User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
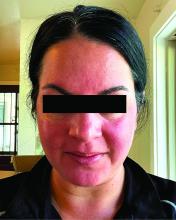
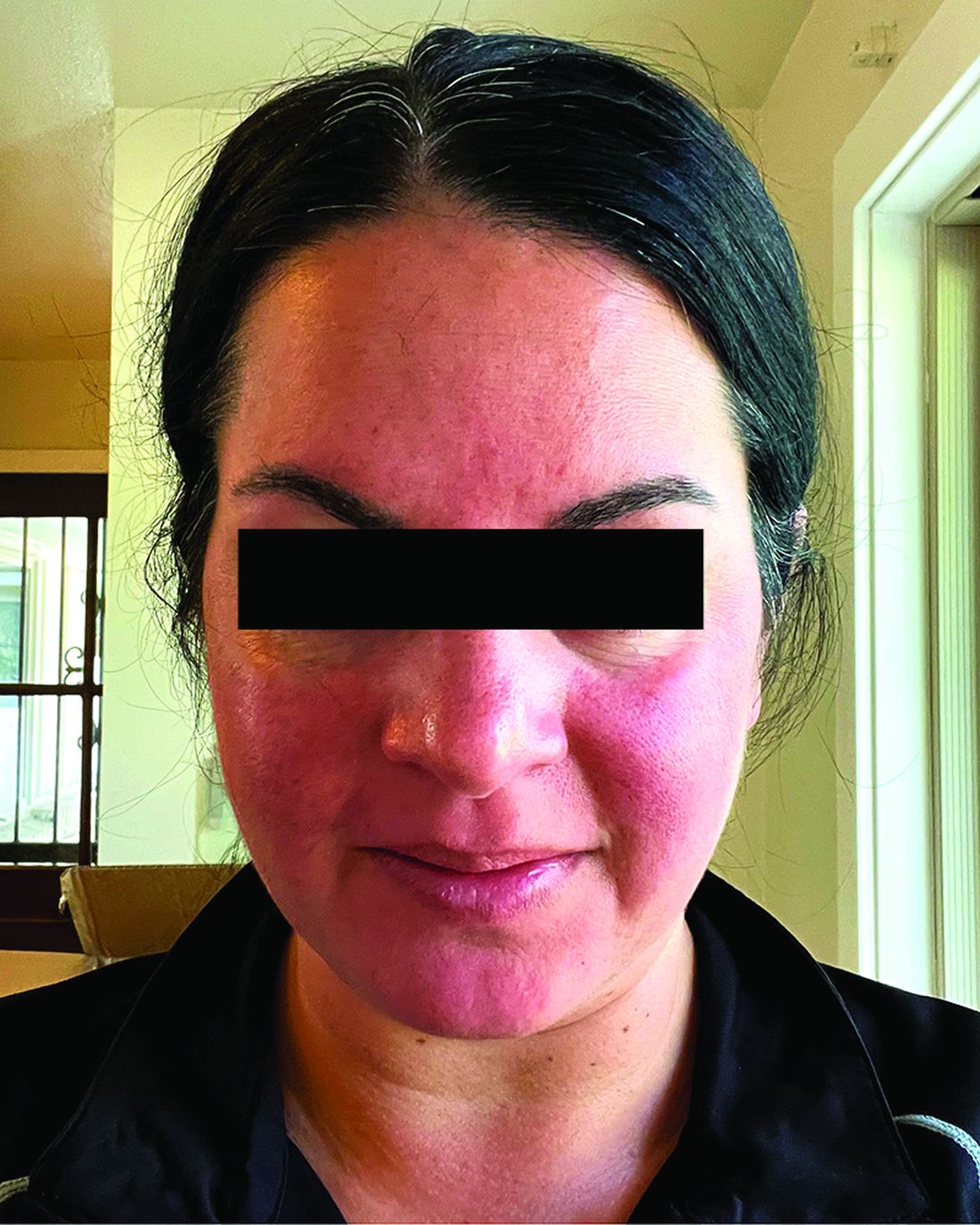
Migraine Drug Reduces Rosacea Flushing, Erythema in Small Study
In. Skin-related quality-of-life (QOL) measures also improved, albeit modestly.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“The transient erythema of rosacea is one of the most challenging rosacea symptoms to treat,” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview. “As flushing can adversely impact quality of life in our rosacea patients, it is important to find therapeutic options for our patients. This study is exciting, not only because the treatment was successful for a notable number of patients, but also because it involved a drug with a novel mode of action in rosacea.” Dr. Graber practices in Boston and is an affiliate clinical instructor at Northeastern University, Boston.
Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD, clinical professor of dermatology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, added, “The interesting thing about this study is that it gives us a new target to think about for therapy. But it’s a long way from saying we can use it tomorrow.” He was not involved with the study but was also asked to comment on the findings.
Spotlight on CGRP
Rosacea’s pathophysiology remains incompletely understood, wrote Nita K.F. Wienholtz, MD, PhD, Department of Dermatology, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and coinvestigators. However, they added, mounting evidence suggests a possible role for CGRP. For example, a study published in JAMA Dermatology in 2015 revealed elevated CGRP levels in facial skin biopsies from patients with rosacea.
For the present study, the investigators enrolled 30 adults (including 23 women) with rosacea who experienced at least 15 days of moderate to severe erythema or extreme flushing during a 4-week, treatment-free run-in period. Most participants (87%) had previously failed one or more rosacea treatments because of a lack of efficacy or adverse reactions, and 43% had failed three or more treatments.
Participants received 3-monthly 140-mg doses of erenumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for migraine prevention. Patients recorded scores on the Patient Self-Assessment (PSA) and item 2 of the Flushing Assessment Tool online daily and made a final follow-up visit 12 weeks after the third dose.
Among the 27 patients who completed the study, the mean number of days with moderate to severe flushing from week 9 to week 12 fell by 6.9 from 23.6 days over 4 weeks at baseline (P < .001). Patients most severely affected by flushing at baseline experienced an 81% decline in days with severe to extreme flushing. Overall, 26% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in moderate to extreme flushing days. The number of days with moderate to severe erythema as measured by PSA fell by 8.1 (mean) from baseline, and 56% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in PSA scores. No unexpected safety signals emerged.
Questions Over QOL Data
“Although there were significant decreases in flushing and erythema,” wrote John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, in an accompanying Editor’s Note, “the present study had relatively modest improvements in quality of life.” He is director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associate editor and evidence-based practice editor of JAMA Dermatology.
Compared with baseline (6.22), mean Dermatology Life Quality Index scores fell 2.08 points and 2.73 points at weeks 8 and 20, respectively (P = .004 and .003). At the same intervals, the mean baseline Rosacea Quality of Life score (48.22) decreased by 2.58 points and 4.14 points, respectively (P = .04 and .02).
No significant changes appeared in gauges of anxiety and depression. These findings, authors wrote, could stem from their decision to omit a follow-up visit at week 12 — where they may have seen mental-health effects which disappeared by week 20 — in response to patients’ logistical concerns.
However, Dr. Webster questioned the value of QOL measurements in rosacea. “Quality-of-life measures are blunt instruments,” he explained, and reducing severe itching or chronic pain improves the lives of affected patients. “But what question are you going to ask to tease out whether being less red-cheeked has made someone’s life easier? It’s not a problem that lends itself to quality-of-life assessments.” Moreover, he said, regulators who increasingly require such measures in clinical trials ignore this point, creating challenges for drug developers and researchers.
Because the study was neither blinded nor controlled, Dr. Webster suggested considering it a tantalizing proof of concept. “If I were putting money into a CGRP inhibitor, I’d want at least a small, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study.”
Study authors and Dr. Barbieri recommended larger randomized studies involving different populations and erenumab doses. For now, Dr. Barbieri wrote, CGRP inhibition represents a promising potential strategy for patients who have rosacea with comorbid migraine or recalcitrant flushing and erythema.
Dr. Wienholtz reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Barbieri had no related disclosures. Dr. Webster reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Graber reported no conflicts related to erenumab but consults for other companies with rosacea-related products including Galderma. The study was supported by and conducted in collaboration with Novartis Pharma AG. Additional funding came from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In. Skin-related quality-of-life (QOL) measures also improved, albeit modestly.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“The transient erythema of rosacea is one of the most challenging rosacea symptoms to treat,” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview. “As flushing can adversely impact quality of life in our rosacea patients, it is important to find therapeutic options for our patients. This study is exciting, not only because the treatment was successful for a notable number of patients, but also because it involved a drug with a novel mode of action in rosacea.” Dr. Graber practices in Boston and is an affiliate clinical instructor at Northeastern University, Boston.
Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD, clinical professor of dermatology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, added, “The interesting thing about this study is that it gives us a new target to think about for therapy. But it’s a long way from saying we can use it tomorrow.” He was not involved with the study but was also asked to comment on the findings.
Spotlight on CGRP
Rosacea’s pathophysiology remains incompletely understood, wrote Nita K.F. Wienholtz, MD, PhD, Department of Dermatology, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and coinvestigators. However, they added, mounting evidence suggests a possible role for CGRP. For example, a study published in JAMA Dermatology in 2015 revealed elevated CGRP levels in facial skin biopsies from patients with rosacea.
For the present study, the investigators enrolled 30 adults (including 23 women) with rosacea who experienced at least 15 days of moderate to severe erythema or extreme flushing during a 4-week, treatment-free run-in period. Most participants (87%) had previously failed one or more rosacea treatments because of a lack of efficacy or adverse reactions, and 43% had failed three or more treatments.
Participants received 3-monthly 140-mg doses of erenumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for migraine prevention. Patients recorded scores on the Patient Self-Assessment (PSA) and item 2 of the Flushing Assessment Tool online daily and made a final follow-up visit 12 weeks after the third dose.
Among the 27 patients who completed the study, the mean number of days with moderate to severe flushing from week 9 to week 12 fell by 6.9 from 23.6 days over 4 weeks at baseline (P < .001). Patients most severely affected by flushing at baseline experienced an 81% decline in days with severe to extreme flushing. Overall, 26% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in moderate to extreme flushing days. The number of days with moderate to severe erythema as measured by PSA fell by 8.1 (mean) from baseline, and 56% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in PSA scores. No unexpected safety signals emerged.
Questions Over QOL Data
“Although there were significant decreases in flushing and erythema,” wrote John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, in an accompanying Editor’s Note, “the present study had relatively modest improvements in quality of life.” He is director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associate editor and evidence-based practice editor of JAMA Dermatology.
Compared with baseline (6.22), mean Dermatology Life Quality Index scores fell 2.08 points and 2.73 points at weeks 8 and 20, respectively (P = .004 and .003). At the same intervals, the mean baseline Rosacea Quality of Life score (48.22) decreased by 2.58 points and 4.14 points, respectively (P = .04 and .02).
No significant changes appeared in gauges of anxiety and depression. These findings, authors wrote, could stem from their decision to omit a follow-up visit at week 12 — where they may have seen mental-health effects which disappeared by week 20 — in response to patients’ logistical concerns.
However, Dr. Webster questioned the value of QOL measurements in rosacea. “Quality-of-life measures are blunt instruments,” he explained, and reducing severe itching or chronic pain improves the lives of affected patients. “But what question are you going to ask to tease out whether being less red-cheeked has made someone’s life easier? It’s not a problem that lends itself to quality-of-life assessments.” Moreover, he said, regulators who increasingly require such measures in clinical trials ignore this point, creating challenges for drug developers and researchers.
Because the study was neither blinded nor controlled, Dr. Webster suggested considering it a tantalizing proof of concept. “If I were putting money into a CGRP inhibitor, I’d want at least a small, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study.”
Study authors and Dr. Barbieri recommended larger randomized studies involving different populations and erenumab doses. For now, Dr. Barbieri wrote, CGRP inhibition represents a promising potential strategy for patients who have rosacea with comorbid migraine or recalcitrant flushing and erythema.
Dr. Wienholtz reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Barbieri had no related disclosures. Dr. Webster reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Graber reported no conflicts related to erenumab but consults for other companies with rosacea-related products including Galderma. The study was supported by and conducted in collaboration with Novartis Pharma AG. Additional funding came from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In. Skin-related quality-of-life (QOL) measures also improved, albeit modestly.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“The transient erythema of rosacea is one of the most challenging rosacea symptoms to treat,” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview. “As flushing can adversely impact quality of life in our rosacea patients, it is important to find therapeutic options for our patients. This study is exciting, not only because the treatment was successful for a notable number of patients, but also because it involved a drug with a novel mode of action in rosacea.” Dr. Graber practices in Boston and is an affiliate clinical instructor at Northeastern University, Boston.
Guy F. Webster, MD, PhD, clinical professor of dermatology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, added, “The interesting thing about this study is that it gives us a new target to think about for therapy. But it’s a long way from saying we can use it tomorrow.” He was not involved with the study but was also asked to comment on the findings.
Spotlight on CGRP
Rosacea’s pathophysiology remains incompletely understood, wrote Nita K.F. Wienholtz, MD, PhD, Department of Dermatology, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and coinvestigators. However, they added, mounting evidence suggests a possible role for CGRP. For example, a study published in JAMA Dermatology in 2015 revealed elevated CGRP levels in facial skin biopsies from patients with rosacea.
For the present study, the investigators enrolled 30 adults (including 23 women) with rosacea who experienced at least 15 days of moderate to severe erythema or extreme flushing during a 4-week, treatment-free run-in period. Most participants (87%) had previously failed one or more rosacea treatments because of a lack of efficacy or adverse reactions, and 43% had failed three or more treatments.
Participants received 3-monthly 140-mg doses of erenumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for migraine prevention. Patients recorded scores on the Patient Self-Assessment (PSA) and item 2 of the Flushing Assessment Tool online daily and made a final follow-up visit 12 weeks after the third dose.
Among the 27 patients who completed the study, the mean number of days with moderate to severe flushing from week 9 to week 12 fell by 6.9 from 23.6 days over 4 weeks at baseline (P < .001). Patients most severely affected by flushing at baseline experienced an 81% decline in days with severe to extreme flushing. Overall, 26% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in moderate to extreme flushing days. The number of days with moderate to severe erythema as measured by PSA fell by 8.1 (mean) from baseline, and 56% of patients experienced at least 50% reductions in PSA scores. No unexpected safety signals emerged.
Questions Over QOL Data
“Although there were significant decreases in flushing and erythema,” wrote John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, in an accompanying Editor’s Note, “the present study had relatively modest improvements in quality of life.” He is director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and associate editor and evidence-based practice editor of JAMA Dermatology.
Compared with baseline (6.22), mean Dermatology Life Quality Index scores fell 2.08 points and 2.73 points at weeks 8 and 20, respectively (P = .004 and .003). At the same intervals, the mean baseline Rosacea Quality of Life score (48.22) decreased by 2.58 points and 4.14 points, respectively (P = .04 and .02).
No significant changes appeared in gauges of anxiety and depression. These findings, authors wrote, could stem from their decision to omit a follow-up visit at week 12 — where they may have seen mental-health effects which disappeared by week 20 — in response to patients’ logistical concerns.
