User login
Richard Franki is the associate editor who writes and creates graphs. He started with the company in 1987, when it was known as the International Medical News Group. In his years as a journalist, Richard has worked for Cap Cities/ABC, Disney, Harcourt, Elsevier, Quadrant, Frontline, and Internet Brands. In the 1990s, he was a contributor to the ill-fated Indications column, predecessor of Livin' on the MDedge.
Early bird gets the worm, night owl gets the diabetes
Metabolism a player in circadian rhythm section
Are you an early bird, or do you wake up and stare at your phone, wondering why you were up watching “The Crown” until 3 a.m.? Recent research suggests that people who wake up earlier tend to be more active during the day and burn more fat than those who sleep in. Fat builds up in the night owls, putting them at higher risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
The study gives physicians something to think about when assessing a patient’s risk factors. “This could help medical professionals consider another behavioral factor contributing to disease risk,” Steven Malin, PhD, lead author of the study and expert in metabolism at Rutgers University in New Brunswick, N.J., said in The Guardian.
For the research, 51 participants were divided into night owls and early birds, depending on their answers to a questionnaire. They were examined, monitored for a week, and assessed while doing various activities. Those who woke up early tended to be more sensitive to insulin and burned off fat faster than those who woke up late, the researchers explained.
“Night owls are reported to have a higher risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease when compared with early birds,” Dr. Malin said. “A potential explanation is they become misaligned with their circadian rhythm for various reasons, but most notably among adults would be work.”
We all know that we may not be at our best when we throw off our internal clocks by going to sleep late and waking up early. Think about that next time you start another episode on Netflix at 2:57 a.m.
Mosquitoes, chemical cocktails, and glass sock beads
We all know that mosquitoes are annoying little disease vectors with a taste for human blood. One of the less-known things about mosquitoes is what attracts them to humans in the first place. It’s so less known that, until now, it was unknown. Oh sure, we knew that odor was involved, and that lactic acid was part of the odor equation, but what are the specific chemicals? Well, there’s carbon dioxide … and ammonia. Those were already known.
Ring Cardé, PhD, an entomologist at the University of California, Riverside, wasn’t convinced. “I suspected there was something undiscovered about the chemistry of odors luring the yellow fever mosquito. I wanted to nail down the exact blend,” he said in a statement from the university.
Dr. Cardé and his associates eventually figured out that the exact chemical cocktail attracting female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes was a combination of carbon dioxide plus two chemicals, 2-ketoglutaric acid and lactic acid. The odor from these chemicals enables mosquitoes to locate and land on their victim and “also encourages probing, the use of piercing mouthparts to find blood,” the university said.
This amazing destination of science is important, but we have to acknowledge the journey as well. To do that we turn to one of Dr. Cardé’s associates, Jan Bello, PhD, formerly of Cal-Riverside and now with insect pest control company Provivi. Turns out that 2-ketoglutaric acid is tricky stuff because the methods typically used to identify chemicals don’t work on it.
Dr. Bello employed a somewhat unorthodox chemical extraction method: He filled his socks with glass beads and walked around with the beads in his socks.
“Wearing the beads felt almost like a massage, like squeezing stress balls full of sand, but with your feet,” Dr. Bello said. “The most frustrating part of doing it for a long time is that they would get stuck in between your toes, so it would be uncomfortable after a while.”
We hate when science gets stuck between our toes, but we love it when scientists write their own punchlines.
The MS drugs are better down where it’s wetter, take it from me
The myth of the mermaid is one with hundreds, if not thousands, of years of history. The ancient Greeks had the mythological siren, while the Babylonians depicted kulullû (which were mermen – never let the Babylonians be known as noninclusive) in artwork as far back as 1600 BC. Cultures as far flung as Japan, southern Africa, and New Zealand have folkloric figures similar to the mermaid. It is most decidedly not a creation of western Europe, Hans Christian Andersen, or Disney.
With that mild rant out of the way, let’s move to Germany and a group of researchers from the University of Bonn, who have not created a mermaid. They did, however, add human genes to a zebrafish for research purposes, which feels uncomfortably close. Nothing better than unholy animal-human hybrids, right?
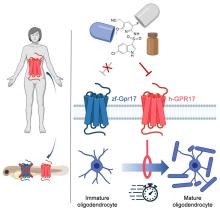
Stick with us here, because the researchers did have a good reason for their gene splicing. Zebrafish and humans both have the GPR17 receptor, which is highly active in nerve tissue. When GPR17 is overactivated, diseases such as multiple sclerosis can develop. Because the zebrafish has this receptor, which performs the same function in its body as in ours, it’s a prime candidate for replacement. Also, zebrafish larvae are transparent, which makes it very easy to observe a drug working.
That said, fish and humans are very far apart, genetically speaking. Big shock right there. But by replacing their GPR17 receptor with ours, the scientists have created a fish that we could test drug candidates on and be assured that they would also work on humans. Actually testing drugs for MS on these humanized zebrafish was beyond the scope of the study, but the researchers said that the new genes function normally in the fish larvae, making them a promising new avenue for MS drug development.
Can we all promise not to tell Disney that human DNA can be spliced into a fish without consequence? Otherwise, we’re just going to have to sit through another “Little Mermaid” adaptation in 30 years, this one in super live-action featuring actual, real-life mermaids. And we’re not ready for that level of man-made horror just yet.
Beware of the fly vomit
Picture this: You’re outside at a picnic or barbecue, loading a plate with food. In a brief moment of conversation a fly lands right on top of your sandwich. You shoo it away and think nothing more of it, eating the sandwich anyway. We’ve all been there.
A recent study is making us think again.
John Stoffolano, an entomology professor at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, claims that too much attention has been focused on pathogen transmission by the biting, blood-feeding flies when really we should be taking note of the nonbiting, or synanthropic, flies we live with, which may have a greater impact on the transmission of pathogens right in our own homes.
Sure, blood-feeding flies can spread pathogens directly, but house flies vomit every time they land on something. Think about that.
The fly that sneakily swooped into your house from a tear in your window screen has just been outside in the neighbor’s garbage or sitting on dog poop and now has who knows what filling its crop, the tank in their body that serves as “a place to store food before it makes its way into the digestive tract where it will get turned into energy for the fly,” Dr. Stoffolano explained in a written statement.
Did that fly land right on the baked potato you were prepping for dinner before you shooed it away? Guess what? Before flying off it emitted excess water that has pathogens from whatever was in its crop. We don’t want to say your potato might have dog poop on it, but you get the idea. The crop doesn’t have a ton of digestive enzymes that would help neutralize pathogens, so whatever that fly regurgitated before buzzing off is still around for you to ingest and there’s not much you can do about it.
More research needs to be done about flies, but at the very least this study should make you think twice before eating that baked potato after a fly has been there.
Metabolism a player in circadian rhythm section
Are you an early bird, or do you wake up and stare at your phone, wondering why you were up watching “The Crown” until 3 a.m.? Recent research suggests that people who wake up earlier tend to be more active during the day and burn more fat than those who sleep in. Fat builds up in the night owls, putting them at higher risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
The study gives physicians something to think about when assessing a patient’s risk factors. “This could help medical professionals consider another behavioral factor contributing to disease risk,” Steven Malin, PhD, lead author of the study and expert in metabolism at Rutgers University in New Brunswick, N.J., said in The Guardian.
For the research, 51 participants were divided into night owls and early birds, depending on their answers to a questionnaire. They were examined, monitored for a week, and assessed while doing various activities. Those who woke up early tended to be more sensitive to insulin and burned off fat faster than those who woke up late, the researchers explained.
“Night owls are reported to have a higher risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease when compared with early birds,” Dr. Malin said. “A potential explanation is they become misaligned with their circadian rhythm for various reasons, but most notably among adults would be work.”
We all know that we may not be at our best when we throw off our internal clocks by going to sleep late and waking up early. Think about that next time you start another episode on Netflix at 2:57 a.m.
Mosquitoes, chemical cocktails, and glass sock beads
We all know that mosquitoes are annoying little disease vectors with a taste for human blood. One of the less-known things about mosquitoes is what attracts them to humans in the first place. It’s so less known that, until now, it was unknown. Oh sure, we knew that odor was involved, and that lactic acid was part of the odor equation, but what are the specific chemicals? Well, there’s carbon dioxide … and ammonia. Those were already known.
Ring Cardé, PhD, an entomologist at the University of California, Riverside, wasn’t convinced. “I suspected there was something undiscovered about the chemistry of odors luring the yellow fever mosquito. I wanted to nail down the exact blend,” he said in a statement from the university.
Dr. Cardé and his associates eventually figured out that the exact chemical cocktail attracting female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes was a combination of carbon dioxide plus two chemicals, 2-ketoglutaric acid and lactic acid. The odor from these chemicals enables mosquitoes to locate and land on their victim and “also encourages probing, the use of piercing mouthparts to find blood,” the university said.
This amazing destination of science is important, but we have to acknowledge the journey as well. To do that we turn to one of Dr. Cardé’s associates, Jan Bello, PhD, formerly of Cal-Riverside and now with insect pest control company Provivi. Turns out that 2-ketoglutaric acid is tricky stuff because the methods typically used to identify chemicals don’t work on it.
Dr. Bello employed a somewhat unorthodox chemical extraction method: He filled his socks with glass beads and walked around with the beads in his socks.
“Wearing the beads felt almost like a massage, like squeezing stress balls full of sand, but with your feet,” Dr. Bello said. “The most frustrating part of doing it for a long time is that they would get stuck in between your toes, so it would be uncomfortable after a while.”
We hate when science gets stuck between our toes, but we love it when scientists write their own punchlines.
The MS drugs are better down where it’s wetter, take it from me
The myth of the mermaid is one with hundreds, if not thousands, of years of history. The ancient Greeks had the mythological siren, while the Babylonians depicted kulullû (which were mermen – never let the Babylonians be known as noninclusive) in artwork as far back as 1600 BC. Cultures as far flung as Japan, southern Africa, and New Zealand have folkloric figures similar to the mermaid. It is most decidedly not a creation of western Europe, Hans Christian Andersen, or Disney.
With that mild rant out of the way, let’s move to Germany and a group of researchers from the University of Bonn, who have not created a mermaid. They did, however, add human genes to a zebrafish for research purposes, which feels uncomfortably close. Nothing better than unholy animal-human hybrids, right?
Stick with us here, because the researchers did have a good reason for their gene splicing. Zebrafish and humans both have the GPR17 receptor, which is highly active in nerve tissue. When GPR17 is overactivated, diseases such as multiple sclerosis can develop. Because the zebrafish has this receptor, which performs the same function in its body as in ours, it’s a prime candidate for replacement. Also, zebrafish larvae are transparent, which makes it very easy to observe a drug working.
That said, fish and humans are very far apart, genetically speaking. Big shock right there. But by replacing their GPR17 receptor with ours, the scientists have created a fish that we could test drug candidates on and be assured that they would also work on humans. Actually testing drugs for MS on these humanized zebrafish was beyond the scope of the study, but the researchers said that the new genes function normally in the fish larvae, making them a promising new avenue for MS drug development.
Can we all promise not to tell Disney that human DNA can be spliced into a fish without consequence? Otherwise, we’re just going to have to sit through another “Little Mermaid” adaptation in 30 years, this one in super live-action featuring actual, real-life mermaids. And we’re not ready for that level of man-made horror just yet.
Beware of the fly vomit
Picture this: You’re outside at a picnic or barbecue, loading a plate with food. In a brief moment of conversation a fly lands right on top of your sandwich. You shoo it away and think nothing more of it, eating the sandwich anyway. We’ve all been there.
A recent study is making us think again.
John Stoffolano, an entomology professor at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, claims that too much attention has been focused on pathogen transmission by the biting, blood-feeding flies when really we should be taking note of the nonbiting, or synanthropic, flies we live with, which may have a greater impact on the transmission of pathogens right in our own homes.
Sure, blood-feeding flies can spread pathogens directly, but house flies vomit every time they land on something. Think about that.
