User login
From epidemic to endemic curse
Evolution is an amazing thing, and its more fascinating aspects are never more apparent than in the endless genetic dance between host and pathogen. And certainly, our fascination with the dance is not merely an intellectual exercise. The evolution of disease is perhaps one of the starkest examples of human misery writ large across the pages of recorded history.
In particular, the evolution of syphilis from dramatically visible, epidemic terror to silent, endemic, and long-term killer is one of the most striking examples of host-pathogen evolution. It is an example noteworthy not only for the profound transformation that occurred, but for the speed of the change, beginning so fast that it was noticed and detailed by physicians at the time as occurring over less than a human generation rather than centuries.
This very speed of the change makes it relatively certain that it was not the human species that evolved resistance, but rather that the syphilis-causing spirochetes transformed in virulence within almost the blink of an evolutionary eye – an epidemiologic mystery of profound importance to the countless lives involved.
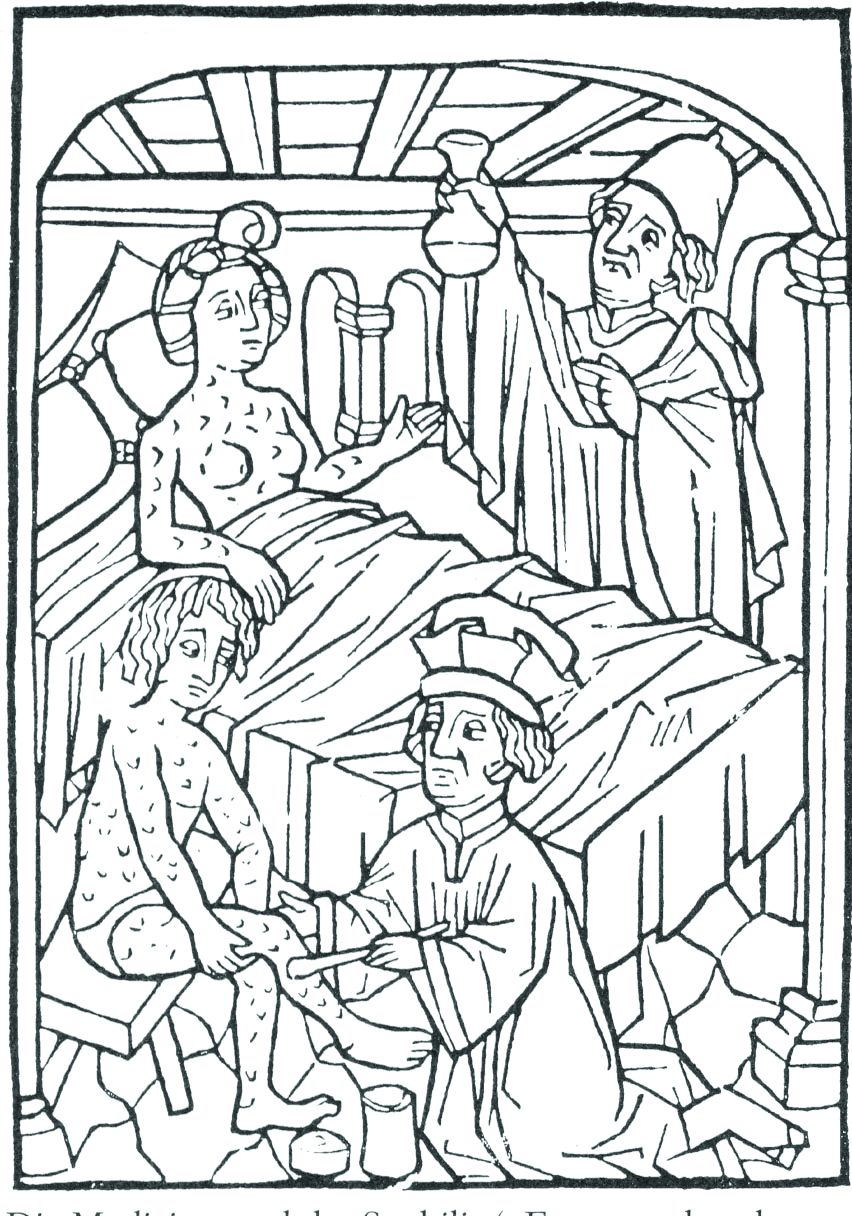
Syphilis was a dramatic new phenomenon in the Old World of the late 15th and early 16th centuries – a hitherto unknown disease of terrible guise and rapid dissemination. It was noted and discussed throughout many of the writings of the time, so much so that one of the first detailed patient accounts in recorded history of the experience of a disease was written in response to a syphilis infection.
