User login
SURMOUNT-OSA Results: ‘Impressive’ in Improving Sleep Apnea
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist in Vancouver, Canada, and with me is a very special guest. Today we have Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician working in Calgary, Canada. Both Dr. Kim and I were fortunate to attend the recently concluded American Diabetes Association annual conference in Orlando in June.
We thought we could share with you some of the key learnings that we found very insightful and clinically quite relevant. We were hoping to bring our own conclusion regarding what these findings were, both from a primary care perspective and an endocrinology perspective.
There were so many different studies that, frankly, it was difficult to pick them, but we handpicked a few studies we felt we could do a bit of a deeper dive on, and we’ll talk about each of these studies.
Welcome, Dr. Kim, and thanks for joining us.
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you so much, Dr Jain. It’s a pleasure to be here.
Dr. Jain: Probably the best place to start would be with the SURMOUNT-OSA study. This was highlighted at the American Diabetes Association conference. Essentially, it looked at people who are living with obesity who also had obstructive sleep apnea.
This was a randomized controlled trial where individuals tested either got tirzepatide (trade name, Mounjaro) or placebo treatment. They looked at the change in their apnea-hypopnea index at the end of the study.
This included both people who were using CPAP machines and those who were not using CPAP machines at baseline. We do know that many individuals with sleep apnea may not use these machines.
That was a big reduction.
Dr. Kim, what’s the relevance of this study in primary care?
Dr. Kim: Oh, it’s massive. Obstructive sleep apnea is probably one of the most underdiagnosed yet huge cardiac risk factors that we tend to overlook in primary care. We sometimes say, oh, it’s just sleep apnea; what’s the big deal? We know it’s a big problem. We know that more than 50% of people with type 2 diabetes have obstructive sleep apnea, and some studies have even quoted that 90% of their population cohorts had sleep apnea. This is a big deal.
What do we know so far? We know that obstructive sleep apnea, which I’m just going to call OSA, increases the risk for hypertension, bad cholesterol, and worsening blood glucose in terms of A1c and fasting glucose, which eventually leads to myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, stroke, and eventually cardiovascular death.
We also know that people with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk for OSA. There seems to be a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and OSA. It seems like weight plays the biggest role in terms of developing OSA, and numerous studies have shown this.
Also, thankfully, some of the studies showed that weight loss improves not just OSA but also blood pressure, cholesterol, blood glucose, and insulin sensitivities. These have been fascinating. We see these patients every single day. If you think about it in your population, for 50%-90% of the patients to have OSA is a large number. If you haven’t seen a person with OSA this week, you probably missed them, very likely.
Therefore, the SURMOUNT-OSA trial was quite fascinating with, as you mentioned, 50%-60% reduction in the severity of OSA, which is very impressive. Even more impressive, I think, is that for about 50% of the patients on tirzepatide, the OSA improves so much that they may not even need to be on CPAP machines.
Those who were on CPAP may not need to be on CPAP any longer. These are huge data, especially for primary care, because as you mentioned, we see these people every single day.
Dr. Jain: Thanks for pointing that out. Clearly, it’s very clinically relevant. I think the most important takeaway for me from this study was the correlation between weight loss and AHI improvement.
Clearly, it showed that placebo had about a 6% drop in AHI, whereas there was a 60% drop in the tirzepatide group, so you can see that it’s significantly different. The placebo group did not have any significant degree of weight loss, whereas the tirzepatide group had nearly 20% weight loss. This again goes to show that there is a very close correlation between weight loss and improvement in OSA.
What’s very important to note is that we’ve seen this in the past as well. We had seen some of these data with other GLP-1 agents, but the extent of improvement that we have seen in the SURMOUNT-OSA trial is significantly more than what we’ve seen in previous studies. There is a ray of hope now where we have medical management to offer people who are living with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Kim: I want to add that, from a primary care perspective, this study also showed the improvement of the sleep apnea–related symptoms as well. The biggest problem with sleep apnea — or at least what patients’ spouses complain of, is the person snoring too much; it’s a symptom.
It’s the next-day symptoms that really do disturb people, like chronic fatigue. I have numerous patients who say that, once they’ve been treated for sleep apnea, they feel like a brand-new person. They have sudden bursts of energy that they never felt before, and over 50% of these people have huge improvements in the symptoms as well.
This is a huge trial. The only thing that I wish this study included were people with mild obstructive sleep apnea who were symptomatic. I do understand that, with other studies in this population, the data have been conflicting, but it would have been really awesome if they had those patients included. However, it is still a significant study for primary care.
Dr. Jain: That’s a really good point. Fatigue improves and overall quality of life improves. That’s very important from a primary care perspective.
From an endocrinology perspective, we know that management of sleep apnea can often lead to improvement in male hypogonadism, polycystic ovary syndrome, and insulin resistance. The amount of insulin required, or the number of medications needed for managing diabetes, can improve. Hypertension can improve as well. There are multiple benefits that you can get from appropriate management of sleep apnea.
Thanks, Dr. Kim. We really appreciate your insights on SURMOUNT-OSA.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist in Vancouver, Canada, and with me is a very special guest. Today we have Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician working in Calgary, Canada. Both Dr. Kim and I were fortunate to attend the recently concluded American Diabetes Association annual conference in Orlando in June.
We thought we could share with you some of the key learnings that we found very insightful and clinically quite relevant. We were hoping to bring our own conclusion regarding what these findings were, both from a primary care perspective and an endocrinology perspective.
There were so many different studies that, frankly, it was difficult to pick them, but we handpicked a few studies we felt we could do a bit of a deeper dive on, and we’ll talk about each of these studies.
Welcome, Dr. Kim, and thanks for joining us.
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you so much, Dr Jain. It’s a pleasure to be here.