The fly that sneakily swooped into your house from a tear in your window screen has just been outside in the neighbor’s garbage or sitting on dog poop and now has who knows what filling its crop, the tank in their body that serves as “a place to store food before it makes its way into the digestive tract where it will get turned into energy for the fly,” Dr. Stoffolano explained in a written statement.
Did that fly land right on the baked potato you were prepping for dinner before you shooed it away? Guess what? Before flying off it emitted excess water that has pathogens from whatever was in its crop. We don’t want to say your potato might have dog poop on it, but you get the idea. The crop doesn’t have a ton of digestive enzymes that would help neutralize pathogens, so whatever that fly regurgitated before buzzing off is still around for you to ingest and there’s not much you can do about it.
More research needs to be done about flies, but at the very least this study should make you think twice before eating that baked potato after a fly has been there.
Metabolism a player in circadian rhythm section
Are you an early bird, or do you wake up and stare at your phone, wondering why you were up watching “The Crown” until 3 a.m.? Recent research suggests that people who wake up earlier tend to be more active during the day and burn more fat than those who sleep in. Fat builds up in the night owls, putting them at higher risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
The study gives physicians something to think about when assessing a patient’s risk factors. “This could help medical professionals consider another behavioral factor contributing to disease risk,” Steven Malin, PhD, lead author of the study and expert in metabolism at Rutgers University in New Brunswick, N.J., said in The Guardian.
For the research, 51 participants were divided into night owls and early birds, depending on their answers to a questionnaire. They were examined, monitored for a week, and assessed while doing various activities. Those who woke up early tended to be more sensitive to insulin and burned off fat faster than those who woke up late, the researchers explained.
“Night owls are reported to have a higher risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease when compared with early birds,” Dr. Malin said. “A potential explanation is they become misaligned with their circadian rhythm for various reasons, but most notably among adults would be work.”
We all know that we may not be at our best when we throw off our internal clocks by going to sleep late and waking up early. Think about that next time you start another episode on Netflix at 2:57 a.m.
Mosquitoes, chemical cocktails, and glass sock beads
We all know that mosquitoes are annoying little disease vectors with a taste for human blood. One of the less-known things about mosquitoes is what attracts them to humans in the first place. It’s so less known that, until now, it was unknown. Oh sure, we knew that odor was involved, and that lactic acid was part of the odor equation, but what are the specific chemicals? Well, there’s carbon dioxide … and ammonia. Those were already known.
Ring Cardé, PhD, an entomologist at the University of California, Riverside, wasn’t convinced. “I suspected there was something undiscovered about the chemistry of odors luring the yellow fever mosquito. I wanted to nail down the exact blend,” he said in a statement from the university.
Dr. Cardé and his associates eventually figured out that the exact chemical cocktail attracting female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes was a combination of carbon dioxide plus two chemicals, 2-ketoglutaric acid and lactic acid. The odor from these chemicals enables mosquitoes to locate and land on their victim and “also encourages probing, the use of piercing mouthparts to find blood,” the university said.
This amazing destination of science is important, but we have to acknowledge the journey as well. To do that we turn to one of Dr. Cardé’s associates, Jan Bello, PhD, formerly of Cal-Riverside and now with insect pest control company Provivi. Turns out that 2-ketoglutaric acid is tricky stuff because the methods typically used to identify chemicals don’t work on it.
Dr. Bello employed a somewhat unorthodox chemical extraction method: He filled his socks with glass beads and walked around with the beads in his socks.
“Wearing the beads felt almost like a massage, like squeezing stress balls full of sand, but with your feet,” Dr. Bello said. “The most frustrating part of doing it for a long time is that they would get stuck in between your toes, so it would be uncomfortable after a while.”
We hate when science gets stuck between our toes, but we love it when scientists write their own punchlines.
The MS drugs are better down where it’s wetter, take it from me
The myth of the mermaid is one with hundreds, if not thousands, of years of history. The ancient Greeks had the mythological siren, while the Babylonians depicted kulullû (which were mermen – never let the Babylonians be known as noninclusive) in artwork as far back as 1600 BC. Cultures as far flung as Japan, southern Africa, and New Zealand have folkloric figures similar to the mermaid. It is most decidedly not a creation of western Europe, Hans Christian Andersen, or Disney.
With that mild rant out of the way, let’s move to Germany and a group of researchers from the University of Bonn, who have not created a mermaid. They did, however, add human genes to a zebrafish for research purposes, which feels uncomfortably close. Nothing better than unholy animal-human hybrids, right?
Stick with us here, because the researchers did have a good reason for their gene splicing. Zebrafish and humans both have the GPR17 receptor, which is highly active in nerve tissue. When GPR17 is overactivated, diseases such as multiple sclerosis can develop. Because the zebrafish has this receptor, which performs the same function in its body as in ours, it’s a prime candidate for replacement. Also, zebrafish larvae are transparent, which makes it very easy to observe a drug working.
That said, fish and humans are very far apart, genetically speaking. Big shock right there. But by replacing their GPR17 receptor with ours, the scientists have created a fish that we could test drug candidates on and be assured that they would also work on humans. Actually testing drugs for MS on these humanized zebrafish was beyond the scope of the study, but the researchers said that the new genes function normally in the fish larvae, making them a promising new avenue for MS drug development.
Can we all promise not to tell Disney that human DNA can be spliced into a fish without consequence? Otherwise, we’re just going to have to sit through another “Little Mermaid” adaptation in 30 years, this one in super live-action featuring actual, real-life mermaids. And we’re not ready for that level of man-made horror just yet.
Beware of the fly vomit
Picture this: You’re outside at a picnic or barbecue, loading a plate with food. In a brief moment of conversation a fly lands right on top of your sandwich. You shoo it away and think nothing more of it, eating the sandwich anyway. We’ve all been there.
A recent study is making us think again.
John Stoffolano, an entomology professor at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, claims that too much attention has been focused on pathogen transmission by the biting, blood-feeding flies when really we should be taking note of the nonbiting, or synanthropic, flies we live with, which may have a greater impact on the transmission of pathogens right in our own homes.
Sure, blood-feeding flies can spread pathogens directly, but house flies vomit every time they land on something. Think about that.
The fly that sneakily swooped into your house from a tear in your window screen has just been outside in the neighbor’s garbage or sitting on dog poop and now has who knows what filling its crop, the tank in their body that serves as “a place to store food before it makes its way into the digestive tract where it will get turned into energy for the fly,” Dr. Stoffolano explained in a written statement.
Did that fly land right on the baked potato you were prepping for dinner before you shooed it away? Guess what? Before flying off it emitted excess water that has pathogens from whatever was in its crop. We don’t want to say your potato might have dog poop on it, but you get the idea. The crop doesn’t have a ton of digestive enzymes that would help neutralize pathogens, so whatever that fly regurgitated before buzzing off is still around for you to ingest and there’s not much you can do about it.
More research needs to be done about flies, but at the very least this study should make you think twice before eating that baked potato after a fly has been there.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases drop to lowest level since April
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.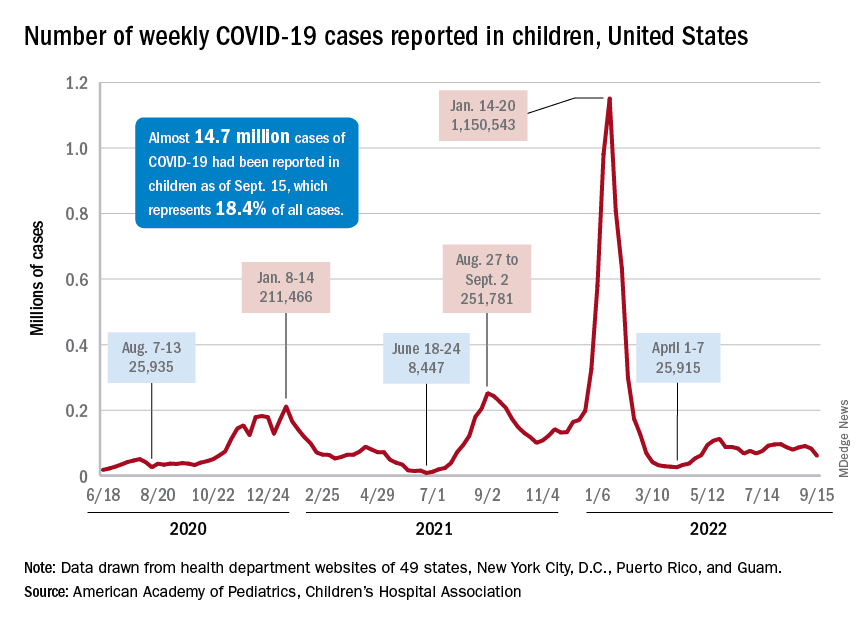
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.
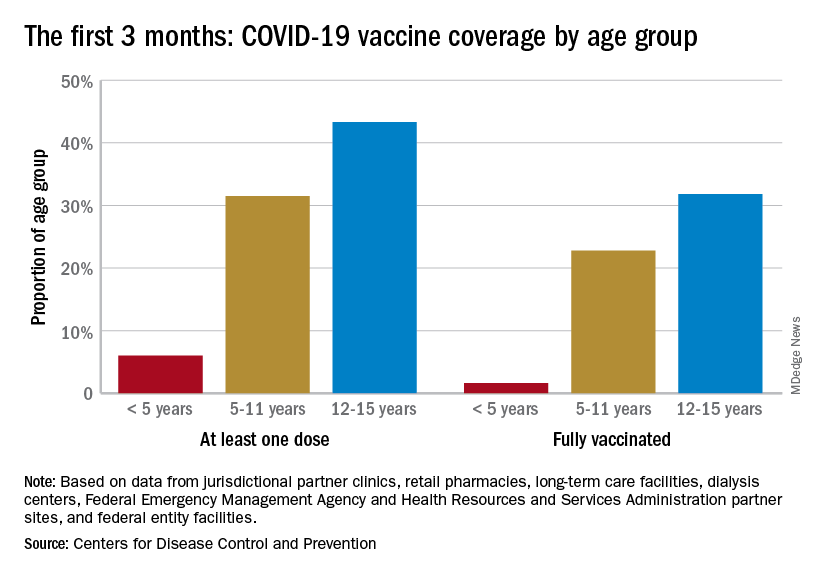
In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.

In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
A hefty decline in new COVID-19 cases among children resulted in the lowest weekly total since late April, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, making for 2 consecutive weeks of declines after almost 91,000 cases were recorded for the week ending Sept. 1, the AAP and CHA said in their latest COVID report of state-level data.
The last time the weekly count was under 60,000 came during the week of April 22-28, when 53,000 were reported by state and territorial health departments in the midst of a 7-week stretch of rising cases. Since that streak ended in mid-May, however, “reported weekly cases have plateaued, fluctuating between a low, now of 60,300 cases and a high of about 112,000,” the AAP noted.
Emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which showed less fluctuation over the summer and more steady rise and fall, have both dropped in recent weeks and are now approaching late May/early June rates, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
On Sept. 15, for example, ED visits for children under 12 years with diagnosed COVID were just 2.2% of all visits, lower than at any time since May 19 and down from a summer high of 6.8% in late July. Hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years also rose steadily through June and July, reaching 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30, but have since slipped to 0.29 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Vaccination continues to be a tough sell
Vaccination activity among the most recently eligible age group, in the meantime, remains tepid. Just 6.0% of children under age 5 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Sept. 13, about 3 months since its final approval in June, and 1.6% were fully vaccinated. For the two older groups of children with separate vaccine approvals, 31.5% of those aged 5-11 years and 43.3% of those aged 12-15 had received at least one dose 3 months after their vaccinations began, the CDC data show.