In 1498, Tommaso di Silvestro, an Italian notary, described his symptoms in depth: “I remember how I, Ser Tomaso, during the day 27th of April 1498, coming back from the fair in Foligno, started to feel pain in the virga [a contemporary euphemism for penis]. And then the pain grew in intensity. Then in June I started to feel the pains of the French disease. And all my body filled with pustules and crusts. I had pains in the right and left arms, in the entire arm, from the shoulder to the hand, I was filled with pain to the bones and I never found peace. And then I had pains in the right knee and all my body got full of boils, at the back at the front and behind.”
Alessandro Benedetti (1450-1512), a military surgeon and chronicler of the expedition of Charles VIII, wrote in 1497 that sufferers lost hands, feet, eyes, and noses to the disease, such that it made “the entire body so repulsive to look at and causes such great suffering.”Another common characteristic was a foul smell typical of the infected.
Careful analysis by historians has shown that, according to records from the time period, 10-15 years after the start of the epidemic in the late 15th century, there was a noticeable decline in disease virulence.
As one historian put it: “Many physicians and contemporary observers noticed the progressive decline in the severity of the disease. Many symptoms were less severe, and the rash, of a reddish color, did not cause itching.” Girolamo Fracastoro writes about some of these transformations, stating that “in the first epidemic periods the pustules were filthier,’ while they were ‘harder and drier’ afterwards.” Similarly, the historian and scholar Bernardino Cirillo dell’Aquila (1500-1575), writing in the 1530s, stated: “This horrible disease in different periods (1494) till the present had different alterations and different effects depending on the complications, and now many people just lose their hair and nothing else.”
As added documentation of the change, the chaplain of the infamous conquistador Hernàn Cortés reported that syphilis was less severe in his time than earlier. He wrote that: “at the beginning this disease was very violent, dirty and indecent; now it is no longer so severe and so indecent.”
The medical literature of the time confirmed that the fever, characteristic of the second stage of the disease, “was less violent, while even the rashes were just a ‘reddening.’ Moreover, the gummy tumors appeared only in a limited number of cases.”
According to another historian, “By the middle of the 16th century, the generation of physicians born between the end of the 15th century and the first decades of the 16th century considered the exceptional virulence manifested by syphilis when it first appeared to be ancient history.”
And Ambroise Paré (1510-1590), a renowned French surgeon, stated: “Today it is much less serious and easier to heal than it was in the past... It is obviously becoming much milder … so that it seems it should disappear in the future.”
Lacking detailed genetic analysis of the changing pathogen, if one were to speculate on why the virulence of syphilis decreased so rapidly, I suggest, in a Just-So story fashion, that one might merely speculate on the evolutionary wisdom of an STD that commonly turned its victims into foul-smelling, scabrous, agonized, and lethargic individuals who lost body parts, including their genitals, according to some reports. None of these outcomes, of course, would be conducive to the natural spread of the disease. In addition, this is a good case for sexual selection as well as early death of the host, which are two main engineers of evolutionary change.
But for whatever reason, the presentation of syphilis changed dramatically over a relatively short period of time, and as the disease was still spreading through a previously unexposed population, a change in pathogenicity rather than host immunity seems the most logical explanation.
As syphilis evolved from its initial onslaught, it showed new and hitherto unseen symptoms, including the aforementioned hair loss, and other manifestations such as tinnitus. Soon it was presenting so many systemic phenotypes similar to the effects of other diseases that Sir William Osler (1849-1919) ultimately proposed that syphilis should be described as the “Great Imitator.”
