User login
Impact of a Pharmacist-Led Emergency Department Urinary Tract Infection Aftercare Program
The emergency department (ED) is estimated to provide half of all medical care in the United States, serving as a conduit between ambulatory care and inpatient settings.1 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 11 million antibiotic prescriptions were written in EDs in 2021.2 A previous study conducted at a US Department of Veterans (VA) Affairs medical center found that about 40% of all antimicrobial use in the ED was inappropriate.3 The ED is a critical and high-yield space for antimicrobial stewardship efforts.4
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common reasons for ED visits.4 In 2018, there were about 3 million UTI discharge diagnoses reported in the US.5 Diagnosis and management of UTIs can vary depending on patient sex, upper or lower urinary tract involvement, and the severity of the infection.6 Most UTIs are uncomplicated and can be safely treated with oral antibiotics at home; however, if mismanaged, they can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.6
Antimicrobial prescribing in the ED is predominantly empiric with challenges such as diverse patient needs, rising antimicrobial resistance, and limited microbiologic data at the time of discharge.6 The lack of a standardized process for urine culture follow-up after discharge represents another major complicating factor in the outpatient management of UTIs. Studies have shown that ED pharmacists play a vital role in providing quality follow-up care by optimizing antimicrobial use, resulting in improved patient outcomes in various infectious syndromes, including UTIs.7-13
Program Description
In June 2021, the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) piloted an ED pharmacist-led aftercare program to optimize postdischarge antimicrobial therapy management of UTIs. After a patient is discharged from the ED, the clinical pharmacist reviews urine culture results, interprets available antimicrobial susceptibility, conducts patient interviews, adjusts for patient-specific factors, and addresses potential antibiotic-associated adverse events. The ED pharmacist is then responsible for managing therapy changes in consultation with an ED health care practitioner (HCP).
Methods
This single center, retrospective chart review included veterans who were discharged with an oral antibiotic for UTI treatment from the VAGLAHS ED and evaluated by clinical pharmacists between June 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. For patients with multiple ED visits, only the initial ED encounter was reviewed. Patients were excluded if they had a complicated UTI diagnosis requiring intravenous antibiotics or if they were admitted to the hospital. Data were generated through the Corporate Data Warehouse by VAGLAHS Pharmacy Informatics Service. Each patient was assigned a random number using the Microsoft Excel formula =RAND( ) and then sorted in chronological order to ensure randomization at baseline prior to data collection.
The primary aim of this quality improvement project was to characterize the impact of ED pharmacist-led interventions by evaluating the proportion of empiric to targeted therapy adjustments, antibiotic therapy discontinuation, and unmodified index treatment. The secondary objectives evaluated time to ED pharmacist aftercare follow-up, days of antibiotic exposure avoided, 30-day ED visits related to a urinary source, and transition of care documentation. Descriptive statistics were performed; median and IQR were calculated in Microsoft Excel.
Results
A total of 548 ED UTI encounters were identified, including 449 patients with an index ED UTI aftercare follow-up evaluation. Of the 246 randomly screened patients, 200 veterans met inclusion criteria. The median age of included patients was 73 years and most (83.0%) were male (Table 1). One hundred thirty-two patients (66.0%) had a cystitis diagnosis, followed by complicated UTI (14.0%) and catheter-associated UTI (11.0%). The most frequently isolated uropathogen was Escherichia coli (30.5%). ß-lactams were prescribed for empiric treatment to 121 patients (60.5%), followed by 36 fluoroquinolones prescriptions (18.0%). The median treatment duration was 7 days.
The median time to ED pharmacist UTI aftercare evaluation was 2 days (Table 2). Sixty-seven cases required pharmacist intervention, which included 34 transitions to targeted therapy (17.0%) and 33 antibiotic discontinuations (16.5%). A total of 144 days of antibiotic exposure was avoided (ie, days antibiotic was prescribed minus days therapy administered). The majority of cases without modification to index therapy were due to appropriate empiric treatment selection (49.0%). Twelve (6.0%) patients had a subsequent urinary-related ED visit within 30 days due to 8 cases of persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms (66.7%) and 2 cases of recurrent UTI (16.7%).
Discussion
Outpatient antibiotic prescribing for UTI management in the ED is challenging due to the absence of microbiologic data at time of diagnosis and lack of consistent transition of care follow-up.6 The VAGLAHS ED UTI aftercare program piloted a pharmacist-driven protocol for review of all urine cultures and optimization of antibiotic therapy.
Most ED UTI discharges that did not require pharmacist intervention had empiric treatment selection active against the clinical isolates. This suggests that the ED prescribing practices concur with theVAGLAHS antibiogram and treatment guidelines. Clinical pharmacists intervened in about one-third of UTI cases, which included modification or discontinuation of therapy. Further review of these cases demonstrated that about half of those with a subsequent 30-day ED visit related to a urinary source had therapy modification. Most patients with a 30-day ED visit had persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms, prompting further exploratory workup.
Although this project did not evaluate time from urine culture results to aftercare review, the VAGLAHS ED pharmacists had a median follow-up time of 48 hours. This timeline mirrors the typical duration for urine culture results, suggesting that the pilot program allowed for real time pharmacist review and intervention. Consequently, this initiative resulted in the avoidance of 144 unnecessary days of antibiotic exposure.
While the current protocol highlights the work that ED pharmacists provide postdischarge, there are additional opportunities for pharmacist intervention. For example, one-third of these clinical encounters were completed without HCP notification, indicating an ongoing need to ensure continuity of care. Additionally, all 16 patients diagnosed with asymptomatic bacteriuria were discharged with an oral antibiotic, highlighting an opportunity to further optimize antibiotic prescribing prior to discharge. ED pharmacists continue to play an important role in mitigating inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic use, which will reduce antibiotic-related adverse drug reactions, Clostridioides difficile infection, and antimicrobial resistance.
Limitations
Inconsistent and incomplete documentation of clinical data in the electronic health record made the characterization of patient encounters challenging. Furthermore, ED HCPs varying clinical practices may have impacted the heterogeneity of UTI diagnosis and management at VAGLAHS.
Conclusions
Implementation of an ED pharmacist-driven UTI aftercare program at VAGLAHS reduced unnecessary antimicrobial exposure, improved antibiotic management, and ensured continuity of care postdischarge. Findings from our project implicate possible future pharmacist involvement predischarge, such as targeting inappropriate asymptomatic bacteriuria treatment.14-16 This pilot program suggested the feasibility of integrating antimicrobial stewardship practices within the ED setting in an ongoing effort to improve the quality of care for veterans.
