physician specialties in negotiations and discussions with the boards, which were represented by Lois Nora, MD, JD, President and CEO of the ABMS, and state medical societies, represented by Donald Palmisano Jr, JD, Executive Director and CEO of the Medical Association of Georgia. Many state medical societies, boards, and physician specialty organizations participated in these meetings.
Throughout months of debate, Dr. Lawrence urged his colleagues to stay at the table and do the hard work of reaching an agreement, rather than ask politicians to solve medicine’s problems. This approach was leveraged by the serious efforts and threats of state legislation, which brought the boards to the table. In August 2017, 41 state medical societies and 33 national medical specialty societies wrote to Dr. Nora expressing their concerns that “professional self-regulation is under attack. Concerns regarding the usefulness of the high-stakes exam, the exorbitant costs of the MOC process, and the lack of transparent communication from the certifying boards have led to damaging the MOC brand, and creating state-based attacks on the MOC process.”6
In December 2017, Dr. Lawrence and Mr. Palmisano led a meeting of principals from the national medical specialty societies and state medical societies with leaders of ABMS and 8 specialty boards, including ABOG, an opportunity to secure meaningful change. Dr. Lawrence began by stressing that the interests of physicians and patients would be best served by all parties coming together and collaborating on a meaningful solution, to repair trust and preserve physician self-regulation.
Dr. Ramin presented ABOG’s approach to continuous certification, lifelong learning, and self-assessment. The American Board of Urology and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology indicated that they were basing important changes in their MOC process on ABOG’s work, including using 5 modules (1 general and 4 specific to the physician’s practice) and multiple open-book mini-exams based on selected journal articles as an alternative to the 10-year MOC exam.
The Vision Initiative. At that meeting and others, the ABMS and other boards heard physicians’ candid and sometimes blunt concerns. Dr. Nora spoke to the recently announced Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future program, also known as the “Vision Initiative,” a process designed to fundamentally rebuild the continuing certification process with input and guidance from practicing physicians. Physician response seemed uniform: Seeing is believing.
Importantly, all participants at the December meeting agreed to work together to rebuild trust and ensure professionalism and professional self-regulation, reflected in this Statement of Shared Purpose:
ABMS certifying boards and national medical specialty societies will collaborate to resolve differences in the process of ongoing certification and to fulfill the principles of professional self-regulation, achieving appropriate standardization, and assuring that ongoing certification is relevant to the practices of physicians without undue burden. Furthermore, the boards and societies, and their organizations (ABMS and CMSS [Council of Medical Specialty Societies]), will undertake necessary changes in a timely manner, and will commit to ongoing communication with state medical associations to solicit their input.4
Two ObGyns participating in the Vision Initiative are Haywood Brown, MD, ACOG’s Immediate Past President, and George Wendel, MD, ABOG’s Executive Director. The Vision Initiative is composed of 3 parts. Part 1, Organization, is complete. The committee is currently working on part 2, Envisioning the Future, an information-gathering component that includes physician surveys, hearings, open solicited input, and identifying new and better approaches. After the final report is delivered to the ABMS in February 2019, part 3, Implementation, will begin.
The Vision Initiative offers physicians an important opportunity to help shape the future of continuing education and certification. ObGyns and other physicians should consider reviewing and commenting on the draft report, due in November, during the public comment period. Visit https://visioninitiative.org for more information and to sign up for email updates.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@mdedge.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology. From pilot to permanent: ABOG's program offering an innovative pathway integrating lifelong learning and self-assessment and external assessment is approved. https://www.abog.org/new/ABOG_PilotToPermanent.aspx. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Ramin S. American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology MOC program. PowerPoint presentation; December 4, 2017.
- Teirstein PS. Boarded to death--why maintenance of certification is bad for doctors and patients. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(2):106-108.
- AMA Council on Medical Education. Executive summary. 2017. https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/default/files/media-browser/public/council-on-med-ed/a18-cme-02.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG-ABOG joint statement: political interference in physician maintenance of skills threatens women's health care. https://www.acog.org/-/media/Departments/State-Legislative-Activities/2017ACOG-ABMS-MOC-Statement.pdf?dmc=1&ts=20180706T1615538746. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Letter to Lois Nora, MD, JD. August 18, 2017. https://www.mainemed.com/sites/default/files/content/MOC%20Letter%20082117.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology. From pilot to permanent: ABOG's program offering an innovative pathway integrating lifelong learning and self-assessment and external assessment is approved. https://www.abog.org/new/ABOG_PilotToPermanent.aspx. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Ramin S. American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology MOC program. PowerPoint presentation; December 4, 2017.
- Teirstein PS. Boarded to death--why maintenance of certification is bad for doctors and patients. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(2):106-108.
- AMA Council on Medical Education. Executive summary. 2017. https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/default/files/media-browser/public/council-on-med-ed/a18-cme-02.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG-ABOG joint statement: political interference in physician maintenance of skills threatens women's health care. https://www.acog.org/-/media/Departments/State-Legislative-Activities/2017ACOG-ABMS-MOC-Statement.pdf?dmc=1&ts=20180706T1615538746. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- Letter to Lois Nora, MD, JD. August 18, 2017. https://www.mainemed.com/sites/default/files/content/MOC%20Letter%20082117.pdf. Accessed July 6, 2018.