User login
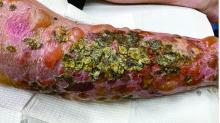
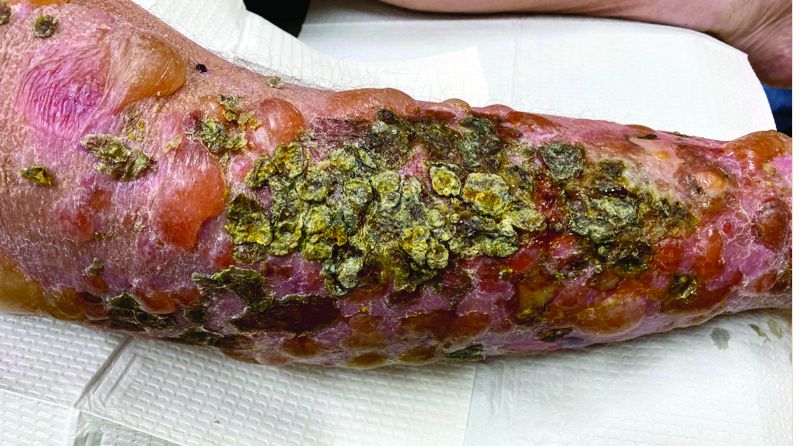
A 72-year-old with an acute, pruritic, bullous eruption involving his right pretibial extremity
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
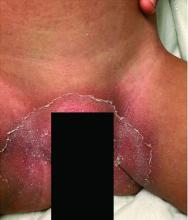
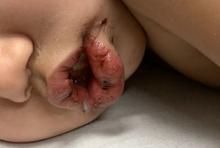
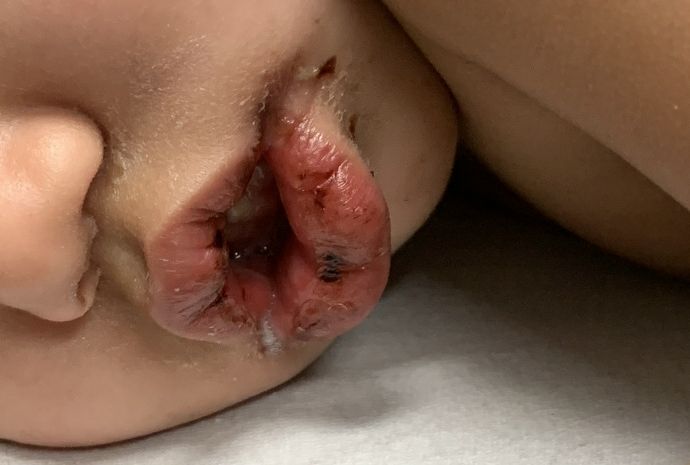
A toddler with a fever and desquamating perineal rash
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
An otherwise healthy 18-month-old female presented to the emergency department with 5 days of fever, erythema, fissuring of the lips, conjunctival injection, and a desquamating perineal rash. In addition, she had nasal congestion and cough for which she was started on amoxicillin 2 days prior to presentation given concern for pneumonia.
On exam, she was also noted to have several palpable cervical lymph nodes and edematous hands with overlying erythema. Laboratory evaluation was notable for respiratory syncytial virus positivity by polymerase chain reaction assay, leukocytosis, and elevated inflammatory markers (erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein).