User login
Diffuse annular lesions
A 24-YEAR-OLD WOMAN with a history of guttate psoriasis, for which she was taking adalimumab, presented with a 2-week history of diffuse papules and plaques on her neck, back, torso, and upper and lower extremities (FIGURE 1). She said that the lesions were pruritic and seemed similar to those that erupted during past outbreaks of psoriasis—although they were more numerous and progressive. So, the patient (a nurse) decided to take her biweekly dose (40 mg) of adalimumab 1 week early. After administration, the rash significantly worsened, spreading to the rest of her trunk and extremities.
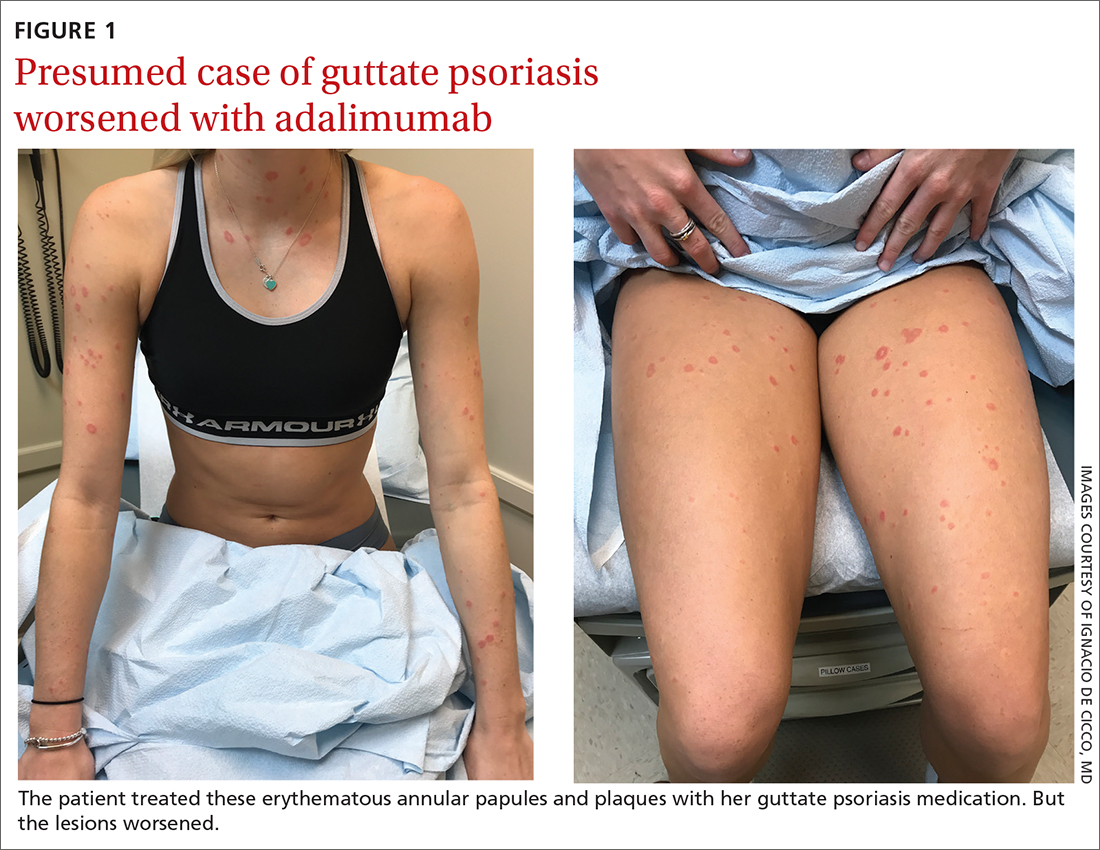
Physical exam was notable for multiple erythematous papules and plaques with central clearing and light peripheral scaling on both arms and legs, as well as her chest and back. The patient also indicated she’d adopted a stray cat 2 weeks prior. Given the patient’s pet exposure and the annular nature of the lesions, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation was done.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Tinea corporis
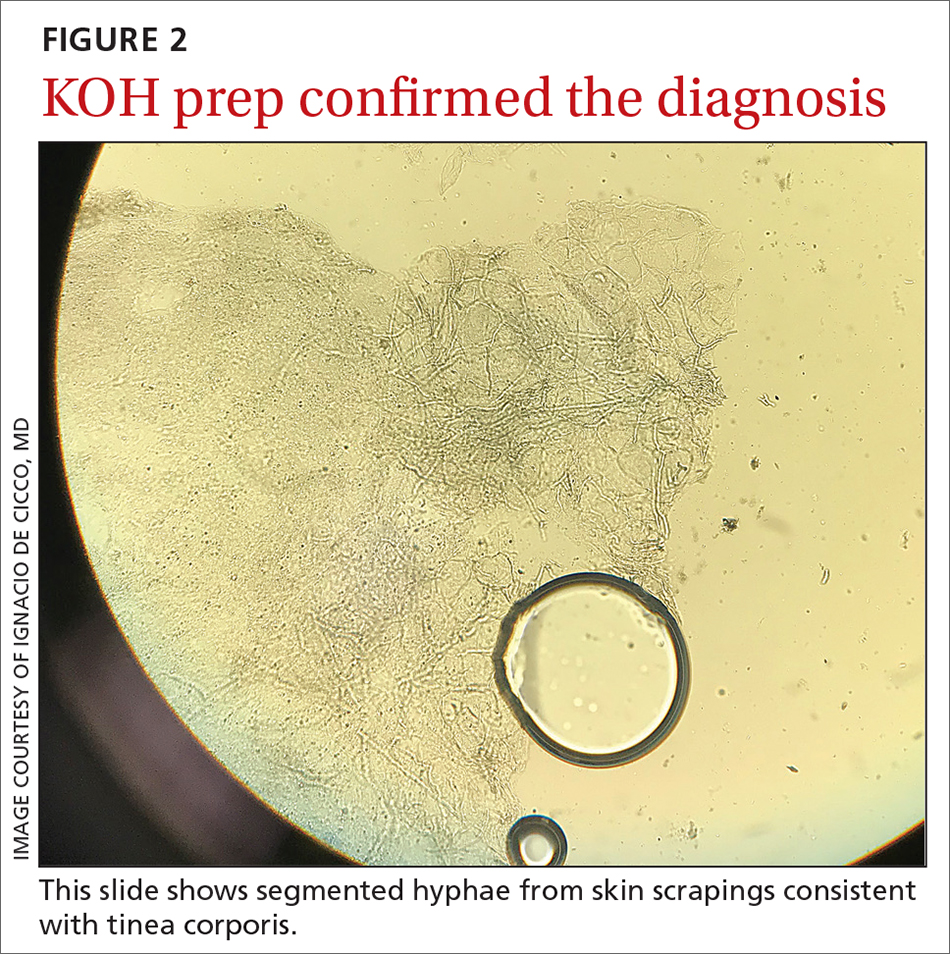
The KOH preparation was positive for hyphae in 4 separate sites (trunk, left arm, left leg, and left neck), confirming the diagnosis of severe extensive tinea corporis (FIGURE 2).
Dermatophyte (tinea) infections are caused by fungi that invade and reproduce in the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatophytes, which include the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton, are the most common cause of superficial mycotic infections. As of 2016, the worldwide prevalence of superficial mycotic infections was 20% to 25%.1 Tinea corporis can result from contact with people, animals, or soil. Infections resulting from animal-to-human contact are often transmitted by domestic animals. In this case, the patient’s exposure was from her new cat.