However, Dr. Webster questioned the value of QOL measurements in rosacea. “Quality-of-life measures are blunt instruments,” he explained, and reducing severe itching or chronic pain improves the lives of affected patients. “But what question are you going to ask to tease out whether being less red-cheeked has made someone’s life easier? It’s not a problem that lends itself to quality-of-life assessments.” Moreover, he said, regulators who increasingly require such measures in clinical trials ignore this point, creating challenges for drug developers and researchers.
Because the study was neither blinded nor controlled, Dr. Webster suggested considering it a tantalizing proof of concept. “If I were putting money into a CGRP inhibitor, I’d want at least a small, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study.”
Study authors and Dr. Barbieri recommended larger randomized studies involving different populations and erenumab doses. For now, Dr. Barbieri wrote, CGRP inhibition represents a promising potential strategy for patients who have rosacea with comorbid migraine or recalcitrant flushing and erythema.
Dr. Wienholtz reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Barbieri had no related disclosures. Dr. Webster reported no relevant financial interests. Dr. Graber reported no conflicts related to erenumab but consults for other companies with rosacea-related products including Galderma. The study was supported by and conducted in collaboration with Novartis Pharma AG. Additional funding came from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and the Lundbeck Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Microbiome Alterations Linked to Growth Hormone Deficiency
, said Chinese researchers.
The research, published recently in Pediatric Research, involved more than 80 children and showed that those with GHD had alterations in microbial populations that have been linked to longevity, as well as a microbial and metabolite signature that allowed accurate discrimination from ISS.
“These findings provide novel insights into potential early diagnosis and innovative treatment alternatives, such as fecal microbiota transplantation, for short stature with varying growth hormone levels,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Dauber, MD, MMSc, chief of endocrinology, Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was not involved in the study, said that while this is “a really interesting area of research,” he expressed “hesitancy about getting too excited about this data yet.”
“One of the problems is how you define growth hormone deficiency,” as it is “not a black and white diagnosis,” and the etiology and child’s growth trajectory also need to be considered, Dr. Dauber told said.
He explained: “The problem is that, when you rely on the growth hormone stimulation test alone, there’s so many false positives and so much overlap between patients with true growth hormone deficiency and those without. And I think that this article fell prey to that.”
He added: “It would be really, really interesting and helpful to have a microbiome signature that allows you to distinguish between true growth hormone deficiency and patients with idiopathic short stature.”
“But you have to make sure that your groups are very well defined for this study to be really valid. And that’s one of my concerns here.”
Dr. Dauber continued: “Now, that being said, they did find some associations that correlated with growth hormone peak levels,” some which replicate previous findings, “so I do think that there are kernels of important findings here.”
‘Tease Out Influences’ to Isolate the Interaction
He pointed out that there are “many factors that influence the microbiome,” such as the use of antibiotics, diet, age, and geographic location. Therefore, a study that could truly tease out all these influences and isolate the interaction with growth hormone levels would need to be “very thoughtfully designed.”
A number of factors contribute to short stature, lead author Lan Li, MD, Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China, and colleagues.
These include genetic factors, environmental factors, and conditions such as being small for gestational age at birth, familial short stature, and chronic systemic diseases, as well as GHD and ISS.
Recent animal studies have suggested that there may be a bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiota and the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis, and it has been shown that individuals with GHD have significant alterations in their gut microbiota compared with healthy controls.
To investigate, they studied 36 children diagnosed with GHD, 32 with ISS, and 16 age- and sex-matched healthy controls, all of whom were recruited between February 2019 and June 2021 from the Pediatric Endocrinology Department of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University.
Fecal samples obtained from the children underwent microbiome analysis using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing, alongside nuclear MRI analysis of the metabolome, or the entire complement of small molecules in the samples.
Patients with GHD had a significantly higher body mass index than those with ISS (P < .05), and their peak growth hormone level was significantly lower (P < .001). Patients with GHD also had significantly higher total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels than patients with ISS (P < .05).
The team reports that the alpha diversity of the fecal microbiome, which measures the microbial diversity within a fecal sample, was similar between the three groups.
However, there was significant variation between the groups in the beta diversity, which quantifies the similarity or dissimilarity between two samples, and allows the overall taxonomic or functional diversity pattern to be linked to environmental features.
Compared with the healthy control group, the abundance of Pelomonas, Rodentibacter, and Rothia was significantly decreased in GHD and patients with ISS, while the abundance of Prevotellaceae_NK3B31_group was increased in the two patient groups, particularly in those with GHD.
In addition, the researchers found a decreased Firmicutes/Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio in participants with short stature, particularly in the GHD group. They noted that “emerging evidence suggests the F/B ratio may play a role in longevity.”
Nocardioides was substantially more common in the ISS group vs both patients with GHD and healthy controls, while Fusobacterium mortiferum was characteristic of GHD. The team suggests this “may serve as a critical intestinal factor contributing to the short stature observed in GHD.”
The metabolome analysis revealed that glucose, pyruvate, and pyrimidine metabolism may also play a significant role in distinguishing between patients with GHD and ISS and healthy control groups.
Finally, the team demonstrated that a panel combining 13 microbiome and metabolome markers was able to discriminate between GHD and ISS at an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.945, with a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 91%.
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau in China. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, said Chinese researchers.
The research, published recently in Pediatric Research, involved more than 80 children and showed that those with GHD had alterations in microbial populations that have been linked to longevity, as well as a microbial and metabolite signature that allowed accurate discrimination from ISS.
“These findings provide novel insights into potential early diagnosis and innovative treatment alternatives, such as fecal microbiota transplantation, for short stature with varying growth hormone levels,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Dauber, MD, MMSc, chief of endocrinology, Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was not involved in the study, said that while this is “a really interesting area of research,” he expressed “hesitancy about getting too excited about this data yet.”
“One of the problems is how you define growth hormone deficiency,” as it is “not a black and white diagnosis,” and the etiology and child’s growth trajectory also need to be considered, Dr. Dauber told said.
He explained: “The problem is that, when you rely on the growth hormone stimulation test alone, there’s so many false positives and so much overlap between patients with true growth hormone deficiency and those without. And I think that this article fell prey to that.”
He added: “It would be really, really interesting and helpful to have a microbiome signature that allows you to distinguish between true growth hormone deficiency and patients with idiopathic short stature.”
“But you have to make sure that your groups are very well defined for this study to be really valid. And that’s one of my concerns here.”
Dr. Dauber continued: “Now, that being said, they did find some associations that correlated with growth hormone peak levels,” some which replicate previous findings, “so I do think that there are kernels of important findings here.”
‘Tease Out Influences’ to Isolate the Interaction
He pointed out that there are “many factors that influence the microbiome,” such as the use of antibiotics, diet, age, and geographic location. Therefore, a study that could truly tease out all these influences and isolate the interaction with growth hormone levels would need to be “very thoughtfully designed.”
A number of factors contribute to short stature, lead author Lan Li, MD, Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China, and colleagues.
These include genetic factors, environmental factors, and conditions such as being small for gestational age at birth, familial short stature, and chronic systemic diseases, as well as GHD and ISS.
Recent animal studies have suggested that there may be a bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiota and the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis, and it has been shown that individuals with GHD have significant alterations in their gut microbiota compared with healthy controls.
To investigate, they studied 36 children diagnosed with GHD, 32 with ISS, and 16 age- and sex-matched healthy controls, all of whom were recruited between February 2019 and June 2021 from the Pediatric Endocrinology Department of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University.
Fecal samples obtained from the children underwent microbiome analysis using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing, alongside nuclear MRI analysis of the metabolome, or the entire complement of small molecules in the samples.
Patients with GHD had a significantly higher body mass index than those with ISS (P < .05), and their peak growth hormone level was significantly lower (P < .001). Patients with GHD also had significantly higher total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels than patients with ISS (P < .05).
The team reports that the alpha diversity of the fecal microbiome, which measures the microbial diversity within a fecal sample, was similar between the three groups.
However, there was significant variation between the groups in the beta diversity, which quantifies the similarity or dissimilarity between two samples, and allows the overall taxonomic or functional diversity pattern to be linked to environmental features.
Compared with the healthy control group, the abundance of Pelomonas, Rodentibacter, and Rothia was significantly decreased in GHD and patients with ISS, while the abundance of Prevotellaceae_NK3B31_group was increased in the two patient groups, particularly in those with GHD.
In addition, the researchers found a decreased Firmicutes/Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio in participants with short stature, particularly in the GHD group. They noted that “emerging evidence suggests the F/B ratio may play a role in longevity.”
Nocardioides was substantially more common in the ISS group vs both patients with GHD and healthy controls, while Fusobacterium mortiferum was characteristic of GHD. The team suggests this “may serve as a critical intestinal factor contributing to the short stature observed in GHD.”
The metabolome analysis revealed that glucose, pyruvate, and pyrimidine metabolism may also play a significant role in distinguishing between patients with GHD and ISS and healthy control groups.
Finally, the team demonstrated that a panel combining 13 microbiome and metabolome markers was able to discriminate between GHD and ISS at an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.945, with a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 91%.
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau in China. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, said Chinese researchers.
The research, published recently in Pediatric Research, involved more than 80 children and showed that those with GHD had alterations in microbial populations that have been linked to longevity, as well as a microbial and metabolite signature that allowed accurate discrimination from ISS.
“These findings provide novel insights into potential early diagnosis and innovative treatment alternatives, such as fecal microbiota transplantation, for short stature with varying growth hormone levels,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Dauber, MD, MMSc, chief of endocrinology, Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was not involved in the study, said that while this is “a really interesting area of research,” he expressed “hesitancy about getting too excited about this data yet.”
“One of the problems is how you define growth hormone deficiency,” as it is “not a black and white diagnosis,” and the etiology and child’s growth trajectory also need to be considered, Dr. Dauber told said.
He explained: “The problem is that, when you rely on the growth hormone stimulation test alone, there’s so many false positives and so much overlap between patients with true growth hormone deficiency and those without. And I think that this article fell prey to that.”
He added: “It would be really, really interesting and helpful to have a microbiome signature that allows you to distinguish between true growth hormone deficiency and patients with idiopathic short stature.”
“But you have to make sure that your groups are very well defined for this study to be really valid. And that’s one of my concerns here.”
Dr. Dauber continued: “Now, that being said, they did find some associations that correlated with growth hormone peak levels,” some which replicate previous findings, “so I do think that there are kernels of important findings here.”
‘Tease Out Influences’ to Isolate the Interaction
He pointed out that there are “many factors that influence the microbiome,” such as the use of antibiotics, diet, age, and geographic location. Therefore, a study that could truly tease out all these influences and isolate the interaction with growth hormone levels would need to be “very thoughtfully designed.”
A number of factors contribute to short stature, lead author Lan Li, MD, Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China, and colleagues.
These include genetic factors, environmental factors, and conditions such as being small for gestational age at birth, familial short stature, and chronic systemic diseases, as well as GHD and ISS.
Recent animal studies have suggested that there may be a bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiota and the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis, and it has been shown that individuals with GHD have significant alterations in their gut microbiota compared with healthy controls.
To investigate, they studied 36 children diagnosed with GHD, 32 with ISS, and 16 age- and sex-matched healthy controls, all of whom were recruited between February 2019 and June 2021 from the Pediatric Endocrinology Department of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University.
Fecal samples obtained from the children underwent microbiome analysis using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing, alongside nuclear MRI analysis of the metabolome, or the entire complement of small molecules in the samples.
Patients with GHD had a significantly higher body mass index than those with ISS (P < .05), and their peak growth hormone level was significantly lower (P < .001). Patients with GHD also had significantly higher total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels than patients with ISS (P < .05).
The team reports that the alpha diversity of the fecal microbiome, which measures the microbial diversity within a fecal sample, was similar between the three groups.
However, there was significant variation between the groups in the beta diversity, which quantifies the similarity or dissimilarity between two samples, and allows the overall taxonomic or functional diversity pattern to be linked to environmental features.
Compared with the healthy control group, the abundance of Pelomonas, Rodentibacter, and Rothia was significantly decreased in GHD and patients with ISS, while the abundance of Prevotellaceae_NK3B31_group was increased in the two patient groups, particularly in those with GHD.
In addition, the researchers found a decreased Firmicutes/Bacteroidota (F/B) ratio in participants with short stature, particularly in the GHD group. They noted that “emerging evidence suggests the F/B ratio may play a role in longevity.”
Nocardioides was substantially more common in the ISS group vs both patients with GHD and healthy controls, while Fusobacterium mortiferum was characteristic of GHD. The team suggests this “may serve as a critical intestinal factor contributing to the short stature observed in GHD.”
The metabolome analysis revealed that glucose, pyruvate, and pyrimidine metabolism may also play a significant role in distinguishing between patients with GHD and ISS and healthy control groups.
Finally, the team demonstrated that a panel combining 13 microbiome and metabolome markers was able to discriminate between GHD and ISS at an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.945, with a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 91%.
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau in China. No relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRIC RESEARCH
Which Emergencies Are Genuine Emergencies?
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WIESBADEN, GERMANY — Crowded waiting rooms, long wait times, irritable patients, and aggression toward nursing staff and doctors are increasingly the reality in German emergency rooms. Clearly, emergencies belong in the emergency room. However, “In about half of all patients in the emergency room, there is no urgent medical emergency,” Norbert Schütz, MD, director of geriatrics and rheumatology at Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Hospital in Wiesbaden, Germany, said at a press conference for the 130th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM).
“In our daily medical practice, we repeatedly experience people either accessing our emergency departments and ambulances too quickly or lingering at home for too long when they have severe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz, who organized the Patient Day during the Internist Congress.
DGIM Educates Patients
What is an emergency? “I think the public is quite well informed about conditions associated with loss of consciousness, severe pain, chest pain, or paralysis: Think stroke or heart attack. This is undoubtedly a success of recent years. The difficulty arises with everything in between. For instance, should I go to the hospital with severe headaches?” asked Dr. Schütz.
When is a patient a case for the emergency room, the physician on-call service, or the general practitioner? At the Patient Day in Wiesbaden, DGIM aims to educate and train interested parties with a dedicated lecture. The focus is on recognizing an emergency, specifically emergencies in children and mental illnesses.
“Our Patient Day aims to contribute to making the right decisions. We want to inform, answer questions, and alleviate fears,” said Dr. Schütz. Interested parties can refresh their emergency knowledge, tour ambulances, and have the equipment explained. The public also has the opportunity to learn about resuscitation techniques theoretically and practically.
“Should, for whatever reason, the general practitioner not be reachable, the physician on-call service can be reached,” said Dr. Schütz. It may happen, however, that neither the general practitioner nor the on-call physician is immediately available.
What Are Emergencies?
In cases of severe health impairment, urgency is required, and a severe emergency should be assumed in the following cases:
- Chest pain
- Circulatory disorder
- Disorders of consciousness
- Breathing difficulties
- Sudden weakness or numbness/paralysis
- Severe bleeding
- Allergic shock
“In such cases, the emergency departments of the hospitals are available around the clock, and if necessary, an emergency doctor should be present during transportation to the hospital,” said Dr. Schütz.
Classifying emergencies is challenging, especially with children. “Children often find it difficult to clearly categorize or describe symptoms,” said Dr. Schütz. A situation is critical if, for example, the child’s breathing or consciousness is impaired.
Mental emergencies pose a particular challenge for patients and relatives because the patient and relatives are often overwhelmed by the situation. If there are suicidal thoughts, the patient should present him- or herself immediately to an emergency room.