Dr. Jain: Probably the best place to start would be with the SURMOUNT-OSA study. This was highlighted at the American Diabetes Association conference. Essentially, it looked at people who are living with obesity who also had obstructive sleep apnea.
This was a randomized controlled trial where individuals tested either got tirzepatide (trade name, Mounjaro) or placebo treatment. They looked at the change in their apnea-hypopnea index at the end of the study.
This included both people who were using CPAP machines and those who were not using CPAP machines at baseline. We do know that many individuals with sleep apnea may not use these machines.
That was a big reduction.
Dr. Kim, what’s the relevance of this study in primary care?
Dr. Kim: Oh, it’s massive. Obstructive sleep apnea is probably one of the most underdiagnosed yet huge cardiac risk factors that we tend to overlook in primary care. We sometimes say, oh, it’s just sleep apnea; what’s the big deal? We know it’s a big problem. We know that more than 50% of people with type 2 diabetes have obstructive sleep apnea, and some studies have even quoted that 90% of their population cohorts had sleep apnea. This is a big deal.
What do we know so far? We know that obstructive sleep apnea, which I’m just going to call OSA, increases the risk for hypertension, bad cholesterol, and worsening blood glucose in terms of A1c and fasting glucose, which eventually leads to myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, stroke, and eventually cardiovascular death.
We also know that people with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk for OSA. There seems to be a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and OSA. It seems like weight plays the biggest role in terms of developing OSA, and numerous studies have shown this.
Also, thankfully, some of the studies showed that weight loss improves not just OSA but also blood pressure, cholesterol, blood glucose, and insulin sensitivities. These have been fascinating. We see these patients every single day. If you think about it in your population, for 50%-90% of the patients to have OSA is a large number. If you haven’t seen a person with OSA this week, you probably missed them, very likely.
Therefore, the SURMOUNT-OSA trial was quite fascinating with, as you mentioned, 50%-60% reduction in the severity of OSA, which is very impressive. Even more impressive, I think, is that for about 50% of the patients on tirzepatide, the OSA improves so much that they may not even need to be on CPAP machines.
Those who were on CPAP may not need to be on CPAP any longer. These are huge data, especially for primary care, because as you mentioned, we see these people every single day.
Dr. Jain: Thanks for pointing that out. Clearly, it’s very clinically relevant. I think the most important takeaway for me from this study was the correlation between weight loss and AHI improvement.
Clearly, it showed that placebo had about a 6% drop in AHI, whereas there was a 60% drop in the tirzepatide group, so you can see that it’s significantly different. The placebo group did not have any significant degree of weight loss, whereas the tirzepatide group had nearly 20% weight loss. This again goes to show that there is a very close correlation between weight loss and improvement in OSA.
What’s very important to note is that we’ve seen this in the past as well. We had seen some of these data with other GLP-1 agents, but the extent of improvement that we have seen in the SURMOUNT-OSA trial is significantly more than what we’ve seen in previous studies. There is a ray of hope now where we have medical management to offer people who are living with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Kim: I want to add that, from a primary care perspective, this study also showed the improvement of the sleep apnea–related symptoms as well. The biggest problem with sleep apnea — or at least what patients’ spouses complain of, is the person snoring too much; it’s a symptom.
It’s the next-day symptoms that really do disturb people, like chronic fatigue. I have numerous patients who say that, once they’ve been treated for sleep apnea, they feel like a brand-new person. They have sudden bursts of energy that they never felt before, and over 50% of these people have huge improvements in the symptoms as well.
This is a huge trial. The only thing that I wish this study included were people with mild obstructive sleep apnea who were symptomatic. I do understand that, with other studies in this population, the data have been conflicting, but it would have been really awesome if they had those patients included. However, it is still a significant study for primary care.
Dr. Jain: That’s a really good point. Fatigue improves and overall quality of life improves. That’s very important from a primary care perspective.
From an endocrinology perspective, we know that management of sleep apnea can often lead to improvement in male hypogonadism, polycystic ovary syndrome, and insulin resistance. The amount of insulin required, or the number of medications needed for managing diabetes, can improve. Hypertension can improve as well. There are multiple benefits that you can get from appropriate management of sleep apnea.
Thanks, Dr. Kim. We really appreciate your insights on SURMOUNT-OSA.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist in Vancouver, Canada, and with me is a very special guest. Today we have Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician working in Calgary, Canada. Both Dr. Kim and I were fortunate to attend the recently concluded American Diabetes Association annual conference in Orlando in June.
We thought we could share with you some of the key learnings that we found very insightful and clinically quite relevant. We were hoping to bring our own conclusion regarding what these findings were, both from a primary care perspective and an endocrinology perspective.
There were so many different studies that, frankly, it was difficult to pick them, but we handpicked a few studies we felt we could do a bit of a deeper dive on, and we’ll talk about each of these studies.
Welcome, Dr. Kim, and thanks for joining us.
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you so much, Dr Jain. It’s a pleasure to be here.
Dr. Jain: Probably the best place to start would be with the SURMOUNT-OSA study. This was highlighted at the American Diabetes Association conference. Essentially, it looked at people who are living with obesity who also had obstructive sleep apnea.
This was a randomized controlled trial where individuals tested either got tirzepatide (trade name, Mounjaro) or placebo treatment. They looked at the change in their apnea-hypopnea index at the end of the study.
This included both people who were using CPAP machines and those who were not using CPAP machines at baseline. We do know that many individuals with sleep apnea may not use these machines.
That was a big reduction.
Dr. Kim, what’s the relevance of this study in primary care?
Dr. Kim: Oh, it’s massive. Obstructive sleep apnea is probably one of the most underdiagnosed yet huge cardiac risk factors that we tend to overlook in primary care. We sometimes say, oh, it’s just sleep apnea; what’s the big deal? We know it’s a big problem. We know that more than 50% of people with type 2 diabetes have obstructive sleep apnea, and some studies have even quoted that 90% of their population cohorts had sleep apnea. This is a big deal.
What do we know so far? We know that obstructive sleep apnea, which I’m just going to call OSA, increases the risk for hypertension, bad cholesterol, and worsening blood glucose in terms of A1c and fasting glucose, which eventually leads to myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, stroke, and eventually cardiovascular death.
We also know that people with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk for OSA. There seems to be a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and OSA. It seems like weight plays the biggest role in terms of developing OSA, and numerous studies have shown this.
Also, thankfully, some of the studies showed that weight loss improves not just OSA but also blood pressure, cholesterol, blood glucose, and insulin sensitivities. These have been fascinating. We see these patients every single day. If you think about it in your population, for 50%-90% of the patients to have OSA is a large number. If you haven’t seen a person with OSA this week, you probably missed them, very likely.
Therefore, the SURMOUNT-OSA trial was quite fascinating with, as you mentioned, 50%-60% reduction in the severity of OSA, which is very impressive. Even more impressive, I think, is that for about 50% of the patients on tirzepatide, the OSA improves so much that they may not even need to be on CPAP machines.
Those who were on CPAP may not need to be on CPAP any longer. These are huge data, especially for primary care, because as you mentioned, we see these people every single day.
Dr. Jain: Thanks for pointing that out. Clearly, it’s very clinically relevant. I think the most important takeaway for me from this study was the correlation between weight loss and AHI improvement.
Clearly, it showed that placebo had about a 6% drop in AHI, whereas there was a 60% drop in the tirzepatide group, so you can see that it’s significantly different. The placebo group did not have any significant degree of weight loss, whereas the tirzepatide group had nearly 20% weight loss. This again goes to show that there is a very close correlation between weight loss and improvement in OSA.
What’s very important to note is that we’ve seen this in the past as well. We had seen some of these data with other GLP-1 agents, but the extent of improvement that we have seen in the SURMOUNT-OSA trial is significantly more than what we’ve seen in previous studies. There is a ray of hope now where we have medical management to offer people who are living with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea.
Dr. Kim: I want to add that, from a primary care perspective, this study also showed the improvement of the sleep apnea–related symptoms as well. The biggest problem with sleep apnea — or at least what patients’ spouses complain of, is the person snoring too much; it’s a symptom.
It’s the next-day symptoms that really do disturb people, like chronic fatigue. I have numerous patients who say that, once they’ve been treated for sleep apnea, they feel like a brand-new person. They have sudden bursts of energy that they never felt before, and over 50% of these people have huge improvements in the symptoms as well.
This is a huge trial. The only thing that I wish this study included were people with mild obstructive sleep apnea who were symptomatic. I do understand that, with other studies in this population, the data have been conflicting, but it would have been really awesome if they had those patients included. However, it is still a significant study for primary care.
Dr. Jain: That’s a really good point. Fatigue improves and overall quality of life improves. That’s very important from a primary care perspective.
From an endocrinology perspective, we know that management of sleep apnea can often lead to improvement in male hypogonadism, polycystic ovary syndrome, and insulin resistance. The amount of insulin required, or the number of medications needed for managing diabetes, can improve. Hypertension can improve as well. There are multiple benefits that you can get from appropriate management of sleep apnea.
Thanks, Dr. Kim. We really appreciate your insights on SURMOUNT-OSA.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Inhaled Insulin Aids Patients With Fear of Needles
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist from Vancouver, and I’m joined by Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician from Calgary, Canada.
Both Dr. Kim and I attended ADA 2024. We went over all our learnings and decided that there was a whole heap of clinical pearls that we learned from the conference. We thought it would be awesome if we could share our learnings with all of you, both from a primary care lens and from an endocrinology perspective.
One study Dr. Kim and I learned about, and we think has some definite nuances in management of people living with diabetes, regards inhaled insulin. When we have patients in our clinic who have perhaps failed multiple oral agents or have very high blood sugars, we obviously want to consider starting them on insulin for type 2 diabetes.
Sometimes there is a significant barrier, which is related to the needles. There’s an actual term for this: trypanophobia — a fear of needles.
Enter now inhaled insulin. We saw studies at the ADA 2024 conference that looked at a new inhaled insulin called Afrezza. Afrezza essentially is a short-acting insulin, so it’s kind of like a prandial insulin derivative, where it can be inhaled by an individual and it will work for mealtime control of blood sugars.
Dr. Kim, in your practice, how often do you see people not wanting to take shots, and has this been a big barrier for you in starting insulin?
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you for having me. To answer your question, absolutely I encounter this on a weekly basis — and I’m not even an endocrinologist. I just have an interest in diabetes. There are a number of patients that I think will benefit massively with insulin but they’re needle-phobic. You taught me that word, but I can never pronounce it, so my apologies for not remembering that phobia. I’m just going to call it needle phobia because I’m a simple-minded person.
The needle phobia is massive. I think there’s a definite fear of the needle, but there’s also a fear of failure. As soon as an injection is mentioned, many patients feel they failed miserably. There’s an emotional roller coaster that happens.
I’m sure, Dr. Jain, you have seen many patients, especially from Asia, who would say: “Oh, my auntie got on insulin and 3 months later, she got a kidney transplant.” “My uncle started on insulin and he unfortunately passed away a couple of months later.” Unfortunately, they’re blaming many of those things on insulin.
I also have a number of patients who said they were on insulin before many years ago, and they experienced some severe hypoglycemic events, and they don’t want to get on the insulin ever again. This is unfortunate because you know that if those patients, those aunties and uncles, were on insulin long before, maybe we could have saved their legs and kidneys, and potentially death.
Now we have advanced so much with insulin that hypoglycemia does occur, but much less than before. We still have many barriers when it comes to insulin initiations. Therefore, having this idea of inhaled insulin is fantastic, and I think we can get many more patients on insulin — the medication they actually need.