Tinea corporis classically manifests as pruritic, erythematous patches or plaques with central clearing, giving it an annular appearance. The response to a tinea infection depends on the immune system of the host and can range in severity from superficial to severe.2 There are 2 forms of severe dermatophytosis: invasive, which involves localized perifollicular sites or deep dermatophytosis, and extensive, which is confined to the stratum corneum but results in numerous lesions.3
The diagnosis of tinea corporis is commonly confirmed using direct microscopic examination with 10% to 20% KOH preparation, which will show branching and septate hyphal filaments.4
Several conditions with annular lesions comprise the differential
The findings of pruritic annular erythematous lesions on the patient’s neck, chest, trunk, and bilateral extremities led the patient to suspect this was a worsening case of her guttate psoriasis. Other possible diagnoses included pityriasis rosea, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), and secondary syphilis.
Continue to: Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis would not typically progress during treatment with adalimumab, although tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors have been associated with worsening psoriasis. Guttate psoriasis manifests with small, pink to red, scaly raindrop-shaped patches over the trunk and extremities.
Pityriasis rosea, a rash that resembles branches of a Christmas tree, was strongly considered given the appearance of the lesions on the patient’s back. It commonly manifests as round to oval lesions with a subtle advancing border and central fine scaling, similar in shape and color to the lesions seen in tinea corporis.
SCLE has been associated with use of TNF inhibitors, but our patient had no other lupus-like symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, headaches, or joint pain. SCLE lesions are often annular with raised pink to red borders similar in appearance to tinea corporis.
Secondary syphilis was ruled out in this patient because she had a negative rapid plasma reagin test. Secondary syphilis most commonly manifests with diffuse, nonpruritic pink to red-brown lesions on the palms and soles of patients. Patients often have prodromal symptoms that include fever, weight loss, myalgias, headache, and sore throat.