In the 2 weeks ending Sept. 14, almost 59,000 children under age 5 received their initial COVID-19 vaccine dose, as did 28,000 5- to 11-year-olds and 14,000 children aged 12-17. Children under age 5 years represented almost 20% of all Americans getting a first dose during Sept. 1-14, compared with 9.7% for those aged 5-11 and 4.8% for the 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
At the state level, children under age 5 years in the District of Columbia, where 28% have received at least one dose, and Vermont, at 24%, are the most likely to be vaccinated. The states with the lowest rates in this age group are Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, all of which are at 2%. Vermont and D.C. have the highest rates for ages 5-11 at 70% each, and Alabama (17%) is the lowest, while D.C. (100%), Rhode Island (99%), and Massachusetts (99%) are highest for children aged 12-17 years and Wyoming (41%) is the lowest, the AAP said in a separate report.
Home BP monitoring in older adults falls short of recommendations
Just over 51% of older hypertensive adults regularly check their own blood pressure, compared with 48% of those with blood pressure–related health conditions (BPHCs), based on a 2021 survey of individuals aged 50-80 years.
“Guidelines recommend that patients use self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SBPM) outside the clinic to diagnose and manage hypertension,” but just 61% of respondents with a BPHC and 68% of those with hypertension said that they had received such a recommendation from a physician, nurse, or other health care professional, Melanie V. Springer, MD, and associates said in JAMA Network Open.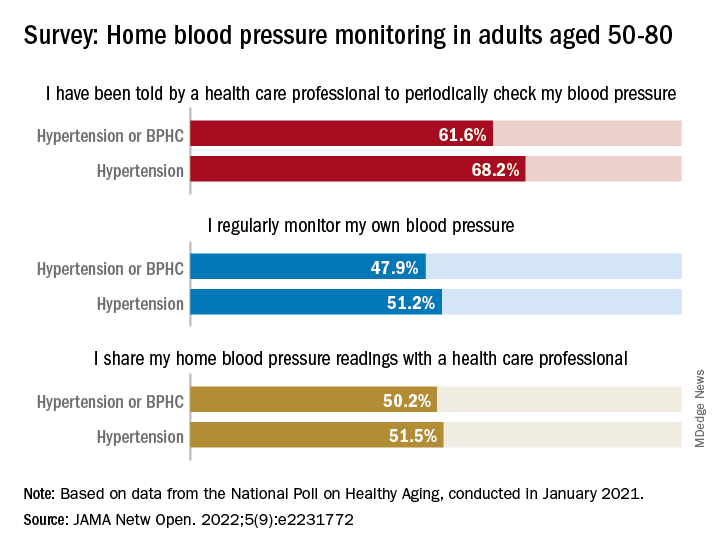
The prevalence of regular monitoring among those with hypertension, 51.2%, does, however, compare favorably with an earlier study showing that 43% of adults aged 18 and older regularly monitored their BP in 2005 and 2008, “which is perhaps associated with our sample’s older age,” said Dr. Springer and associates of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The current study, they noted, is the first to report “SBPM prevalence in adults ages 50 to 80 years with hypertension or BPHCs, who have a higher risk of adverse outcomes from uncontrolled BP than younger adults.” The analysis is based on data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, conducted by the University of Michigan in January 2021 and completed by 2,023 individuals.
The frequency of home monitoring varied among adults with BPHCs, as just under 15% reported daily checks and the largest proportion, about 28%, used their device one to three times per month. The results of home monitoring were shared with health care professionals by 50.2% of respondents with a BPHC and by 51.5% of those with hypertension, they said in the research letter.
Home monitoring’s less-than-universal recommendation by providers and use by patients “suggest that protocols should be developed to educate patients about the importance of SBPM and sharing readings with clinicians and the frequency that SBPM should be performed,” Dr. Springer and associates wrote.
The study was funded by AARP, Michigan Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. One investigator has received consulting fees or honoraria from SeeChange Health, HealthMine, the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, AbilTo, Kansas City Area Life Sciences Institute, American Diabetes Association, Donaghue Foundation, and Luxembourg National Research Fund.
Just over 51% of older hypertensive adults regularly check their own blood pressure, compared with 48% of those with blood pressure–related health conditions (BPHCs), based on a 2021 survey of individuals aged 50-80 years.
“Guidelines recommend that patients use self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SBPM) outside the clinic to diagnose and manage hypertension,” but just 61% of respondents with a BPHC and 68% of those with hypertension said that they had received such a recommendation from a physician, nurse, or other health care professional, Melanie V. Springer, MD, and associates said in JAMA Network Open.
The prevalence of regular monitoring among those with hypertension, 51.2%, does, however, compare favorably with an earlier study showing that 43% of adults aged 18 and older regularly monitored their BP in 2005 and 2008, “which is perhaps associated with our sample’s older age,” said Dr. Springer and associates of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The current study, they noted, is the first to report “SBPM prevalence in adults ages 50 to 80 years with hypertension or BPHCs, who have a higher risk of adverse outcomes from uncontrolled BP than younger adults.” The analysis is based on data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, conducted by the University of Michigan in January 2021 and completed by 2,023 individuals.
The frequency of home monitoring varied among adults with BPHCs, as just under 15% reported daily checks and the largest proportion, about 28%, used their device one to three times per month. The results of home monitoring were shared with health care professionals by 50.2% of respondents with a BPHC and by 51.5% of those with hypertension, they said in the research letter.
Home monitoring’s less-than-universal recommendation by providers and use by patients “suggest that protocols should be developed to educate patients about the importance of SBPM and sharing readings with clinicians and the frequency that SBPM should be performed,” Dr. Springer and associates wrote.
The study was funded by AARP, Michigan Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. One investigator has received consulting fees or honoraria from SeeChange Health, HealthMine, the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, AbilTo, Kansas City Area Life Sciences Institute, American Diabetes Association, Donaghue Foundation, and Luxembourg National Research Fund.
Just over 51% of older hypertensive adults regularly check their own blood pressure, compared with 48% of those with blood pressure–related health conditions (BPHCs), based on a 2021 survey of individuals aged 50-80 years.
“Guidelines recommend that patients use self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SBPM) outside the clinic to diagnose and manage hypertension,” but just 61% of respondents with a BPHC and 68% of those with hypertension said that they had received such a recommendation from a physician, nurse, or other health care professional, Melanie V. Springer, MD, and associates said in JAMA Network Open.
The prevalence of regular monitoring among those with hypertension, 51.2%, does, however, compare favorably with an earlier study showing that 43% of adults aged 18 and older regularly monitored their BP in 2005 and 2008, “which is perhaps associated with our sample’s older age,” said Dr. Springer and associates of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The current study, they noted, is the first to report “SBPM prevalence in adults ages 50 to 80 years with hypertension or BPHCs, who have a higher risk of adverse outcomes from uncontrolled BP than younger adults.” The analysis is based on data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, conducted by the University of Michigan in January 2021 and completed by 2,023 individuals.
The frequency of home monitoring varied among adults with BPHCs, as just under 15% reported daily checks and the largest proportion, about 28%, used their device one to three times per month. The results of home monitoring were shared with health care professionals by 50.2% of respondents with a BPHC and by 51.5% of those with hypertension, they said in the research letter.
Home monitoring’s less-than-universal recommendation by providers and use by patients “suggest that protocols should be developed to educate patients about the importance of SBPM and sharing readings with clinicians and the frequency that SBPM should be performed,” Dr. Springer and associates wrote.
The study was funded by AARP, Michigan Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. One investigator has received consulting fees or honoraria from SeeChange Health, HealthMine, the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, AbilTo, Kansas City Area Life Sciences Institute, American Diabetes Association, Donaghue Foundation, and Luxembourg National Research Fund.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
‘Dr. Caveman’ had a leg up on amputation
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
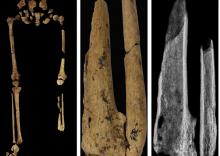
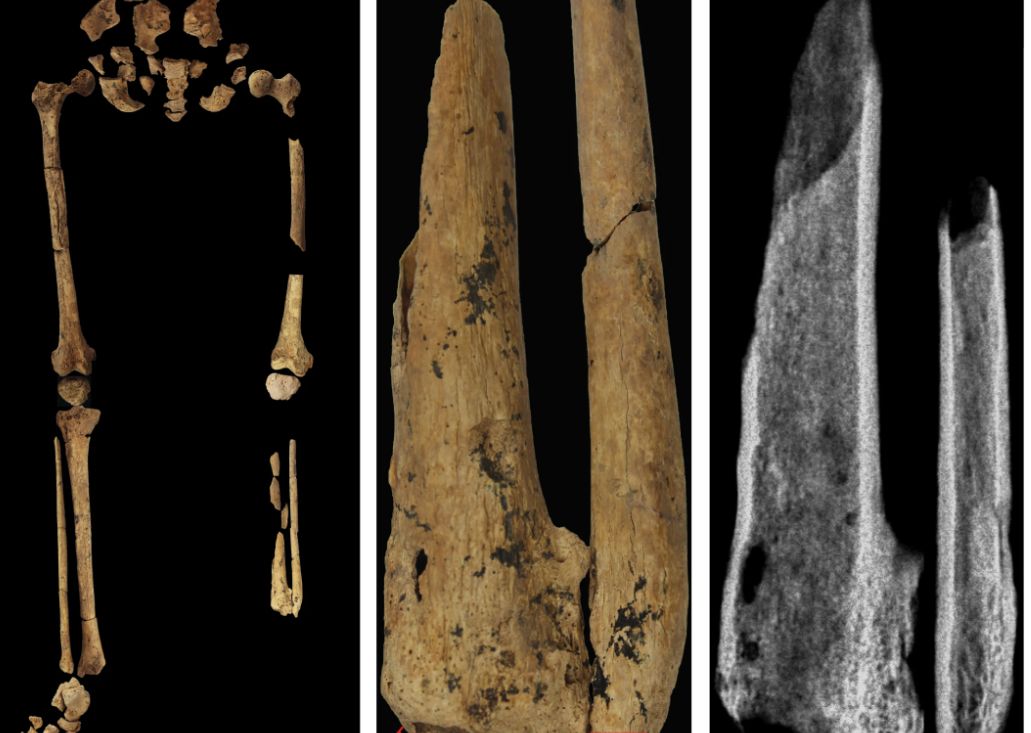
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
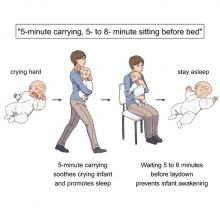
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Children and COVID: New cases took a downturn in September
After 2 weeks of increases in the number of new COVID-19 cases in children – a trend that just happened to coincide with the start of a new school year – there were fewer cases reported during the first full week of September, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report, noting also that seven states and the District of Columbia no longer update their online dashboards while others publish new data less often than every week.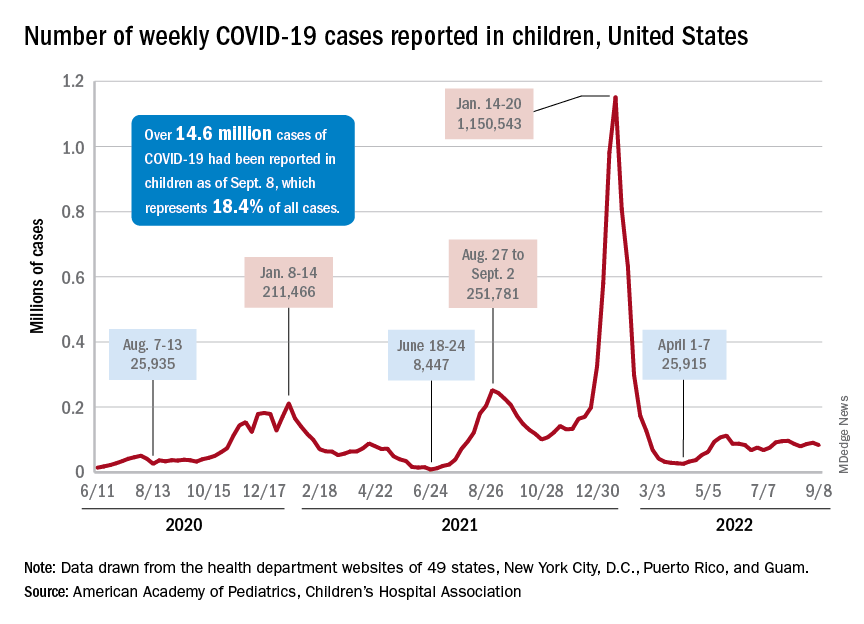
The drop in new cases was accompanied by declines in emergency department visits and hospital admissions, both of which had shown some signs of resurgence in mid- to late August. The brief rise in ED visits seemed to be age-related, occurring in those aged 12 years and older but not in younger children, whose ED visit rate fell steadily through August. Through the first week of September, however, 7-day averages were down for both those aged 12-15 and for 16- to 17-year-olds, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The rate of new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID-19, available only for ages 0-17 years, has declined every day since Aug. 28, when it reached 0.44 per 100,000 population after a week of climbing, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulatively, about 156,000 children were hospitalized with COVID from Aug. 1, 2020 to Sept. 10, 2022, according to the CDC, which puts the total number of pediatric cases at just over 15 million and deaths at 1,778. Those last two figures represent 17.4% and about 0.4% of all U.S. cases and deaths. The AAP and CHA estimate that about 14.6 million child cases have been reported so far, which is 18.4% of cases in all ages.