1. Marcozzi D, Carr B, Liferidge A, Baehr N, Browne B.. Trends in the contribution of emergency departments to the provision of hospital-associated health care in the USA. Int J Health Serv. 2018;48(2):267–288. doi:10.1177/0020731417734498
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outpatient antibiotic prescriptions — United States, 2021. Updated October 4, 2022. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://archive.cdc.gov/#/details?url=https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/data/report-2021.html
3. Timbrook TT, Caffrey AR, Ovalle A, et al. Assessments of opportunities to improve antibiotic prescribing in an emergency department: a period prevalence survey. Infect Dis Ther. 2017;6(4):497-505. doi:10.1007/s40121-017-0175-9
4. Pulia M, Redwood R, May L. Antimicrobial stewardship in the emergency department. Emerg Med Clin North. 2018;36(4):853-872. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2018.06.012
5. Weiss A, Jiang H. Most frequent reasons for emergency department visits, 2018. December 16, 2021. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb286-ED-Frequent-Conditions-2018.pdf
6. Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008;22(1):73-87. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2007.10.002
7. Dumkow LE, Kenney RM, MacDonald NC, Carreno JJ, Malhotra MK, Davis SL. Impact of a multidisciplinary culture follow-up program of antimicrobial therapy in the emergency department. Infect Dis Ther. 2014;3(1):45-53. doi:10.1007/s40121-014-0026-x
8. Davis LC, Covey RB, Weston JS, Hu BB, Laine GA. Pharmacist-driven antimicrobial optimization in the emergency department. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(5 Suppl 1):S49-S56. doi:10.2146/sp150036
9. Lingenfelter E, Darkin Z, Fritz K, Youngquist S, Madsen T, Fix M. ED pharmacist monitoring of provider antibiotic selection aids appropriate treatment for outpatient UTI. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(8):1600-1603. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.05.076
10. Zhang X, Rowan N, Pflugeisen BM, Alajbegovic S. Urine culture guided antibiotic interventions: a pharmacist driven antimicrobial stewardship effort in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35(4):594-598. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.12.036
11. Percival KM, Valenti KM, Schmittling SE, Strader BD, Lopez RR, Bergman SJ. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship intervention on urinary tract infection treatment in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(9):1129-1133. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.04.067
12. Almulhim AS, Aldayyen A, Yenina K, Chiappini A, Khan TM. Optimization of antibiotic selection in the emergency department for urine culture follow ups, a retrospective pre-post intervention study: clinical pharmacist efforts. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2019;12(1):8. Published online April 9, 2019. doi:10.1186/s40545-019-0168-z
13. Stoll K, Feltz E, Ebert S. Pharmacist-driven implementation of outpatient antibiotic prescribing algorithms improves guideline adherence in the emergency department. J Pharm Pract. 2021;34(6):875-881. doi:10.1177/0897190020930979
14. Petty LA, Vaughn VM, Flanders SA, et al. Assessment of testing and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria initiated in the emergency department. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7(12):ofaa537. Published online November 3, 2020. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa537
15. Ingalls EM, Veillette JJ, Olson J, et al. Impact of a multifaceted intervention on antibiotic prescribing for cystitis and asymptomatic bacteriuria in 23 community hospital emergency departments. Hosp Pharm. 2023;58(4):401-407. doi:10.1177/00185787231159578
16. Daniel M, Keller S, Mozafarihashjin M, Pahwa A, Soong C. An implementation guide to reducing overtreatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(2):271-276.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.7290
The emergency department (ED) is estimated to provide half of all medical care in the United States, serving as a conduit between ambulatory care and inpatient settings.1 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 11 million antibiotic prescriptions were written in EDs in 2021.2 A previous study conducted at a US Department of Veterans (VA) Affairs medical center found that about 40% of all antimicrobial use in the ED was inappropriate.3 The ED is a critical and high-yield space for antimicrobial stewardship efforts.4
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common reasons for ED visits.4 In 2018, there were about 3 million UTI discharge diagnoses reported in the US.5 Diagnosis and management of UTIs can vary depending on patient sex, upper or lower urinary tract involvement, and the severity of the infection.6 Most UTIs are uncomplicated and can be safely treated with oral antibiotics at home; however, if mismanaged, they can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.6
Antimicrobial prescribing in the ED is predominantly empiric with challenges such as diverse patient needs, rising antimicrobial resistance, and limited microbiologic data at the time of discharge.6 The lack of a standardized process for urine culture follow-up after discharge represents another major complicating factor in the outpatient management of UTIs. Studies have shown that ED pharmacists play a vital role in providing quality follow-up care by optimizing antimicrobial use, resulting in improved patient outcomes in various infectious syndromes, including UTIs.7-13
Program Description
In June 2021, the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) piloted an ED pharmacist-led aftercare program to optimize postdischarge antimicrobial therapy management of UTIs. After a patient is discharged from the ED, the clinical pharmacist reviews urine culture results, interprets available antimicrobial susceptibility, conducts patient interviews, adjusts for patient-specific factors, and addresses potential antibiotic-associated adverse events. The ED pharmacist is then responsible for managing therapy changes in consultation with an ED health care practitioner (HCP).
Methods
This single center, retrospective chart review included veterans who were discharged with an oral antibiotic for UTI treatment from the VAGLAHS ED and evaluated by clinical pharmacists between June 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. For patients with multiple ED visits, only the initial ED encounter was reviewed. Patients were excluded if they had a complicated UTI diagnosis requiring intravenous antibiotics or if they were admitted to the hospital. Data were generated through the Corporate Data Warehouse by VAGLAHS Pharmacy Informatics Service. Each patient was assigned a random number using the Microsoft Excel formula =RAND( ) and then sorted in chronological order to ensure randomization at baseline prior to data collection.
The primary aim of this quality improvement project was to characterize the impact of ED pharmacist-led interventions by evaluating the proportion of empiric to targeted therapy adjustments, antibiotic therapy discontinuation, and unmodified index treatment. The secondary objectives evaluated time to ED pharmacist aftercare follow-up, days of antibiotic exposure avoided, 30-day ED visits related to a urinary source, and transition of care documentation. Descriptive statistics were performed; median and IQR were calculated in Microsoft Excel.
Results
A total of 548 ED UTI encounters were identified, including 449 patients with an index ED UTI aftercare follow-up evaluation. Of the 246 randomly screened patients, 200 veterans met inclusion criteria. The median age of included patients was 73 years and most (83.0%) were male (Table 1). One hundred thirty-two patients (66.0%) had a cystitis diagnosis, followed by complicated UTI (14.0%) and catheter-associated UTI (11.0%). The most frequently isolated uropathogen was Escherichia coli (30.5%). ß-lactams were prescribed for empiric treatment to 121 patients (60.5%), followed by 36 fluoroquinolones prescriptions (18.0%). The median treatment duration was 7 days.
The median time to ED pharmacist UTI aftercare evaluation was 2 days (Table 2). Sixty-seven cases required pharmacist intervention, which included 34 transitions to targeted therapy (17.0%) and 33 antibiotic discontinuations (16.5%). A total of 144 days of antibiotic exposure was avoided (ie, days antibiotic was prescribed minus days therapy administered). The majority of cases without modification to index therapy were due to appropriate empiric treatment selection (49.0%). Twelve (6.0%) patients had a subsequent urinary-related ED visit within 30 days due to 8 cases of persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms (66.7%) and 2 cases of recurrent UTI (16.7%).
