User login
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Secondary to Application of Tapinarof Cream 1%
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Secondary to Application of Tapinarof Cream 1%
To the Editor:
For many years, topical treatment of plaque psoriasis was limited to steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, coal tar products, and anthralin. In recent years, 2 new nonsteroidal treatment options with alternative mechanisms of action, roflumilast 0.3% and tapinarof 1%, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.1 Roflumilast 0.3%, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was shown in phase 3 clinical trials to reach an Investigator Global Assessment response of 37.5% to 42.2% in 8 weeks using once-daily application with minimal cutaneous adverse effects.1 Furthermore, it has demonstrated efficacy in treating psoriasis in intertriginous areas in subset analyses.1 Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that suppresses Th17 cell differentiation by downregulating IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23.1 In phase 3 clinical trials, 35% to 40% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% once daily demonstrated improvement in psoriasis compared with 6% who used the vehicle alone.2 In these studies, 18% to 24% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% experienced folliculitis.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a nonfollicular pustular drug reaction with systemic symptoms that typically occurs within 2 weeks of exposure to an inciting medication. Systemic antibiotics are the most commonly reported cause of AGEP.3 There are few reports in the literature of AGEP induced by topical agents.4,5 We report a case of AGEP in a young man following the use of tapinarof cream 1%.
A 23-year-old man with a history of psoriasis presented to the emergency department with fever and a pustular rash. One week prior to presentation, he developed a pustular eruption around plaques of psoriasis on the arms and legs. The patient had been prescribed tapinarof cream 1% by an outside dermatologist and was applying the medication to the affected areas once daily for 1 month prior to onset of symptoms. He discontinued tapinarof a few days prior to the eruption starting, but the rash progressed centrifugally and was associated with fevers and fatigue despite treatment with a brief course of empiric cephalexin prescribed by his primary care provider.
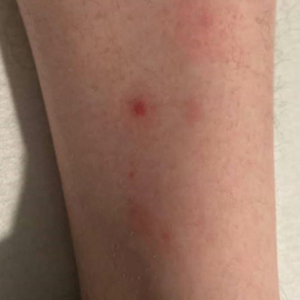
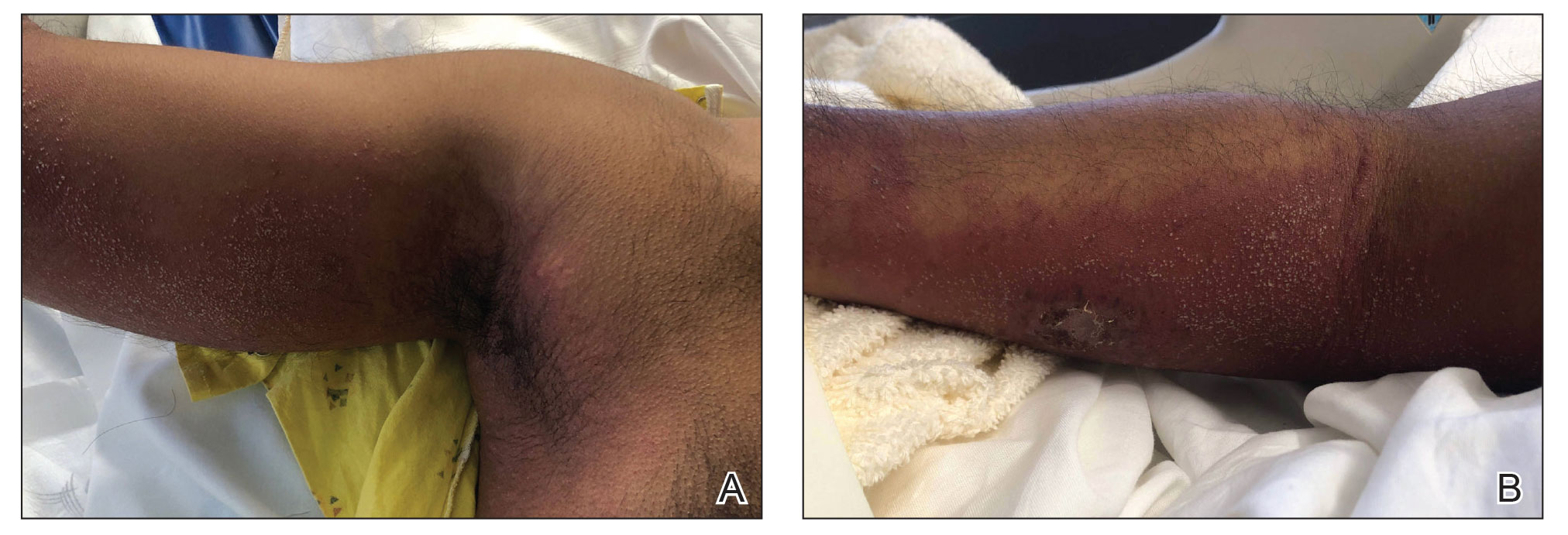
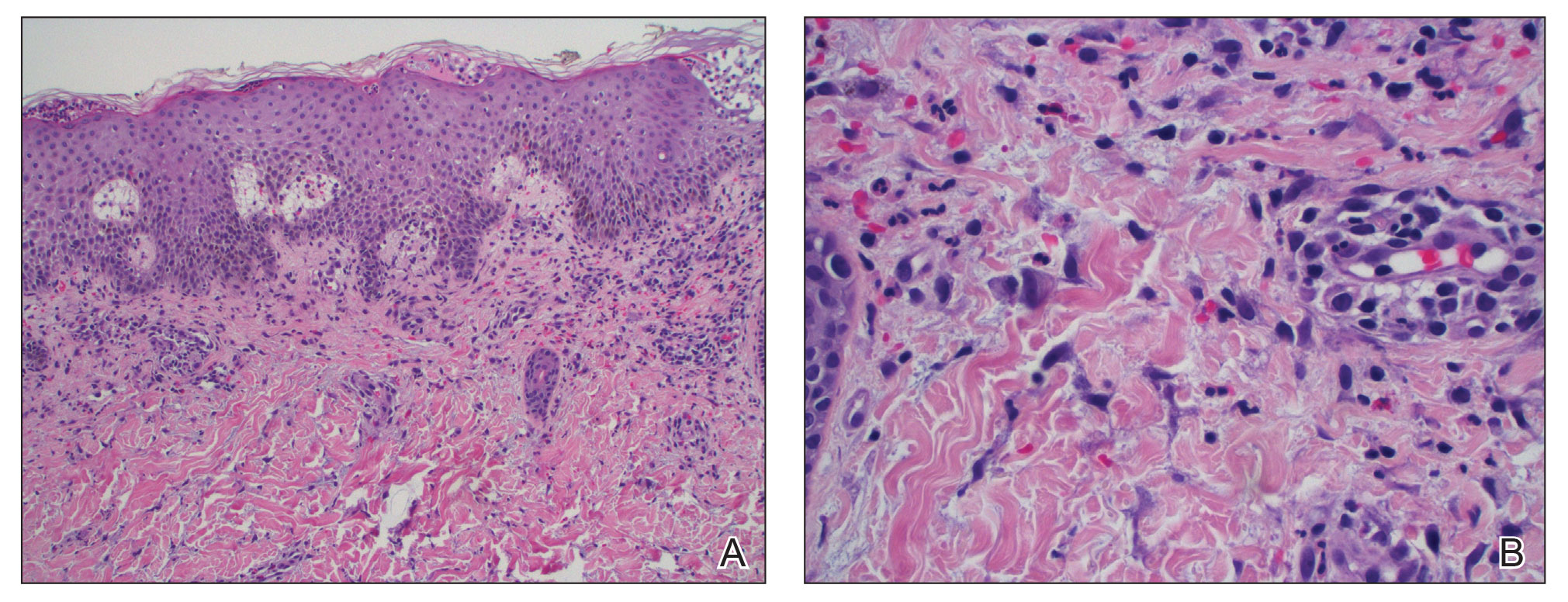