“Patients who come to the emergency room because they cannot get appointments with their general practitioner or specialist, for whatever reason, are no emergency. We also see this in the emergency room from time to time,” said Dr. Schütz. Emergency rooms are not intended for this purpose. “And generally, these are not emergencies.”
Four of 10 Cases
The number of patients in emergency rooms has steadily increased in recent years. Statistically, only 4 out of 10 cases are genuine emergencies, as detailed surveys of patients in the emergency rooms of northern German hospitals have shown.
In the PiNo Nord cross-sectional study, Martin Scherer, MD, of University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf in Hamburg, Germany, and his team examined the reasons why patients visit the emergency room. They interviewed 1175 patients in five hospitals and documented the medical diagnoses. Patients classified as “immediately” or “very urgently” in need of treatment were excluded.
The surveyed patients were on average 41.8 years old, 52.9% were men, and 54.7% of the patients indicated a low urgency of treatment. About 41% of the patients visited the emergency room on their own initiative, 17% stated they were referred or entrusted by their general practitioner, and 8% were referred by a specialist in the emergency room.
The strongest predictors for low subjective treatment urgency were musculoskeletal trauma (odds ratio [OR], 2.18), skin afflictions (OR, 2.15), and the unavailability of an open general practitioner’s office (OR, 1.70).
According to Dr. Scherer and his colleagues, the reasons for visiting an emergency room are diverse and can be based on the perceived structural conditions and individual patient preferences in addition to the urgency of the health problem.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Which Drug for Which Patient?
With all the excitement about GLP-1 agonists,
Of course, we want to make sure that we’re treating the right condition. If the patient has type 2 diabetes, we tend to give them medication that is indicated for type 2 diabetes. Many GLP-1 agonists are available in a diabetes version and a chronic weight management or obesity version. If a patient has diabetes and obesity, they can receive either one. If a patient has only diabetes but not obesity, they should be prescribed the diabetes version. For obesity without diabetes, we tend to stick with the drugs that are indicated for chronic weight management.
Let’s go through them.
Exenatide. In chronological order of approval, the first GLP-1 drug that was used for diabetes dates back to exenatide (Bydureon). Bydureon had a partner called Byetta (also exenatide), both of which are still on the market but infrequently used. Some patients reported that these medications were inconvenient because they required twice-daily injections and caused painful injection-site nodules.
Diabetes drugs in more common use include liraglutide (Victoza) for type 2 diabetes. It is a daily injection and has various doses. We always start low and increase with tolerance and desired effect for A1c.
Liraglutide. Victoza has an antiobesity counterpart called Saxenda. The Saxenda pen looks very similar to the Victoza pen. It is a daily GLP-1 agonist for chronic weight management. The SCALE trial demonstrated 8%-12% weight loss with Saxenda.
Those are the daily injections: Victoza for diabetes and Saxenda for weight loss.
Our patients are very excited about the advent of weekly injections for diabetes and weight management. Ozempic is very popular. It is a weekly GLP-1 agonist for type 2 diabetes. Many patients come in asking for Ozempic, and we must make sure that we’re moving them in the right direction depending on their condition.
Semaglutide. Ozempic has a few different doses. It is a weekly injection and has been found to be quite efficacious for treating diabetes. The drug’s weight loss counterpart is called Wegovy, which comes in a different pen. Both forms contain the compound semaglutide. While all of these GLP-1 agonists are indicated to treat type 2 diabetes or for weight management, Wegovy has a special indication that none of the others have. In March 2024, Wegovy acquired an indication to decrease cardiac risk in those with a BMI ≥ 27 and a previous cardiac history. This will really change the accessibility of this medication because patients with heart conditions who are on Medicare are expected to have access to Wegovy.
Tirzepatide. Another weekly injection for treatment of type 2 diabetes is called Mounjaro. Its counterpart for weight management is called Zepbound, which was found to have about 20.9% weight loss over 72 weeks. These medications have similar side effects in differing degrees, but the most-often reported are nausea, stool changes, abdominal pain, and reflux. There are some other potential side effects; I recommend that you read the individual prescribing information available for each drug to have more clarity about that.
It is important that we stay on label for using the GLP-1 receptor agonists, for many reasons. One, it increases our patients’ accessibility to the right medication for them, and we can also make sure that we’re treating the patient with the right drug according to the clinical trials. When the clinical trials are done, the study populations demonstrate safety and efficacy for that population. But if we’re prescribing a GLP-1 for a different population, it is considered off-label use.
Dr. Lofton, an obesity medicine specialist, is clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of the medical weight management program at NYU Langone Weight Management Center, New York. She disclosed ties to Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With all the excitement about GLP-1 agonists,
Of course, we want to make sure that we’re treating the right condition. If the patient has type 2 diabetes, we tend to give them medication that is indicated for type 2 diabetes. Many GLP-1 agonists are available in a diabetes version and a chronic weight management or obesity version. If a patient has diabetes and obesity, they can receive either one. If a patient has only diabetes but not obesity, they should be prescribed the diabetes version. For obesity without diabetes, we tend to stick with the drugs that are indicated for chronic weight management.
Let’s go through them.
Exenatide. In chronological order of approval, the first GLP-1 drug that was used for diabetes dates back to exenatide (Bydureon). Bydureon had a partner called Byetta (also exenatide), both of which are still on the market but infrequently used. Some patients reported that these medications were inconvenient because they required twice-daily injections and caused painful injection-site nodules.
Diabetes drugs in more common use include liraglutide (Victoza) for type 2 diabetes. It is a daily injection and has various doses. We always start low and increase with tolerance and desired effect for A1c.
Liraglutide. Victoza has an antiobesity counterpart called Saxenda. The Saxenda pen looks very similar to the Victoza pen. It is a daily GLP-1 agonist for chronic weight management. The SCALE trial demonstrated 8%-12% weight loss with Saxenda.
Those are the daily injections: Victoza for diabetes and Saxenda for weight loss.
Our patients are very excited about the advent of weekly injections for diabetes and weight management. Ozempic is very popular. It is a weekly GLP-1 agonist for type 2 diabetes. Many patients come in asking for Ozempic, and we must make sure that we’re moving them in the right direction depending on their condition.
Semaglutide. Ozempic has a few different doses. It is a weekly injection and has been found to be quite efficacious for treating diabetes. The drug’s weight loss counterpart is called Wegovy, which comes in a different pen. Both forms contain the compound semaglutide. While all of these GLP-1 agonists are indicated to treat type 2 diabetes or for weight management, Wegovy has a special indication that none of the others have. In March 2024, Wegovy acquired an indication to decrease cardiac risk in those with a BMI ≥ 27 and a previous cardiac history. This will really change the accessibility of this medication because patients with heart conditions who are on Medicare are expected to have access to Wegovy.
Tirzepatide. Another weekly injection for treatment of type 2 diabetes is called Mounjaro. Its counterpart for weight management is called Zepbound, which was found to have about 20.9% weight loss over 72 weeks. These medications have similar side effects in differing degrees, but the most-often reported are nausea, stool changes, abdominal pain, and reflux. There are some other potential side effects; I recommend that you read the individual prescribing information available for each drug to have more clarity about that.
It is important that we stay on label for using the GLP-1 receptor agonists, for many reasons. One, it increases our patients’ accessibility to the right medication for them, and we can also make sure that we’re treating the patient with the right drug according to the clinical trials. When the clinical trials are done, the study populations demonstrate safety and efficacy for that population. But if we’re prescribing a GLP-1 for a different population, it is considered off-label use.
Dr. Lofton, an obesity medicine specialist, is clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of the medical weight management program at NYU Langone Weight Management Center, New York. She disclosed ties to Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With all the excitement about GLP-1 agonists,
Of course, we want to make sure that we’re treating the right condition. If the patient has type 2 diabetes, we tend to give them medication that is indicated for type 2 diabetes. Many GLP-1 agonists are available in a diabetes version and a chronic weight management or obesity version. If a patient has diabetes and obesity, they can receive either one. If a patient has only diabetes but not obesity, they should be prescribed the diabetes version. For obesity without diabetes, we tend to stick with the drugs that are indicated for chronic weight management.
Let’s go through them.
Exenatide. In chronological order of approval, the first GLP-1 drug that was used for diabetes dates back to exenatide (Bydureon). Bydureon had a partner called Byetta (also exenatide), both of which are still on the market but infrequently used. Some patients reported that these medications were inconvenient because they required twice-daily injections and caused painful injection-site nodules.
Diabetes drugs in more common use include liraglutide (Victoza) for type 2 diabetes. It is a daily injection and has various doses. We always start low and increase with tolerance and desired effect for A1c.
Liraglutide. Victoza has an antiobesity counterpart called Saxenda. The Saxenda pen looks very similar to the Victoza pen. It is a daily GLP-1 agonist for chronic weight management. The SCALE trial demonstrated 8%-12% weight loss with Saxenda.
Those are the daily injections: Victoza for diabetes and Saxenda for weight loss.
Our patients are very excited about the advent of weekly injections for diabetes and weight management. Ozempic is very popular. It is a weekly GLP-1 agonist for type 2 diabetes. Many patients come in asking for Ozempic, and we must make sure that we’re moving them in the right direction depending on their condition.
Semaglutide. Ozempic has a few different doses. It is a weekly injection and has been found to be quite efficacious for treating diabetes. The drug’s weight loss counterpart is called Wegovy, which comes in a different pen. Both forms contain the compound semaglutide. While all of these GLP-1 agonists are indicated to treat type 2 diabetes or for weight management, Wegovy has a special indication that none of the others have. In March 2024, Wegovy acquired an indication to decrease cardiac risk in those with a BMI ≥ 27 and a previous cardiac history. This will really change the accessibility of this medication because patients with heart conditions who are on Medicare are expected to have access to Wegovy.
Tirzepatide. Another weekly injection for treatment of type 2 diabetes is called Mounjaro. Its counterpart for weight management is called Zepbound, which was found to have about 20.9% weight loss over 72 weeks. These medications have similar side effects in differing degrees, but the most-often reported are nausea, stool changes, abdominal pain, and reflux. There are some other potential side effects; I recommend that you read the individual prescribing information available for each drug to have more clarity about that.
It is important that we stay on label for using the GLP-1 receptor agonists, for many reasons. One, it increases our patients’ accessibility to the right medication for them, and we can also make sure that we’re treating the patient with the right drug according to the clinical trials. When the clinical trials are done, the study populations demonstrate safety and efficacy for that population. But if we’re prescribing a GLP-1 for a different population, it is considered off-label use.
Dr. Lofton, an obesity medicine specialist, is clinical associate professor of surgery and medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of the medical weight management program at NYU Langone Weight Management Center, New York. She disclosed ties to Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Obesogenic Environment of Preschool and Day Care
Thirty years ago I had an experience in the office that influenced my approach to obesity for the rest of my career. The patient was a 4-year-old whom I had been seeing since her birth. At her annual well-child visit her weight had jumped up significantly from the previous year’s visit. She appeared well, but the change in her growth trajectory prompted a bit more in-depth history taking.
It turned out that finances had forced the family to employ one of the child’s grandmothers as the day care provider. Unfortunately, this grandmother’s passion was cooking and she was particularly adept at baking. She had no other hobbies and a sore hip limited her mobility, so she seldom went outside. When I eventually met her she was a cheerful, overweight, and delightful woman.
Deconstructing this obesogenic environment without disrupting this otherwise healthy family was an exercise that required tact, patience, and creativity. Fortunately, the young girl’s mother had already harbored some concerns about her child’s weight and was more than willing to participate in this environmental re-engineering project. It’s a long story, but she and I achieved our goals and the child eventually coasted back toward her previous growth curve.
I have always suspected that this scenario is being replayed hundreds of thousands of time across this country. But, sadly most don’t share this one’s happy ending. Parents don’t alway perceive the seriousness of the problem. The economic hurdles are often too steep to overcome, even when the most creative minds are involved.
How prevalent are obesogenic day care environments? We certainly know childhood obesity is a problem and the statistics in the preschool age group are particularly concerning. More than 14 million children are in non-parental early care and education programs; these environments would seem to be a logical place to target our prevention strategies. Understandably, there seems to be a hesitancy to point fingers, but how many day care providers are similar to the well-intentioned grandmother in the scenario I described? We must at least suspect that the example set by the adults in the preschool and day care environment might be having some influence on the children under their care.
There has been some research that sheds some light on this question. A paper from the University of Oklahoma has looked at the predictors of overweight and obesity in early care and education (ECE) teachers in hopes of “finding modifiable opportunities to enhance the health of this critical workforce.” In their paper, the investigators refer to other research that has found the prevalence of overweight and obesity among ECE teachers is higher than our national average and their waist circumference is significantly greater than the standard recommendation for women.
A study from Norway has looked at the association between preschool staff’s activity level and that of the children under their care using accelerometers. This particular investigation couldn’t determine whether it was the staff’s activity level that influenced the children or vice versa because it wasn’t an observational study. Common sense would lead one to believe it was the staff’s relative inactivity that was being reflected in the children’s.
It is interesting that in this Norwegian study when the teachers were asked about their attitudes toward activity and their self-perception of their own activity, there was no relationship between the staff’s and the children’s level of activity. In other words, the educators and caregivers bought into the importance of activity but had difficulty translating this philosophy into own behavior.
So where does this leave us? It turns out my experience decades ago was not a one-off event, but instead represents the tip of very large iceberg. Should we immediately create a system of day care provider boot camps? Let’s remember that each educator and caregiver is one of us. They may be slight outliers but not a group of individuals deserving of forced marches and half-rations to get them in shape.
ECEs have listened to the same message we have all heard about diet and activity and their importance for a child’s health. It’s for their own health and that of their charges. This could be as simple as providing accelerometers or step-counting smartwatches. Or, by having physical educators perform on-site audits that could then be used to create site-specific plans for increasing both teacher and student activity.
Modifying the educators’ diet is a more complex procedure and can quickly become entangled in the socio-economic background of each individual teacher. A healthy diet is not always equally available to everyone. The solution may involve providing the teachers with food to be eaten at work and to be prepared at home. But, creative answers can be found if we look for them.
Before we get too far down the obesity-is-a-disease pathway, we must take a closer look at the role the early care and early school milieu are playing in the obesity problem. A little common sense behavior modification when children are in the controlled environment of school/day care may allow us to be less reliant on the those new wonder drugs in the long run.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Thirty years ago I had an experience in the office that influenced my approach to obesity for the rest of my career. The patient was a 4-year-old whom I had been seeing since her birth. At her annual well-child visit her weight had jumped up significantly from the previous year’s visit. She appeared well, but the change in her growth trajectory prompted a bit more in-depth history taking.
It turned out that finances had forced the family to employ one of the child’s grandmothers as the day care provider. Unfortunately, this grandmother’s passion was cooking and she was particularly adept at baking. She had no other hobbies and a sore hip limited her mobility, so she seldom went outside. When I eventually met her she was a cheerful, overweight, and delightful woman.
Deconstructing this obesogenic environment without disrupting this otherwise healthy family was an exercise that required tact, patience, and creativity. Fortunately, the young girl’s mother had already harbored some concerns about her child’s weight and was more than willing to participate in this environmental re-engineering project. It’s a long story, but she and I achieved our goals and the child eventually coasted back toward her previous growth curve.
I have always suspected that this scenario is being replayed hundreds of thousands of time across this country. But, sadly most don’t share this one’s happy ending. Parents don’t alway perceive the seriousness of the problem. The economic hurdles are often too steep to overcome, even when the most creative minds are involved.
How prevalent are obesogenic day care environments? We certainly know childhood obesity is a problem and the statistics in the preschool age group are particularly concerning. More than 14 million children are in non-parental early care and education programs; these environments would seem to be a logical place to target our prevention strategies. Understandably, there seems to be a hesitancy to point fingers, but how many day care providers are similar to the well-intentioned grandmother in the scenario I described? We must at least suspect that the example set by the adults in the preschool and day care environment might be having some influence on the children under their care.
There has been some research that sheds some light on this question. A paper from the University of Oklahoma has looked at the predictors of overweight and obesity in early care and education (ECE) teachers in hopes of “finding modifiable opportunities to enhance the health of this critical workforce.” In their paper, the investigators refer to other research that has found the prevalence of overweight and obesity among ECE teachers is higher than our national average and their waist circumference is significantly greater than the standard recommendation for women.
A study from Norway has looked at the association between preschool staff’s activity level and that of the children under their care using accelerometers. This particular investigation couldn’t determine whether it was the staff’s activity level that influenced the children or vice versa because it wasn’t an observational study. Common sense would lead one to believe it was the staff’s relative inactivity that was being reflected in the children’s.
It is interesting that in this Norwegian study when the teachers were asked about their attitudes toward activity and their self-perception of their own activity, there was no relationship between the staff’s and the children’s level of activity. In other words, the educators and caregivers bought into the importance of activity but had difficulty translating this philosophy into own behavior.
So where does this leave us? It turns out my experience decades ago was not a one-off event, but instead represents the tip of very large iceberg. Should we immediately create a system of day care provider boot camps? Let’s remember that each educator and caregiver is one of us. They may be slight outliers but not a group of individuals deserving of forced marches and half-rations to get them in shape.
ECEs have listened to the same message we have all heard about diet and activity and their importance for a child’s health. It’s for their own health and that of their charges. This could be as simple as providing accelerometers or step-counting smartwatches. Or, by having physical educators perform on-site audits that could then be used to create site-specific plans for increasing both teacher and student activity.
Modifying the educators’ diet is a more complex procedure and can quickly become entangled in the socio-economic background of each individual teacher. A healthy diet is not always equally available to everyone. The solution may involve providing the teachers with food to be eaten at work and to be prepared at home. But, creative answers can be found if we look for them.
Before we get too far down the obesity-is-a-disease pathway, we must take a closer look at the role the early care and early school milieu are playing in the obesity problem. A little common sense behavior modification when children are in the controlled environment of school/day care may allow us to be less reliant on the those new wonder drugs in the long run.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Thirty years ago I had an experience in the office that influenced my approach to obesity for the rest of my career. The patient was a 4-year-old whom I had been seeing since her birth. At her annual well-child visit her weight had jumped up significantly from the previous year’s visit. She appeared well, but the change in her growth trajectory prompted a bit more in-depth history taking.
It turned out that finances had forced the family to employ one of the child’s grandmothers as the day care provider. Unfortunately, this grandmother’s passion was cooking and she was particularly adept at baking. She had no other hobbies and a sore hip limited her mobility, so she seldom went outside. When I eventually met her she was a cheerful, overweight, and delightful woman.
Deconstructing this obesogenic environment without disrupting this otherwise healthy family was an exercise that required tact, patience, and creativity. Fortunately, the young girl’s mother had already harbored some concerns about her child’s weight and was more than willing to participate in this environmental re-engineering project. It’s a long story, but she and I achieved our goals and the child eventually coasted back toward her previous growth curve.
I have always suspected that this scenario is being replayed hundreds of thousands of time across this country. But, sadly most don’t share this one’s happy ending. Parents don’t alway perceive the seriousness of the problem. The economic hurdles are often too steep to overcome, even when the most creative minds are involved.
How prevalent are obesogenic day care environments? We certainly know childhood obesity is a problem and the statistics in the preschool age group are particularly concerning. More than 14 million children are in non-parental early care and education programs; these environments would seem to be a logical place to target our prevention strategies. Understandably, there seems to be a hesitancy to point fingers, but how many day care providers are similar to the well-intentioned grandmother in the scenario I described? We must at least suspect that the example set by the adults in the preschool and day care environment might be having some influence on the children under their care.
There has been some research that sheds some light on this question. A paper from the University of Oklahoma has looked at the predictors of overweight and obesity in early care and education (ECE) teachers in hopes of “finding modifiable opportunities to enhance the health of this critical workforce.” In their paper, the investigators refer to other research that has found the prevalence of overweight and obesity among ECE teachers is higher than our national average and their waist circumference is significantly greater than the standard recommendation for women.
A study from Norway has looked at the association between preschool staff’s activity level and that of the children under their care using accelerometers. This particular investigation couldn’t determine whether it was the staff’s activity level that influenced the children or vice versa because it wasn’t an observational study. Common sense would lead one to believe it was the staff’s relative inactivity that was being reflected in the children’s.
It is interesting that in this Norwegian study when the teachers were asked about their attitudes toward activity and their self-perception of their own activity, there was no relationship between the staff’s and the children’s level of activity. In other words, the educators and caregivers bought into the importance of activity but had difficulty translating this philosophy into own behavior.
So where does this leave us? It turns out my experience decades ago was not a one-off event, but instead represents the tip of very large iceberg. Should we immediately create a system of day care provider boot camps? Let’s remember that each educator and caregiver is one of us. They may be slight outliers but not a group of individuals deserving of forced marches and half-rations to get them in shape.
ECEs have listened to the same message we have all heard about diet and activity and their importance for a child’s health. It’s for their own health and that of their charges. This could be as simple as providing accelerometers or step-counting smartwatches. Or, by having physical educators perform on-site audits that could then be used to create site-specific plans for increasing both teacher and student activity.
Modifying the educators’ diet is a more complex procedure and can quickly become entangled in the socio-economic background of each individual teacher. A healthy diet is not always equally available to everyone. The solution may involve providing the teachers with food to be eaten at work and to be prepared at home. But, creative answers can be found if we look for them.
Before we get too far down the obesity-is-a-disease pathway, we must take a closer look at the role the early care and early school milieu are playing in the obesity problem. A little common sense behavior modification when children are in the controlled environment of school/day care may allow us to be less reliant on the those new wonder drugs in the long run.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Semaglutide Trial for Knee Osteoarthritis Shows Improvements in Pain, Physical Function
VIENNA — The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) not only induced weight loss but also improved knee pain in people with knee osteoarthritis (OA) and obesity, according to results from the STEP 9 study reported at the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) 2024 World Congress.
From baseline to week 68, the mean change in knee pain assessed using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score was a reduction of 41.7 points for semaglutide and a decrease of 27.5 points for a matching placebo. The estimated treatment difference of 14.1 points between the groups was statistically significant (P < .001).
As for weight loss, this also fell by a significantly greater amount in the people treated with semaglutide vs those given placebo, with respective reductions of 13.7% and 3.2% from baseline, with an estimated 10.5% greater weight loss with semaglutide.
“The interesting thing is whether there’s a specific action of GLP-1 receptor agonists on the joint, not through the weight loss but by itself,” principal study investigator Henning Bliddal, MD, DMSc, told this news organization ahead of reporting the results at OARSI 2024.
Weight loss is “obviously good” because “the knees suffer from the weight. But whether it’s good for the knee or just for the health or the well-being of the person is another matter,” said Dr. Bliddal, who is director of the Parker Institute at Bispebjerg Frederiksberg Hospital in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Not Approved in OA
Semaglutide and other potentially weight loss-inducing drugs are not currently indicated for use specifically in OA, Tonia Vincent, MBBS, PhD, told this news organization, and so “I think we have to be very cautious,” she said.
“Weight loss is one of the few things that has been shown to be successful in clinical trials,” said Dr. Vincent, who is a professor of musculoskeletal biology and an honorary rheumatologist at the Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology at Oxford University in Oxford, England.
“People always feel better too when they lose weight, so that helps manage pain. So, I’d be very surprised if there isn’t a benefit,” she added.
“I just think we need to know more about the long-term use of these drugs, whether the healthcare system can afford them, and how we would ration them.”
Previous Work
The STEP 9 study is not the first time that Dr. Bliddal has investigated the effects of a GLP-1 receptor agonist in people with knee OA, but it is the first to have shown a significant effect on knee pain.
Previously, results from the LOSEIT trial with liraglutide demonstrated that, after an 8-week dietary intervention run-in phase, people who were treated with the GLP-1 receptor agonist lost an average of 2.8 kg in body weight over a period of 1 year, vs a 1.2 kg gain in the placebo group. Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Scores, however, were largely unaffected.
“The study was more or less negative for knee pain because at that time we had to pretreat patients with some kind of weight loss before they were allowed to have the liraglutide,” Dr. Bliddal said.
“There’s so many different considerations with diets and the different ways that [dietary modification] is performed, that could be part of the explanation why some people didn’t find the pain relief,” Dr. Bliddal suggested.
STEP 9 Study Design
No pre-study dietary intervention was required in the STEP 9 trial, although a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical exercise were used alongside both semaglutide and placebo treatment.
STEP 9 was a multicenter, multinational phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled people if they had a body mass index (BMI) of > 30, had a clinical diagnosis of knee OA with moderate radiographic changes (Kellgren-Lawrence grade of 2-3), and were experiencing knee pain.
In addition to a baseline WOMAC pain score of at least 40 points (where 0 represents no and 100 the worst pain), the participants had to have a WOMAC numerical rating scale (NRS) score of ≥ 3.1.
A total of 407 participants were recruited and randomly allocated, 2:1, to receive once-weekly subcutaneous injections of either semaglutide 2.4 mg or placebo for a total of 68 weeks.
Dr. Bliddal presented demographic information only for the study population as a whole, showing that the mean was 56 years, 81.6% were women, 60.9% were White, 11.8% Native American, 7.6% Black, and 19.7% of other ethnic origin.
Moreover, the mean bodyweight at baseline was 108.6 kg, and the mean baseline BMI was 40.3, with 75% of participants having a BMI ≥ 35. The mean waist circumference was 118.7 cm. The mean baseline WOMAC pain score was 70.9.
Other Findings
In addition to the reductions seen in the coprimary endpoints of weight loss and knee pain, the WOMAC physical function score was also reduced from baseline to week 68 to a greater degree in the semaglutide than placebo arm, by a respective 41.5 vs 26.7 points, with a significant estimated treatment difference of -14.9 points.
“The use of pain medication went down as well; you can see the drop was faster in the semaglutide group than the placebo group, and it was maintained throughout the study,” Dr. Bliddal said during his presentation. He noted that patients had to temporarily stop taking pain relievers such as acetaminophen 3 days before their pain was assessed.
Additional findings reported in the abstract, but not presented at the meeting, were a significant estimated treatment difference of -1.0 in NRS pain intensity, more people treated with semaglutide than placebo achieving ≥ 5% (87.0% vs 29.2%) or ≥ 10% (70.4% vs 9.2%) weight loss.
“Safety and tolerability with semaglutide were consistent with the global STEP program and the GLP-1 receptor agonist class in general,” Dr. Bliddal reported.
Serious adverse events occurred in a respective 10.0% and 8.1% of participants, and adverse events leading to discontinuation were recorded in 6.7% and 3%. Around one third (2.2%) of those leading to discontinuation in the semaglutide arm were gastrointestinal adverse events.
The STEP 9 study was funded by Novo Nordisk. Henning is a principal investigator for the trial and acknowledged that research grants were received from Novo Nordisk to his institution, as well as consulting fees and honoraria. He has also received congress and travel support from Contura. Dr. Vincent was not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) not only induced weight loss but also improved knee pain in people with knee osteoarthritis (OA) and obesity, according to results from the STEP 9 study reported at the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) 2024 World Congress.
From baseline to week 68, the mean change in knee pain assessed using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score was a reduction of 41.7 points for semaglutide and a decrease of 27.5 points for a matching placebo. The estimated treatment difference of 14.1 points between the groups was statistically significant (P < .001).
As for weight loss, this also fell by a significantly greater amount in the people treated with semaglutide vs those given placebo, with respective reductions of 13.7% and 3.2% from baseline, with an estimated 10.5% greater weight loss with semaglutide.
“The interesting thing is whether there’s a specific action of GLP-1 receptor agonists on the joint, not through the weight loss but by itself,” principal study investigator Henning Bliddal, MD, DMSc, told this news organization ahead of reporting the results at OARSI 2024.
Weight loss is “obviously good” because “the knees suffer from the weight. But whether it’s good for the knee or just for the health or the well-being of the person is another matter,” said Dr. Bliddal, who is director of the Parker Institute at Bispebjerg Frederiksberg Hospital in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Not Approved in OA
Semaglutide and other potentially weight loss-inducing drugs are not currently indicated for use specifically in OA, Tonia Vincent, MBBS, PhD, told this news organization, and so “I think we have to be very cautious,” she said.
“Weight loss is one of the few things that has been shown to be successful in clinical trials,” said Dr. Vincent, who is a professor of musculoskeletal biology and an honorary rheumatologist at the Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology at Oxford University in Oxford, England.
“People always feel better too when they lose weight, so that helps manage pain. So, I’d be very surprised if there isn’t a benefit,” she added.
“I just think we need to know more about the long-term use of these drugs, whether the healthcare system can afford them, and how we would ration them.”
Previous Work
The STEP 9 study is not the first time that Dr. Bliddal has investigated the effects of a GLP-1 receptor agonist in people with knee OA, but it is the first to have shown a significant effect on knee pain.
Previously, results from the LOSEIT trial with liraglutide demonstrated that, after an 8-week dietary intervention run-in phase, people who were treated with the GLP-1 receptor agonist lost an average of 2.8 kg in body weight over a period of 1 year, vs a 1.2 kg gain in the placebo group. Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Scores, however, were largely unaffected.
“The study was more or less negative for knee pain because at that time we had to pretreat patients with some kind of weight loss before they were allowed to have the liraglutide,” Dr. Bliddal said.
“There’s so many different considerations with diets and the different ways that [dietary modification] is performed, that could be part of the explanation why some people didn’t find the pain relief,” Dr. Bliddal suggested.
STEP 9 Study Design
No pre-study dietary intervention was required in the STEP 9 trial, although a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical exercise were used alongside both semaglutide and placebo treatment.
STEP 9 was a multicenter, multinational phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled people if they had a body mass index (BMI) of > 30, had a clinical diagnosis of knee OA with moderate radiographic changes (Kellgren-Lawrence grade of 2-3), and were experiencing knee pain.
In addition to a baseline WOMAC pain score of at least 40 points (where 0 represents no and 100 the worst pain), the participants had to have a WOMAC numerical rating scale (NRS) score of ≥ 3.1.
A total of 407 participants were recruited and randomly allocated, 2:1, to receive once-weekly subcutaneous injections of either semaglutide 2.4 mg or placebo for a total of 68 weeks.
Dr. Bliddal presented demographic information only for the study population as a whole, showing that the mean was 56 years, 81.6% were women, 60.9% were White, 11.8% Native American, 7.6% Black, and 19.7% of other ethnic origin.
Moreover, the mean bodyweight at baseline was 108.6 kg, and the mean baseline BMI was 40.3, with 75% of participants having a BMI ≥ 35. The mean waist circumference was 118.7 cm. The mean baseline WOMAC pain score was 70.9.
Other Findings
In addition to the reductions seen in the coprimary endpoints of weight loss and knee pain, the WOMAC physical function score was also reduced from baseline to week 68 to a greater degree in the semaglutide than placebo arm, by a respective 41.5 vs 26.7 points, with a significant estimated treatment difference of -14.9 points.
“The use of pain medication went down as well; you can see the drop was faster in the semaglutide group than the placebo group, and it was maintained throughout the study,” Dr. Bliddal said during his presentation. He noted that patients had to temporarily stop taking pain relievers such as acetaminophen 3 days before their pain was assessed.
Additional findings reported in the abstract, but not presented at the meeting, were a significant estimated treatment difference of -1.0 in NRS pain intensity, more people treated with semaglutide than placebo achieving ≥ 5% (87.0% vs 29.2%) or ≥ 10% (70.4% vs 9.2%) weight loss.
“Safety and tolerability with semaglutide were consistent with the global STEP program and the GLP-1 receptor agonist class in general,” Dr. Bliddal reported.
Serious adverse events occurred in a respective 10.0% and 8.1% of participants, and adverse events leading to discontinuation were recorded in 6.7% and 3%. Around one third (2.2%) of those leading to discontinuation in the semaglutide arm were gastrointestinal adverse events.
The STEP 9 study was funded by Novo Nordisk. Henning is a principal investigator for the trial and acknowledged that research grants were received from Novo Nordisk to his institution, as well as consulting fees and honoraria. He has also received congress and travel support from Contura. Dr. Vincent was not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) not only induced weight loss but also improved knee pain in people with knee osteoarthritis (OA) and obesity, according to results from the STEP 9 study reported at the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) 2024 World Congress.
From baseline to week 68, the mean change in knee pain assessed using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score was a reduction of 41.7 points for semaglutide and a decrease of 27.5 points for a matching placebo. The estimated treatment difference of 14.1 points between the groups was statistically significant (P < .001).
As for weight loss, this also fell by a significantly greater amount in the people treated with semaglutide vs those given placebo, with respective reductions of 13.7% and 3.2% from baseline, with an estimated 10.5% greater weight loss with semaglutide.
“The interesting thing is whether there’s a specific action of GLP-1 receptor agonists on the joint, not through the weight loss but by itself,” principal study investigator Henning Bliddal, MD, DMSc, told this news organization ahead of reporting the results at OARSI 2024.
Weight loss is “obviously good” because “the knees suffer from the weight. But whether it’s good for the knee or just for the health or the well-being of the person is another matter,” said Dr. Bliddal, who is director of the Parker Institute at Bispebjerg Frederiksberg Hospital in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Not Approved in OA
Semaglutide and other potentially weight loss-inducing drugs are not currently indicated for use specifically in OA, Tonia Vincent, MBBS, PhD, told this news organization, and so “I think we have to be very cautious,” she said.
“Weight loss is one of the few things that has been shown to be successful in clinical trials,” said Dr. Vincent, who is a professor of musculoskeletal biology and an honorary rheumatologist at the Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology at Oxford University in Oxford, England.
“People always feel better too when they lose weight, so that helps manage pain. So, I’d be very surprised if there isn’t a benefit,” she added.
“I just think we need to know more about the long-term use of these drugs, whether the healthcare system can afford them, and how we would ration them.”
Previous Work
The STEP 9 study is not the first time that Dr. Bliddal has investigated the effects of a GLP-1 receptor agonist in people with knee OA, but it is the first to have shown a significant effect on knee pain.
Previously, results from the LOSEIT trial with liraglutide demonstrated that, after an 8-week dietary intervention run-in phase, people who were treated with the GLP-1 receptor agonist lost an average of 2.8 kg in body weight over a period of 1 year, vs a 1.2 kg gain in the placebo group. Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Scores, however, were largely unaffected.
“The study was more or less negative for knee pain because at that time we had to pretreat patients with some kind of weight loss before they were allowed to have the liraglutide,” Dr. Bliddal said.
“There’s so many different considerations with diets and the different ways that [dietary modification] is performed, that could be part of the explanation why some people didn’t find the pain relief,” Dr. Bliddal suggested.
STEP 9 Study Design
No pre-study dietary intervention was required in the STEP 9 trial, although a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical exercise were used alongside both semaglutide and placebo treatment.
STEP 9 was a multicenter, multinational phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled people if they had a body mass index (BMI) of > 30, had a clinical diagnosis of knee OA with moderate radiographic changes (Kellgren-Lawrence grade of 2-3), and were experiencing knee pain.
In addition to a baseline WOMAC pain score of at least 40 points (where 0 represents no and 100 the worst pain), the participants had to have a WOMAC numerical rating scale (NRS) score of ≥ 3.1.
A total of 407 participants were recruited and randomly allocated, 2:1, to receive once-weekly subcutaneous injections of either semaglutide 2.4 mg or placebo for a total of 68 weeks.
Dr. Bliddal presented demographic information only for the study population as a whole, showing that the mean was 56 years, 81.6% were women, 60.9% were White, 11.8% Native American, 7.6% Black, and 19.7% of other ethnic origin.
Moreover, the mean bodyweight at baseline was 108.6 kg, and the mean baseline BMI was 40.3, with 75% of participants having a BMI ≥ 35. The mean waist circumference was 118.7 cm. The mean baseline WOMAC pain score was 70.9.
Other Findings
In addition to the reductions seen in the coprimary endpoints of weight loss and knee pain, the WOMAC physical function score was also reduced from baseline to week 68 to a greater degree in the semaglutide than placebo arm, by a respective 41.5 vs 26.7 points, with a significant estimated treatment difference of -14.9 points.
“The use of pain medication went down as well; you can see the drop was faster in the semaglutide group than the placebo group, and it was maintained throughout the study,” Dr. Bliddal said during his presentation. He noted that patients had to temporarily stop taking pain relievers such as acetaminophen 3 days before their pain was assessed.
Additional findings reported in the abstract, but not presented at the meeting, were a significant estimated treatment difference of -1.0 in NRS pain intensity, more people treated with semaglutide than placebo achieving ≥ 5% (87.0% vs 29.2%) or ≥ 10% (70.4% vs 9.2%) weight loss.
“Safety and tolerability with semaglutide were consistent with the global STEP program and the GLP-1 receptor agonist class in general,” Dr. Bliddal reported.
Serious adverse events occurred in a respective 10.0% and 8.1% of participants, and adverse events leading to discontinuation were recorded in 6.7% and 3%. Around one third (2.2%) of those leading to discontinuation in the semaglutide arm were gastrointestinal adverse events.
The STEP 9 study was funded by Novo Nordisk. Henning is a principal investigator for the trial and acknowledged that research grants were received from Novo Nordisk to his institution, as well as consulting fees and honoraria. He has also received congress and travel support from Contura. Dr. Vincent was not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OARSI 2024
Are Carbs Really the Enemy?
Recent headlines scream that we have an obesity problem and that carbs are the culprit for the problem. That leads me to ask: How did we get to blaming carbs as the enemy in the war against obesity?
First, a quick review of the history of diet and macronutrient content.
A long time ago, prehistoric humans foraged and hunted for food. Protein and fat were procured from animal meat, which was very important for encephalization, or evolutionary increase in the complexity or relative size of the brain. Most of the requirements for protein and iron were satisfied by hunting and eating land animals as well as consuming marine life that washed up on shore.
Carbohydrates in the form of plant foods served as the only sources of energy available to prehistoric hunter-gatherers, which offset the high protein content of the rest of their diet. These were only available during spring and summer.
Then, about 10,000 years ago, plant and animal agriculture began, and humans saw a permanent shift in the macronutrient content of our daily intake so that it was more consistent and stable. Initially, the nutrient characteristic changes were subtle, going from wild food to cultivated food with the Agricultural Revolution in the mid-17th century. Then, it changed even more rapidly less than 200 years ago with the Industrial Revolution, resulting in semiprocessed and ultraprocessed foods.
This change in food intake altered human physiology, with major changes in our digestive, immune, and neural physiology and an increase in chronic disease prevalence. The last 50 years has seen an increase in obesity in the United States, along with increases in chronic disease such as type 2 diabetes, which leads cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
Back to Carbohydrates: Do We Need Them? How Much? What Kind?
Unfortunately, ultraprocessed foods have become a staple of the standard American or Western diet.
Ultraprocessed foods such as cakes, cookies, crackers, sugary breakfast cereals, pizza, potato chips, soft drinks, and ice cream are eons away from our prehistoric diet of wild game, nuts, fruits, and berries, at which time, our digestive immune and nervous systems evolved. The pace at which ultraprocessed foods have entered our diet outpaces the time necessary for adaptation of our digestive systems and genes to these foods. They are indeed pathogenic in this context.
So when was the time when humans consumed an “optimal” diet? This is hard to say because during the time of brain evolution, we needed protein and iron and succumbed to infections and trauma. In the early 1900s, we continued to succumb to infection until the discovery of antibiotics. Soon thereafter, industrialization and processed foods led to weight gain and the chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system and type 2 diabetes.
Carbohydrates provide calories and fiber and some micronutrients, which are needed for energy, metabolism, and bowel and immune health. But how much do we need?
Currently in the United States, the percentage of total food energy derived from the three major macronutrients is: carbohydrates, 51.8%; fat, 32.8%; and protein, 15.4%. Current advice for a healthy diet to lower risk for cardiovascular disease is to limit fat intake to 30% of total energy, protein to 15%, and to increase complex carbohydrates to 55%-60% of total energy. But we also need to qualify this in terms of the quality of the macronutrient, particularly carbohydrates.
In addition to the quality, the macronutrient content of the diet has varied considerably from our prehistoric times when dietary protein intakes were high at 19%-35% of energy at the expense of carbohydrate (22%-40% of energy).
If our genes haven’t kept up with industrialization, then why do we need so many carbohydrates to equate to 55%-60% of energy? Is it possible that we are confusing what is available with what we actually need? What do I mean by this?
We certainly have changed the landscape of the world due to agriculture, which has allowed us to procreate and feed ourselves, and certainly, industrialization has increased the availability of accessible cheap food. Protein in the form of meat, fish, and fowl are harder to get in industrialized nations as are fruits and vegetables. These macronutrients were the foods of our ancestors. It may be that a healthy diet is considered the one that is available.
For instance, the Mediterranean diet is somewhat higher in fat content, 40%-50% fat (mostly mono and unsaturated), and similar in protein content but lower in carbohydrate content than the typical Western diet. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is lower in fat at 25% total calories, is higher in carbohydrates at 55%, and is lower in protein, but this diet was generated in the United States, therefore it is more Western.
We need high-quality protein for organ and muscle function, high-quality unsaturated and monounsaturated fats for brain function and cellular functions, and high-quality complex carbohydrates for energy and gut health as well as micronutrients for many cellular functions. A ketogenic diet is not sustainable in the long-term for these reasons: chiefly the need for some carbohydrates for gut health and micronutrients.
How much carbohydrate content is needed should take into consideration energy expenditure as well as micronutrients and fiber intake. Protein and fat can contribute to energy production but not as readily as carbohydrates that can quickly restore glycogen in the muscle and liver. What’s interesting is that our ancestors were able to hunt and run away from danger with the small amounts of carbohydrates from plants and berries plus the protein and fat intake from animals and fish — but the Olympics weren’t a thing then!
It may be another 200,000 years before our genes catch up to ultraprocessed foods and the simple carbohydrates and sugars contained in these products. Evidence suggests that ultraprocessed foods cause inflammation in organs like the liver, adipose tissue, the heart, and even the brain. In the brain, this inflammation may be what’s causing us to defend a higher body weight set point in this environment of easily obtained highly palatable ultraprocessed foods.
Let’s not wait until our genes catch up and our bodies tolerate junk food without disease progression. It could be like waiting for Godot!
Dr. Apovian is professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. She disclosed ties to Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, and L-Nutra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent headlines scream that we have an obesity problem and that carbs are the culprit for the problem. That leads me to ask: How did we get to blaming carbs as the enemy in the war against obesity?
First, a quick review of the history of diet and macronutrient content.
A long time ago, prehistoric humans foraged and hunted for food. Protein and fat were procured from animal meat, which was very important for encephalization, or evolutionary increase in the complexity or relative size of the brain. Most of the requirements for protein and iron were satisfied by hunting and eating land animals as well as consuming marine life that washed up on shore.
Carbohydrates in the form of plant foods served as the only sources of energy available to prehistoric hunter-gatherers, which offset the high protein content of the rest of their diet. These were only available during spring and summer.
Then, about 10,000 years ago, plant and animal agriculture began, and humans saw a permanent shift in the macronutrient content of our daily intake so that it was more consistent and stable. Initially, the nutrient characteristic changes were subtle, going from wild food to cultivated food with the Agricultural Revolution in the mid-17th century. Then, it changed even more rapidly less than 200 years ago with the Industrial Revolution, resulting in semiprocessed and ultraprocessed foods.
This change in food intake altered human physiology, with major changes in our digestive, immune, and neural physiology and an increase in chronic disease prevalence. The last 50 years has seen an increase in obesity in the United States, along with increases in chronic disease such as type 2 diabetes, which leads cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
Back to Carbohydrates: Do We Need Them? How Much? What Kind?
Unfortunately, ultraprocessed foods have become a staple of the standard American or Western diet.
Ultraprocessed foods such as cakes, cookies, crackers, sugary breakfast cereals, pizza, potato chips, soft drinks, and ice cream are eons away from our prehistoric diet of wild game, nuts, fruits, and berries, at which time, our digestive immune and nervous systems evolved. The pace at which ultraprocessed foods have entered our diet outpaces the time necessary for adaptation of our digestive systems and genes to these foods. They are indeed pathogenic in this context.
So when was the time when humans consumed an “optimal” diet? This is hard to say because during the time of brain evolution, we needed protein and iron and succumbed to infections and trauma. In the early 1900s, we continued to succumb to infection until the discovery of antibiotics. Soon thereafter, industrialization and processed foods led to weight gain and the chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system and type 2 diabetes.
Carbohydrates provide calories and fiber and some micronutrients, which are needed for energy, metabolism, and bowel and immune health. But how much do we need?
Currently in the United States, the percentage of total food energy derived from the three major macronutrients is: carbohydrates, 51.8%; fat, 32.8%; and protein, 15.4%. Current advice for a healthy diet to lower risk for cardiovascular disease is to limit fat intake to 30% of total energy, protein to 15%, and to increase complex carbohydrates to 55%-60% of total energy. But we also need to qualify this in terms of the quality of the macronutrient, particularly carbohydrates.
In addition to the quality, the macronutrient content of the diet has varied considerably from our prehistoric times when dietary protein intakes were high at 19%-35% of energy at the expense of carbohydrate (22%-40% of energy).
