User login
The diagnosis in this patient is ulcerative colitis (UC) on the basis of physical examination, laboratory values, and endoscopy. However, this patient has the most extensive form, pancolitis, which means that inflammation and damage extend the entire length of the colon.
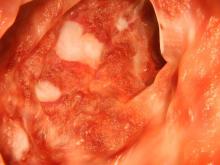
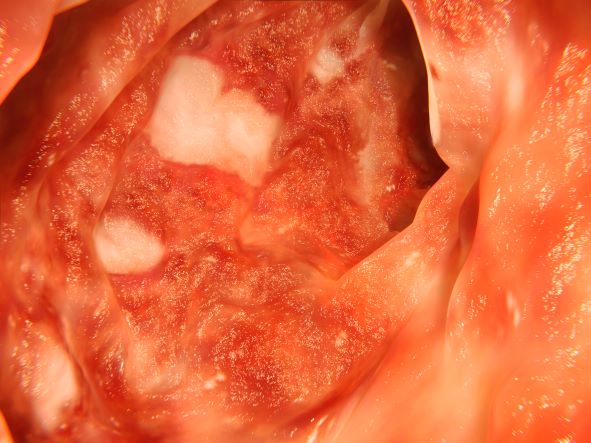
The diagnosis of UC is best made with endoscopy and mucosal biopsy for histopathology. Characteristic findings are abnormal erythematous mucosa, with or without ulceration, extending from the rectum to a part or all of the colon and uniform inflammation, without intervening areas of normal mucosa (skip lesions tend to characterize Crohn disease). Contact bleeding may also be observed, with mucus identified in the lumen of the bowel.
The bowel wall is thin or of normal thickness, but edema, accumulation of fat, and hypertrophy of the muscle layer may give it the appearance of a thickened bowel wall. The disease is largely confined to the mucosa and, to a lesser extent, the submucosa.
Laboratory studies are helpful to exclude other diagnoses and assess the patient's nutritional status, and serologic markers aid in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Radiographic imaging has an important role in differentiation of UC from Crohn disease. Fistulas or the presence of small bowel disease are seen only in Crohn disease.
According the American Gastroenterological Association, drug classes for the long-term management of moderate to severe UC include tumor necrosis factor–alpha antagonists, anti-integrin agent (vedolizumab), Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib), interleukin 12/23 antagonist (ustekinumab), and immunomodulators (thiopurines, methotrexate). Most drugs that are initiated for the induction of remission are continued as maintenance therapy if they are effective. This is not the case, however, if corticosteroids or cyclosporine are necessary to induce remission.
This patient's pancolitis presentation is also acute and severe, defined as more than 6 bloody bowel movements per day plus one of the following: fever > 100.4 °F, hemoglobin level < 10.5 g/dL, heart rate > 90 beats/min, erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 30 mm/h, or C-reactive protein level > 30 mg/dL). This requires hospitalization and treatment with intravenous corticosteroids (hydrocortisone 400 mg/d or methylprednisolone 60 mg/d). Considered a medical emergency, the situation requires prompt recognition and multidisciplinary management. In patients who fail therapy with 3-5 days of intravenous corticosteroids, medical rescue therapy is indicated with either infliximab or cyclosporine. If all measures fail, the patient may need emergency surgery.
Hospitalized patients with acute severe UC have short-term colectomy rates of 25%-30%.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The diagnosis in this patient is ulcerative colitis (UC) on the basis of physical examination, laboratory values, and endoscopy. However, this patient has the most extensive form, pancolitis, which means that inflammation and damage extend the entire length of the colon.
The diagnosis of UC is best made with endoscopy and mucosal biopsy for histopathology. Characteristic findings are abnormal erythematous mucosa, with or without ulceration, extending from the rectum to a part or all of the colon and uniform inflammation, without intervening areas of normal mucosa (skip lesions tend to characterize Crohn disease). Contact bleeding may also be observed, with mucus identified in the lumen of the bowel.
The bowel wall is thin or of normal thickness, but edema, accumulation of fat, and hypertrophy of the muscle layer may give it the appearance of a thickened bowel wall. The disease is largely confined to the mucosa and, to a lesser extent, the submucosa.
Laboratory studies are helpful to exclude other diagnoses and assess the patient's nutritional status, and serologic markers aid in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Radiographic imaging has an important role in differentiation of UC from Crohn disease. Fistulas or the presence of small bowel disease are seen only in Crohn disease.