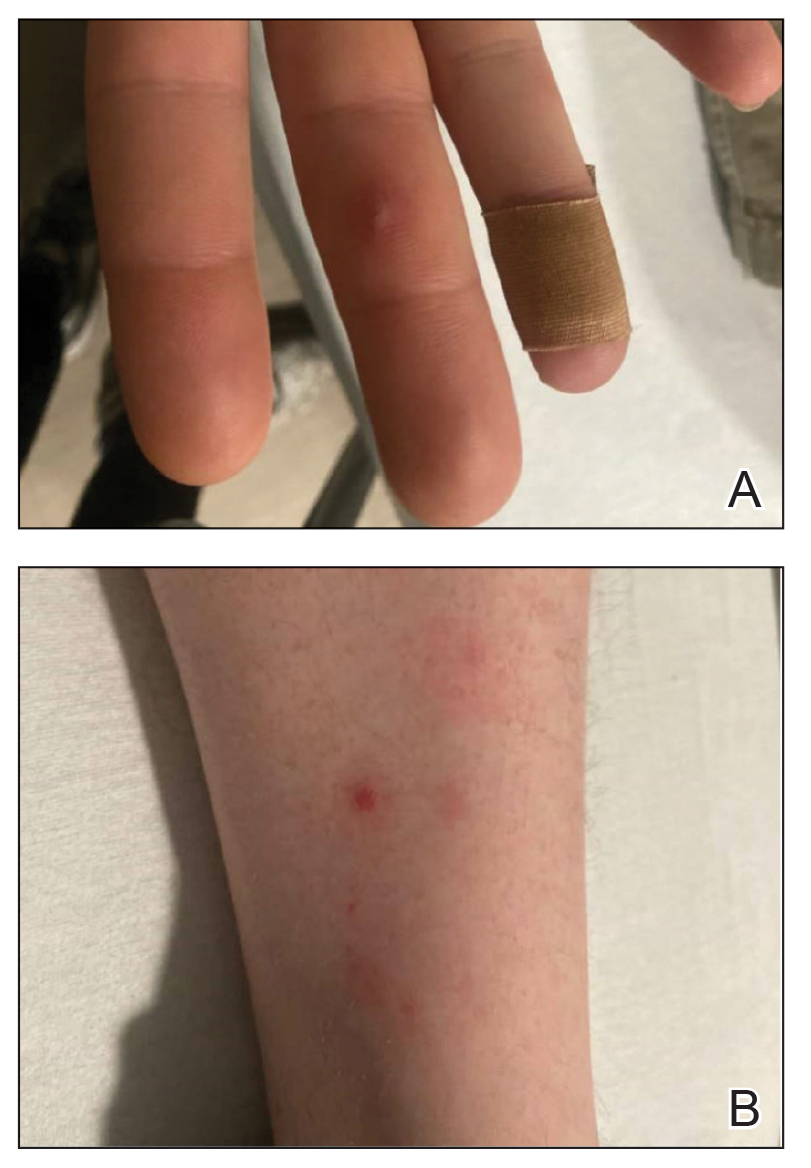
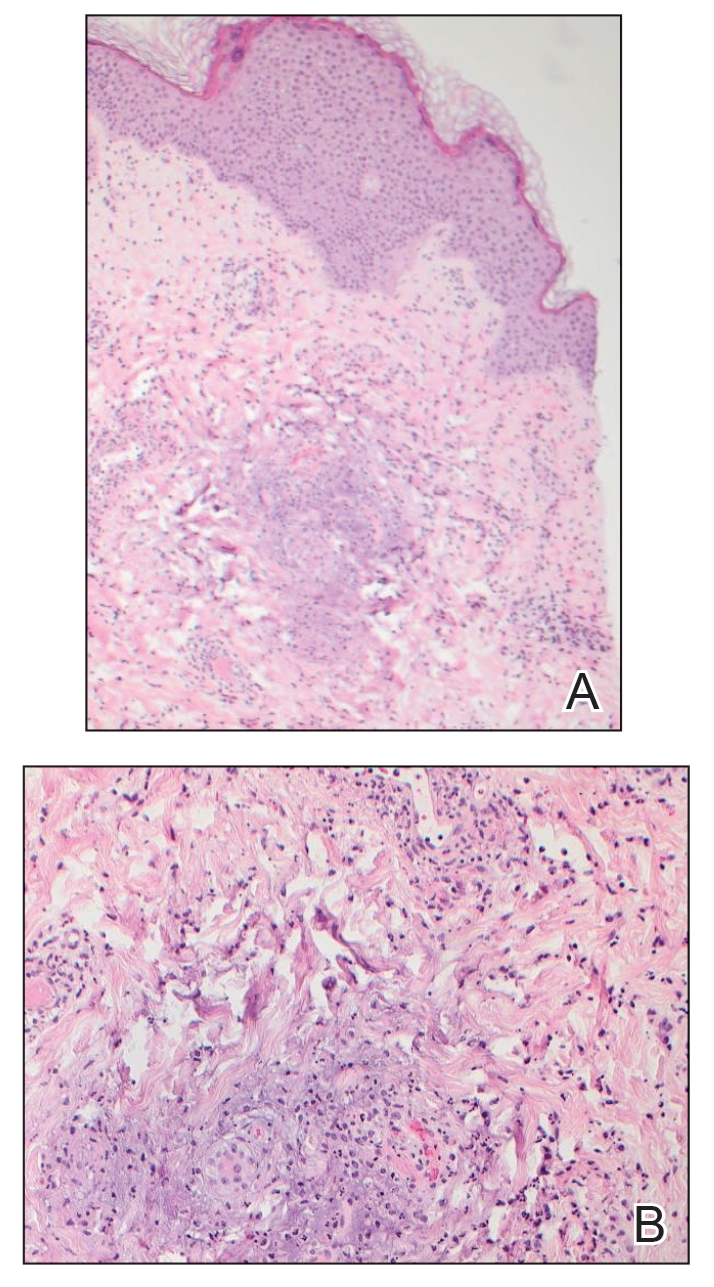
At presentation to our institution, the patient had widespread erythematous patches studded with pustules located on the arms, legs, and flexural areas as well as plaques of psoriasis involving approximately 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1). Furthermore, the patient was noted to have large noninflammatory bullae along the legs. The new eruption occurred on areas that were both treated and spared from the tapinarof cream 1%. Laboratory evaluation showed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 15.9×103/µL [reference range, 4.0-11.0×103/µL]; absolute neutrophil count, 10.3×103/µL [reference range, 1.5-8.0×103/µL]), absolute eosinophilia (1930/µL [reference range, 0-0.5×103/µL]), hypocalcemia (8.4 mg/dL [reference range, 8.5-10.5 mg/dL]), and a mild transaminitis (aspartate aminotransferase, 37 IU/L [reference range, 10-40 IU/L]; alanine aminotransferase, 53 IU/L [reference range, 7-56 U/L]). Histopathology demonstrated spongiosis with subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules and mixed dermal inflammation containing eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence revealed mild granular staining of C3 at the basement membrane zone.