Terbinafine, Yes, but for how long?
Historically, terbinafine has been prescribed at 250 mg once daily for 2 weeks for extensive tinea corporis. However, recent studies in India suggest that terbinafine should be dosed at 250 mg twice daily, with longer durations of treatment, due to resistance.5 In the United States, it is reasonable to prescribe oral terbinafine 250 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then re-evaluate the patient in a case of extensive tinea corporis.
Other oral antifungals that can effectively treat extensive tinea corporis include itraconazole, fluconazole, and griseofulvin.1 Itraconazole and terbinafine are equally effective and safe in the treatment of tinea corporis, although itraconazole is significantly more expensive.6 Furthermore, a recent study found that combination therapy with oral terbinafine and itraconazole is as safe as monotherapy and is an option when terbinafine resistance is suspected.7
Our patient was initially started on oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. After the first dose, the patient requested a change in medication because there was no improvement in the rash. The patient was then prescribed oral fluconazole 300 mg daily and the tinea cleared after 2 months of daily therapy. (We surmise the treatment course may have been prolonged due to the possible immunosuppressant effects of adalimumab.) At the completion of treatment for the tinea corporis, the patient was restarted on adalimumab 40 mg biweekly for her psoriasis.
1. Sahoo AK, Mahajan R. Management of tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis: a comprehensive review. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:77-86. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.178099
2. Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The dermatophytes. Clin Microbial Rev. 1995:8:240-259. doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.2.240
3. Rouzaud C, Hay R, Chosidow O, et al. Severe dermatophytosis and acquired or innate immunodeficiency: a review. J Fungi (Basel). 2015;2:4. doi: 10.3390/jof2010004
4. Kurade SM, Amladi SA, Miskeen AK. Skin scraping and a potassium hydroxide mount. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:238-41. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.25794
5. Khurana A, Sardana K, Chowdhary A. Antifungal resistance in dermatophytes: recent trends and therapeutic implications. Fungal Genet Biol. 2019;132:103255. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2019.103255
6. Bhatia A, Kanish B, Badyal DK, et al. Efficacy of oral terbinafine versus itraconazole in treatment of dermatophytic infection of skin - a prospective, randomized comparative study. Indian J Pharmacol. 2019;51:116-119.
7. Sharma P, Bhalla M, Thami GP, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of oral terbinafine and itraconazole combination therapy in the management of dermatophytosis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:749-753. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1612835
A 24-YEAR-OLD WOMAN with a history of guttate psoriasis, for which she was taking adalimumab, presented with a 2-week history of diffuse papules and plaques on her neck, back, torso, and upper and lower extremities (FIGURE 1). She said that the lesions were pruritic and seemed similar to those that erupted during past outbreaks of psoriasis—although they were more numerous and progressive. So, the patient (a nurse) decided to take her biweekly dose (40 mg) of adalimumab 1 week early. After administration, the rash significantly worsened, spreading to the rest of her trunk and extremities.

Physical exam was notable for multiple erythematous papules and plaques with central clearing and light peripheral scaling on both arms and legs, as well as her chest and back. The patient also indicated she’d adopted a stray cat 2 weeks prior. Given the patient’s pet exposure and the annular nature of the lesions, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation was done.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Tinea corporis
The KOH preparation was positive for hyphae in 4 separate sites (trunk, left arm, left leg, and left neck), confirming the diagnosis of severe extensive tinea corporis (FIGURE 2).

Dermatophyte (tinea) infections are caused by fungi that invade and reproduce in the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatophytes, which include the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton, are the most common cause of superficial mycotic infections. As of 2016, the worldwide prevalence of superficial mycotic infections was 20% to 25%.1 Tinea corporis can result from contact with people, animals, or soil. Infections resulting from animal-to-human contact are often transmitted by domestic animals. In this case, the patient’s exposure was from her new cat.
Tinea corporis classically manifests as pruritic, erythematous patches or plaques with central clearing, giving it an annular appearance. The response to a tinea infection depends on the immune system of the host and can range in severity from superficial to severe.2 There are 2 forms of severe dermatophytosis: invasive, which involves localized perifollicular sites or deep dermatophytosis, and extensive, which is confined to the stratum corneum but results in numerous lesions.3
The diagnosis of tinea corporis is commonly confirmed using direct microscopic examination with 10% to 20% KOH preparation, which will show branching and septate hyphal filaments.4
Several conditions with annular lesions comprise the differential
The findings of pruritic annular erythematous lesions on the patient’s neck, chest, trunk, and bilateral extremities led the patient to suspect this was a worsening case of her guttate psoriasis. Other possible diagnoses included pityriasis rosea, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), and secondary syphilis.