Dr. Jain: Absolutely. From the studies on inhaled insulin at ADA 2024, the key thing I found very interesting, regarding the pharmacokinetics of the insulin, was that it’s working very quickly. It starts working within minutes of administering it.
Additionally, it lasts in the body only for a shorter duration of time, compared with other injectable short-acting insulins, so it lasts in the body. The active insulin time is roughly about 2 hours or so, based on the studies, which in my mind opens up a whole world of possibilities because it means that people can take another correctional insulin if the blood sugars are still high after taking their first inhaled dose. You can take another dose subsequently without worrying about stacking of insulin.
Many of us are familiar with this term, which is if you take two shots of short-acting insulin too close to each other, the insulin doses might add up and there can be a big drop in the blood sugars; it’s called stacking of insulin. This can be potentially avoided.
Similarly, if you take your dinnertime inhaled insulin and the sugars are still high around bedtime, you could take a smaller dose of the inhaled insulin and not worry about middle-of-the-night hypoglycemia because the effect of the insulin would be only for a little while.
That’s one key learning that I found very helpful. The other important thing that I found was that this is not for everyone, so there are some restrictions. Essentially, the contraindication is that people who have asthma or COPD cannot be prescribed an inhaled insulin.
What are your thoughts, Dr. Kim, based on this for your practice in primary care?
Dr. Kim: It is very fascinating, for sure. I cannot wait to get hold of this insulin. I can already think of some patients who may benefit. You’ve mentioned the asthma and COPD patients, and that makes more sense because there is an actual airway problem.
I also wonder what will happen to patients who have restrictive airway disease, where asthma and COPD fall under obstructive airway disease. What if they have obesity, where it’s really pressing into the diaphragm, and where they may not be able to take the deep breath in? How will they react?
What about someone who’s got a cold, someone who has postnasal drip, or someone who tends to cough frequently? What about egg allergies? There are many question marks around this insulin before initiating these medications. There is excitement, but there are also many questions at the same time.
Dr. Jain: I think these are very important, practical considerations that we’ll uncover as we start using more of this in clinical practice. The other important thing to note is that the presenters told us it’s important to monitor pulmonary function tests. It’s important to get a baseline pulmonary function test, and then we have to do another one in 6 months, followed by annually thereafter.
If, at any point of time, the FEV1 drops by 20% or more, then that would be an indication for discontinuation of the inhaled insulin. The pulmonary function test does not need to be one of those fancier ones. The study group would just do office spirometries. I’m wondering, Dr. Kim, in primary care, do you think this could potentially be a rate-limiting factor?
Dr. Kim: In Alberta, where I reside, no. Spirometry is very easily accessible in the province. For example, in Calgary alone, we have a population of about 1.3 million people. We have over 13 or 15 companies that can do this spirometry. We can get these things done literally within a week or 2.
However, I am aware that, in other provinces in Canada, it can definitely be a huge rate-limiting factor. Not everyone has the office-based spirometry, and definitely not within the primary care office. It has to be referred out to these private companies, most likely, and some of the rural areas will have to rely on the provincial hospitals, where the access can be even more challenging.
On the day of the actual spirometry, if the person has a cough or is not feeling well, it’s going to be a problem because you don’t want the spirometry to be infected with a whole bunch of viruses. You’ll have to cancel that and it can be a bit of an issue.
Dr. Jain: Many of our viewers are from the United States and other parts of the world, and spirometry is quite easily accessible in most places. As an endocrinologist, I must confess that it’s been a long time since I’ve even ordered a spirometry or any clinical form of pulmonary function test. Once I start using the inhaled insulin, I’ll need to start brushing up on my pulmonary function test knowledge.
I think these are exciting times. At least we’ve got something to offer to people who would have otherwise not taken any insulin at all. There’s certainly that hope that now there’s a different way to administer this, and hopefully it can only get better from here on.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist from Vancouver, and I’m joined by Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician from Calgary, Canada.
Both Dr. Kim and I attended ADA 2024. We went over all our learnings and decided that there was a whole heap of clinical pearls that we learned from the conference. We thought it would be awesome if we could share our learnings with all of you, both from a primary care lens and from an endocrinology perspective.
One study Dr. Kim and I learned about, and we think has some definite nuances in management of people living with diabetes, regards inhaled insulin. When we have patients in our clinic who have perhaps failed multiple oral agents or have very high blood sugars, we obviously want to consider starting them on insulin for type 2 diabetes.
Sometimes there is a significant barrier, which is related to the needles. There’s an actual term for this: trypanophobia — a fear of needles.
Enter now inhaled insulin. We saw studies at the ADA 2024 conference that looked at a new inhaled insulin called Afrezza. Afrezza essentially is a short-acting insulin, so it’s kind of like a prandial insulin derivative, where it can be inhaled by an individual and it will work for mealtime control of blood sugars.
Dr. Kim, in your practice, how often do you see people not wanting to take shots, and has this been a big barrier for you in starting insulin?
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you for having me. To answer your question, absolutely I encounter this on a weekly basis — and I’m not even an endocrinologist. I just have an interest in diabetes. There are a number of patients that I think will benefit massively with insulin but they’re needle-phobic. You taught me that word, but I can never pronounce it, so my apologies for not remembering that phobia. I’m just going to call it needle phobia because I’m a simple-minded person.
The needle phobia is massive. I think there’s a definite fear of the needle, but there’s also a fear of failure. As soon as an injection is mentioned, many patients feel they failed miserably. There’s an emotional roller coaster that happens.
I’m sure, Dr. Jain, you have seen many patients, especially from Asia, who would say: “Oh, my auntie got on insulin and 3 months later, she got a kidney transplant.” “My uncle started on insulin and he unfortunately passed away a couple of months later.” Unfortunately, they’re blaming many of those things on insulin.