The evolution of syphilis from epidemic to endemic does not diminish the horrors of those afflicted with active tertiary syphilis, but as the disease transformed, these effects were greatly postponed and occurred less commonly, compared with their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
Although still lethal, especially in its congenital form, by the end of the 16th century, syphilis had completed its rapid evolution from a devastating, highly visible plague to the covert disease “so sinful that it could not be discussed by name.” It would remain so until the rise of modern antibiotics finally provided a reliable cure. Active tertiary syphilis remained a severe affliction, but the effects were postponed from their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
So, syphilis remains a unique example of host-pathogen evolution, an endemic part of the global human condition, battled by physicians in mostly futile efforts for nearly 500 years, and a disease tracking closely with the rise of modern medicine.
References
Frith J. 2012. Syphilis – Its Early History and Treatment Until Penicillin and the Debate on its Origins. J Military and Veteran’s Health. 20(4):49-58.
Tognoti B. 2009. The Rise and Fall of Syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & celluar biology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
From epidemic to endemic curse
From epidemic to endemic curse
Evolution is an amazing thing, and its more fascinating aspects are never more apparent than in the endless genetic dance between host and pathogen. And certainly, our fascination with the dance is not merely an intellectual exercise. The evolution of disease is perhaps one of the starkest examples of human misery writ large across the pages of recorded history.
In particular, the evolution of syphilis from dramatically visible, epidemic terror to silent, endemic, and long-term killer is one of the most striking examples of host-pathogen evolution. It is an example noteworthy not only for the profound transformation that occurred, but for the speed of the change, beginning so fast that it was noticed and detailed by physicians at the time as occurring over less than a human generation rather than centuries.
This very speed of the change makes it relatively certain that it was not the human species that evolved resistance, but rather that the syphilis-causing spirochetes transformed in virulence within almost the blink of an evolutionary eye – an epidemiologic mystery of profound importance to the countless lives involved.
Syphilis was a dramatic new phenomenon in the Old World of the late 15th and early 16th centuries – a hitherto unknown disease of terrible guise and rapid dissemination. It was noted and discussed throughout many of the writings of the time, so much so that one of the first detailed patient accounts in recorded history of the experience of a disease was written in response to a syphilis infection.
In 1498, Tommaso di Silvestro, an Italian notary, described his symptoms in depth: “I remember how I, Ser Tomaso, during the day 27th of April 1498, coming back from the fair in Foligno, started to feel pain in the virga [a contemporary euphemism for penis]. And then the pain grew in intensity. Then in June I started to feel the pains of the French disease. And all my body filled with pustules and crusts. I had pains in the right and left arms, in the entire arm, from the shoulder to the hand, I was filled with pain to the bones and I never found peace. And then I had pains in the right knee and all my body got full of boils, at the back at the front and behind.”
Alessandro Benedetti (1450-1512), a military surgeon and chronicler of the expedition of Charles VIII, wrote in 1497 that sufferers lost hands, feet, eyes, and noses to the disease, such that it made “the entire body so repulsive to look at and causes such great suffering.”Another common characteristic was a foul smell typical of the infected.
Careful analysis by historians has shown that, according to records from the time period, 10-15 years after the start of the epidemic in the late 15th century, there was a noticeable decline in disease virulence.
As one historian put it: “Many physicians and contemporary observers noticed the progressive decline in the severity of the disease. Many symptoms were less severe, and the rash, of a reddish color, did not cause itching.” Girolamo Fracastoro writes about some of these transformations, stating that “in the first epidemic periods the pustules were filthier,’ while they were ‘harder and drier’ afterwards.” Similarly, the historian and scholar Bernardino Cirillo dell’Aquila (1500-1575), writing in the 1530s, stated: “This horrible disease in different periods (1494) till the present had different alterations and different effects depending on the complications, and now many people just lose their hair and nothing else.”
As added documentation of the change, the chaplain of the infamous conquistador Hernàn Cortés reported that syphilis was less severe in his time than earlier. He wrote that: “at the beginning this disease was very violent, dirty and indecent; now it is no longer so severe and so indecent.”
The medical literature of the time confirmed that the fever, characteristic of the second stage of the disease, “was less violent, while even the rashes were just a ‘reddening.’ Moreover, the gummy tumors appeared only in a limited number of cases.”
