User login
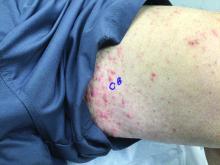
75-year-old White male presenting with progressive pruritus and a worsening rash
, although it can also be contracted through contaminated bedding and clothing. It can affect all races and ages.
Patients typically present with extremely pruritic, symmetric papules and excoriations. In nodular scabies, nodules and large papules are seen on exam. Thin lines in the skin called burrows may be present, especially in the webs between fingers. Female mites create burrows as they tunnel through the epidermis and lay eggs. The wrists, areola, waistline, and groin may all be involved, creating an imaginary circle between the areas described as the “circle of Hebra.” Penile and scrotal lesions are common in men.
Patients usually experience worse pruritus at night, which disturbs sleep. Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies more often seen in those with immunocompromised immune systems. Clinically, thick crusted and scaly patches are present that are teeming with mites.
Diagnosis can be confirmed by performing a scabies prep, during which a burrow is scraped with a surgical blade. A drop of mineral oil is placed on the skin cells. The mite, ova, and feces can be visualized under the microscope. Wrists and hands usually have the highest yield for finding the parasites.
Topical treatments include permethrin 5% cream, lindane, benzyl benzoate, and crotamiton, and should be applied as two treatments a week apart. In the United States, permethrin is most commonly used. Ivermectin pills are used off label and are very effective and may be repeated for 1-2 weeks. All household contacts should be treated. Patients may still have pruritus for 2-4 weeks following treatment.
In this patient, a scabies prep was performed prior to performing repeat skin biopsies. Microscopic examination revealed ova, one mite, and feces. Treatment was initiated with ivermectin and permethrin.
Photos and case were submitted by Susannah Berke, MD, and Damon McClain, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
, although it can also be contracted through contaminated bedding and clothing. It can affect all races and ages.
Patients typically present with extremely pruritic, symmetric papules and excoriations. In nodular scabies, nodules and large papules are seen on exam. Thin lines in the skin called burrows may be present, especially in the webs between fingers. Female mites create burrows as they tunnel through the epidermis and lay eggs. The wrists, areola, waistline, and groin may all be involved, creating an imaginary circle between the areas described as the “circle of Hebra.” Penile and scrotal lesions are common in men.
Patients usually experience worse pruritus at night, which disturbs sleep. Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies more often seen in those with immunocompromised immune systems. Clinically, thick crusted and scaly patches are present that are teeming with mites.
Diagnosis can be confirmed by performing a scabies prep, during which a burrow is scraped with a surgical blade. A drop of mineral oil is placed on the skin cells. The mite, ova, and feces can be visualized under the microscope. Wrists and hands usually have the highest yield for finding the parasites.
Topical treatments include permethrin 5% cream, lindane, benzyl benzoate, and crotamiton, and should be applied as two treatments a week apart. In the United States, permethrin is most commonly used. Ivermectin pills are used off label and are very effective and may be repeated for 1-2 weeks. All household contacts should be treated. Patients may still have pruritus for 2-4 weeks following treatment.
In this patient, a scabies prep was performed prior to performing repeat skin biopsies. Microscopic examination revealed ova, one mite, and feces. Treatment was initiated with ivermectin and permethrin.
Photos and case were submitted by Susannah Berke, MD, and Damon McClain, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
, although it can also be contracted through contaminated bedding and clothing. It can affect all races and ages.
Patients typically present with extremely pruritic, symmetric papules and excoriations. In nodular scabies, nodules and large papules are seen on exam. Thin lines in the skin called burrows may be present, especially in the webs between fingers. Female mites create burrows as they tunnel through the epidermis and lay eggs. The wrists, areola, waistline, and groin may all be involved, creating an imaginary circle between the areas described as the “circle of Hebra.” Penile and scrotal lesions are common in men.
Patients usually experience worse pruritus at night, which disturbs sleep. Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies more often seen in those with immunocompromised immune systems. Clinically, thick crusted and scaly patches are present that are teeming with mites.
Diagnosis can be confirmed by performing a scabies prep, during which a burrow is scraped with a surgical blade. A drop of mineral oil is placed on the skin cells. The mite, ova, and feces can be visualized under the microscope. Wrists and hands usually have the highest yield for finding the parasites.
Topical treatments include permethrin 5% cream, lindane, benzyl benzoate, and crotamiton, and should be applied as two treatments a week apart. In the United States, permethrin is most commonly used. Ivermectin pills are used off label and are very effective and may be repeated for 1-2 weeks. All household contacts should be treated. Patients may still have pruritus for 2-4 weeks following treatment.
In this patient, a scabies prep was performed prior to performing repeat skin biopsies. Microscopic examination revealed ova, one mite, and feces. Treatment was initiated with ivermectin and permethrin.
Photos and case were submitted by Susannah Berke, MD, and Damon McClain, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa.; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.