If our genes haven’t kept up with industrialization, then why do we need so many carbohydrates to equate to 55%-60% of energy? Is it possible that we are confusing what is available with what we actually need? What do I mean by this?
We certainly have changed the landscape of the world due to agriculture, which has allowed us to procreate and feed ourselves, and certainly, industrialization has increased the availability of accessible cheap food. Protein in the form of meat, fish, and fowl are harder to get in industrialized nations as are fruits and vegetables. These macronutrients were the foods of our ancestors. It may be that a healthy diet is considered the one that is available.
For instance, the Mediterranean diet is somewhat higher in fat content, 40%-50% fat (mostly mono and unsaturated), and similar in protein content but lower in carbohydrate content than the typical Western diet. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is lower in fat at 25% total calories, is higher in carbohydrates at 55%, and is lower in protein, but this diet was generated in the United States, therefore it is more Western.
We need high-quality protein for organ and muscle function, high-quality unsaturated and monounsaturated fats for brain function and cellular functions, and high-quality complex carbohydrates for energy and gut health as well as micronutrients for many cellular functions. A ketogenic diet is not sustainable in the long-term for these reasons: chiefly the need for some carbohydrates for gut health and micronutrients.
How much carbohydrate content is needed should take into consideration energy expenditure as well as micronutrients and fiber intake. Protein and fat can contribute to energy production but not as readily as carbohydrates that can quickly restore glycogen in the muscle and liver. What’s interesting is that our ancestors were able to hunt and run away from danger with the small amounts of carbohydrates from plants and berries plus the protein and fat intake from animals and fish — but the Olympics weren’t a thing then!
It may be another 200,000 years before our genes catch up to ultraprocessed foods and the simple carbohydrates and sugars contained in these products. Evidence suggests that ultraprocessed foods cause inflammation in organs like the liver, adipose tissue, the heart, and even the brain. In the brain, this inflammation may be what’s causing us to defend a higher body weight set point in this environment of easily obtained highly palatable ultraprocessed foods.
Let’s not wait until our genes catch up and our bodies tolerate junk food without disease progression. It could be like waiting for Godot!
Dr. Apovian is professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. She disclosed ties to Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, and L-Nutra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent headlines scream that we have an obesity problem and that carbs are the culprit for the problem. That leads me to ask: How did we get to blaming carbs as the enemy in the war against obesity?
First, a quick review of the history of diet and macronutrient content.
A long time ago, prehistoric humans foraged and hunted for food. Protein and fat were procured from animal meat, which was very important for encephalization, or evolutionary increase in the complexity or relative size of the brain. Most of the requirements for protein and iron were satisfied by hunting and eating land animals as well as consuming marine life that washed up on shore.
Carbohydrates in the form of plant foods served as the only sources of energy available to prehistoric hunter-gatherers, which offset the high protein content of the rest of their diet. These were only available during spring and summer.
Then, about 10,000 years ago, plant and animal agriculture began, and humans saw a permanent shift in the macronutrient content of our daily intake so that it was more consistent and stable. Initially, the nutrient characteristic changes were subtle, going from wild food to cultivated food with the Agricultural Revolution in the mid-17th century. Then, it changed even more rapidly less than 200 years ago with the Industrial Revolution, resulting in semiprocessed and ultraprocessed foods.
This change in food intake altered human physiology, with major changes in our digestive, immune, and neural physiology and an increase in chronic disease prevalence. The last 50 years has seen an increase in obesity in the United States, along with increases in chronic disease such as type 2 diabetes, which leads cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
Back to Carbohydrates: Do We Need Them? How Much? What Kind?
Unfortunately, ultraprocessed foods have become a staple of the standard American or Western diet.
Ultraprocessed foods such as cakes, cookies, crackers, sugary breakfast cereals, pizza, potato chips, soft drinks, and ice cream are eons away from our prehistoric diet of wild game, nuts, fruits, and berries, at which time, our digestive immune and nervous systems evolved. The pace at which ultraprocessed foods have entered our diet outpaces the time necessary for adaptation of our digestive systems and genes to these foods. They are indeed pathogenic in this context.
So when was the time when humans consumed an “optimal” diet? This is hard to say because during the time of brain evolution, we needed protein and iron and succumbed to infections and trauma. In the early 1900s, we continued to succumb to infection until the discovery of antibiotics. Soon thereafter, industrialization and processed foods led to weight gain and the chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system and type 2 diabetes.
Carbohydrates provide calories and fiber and some micronutrients, which are needed for energy, metabolism, and bowel and immune health. But how much do we need?
Currently in the United States, the percentage of total food energy derived from the three major macronutrients is: carbohydrates, 51.8%; fat, 32.8%; and protein, 15.4%. Current advice for a healthy diet to lower risk for cardiovascular disease is to limit fat intake to 30% of total energy, protein to 15%, and to increase complex carbohydrates to 55%-60% of total energy. But we also need to qualify this in terms of the quality of the macronutrient, particularly carbohydrates.
In addition to the quality, the macronutrient content of the diet has varied considerably from our prehistoric times when dietary protein intakes were high at 19%-35% of energy at the expense of carbohydrate (22%-40% of energy).
If our genes haven’t kept up with industrialization, then why do we need so many carbohydrates to equate to 55%-60% of energy? Is it possible that we are confusing what is available with what we actually need? What do I mean by this?
We certainly have changed the landscape of the world due to agriculture, which has allowed us to procreate and feed ourselves, and certainly, industrialization has increased the availability of accessible cheap food. Protein in the form of meat, fish, and fowl are harder to get in industrialized nations as are fruits and vegetables. These macronutrients were the foods of our ancestors. It may be that a healthy diet is considered the one that is available.
For instance, the Mediterranean diet is somewhat higher in fat content, 40%-50% fat (mostly mono and unsaturated), and similar in protein content but lower in carbohydrate content than the typical Western diet. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is lower in fat at 25% total calories, is higher in carbohydrates at 55%, and is lower in protein, but this diet was generated in the United States, therefore it is more Western.
We need high-quality protein for organ and muscle function, high-quality unsaturated and monounsaturated fats for brain function and cellular functions, and high-quality complex carbohydrates for energy and gut health as well as micronutrients for many cellular functions. A ketogenic diet is not sustainable in the long-term for these reasons: chiefly the need for some carbohydrates for gut health and micronutrients.
How much carbohydrate content is needed should take into consideration energy expenditure as well as micronutrients and fiber intake. Protein and fat can contribute to energy production but not as readily as carbohydrates that can quickly restore glycogen in the muscle and liver. What’s interesting is that our ancestors were able to hunt and run away from danger with the small amounts of carbohydrates from plants and berries plus the protein and fat intake from animals and fish — but the Olympics weren’t a thing then!
It may be another 200,000 years before our genes catch up to ultraprocessed foods and the simple carbohydrates and sugars contained in these products. Evidence suggests that ultraprocessed foods cause inflammation in organs like the liver, adipose tissue, the heart, and even the brain. In the brain, this inflammation may be what’s causing us to defend a higher body weight set point in this environment of easily obtained highly palatable ultraprocessed foods.
Let’s not wait until our genes catch up and our bodies tolerate junk food without disease progression. It could be like waiting for Godot!
Dr. Apovian is professor of medicine, Harvard Medical School, and codirector, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. She disclosed ties to Altimmune, CinFina Pharma, Cowen and Company, EPG Communication Holdings, Form Health, Gelesis, and L-Nutra.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Temporary Gut Liner Lowers Weight, A1c
LONDON — , showed data.
Two years after the liner’s removal, 80% of patients continued to show significant improvement, while 20% returned to baseline.
Presenting results at the Diabetes UK Professional Conference (DUKPC) 2024, the researchers, led by Bob Ryder, MD, FRCP, from the Department of Diabetes, Birmingham City Hospital, Birmingham, England, aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of EndoBarrier, as well as maintenance of efficacy 24 months after the device removal.
“We think EndoBarrier finds its place between the end of all the earlier measures and the possible option of bariatric surgery, and these data show that it can lead to tremendous weight loss and improvement in A1c,” Dr. Ryder said in an interview.
Commenting on how most patients had responded to use of the device, Dr. Ryder said, “People with obesity are often very unhappy and have tried everything over many years to no effect; however, this gut liner provided the opportunity to shift out of this state, and they often become so happy with the result they were determined to stick with it and continue with a healthier lifestyle including much more exercise.”
Convenient, Reversible Procedure
Ninety consecutive patients from Birmingham, all with longstanding, poorly controlled, type 2 diabetes and obesity, underwent the implantation procedure, and 60 of these attended follow-up visits 2 years post implantation.
Unlike permanent and more invasive weight loss surgeries, the EndoBarrier device is reversible and fitted with a straightforward procedure.
The thin impermeable sleeve is inserted via an approximate 1-hour endoscopy, enabling the patient to return home the same day. It lines the first 60 cm of the small intestine. Digested food passes through it without absorption and then makes contact with pancreatic and bile juices at the other end. This triggers a change in the metabolism of glucose and nutrients through modulating gut hormones and gut bacteria, as well as disrupting bile flow.
“Because the food bypasses the small intestine, the first time the food is encountered is in an area where it is not normally found, and this causes a reaction where signals are sent to the brain to stop eating,” explained Dr. Ryder.
Due to a license for 1 year of use, the gut liner was removed after a year via a 30-minute endoscopy procedure.
Over Half Maintained Full Improvement 2 Years Post Removal
A total of 60/90 (66%) attended follow-up visits and comprised the data presented. Mean age was 51.2 years, 47% were men, 50% were White, mean body mass index (BMI) was 41.5 kg/m2, and mean A1c was 9.3%. Duration of type 2 diabetes was a median of 11 years, and 60% were taking insulin.
Patients followed dietary requirements for the initial phase after implantation. “During the first week, they followed a liquid diet, then during week 2 — mushy food, and then they were told to chew it really well to avoid blockage,” said Dr. Ryder.
Mean weight loss on removal of the liner (at 12 months post implantation) was 16.7 kg (P < .001), while BMI dropped by mean 6 kg/m2, A1c dropped by a mean of 1.8%, and mean systolic blood pressure by 10.9 mm Hg.
Just over half (32/60, 53%) showed maintenance of fully sustained improvement 2 years after removal of the liner — defined as no significant difference after 2 years between weight loss (mean, 96-97 kg) and similarly for A1c improvement (7.6%-7.4%).
Sixteen of 60 (27%) showed partially sustained improvement over the 2 years of follow-up, with BMI increasing from a mean of 116.8 kg to 128.6 kg and A1c increasing from 7.5% to 8.4%. While 20% (12/60) returned to baseline.
Of the 36/60 people using insulin prior to EndoBarrier treatment, 10 (27.8%) were no longer using insulin at 2 years post removal.
Thirteen of 90 (14%) had early removal of the gut liner due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage (five), liver abscess (two), other abscess (one), and gastrointestinal symptoms (five), but they all made a full recovery; after removal, most experienced benefit despite the adverse event, reported Dr. Ryder.
Sarah Davies, MBBCh, a GP at Woodlands Medical Centre, Cardiff, Wales, agreed that EndoBarrier might be a viable option for patients struggling with obesity. “As GPs, we are the first port of call for these patients. It’s very novel, I hadn’t heard of it before. I like how it’s a noninvasive way for my patients to lose weight and maintain that even after EndoBarrier has been removed.”
Outcomes are being monitored in an ongoing global registry to help determine if EndoBarrier is a safe and effective treatment for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Dr. Ryder noted that a similar study with 3 years of follow-up showed similar results. Further results will be presented by Dr. Ryder at the upcoming meeting of the American Diabetes Association.
EndoBarrier is currently not approved in the United States. It is awaiting United Kingdom and European CE mark, which the manufacturer hope will be granted this summer. The license will be for patients with BMI of 35-50 kg/m2.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON — , showed data.
Two years after the liner’s removal, 80% of patients continued to show significant improvement, while 20% returned to baseline.
Presenting results at the Diabetes UK Professional Conference (DUKPC) 2024, the researchers, led by Bob Ryder, MD, FRCP, from the Department of Diabetes, Birmingham City Hospital, Birmingham, England, aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of EndoBarrier, as well as maintenance of efficacy 24 months after the device removal.
“We think EndoBarrier finds its place between the end of all the earlier measures and the possible option of bariatric surgery, and these data show that it can lead to tremendous weight loss and improvement in A1c,” Dr. Ryder said in an interview.
Commenting on how most patients had responded to use of the device, Dr. Ryder said, “People with obesity are often very unhappy and have tried everything over many years to no effect; however, this gut liner provided the opportunity to shift out of this state, and they often become so happy with the result they were determined to stick with it and continue with a healthier lifestyle including much more exercise.”
Convenient, Reversible Procedure
Ninety consecutive patients from Birmingham, all with longstanding, poorly controlled, type 2 diabetes and obesity, underwent the implantation procedure, and 60 of these attended follow-up visits 2 years post implantation.
Unlike permanent and more invasive weight loss surgeries, the EndoBarrier device is reversible and fitted with a straightforward procedure.
The thin impermeable sleeve is inserted via an approximate 1-hour endoscopy, enabling the patient to return home the same day. It lines the first 60 cm of the small intestine. Digested food passes through it without absorption and then makes contact with pancreatic and bile juices at the other end. This triggers a change in the metabolism of glucose and nutrients through modulating gut hormones and gut bacteria, as well as disrupting bile flow.
“Because the food bypasses the small intestine, the first time the food is encountered is in an area where it is not normally found, and this causes a reaction where signals are sent to the brain to stop eating,” explained Dr. Ryder.
Due to a license for 1 year of use, the gut liner was removed after a year via a 30-minute endoscopy procedure.
Over Half Maintained Full Improvement 2 Years Post Removal
A total of 60/90 (66%) attended follow-up visits and comprised the data presented. Mean age was 51.2 years, 47% were men, 50% were White, mean body mass index (BMI) was 41.5 kg/m2, and mean A1c was 9.3%. Duration of type 2 diabetes was a median of 11 years, and 60% were taking insulin.
Patients followed dietary requirements for the initial phase after implantation. “During the first week, they followed a liquid diet, then during week 2 — mushy food, and then they were told to chew it really well to avoid blockage,” said Dr. Ryder.
Mean weight loss on removal of the liner (at 12 months post implantation) was 16.7 kg (P < .001), while BMI dropped by mean 6 kg/m2, A1c dropped by a mean of 1.8%, and mean systolic blood pressure by 10.9 mm Hg.
Just over half (32/60, 53%) showed maintenance of fully sustained improvement 2 years after removal of the liner — defined as no significant difference after 2 years between weight loss (mean, 96-97 kg) and similarly for A1c improvement (7.6%-7.4%).
Sixteen of 60 (27%) showed partially sustained improvement over the 2 years of follow-up, with BMI increasing from a mean of 116.8 kg to 128.6 kg and A1c increasing from 7.5% to 8.4%. While 20% (12/60) returned to baseline.
Of the 36/60 people using insulin prior to EndoBarrier treatment, 10 (27.8%) were no longer using insulin at 2 years post removal.
Thirteen of 90 (14%) had early removal of the gut liner due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage (five), liver abscess (two), other abscess (one), and gastrointestinal symptoms (five), but they all made a full recovery; after removal, most experienced benefit despite the adverse event, reported Dr. Ryder.