Continue to: Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis would not typically progress during treatment with adalimumab, although tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors have been associated with worsening psoriasis. Guttate psoriasis manifests with small, pink to red, scaly raindrop-shaped patches over the trunk and extremities.
Pityriasis rosea, a rash that resembles branches of a Christmas tree, was strongly considered given the appearance of the lesions on the patient’s back. It commonly manifests as round to oval lesions with a subtle advancing border and central fine scaling, similar in shape and color to the lesions seen in tinea corporis.
SCLE has been associated with use of TNF inhibitors, but our patient had no other lupus-like symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, headaches, or joint pain. SCLE lesions are often annular with raised pink to red borders similar in appearance to tinea corporis.
Secondary syphilis was ruled out in this patient because she had a negative rapid plasma reagin test. Secondary syphilis most commonly manifests with diffuse, nonpruritic pink to red-brown lesions on the palms and soles of patients. Patients often have prodromal symptoms that include fever, weight loss, myalgias, headache, and sore throat.
Terbinafine, Yes, but for how long?
Historically, terbinafine has been prescribed at 250 mg once daily for 2 weeks for extensive tinea corporis. However, recent studies in India suggest that terbinafine should be dosed at 250 mg twice daily, with longer durations of treatment, due to resistance.5 In the United States, it is reasonable to prescribe oral terbinafine 250 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then re-evaluate the patient in a case of extensive tinea corporis.
Other oral antifungals that can effectively treat extensive tinea corporis include itraconazole, fluconazole, and griseofulvin.1 Itraconazole and terbinafine are equally effective and safe in the treatment of tinea corporis, although itraconazole is significantly more expensive.6 Furthermore, a recent study found that combination therapy with oral terbinafine and itraconazole is as safe as monotherapy and is an option when terbinafine resistance is suspected.7
Our patient was initially started on oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. After the first dose, the patient requested a change in medication because there was no improvement in the rash. The patient was then prescribed oral fluconazole 300 mg daily and the tinea cleared after 2 months of daily therapy. (We surmise the treatment course may have been prolonged due to the possible immunosuppressant effects of adalimumab.) At the completion of treatment for the tinea corporis, the patient was restarted on adalimumab 40 mg biweekly for her psoriasis.
A 24-YEAR-OLD WOMAN with a history of guttate psoriasis, for which she was taking adalimumab, presented with a 2-week history of diffuse papules and plaques on her neck, back, torso, and upper and lower extremities (FIGURE 1). She said that the lesions were pruritic and seemed similar to those that erupted during past outbreaks of psoriasis—although they were more numerous and progressive. So, the patient (a nurse) decided to take her biweekly dose (40 mg) of adalimumab 1 week early. After administration, the rash significantly worsened, spreading to the rest of her trunk and extremities.

Physical exam was notable for multiple erythematous papules and plaques with central clearing and light peripheral scaling on both arms and legs, as well as her chest and back. The patient also indicated she’d adopted a stray cat 2 weeks prior. Given the patient’s pet exposure and the annular nature of the lesions, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation was done.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Tinea corporis
The KOH preparation was positive for hyphae in 4 separate sites (trunk, left arm, left leg, and left neck), confirming the diagnosis of severe extensive tinea corporis (FIGURE 2).

Dermatophyte (tinea) infections are caused by fungi that invade and reproduce in the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatophytes, which include the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton, are the most common cause of superficial mycotic infections. As of 2016, the worldwide prevalence of superficial mycotic infections was 20% to 25%.1 Tinea corporis can result from contact with people, animals, or soil. Infections resulting from animal-to-human contact are often transmitted by domestic animals. In this case, the patient’s exposure was from her new cat.
Tinea corporis classically manifests as pruritic, erythematous patches or plaques with central clearing, giving it an annular appearance. The response to a tinea infection depends on the immune system of the host and can range in severity from superficial to severe.2 There are 2 forms of severe dermatophytosis: invasive, which involves localized perifollicular sites or deep dermatophytosis, and extensive, which is confined to the stratum corneum but results in numerous lesions.3
The diagnosis of tinea corporis is commonly confirmed using direct microscopic examination with 10% to 20% KOH preparation, which will show branching and septate hyphal filaments.4
Several conditions with annular lesions comprise the differential
The findings of pruritic annular erythematous lesions on the patient’s neck, chest, trunk, and bilateral extremities led the patient to suspect this was a worsening case of her guttate psoriasis. Other possible diagnoses included pityriasis rosea, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), and secondary syphilis.