Discussion
Outpatient antibiotic prescribing for UTI management in the ED is challenging due to the absence of microbiologic data at time of diagnosis and lack of consistent transition of care follow-up.6 The VAGLAHS ED UTI aftercare program piloted a pharmacist-driven protocol for review of all urine cultures and optimization of antibiotic therapy.
Most ED UTI discharges that did not require pharmacist intervention had empiric treatment selection active against the clinical isolates. This suggests that the ED prescribing practices concur with theVAGLAHS antibiogram and treatment guidelines. Clinical pharmacists intervened in about one-third of UTI cases, which included modification or discontinuation of therapy. Further review of these cases demonstrated that about half of those with a subsequent 30-day ED visit related to a urinary source had therapy modification. Most patients with a 30-day ED visit had persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms, prompting further exploratory workup.
Although this project did not evaluate time from urine culture results to aftercare review, the VAGLAHS ED pharmacists had a median follow-up time of 48 hours. This timeline mirrors the typical duration for urine culture results, suggesting that the pilot program allowed for real time pharmacist review and intervention. Consequently, this initiative resulted in the avoidance of 144 unnecessary days of antibiotic exposure.
While the current protocol highlights the work that ED pharmacists provide postdischarge, there are additional opportunities for pharmacist intervention. For example, one-third of these clinical encounters were completed without HCP notification, indicating an ongoing need to ensure continuity of care. Additionally, all 16 patients diagnosed with asymptomatic bacteriuria were discharged with an oral antibiotic, highlighting an opportunity to further optimize antibiotic prescribing prior to discharge. ED pharmacists continue to play an important role in mitigating inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic use, which will reduce antibiotic-related adverse drug reactions, Clostridioides difficile infection, and antimicrobial resistance.
Limitations
Inconsistent and incomplete documentation of clinical data in the electronic health record made the characterization of patient encounters challenging. Furthermore, ED HCPs varying clinical practices may have impacted the heterogeneity of UTI diagnosis and management at VAGLAHS.
Conclusions
Implementation of an ED pharmacist-driven UTI aftercare program at VAGLAHS reduced unnecessary antimicrobial exposure, improved antibiotic management, and ensured continuity of care postdischarge. Findings from our project implicate possible future pharmacist involvement predischarge, such as targeting inappropriate asymptomatic bacteriuria treatment.14-16 This pilot program suggested the feasibility of integrating antimicrobial stewardship practices within the ED setting in an ongoing effort to improve the quality of care for veterans.
The emergency department (ED) is estimated to provide half of all medical care in the United States, serving as a conduit between ambulatory care and inpatient settings.1 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, around 11 million antibiotic prescriptions were written in EDs in 2021.2 A previous study conducted at a US Department of Veterans (VA) Affairs medical center found that about 40% of all antimicrobial use in the ED was inappropriate.3 The ED is a critical and high-yield space for antimicrobial stewardship efforts.4
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common reasons for ED visits.4 In 2018, there were about 3 million UTI discharge diagnoses reported in the US.5 Diagnosis and management of UTIs can vary depending on patient sex, upper or lower urinary tract involvement, and the severity of the infection.6 Most UTIs are uncomplicated and can be safely treated with oral antibiotics at home; however, if mismanaged, they can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.6
Antimicrobial prescribing in the ED is predominantly empiric with challenges such as diverse patient needs, rising antimicrobial resistance, and limited microbiologic data at the time of discharge.6 The lack of a standardized process for urine culture follow-up after discharge represents another major complicating factor in the outpatient management of UTIs. Studies have shown that ED pharmacists play a vital role in providing quality follow-up care by optimizing antimicrobial use, resulting in improved patient outcomes in various infectious syndromes, including UTIs.7-13
Program Description
In June 2021, the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) piloted an ED pharmacist-led aftercare program to optimize postdischarge antimicrobial therapy management of UTIs. After a patient is discharged from the ED, the clinical pharmacist reviews urine culture results, interprets available antimicrobial susceptibility, conducts patient interviews, adjusts for patient-specific factors, and addresses potential antibiotic-associated adverse events. The ED pharmacist is then responsible for managing therapy changes in consultation with an ED health care practitioner (HCP).
Methods
This single center, retrospective chart review included veterans who were discharged with an oral antibiotic for UTI treatment from the VAGLAHS ED and evaluated by clinical pharmacists between June 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. For patients with multiple ED visits, only the initial ED encounter was reviewed. Patients were excluded if they had a complicated UTI diagnosis requiring intravenous antibiotics or if they were admitted to the hospital. Data were generated through the Corporate Data Warehouse by VAGLAHS Pharmacy Informatics Service. Each patient was assigned a random number using the Microsoft Excel formula =RAND( ) and then sorted in chronological order to ensure randomization at baseline prior to data collection.
The primary aim of this quality improvement project was to characterize the impact of ED pharmacist-led interventions by evaluating the proportion of empiric to targeted therapy adjustments, antibiotic therapy discontinuation, and unmodified index treatment. The secondary objectives evaluated time to ED pharmacist aftercare follow-up, days of antibiotic exposure avoided, 30-day ED visits related to a urinary source, and transition of care documentation. Descriptive statistics were performed; median and IQR were calculated in Microsoft Excel.
Results
A total of 548 ED UTI encounters were identified, including 449 patients with an index ED UTI aftercare follow-up evaluation. Of the 246 randomly screened patients, 200 veterans met inclusion criteria. The median age of included patients was 73 years and most (83.0%) were male (Table 1). One hundred thirty-two patients (66.0%) had a cystitis diagnosis, followed by complicated UTI (14.0%) and catheter-associated UTI (11.0%). The most frequently isolated uropathogen was Escherichia coli (30.5%). ß-lactams were prescribed for empiric treatment to 121 patients (60.5%), followed by 36 fluoroquinolones prescriptions (18.0%). The median treatment duration was 7 days.
The median time to ED pharmacist UTI aftercare evaluation was 2 days (Table 2). Sixty-seven cases required pharmacist intervention, which included 34 transitions to targeted therapy (17.0%) and 33 antibiotic discontinuations (16.5%). A total of 144 days of antibiotic exposure was avoided (ie, days antibiotic was prescribed minus days therapy administered). The majority of cases without modification to index therapy were due to appropriate empiric treatment selection (49.0%). Twelve (6.0%) patients had a subsequent urinary-related ED visit within 30 days due to 8 cases of persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms (66.7%) and 2 cases of recurrent UTI (16.7%).
Discussion
Outpatient antibiotic prescribing for UTI management in the ED is challenging due to the absence of microbiologic data at time of diagnosis and lack of consistent transition of care follow-up.6 The VAGLAHS ED UTI aftercare program piloted a pharmacist-driven protocol for review of all urine cultures and optimization of antibiotic therapy.
Most ED UTI discharges that did not require pharmacist intervention had empiric treatment selection active against the clinical isolates. This suggests that the ED prescribing practices concur with theVAGLAHS antibiogram and treatment guidelines. Clinical pharmacists intervened in about one-third of UTI cases, which included modification or discontinuation of therapy. Further review of these cases demonstrated that about half of those with a subsequent 30-day ED visit related to a urinary source had therapy modification. Most patients with a 30-day ED visit had persistent and/or worsening urinary symptoms, prompting further exploratory workup.
Although this project did not evaluate time from urine culture results to aftercare review, the VAGLAHS ED pharmacists had a median follow-up time of 48 hours. This timeline mirrors the typical duration for urine culture results, suggesting that the pilot program allowed for real time pharmacist review and intervention. Consequently, this initiative resulted in the avoidance of 144 unnecessary days of antibiotic exposure.
While the current protocol highlights the work that ED pharmacists provide postdischarge, there are additional opportunities for pharmacist intervention. For example, one-third of these clinical encounters were completed without HCP notification, indicating an ongoing need to ensure continuity of care. Additionally, all 16 patients diagnosed with asymptomatic bacteriuria were discharged with an oral antibiotic, highlighting an opportunity to further optimize antibiotic prescribing prior to discharge. ED pharmacists continue to play an important role in mitigating inappropriate and unnecessary antibiotic use, which will reduce antibiotic-related adverse drug reactions, Clostridioides difficile infection, and antimicrobial resistance.
Limitations
Inconsistent and incomplete documentation of clinical data in the electronic health record made the characterization of patient encounters challenging. Furthermore, ED HCPs varying clinical practices may have impacted the heterogeneity of UTI diagnosis and management at VAGLAHS.
Conclusions
Implementation of an ED pharmacist-driven UTI aftercare program at VAGLAHS reduced unnecessary antimicrobial exposure, improved antibiotic management, and ensured continuity of care postdischarge. Findings from our project implicate possible future pharmacist involvement predischarge, such as targeting inappropriate asymptomatic bacteriuria treatment.14-16 This pilot program suggested the feasibility of integrating antimicrobial stewardship practices within the ED setting in an ongoing effort to improve the quality of care for veterans.
1. Marcozzi D, Carr B, Liferidge A, Baehr N, Browne B.. Trends in the contribution of emergency departments to the provision of hospital-associated health care in the USA. Int J Health Serv. 2018;48(2):267–288. doi:10.1177/0020731417734498
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outpatient antibiotic prescriptions — United States, 2021. Updated October 4, 2022. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://archive.cdc.gov/#/details?url=https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/data/report-2021.html
3. Timbrook TT, Caffrey AR, Ovalle A, et al. Assessments of opportunities to improve antibiotic prescribing in an emergency department: a period prevalence survey. Infect Dis Ther. 2017;6(4):497-505. doi:10.1007/s40121-017-0175-9
4. Pulia M, Redwood R, May L. Antimicrobial stewardship in the emergency department. Emerg Med Clin North. 2018;36(4):853-872. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2018.06.012
5. Weiss A, Jiang H. Most frequent reasons for emergency department visits, 2018. December 16, 2021. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb286-ED-Frequent-Conditions-2018.pdf
6. Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008;22(1):73-87. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2007.10.002
7. Dumkow LE, Kenney RM, MacDonald NC, Carreno JJ, Malhotra MK, Davis SL. Impact of a multidisciplinary culture follow-up program of antimicrobial therapy in the emergency department. Infect Dis Ther. 2014;3(1):45-53. doi:10.1007/s40121-014-0026-x
8. Davis LC, Covey RB, Weston JS, Hu BB, Laine GA. Pharmacist-driven antimicrobial optimization in the emergency department. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(5 Suppl 1):S49-S56. doi:10.2146/sp150036
9. Lingenfelter E, Darkin Z, Fritz K, Youngquist S, Madsen T, Fix M. ED pharmacist monitoring of provider antibiotic selection aids appropriate treatment for outpatient UTI. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(8):1600-1603. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.05.076
10. Zhang X, Rowan N, Pflugeisen BM, Alajbegovic S. Urine culture guided antibiotic interventions: a pharmacist driven antimicrobial stewardship effort in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35(4):594-598. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.12.036
11. Percival KM, Valenti KM, Schmittling SE, Strader BD, Lopez RR, Bergman SJ. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship intervention on urinary tract infection treatment in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(9):1129-1133. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.04.067
12. Almulhim AS, Aldayyen A, Yenina K, Chiappini A, Khan TM. Optimization of antibiotic selection in the emergency department for urine culture follow ups, a retrospective pre-post intervention study: clinical pharmacist efforts. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2019;12(1):8. Published online April 9, 2019. doi:10.1186/s40545-019-0168-z
13. Stoll K, Feltz E, Ebert S. Pharmacist-driven implementation of outpatient antibiotic prescribing algorithms improves guideline adherence in the emergency department. J Pharm Pract. 2021;34(6):875-881. doi:10.1177/0897190020930979
14. Petty LA, Vaughn VM, Flanders SA, et al. Assessment of testing and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria initiated in the emergency department. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7(12):ofaa537. Published online November 3, 2020. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa537
15. Ingalls EM, Veillette JJ, Olson J, et al. Impact of a multifaceted intervention on antibiotic prescribing for cystitis and asymptomatic bacteriuria in 23 community hospital emergency departments. Hosp Pharm. 2023;58(4):401-407. doi:10.1177/00185787231159578
16. Daniel M, Keller S, Mozafarihashjin M, Pahwa A, Soong C. An implementation guide to reducing overtreatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(2):271-276.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.7290
1. Marcozzi D, Carr B, Liferidge A, Baehr N, Browne B.. Trends in the contribution of emergency departments to the provision of hospital-associated health care in the USA. Int J Health Serv. 2018;48(2):267–288. doi:10.1177/0020731417734498
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outpatient antibiotic prescriptions — United States, 2021. Updated October 4, 2022. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://archive.cdc.gov/#/details?url=https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/data/report-2021.html
3. Timbrook TT, Caffrey AR, Ovalle A, et al. Assessments of opportunities to improve antibiotic prescribing in an emergency department: a period prevalence survey. Infect Dis Ther. 2017;6(4):497-505. doi:10.1007/s40121-017-0175-9
4. Pulia M, Redwood R, May L. Antimicrobial stewardship in the emergency department. Emerg Med Clin North. 2018;36(4):853-872. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2018.06.012
5. Weiss A, Jiang H. Most frequent reasons for emergency department visits, 2018. December 16, 2021. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb286-ED-Frequent-Conditions-2018.pdf
6. Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008;22(1):73-87. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2007.10.002
7. Dumkow LE, Kenney RM, MacDonald NC, Carreno JJ, Malhotra MK, Davis SL. Impact of a multidisciplinary culture follow-up program of antimicrobial therapy in the emergency department. Infect Dis Ther. 2014;3(1):45-53. doi:10.1007/s40121-014-0026-x
8. Davis LC, Covey RB, Weston JS, Hu BB, Laine GA. Pharmacist-driven antimicrobial optimization in the emergency department. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(5 Suppl 1):S49-S56. doi:10.2146/sp150036
9. Lingenfelter E, Darkin Z, Fritz K, Youngquist S, Madsen T, Fix M. ED pharmacist monitoring of provider antibiotic selection aids appropriate treatment for outpatient UTI. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(8):1600-1603. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.05.076
10. Zhang X, Rowan N, Pflugeisen BM, Alajbegovic S. Urine culture guided antibiotic interventions: a pharmacist driven antimicrobial stewardship effort in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35(4):594-598. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.12.036
11. Percival KM, Valenti KM, Schmittling SE, Strader BD, Lopez RR, Bergman SJ. Impact of an antimicrobial stewardship intervention on urinary tract infection treatment in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(9):1129-1133. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.04.067