Vaccinations are slowly adding up
On the prevention side of the health care system’s response to COVID, the CDC’s cumulative numbers looked like this as of Sept. 6:
- 1.1 million children under age 5 (about 5.8% of the age group) had received at least one dose of vaccine, and 280,000 (1.4%) were fully vaccinated.
- Almost 11 million (38.2%) children aged 5-11 had gotten one dose, and 8.9 million (31.1%) were fully vaccinated.
- 17.9 million (70.8%) children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose, and 15.3 million (60.5%) were fully vaccinated.
Over the 14 days ending Sept. 7, children aged 2-4 years made up the largest group (21.4%) of Americans getting their first vaccine doses, while those aged 5-11 years were the third largest age group at 16.7% of all vaccinees (25- to 49-year-olds were second). The situation was reversed for vaccine completion over the last 2 weeks: Those aged 5-11 were first at 24.7%, and the 2- to 4-year-olds were third at 16.7% (those aged 25-49 were second again), according to the COVID Data Tracker.
After 2 weeks of increases in the number of new COVID-19 cases in children – a trend that just happened to coincide with the start of a new school year – there were fewer cases reported during the first full week of September, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report, noting also that seven states and the District of Columbia no longer update their online dashboards while others publish new data less often than every week.
The drop in new cases was accompanied by declines in emergency department visits and hospital admissions, both of which had shown some signs of resurgence in mid- to late August. The brief rise in ED visits seemed to be age-related, occurring in those aged 12 years and older but not in younger children, whose ED visit rate fell steadily through August. Through the first week of September, however, 7-day averages were down for both those aged 12-15 and for 16- to 17-year-olds, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The rate of new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID-19, available only for ages 0-17 years, has declined every day since Aug. 28, when it reached 0.44 per 100,000 population after a week of climbing, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulatively, about 156,000 children were hospitalized with COVID from Aug. 1, 2020 to Sept. 10, 2022, according to the CDC, which puts the total number of pediatric cases at just over 15 million and deaths at 1,778. Those last two figures represent 17.4% and about 0.4% of all U.S. cases and deaths. The AAP and CHA estimate that about 14.6 million child cases have been reported so far, which is 18.4% of cases in all ages.
Vaccinations are slowly adding up
On the prevention side of the health care system’s response to COVID, the CDC’s cumulative numbers looked like this as of Sept. 6:
- 1.1 million children under age 5 (about 5.8% of the age group) had received at least one dose of vaccine, and 280,000 (1.4%) were fully vaccinated.
- Almost 11 million (38.2%) children aged 5-11 had gotten one dose, and 8.9 million (31.1%) were fully vaccinated.
- 17.9 million (70.8%) children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose, and 15.3 million (60.5%) were fully vaccinated.
Over the 14 days ending Sept. 7, children aged 2-4 years made up the largest group (21.4%) of Americans getting their first vaccine doses, while those aged 5-11 years were the third largest age group at 16.7% of all vaccinees (25- to 49-year-olds were second). The situation was reversed for vaccine completion over the last 2 weeks: Those aged 5-11 were first at 24.7%, and the 2- to 4-year-olds were third at 16.7% (those aged 25-49 were second again), according to the COVID Data Tracker.
After 2 weeks of increases in the number of new COVID-19 cases in children – a trend that just happened to coincide with the start of a new school year – there were fewer cases reported during the first full week of September, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report, noting also that seven states and the District of Columbia no longer update their online dashboards while others publish new data less often than every week.
The drop in new cases was accompanied by declines in emergency department visits and hospital admissions, both of which had shown some signs of resurgence in mid- to late August. The brief rise in ED visits seemed to be age-related, occurring in those aged 12 years and older but not in younger children, whose ED visit rate fell steadily through August. Through the first week of September, however, 7-day averages were down for both those aged 12-15 and for 16- to 17-year-olds, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The rate of new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID-19, available only for ages 0-17 years, has declined every day since Aug. 28, when it reached 0.44 per 100,000 population after a week of climbing, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulatively, about 156,000 children were hospitalized with COVID from Aug. 1, 2020 to Sept. 10, 2022, according to the CDC, which puts the total number of pediatric cases at just over 15 million and deaths at 1,778. Those last two figures represent 17.4% and about 0.4% of all U.S. cases and deaths. The AAP and CHA estimate that about 14.6 million child cases have been reported so far, which is 18.4% of cases in all ages.
Vaccinations are slowly adding up
On the prevention side of the health care system’s response to COVID, the CDC’s cumulative numbers looked like this as of Sept. 6:
- 1.1 million children under age 5 (about 5.8% of the age group) had received at least one dose of vaccine, and 280,000 (1.4%) were fully vaccinated.
- Almost 11 million (38.2%) children aged 5-11 had gotten one dose, and 8.9 million (31.1%) were fully vaccinated.
- 17.9 million (70.8%) children aged 12-17 had received at least one dose, and 15.3 million (60.5%) were fully vaccinated.
Over the 14 days ending Sept. 7, children aged 2-4 years made up the largest group (21.4%) of Americans getting their first vaccine doses, while those aged 5-11 years were the third largest age group at 16.7% of all vaccinees (25- to 49-year-olds were second). The situation was reversed for vaccine completion over the last 2 weeks: Those aged 5-11 were first at 24.7%, and the 2- to 4-year-olds were third at 16.7% (those aged 25-49 were second again), according to the COVID Data Tracker.
One fish, two fish, are good fish for you ... fish
Good news for pregnant women; bad news for fish
As soon as women find out they’re pregnant, doctors recommend they give up smoking, drinking, and eating certain types of fish. That last item may need to be reconsidered, since a recent study supports the idea that it doesn’t matter what type of fish pregnant women are eating, as long as they’re eating it.
Researchers collected data from two different studies that reviewed the mercury levels of mothers from Bristol, England, and the Seychelles, a island chain off East Africa where “fish consumption is high and prenatal mercury levels are 10 times higher than in the [United States],” they said in NeuroToxicology.
Those data showed that the mercury levels had no adverse effects on child development as long as the mother ate fish. The nutrients and vitamins in the fish – vitamin D, long-chain fatty acids, selenium, and iodine – provide protection against mercury. There’s also the already-known benefits to eyesight and intellectual abilities that have been associated with fish consumption.
This analysis goes starkly against the grain of what is commonly recommended to expectant mothers, which is to cut out fish altogether. The researchers suggested that governments should review and change those recommendations to focus on the benefits instead.
As long as women follow the researchers’ recommendation to eat “at least two portions of fish a week, one of which should be oily,” they may not have to lay off on the sushi after all.
We’ll show our gut worms the world
Never let it be said that mankind is not a generous species. Sure, we could maybe be kinder to our fellow human beings, maybe declare a little less war on each other, but for the past 50,000 years, we’ve been giving a free ride to millions upon millions to one of mankind’s closest companions: the whipworm.
This revelation into human kindness comes from Denmark, where researchers from Copenhagen conducted a genetic analysis of ancient preserved whipworm eggs found in old Viking and Norse settlements, some of which date back over 2,000 years. In normal conditions genetic material wouldn’t last very long, but these were Viking whipworms eggs with tiny little horned helmets, so the DNA within has remained unchanged. Or it may be the tough chitinous exterior of the eggs protecting the DNA from degrading, combined with their preservation in moist soil.
Once they had their Viking whipworm DNA, the researchers compared it with whipworm DNA from all over the world, tracing its history as it followed mankind from Africa. And it’s been a while: We brought whipworms with us during our initial migration into Asia and Europe over 50,000 years ago. When the Bering land bridge opened up and humanity moved into the Americas, the worms came as well.
This is all possible because the whipworm goes about its parasitic business quietly and cleverly. It mostly sits harmlessly in our digestive systems, producing thousands of eggs a day that get expelled through poop and picked up by another host (human or otherwise); whipworms only cause disease in those with compromised immune systems.
The researchers noted that their study, the first complete genetic analysis of the whipworm, could help combat the parasite, which to this day infects hundred of millions who don’t have access to modern medicine or sanitary conditions. Hopefully, though, the days of free rides will soon be over for the whipworm. After all, if we have to pay hundreds or thousands of dollars to visit other countries, it’s only fair that our parasites do as well.
From zero to vasectomy in 6.7 seconds
There’s an old saying that you’ve probably heard: When life gives you lemons, make lemonade. It’s meant to encourage optimism in the face of adversity. Then there’s the new saying we just made up: When life gives you a power outage, plug your surgical instruments into an electric pickup.
That’s what Dr. Christopher Yang did, and now we’re making the urologist from Austin, Tex., famous by sharing his surgical/electrical adventure with all 17 of LOTME’s regular readers. That’s some serious lemonade.
Dr. Yang’s tale begins when the electricity went out at his clinic, seemingly forcing him to cancel or reschedule several surgical procedures. Not so fast. Dr. Yang happens to own a Rivian R1T, an electric pickup truck that has four power outlets. A staff member suggested plugging the surgical instruments into the truck and, surprisingly, one of the day’s patients agreed to go ahead with his vasectomy.
“We were fortunate that my normal parking spot is close enough to a patient room to run an extension cord,” Dr. Yang said on TheDrive.com. That extension cord was attached to an electrocautery device, with a handheld device available as backup, and “after we were done, I told his family. We all had a good laugh together too,” Dr. Yang told radio station WGLT in Normal, Ill.
To us, anyway, this opens up all sorts of alternative energy possibilities. Can a windmill power a liposuction? Is a gerbil running in a wheel enough to do a colonoscopy? How many potatoes do you need to keep an EHR going?
Learning through random acts of not-exactly noisiness
First things first. Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) is not really noise in the auditory sense of the word. For some people with learning disabilities, though, it can actually be very helpful. The technology, which uses electrodes attached to the head so a weak current can pass through specific parts of the brain, may help those with learning disabilities, perhaps even those with brain injuries and visual deficits, learn, said Dr. Onno van der Groen of Edith Cowan University in Perth, Australia.
“When you add this type of stimulation during learning, you get better performance, faster learning and better attention afterwards as well,” he said in a statement from the university.
The researchers say that tRNS can allow the brain to form new connections and pathways, which in turn help a person learn more effectively. “If you do 10 sessions of a visual perception task with the tRNS and then come back and do it again without it, you’ll find you perform better than the control group who hasn’t used it,” Dr. van der Groen noted.
Can this also work for the average person? It’s possible, but tRNS didn’t seem to improve the math skills of a top-level mathematician who underwent the process, according to a case study that Dr. van der Groen mentioned.
This line of work is still pretty new, though, so researchers don’t have all the answers yet. As always, we’re rooting for you, science!
Good news for pregnant women; bad news for fish
As soon as women find out they’re pregnant, doctors recommend they give up smoking, drinking, and eating certain types of fish. That last item may need to be reconsidered, since a recent study supports the idea that it doesn’t matter what type of fish pregnant women are eating, as long as they’re eating it.
Researchers collected data from two different studies that reviewed the mercury levels of mothers from Bristol, England, and the Seychelles, a island chain off East Africa where “fish consumption is high and prenatal mercury levels are 10 times higher than in the [United States],” they said in NeuroToxicology.
Those data showed that the mercury levels had no adverse effects on child development as long as the mother ate fish. The nutrients and vitamins in the fish – vitamin D, long-chain fatty acids, selenium, and iodine – provide protection against mercury. There’s also the already-known benefits to eyesight and intellectual abilities that have been associated with fish consumption.
This analysis goes starkly against the grain of what is commonly recommended to expectant mothers, which is to cut out fish altogether. The researchers suggested that governments should review and change those recommendations to focus on the benefits instead.
As long as women follow the researchers’ recommendation to eat “at least two portions of fish a week, one of which should be oily,” they may not have to lay off on the sushi after all.
We’ll show our gut worms the world
Never let it be said that mankind is not a generous species. Sure, we could maybe be kinder to our fellow human beings, maybe declare a little less war on each other, but for the past 50,000 years, we’ve been giving a free ride to millions upon millions to one of mankind’s closest companions: the whipworm.
This revelation into human kindness comes from Denmark, where researchers from Copenhagen conducted a genetic analysis of ancient preserved whipworm eggs found in old Viking and Norse settlements, some of which date back over 2,000 years. In normal conditions genetic material wouldn’t last very long, but these were Viking whipworms eggs with tiny little horned helmets, so the DNA within has remained unchanged. Or it may be the tough chitinous exterior of the eggs protecting the DNA from degrading, combined with their preservation in moist soil.
Once they had their Viking whipworm DNA, the researchers compared it with whipworm DNA from all over the world, tracing its history as it followed mankind from Africa. And it’s been a while: We brought whipworms with us during our initial migration into Asia and Europe over 50,000 years ago. When the Bering land bridge opened up and humanity moved into the Americas, the worms came as well.
This is all possible because the whipworm goes about its parasitic business quietly and cleverly. It mostly sits harmlessly in our digestive systems, producing thousands of eggs a day that get expelled through poop and picked up by another host (human or otherwise); whipworms only cause disease in those with compromised immune systems.
The researchers noted that their study, the first complete genetic analysis of the whipworm, could help combat the parasite, which to this day infects hundred of millions who don’t have access to modern medicine or sanitary conditions. Hopefully, though, the days of free rides will soon be over for the whipworm. After all, if we have to pay hundreds or thousands of dollars to visit other countries, it’s only fair that our parasites do as well.
From zero to vasectomy in 6.7 seconds
There’s an old saying that you’ve probably heard: When life gives you lemons, make lemonade. It’s meant to encourage optimism in the face of adversity. Then there’s the new saying we just made up: When life gives you a power outage, plug your surgical instruments into an electric pickup.
That’s what Dr. Christopher Yang did, and now we’re making the urologist from Austin, Tex., famous by sharing his surgical/electrical adventure with all 17 of LOTME’s regular readers. That’s some serious lemonade.
Dr. Yang’s tale begins when the electricity went out at his clinic, seemingly forcing him to cancel or reschedule several surgical procedures. Not so fast. Dr. Yang happens to own a Rivian R1T, an electric pickup truck that has four power outlets. A staff member suggested plugging the surgical instruments into the truck and, surprisingly, one of the day’s patients agreed to go ahead with his vasectomy.
“We were fortunate that my normal parking spot is close enough to a patient room to run an extension cord,” Dr. Yang said on TheDrive.com. That extension cord was attached to an electrocautery device, with a handheld device available as backup, and “after we were done, I told his family. We all had a good laugh together too,” Dr. Yang told radio station WGLT in Normal, Ill.
To us, anyway, this opens up all sorts of alternative energy possibilities. Can a windmill power a liposuction? Is a gerbil running in a wheel enough to do a colonoscopy? How many potatoes do you need to keep an EHR going?
Learning through random acts of not-exactly noisiness
First things first. Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) is not really noise in the auditory sense of the word. For some people with learning disabilities, though, it can actually be very helpful. The technology, which uses electrodes attached to the head so a weak current can pass through specific parts of the brain, may help those with learning disabilities, perhaps even those with brain injuries and visual deficits, learn, said Dr. Onno van der Groen of Edith Cowan University in Perth, Australia.
“When you add this type of stimulation during learning, you get better performance, faster learning and better attention afterwards as well,” he said in a statement from the university.
The researchers say that tRNS can allow the brain to form new connections and pathways, which in turn help a person learn more effectively. “If you do 10 sessions of a visual perception task with the tRNS and then come back and do it again without it, you’ll find you perform better than the control group who hasn’t used it,” Dr. van der Groen noted.
Can this also work for the average person? It’s possible, but tRNS didn’t seem to improve the math skills of a top-level mathematician who underwent the process, according to a case study that Dr. van der Groen mentioned.
This line of work is still pretty new, though, so researchers don’t have all the answers yet. As always, we’re rooting for you, science!
Good news for pregnant women; bad news for fish
As soon as women find out they’re pregnant, doctors recommend they give up smoking, drinking, and eating certain types of fish. That last item may need to be reconsidered, since a recent study supports the idea that it doesn’t matter what type of fish pregnant women are eating, as long as they’re eating it.
Researchers collected data from two different studies that reviewed the mercury levels of mothers from Bristol, England, and the Seychelles, a island chain off East Africa where “fish consumption is high and prenatal mercury levels are 10 times higher than in the [United States],” they said in NeuroToxicology.
Those data showed that the mercury levels had no adverse effects on child development as long as the mother ate fish. The nutrients and vitamins in the fish – vitamin D, long-chain fatty acids, selenium, and iodine – provide protection against mercury. There’s also the already-known benefits to eyesight and intellectual abilities that have been associated with fish consumption.
This analysis goes starkly against the grain of what is commonly recommended to expectant mothers, which is to cut out fish altogether. The researchers suggested that governments should review and change those recommendations to focus on the benefits instead.
As long as women follow the researchers’ recommendation to eat “at least two portions of fish a week, one of which should be oily,” they may not have to lay off on the sushi after all.
We’ll show our gut worms the world
Never let it be said that mankind is not a generous species. Sure, we could maybe be kinder to our fellow human beings, maybe declare a little less war on each other, but for the past 50,000 years, we’ve been giving a free ride to millions upon millions to one of mankind’s closest companions: the whipworm.
This revelation into human kindness comes from Denmark, where researchers from Copenhagen conducted a genetic analysis of ancient preserved whipworm eggs found in old Viking and Norse settlements, some of which date back over 2,000 years. In normal conditions genetic material wouldn’t last very long, but these were Viking whipworms eggs with tiny little horned helmets, so the DNA within has remained unchanged. Or it may be the tough chitinous exterior of the eggs protecting the DNA from degrading, combined with their preservation in moist soil.
Once they had their Viking whipworm DNA, the researchers compared it with whipworm DNA from all over the world, tracing its history as it followed mankind from Africa. And it’s been a while: We brought whipworms with us during our initial migration into Asia and Europe over 50,000 years ago. When the Bering land bridge opened up and humanity moved into the Americas, the worms came as well.
This is all possible because the whipworm goes about its parasitic business quietly and cleverly. It mostly sits harmlessly in our digestive systems, producing thousands of eggs a day that get expelled through poop and picked up by another host (human or otherwise); whipworms only cause disease in those with compromised immune systems.
The researchers noted that their study, the first complete genetic analysis of the whipworm, could help combat the parasite, which to this day infects hundred of millions who don’t have access to modern medicine or sanitary conditions. Hopefully, though, the days of free rides will soon be over for the whipworm. After all, if we have to pay hundreds or thousands of dollars to visit other countries, it’s only fair that our parasites do as well.
From zero to vasectomy in 6.7 seconds
There’s an old saying that you’ve probably heard: When life gives you lemons, make lemonade. It’s meant to encourage optimism in the face of adversity. Then there’s the new saying we just made up: When life gives you a power outage, plug your surgical instruments into an electric pickup.
That’s what Dr. Christopher Yang did, and now we’re making the urologist from Austin, Tex., famous by sharing his surgical/electrical adventure with all 17 of LOTME’s regular readers. That’s some serious lemonade.
Dr. Yang’s tale begins when the electricity went out at his clinic, seemingly forcing him to cancel or reschedule several surgical procedures. Not so fast. Dr. Yang happens to own a Rivian R1T, an electric pickup truck that has four power outlets. A staff member suggested plugging the surgical instruments into the truck and, surprisingly, one of the day’s patients agreed to go ahead with his vasectomy.
“We were fortunate that my normal parking spot is close enough to a patient room to run an extension cord,” Dr. Yang said on TheDrive.com. That extension cord was attached to an electrocautery device, with a handheld device available as backup, and “after we were done, I told his family. We all had a good laugh together too,” Dr. Yang told radio station WGLT in Normal, Ill.
To us, anyway, this opens up all sorts of alternative energy possibilities. Can a windmill power a liposuction? Is a gerbil running in a wheel enough to do a colonoscopy? How many potatoes do you need to keep an EHR going?
Learning through random acts of not-exactly noisiness
First things first. Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) is not really noise in the auditory sense of the word. For some people with learning disabilities, though, it can actually be very helpful. The technology, which uses electrodes attached to the head so a weak current can pass through specific parts of the brain, may help those with learning disabilities, perhaps even those with brain injuries and visual deficits, learn, said Dr. Onno van der Groen of Edith Cowan University in Perth, Australia.
“When you add this type of stimulation during learning, you get better performance, faster learning and better attention afterwards as well,” he said in a statement from the university.
The researchers say that tRNS can allow the brain to form new connections and pathways, which in turn help a person learn more effectively. “If you do 10 sessions of a visual perception task with the tRNS and then come back and do it again without it, you’ll find you perform better than the control group who hasn’t used it,” Dr. van der Groen noted.
Can this also work for the average person? It’s possible, but tRNS didn’t seem to improve the math skills of a top-level mathematician who underwent the process, according to a case study that Dr. van der Groen mentioned.
This line of work is still pretty new, though, so researchers don’t have all the answers yet. As always, we’re rooting for you, science!
Children and COVID: Weekly cases close out August with a second straight increase
New cases rose by 4.6% for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, following a week in which cases increased by almost 9%, as the second half of August basically reversed the two consecutive weeks of decreases during the first half of the month, based on the AAP/CHA data collected from state and territorial health departments.
Similar trends can be seen for emergency department visits, with the exception of children aged 0-11 years, whose ED visit rates have continued to fall since late July. Children aged 12-15, however, had a 7-day average of 4.4% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID on Aug. 25, compared with 3.1% for Aug. 12. Children aged 16-17 years were at 3.4% on Aug. 27, compared with 3.1% as late as Aug. 15, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Hospital admissions with confirmed COVID-19, reported only for children aged 0-17 years, also reflect the late-August trend of increased cases. New hospitalizations dropped from 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30 to 0.40 per 100,000 on Aug. 19 but have since risen to 0.44 per 100,000 as of Aug. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Initial vaccinations, meanwhile, have declined since early August for all children, according to a separate report from the AAP. A look at CDC data for two specific days – the first and last Mondays of the month – shows that those aged under 5 received 12,982 doses on Aug. 1, compared with 5,824 doses on Aug. 29. Over that same time, initial vaccinations in 5- to 11-year-olds went from 9,058 to 2,879, while among those aged 12-17 they dropped from 4,245 to 1,226.
Cumulatively, 5.5% of all children under age 5 had received at least one dose and 1.3% were fully vaccinated by Aug. 30, compared with 38.1% and 30.7%, respectively, of those aged 5-11 and 70.7% and 60.5% of 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
New cases rose by 4.6% for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, following a week in which cases increased by almost 9%, as the second half of August basically reversed the two consecutive weeks of decreases during the first half of the month, based on the AAP/CHA data collected from state and territorial health departments.