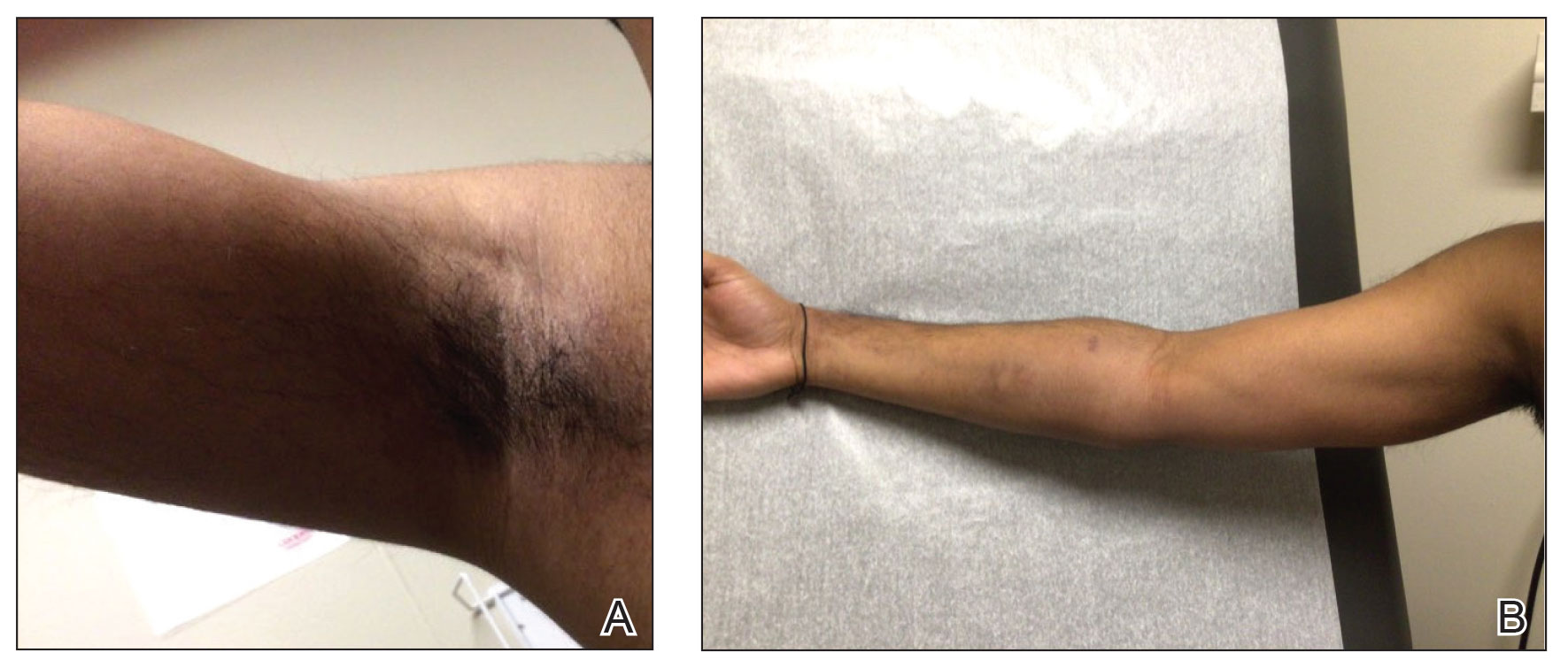
The patient was started on 1 mg/kg/d of prednisone tapered over 20 days, and he rapidly improved. Alanine aminotransferase levels peaked at 120 IU/L 2 weeks later. At that time, he had complete resolution of the original eruption and was transitioned to topical steroids for continued management of the psoriasis (Figure 3).
The differential diagnosis for our patient included AGEP, generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), miliaria pustulosa, generalized cutaneous candidiasis, exuberant allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD). Based on the clinical manifestations, laboratory results, and histopathologic evaluation, we made the diagnosis of AGEP secondary to tapinarof with systemic absorption. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis has been reported with topical use of morphine and diphenhydramine, among other agents.4,5 To our knowledge, AGEP due to tapinarof cream 1% has not been reported. In the original clinical trials of tapinarof, folliculitis was contained to sites of application.2 Our patient developed pustules at sites distant to areas of application, as well as systemic symptoms and laboratory abnormalities, indicating a systemic reaction. It can be difficult to distinguish AGEP clinically and histologically from GPP. Both conditions can manifest with fever, hypocalcemia, and sterile pustules on a background of erythema that favors intertriginous areas.6 Infection, rapid oral steroid withdrawal, pregnancy, and rarely oral medications have been reported causes of GPP.6 Our patient did not have any of these exposures. There is overlap in the histology of AGEP and GPP. One retrospective series compared histologic samples to help distinguish these 2 entities. Reliable markers that favored AGEP over GPP included eosinophilic spongiosis, interface dermatitis, and dermal eosinophilia (>2/mm2).7 In contrast, the presence of CD161 positivity in the dermis with at least 10 cells favored a diagnosis of GPP.7 In our case, the presence of spongiosis with eosinophils in the dermis favored a diagnosis of AGEP over GPP.