12. Almulhim AS, Aldayyen A, Yenina K, Chiappini A, Khan TM. Optimization of antibiotic selection in the emergency department for urine culture follow ups, a retrospective pre-post intervention study: clinical pharmacist efforts. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2019;12(1):8. Published online April 9, 2019. doi:10.1186/s40545-019-0168-z
13. Stoll K, Feltz E, Ebert S. Pharmacist-driven implementation of outpatient antibiotic prescribing algorithms improves guideline adherence in the emergency department. J Pharm Pract. 2021;34(6):875-881. doi:10.1177/0897190020930979
14. Petty LA, Vaughn VM, Flanders SA, et al. Assessment of testing and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria initiated in the emergency department. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7(12):ofaa537. Published online November 3, 2020. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaa537
15. Ingalls EM, Veillette JJ, Olson J, et al. Impact of a multifaceted intervention on antibiotic prescribing for cystitis and asymptomatic bacteriuria in 23 community hospital emergency departments. Hosp Pharm. 2023;58(4):401-407. doi:10.1177/00185787231159578
16. Daniel M, Keller S, Mozafarihashjin M, Pahwa A, Soong C. An implementation guide to reducing overtreatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(2):271-276.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.7290
COVID-19 Incidence After Emergency Department Visit
At the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, patient encounters with the health care system plummeted.1-3 The perceived increased risk of contracting COVID-19 while obtaining care was thought to be a contributing factor. In outpatient settings, one study noted a 63% decrease in visits to otolaryngology visits in Massachusetts, and another noted a 33% decrease in dental office visits at the onset of the pandemic in 2020 compared with the same time frame in 2019.2,4 Along with mask mandates and stay-at-home orders, various institutions sought to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 through different protocols, including the use of social distancing, limitation of visitors, and telehealth. Despite some of these measures, nosocomial infections were not uncommon. For example, one hospital in the United Kingdom reported that 15% of COVID-19 inpatient cases in a 6-week period in 2020 were probably or definitely hospital acquired. These patients had a 36% case fatality rate.5
Unlike outpatient treatment centers, however, the emergency department (ED) is mandated by the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act to provide a medical screening examination and to stabilize emergency medical conditions to all patients presenting to the ED. Thus, high numbers of undifferentiated and symptomatic patients are forced to congregate in EDs, increasing the risk of transmission of COVID-19. This perception of increased risk led to a 42% decrease in ED visits during March and April 2020 at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 Correspondingly, there was a 20% decrease in code stroke activations at a hospital in Canada and a 38% decrease in ST-elevation myocardial infarction activations across 9 United States hospital systems.6,7
Limited studies have been conducted to date to determine whether contracting COVID-19 while in the ED is a risk. One retrospective case-control study evaluating 39 EDs in the US showed that ED colocation with known patients with COVID-19 was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 transmission.5 However, this study also recognized that infection control strategies widely varied by location and date.
In this study, we report the incidence of COVID-19 infections within 21 days after the initial visit for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection to the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) ED and compared it with that of COVID-19 infections for tests performed within the VAGLAHS.
Program Description
As a quality improvement measure, the
Patients with specific symptoms noted during triage, such as those associated with COVID-19 diagnosis, respiratory infections, fever, and/or myalgias, were isolated in their own patient room. Electronic tablets were used for persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 to communicate with family and/or medical staff who did not need to enter the patient’s room. Two-hour disinfection protocols were instituted for high-risk patients who were moved during the course of their treatment (ie, transfer to another bed for admission or discharge). All staff was specifically trained in personal protective equipment (PPE) donning and doffing, and 2-physician airway teams were implemented to ensure proper PPE use and safe COVID-19 intubations.
COVID-19 Infections
Electronic health records of patients who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not related to COVID-19 were reviewed from
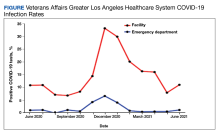
A total of 8708 patients who came to the ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection and had a COVID-19 test within 21 days of the ED visit met the inclusion criteria. The overall average positivity rate at the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection was 1.1% from June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021. The positivity rate by month ranged from 0% to 6.7% for this period (Figure).
Discussion
Implementing COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED helped minimize exposure and subsequent infection of COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection. Contextualizing this with the overall average monthly positivity rate of veterans in the VAGLAHS catchment area (10.9%) or Los Angeles County (7.9%) between June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021, veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection were less likely to test positive for COVID-19 within 21 days (1.1%), suggesting that the extensive measures taken at the VAGLAHS ED were effective.8
Many health care systems in the US and abroad have experimented with different transmission mitigation strategies in the ED. These tactics have included careful resource allocation when PPE shortages occur, incorporation of airway teams with appropriate safety measures to reduce nosocomial spread to health care workers, and use of a cohorting plan to separate persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 from other patients.9-15 Additionally, forward screening areas were incorporated similar to the COVID-19 tent that was instituted at the VAGLAHS ED to manage patients who were referred to the ED for COVID-19 testing during the beginning of the pandemic, which prevented symptomatic patients from congregating with asymptomatic patients.14,15
Encouragingly, some of these studies reported no cases of nosocomial transmission in the ED.11,13 In a separate study, 14 clusters of COVID-19 cases were identified at one VA health care system in which nosocomial transmission was suspected, including one in the ED.16 Using contact tracing, no patients and 9 employees were found to have contracted COVID-19 in that cluster. Overall, among all clusters examined within the health care system, either by contact tracing or by whole-genome sequencing, the authors found that transmission from health care personnel to patients was rare. Despite different methodologies, we also similarly found that ED patients in our VA facility were unlikely to become infected with COVID-19.
While the low incidence of positive COVID-19 tests cannot be attributed to any one method, our data provide a working blueprint for enhanced ED precautions in future surges of COVID-19 or other airborne diseases, including that of future pandemics.
Limitations
Notably, although the VA is the largest health care system in the US, a considerable number of veterans may present to non-VA EDs to seek care, and thus their data are not included here; these veterans may live farther from a VA facility or experience higher barriers to care than veterans who exclusively or almost exclusively seek care within the VA. As a result, we are unable to account for COVID-19 tests completed outside the VA. Moreover, the wild type SARS-CoV-2 virus was dominant during the time frame chosen for this assessment, and data may not be generalizable to other variants (eg, omicron) that are known to be more highly transmissible.17 Lastly, although our observation was performed at a single VA ED and may not apply to other facilities, especially in light of different mitigation strategies, our findings still provide support for approaches to minimizing patient and staff exposure to COVID-19 in ED settings.