Similar trends can be seen for emergency department visits, with the exception of children aged 0-11 years, whose ED visit rates have continued to fall since late July. Children aged 12-15, however, had a 7-day average of 4.4% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID on Aug. 25, compared with 3.1% for Aug. 12. Children aged 16-17 years were at 3.4% on Aug. 27, compared with 3.1% as late as Aug. 15, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Hospital admissions with confirmed COVID-19, reported only for children aged 0-17 years, also reflect the late-August trend of increased cases. New hospitalizations dropped from 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30 to 0.40 per 100,000 on Aug. 19 but have since risen to 0.44 per 100,000 as of Aug. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Initial vaccinations, meanwhile, have declined since early August for all children, according to a separate report from the AAP. A look at CDC data for two specific days – the first and last Mondays of the month – shows that those aged under 5 received 12,982 doses on Aug. 1, compared with 5,824 doses on Aug. 29. Over that same time, initial vaccinations in 5- to 11-year-olds went from 9,058 to 2,879, while among those aged 12-17 they dropped from 4,245 to 1,226.
Cumulatively, 5.5% of all children under age 5 had received at least one dose and 1.3% were fully vaccinated by Aug. 30, compared with 38.1% and 30.7%, respectively, of those aged 5-11 and 70.7% and 60.5% of 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
New cases rose by 4.6% for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, following a week in which cases increased by almost 9%, as the second half of August basically reversed the two consecutive weeks of decreases during the first half of the month, based on the AAP/CHA data collected from state and territorial health departments.
Similar trends can be seen for emergency department visits, with the exception of children aged 0-11 years, whose ED visit rates have continued to fall since late July. Children aged 12-15, however, had a 7-day average of 4.4% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID on Aug. 25, compared with 3.1% for Aug. 12. Children aged 16-17 years were at 3.4% on Aug. 27, compared with 3.1% as late as Aug. 15, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
Hospital admissions with confirmed COVID-19, reported only for children aged 0-17 years, also reflect the late-August trend of increased cases. New hospitalizations dropped from 0.46 per 100,000 population on July 30 to 0.40 per 100,000 on Aug. 19 but have since risen to 0.44 per 100,000 as of Aug. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Initial vaccinations, meanwhile, have declined since early August for all children, according to a separate report from the AAP. A look at CDC data for two specific days – the first and last Mondays of the month – shows that those aged under 5 received 12,982 doses on Aug. 1, compared with 5,824 doses on Aug. 29. Over that same time, initial vaccinations in 5- to 11-year-olds went from 9,058 to 2,879, while among those aged 12-17 they dropped from 4,245 to 1,226.
Cumulatively, 5.5% of all children under age 5 had received at least one dose and 1.3% were fully vaccinated by Aug. 30, compared with 38.1% and 30.7%, respectively, of those aged 5-11 and 70.7% and 60.5% of 12- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said.
Real medical news: Many teens trust fake medical news
The kids aren’t alright (at identifying fake news online)
If there’s one thing today’s teenagers are good at, it’s the Internet. What with their TokTiks, Fortnights, and memes whose lifespans are measured in milliseconds, it’s only natural that a contingent of people who have never known a world where the Internet wasn’t omnipresent would be highly skilled at navigating the dense, labyrinthine virtual world and the many falsehoods contained within.
Ladies and gentlemen, we’ve been duped, bamboozled, and smeckledorfed. New research from Slovakia suggests the opposite, in fact: Teenagers are just as bad as the rest of us, if not worse, at distinguishing between fake and real online health messaging.
For the study, 300 teenagers aged 16-19 years old were shown a group of messages about the health-promoting effects of fruits and vegetables; these messages were either false, true and neutral, or true with some sort of editing (a clickbait title or grammar mistakes) to mask their trustworthiness. Just under half of the subjects identified and trusted the true neutral messages over fake messages, while 41% couldn’t tell the difference and 11% trusted the fake messages more. In addition, they couldn’t tell the difference between fake and true messages when the content seemed plausible.
In a bit of good news, teenagers were just as likely to trust the edited true messages as the true neutral ones, except in instances when the edited message had a clickbait title. They were much less likely to trust those.
Based on their subjects’ rather poor performance, the study authors suggested teenagers go through health literacy and media literacy training, as well as develop their analytical and scientific reasoning. The LOTME staff rather suspects the study authors have never met a teenager. The only thing teenagers are going to get out of health literacy training is fodder for memes to put up on Myspace. Myspace is still a thing, right? We’re not old, we swear.
Can a computer help deliver babies?
Delivering babies can be a complicated business. Most doctors and midwives rely on their years of experience and training to make certain decisions for mothers in labor, but an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm could make the entire process easier and safer.
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic recently reported that using an AI to analyze women’s labor patterns was very successful in determining whether a vaginal or cesarean delivery was appropriate.
They examined over 700 factors and over 66,000 deliveries from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development’s multicenter Consortium on Safe Labor database to produce a risk-prediction model that may “provide an alternative to conventional labor charts and promote individualization of clinical decisions using baseline and labor characteristics of each patient,” they said in a written statement from the clinic.
It is hoped that the AI will reduce the risk of possible complications and the costs associated with maternal mortality. The AI also could be a significant tool for doctors and midwives in rural areas to determine when a patient needs to be moved to a location with a higher level of care.
“We believe the algorithm will work in real time, meaning every input of new data during an expectant woman’s labor automatically recalculates the risk of adverse outcome,” said senior author Abimbola Famuyide, MD, of the Mayo Clinic.
If it all works out, many lives and dollars could be saved, thanks to science.
Democracy, meet COVID-19
Everywhere you look, it seems, someone is trying to keep someone else from doing something: Don’t carry a gun. Don’t get an abortion. Don’t drive so fast. Don’t inhale that whipped cream. Don’t get a vaccine. Don’t put that in your mouth.
One of the biggies these days is voting rights. Some people are trying to prevent other people from voting. But why? Well, turns out that turnout can be bad for your health … at least during a worldwide pandemic event.
The evidence for that claim comes from researchers who examined the Italian national constitutional referendum conducted in September 2020 along with elections for assembly representatives in 7 of the country’s 20 regions and for mayors in about 12% of municipalities. The combination mattered: Voter turnout was higher in the municipalities that voted for both the referendum and local elections (69%), compared with municipalities voting only for the referendum (47%), the investigators reported in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Also occurring in September of 2020 was, as we mentioned, a worldwide pandemic event. You may have heard about it.
The investigators considered the differences in election turnout between the various municipalities and compared them with new weekly COVID-19 infections at the municipality level. “Our model shows that something as fundamental as casting a vote can come at a cost,” investigator Giuseppe Moscelli, PhD, of the University of Surrey (England) said in a written statement.
What was the cost? Each 1% increase in turnout, they found, amounted to an average 1.1% increase in COVID infections after the elections.
See? More people voting means more COVID, which is bad. Which brings us to today’s lesson in people preventing other people from doing something. Don’t let COVID win. Stay in your house and never come out. And get that smeckledorf out of your mouth. You don’t know where it’s been.
The kids aren’t alright (at identifying fake news online)
If there’s one thing today’s teenagers are good at, it’s the Internet. What with their TokTiks, Fortnights, and memes whose lifespans are measured in milliseconds, it’s only natural that a contingent of people who have never known a world where the Internet wasn’t omnipresent would be highly skilled at navigating the dense, labyrinthine virtual world and the many falsehoods contained within.
Ladies and gentlemen, we’ve been duped, bamboozled, and smeckledorfed. New research from Slovakia suggests the opposite, in fact: Teenagers are just as bad as the rest of us, if not worse, at distinguishing between fake and real online health messaging.
For the study, 300 teenagers aged 16-19 years old were shown a group of messages about the health-promoting effects of fruits and vegetables; these messages were either false, true and neutral, or true with some sort of editing (a clickbait title or grammar mistakes) to mask their trustworthiness. Just under half of the subjects identified and trusted the true neutral messages over fake messages, while 41% couldn’t tell the difference and 11% trusted the fake messages more. In addition, they couldn’t tell the difference between fake and true messages when the content seemed plausible.
In a bit of good news, teenagers were just as likely to trust the edited true messages as the true neutral ones, except in instances when the edited message had a clickbait title. They were much less likely to trust those.
Based on their subjects’ rather poor performance, the study authors suggested teenagers go through health literacy and media literacy training, as well as develop their analytical and scientific reasoning. The LOTME staff rather suspects the study authors have never met a teenager. The only thing teenagers are going to get out of health literacy training is fodder for memes to put up on Myspace. Myspace is still a thing, right? We’re not old, we swear.
Can a computer help deliver babies?
Delivering babies can be a complicated business. Most doctors and midwives rely on their years of experience and training to make certain decisions for mothers in labor, but an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm could make the entire process easier and safer.
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic recently reported that using an AI to analyze women’s labor patterns was very successful in determining whether a vaginal or cesarean delivery was appropriate.
They examined over 700 factors and over 66,000 deliveries from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development’s multicenter Consortium on Safe Labor database to produce a risk-prediction model that may “provide an alternative to conventional labor charts and promote individualization of clinical decisions using baseline and labor characteristics of each patient,” they said in a written statement from the clinic.
It is hoped that the AI will reduce the risk of possible complications and the costs associated with maternal mortality. The AI also could be a significant tool for doctors and midwives in rural areas to determine when a patient needs to be moved to a location with a higher level of care.
“We believe the algorithm will work in real time, meaning every input of new data during an expectant woman’s labor automatically recalculates the risk of adverse outcome,” said senior author Abimbola Famuyide, MD, of the Mayo Clinic.
If it all works out, many lives and dollars could be saved, thanks to science.
Democracy, meet COVID-19
Everywhere you look, it seems, someone is trying to keep someone else from doing something: Don’t carry a gun. Don’t get an abortion. Don’t drive so fast. Don’t inhale that whipped cream. Don’t get a vaccine. Don’t put that in your mouth.
One of the biggies these days is voting rights. Some people are trying to prevent other people from voting. But why? Well, turns out that turnout can be bad for your health … at least during a worldwide pandemic event.
The evidence for that claim comes from researchers who examined the Italian national constitutional referendum conducted in September 2020 along with elections for assembly representatives in 7 of the country’s 20 regions and for mayors in about 12% of municipalities. The combination mattered: Voter turnout was higher in the municipalities that voted for both the referendum and local elections (69%), compared with municipalities voting only for the referendum (47%), the investigators reported in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Also occurring in September of 2020 was, as we mentioned, a worldwide pandemic event. You may have heard about it.
The investigators considered the differences in election turnout between the various municipalities and compared them with new weekly COVID-19 infections at the municipality level. “Our model shows that something as fundamental as casting a vote can come at a cost,” investigator Giuseppe Moscelli, PhD, of the University of Surrey (England) said in a written statement.
What was the cost? Each 1% increase in turnout, they found, amounted to an average 1.1% increase in COVID infections after the elections.
See? More people voting means more COVID, which is bad. Which brings us to today’s lesson in people preventing other people from doing something. Don’t let COVID win. Stay in your house and never come out. And get that smeckledorf out of your mouth. You don’t know where it’s been.
The kids aren’t alright (at identifying fake news online)
If there’s one thing today’s teenagers are good at, it’s the Internet. What with their TokTiks, Fortnights, and memes whose lifespans are measured in milliseconds, it’s only natural that a contingent of people who have never known a world where the Internet wasn’t omnipresent would be highly skilled at navigating the dense, labyrinthine virtual world and the many falsehoods contained within.
Ladies and gentlemen, we’ve been duped, bamboozled, and smeckledorfed. New research from Slovakia suggests the opposite, in fact: Teenagers are just as bad as the rest of us, if not worse, at distinguishing between fake and real online health messaging.
For the study, 300 teenagers aged 16-19 years old were shown a group of messages about the health-promoting effects of fruits and vegetables; these messages were either false, true and neutral, or true with some sort of editing (a clickbait title or grammar mistakes) to mask their trustworthiness. Just under half of the subjects identified and trusted the true neutral messages over fake messages, while 41% couldn’t tell the difference and 11% trusted the fake messages more. In addition, they couldn’t tell the difference between fake and true messages when the content seemed plausible.