Miliaria pustulosa is a benign condition caused by the occlusion of the epidermal portion of eccrine glands related to either high fever or hot and humid environmental conditions. While it can be present in intertriginous areas like AGEP, miliaria pustulosa can be seen extensively on the back, most commonly in immobile hospitalized patients.8 Generalized cutaneous candidiasis usually is caused by the yeast Candida albicans and can take on multiple morphologies, including folliculitis.9 The eruption may be disseminated but often is accentuated in intertriginous areas and the anogenital folds. Predisposing factors include immunosuppression, endocrinopathies, recent use of systemic antibiotics or steroids, chemotherapy, and indwelling catheters.9 Outside of recent antibiotic use, our patient did not have any risk factors for miliaria pustulosa, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Given the presence of overlapping bullae along the lower extremities, an exuberant ACD and LABD were considered. Bullae formation can occur in ACD secondary to robust inflammation and edema leading to acantholysis.10 While a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to topical tapinarof cream 1% was considered given that the patient used the medication for approximately 1 month prior to the onset of symptoms, it would be unlikely for ACD to present with a concomitant pustular eruption. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is an autoimmune blistering disease in which antibodies target bullous pemphigoid antigen 2, and there is characteristically linear deposition of IgA at the dermal-epidermal junction that leads to subepidermal blistering.11 This often manifests clinically as widespread tense vesicles in an annular or string-of-pearls appearance. However, morphologies can vary, and large bullae may be seen. In adults, LABD typically is associated with inflammatory bowel disease, malignancy, or medications, notably vancomycin.11,12 Our patient did not have any of these predisposing factors, and his biopsy for direct immunofluorescence did not reveal the classic pattern described above.
Interestingly, there have been reports in the literature of bullous AGEP in the setting of oral anti-infectives. One report described a 62-year-old woman who developed widespread nonfollicular pustules with multiple tense serous blisters 24 hours after taking oral terbinafine.13 Another case described an 80-year-old woman with a similar presentation following a course of ciprofloxacin (although the timeline of medication administration was not described).14 In this case, patch testing to the culprit medication reproduced the response.14 In both cases, a biopsy revealed subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules with marked dermal edema.13,14 As previously described, spongiosis is a common feature of AGEP. We hypothesize that, similar to these reports, our patient had a robust inflammatory response leading to spongiosis, acantholysis, and blister formation secondary to AGEP.
Dermatologists should be aware of this case of AGEP secondary to tapinarof cream 1%, as reports in the literature are rare and it is a reminder that topical medications can cause serious systemic reactions.
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103629
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017
- Ghazawi FM, Colantonio S, Bradshaw S, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical morphine and confirmed by patch testing. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E22-E23. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000573
- Hanafusa T, Igawa K, Azukizawa H, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical diphenhydramine. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:994-995. doi:10.1684/ejd.2011.1500
- Reynolds KA, Pithadia DJ, Lee EB, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations,diagnosis, and treatment. Cutis. 2022;110:19-25. doi:10.12788/cutis.0579
- Isom J, Braswell DS, Siroy A, et al. Clinical and histopathologic features differentiating acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and pustular psoriasis: a retrospective series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:265-267. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.015
- Fealey RD, Hebert AA. Disorders of the eccrine sweat glands and sweating. In: Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine.8th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2012:946.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Marchiony Hunt K, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:1329-1363.
- Elmas ÖF, Akdeniz N, Atasoy M, et al. Contact dermatitis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:176-192. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.003
- Hull CM, Zone JZ. Dermatitis herpetiforms and linear IgA bullous dermatosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:527-537.
- Yamagami J, Nakamura Y, Nagao K, et al. Vancomycin mediates IgA autoreactivity in drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:1473-1480.
- Bullous acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to oral terbinafine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:P115. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.10.468
- Hausermann P, Scherer K, Weber M, et al. Ciprofloxacin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis mimicking bullous drug eruption confirmed by a positive patch test. Dermatology. 2005;211:277-280. doi:10.1159/000087024
To the Editor:
For many years, topical treatment of plaque psoriasis was limited to steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, coal tar products, and anthralin. In recent years, 2 new nonsteroidal treatment options with alternative mechanisms of action, roflumilast 0.3% and tapinarof 1%, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.1 Roflumilast 0.3%, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was shown in phase 3 clinical trials to reach an Investigator Global Assessment response of 37.5% to 42.2% in 8 weeks using once-daily application with minimal cutaneous adverse effects.1 Furthermore, it has demonstrated efficacy in treating psoriasis in intertriginous areas in subset analyses.1 Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that suppresses Th17 cell differentiation by downregulating IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23.1 In phase 3 clinical trials, 35% to 40% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% once daily demonstrated improvement in psoriasis compared with 6% who used the vehicle alone.2 In these studies, 18% to 24% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% experienced folliculitis.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a nonfollicular pustular drug reaction with systemic symptoms that typically occurs within 2 weeks of exposure to an inciting medication. Systemic antibiotics are the most commonly reported cause of AGEP.3 There are few reports in the literature of AGEP induced by topical agents.4,5 We report a case of AGEP in a young man following the use of tapinarof cream 1%.
A 23-year-old man with a history of psoriasis presented to the emergency department with fever and a pustular rash. One week prior to presentation, he developed a pustular eruption around plaques of psoriasis on the arms and legs. The patient had been prescribed tapinarof cream 1% by an outside dermatologist and was applying the medication to the affected areas once daily for 1 month prior to onset of symptoms. He discontinued tapinarof a few days prior to the eruption starting, but the rash progressed centrifugally and was associated with fevers and fatigue despite treatment with a brief course of empiric cephalexin prescribed by his primary care provider.
At presentation to our institution, the patient had widespread erythematous patches studded with pustules located on the arms, legs, and flexural areas as well as plaques of psoriasis involving approximately 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1). Furthermore, the patient was noted to have large noninflammatory bullae along the legs. The new eruption occurred on areas that were both treated and spared from the tapinarof cream 1%. Laboratory evaluation showed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 15.9×103/µL [reference range, 4.0-11.0×103/µL]; absolute neutrophil count, 10.3×103/µL [reference range, 1.5-8.0×103/µL]), absolute eosinophilia (1930/µL [reference range, 0-0.5×103/µL]), hypocalcemia (8.4 mg/dL [reference range, 8.5-10.5 mg/dL]), and a mild transaminitis (aspartate aminotransferase, 37 IU/L [reference range, 10-40 IU/L]; alanine aminotransferase, 53 IU/L [reference range, 7-56 U/L]). Histopathology demonstrated spongiosis with subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules and mixed dermal inflammation containing eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence revealed mild granular staining of C3 at the basement membrane zone.


The patient was started on 1 mg/kg/d of prednisone tapered over 20 days, and he rapidly improved. Alanine aminotransferase levels peaked at 120 IU/L 2 weeks later. At that time, he had complete resolution of the original eruption and was transitioned to topical steroids for continued management of the psoriasis (Figure 3).

The differential diagnosis for our patient included AGEP, generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), miliaria pustulosa, generalized cutaneous candidiasis, exuberant allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD). Based on the clinical manifestations, laboratory results, and histopathologic evaluation, we made the diagnosis of AGEP secondary to tapinarof with systemic absorption. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis has been reported with topical use of morphine and diphenhydramine, among other agents.4,5 To our knowledge, AGEP due to tapinarof cream 1% has not been reported. In the original clinical trials of tapinarof, folliculitis was contained to sites of application.2 Our patient developed pustules at sites distant to areas of application, as well as systemic symptoms and laboratory abnormalities, indicating a systemic reaction. It can be difficult to distinguish AGEP clinically and histologically from GPP. Both conditions can manifest with fever, hypocalcemia, and sterile pustules on a background of erythema that favors intertriginous areas.6 Infection, rapid oral steroid withdrawal, pregnancy, and rarely oral medications have been reported causes of GPP.6 Our patient did not have any of these exposures. There is overlap in the histology of AGEP and GPP. One retrospective series compared histologic samples to help distinguish these 2 entities. Reliable markers that favored AGEP over GPP included eosinophilic spongiosis, interface dermatitis, and dermal eosinophilia (>2/mm2).7 In contrast, the presence of CD161 positivity in the dermis with at least 10 cells favored a diagnosis of GPP.7 In our case, the presence of spongiosis with eosinophils in the dermis favored a diagnosis of AGEP over GPP.
Miliaria pustulosa is a benign condition caused by the occlusion of the epidermal portion of eccrine glands related to either high fever or hot and humid environmental conditions. While it can be present in intertriginous areas like AGEP, miliaria pustulosa can be seen extensively on the back, most commonly in immobile hospitalized patients.8 Generalized cutaneous candidiasis usually is caused by the yeast Candida albicans and can take on multiple morphologies, including folliculitis.9 The eruption may be disseminated but often is accentuated in intertriginous areas and the anogenital folds. Predisposing factors include immunosuppression, endocrinopathies, recent use of systemic antibiotics or steroids, chemotherapy, and indwelling catheters.9 Outside of recent antibiotic use, our patient did not have any risk factors for miliaria pustulosa, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Given the presence of overlapping bullae along the lower extremities, an exuberant ACD and LABD were considered. Bullae formation can occur in ACD secondary to robust inflammation and edema leading to acantholysis.10 While a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to topical tapinarof cream 1% was considered given that the patient used the medication for approximately 1 month prior to the onset of symptoms, it would be unlikely for ACD to present with a concomitant pustular eruption. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is an autoimmune blistering disease in which antibodies target bullous pemphigoid antigen 2, and there is characteristically linear deposition of IgA at the dermal-epidermal junction that leads to subepidermal blistering.11 This often manifests clinically as widespread tense vesicles in an annular or string-of-pearls appearance. However, morphologies can vary, and large bullae may be seen. In adults, LABD typically is associated with inflammatory bowel disease, malignancy, or medications, notably vancomycin.11,12 Our patient did not have any of these predisposing factors, and his biopsy for direct immunofluorescence did not reveal the classic pattern described above.