Conclusions
Implementation of COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED may have minimized exposure to COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 and did not put one at higher risk of contracting COVID-19. Taken together, our data suggest that patients should not avoid seeking emergency care out of fear of contracting COVID-19 if EDs have adequately instituted mitigation techniques.
1. Hartnett KP, Kite-Powell A, DeVies J, et al; National Syndromic Surveillance Program Community of Practice. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department visits—United States, January 1, 2019-May 30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(23):699-704. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e1
2. Fan T, Workman AD, Miller LE, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on otolaryngology community practice in Massachusetts. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;165(3):424-430. doi:10.1177/0194599820983732
3. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
4. Kranz AM, Chen A, Gahlon G, Stein BD. 2020 trends in dental office visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Dent Assoc. 2021;152(7):535-541,e1. doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2021.02.01
5. Ridgway JP, Robicsek AA. Risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) acquisition among emergency department patients: a retrospective case control study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42(1):105-107. doi:10.1017/ice.2020.1224
6. Bres Bullrich M, Fridman S, Mandzia JL, et al. COVID-19: stroke admissions, emergency department visits, and prevention clinic referrals. Can J Neurol Sci. 2020;47(5):693-696. doi:10.1017/cjn.2020.101
7. Garcia S, Albaghdadi MS, Meraj PM, et al. Reduction in ST-segment elevation cardiac catheterization laboratory activations in the United States during COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(22):2871-2872. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.011
8. LA County COVID-19 Surveillance Dashboard. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://covid19.lacounty.gov/dashboards
9. Wallace DW, Burleson SL, Heimann MA, et al. An adapted emergency department triage algorithm for the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2020;1:1374-1379. doi:10.1002/emp2.12210
10. Montrief T, Ramzy M, Long B, Gottlieb M, Hercz D. COVID-19 respiratory support in the emergency department setting. Am Journal Emerg Med. 2020;38(10):2160-2168. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.001
11. Alqahtani F, Alanazi M, Alassaf W, et al. Preventing SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the emergency department by implementing a separate pathway for patients with respiratory conditions. J Complement Integr Med. 2022;19(2):383-388. doi:10.1515/jcim-2020-0422
12. Odorizzi S, Clark E, Nemnom MJ, et al. Flow impacts of hot/cold zone infection control procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic in the emergency department. CJEM. 2022;24(4):390-396. doi:10.1007/s43678-022-00278-0
13. Wee LE, Fua TP, Chua YY, et al. Containing COVID-19 in the emergency department: the role of improved case detection and segregation of suspect cases. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(5):379-387. doi:10.1111/acem.13984
14. Tan RMR, Ong GYK, Chong SL, Ganapathy S, Tyebally A, Lee KP. Dynamic adaptation to COVID-19 in a Singapore paediatric emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2020;37(5):252-254. doi:10.1136/emermed-2020-20963
15. Quah LJJ, Tan BKK, Fua TP, et al. Reorganising the emergency department to manage the COVID-19 outbreak. Int J Emerg Med. 2020;13(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12245-020-00294-w
16. Jinadatha C, Jones LD, Choi H, et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in inpatient and outpatient settings in a Veterans Affairs health care system. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021;8(8):ofab328. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab328
17. Riediker M, Briceno-Ayala L, Ichihara G, et al. Higher viral load and infectivity increase risk of aerosol transmission for Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. Swiss Med Wkly. 2022;152:w30133. doi:10.4414/smw.2022.w30133
At the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, patient encounters with the health care system plummeted.1-3 The perceived increased risk of contracting COVID-19 while obtaining care was thought to be a contributing factor. In outpatient settings, one study noted a 63% decrease in visits to otolaryngology visits in Massachusetts, and another noted a 33% decrease in dental office visits at the onset of the pandemic in 2020 compared with the same time frame in 2019.2,4 Along with mask mandates and stay-at-home orders, various institutions sought to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 through different protocols, including the use of social distancing, limitation of visitors, and telehealth. Despite some of these measures, nosocomial infections were not uncommon. For example, one hospital in the United Kingdom reported that 15% of COVID-19 inpatient cases in a 6-week period in 2020 were probably or definitely hospital acquired. These patients had a 36% case fatality rate.5
Unlike outpatient treatment centers, however, the emergency department (ED) is mandated by the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act to provide a medical screening examination and to stabilize emergency medical conditions to all patients presenting to the ED. Thus, high numbers of undifferentiated and symptomatic patients are forced to congregate in EDs, increasing the risk of transmission of COVID-19. This perception of increased risk led to a 42% decrease in ED visits during March and April 2020 at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 Correspondingly, there was a 20% decrease in code stroke activations at a hospital in Canada and a 38% decrease in ST-elevation myocardial infarction activations across 9 United States hospital systems.6,7
Limited studies have been conducted to date to determine whether contracting COVID-19 while in the ED is a risk. One retrospective case-control study evaluating 39 EDs in the US showed that ED colocation with known patients with COVID-19 was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 transmission.5 However, this study also recognized that infection control strategies widely varied by location and date.
In this study, we report the incidence of COVID-19 infections within 21 days after the initial visit for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection to the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) ED and compared it with that of COVID-19 infections for tests performed within the VAGLAHS.
Program Description
As a quality improvement measure, the
Patients with specific symptoms noted during triage, such as those associated with COVID-19 diagnosis, respiratory infections, fever, and/or myalgias, were isolated in their own patient room. Electronic tablets were used for persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 to communicate with family and/or medical staff who did not need to enter the patient’s room. Two-hour disinfection protocols were instituted for high-risk patients who were moved during the course of their treatment (ie, transfer to another bed for admission or discharge). All staff was specifically trained in personal protective equipment (PPE) donning and doffing, and 2-physician airway teams were implemented to ensure proper PPE use and safe COVID-19 intubations.
COVID-19 Infections
Electronic health records of patients who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not related to COVID-19 were reviewed from
A total of 8708 patients who came to the ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection and had a COVID-19 test within 21 days of the ED visit met the inclusion criteria. The overall average positivity rate at the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection was 1.1% from June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021. The positivity rate by month ranged from 0% to 6.7% for this period (Figure).