According to another historian, “By the middle of the 16th century, the generation of physicians born between the end of the 15th century and the first decades of the 16th century considered the exceptional virulence manifested by syphilis when it first appeared to be ancient history.”
And Ambroise Paré (1510-1590), a renowned French surgeon, stated: “Today it is much less serious and easier to heal than it was in the past... It is obviously becoming much milder … so that it seems it should disappear in the future.”
Lacking detailed genetic analysis of the changing pathogen, if one were to speculate on why the virulence of syphilis decreased so rapidly, I suggest, in a Just-So story fashion, that one might merely speculate on the evolutionary wisdom of an STD that commonly turned its victims into foul-smelling, scabrous, agonized, and lethargic individuals who lost body parts, including their genitals, according to some reports. None of these outcomes, of course, would be conducive to the natural spread of the disease. In addition, this is a good case for sexual selection as well as early death of the host, which are two main engineers of evolutionary change.
But for whatever reason, the presentation of syphilis changed dramatically over a relatively short period of time, and as the disease was still spreading through a previously unexposed population, a change in pathogenicity rather than host immunity seems the most logical explanation.
As syphilis evolved from its initial onslaught, it showed new and hitherto unseen symptoms, including the aforementioned hair loss, and other manifestations such as tinnitus. Soon it was presenting so many systemic phenotypes similar to the effects of other diseases that Sir William Osler (1849-1919) ultimately proposed that syphilis should be described as the “Great Imitator.”
The evolution of syphilis from epidemic to endemic does not diminish the horrors of those afflicted with active tertiary syphilis, but as the disease transformed, these effects were greatly postponed and occurred less commonly, compared with their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
Although still lethal, especially in its congenital form, by the end of the 16th century, syphilis had completed its rapid evolution from a devastating, highly visible plague to the covert disease “so sinful that it could not be discussed by name.” It would remain so until the rise of modern antibiotics finally provided a reliable cure. Active tertiary syphilis remained a severe affliction, but the effects were postponed from their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
So, syphilis remains a unique example of host-pathogen evolution, an endemic part of the global human condition, battled by physicians in mostly futile efforts for nearly 500 years, and a disease tracking closely with the rise of modern medicine.
References
Frith J. 2012. Syphilis – Its Early History and Treatment Until Penicillin and the Debate on its Origins. J Military and Veteran’s Health. 20(4):49-58.
Tognoti B. 2009. The Rise and Fall of Syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & celluar biology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.
Evolution is an amazing thing, and its more fascinating aspects are never more apparent than in the endless genetic dance between host and pathogen. And certainly, our fascination with the dance is not merely an intellectual exercise. The evolution of disease is perhaps one of the starkest examples of human misery writ large across the pages of recorded history.
In particular, the evolution of syphilis from dramatically visible, epidemic terror to silent, endemic, and long-term killer is one of the most striking examples of host-pathogen evolution. It is an example noteworthy not only for the profound transformation that occurred, but for the speed of the change, beginning so fast that it was noticed and detailed by physicians at the time as occurring over less than a human generation rather than centuries.
This very speed of the change makes it relatively certain that it was not the human species that evolved resistance, but rather that the syphilis-causing spirochetes transformed in virulence within almost the blink of an evolutionary eye – an epidemiologic mystery of profound importance to the countless lives involved.
Syphilis was a dramatic new phenomenon in the Old World of the late 15th and early 16th centuries – a hitherto unknown disease of terrible guise and rapid dissemination. It was noted and discussed throughout many of the writings of the time, so much so that one of the first detailed patient accounts in recorded history of the experience of a disease was written in response to a syphilis infection.
In 1498, Tommaso di Silvestro, an Italian notary, described his symptoms in depth: “I remember how I, Ser Tomaso, during the day 27th of April 1498, coming back from the fair in Foligno, started to feel pain in the virga [a contemporary euphemism for penis]. And then the pain grew in intensity. Then in June I started to feel the pains of the French disease. And all my body filled with pustules and crusts. I had pains in the right and left arms, in the entire arm, from the shoulder to the hand, I was filled with pain to the bones and I never found peace. And then I had pains in the right knee and all my body got full of boils, at the back at the front and behind.”