Interestingly, there have been reports in the literature of bullous AGEP in the setting of oral anti-infectives. One report described a 62-year-old woman who developed widespread nonfollicular pustules with multiple tense serous blisters 24 hours after taking oral terbinafine.13 Another case described an 80-year-old woman with a similar presentation following a course of ciprofloxacin (although the timeline of medication administration was not described).14 In this case, patch testing to the culprit medication reproduced the response.14 In both cases, a biopsy revealed subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules with marked dermal edema.13,14 As previously described, spongiosis is a common feature of AGEP. We hypothesize that, similar to these reports, our patient had a robust inflammatory response leading to spongiosis, acantholysis, and blister formation secondary to AGEP.
Dermatologists should be aware of this case of AGEP secondary to tapinarof cream 1%, as reports in the literature are rare and it is a reminder that topical medications can cause serious systemic reactions.
To the Editor:
For many years, topical treatment of plaque psoriasis was limited to steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, coal tar products, and anthralin. In recent years, 2 new nonsteroidal treatment options with alternative mechanisms of action, roflumilast 0.3% and tapinarof 1%, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.1 Roflumilast 0.3%, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, was shown in phase 3 clinical trials to reach an Investigator Global Assessment response of 37.5% to 42.2% in 8 weeks using once-daily application with minimal cutaneous adverse effects.1 Furthermore, it has demonstrated efficacy in treating psoriasis in intertriginous areas in subset analyses.1 Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that suppresses Th17 cell differentiation by downregulating IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23.1 In phase 3 clinical trials, 35% to 40% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% once daily demonstrated improvement in psoriasis compared with 6% who used the vehicle alone.2 In these studies, 18% to 24% of patients who used tapinarof cream 1% experienced folliculitis.2
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a nonfollicular pustular drug reaction with systemic symptoms that typically occurs within 2 weeks of exposure to an inciting medication. Systemic antibiotics are the most commonly reported cause of AGEP.3 There are few reports in the literature of AGEP induced by topical agents.4,5 We report a case of AGEP in a young man following the use of tapinarof cream 1%.
A 23-year-old man with a history of psoriasis presented to the emergency department with fever and a pustular rash. One week prior to presentation, he developed a pustular eruption around plaques of psoriasis on the arms and legs. The patient had been prescribed tapinarof cream 1% by an outside dermatologist and was applying the medication to the affected areas once daily for 1 month prior to onset of symptoms. He discontinued tapinarof a few days prior to the eruption starting, but the rash progressed centrifugally and was associated with fevers and fatigue despite treatment with a brief course of empiric cephalexin prescribed by his primary care provider.
At presentation to our institution, the patient had widespread erythematous patches studded with pustules located on the arms, legs, and flexural areas as well as plaques of psoriasis involving approximately 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1). Furthermore, the patient was noted to have large noninflammatory bullae along the legs. The new eruption occurred on areas that were both treated and spared from the tapinarof cream 1%. Laboratory evaluation showed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 15.9×103/µL [reference range, 4.0-11.0×103/µL]; absolute neutrophil count, 10.3×103/µL [reference range, 1.5-8.0×103/µL]), absolute eosinophilia (1930/µL [reference range, 0-0.5×103/µL]), hypocalcemia (8.4 mg/dL [reference range, 8.5-10.5 mg/dL]), and a mild transaminitis (aspartate aminotransferase, 37 IU/L [reference range, 10-40 IU/L]; alanine aminotransferase, 53 IU/L [reference range, 7-56 U/L]). Histopathology demonstrated spongiosis with subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules and mixed dermal inflammation containing eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence revealed mild granular staining of C3 at the basement membrane zone.


The patient was started on 1 mg/kg/d of prednisone tapered over 20 days, and he rapidly improved. Alanine aminotransferase levels peaked at 120 IU/L 2 weeks later. At that time, he had complete resolution of the original eruption and was transitioned to topical steroids for continued management of the psoriasis (Figure 3).

The differential diagnosis for our patient included AGEP, generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), miliaria pustulosa, generalized cutaneous candidiasis, exuberant allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD). Based on the clinical manifestations, laboratory results, and histopathologic evaluation, we made the diagnosis of AGEP secondary to tapinarof with systemic absorption. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis has been reported with topical use of morphine and diphenhydramine, among other agents.4,5 To our knowledge, AGEP due to tapinarof cream 1% has not been reported. In the original clinical trials of tapinarof, folliculitis was contained to sites of application.2 Our patient developed pustules at sites distant to areas of application, as well as systemic symptoms and laboratory abnormalities, indicating a systemic reaction. It can be difficult to distinguish AGEP clinically and histologically from GPP. Both conditions can manifest with fever, hypocalcemia, and sterile pustules on a background of erythema that favors intertriginous areas.6 Infection, rapid oral steroid withdrawal, pregnancy, and rarely oral medications have been reported causes of GPP.6 Our patient did not have any of these exposures. There is overlap in the histology of AGEP and GPP. One retrospective series compared histologic samples to help distinguish these 2 entities. Reliable markers that favored AGEP over GPP included eosinophilic spongiosis, interface dermatitis, and dermal eosinophilia (>2/mm2).7 In contrast, the presence of CD161 positivity in the dermis with at least 10 cells favored a diagnosis of GPP.7 In our case, the presence of spongiosis with eosinophils in the dermis favored a diagnosis of AGEP over GPP.