Discussion
Implementing COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED helped minimize exposure and subsequent infection of COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection. Contextualizing this with the overall average monthly positivity rate of veterans in the VAGLAHS catchment area (10.9%) or Los Angeles County (7.9%) between June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021, veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection were less likely to test positive for COVID-19 within 21 days (1.1%), suggesting that the extensive measures taken at the VAGLAHS ED were effective.8
Many health care systems in the US and abroad have experimented with different transmission mitigation strategies in the ED. These tactics have included careful resource allocation when PPE shortages occur, incorporation of airway teams with appropriate safety measures to reduce nosocomial spread to health care workers, and use of a cohorting plan to separate persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 from other patients.9-15 Additionally, forward screening areas were incorporated similar to the COVID-19 tent that was instituted at the VAGLAHS ED to manage patients who were referred to the ED for COVID-19 testing during the beginning of the pandemic, which prevented symptomatic patients from congregating with asymptomatic patients.14,15
Encouragingly, some of these studies reported no cases of nosocomial transmission in the ED.11,13 In a separate study, 14 clusters of COVID-19 cases were identified at one VA health care system in which nosocomial transmission was suspected, including one in the ED.16 Using contact tracing, no patients and 9 employees were found to have contracted COVID-19 in that cluster. Overall, among all clusters examined within the health care system, either by contact tracing or by whole-genome sequencing, the authors found that transmission from health care personnel to patients was rare. Despite different methodologies, we also similarly found that ED patients in our VA facility were unlikely to become infected with COVID-19.
While the low incidence of positive COVID-19 tests cannot be attributed to any one method, our data provide a working blueprint for enhanced ED precautions in future surges of COVID-19 or other airborne diseases, including that of future pandemics.
Limitations
Notably, although the VA is the largest health care system in the US, a considerable number of veterans may present to non-VA EDs to seek care, and thus their data are not included here; these veterans may live farther from a VA facility or experience higher barriers to care than veterans who exclusively or almost exclusively seek care within the VA. As a result, we are unable to account for COVID-19 tests completed outside the VA. Moreover, the wild type SARS-CoV-2 virus was dominant during the time frame chosen for this assessment, and data may not be generalizable to other variants (eg, omicron) that are known to be more highly transmissible.17 Lastly, although our observation was performed at a single VA ED and may not apply to other facilities, especially in light of different mitigation strategies, our findings still provide support for approaches to minimizing patient and staff exposure to COVID-19 in ED settings.
Conclusions
Implementation of COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED may have minimized exposure to COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 and did not put one at higher risk of contracting COVID-19. Taken together, our data suggest that patients should not avoid seeking emergency care out of fear of contracting COVID-19 if EDs have adequately instituted mitigation techniques.
At the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, patient encounters with the health care system plummeted.1-3 The perceived increased risk of contracting COVID-19 while obtaining care was thought to be a contributing factor. In outpatient settings, one study noted a 63% decrease in visits to otolaryngology visits in Massachusetts, and another noted a 33% decrease in dental office visits at the onset of the pandemic in 2020 compared with the same time frame in 2019.2,4 Along with mask mandates and stay-at-home orders, various institutions sought to mitigate the spread of COVID-19 through different protocols, including the use of social distancing, limitation of visitors, and telehealth. Despite some of these measures, nosocomial infections were not uncommon. For example, one hospital in the United Kingdom reported that 15% of COVID-19 inpatient cases in a 6-week period in 2020 were probably or definitely hospital acquired. These patients had a 36% case fatality rate.5
Unlike outpatient treatment centers, however, the emergency department (ED) is mandated by the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act to provide a medical screening examination and to stabilize emergency medical conditions to all patients presenting to the ED. Thus, high numbers of undifferentiated and symptomatic patients are forced to congregate in EDs, increasing the risk of transmission of COVID-19. This perception of increased risk led to a 42% decrease in ED visits during March and April 2020 at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 Correspondingly, there was a 20% decrease in code stroke activations at a hospital in Canada and a 38% decrease in ST-elevation myocardial infarction activations across 9 United States hospital systems.6,7
Limited studies have been conducted to date to determine whether contracting COVID-19 while in the ED is a risk. One retrospective case-control study evaluating 39 EDs in the US showed that ED colocation with known patients with COVID-19 was not associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 transmission.5 However, this study also recognized that infection control strategies widely varied by location and date.
In this study, we report the incidence of COVID-19 infections within 21 days after the initial visit for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection to the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS) ED and compared it with that of COVID-19 infections for tests performed within the VAGLAHS.
Program Description
As a quality improvement measure, the
Patients with specific symptoms noted during triage, such as those associated with COVID-19 diagnosis, respiratory infections, fever, and/or myalgias, were isolated in their own patient room. Electronic tablets were used for persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 to communicate with family and/or medical staff who did not need to enter the patient’s room. Two-hour disinfection protocols were instituted for high-risk patients who were moved during the course of their treatment (ie, transfer to another bed for admission or discharge). All staff was specifically trained in personal protective equipment (PPE) donning and doffing, and 2-physician airway teams were implemented to ensure proper PPE use and safe COVID-19 intubations.
COVID-19 Infections
Electronic health records of patients who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not related to COVID-19 were reviewed from
A total of 8708 patients who came to the ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection and had a COVID-19 test within 21 days of the ED visit met the inclusion criteria. The overall average positivity rate at the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection was 1.1% from June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021. The positivity rate by month ranged from 0% to 6.7% for this period (Figure).
Discussion
Implementing COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED helped minimize exposure and subsequent infection of COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED with symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection. Contextualizing this with the overall average monthly positivity rate of veterans in the VAGLAHS catchment area (10.9%) or Los Angeles County (7.9%) between June 1, 2020, to June 30, 2021, veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 infection were less likely to test positive for COVID-19 within 21 days (1.1%), suggesting that the extensive measures taken at the VAGLAHS ED were effective.8
Many health care systems in the US and abroad have experimented with different transmission mitigation strategies in the ED. These tactics have included careful resource allocation when PPE shortages occur, incorporation of airway teams with appropriate safety measures to reduce nosocomial spread to health care workers, and use of a cohorting plan to separate persons under investigation and patients with COVID-19 from other patients.9-15 Additionally, forward screening areas were incorporated similar to the COVID-19 tent that was instituted at the VAGLAHS ED to manage patients who were referred to the ED for COVID-19 testing during the beginning of the pandemic, which prevented symptomatic patients from congregating with asymptomatic patients.14,15
Encouragingly, some of these studies reported no cases of nosocomial transmission in the ED.11,13 In a separate study, 14 clusters of COVID-19 cases were identified at one VA health care system in which nosocomial transmission was suspected, including one in the ED.16 Using contact tracing, no patients and 9 employees were found to have contracted COVID-19 in that cluster. Overall, among all clusters examined within the health care system, either by contact tracing or by whole-genome sequencing, the authors found that transmission from health care personnel to patients was rare. Despite different methodologies, we also similarly found that ED patients in our VA facility were unlikely to become infected with COVID-19.
While the low incidence of positive COVID-19 tests cannot be attributed to any one method, our data provide a working blueprint for enhanced ED precautions in future surges of COVID-19 or other airborne diseases, including that of future pandemics.
Limitations
Notably, although the VA is the largest health care system in the US, a considerable number of veterans may present to non-VA EDs to seek care, and thus their data are not included here; these veterans may live farther from a VA facility or experience higher barriers to care than veterans who exclusively or almost exclusively seek care within the VA. As a result, we are unable to account for COVID-19 tests completed outside the VA. Moreover, the wild type SARS-CoV-2 virus was dominant during the time frame chosen for this assessment, and data may not be generalizable to other variants (eg, omicron) that are known to be more highly transmissible.17 Lastly, although our observation was performed at a single VA ED and may not apply to other facilities, especially in light of different mitigation strategies, our findings still provide support for approaches to minimizing patient and staff exposure to COVID-19 in ED settings.