I also have a number of patients who said they were on insulin before many years ago, and they experienced some severe hypoglycemic events, and they don’t want to get on the insulin ever again. This is unfortunate because you know that if those patients, those aunties and uncles, were on insulin long before, maybe we could have saved their legs and kidneys, and potentially death.
Now we have advanced so much with insulin that hypoglycemia does occur, but much less than before. We still have many barriers when it comes to insulin initiations. Therefore, having this idea of inhaled insulin is fantastic, and I think we can get many more patients on insulin — the medication they actually need.
Dr. Jain: Absolutely. From the studies on inhaled insulin at ADA 2024, the key thing I found very interesting, regarding the pharmacokinetics of the insulin, was that it’s working very quickly. It starts working within minutes of administering it.
Additionally, it lasts in the body only for a shorter duration of time, compared with other injectable short-acting insulins, so it lasts in the body. The active insulin time is roughly about 2 hours or so, based on the studies, which in my mind opens up a whole world of possibilities because it means that people can take another correctional insulin if the blood sugars are still high after taking their first inhaled dose. You can take another dose subsequently without worrying about stacking of insulin.
Many of us are familiar with this term, which is if you take two shots of short-acting insulin too close to each other, the insulin doses might add up and there can be a big drop in the blood sugars; it’s called stacking of insulin. This can be potentially avoided.
Similarly, if you take your dinnertime inhaled insulin and the sugars are still high around bedtime, you could take a smaller dose of the inhaled insulin and not worry about middle-of-the-night hypoglycemia because the effect of the insulin would be only for a little while.
That’s one key learning that I found very helpful. The other important thing that I found was that this is not for everyone, so there are some restrictions. Essentially, the contraindication is that people who have asthma or COPD cannot be prescribed an inhaled insulin.
What are your thoughts, Dr. Kim, based on this for your practice in primary care?
Dr. Kim: It is very fascinating, for sure. I cannot wait to get hold of this insulin. I can already think of some patients who may benefit. You’ve mentioned the asthma and COPD patients, and that makes more sense because there is an actual airway problem.
I also wonder what will happen to patients who have restrictive airway disease, where asthma and COPD fall under obstructive airway disease. What if they have obesity, where it’s really pressing into the diaphragm, and where they may not be able to take the deep breath in? How will they react?
What about someone who’s got a cold, someone who has postnasal drip, or someone who tends to cough frequently? What about egg allergies? There are many question marks around this insulin before initiating these medications. There is excitement, but there are also many questions at the same time.
Dr. Jain: I think these are very important, practical considerations that we’ll uncover as we start using more of this in clinical practice. The other important thing to note is that the presenters told us it’s important to monitor pulmonary function tests. It’s important to get a baseline pulmonary function test, and then we have to do another one in 6 months, followed by annually thereafter.
If, at any point of time, the FEV1 drops by 20% or more, then that would be an indication for discontinuation of the inhaled insulin. The pulmonary function test does not need to be one of those fancier ones. The study group would just do office spirometries. I’m wondering, Dr. Kim, in primary care, do you think this could potentially be a rate-limiting factor?
Dr. Kim: In Alberta, where I reside, no. Spirometry is very easily accessible in the province. For example, in Calgary alone, we have a population of about 1.3 million people. We have over 13 or 15 companies that can do this spirometry. We can get these things done literally within a week or 2.
However, I am aware that, in other provinces in Canada, it can definitely be a huge rate-limiting factor. Not everyone has the office-based spirometry, and definitely not within the primary care office. It has to be referred out to these private companies, most likely, and some of the rural areas will have to rely on the provincial hospitals, where the access can be even more challenging.
On the day of the actual spirometry, if the person has a cough or is not feeling well, it’s going to be a problem because you don’t want the spirometry to be infected with a whole bunch of viruses. You’ll have to cancel that and it can be a bit of an issue.
Dr. Jain: Many of our viewers are from the United States and other parts of the world, and spirometry is quite easily accessible in most places. As an endocrinologist, I must confess that it’s been a long time since I’ve even ordered a spirometry or any clinical form of pulmonary function test. Once I start using the inhaled insulin, I’ll need to start brushing up on my pulmonary function test knowledge.
I think these are exciting times. At least we’ve got something to offer to people who would have otherwise not taken any insulin at all. There’s certainly that hope that now there’s a different way to administer this, and hopefully it can only get better from here on.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: I’m Dr. Akshay Jain, an endocrinologist from Vancouver, and I’m joined by Dr. James Kim, a primary care physician from Calgary, Canada.
Both Dr. Kim and I attended ADA 2024. We went over all our learnings and decided that there was a whole heap of clinical pearls that we learned from the conference. We thought it would be awesome if we could share our learnings with all of you, both from a primary care lens and from an endocrinology perspective.
One study Dr. Kim and I learned about, and we think has some definite nuances in management of people living with diabetes, regards inhaled insulin. When we have patients in our clinic who have perhaps failed multiple oral agents or have very high blood sugars, we obviously want to consider starting them on insulin for type 2 diabetes.
Sometimes there is a significant barrier, which is related to the needles. There’s an actual term for this: trypanophobia — a fear of needles.
Enter now inhaled insulin. We saw studies at the ADA 2024 conference that looked at a new inhaled insulin called Afrezza. Afrezza essentially is a short-acting insulin, so it’s kind of like a prandial insulin derivative, where it can be inhaled by an individual and it will work for mealtime control of blood sugars.
Dr. Kim, in your practice, how often do you see people not wanting to take shots, and has this been a big barrier for you in starting insulin?