Continue to: Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis would not typically progress during treatment with adalimumab, although tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors have been associated with worsening psoriasis. Guttate psoriasis manifests with small, pink to red, scaly raindrop-shaped patches over the trunk and extremities.
Pityriasis rosea, a rash that resembles branches of a Christmas tree, was strongly considered given the appearance of the lesions on the patient’s back. It commonly manifests as round to oval lesions with a subtle advancing border and central fine scaling, similar in shape and color to the lesions seen in tinea corporis.
SCLE has been associated with use of TNF inhibitors, but our patient had no other lupus-like symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, headaches, or joint pain. SCLE lesions are often annular with raised pink to red borders similar in appearance to tinea corporis.
Secondary syphilis was ruled out in this patient because she had a negative rapid plasma reagin test. Secondary syphilis most commonly manifests with diffuse, nonpruritic pink to red-brown lesions on the palms and soles of patients. Patients often have prodromal symptoms that include fever, weight loss, myalgias, headache, and sore throat.
Terbinafine, Yes, but for how long?
Historically, terbinafine has been prescribed at 250 mg once daily for 2 weeks for extensive tinea corporis. However, recent studies in India suggest that terbinafine should be dosed at 250 mg twice daily, with longer durations of treatment, due to resistance.5 In the United States, it is reasonable to prescribe oral terbinafine 250 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then re-evaluate the patient in a case of extensive tinea corporis.
Other oral antifungals that can effectively treat extensive tinea corporis include itraconazole, fluconazole, and griseofulvin.1 Itraconazole and terbinafine are equally effective and safe in the treatment of tinea corporis, although itraconazole is significantly more expensive.6 Furthermore, a recent study found that combination therapy with oral terbinafine and itraconazole is as safe as monotherapy and is an option when terbinafine resistance is suspected.7
Our patient was initially started on oral terbinafine 250 mg/d. After the first dose, the patient requested a change in medication because there was no improvement in the rash. The patient was then prescribed oral fluconazole 300 mg daily and the tinea cleared after 2 months of daily therapy. (We surmise the treatment course may have been prolonged due to the possible immunosuppressant effects of adalimumab.) At the completion of treatment for the tinea corporis, the patient was restarted on adalimumab 40 mg biweekly for her psoriasis.
1. Sahoo AK, Mahajan R. Management of tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis: a comprehensive review. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:77-86. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.178099
2. Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The dermatophytes. Clin Microbial Rev. 1995:8:240-259. doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.2.240
3. Rouzaud C, Hay R, Chosidow O, et al. Severe dermatophytosis and acquired or innate immunodeficiency: a review. J Fungi (Basel). 2015;2:4. doi: 10.3390/jof2010004
4. Kurade SM, Amladi SA, Miskeen AK. Skin scraping and a potassium hydroxide mount. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:238-41. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.25794
5. Khurana A, Sardana K, Chowdhary A. Antifungal resistance in dermatophytes: recent trends and therapeutic implications. Fungal Genet Biol. 2019;132:103255. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2019.103255
6. Bhatia A, Kanish B, Badyal DK, et al. Efficacy of oral terbinafine versus itraconazole in treatment of dermatophytic infection of skin - a prospective, randomized comparative study. Indian J Pharmacol. 2019;51:116-119.
7. Sharma P, Bhalla M, Thami GP, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of oral terbinafine and itraconazole combination therapy in the management of dermatophytosis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:749-753. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1612835
1. Sahoo AK, Mahajan R. Management of tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis: a comprehensive review. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:77-86. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.178099
2. Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The dermatophytes. Clin Microbial Rev. 1995:8:240-259. doi: 10.1128/CMR.8.2.240
3. Rouzaud C, Hay R, Chosidow O, et al. Severe dermatophytosis and acquired or innate immunodeficiency: a review. J Fungi (Basel). 2015;2:4. doi: 10.3390/jof2010004
4. Kurade SM, Amladi SA, Miskeen AK. Skin scraping and a potassium hydroxide mount. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:238-41. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.25794
5. Khurana A, Sardana K, Chowdhary A. Antifungal resistance in dermatophytes: recent trends and therapeutic implications. Fungal Genet Biol. 2019;132:103255. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2019.103255
6. Bhatia A, Kanish B, Badyal DK, et al. Efficacy of oral terbinafine versus itraconazole in treatment of dermatophytic infection of skin - a prospective, randomized comparative study. Indian J Pharmacol. 2019;51:116-119.
7. Sharma P, Bhalla M, Thami GP, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of oral terbinafine and itraconazole combination therapy in the management of dermatophytosis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:749-753. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1612835