In a bit of good news, teenagers were just as likely to trust the edited true messages as the true neutral ones, except in instances when the edited message had a clickbait title. They were much less likely to trust those.
Based on their subjects’ rather poor performance, the study authors suggested teenagers go through health literacy and media literacy training, as well as develop their analytical and scientific reasoning. The LOTME staff rather suspects the study authors have never met a teenager. The only thing teenagers are going to get out of health literacy training is fodder for memes to put up on Myspace. Myspace is still a thing, right? We’re not old, we swear.
Can a computer help deliver babies?
Delivering babies can be a complicated business. Most doctors and midwives rely on their years of experience and training to make certain decisions for mothers in labor, but an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm could make the entire process easier and safer.
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic recently reported that using an AI to analyze women’s labor patterns was very successful in determining whether a vaginal or cesarean delivery was appropriate.
They examined over 700 factors and over 66,000 deliveries from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development’s multicenter Consortium on Safe Labor database to produce a risk-prediction model that may “provide an alternative to conventional labor charts and promote individualization of clinical decisions using baseline and labor characteristics of each patient,” they said in a written statement from the clinic.
It is hoped that the AI will reduce the risk of possible complications and the costs associated with maternal mortality. The AI also could be a significant tool for doctors and midwives in rural areas to determine when a patient needs to be moved to a location with a higher level of care.
“We believe the algorithm will work in real time, meaning every input of new data during an expectant woman’s labor automatically recalculates the risk of adverse outcome,” said senior author Abimbola Famuyide, MD, of the Mayo Clinic.
If it all works out, many lives and dollars could be saved, thanks to science.
Democracy, meet COVID-19
Everywhere you look, it seems, someone is trying to keep someone else from doing something: Don’t carry a gun. Don’t get an abortion. Don’t drive so fast. Don’t inhale that whipped cream. Don’t get a vaccine. Don’t put that in your mouth.
One of the biggies these days is voting rights. Some people are trying to prevent other people from voting. But why? Well, turns out that turnout can be bad for your health … at least during a worldwide pandemic event.
The evidence for that claim comes from researchers who examined the Italian national constitutional referendum conducted in September 2020 along with elections for assembly representatives in 7 of the country’s 20 regions and for mayors in about 12% of municipalities. The combination mattered: Voter turnout was higher in the municipalities that voted for both the referendum and local elections (69%), compared with municipalities voting only for the referendum (47%), the investigators reported in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Also occurring in September of 2020 was, as we mentioned, a worldwide pandemic event. You may have heard about it.
The investigators considered the differences in election turnout between the various municipalities and compared them with new weekly COVID-19 infections at the municipality level. “Our model shows that something as fundamental as casting a vote can come at a cost,” investigator Giuseppe Moscelli, PhD, of the University of Surrey (England) said in a written statement.
What was the cost? Each 1% increase in turnout, they found, amounted to an average 1.1% increase in COVID infections after the elections.
See? More people voting means more COVID, which is bad. Which brings us to today’s lesson in people preventing other people from doing something. Don’t let COVID win. Stay in your house and never come out. And get that smeckledorf out of your mouth. You don’t know where it’s been.
Children and COVID: New cases increase; hospital admissions could follow
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.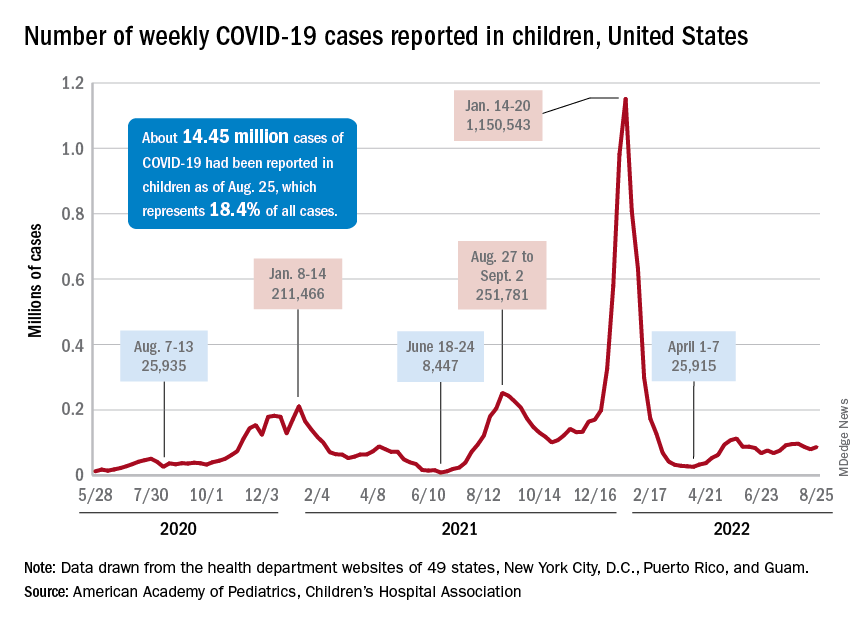
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.
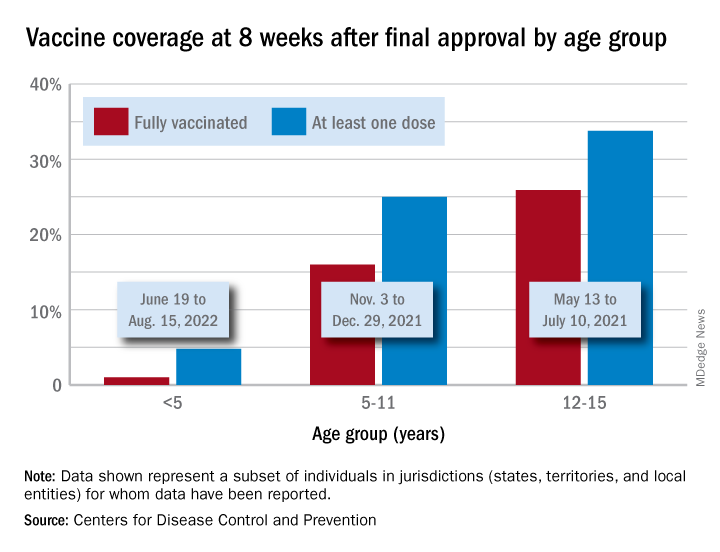
Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.

Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
New cases of COVID-19 in children were up again after 2 weeks of declines, and preliminary data suggest that hospitalizations may be on the rise as well.
, based on data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
A similar increase seems to be reflected by hospital-level data. The latest 7-day (Aug. 21-27) average is 305 new admissions with diagnosed COVID per day among children aged 0-17 years, compared with 290 per day for the week of Aug. 14-20, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported, while also noting the potential for reporting delays in the most recent 7-day period.
Daily hospital admissions for COVID had been headed downward through the first half of August, falling from 0.46 per 100,000 population at the end of July to 0.40 on Aug. 19, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Since then, however, admissions have gone the other way, with the preliminary nature of the latest data suggesting that the numbers will be even higher as more hospitals report over the next few days.
Vaccine initiations continue to fall
Initiations among school-age children have fallen for 3 consecutive weeks since Aug. 3, when numbers receiving their first vaccinations reached late-summer highs for those aged 5-11 and 12-17 years. Children under age 5, included in the CDC data for the first time on Aug. 11 as separate groups – under 2 years and 2-4 years – have had vaccine initiations drop by 8.0% and 19.8% over the 2 following weeks, the CDC said.

Through their first 8 weeks of vaccine eligibility (June 19 to Aug. 15), 4.8% of children under 5 years of age had received a first vaccination and 1.0% were fully vaccinated. For the two other age groups (5-11 and 12-15) who became eligible after the very first emergency authorization back in 2020, the respective proportions were 25.0% and 16.0% (5-11) and 33.8% and 26.1% (12-15) through the first 8 weeks, according to CDC data.
No fish can escape this net ... of COVID testing
Something about this COVID testing smells fishy
The Chinese have been challenging America’s political and economic hegemony (yes, we did have to look that one up – you’re rude to ask) for some time, but now they’ve gone too far. Are we going to just sit here and let China do something more ridiculous than us in response to COVID? No way!
Here’s the deal: The government of the Chinese coastal city of Xiamen has decided that it’s not just the workers on returning fishing boats who have the potential to introduce COVID to the rest of the population. The fish also present a problem. So when the authorities say that everyone needs to be tested before they can enter the city, they mean everyone.
An employee of the municipal ocean development bureau told local media that “all people in Xiamen City need nucleic acid testing, and the fish catches must be tested as well,” according to the Guardian, which also said that “TV news reports showed officials swabbing the mouths of fish and the underside of crabs.”
In the words of George Takei: “Oh my.”
Hold on there a second, George Takei, because we here in the good old US of A have still got Los Angeles, where COVID testing also has taken a nonhuman turn. The LA County public health department recently announced that pets are now eligible for a free SARS-CoV-2 test through veterinarians and other animal care facilities.
“Our goal is to test many different species of animals including wildlife (deer, bats, raccoons), pets (dogs, cats, hamsters, pocket pets), marine mammals (seals), and more,” Veterinary Public Health announced.
Hegemony restored.
Not even God could save them from worms
The Dark Ages may not have been as dark and violent as many people think, but there’s no denying that life in medieval Europe kind of sucked. The only real alternative to serfdom was a job with the Catholic Church. Medieval friars, for example, lived in stone buildings, had access to fresh fruits and vegetables, and even had latrines and running water. Luxuries compared with the life of the average peasant.
So why then, despite having access to more modern sanitation and amenities, did the friars have so many gut parasites? That’s the question raised by a group of researchers from the University of Cambridge, who conducted a study of 19 medieval friars buried at a local friary (Oh, doesn’t your town have one of those?) and 25 local people buried at a nonreligious cemetery during a similar time period. Of those 19 friars, 11 were infected with worms and parasites, compared with just 8 of 25 townspeople.
This doesn’t make a lot of sense. The friars had a good life by old-time standards: They had basic sanitation down and a solid diet. These things should lead to a healthier population. The problem, the researchers found, is two pronged and a vicious cycle. First off, the friars had plenty of fresh food, but they used human feces to fertilize their produce. There’s a reason modern practice for human waste fertilization is to let the waste compost for 6 months: The waiting period allows the parasites a chance to kindly die off, which prevents reinfection.
Secondly, the friars’ diet of fresh fruits and vegetables mixed together into a salad, while appealing to our modern-day sensibilities, was not a great choice. By comparison, laypeople tended to eat a boiled mishmash of whatever they could find, and while that’s kind of gross, the key here is that their food was cooked. And heat kills parasites. The uncooked salads did no such thing, so the monks ate infected food, expelled infected poop, and grew more infected food with their infected poop.
Once the worms arrived, they never left, making them the worst kind of house guest. Read the room, worms, take your dinner and move on. You don’t have to go home, but you can’t stay here.
What’s a shared genotype between friends?
Do you find it hard to tell the difference between Katy Perry and Zooey Deschanel? They look alike, but they’re not related. Or are they? According to new research, people who look and act very similar but are not related may share DNA.
“Our study provides a rare insight into human likeness by showing that people with extreme look-alike faces share common genotypes, whereas they are discordant at the epigenome and microbiome levels,” senior author Manel Esteller of the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute in Barcelona said in a written statement. “Genomics clusters them together, and the rest sets them apart.”
The Internet has been a great source in being able to find look-alikes. The research team found photos of doppelgangers photographed by François Brunelle, a Canadian artist. Using facial recognition algorithms, the investigators were able to measure likeness between the each pair of look-alikes. The participants also completed a questionnaire about lifestyle and provided a saliva sample.
The results showed that the look-alikes had similar genotypes but different DNA methylation and microbiome landscapes. The look-alikes also seemed to have similarities in weight, height, and behaviors such as smoking, proving that doppelgangers not only look alike but also share common interests.