James W. Kim, MBBCh, PgDip, MScCH: Thank you for having me. To answer your question, absolutely I encounter this on a weekly basis — and I’m not even an endocrinologist. I just have an interest in diabetes. There are a number of patients that I think will benefit massively with insulin but they’re needle-phobic. You taught me that word, but I can never pronounce it, so my apologies for not remembering that phobia. I’m just going to call it needle phobia because I’m a simple-minded person.
The needle phobia is massive. I think there’s a definite fear of the needle, but there’s also a fear of failure. As soon as an injection is mentioned, many patients feel they failed miserably. There’s an emotional roller coaster that happens.
I’m sure, Dr. Jain, you have seen many patients, especially from Asia, who would say: “Oh, my auntie got on insulin and 3 months later, she got a kidney transplant.” “My uncle started on insulin and he unfortunately passed away a couple of months later.” Unfortunately, they’re blaming many of those things on insulin.
I also have a number of patients who said they were on insulin before many years ago, and they experienced some severe hypoglycemic events, and they don’t want to get on the insulin ever again. This is unfortunate because you know that if those patients, those aunties and uncles, were on insulin long before, maybe we could have saved their legs and kidneys, and potentially death.
Now we have advanced so much with insulin that hypoglycemia does occur, but much less than before. We still have many barriers when it comes to insulin initiations. Therefore, having this idea of inhaled insulin is fantastic, and I think we can get many more patients on insulin — the medication they actually need.
Dr. Jain: Absolutely. From the studies on inhaled insulin at ADA 2024, the key thing I found very interesting, regarding the pharmacokinetics of the insulin, was that it’s working very quickly. It starts working within minutes of administering it.
Additionally, it lasts in the body only for a shorter duration of time, compared with other injectable short-acting insulins, so it lasts in the body. The active insulin time is roughly about 2 hours or so, based on the studies, which in my mind opens up a whole world of possibilities because it means that people can take another correctional insulin if the blood sugars are still high after taking their first inhaled dose. You can take another dose subsequently without worrying about stacking of insulin.
Many of us are familiar with this term, which is if you take two shots of short-acting insulin too close to each other, the insulin doses might add up and there can be a big drop in the blood sugars; it’s called stacking of insulin. This can be potentially avoided.
Similarly, if you take your dinnertime inhaled insulin and the sugars are still high around bedtime, you could take a smaller dose of the inhaled insulin and not worry about middle-of-the-night hypoglycemia because the effect of the insulin would be only for a little while.
That’s one key learning that I found very helpful. The other important thing that I found was that this is not for everyone, so there are some restrictions. Essentially, the contraindication is that people who have asthma or COPD cannot be prescribed an inhaled insulin.
What are your thoughts, Dr. Kim, based on this for your practice in primary care?
Dr. Kim: It is very fascinating, for sure. I cannot wait to get hold of this insulin. I can already think of some patients who may benefit. You’ve mentioned the asthma and COPD patients, and that makes more sense because there is an actual airway problem.
I also wonder what will happen to patients who have restrictive airway disease, where asthma and COPD fall under obstructive airway disease. What if they have obesity, where it’s really pressing into the diaphragm, and where they may not be able to take the deep breath in? How will they react?
What about someone who’s got a cold, someone who has postnasal drip, or someone who tends to cough frequently? What about egg allergies? There are many question marks around this insulin before initiating these medications. There is excitement, but there are also many questions at the same time.
Dr. Jain: I think these are very important, practical considerations that we’ll uncover as we start using more of this in clinical practice. The other important thing to note is that the presenters told us it’s important to monitor pulmonary function tests. It’s important to get a baseline pulmonary function test, and then we have to do another one in 6 months, followed by annually thereafter.
If, at any point of time, the FEV1 drops by 20% or more, then that would be an indication for discontinuation of the inhaled insulin. The pulmonary function test does not need to be one of those fancier ones. The study group would just do office spirometries. I’m wondering, Dr. Kim, in primary care, do you think this could potentially be a rate-limiting factor?
Dr. Kim: In Alberta, where I reside, no. Spirometry is very easily accessible in the province. For example, in Calgary alone, we have a population of about 1.3 million people. We have over 13 or 15 companies that can do this spirometry. We can get these things done literally within a week or 2.
However, I am aware that, in other provinces in Canada, it can definitely be a huge rate-limiting factor. Not everyone has the office-based spirometry, and definitely not within the primary care office. It has to be referred out to these private companies, most likely, and some of the rural areas will have to rely on the provincial hospitals, where the access can be even more challenging.
On the day of the actual spirometry, if the person has a cough or is not feeling well, it’s going to be a problem because you don’t want the spirometry to be infected with a whole bunch of viruses. You’ll have to cancel that and it can be a bit of an issue.
Dr. Jain: Many of our viewers are from the United States and other parts of the world, and spirometry is quite easily accessible in most places. As an endocrinologist, I must confess that it’s been a long time since I’ve even ordered a spirometry or any clinical form of pulmonary function test. Once I start using the inhaled insulin, I’ll need to start brushing up on my pulmonary function test knowledge.
I think these are exciting times. At least we’ve got something to offer to people who would have otherwise not taken any insulin at all. There’s certainly that hope that now there’s a different way to administer this, and hopefully it can only get better from here on.
Dr. Jain is a clinical instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Dr. Kim is a clinical assistant professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Calgary in Alberta. Both disclosed conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
A Case of Shortness of Breath, Abdominal Pain, and Hematuria
A48-year-old male presents with three weeks of worsening shortness of breath and pleuritic chest discomfort. A week before the onset of these symptoms, he noticed increasing fatigue, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and persistent hematuria He was otherwise healthy and was taking no medications.
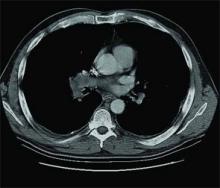
Physical examination reveals a tachypneic yet hemodynamically stable patient, with left upper quadrant fullness. CT chest and abdomen, reveal the following (see right).