According the American Gastroenterological Association, drug classes for the long-term management of moderate to severe UC include tumor necrosis factor–alpha antagonists, anti-integrin agent (vedolizumab), Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib), interleukin 12/23 antagonist (ustekinumab), and immunomodulators (thiopurines, methotrexate). Most drugs that are initiated for the induction of remission are continued as maintenance therapy if they are effective. This is not the case, however, if corticosteroids or cyclosporine are necessary to induce remission.
This patient's pancolitis presentation is also acute and severe, defined as more than 6 bloody bowel movements per day plus one of the following: fever > 100.4 °F, hemoglobin level < 10.5 g/dL, heart rate > 90 beats/min, erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 30 mm/h, or C-reactive protein level > 30 mg/dL). This requires hospitalization and treatment with intravenous corticosteroids (hydrocortisone 400 mg/d or methylprednisolone 60 mg/d). Considered a medical emergency, the situation requires prompt recognition and multidisciplinary management. In patients who fail therapy with 3-5 days of intravenous corticosteroids, medical rescue therapy is indicated with either infliximab or cyclosporine. If all measures fail, the patient may need emergency surgery.
Hospitalized patients with acute severe UC have short-term colectomy rates of 25%-30%.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The diagnosis in this patient is ulcerative colitis (UC) on the basis of physical examination, laboratory values, and endoscopy. However, this patient has the most extensive form, pancolitis, which means that inflammation and damage extend the entire length of the colon.
The diagnosis of UC is best made with endoscopy and mucosal biopsy for histopathology. Characteristic findings are abnormal erythematous mucosa, with or without ulceration, extending from the rectum to a part or all of the colon and uniform inflammation, without intervening areas of normal mucosa (skip lesions tend to characterize Crohn disease). Contact bleeding may also be observed, with mucus identified in the lumen of the bowel.
The bowel wall is thin or of normal thickness, but edema, accumulation of fat, and hypertrophy of the muscle layer may give it the appearance of a thickened bowel wall. The disease is largely confined to the mucosa and, to a lesser extent, the submucosa.
Laboratory studies are helpful to exclude other diagnoses and assess the patient's nutritional status, and serologic markers aid in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Radiographic imaging has an important role in differentiation of UC from Crohn disease. Fistulas or the presence of small bowel disease are seen only in Crohn disease.
According the American Gastroenterological Association, drug classes for the long-term management of moderate to severe UC include tumor necrosis factor–alpha antagonists, anti-integrin agent (vedolizumab), Janus kinase inhibitor (tofacitinib), interleukin 12/23 antagonist (ustekinumab), and immunomodulators (thiopurines, methotrexate). Most drugs that are initiated for the induction of remission are continued as maintenance therapy if they are effective. This is not the case, however, if corticosteroids or cyclosporine are necessary to induce remission.
This patient's pancolitis presentation is also acute and severe, defined as more than 6 bloody bowel movements per day plus one of the following: fever > 100.4 °F, hemoglobin level < 10.5 g/dL, heart rate > 90 beats/min, erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 30 mm/h, or C-reactive protein level > 30 mg/dL). This requires hospitalization and treatment with intravenous corticosteroids (hydrocortisone 400 mg/d or methylprednisolone 60 mg/d). Considered a medical emergency, the situation requires prompt recognition and multidisciplinary management. In patients who fail therapy with 3-5 days of intravenous corticosteroids, medical rescue therapy is indicated with either infliximab or cyclosporine. If all measures fail, the patient may need emergency surgery.
Hospitalized patients with acute severe UC have short-term colectomy rates of 25%-30%.
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Bhupinder S. Anand, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 76-year-old man presents with complaints of severe lower abdominal pain and dehydration. He reports bloody diarrhea of 2 weeks' duration and an unintentional 12-lb weight loss. Dietary alterations and loperamide have not helped. He has a fever of 102.1 °F. Medications include naproxen 440 mg/d for osteoarthritis, losartan 50 mg/d and amlodipine 5 mg/d for hypertension, and simvastatin 20 mg/d for dyslipidemia.
Physical examination reveals tenderness, particularly at the left lower quadrant of the abdomen, without rebound tenderness or guarding. Bowel sounds are active. He has a purulent rectal discharge. Stool cultures for the pathogens are negative. He has hypoalbuminemia (2.5 g/dL). He is positive for perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Serum carcinoembryonic antigen test is negative. C-reactive protein is 32 mg/dL.
The patient is admitted to the hospital and receives intravenous fluids. Colonoscopy reveals inflammation and visible ulcers in the mucosa throughout the entire length of the colon.