Next time someone tells you that you look like their best friend Steve, you won’t have to wonder much what Steve is like.
The secret to a good relationship? It’s a secret
Strong relationships are built on honesty and trust, right? Being open with your partner and/or friends is usually a good practice for keeping the relationship healthy, but the latest evidence suggests that maybe you shouldn’t share everything.
According to the first known study on the emotional, behavioral, and relational aspect of consumer behavior, not disclosing certain purchases to your partner can actually be a good thing for the relationship. How? Well, it all has to do with guilt.
In a series of studies, the researchers asked couples about their secret consumptions. The most commonly hidden thing by far was a product (65%).
“We found that 90% of people have recently kept everyday consumer behaviors a secret from a close other – like a friend or spouse – even though they also report that they don’t think their partner would care if they knew about it,” Kelley Gullo Wight, one of the study’s two lead authors, said in a written statement.
Keeping a hidden stash of chocolate produces guilt, which the researchers found to be the key factor, making the perpetrator want to do more in the relationship to ease that sense of betrayal or dishonesty. They called it a “greater relationship investment,” meaning the person is more likely to do a little extra for their partner, like shell out more money for the next anniversary gift or yield to watching their partner’s favorite program.
So don’t feel too bad about that secret Amazon purchase. As long as the other person doesn’t see the box, nobody has to know. Your relationship can only improve.
Something about this COVID testing smells fishy
The Chinese have been challenging America’s political and economic hegemony (yes, we did have to look that one up – you’re rude to ask) for some time, but now they’ve gone too far. Are we going to just sit here and let China do something more ridiculous than us in response to COVID? No way!
Here’s the deal: The government of the Chinese coastal city of Xiamen has decided that it’s not just the workers on returning fishing boats who have the potential to introduce COVID to the rest of the population. The fish also present a problem. So when the authorities say that everyone needs to be tested before they can enter the city, they mean everyone.
An employee of the municipal ocean development bureau told local media that “all people in Xiamen City need nucleic acid testing, and the fish catches must be tested as well,” according to the Guardian, which also said that “TV news reports showed officials swabbing the mouths of fish and the underside of crabs.”
In the words of George Takei: “Oh my.”
Hold on there a second, George Takei, because we here in the good old US of A have still got Los Angeles, where COVID testing also has taken a nonhuman turn. The LA County public health department recently announced that pets are now eligible for a free SARS-CoV-2 test through veterinarians and other animal care facilities.
“Our goal is to test many different species of animals including wildlife (deer, bats, raccoons), pets (dogs, cats, hamsters, pocket pets), marine mammals (seals), and more,” Veterinary Public Health announced.
Hegemony restored.
Not even God could save them from worms
The Dark Ages may not have been as dark and violent as many people think, but there’s no denying that life in medieval Europe kind of sucked. The only real alternative to serfdom was a job with the Catholic Church. Medieval friars, for example, lived in stone buildings, had access to fresh fruits and vegetables, and even had latrines and running water. Luxuries compared with the life of the average peasant.
So why then, despite having access to more modern sanitation and amenities, did the friars have so many gut parasites? That’s the question raised by a group of researchers from the University of Cambridge, who conducted a study of 19 medieval friars buried at a local friary (Oh, doesn’t your town have one of those?) and 25 local people buried at a nonreligious cemetery during a similar time period. Of those 19 friars, 11 were infected with worms and parasites, compared with just 8 of 25 townspeople.
This doesn’t make a lot of sense. The friars had a good life by old-time standards: They had basic sanitation down and a solid diet. These things should lead to a healthier population. The problem, the researchers found, is two pronged and a vicious cycle. First off, the friars had plenty of fresh food, but they used human feces to fertilize their produce. There’s a reason modern practice for human waste fertilization is to let the waste compost for 6 months: The waiting period allows the parasites a chance to kindly die off, which prevents reinfection.
Secondly, the friars’ diet of fresh fruits and vegetables mixed together into a salad, while appealing to our modern-day sensibilities, was not a great choice. By comparison, laypeople tended to eat a boiled mishmash of whatever they could find, and while that’s kind of gross, the key here is that their food was cooked. And heat kills parasites. The uncooked salads did no such thing, so the monks ate infected food, expelled infected poop, and grew more infected food with their infected poop.
Once the worms arrived, they never left, making them the worst kind of house guest. Read the room, worms, take your dinner and move on. You don’t have to go home, but you can’t stay here.
What’s a shared genotype between friends?
Do you find it hard to tell the difference between Katy Perry and Zooey Deschanel? They look alike, but they’re not related. Or are they? According to new research, people who look and act very similar but are not related may share DNA.
“Our study provides a rare insight into human likeness by showing that people with extreme look-alike faces share common genotypes, whereas they are discordant at the epigenome and microbiome levels,” senior author Manel Esteller of the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute in Barcelona said in a written statement. “Genomics clusters them together, and the rest sets them apart.”
The Internet has been a great source in being able to find look-alikes. The research team found photos of doppelgangers photographed by François Brunelle, a Canadian artist. Using facial recognition algorithms, the investigators were able to measure likeness between the each pair of look-alikes. The participants also completed a questionnaire about lifestyle and provided a saliva sample.
The results showed that the look-alikes had similar genotypes but different DNA methylation and microbiome landscapes. The look-alikes also seemed to have similarities in weight, height, and behaviors such as smoking, proving that doppelgangers not only look alike but also share common interests.
Next time someone tells you that you look like their best friend Steve, you won’t have to wonder much what Steve is like.
The secret to a good relationship? It’s a secret
Strong relationships are built on honesty and trust, right? Being open with your partner and/or friends is usually a good practice for keeping the relationship healthy, but the latest evidence suggests that maybe you shouldn’t share everything.
According to the first known study on the emotional, behavioral, and relational aspect of consumer behavior, not disclosing certain purchases to your partner can actually be a good thing for the relationship. How? Well, it all has to do with guilt.
In a series of studies, the researchers asked couples about their secret consumptions. The most commonly hidden thing by far was a product (65%).
“We found that 90% of people have recently kept everyday consumer behaviors a secret from a close other – like a friend or spouse – even though they also report that they don’t think their partner would care if they knew about it,” Kelley Gullo Wight, one of the study’s two lead authors, said in a written statement.
Keeping a hidden stash of chocolate produces guilt, which the researchers found to be the key factor, making the perpetrator want to do more in the relationship to ease that sense of betrayal or dishonesty. They called it a “greater relationship investment,” meaning the person is more likely to do a little extra for their partner, like shell out more money for the next anniversary gift or yield to watching their partner’s favorite program.
So don’t feel too bad about that secret Amazon purchase. As long as the other person doesn’t see the box, nobody has to know. Your relationship can only improve.
Something about this COVID testing smells fishy
The Chinese have been challenging America’s political and economic hegemony (yes, we did have to look that one up – you’re rude to ask) for some time, but now they’ve gone too far. Are we going to just sit here and let China do something more ridiculous than us in response to COVID? No way!
Here’s the deal: The government of the Chinese coastal city of Xiamen has decided that it’s not just the workers on returning fishing boats who have the potential to introduce COVID to the rest of the population. The fish also present a problem. So when the authorities say that everyone needs to be tested before they can enter the city, they mean everyone.
An employee of the municipal ocean development bureau told local media that “all people in Xiamen City need nucleic acid testing, and the fish catches must be tested as well,” according to the Guardian, which also said that “TV news reports showed officials swabbing the mouths of fish and the underside of crabs.”
In the words of George Takei: “Oh my.”
Hold on there a second, George Takei, because we here in the good old US of A have still got Los Angeles, where COVID testing also has taken a nonhuman turn. The LA County public health department recently announced that pets are now eligible for a free SARS-CoV-2 test through veterinarians and other animal care facilities.
“Our goal is to test many different species of animals including wildlife (deer, bats, raccoons), pets (dogs, cats, hamsters, pocket pets), marine mammals (seals), and more,” Veterinary Public Health announced.
Hegemony restored.
Not even God could save them from worms
The Dark Ages may not have been as dark and violent as many people think, but there’s no denying that life in medieval Europe kind of sucked. The only real alternative to serfdom was a job with the Catholic Church. Medieval friars, for example, lived in stone buildings, had access to fresh fruits and vegetables, and even had latrines and running water. Luxuries compared with the life of the average peasant.
So why then, despite having access to more modern sanitation and amenities, did the friars have so many gut parasites? That’s the question raised by a group of researchers from the University of Cambridge, who conducted a study of 19 medieval friars buried at a local friary (Oh, doesn’t your town have one of those?) and 25 local people buried at a nonreligious cemetery during a similar time period. Of those 19 friars, 11 were infected with worms and parasites, compared with just 8 of 25 townspeople.
This doesn’t make a lot of sense. The friars had a good life by old-time standards: They had basic sanitation down and a solid diet. These things should lead to a healthier population. The problem, the researchers found, is two pronged and a vicious cycle. First off, the friars had plenty of fresh food, but they used human feces to fertilize their produce. There’s a reason modern practice for human waste fertilization is to let the waste compost for 6 months: The waiting period allows the parasites a chance to kindly die off, which prevents reinfection.
Secondly, the friars’ diet of fresh fruits and vegetables mixed together into a salad, while appealing to our modern-day sensibilities, was not a great choice. By comparison, laypeople tended to eat a boiled mishmash of whatever they could find, and while that’s kind of gross, the key here is that their food was cooked. And heat kills parasites. The uncooked salads did no such thing, so the monks ate infected food, expelled infected poop, and grew more infected food with their infected poop.
Once the worms arrived, they never left, making them the worst kind of house guest. Read the room, worms, take your dinner and move on. You don’t have to go home, but you can’t stay here.
What’s a shared genotype between friends?
Do you find it hard to tell the difference between Katy Perry and Zooey Deschanel? They look alike, but they’re not related. Or are they? According to new research, people who look and act very similar but are not related may share DNA.
“Our study provides a rare insight into human likeness by showing that people with extreme look-alike faces share common genotypes, whereas they are discordant at the epigenome and microbiome levels,” senior author Manel Esteller of the Josep Carreras Leukemia Research Institute in Barcelona said in a written statement. “Genomics clusters them together, and the rest sets them apart.”
The Internet has been a great source in being able to find look-alikes. The research team found photos of doppelgangers photographed by François Brunelle, a Canadian artist. Using facial recognition algorithms, the investigators were able to measure likeness between the each pair of look-alikes. The participants also completed a questionnaire about lifestyle and provided a saliva sample.
The results showed that the look-alikes had similar genotypes but different DNA methylation and microbiome landscapes. The look-alikes also seemed to have similarities in weight, height, and behaviors such as smoking, proving that doppelgangers not only look alike but also share common interests.
Next time someone tells you that you look like their best friend Steve, you won’t have to wonder much what Steve is like.
The secret to a good relationship? It’s a secret
Strong relationships are built on honesty and trust, right? Being open with your partner and/or friends is usually a good practice for keeping the relationship healthy, but the latest evidence suggests that maybe you shouldn’t share everything.
According to the first known study on the emotional, behavioral, and relational aspect of consumer behavior, not disclosing certain purchases to your partner can actually be a good thing for the relationship. How? Well, it all has to do with guilt.
In a series of studies, the researchers asked couples about their secret consumptions. The most commonly hidden thing by far was a product (65%).
“We found that 90% of people have recently kept everyday consumer behaviors a secret from a close other – like a friend or spouse – even though they also report that they don’t think their partner would care if they knew about it,” Kelley Gullo Wight, one of the study’s two lead authors, said in a written statement.
Keeping a hidden stash of chocolate produces guilt, which the researchers found to be the key factor, making the perpetrator want to do more in the relationship to ease that sense of betrayal or dishonesty. They called it a “greater relationship investment,” meaning the person is more likely to do a little extra for their partner, like shell out more money for the next anniversary gift or yield to watching their partner’s favorite program.
So don’t feel too bad about that secret Amazon purchase. As long as the other person doesn’t see the box, nobody has to know. Your relationship can only improve.