You suspect that this finding is secondary to an extrapulmonary process. What unifying diagnosis most likely accounts for these findings? What is your diagnosis?
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Antithrombin III deficiency
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Protein C deficiency
- Prostate carcinoma
Discussion
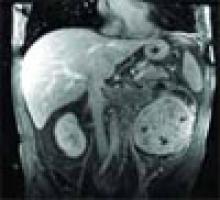
The answer is C: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with caval extension causing PE; this suggests that the PE was due to tumor thrombus. The photo on p. 8 shows areas of increased attenuation in the prominent right and left pulmonary arteries, consistent with a saddle pulmonary embolism. An MRI of the abdomen (see photo above) reveals a large left renal mass extending to Gerota’s fascia and into the left renal vein, protruding slightly into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
The MRI demonstrates an occlusive thrombus in the left renal vein with propagation into the inferior vena cava. The patient underwent a left radical nephrectomy, an inferior vena cava thrombectomy, and a saddle embolectomy. Histological examination of the mass and thrombus confirmed the diagnosis. He had an uneventful recovery and was discharged from the hospital.
RCC accounts for approximately 80% of all primary renal neoplasms, and commonly is termed the “internist’s tumor.” Hematuria is the most common symptom. It is accompanied by flank pain and a palpable abdominal mass in less than 15% of cases.1 Diagnosis of RCC is often made late due to delayed clinical presentation and 20% of patients have metastatic disease at initial diagnosis.2 PE due to tumor thrombus as an initial manifestation of RCC is rare, but is a well-recognized entity leading to dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, hypoxemia, and—in severe cases—acute cor pulmonale with hemodynamic failure.3-5
Staging CT is required in patients with suspected RCC, and MRI is needed, with transesophageal echocardiography used adjunctively, to evaluate cephalic thrombus extension when indicated.6 IVC tumor thrombus occurs in 4%-10% of all cases, most often originating in the renal vein and extending cranially, subsequently propagating to the lungs.7 Survival in local non-metastatic disease with IVC thrombus is no different whether renal vein extension occurs or not, and ranges from 40%-69%, following surgical resection and thrombectomy.8 In those with distant metastases who require venal caval thrombectomy, five-year survivals range from 0%-12.5%.2
The first case of successful removal of a PE secondary to RCC was documented in 1977.1 The goal of surgery is tumor resection and prevention of recurrent embolic events. It is the only effective means of improving survival in the presence of intravascular tumor. Preoperative anticoagulation may be warranted in patients who present with PE, but should be discontinued following definitive surgical treatment secondary to increased risks of hemorrhage.8 TH
References
- Daughtry JD, Stewart BH, Golding LAR, Groves LK. Pulmonary embolus presenting as the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1977;24:178-181.
- Goetzl MA, Goluboff ET, Murphy AM, et al. A contemporary evaluation of cytoreductive nephrectomy with tumor thrombus: morbidity and long term survival. Urol Oncol. 2004; 22:182-187.
- Kubota H, Furuse A, Kotsuka Y, et al. Successful management of massive pulmonary tumor embolism from renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:708-710.
- Gayer G, Mini S, Olchovsky D, et al. Pulmonary embolism—the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma in a young woman. Emerg Radiol. 2003;10:43-45.
- Eggener SE, Dalton DP. Bilateral pulmonary artery tumour emboli from renal carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:173.
- Tsuji Y, Goto A, Hara I, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with extension of tumor thrombus into vena cava: Surgical strategy and prognosis. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:789-796.
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Chao DH, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: is cytoreductive nephrectomy for advanced disease associated with an increased complication rate? J Urol. 2002;168:962-967.
- Nesbitt JC, Soltero ER, Dinney CPN, et al. Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;63:1592-1600.
A48-year-old male presents with three weeks of worsening shortness of breath and pleuritic chest discomfort. A week before the onset of these symptoms, he noticed increasing fatigue, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and persistent hematuria He was otherwise healthy and was taking no medications.
Physical examination reveals a tachypneic yet hemodynamically stable patient, with left upper quadrant fullness. CT chest and abdomen, reveal the following (see right).
You suspect that this finding is secondary to an extrapulmonary process. What unifying diagnosis most likely accounts for these findings? What is your diagnosis?
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Antithrombin III deficiency
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Protein C deficiency
- Prostate carcinoma
Discussion
The answer is C: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with caval extension causing PE; this suggests that the PE was due to tumor thrombus. The photo on p. 8 shows areas of increased attenuation in the prominent right and left pulmonary arteries, consistent with a saddle pulmonary embolism. An MRI of the abdomen (see photo above) reveals a large left renal mass extending to Gerota’s fascia and into the left renal vein, protruding slightly into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
The MRI demonstrates an occlusive thrombus in the left renal vein with propagation into the inferior vena cava. The patient underwent a left radical nephrectomy, an inferior vena cava thrombectomy, and a saddle embolectomy. Histological examination of the mass and thrombus confirmed the diagnosis. He had an uneventful recovery and was discharged from the hospital.