Conclusions
Implementation of COVID-19 mitigation measures in the VAGLAHS ED may have minimized exposure to COVID-19 for veterans who visited the VAGLAHS ED for symptoms not associated with COVID-19 and did not put one at higher risk of contracting COVID-19. Taken together, our data suggest that patients should not avoid seeking emergency care out of fear of contracting COVID-19 if EDs have adequately instituted mitigation techniques.
1. Hartnett KP, Kite-Powell A, DeVies J, et al; National Syndromic Surveillance Program Community of Practice. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department visits—United States, January 1, 2019-May 30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(23):699-704. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e1
2. Fan T, Workman AD, Miller LE, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on otolaryngology community practice in Massachusetts. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;165(3):424-430. doi:10.1177/0194599820983732
3. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
4. Kranz AM, Chen A, Gahlon G, Stein BD. 2020 trends in dental office visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Dent Assoc. 2021;152(7):535-541,e1. doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2021.02.01
5. Ridgway JP, Robicsek AA. Risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) acquisition among emergency department patients: a retrospective case control study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42(1):105-107. doi:10.1017/ice.2020.1224
6. Bres Bullrich M, Fridman S, Mandzia JL, et al. COVID-19: stroke admissions, emergency department visits, and prevention clinic referrals. Can J Neurol Sci. 2020;47(5):693-696. doi:10.1017/cjn.2020.101
7. Garcia S, Albaghdadi MS, Meraj PM, et al. Reduction in ST-segment elevation cardiac catheterization laboratory activations in the United States during COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(22):2871-2872. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.011
8. LA County COVID-19 Surveillance Dashboard. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://covid19.lacounty.gov/dashboards
9. Wallace DW, Burleson SL, Heimann MA, et al. An adapted emergency department triage algorithm for the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2020;1:1374-1379. doi:10.1002/emp2.12210
10. Montrief T, Ramzy M, Long B, Gottlieb M, Hercz D. COVID-19 respiratory support in the emergency department setting. Am Journal Emerg Med. 2020;38(10):2160-2168. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.001
11. Alqahtani F, Alanazi M, Alassaf W, et al. Preventing SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the emergency department by implementing a separate pathway for patients with respiratory conditions. J Complement Integr Med. 2022;19(2):383-388. doi:10.1515/jcim-2020-0422
12. Odorizzi S, Clark E, Nemnom MJ, et al. Flow impacts of hot/cold zone infection control procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic in the emergency department. CJEM. 2022;24(4):390-396. doi:10.1007/s43678-022-00278-0
13. Wee LE, Fua TP, Chua YY, et al. Containing COVID-19 in the emergency department: the role of improved case detection and segregation of suspect cases. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(5):379-387. doi:10.1111/acem.13984
14. Tan RMR, Ong GYK, Chong SL, Ganapathy S, Tyebally A, Lee KP. Dynamic adaptation to COVID-19 in a Singapore paediatric emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2020;37(5):252-254. doi:10.1136/emermed-2020-20963
15. Quah LJJ, Tan BKK, Fua TP, et al. Reorganising the emergency department to manage the COVID-19 outbreak. Int J Emerg Med. 2020;13(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12245-020-00294-w
16. Jinadatha C, Jones LD, Choi H, et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in inpatient and outpatient settings in a Veterans Affairs health care system. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021;8(8):ofab328. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab328
17. Riediker M, Briceno-Ayala L, Ichihara G, et al. Higher viral load and infectivity increase risk of aerosol transmission for Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. Swiss Med Wkly. 2022;152:w30133. doi:10.4414/smw.2022.w30133
1. Hartnett KP, Kite-Powell A, DeVies J, et al; National Syndromic Surveillance Program Community of Practice. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department visits—United States, January 1, 2019-May 30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(23):699-704. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e1
2. Fan T, Workman AD, Miller LE, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on otolaryngology community practice in Massachusetts. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;165(3):424-430. doi:10.1177/0194599820983732
3. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
4. Kranz AM, Chen A, Gahlon G, Stein BD. 2020 trends in dental office visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Dent Assoc. 2021;152(7):535-541,e1. doi:10.1016/j.adaj.2021.02.01
5. Ridgway JP, Robicsek AA. Risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) acquisition among emergency department patients: a retrospective case control study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42(1):105-107. doi:10.1017/ice.2020.1224
6. Bres Bullrich M, Fridman S, Mandzia JL, et al. COVID-19: stroke admissions, emergency department visits, and prevention clinic referrals. Can J Neurol Sci. 2020;47(5):693-696. doi:10.1017/cjn.2020.101
7. Garcia S, Albaghdadi MS, Meraj PM, et al. Reduction in ST-segment elevation cardiac catheterization laboratory activations in the United States during COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(22):2871-2872. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.011
8. LA County COVID-19 Surveillance Dashboard. Accessed July 25, 2022. https://covid19.lacounty.gov/dashboards
9. Wallace DW, Burleson SL, Heimann MA, et al. An adapted emergency department triage algorithm for the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2020;1:1374-1379. doi:10.1002/emp2.12210
10. Montrief T, Ramzy M, Long B, Gottlieb M, Hercz D. COVID-19 respiratory support in the emergency department setting. Am Journal Emerg Med. 2020;38(10):2160-2168. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.001
11. Alqahtani F, Alanazi M, Alassaf W, et al. Preventing SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the emergency department by implementing a separate pathway for patients with respiratory conditions. J Complement Integr Med. 2022;19(2):383-388. doi:10.1515/jcim-2020-0422
12. Odorizzi S, Clark E, Nemnom MJ, et al. Flow impacts of hot/cold zone infection control procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic in the emergency department. CJEM. 2022;24(4):390-396. doi:10.1007/s43678-022-00278-0
13. Wee LE, Fua TP, Chua YY, et al. Containing COVID-19 in the emergency department: the role of improved case detection and segregation of suspect cases. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(5):379-387. doi:10.1111/acem.13984
14. Tan RMR, Ong GYK, Chong SL, Ganapathy S, Tyebally A, Lee KP. Dynamic adaptation to COVID-19 in a Singapore paediatric emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2020;37(5):252-254. doi:10.1136/emermed-2020-20963
15. Quah LJJ, Tan BKK, Fua TP, et al. Reorganising the emergency department to manage the COVID-19 outbreak. Int J Emerg Med. 2020;13(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12245-020-00294-w
16. Jinadatha C, Jones LD, Choi H, et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in inpatient and outpatient settings in a Veterans Affairs health care system. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021;8(8):ofab328. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab328
17. Riediker M, Briceno-Ayala L, Ichihara G, et al. Higher viral load and infectivity increase risk of aerosol transmission for Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. Swiss Med Wkly. 2022;152:w30133. doi:10.4414/smw.2022.w30133