Sarah Davies, MBBCh, a GP at Woodlands Medical Centre, Cardiff, Wales, agreed that EndoBarrier might be a viable option for patients struggling with obesity. “As GPs, we are the first port of call for these patients. It’s very novel, I hadn’t heard of it before. I like how it’s a noninvasive way for my patients to lose weight and maintain that even after EndoBarrier has been removed.”
Outcomes are being monitored in an ongoing global registry to help determine if EndoBarrier is a safe and effective treatment for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Dr. Ryder noted that a similar study with 3 years of follow-up showed similar results. Further results will be presented by Dr. Ryder at the upcoming meeting of the American Diabetes Association.
EndoBarrier is currently not approved in the United States. It is awaiting United Kingdom and European CE mark, which the manufacturer hope will be granted this summer. The license will be for patients with BMI of 35-50 kg/m2.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON — , showed data.
Two years after the liner’s removal, 80% of patients continued to show significant improvement, while 20% returned to baseline.
Presenting results at the Diabetes UK Professional Conference (DUKPC) 2024, the researchers, led by Bob Ryder, MD, FRCP, from the Department of Diabetes, Birmingham City Hospital, Birmingham, England, aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of EndoBarrier, as well as maintenance of efficacy 24 months after the device removal.
“We think EndoBarrier finds its place between the end of all the earlier measures and the possible option of bariatric surgery, and these data show that it can lead to tremendous weight loss and improvement in A1c,” Dr. Ryder said in an interview.
Commenting on how most patients had responded to use of the device, Dr. Ryder said, “People with obesity are often very unhappy and have tried everything over many years to no effect; however, this gut liner provided the opportunity to shift out of this state, and they often become so happy with the result they were determined to stick with it and continue with a healthier lifestyle including much more exercise.”
Convenient, Reversible Procedure
Ninety consecutive patients from Birmingham, all with longstanding, poorly controlled, type 2 diabetes and obesity, underwent the implantation procedure, and 60 of these attended follow-up visits 2 years post implantation.
Unlike permanent and more invasive weight loss surgeries, the EndoBarrier device is reversible and fitted with a straightforward procedure.
The thin impermeable sleeve is inserted via an approximate 1-hour endoscopy, enabling the patient to return home the same day. It lines the first 60 cm of the small intestine. Digested food passes through it without absorption and then makes contact with pancreatic and bile juices at the other end. This triggers a change in the metabolism of glucose and nutrients through modulating gut hormones and gut bacteria, as well as disrupting bile flow.
“Because the food bypasses the small intestine, the first time the food is encountered is in an area where it is not normally found, and this causes a reaction where signals are sent to the brain to stop eating,” explained Dr. Ryder.
Due to a license for 1 year of use, the gut liner was removed after a year via a 30-minute endoscopy procedure.
Over Half Maintained Full Improvement 2 Years Post Removal
A total of 60/90 (66%) attended follow-up visits and comprised the data presented. Mean age was 51.2 years, 47% were men, 50% were White, mean body mass index (BMI) was 41.5 kg/m2, and mean A1c was 9.3%. Duration of type 2 diabetes was a median of 11 years, and 60% were taking insulin.
Patients followed dietary requirements for the initial phase after implantation. “During the first week, they followed a liquid diet, then during week 2 — mushy food, and then they were told to chew it really well to avoid blockage,” said Dr. Ryder.
Mean weight loss on removal of the liner (at 12 months post implantation) was 16.7 kg (P < .001), while BMI dropped by mean 6 kg/m2, A1c dropped by a mean of 1.8%, and mean systolic blood pressure by 10.9 mm Hg.
Just over half (32/60, 53%) showed maintenance of fully sustained improvement 2 years after removal of the liner — defined as no significant difference after 2 years between weight loss (mean, 96-97 kg) and similarly for A1c improvement (7.6%-7.4%).
Sixteen of 60 (27%) showed partially sustained improvement over the 2 years of follow-up, with BMI increasing from a mean of 116.8 kg to 128.6 kg and A1c increasing from 7.5% to 8.4%. While 20% (12/60) returned to baseline.
Of the 36/60 people using insulin prior to EndoBarrier treatment, 10 (27.8%) were no longer using insulin at 2 years post removal.
Thirteen of 90 (14%) had early removal of the gut liner due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage (five), liver abscess (two), other abscess (one), and gastrointestinal symptoms (five), but they all made a full recovery; after removal, most experienced benefit despite the adverse event, reported Dr. Ryder.
Sarah Davies, MBBCh, a GP at Woodlands Medical Centre, Cardiff, Wales, agreed that EndoBarrier might be a viable option for patients struggling with obesity. “As GPs, we are the first port of call for these patients. It’s very novel, I hadn’t heard of it before. I like how it’s a noninvasive way for my patients to lose weight and maintain that even after EndoBarrier has been removed.”
Outcomes are being monitored in an ongoing global registry to help determine if EndoBarrier is a safe and effective treatment for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Dr. Ryder noted that a similar study with 3 years of follow-up showed similar results. Further results will be presented by Dr. Ryder at the upcoming meeting of the American Diabetes Association.
EndoBarrier is currently not approved in the United States. It is awaiting United Kingdom and European CE mark, which the manufacturer hope will be granted this summer. The license will be for patients with BMI of 35-50 kg/m2.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel PCSK9 Inhibitor Reduced LDL by 50%
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lerodalcibep, a novel, third-generation proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor, reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% after 1 year in patients with or at a high risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), new phase 3 results showed.
Newer, more stringent LDL targets in 90% of patients receiving lerodalcibep vs only 16% of those on placebo, despite concurrent treatment with a statin or statin plus ezetimibe.
“This hopefully gives doctors a more practical PCSK9 antagonist that’s small volume, can be administered monthly, and is an alternative to the every 2 week injection of monoclonal antibodies and probably more effective in LDL cholesterol–lowering compared to the small interfering RNA” medicines, study author Eric Klug, MBBCh, MMed, associate professor, Division of Cardiology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, told this news organization.
The findings from the LIBerate-HR trial were presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Scientific Session 2024.
Additional Therapy Needed
The first goal is to get at least a 50% reduction in LDL-C, said Dr. Klug. The ACC, the American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology recommended LDL-C of no more than 55 mg/dL as a goal for patients with CVD or who are at a very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke and no more than 70 mg/dL for high-risk patients.
Most patients don’t get to that combined goal with statins and ezetimibe and need additional therapy, “and it appears the earlier you give the therapy the better,” said Dr. Klug.
Lerodalcibep is given as a low-dose (1.2-mL) monthly injection and is more convenient than other LDL-C–lowering options, said Dr. Klug. “This is a small-volume molecule that can be delivered subcutaneously once a month and can be kept on the shelf so it doesn’t need to be kept in the fridge, and you can travel with it.”
LIBerate-HR included 922 patients with CVD or at a high or very high risk for myocardial infarction or stroke at 66 centers in 11 countries. Over half (52%) fell into the at-risk category.
The mean age of participants was 64.5 years, 77% were White, and, notably, about 45% were women. Some 84% were taking a statin, 16.6% ezetimibe, a quarter had diabetes, and 10% had the more severe inherited familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
Patients were randomly assigned to receive monthly 300-mg (1.2-mL) subcutaneous injections of lerodalcibep (n = 615) or placebo (n = 307) for 52 weeks.
The mean LDL-C at baseline was 116.9 mg/dL in the placebo group and 116.3 mg/dL in the treatment group.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent change from baseline in LDL-C at week 52 and the mean of weeks 50 and 52 (average of the peak and trough dose).
Compared with placebo, lerodalcibep reduced LDL-C by 56.19% at week 52 (P < .0001) and by 62.69% at mean week 50/52 (P < .0001). The absolute decreases were 60.6 mg/dL at week 52 and 74.5 mg/dL for mean week 50/52.
Rule of Thumb
“There’s a sort of rule of thumb that for every 40 mg/dL that LDL-C is reduced, you reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) by 20%-23%,” said Dr. Klug. “So, by reducing LDL-C by 60 mg/dL at week 52, you’re reducing your risk of MACE maybe by 30% or 35%.”
All subgroups reaped the same benefit from the intervention, noted Dr. Klug. “Whether you were male or female, under age 65, over age 65, baseline BMI less than median or more than median, White, Black or other, baseline statin intensity, diabetic or not diabetic, diagnosis of FH or not, it made no difference.”
As for secondary outcomes, most patients attained the newer, more stringent guideline-recommended LDL targets.
The treatment also reduced non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 47%, apolipoprotein B by 43%, and Lp(a) by 33%.
Lerodalcibep was well-tolerated, with the number of patients with at least one adverse event similar to placebo (71.6% vs 68.1%) as was the case for the number with at least one serious adverse event (12.4% vs 13.4%).
Injection site reactions were mild to moderate. There was no difference in discontinuation rates due to these reactions (4.2% for the treatment and 4.6% for placebo).
A larger and longer trial to begin later this year should determine if the amount of LDL-C–lowering seen with lerodalcibep translates to greater reductions in cardiovascular events.
The company plans to file an application for approval to the US Food and Drug Administration in the next 2-4 months, said Dr. Klug.
Still Work to Do
During a press briefing, Dave L, Dixon, PharmD, professor and chair, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Pharmacy, Richmond, and member of the ACC Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Council, congratulated the investigators “on moving this product forward and demonstrating the LDL-lowering efficacy, as well as providing some additional safety and tolerability data.”
He added it’s “clear” from the baseline LDL characteristics that “we have a lot of work to do in terms of helping patients achieve their lipid goals.”
Dr. Dixon noted up to about 30% of patients have some form of statin intolerance. “So, we really have to utilize our non-statin therapies, and unfortunately, we’re not doing a great job of that.”
That the trial enrolled so many women is “fantastic,” said Dr. Dixon, adding the investigators also “did a great job” of enrolling underrepresented minorities.
Having a once-a-month self-injection option “is great” and “fills a nice niche” for patients, said Dr. Dixon.
The study was funded by LIB Therapeutics, which manufactures lerodalcibep. Dr. Klug had no conflicts relevant to this study (he received honoraria from Novartis, Amgen, and Sanofi-Aventis).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2024
Which Probiotics Are Effective in Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
PARIS — Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common brain-gut axis disorder, and patients are often dissatisfied with conventional treatments.
The role of the microbiota in IBS is now well established, and patients frequently take probiotics on their own initiative or on the advice of a physician or pharmacist. However, not all probiotics have equal efficacy, so which ones should be recommended?
Jean-Marc Sabaté, MD, PhD, a gastroenterologist at Avicenne Hospital in Bobigny, France, shared insights about probiotics at the Francophone Days of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, and Digestive Oncology.
IBS, according to the Rome IV symptom-based classification, is a “disorder of brain-gut axis interactions” with a prevalence of about 4% in the adult population. In France, during an average care pathway of about 8 years, patients try an average of five therapeutic strategies (and as many as 11), including antispasmodics (85%), diets (78%), and probiotics. In addition, 66.4% of patients had either taken or were taking probiotics at the time of a recent survey.
While the 2022 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology on the diagnosis and management of IBS do not support the use of probiotics for overall symptom relief — a recommendation for which they cite a low level of evidence — “there is nevertheless a rationale for prescribing probiotics in IBS due to the significant role of the microbiota (or dysbiosis) in this condition,” said Dr. Sabaté.
Microbiota in IBS
Evidence indicating that antibiotics exacerbate IBS symptoms and revealing chronic bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine of patients with IBS supports the role of the microbiota. Studies using a molecular approach (16s rRNA) have settled the debate, confirming differences in the intestinal flora between patients with IBS and healthy subjects. Data also indicate differences in flora between patient subtypes, such as an increased Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio. However, one subgroup, which can represent as much as a third of patients, seems to harbor a “normal” microbiota.
Nonetheless, the microbiota plays a significant role in IBS. A Swedish study highlighted the influence of bacterial enterotypes on transit type associated with IBS and symptom severity, independent of diet composition or medication use.
This dysbiosis could play a significant role as it interacts with other mechanisms involved in IBS, including changes in intestinal motility related to diet (related to fermentable carbohydrates, for example). Moreover, the microbiota seems to induce a low level of immune activation in patients with IBS, leading to microinflammation and increased intestinal permeability, especially after an infection.
Furthermore, alterations in the regulation of bile acid deconjugation by the microbiota partly explain the frequency and consistency of stools in diarrhea-predominant IBS patients.
In addition, colonic gas production is higher in these patients. Those complaining of flatulence have poor tolerance to intestinal gases after a flatulent meal, associated with microbiota instability.
Data regarding the interaction between the microbiota and central mechanisms mainly come from animal studies. In rodents, microbiota constituents seem to affect brain development, function, and morphology. Emotional and physical traumas during childhood appear to be risk factors. Moreover, even brief exposure to broad-spectrum antibiotics in neonates could cause subsequent visceral hypersensitivity.
Lastly, the role of the microbiota in changes in medullary pain control after visceral stimulation (eg, rectal distension) has still not been demonstrated in humans.
Recent Guideline
In its February 2023 Global Guideline “Probiotics and Prebiotics” for IBS, the World Gastroenterology Organization looked at the level of evidence for probiotics.
Three strains, as well as a combination of several strains, were supported by level 2 evidence, meaning at least two randomized studies with converging results. These are Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75, which improves overall symptoms and quality of life; Lactobacillus plantarum 299v (DSM 9843), which acts on the severity of abdominal pain and bloating; and B infantis 35624 (new name: B longum 35624), which improves the overall assessment of IBS symptoms, as does the multistrain product containing L rhamnosus GG, L rhamnosus LC705, Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp shermanii JS DSM 7067, and B animalis ssp lactis B012 DSM 15954.
Efficacy and Availability
Probiotics belonging to the category of dietary supplements or medical devices are not required to provide evidence for a mechanism of action or even efficacy to be marketed. Thus, for most probiotics sold, there are no human or even animal studies available.
Dr. Sabaté proposed a choice of probiotics based on the literature and the presence of at least one randomized placebo-controlled trial conducted in patients with IBS showing positive results.
“,” he emphasized. The parameters that can be improved include symptom severity, quality of life, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Effective Probiotics
B longum 35624, which was developed with researchers from University College Cork in Ireland, is probably the most studied in animals and humans. Research has encompassed the mechanistic, clinical, and safety aspects of the probiotic. It has shown good results on the IBS-Symptom Severity Score (SSS), quality of life, abdominal pain, bowel disturbances, and bloating. The treatment duration in studies is 4-8 weeks.
L plantarum 299v (DSM 9843) affects the frequency of abdominal pain and pain score. The treatment duration in studies is 4 weeks.
The multistrain product that includes L plantarum CECT 7484/L plantarum CECT 7485/ Pediococcus acidilactici CECT 7483 allows for an improvement in quality of life and anxiety related to digestive symptoms. No positive effect has been described on digestive symptoms, especially diarrhea. The treatment duration is 6 weeks.
B bifidum MIMBb75 (both normal and heat-inactivated forms) is beneficial for pain, the composite IBS-SSS score, and quality of life. The treatment duration is 4-8 weeks.