RCC accounts for approximately 80% of all primary renal neoplasms, and commonly is termed the “internist’s tumor.” Hematuria is the most common symptom. It is accompanied by flank pain and a palpable abdominal mass in less than 15% of cases.1 Diagnosis of RCC is often made late due to delayed clinical presentation and 20% of patients have metastatic disease at initial diagnosis.2 PE due to tumor thrombus as an initial manifestation of RCC is rare, but is a well-recognized entity leading to dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, hypoxemia, and—in severe cases—acute cor pulmonale with hemodynamic failure.3-5
Staging CT is required in patients with suspected RCC, and MRI is needed, with transesophageal echocardiography used adjunctively, to evaluate cephalic thrombus extension when indicated.6 IVC tumor thrombus occurs in 4%-10% of all cases, most often originating in the renal vein and extending cranially, subsequently propagating to the lungs.7 Survival in local non-metastatic disease with IVC thrombus is no different whether renal vein extension occurs or not, and ranges from 40%-69%, following surgical resection and thrombectomy.8 In those with distant metastases who require venal caval thrombectomy, five-year survivals range from 0%-12.5%.2
The first case of successful removal of a PE secondary to RCC was documented in 1977.1 The goal of surgery is tumor resection and prevention of recurrent embolic events. It is the only effective means of improving survival in the presence of intravascular tumor. Preoperative anticoagulation may be warranted in patients who present with PE, but should be discontinued following definitive surgical treatment secondary to increased risks of hemorrhage.8 TH
References
- Daughtry JD, Stewart BH, Golding LAR, Groves LK. Pulmonary embolus presenting as the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1977;24:178-181.
- Goetzl MA, Goluboff ET, Murphy AM, et al. A contemporary evaluation of cytoreductive nephrectomy with tumor thrombus: morbidity and long term survival. Urol Oncol. 2004; 22:182-187.
- Kubota H, Furuse A, Kotsuka Y, et al. Successful management of massive pulmonary tumor embolism from renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:708-710.
- Gayer G, Mini S, Olchovsky D, et al. Pulmonary embolism—the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma in a young woman. Emerg Radiol. 2003;10:43-45.
- Eggener SE, Dalton DP. Bilateral pulmonary artery tumour emboli from renal carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:173.
- Tsuji Y, Goto A, Hara I, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with extension of tumor thrombus into vena cava: Surgical strategy and prognosis. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:789-796.
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Chao DH, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: is cytoreductive nephrectomy for advanced disease associated with an increased complication rate? J Urol. 2002;168:962-967.
- Nesbitt JC, Soltero ER, Dinney CPN, et al. Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;63:1592-1600.
A48-year-old male presents with three weeks of worsening shortness of breath and pleuritic chest discomfort. A week before the onset of these symptoms, he noticed increasing fatigue, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and persistent hematuria He was otherwise healthy and was taking no medications.
Physical examination reveals a tachypneic yet hemodynamically stable patient, with left upper quadrant fullness. CT chest and abdomen, reveal the following (see right).
You suspect that this finding is secondary to an extrapulmonary process. What unifying diagnosis most likely accounts for these findings? What is your diagnosis?
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Antithrombin III deficiency
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Protein C deficiency
- Prostate carcinoma
Discussion
The answer is C: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with caval extension causing PE; this suggests that the PE was due to tumor thrombus. The photo on p. 8 shows areas of increased attenuation in the prominent right and left pulmonary arteries, consistent with a saddle pulmonary embolism. An MRI of the abdomen (see photo above) reveals a large left renal mass extending to Gerota’s fascia and into the left renal vein, protruding slightly into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
The MRI demonstrates an occlusive thrombus in the left renal vein with propagation into the inferior vena cava. The patient underwent a left radical nephrectomy, an inferior vena cava thrombectomy, and a saddle embolectomy. Histological examination of the mass and thrombus confirmed the diagnosis. He had an uneventful recovery and was discharged from the hospital.
RCC accounts for approximately 80% of all primary renal neoplasms, and commonly is termed the “internist’s tumor.” Hematuria is the most common symptom. It is accompanied by flank pain and a palpable abdominal mass in less than 15% of cases.1 Diagnosis of RCC is often made late due to delayed clinical presentation and 20% of patients have metastatic disease at initial diagnosis.2 PE due to tumor thrombus as an initial manifestation of RCC is rare, but is a well-recognized entity leading to dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, hypoxemia, and—in severe cases—acute cor pulmonale with hemodynamic failure.3-5
Staging CT is required in patients with suspected RCC, and MRI is needed, with transesophageal echocardiography used adjunctively, to evaluate cephalic thrombus extension when indicated.6 IVC tumor thrombus occurs in 4%-10% of all cases, most often originating in the renal vein and extending cranially, subsequently propagating to the lungs.7 Survival in local non-metastatic disease with IVC thrombus is no different whether renal vein extension occurs or not, and ranges from 40%-69%, following surgical resection and thrombectomy.8 In those with distant metastases who require venal caval thrombectomy, five-year survivals range from 0%-12.5%.2
The first case of successful removal of a PE secondary to RCC was documented in 1977.1 The goal of surgery is tumor resection and prevention of recurrent embolic events. It is the only effective means of improving survival in the presence of intravascular tumor. Preoperative anticoagulation may be warranted in patients who present with PE, but should be discontinued following definitive surgical treatment secondary to increased risks of hemorrhage.8 TH
References
- Daughtry JD, Stewart BH, Golding LAR, Groves LK. Pulmonary embolus presenting as the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1977;24:178-181.
- Goetzl MA, Goluboff ET, Murphy AM, et al. A contemporary evaluation of cytoreductive nephrectomy with tumor thrombus: morbidity and long term survival. Urol Oncol. 2004; 22:182-187.
- Kubota H, Furuse A, Kotsuka Y, et al. Successful management of massive pulmonary tumor embolism from renal cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:708-710.
- Gayer G, Mini S, Olchovsky D, et al. Pulmonary embolism—the initial manifestation of renal cell carcinoma in a young woman. Emerg Radiol. 2003;10:43-45.
- Eggener SE, Dalton DP. Bilateral pulmonary artery tumour emboli from renal carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:173.
- Tsuji Y, Goto A, Hara I, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with extension of tumor thrombus into vena cava: Surgical strategy and prognosis. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:789-796.
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Chao DH, et al. Renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: is cytoreductive nephrectomy for advanced disease associated with an increased complication rate? J Urol. 2002;168:962-967.
- Nesbitt JC, Soltero ER, Dinney CPN, et al. Surgical management of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;63:1592-1600.