Alessandro Benedetti (1450-1512), a military surgeon and chronicler of the expedition of Charles VIII, wrote in 1497 that sufferers lost hands, feet, eyes, and noses to the disease, such that it made “the entire body so repulsive to look at and causes such great suffering.”Another common characteristic was a foul smell typical of the infected.
Careful analysis by historians has shown that, according to records from the time period, 10-15 years after the start of the epidemic in the late 15th century, there was a noticeable decline in disease virulence.
As one historian put it: “Many physicians and contemporary observers noticed the progressive decline in the severity of the disease. Many symptoms were less severe, and the rash, of a reddish color, did not cause itching.” Girolamo Fracastoro writes about some of these transformations, stating that “in the first epidemic periods the pustules were filthier,’ while they were ‘harder and drier’ afterwards.” Similarly, the historian and scholar Bernardino Cirillo dell’Aquila (1500-1575), writing in the 1530s, stated: “This horrible disease in different periods (1494) till the present had different alterations and different effects depending on the complications, and now many people just lose their hair and nothing else.”
As added documentation of the change, the chaplain of the infamous conquistador Hernàn Cortés reported that syphilis was less severe in his time than earlier. He wrote that: “at the beginning this disease was very violent, dirty and indecent; now it is no longer so severe and so indecent.”
The medical literature of the time confirmed that the fever, characteristic of the second stage of the disease, “was less violent, while even the rashes were just a ‘reddening.’ Moreover, the gummy tumors appeared only in a limited number of cases.”
According to another historian, “By the middle of the 16th century, the generation of physicians born between the end of the 15th century and the first decades of the 16th century considered the exceptional virulence manifested by syphilis when it first appeared to be ancient history.”
And Ambroise Paré (1510-1590), a renowned French surgeon, stated: “Today it is much less serious and easier to heal than it was in the past... It is obviously becoming much milder … so that it seems it should disappear in the future.”
Lacking detailed genetic analysis of the changing pathogen, if one were to speculate on why the virulence of syphilis decreased so rapidly, I suggest, in a Just-So story fashion, that one might merely speculate on the evolutionary wisdom of an STD that commonly turned its victims into foul-smelling, scabrous, agonized, and lethargic individuals who lost body parts, including their genitals, according to some reports. None of these outcomes, of course, would be conducive to the natural spread of the disease. In addition, this is a good case for sexual selection as well as early death of the host, which are two main engineers of evolutionary change.
But for whatever reason, the presentation of syphilis changed dramatically over a relatively short period of time, and as the disease was still spreading through a previously unexposed population, a change in pathogenicity rather than host immunity seems the most logical explanation.
As syphilis evolved from its initial onslaught, it showed new and hitherto unseen symptoms, including the aforementioned hair loss, and other manifestations such as tinnitus. Soon it was presenting so many systemic phenotypes similar to the effects of other diseases that Sir William Osler (1849-1919) ultimately proposed that syphilis should be described as the “Great Imitator.”
The evolution of syphilis from epidemic to endemic does not diminish the horrors of those afflicted with active tertiary syphilis, but as the disease transformed, these effects were greatly postponed and occurred less commonly, compared with their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
Although still lethal, especially in its congenital form, by the end of the 16th century, syphilis had completed its rapid evolution from a devastating, highly visible plague to the covert disease “so sinful that it could not be discussed by name.” It would remain so until the rise of modern antibiotics finally provided a reliable cure. Active tertiary syphilis remained a severe affliction, but the effects were postponed from their relatively rapid onset in an earlier era and in a greater proportion of the infected individuals.
So, syphilis remains a unique example of host-pathogen evolution, an endemic part of the global human condition, battled by physicians in mostly futile efforts for nearly 500 years, and a disease tracking closely with the rise of modern medicine.
References
Frith J. 2012. Syphilis – Its Early History and Treatment Until Penicillin and the Debate on its Origins. J Military and Veteran’s Health. 20(4):49-58.
Tognoti B. 2009. The Rise and Fall of Syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & celluar biology at Georgetown University, Washington, D.C.