“Except for the multistrain combination, which is more suited to patients with diarrhea-predominant IBS, the other three probiotics can be prescribed regardless of the IBS subtype,” said Dr. Sabaté. “Treatment durations are typically 4 weeks, but it is possible to continue up to 8 weeks, which is the maximum duration of these studies. In practice, there are no tolerance issues with probiotics prescribed for IBS based on the literature. These should be tested under the conditions and for the duration of the published studies and should only be continued if there is individual benefit on symptoms or quality of life.”
Note that microbiota analyses conducted for individual purposes are of no help in choosing probiotics.
Mechanisms of Action
In a murine model, but not in humans, some strains, especially L acidophilus NCFM, have shown an antinociceptive effect by inducing opioid and cannabinoid receptors.
Only in animals to date, L farciminis and B lactis CNCM I-2494 have shown prevention of induced hypersensitivity (ie, inhibition of the cytoskeleton contraction of colon epithelial cells and subsequent opening of tight junctions).
B infantis 35624 has an anti-inflammatory action by modifying the IL-10 and IL-12 cytokine ratio in animals and humans. It has an immunomodulatory action by increasing dendritic cells in the mucosa and decreasing Th1 and Th7 helper T cells.
B infantis 35624 and L farciminis are two strains that decrease visceral sensitivity in mice.
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 acts on lipopeptide production with an antinociceptive effect, as observed in mice, by decreasing visceral sensitivity through calcium nociceptor flux blockade (action on GABA type B receptor).
Acting on dysbiosis by modifying fecal microbiota during probiotic intake is possible but depends on the probiotics, like B infantis 35624. In humans, B longum NCC 3001 could modify brain activations.
Dr. Sabaté disclosed financial relationships with Mayoly Spindler, Kyowa Kirin, Tillotts, Servier, Norgine, Biocodex, Merck, Viatris, Abivax, and Inventiva.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS — Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common brain-gut axis disorder, and patients are often dissatisfied with conventional treatments.
The role of the microbiota in IBS is now well established, and patients frequently take probiotics on their own initiative or on the advice of a physician or pharmacist. However, not all probiotics have equal efficacy, so which ones should be recommended?
Jean-Marc Sabaté, MD, PhD, a gastroenterologist at Avicenne Hospital in Bobigny, France, shared insights about probiotics at the Francophone Days of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, and Digestive Oncology.
IBS, according to the Rome IV symptom-based classification, is a “disorder of brain-gut axis interactions” with a prevalence of about 4% in the adult population. In France, during an average care pathway of about 8 years, patients try an average of five therapeutic strategies (and as many as 11), including antispasmodics (85%), diets (78%), and probiotics. In addition, 66.4% of patients had either taken or were taking probiotics at the time of a recent survey.
While the 2022 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology on the diagnosis and management of IBS do not support the use of probiotics for overall symptom relief — a recommendation for which they cite a low level of evidence — “there is nevertheless a rationale for prescribing probiotics in IBS due to the significant role of the microbiota (or dysbiosis) in this condition,” said Dr. Sabaté.
Microbiota in IBS
Evidence indicating that antibiotics exacerbate IBS symptoms and revealing chronic bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine of patients with IBS supports the role of the microbiota. Studies using a molecular approach (16s rRNA) have settled the debate, confirming differences in the intestinal flora between patients with IBS and healthy subjects. Data also indicate differences in flora between patient subtypes, such as an increased Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio. However, one subgroup, which can represent as much as a third of patients, seems to harbor a “normal” microbiota.
Nonetheless, the microbiota plays a significant role in IBS. A Swedish study highlighted the influence of bacterial enterotypes on transit type associated with IBS and symptom severity, independent of diet composition or medication use.
This dysbiosis could play a significant role as it interacts with other mechanisms involved in IBS, including changes in intestinal motility related to diet (related to fermentable carbohydrates, for example). Moreover, the microbiota seems to induce a low level of immune activation in patients with IBS, leading to microinflammation and increased intestinal permeability, especially after an infection.
Furthermore, alterations in the regulation of bile acid deconjugation by the microbiota partly explain the frequency and consistency of stools in diarrhea-predominant IBS patients.
In addition, colonic gas production is higher in these patients. Those complaining of flatulence have poor tolerance to intestinal gases after a flatulent meal, associated with microbiota instability.
Data regarding the interaction between the microbiota and central mechanisms mainly come from animal studies. In rodents, microbiota constituents seem to affect brain development, function, and morphology. Emotional and physical traumas during childhood appear to be risk factors. Moreover, even brief exposure to broad-spectrum antibiotics in neonates could cause subsequent visceral hypersensitivity.
Lastly, the role of the microbiota in changes in medullary pain control after visceral stimulation (eg, rectal distension) has still not been demonstrated in humans.
Recent Guideline
In its February 2023 Global Guideline “Probiotics and Prebiotics” for IBS, the World Gastroenterology Organization looked at the level of evidence for probiotics.
Three strains, as well as a combination of several strains, were supported by level 2 evidence, meaning at least two randomized studies with converging results. These are Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75, which improves overall symptoms and quality of life; Lactobacillus plantarum 299v (DSM 9843), which acts on the severity of abdominal pain and bloating; and B infantis 35624 (new name: B longum 35624), which improves the overall assessment of IBS symptoms, as does the multistrain product containing L rhamnosus GG, L rhamnosus LC705, Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp shermanii JS DSM 7067, and B animalis ssp lactis B012 DSM 15954.
Efficacy and Availability
Probiotics belonging to the category of dietary supplements or medical devices are not required to provide evidence for a mechanism of action or even efficacy to be marketed. Thus, for most probiotics sold, there are no human or even animal studies available.
Dr. Sabaté proposed a choice of probiotics based on the literature and the presence of at least one randomized placebo-controlled trial conducted in patients with IBS showing positive results.
“,” he emphasized. The parameters that can be improved include symptom severity, quality of life, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Effective Probiotics
B longum 35624, which was developed with researchers from University College Cork in Ireland, is probably the most studied in animals and humans. Research has encompassed the mechanistic, clinical, and safety aspects of the probiotic. It has shown good results on the IBS-Symptom Severity Score (SSS), quality of life, abdominal pain, bowel disturbances, and bloating. The treatment duration in studies is 4-8 weeks.
L plantarum 299v (DSM 9843) affects the frequency of abdominal pain and pain score. The treatment duration in studies is 4 weeks.
The multistrain product that includes L plantarum CECT 7484/L plantarum CECT 7485/ Pediococcus acidilactici CECT 7483 allows for an improvement in quality of life and anxiety related to digestive symptoms. No positive effect has been described on digestive symptoms, especially diarrhea. The treatment duration is 6 weeks.
B bifidum MIMBb75 (both normal and heat-inactivated forms) is beneficial for pain, the composite IBS-SSS score, and quality of life. The treatment duration is 4-8 weeks.
“Except for the multistrain combination, which is more suited to patients with diarrhea-predominant IBS, the other three probiotics can be prescribed regardless of the IBS subtype,” said Dr. Sabaté. “Treatment durations are typically 4 weeks, but it is possible to continue up to 8 weeks, which is the maximum duration of these studies. In practice, there are no tolerance issues with probiotics prescribed for IBS based on the literature. These should be tested under the conditions and for the duration of the published studies and should only be continued if there is individual benefit on symptoms or quality of life.”
Note that microbiota analyses conducted for individual purposes are of no help in choosing probiotics.
Mechanisms of Action
In a murine model, but not in humans, some strains, especially L acidophilus NCFM, have shown an antinociceptive effect by inducing opioid and cannabinoid receptors.
Only in animals to date, L farciminis and B lactis CNCM I-2494 have shown prevention of induced hypersensitivity (ie, inhibition of the cytoskeleton contraction of colon epithelial cells and subsequent opening of tight junctions).
B infantis 35624 has an anti-inflammatory action by modifying the IL-10 and IL-12 cytokine ratio in animals and humans. It has an immunomodulatory action by increasing dendritic cells in the mucosa and decreasing Th1 and Th7 helper T cells.
B infantis 35624 and L farciminis are two strains that decrease visceral sensitivity in mice.
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 acts on lipopeptide production with an antinociceptive effect, as observed in mice, by decreasing visceral sensitivity through calcium nociceptor flux blockade (action on GABA type B receptor).
Acting on dysbiosis by modifying fecal microbiota during probiotic intake is possible but depends on the probiotics, like B infantis 35624. In humans, B longum NCC 3001 could modify brain activations.
Dr. Sabaté disclosed financial relationships with Mayoly Spindler, Kyowa Kirin, Tillotts, Servier, Norgine, Biocodex, Merck, Viatris, Abivax, and Inventiva.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS — Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common brain-gut axis disorder, and patients are often dissatisfied with conventional treatments.
The role of the microbiota in IBS is now well established, and patients frequently take probiotics on their own initiative or on the advice of a physician or pharmacist. However, not all probiotics have equal efficacy, so which ones should be recommended?
Jean-Marc Sabaté, MD, PhD, a gastroenterologist at Avicenne Hospital in Bobigny, France, shared insights about probiotics at the Francophone Days of Hepatology, Gastroenterology, and Digestive Oncology.
IBS, according to the Rome IV symptom-based classification, is a “disorder of brain-gut axis interactions” with a prevalence of about 4% in the adult population. In France, during an average care pathway of about 8 years, patients try an average of five therapeutic strategies (and as many as 11), including antispasmodics (85%), diets (78%), and probiotics. In addition, 66.4% of patients had either taken or were taking probiotics at the time of a recent survey.
While the 2022 recommendations from the American College of Gastroenterology on the diagnosis and management of IBS do not support the use of probiotics for overall symptom relief — a recommendation for which they cite a low level of evidence — “there is nevertheless a rationale for prescribing probiotics in IBS due to the significant role of the microbiota (or dysbiosis) in this condition,” said Dr. Sabaté.
Microbiota in IBS
Evidence indicating that antibiotics exacerbate IBS symptoms and revealing chronic bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine of patients with IBS supports the role of the microbiota. Studies using a molecular approach (16s rRNA) have settled the debate, confirming differences in the intestinal flora between patients with IBS and healthy subjects. Data also indicate differences in flora between patient subtypes, such as an increased Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio. However, one subgroup, which can represent as much as a third of patients, seems to harbor a “normal” microbiota.
Nonetheless, the microbiota plays a significant role in IBS. A Swedish study highlighted the influence of bacterial enterotypes on transit type associated with IBS and symptom severity, independent of diet composition or medication use.
This dysbiosis could play a significant role as it interacts with other mechanisms involved in IBS, including changes in intestinal motility related to diet (related to fermentable carbohydrates, for example). Moreover, the microbiota seems to induce a low level of immune activation in patients with IBS, leading to microinflammation and increased intestinal permeability, especially after an infection.
Furthermore, alterations in the regulation of bile acid deconjugation by the microbiota partly explain the frequency and consistency of stools in diarrhea-predominant IBS patients.
In addition, colonic gas production is higher in these patients. Those complaining of flatulence have poor tolerance to intestinal gases after a flatulent meal, associated with microbiota instability.
Data regarding the interaction between the microbiota and central mechanisms mainly come from animal studies. In rodents, microbiota constituents seem to affect brain development, function, and morphology. Emotional and physical traumas during childhood appear to be risk factors. Moreover, even brief exposure to broad-spectrum antibiotics in neonates could cause subsequent visceral hypersensitivity.
Lastly, the role of the microbiota in changes in medullary pain control after visceral stimulation (eg, rectal distension) has still not been demonstrated in humans.
Recent Guideline
In its February 2023 Global Guideline “Probiotics and Prebiotics” for IBS, the World Gastroenterology Organization looked at the level of evidence for probiotics.
Three strains, as well as a combination of several strains, were supported by level 2 evidence, meaning at least two randomized studies with converging results. These are Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75, which improves overall symptoms and quality of life; Lactobacillus plantarum 299v (DSM 9843), which acts on the severity of abdominal pain and bloating; and B infantis 35624 (new name: B longum 35624), which improves the overall assessment of IBS symptoms, as does the multistrain product containing L rhamnosus GG, L rhamnosus LC705, Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp shermanii JS DSM 7067, and B animalis ssp lactis B012 DSM 15954.
Efficacy and Availability
Probiotics belonging to the category of dietary supplements or medical devices are not required to provide evidence for a mechanism of action or even efficacy to be marketed. Thus, for most probiotics sold, there are no human or even animal studies available.
Dr. Sabaté proposed a choice of probiotics based on the literature and the presence of at least one randomized placebo-controlled trial conducted in patients with IBS showing positive results.
“,” he emphasized. The parameters that can be improved include symptom severity, quality of life, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Effective Probiotics
B longum 35624, which was developed with researchers from University College Cork in Ireland, is probably the most studied in animals and humans. Research has encompassed the mechanistic, clinical, and safety aspects of the probiotic. It has shown good results on the IBS-Symptom Severity Score (SSS), quality of life, abdominal pain, bowel disturbances, and bloating. The treatment duration in studies is 4-8 weeks.
L plantarum 299v (DSM 9843) affects the frequency of abdominal pain and pain score. The treatment duration in studies is 4 weeks.
The multistrain product that includes L plantarum CECT 7484/L plantarum CECT 7485/ Pediococcus acidilactici CECT 7483 allows for an improvement in quality of life and anxiety related to digestive symptoms. No positive effect has been described on digestive symptoms, especially diarrhea. The treatment duration is 6 weeks.
B bifidum MIMBb75 (both normal and heat-inactivated forms) is beneficial for pain, the composite IBS-SSS score, and quality of life. The treatment duration is 4-8 weeks.
“Except for the multistrain combination, which is more suited to patients with diarrhea-predominant IBS, the other three probiotics can be prescribed regardless of the IBS subtype,” said Dr. Sabaté. “Treatment durations are typically 4 weeks, but it is possible to continue up to 8 weeks, which is the maximum duration of these studies. In practice, there are no tolerance issues with probiotics prescribed for IBS based on the literature. These should be tested under the conditions and for the duration of the published studies and should only be continued if there is individual benefit on symptoms or quality of life.”
Note that microbiota analyses conducted for individual purposes are of no help in choosing probiotics.
Mechanisms of Action
In a murine model, but not in humans, some strains, especially L acidophilus NCFM, have shown an antinociceptive effect by inducing opioid and cannabinoid receptors.
Only in animals to date, L farciminis and B lactis CNCM I-2494 have shown prevention of induced hypersensitivity (ie, inhibition of the cytoskeleton contraction of colon epithelial cells and subsequent opening of tight junctions).
B infantis 35624 has an anti-inflammatory action by modifying the IL-10 and IL-12 cytokine ratio in animals and humans. It has an immunomodulatory action by increasing dendritic cells in the mucosa and decreasing Th1 and Th7 helper T cells.
B infantis 35624 and L farciminis are two strains that decrease visceral sensitivity in mice.
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 acts on lipopeptide production with an antinociceptive effect, as observed in mice, by decreasing visceral sensitivity through calcium nociceptor flux blockade (action on GABA type B receptor).
Acting on dysbiosis by modifying fecal microbiota during probiotic intake is possible but depends on the probiotics, like B infantis 35624. In humans, B longum NCC 3001 could modify brain activations.
Dr. Sabaté disclosed financial relationships with Mayoly Spindler, Kyowa Kirin, Tillotts, Servier, Norgine, Biocodex, Merck, Viatris, Abivax, and Inventiva.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.