Miliaria pustulosa is a benign condition caused by the occlusion of the epidermal portion of eccrine glands related to either high fever or hot and humid environmental conditions. While it can be present in intertriginous areas like AGEP, miliaria pustulosa can be seen extensively on the back, most commonly in immobile hospitalized patients.8 Generalized cutaneous candidiasis usually is caused by the yeast Candida albicans and can take on multiple morphologies, including folliculitis.9 The eruption may be disseminated but often is accentuated in intertriginous areas and the anogenital folds. Predisposing factors include immunosuppression, endocrinopathies, recent use of systemic antibiotics or steroids, chemotherapy, and indwelling catheters.9 Outside of recent antibiotic use, our patient did not have any risk factors for miliaria pustulosa, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Given the presence of overlapping bullae along the lower extremities, an exuberant ACD and LABD were considered. Bullae formation can occur in ACD secondary to robust inflammation and edema leading to acantholysis.10 While a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to topical tapinarof cream 1% was considered given that the patient used the medication for approximately 1 month prior to the onset of symptoms, it would be unlikely for ACD to present with a concomitant pustular eruption. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is an autoimmune blistering disease in which antibodies target bullous pemphigoid antigen 2, and there is characteristically linear deposition of IgA at the dermal-epidermal junction that leads to subepidermal blistering.11 This often manifests clinically as widespread tense vesicles in an annular or string-of-pearls appearance. However, morphologies can vary, and large bullae may be seen. In adults, LABD typically is associated with inflammatory bowel disease, malignancy, or medications, notably vancomycin.11,12 Our patient did not have any of these predisposing factors, and his biopsy for direct immunofluorescence did not reveal the classic pattern described above.
Interestingly, there have been reports in the literature of bullous AGEP in the setting of oral anti-infectives. One report described a 62-year-old woman who developed widespread nonfollicular pustules with multiple tense serous blisters 24 hours after taking oral terbinafine.13 Another case described an 80-year-old woman with a similar presentation following a course of ciprofloxacin (although the timeline of medication administration was not described).14 In this case, patch testing to the culprit medication reproduced the response.14 In both cases, a biopsy revealed subcorneal and intraepidermal pustules with marked dermal edema.13,14 As previously described, spongiosis is a common feature of AGEP. We hypothesize that, similar to these reports, our patient had a robust inflammatory response leading to spongiosis, acantholysis, and blister formation secondary to AGEP.
Dermatologists should be aware of this case of AGEP secondary to tapinarof cream 1%, as reports in the literature are rare and it is a reminder that topical medications can cause serious systemic reactions.
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103629
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017
- Ghazawi FM, Colantonio S, Bradshaw S, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical morphine and confirmed by patch testing. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E22-E23. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000573
- Hanafusa T, Igawa K, Azukizawa H, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical diphenhydramine. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:994-995. doi:10.1684/ejd.2011.1500
- Reynolds KA, Pithadia DJ, Lee EB, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations,diagnosis, and treatment. Cutis. 2022;110:19-25. doi:10.12788/cutis.0579
- Isom J, Braswell DS, Siroy A, et al. Clinical and histopathologic features differentiating acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and pustular psoriasis: a retrospective series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:265-267. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.015
- Fealey RD, Hebert AA. Disorders of the eccrine sweat glands and sweating. In: Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine.8th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2012:946.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Marchiony Hunt K, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:1329-1363.
- Elmas ÖF, Akdeniz N, Atasoy M, et al. Contact dermatitis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:176-192. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.003
- Hull CM, Zone JZ. Dermatitis herpetiforms and linear IgA bullous dermatosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:527-537.
- Yamagami J, Nakamura Y, Nagao K, et al. Vancomycin mediates IgA autoreactivity in drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:1473-1480.
- Bullous acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to oral terbinafine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:P115. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.10.468
- Hausermann P, Scherer K, Weber M, et al. Ciprofloxacin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis mimicking bullous drug eruption confirmed by a positive patch test. Dermatology. 2005;211:277-280. doi:10.1159/000087024
- Lebwohl MG, Kircik LH, Moore AY, et al. Effect of roflumilast cream vs vehicle cream on chronic plaque psoriasis: the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2022;328:1073-1084. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.15632
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, et al. Phase 3 trials of tapinarof cream for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2219-2229. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103629
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017
- Ghazawi FM, Colantonio S, Bradshaw S, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical morphine and confirmed by patch testing. Dermat Contact Atopic Occup Drug. 2020;31:E22-E23. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000573
- Hanafusa T, Igawa K, Azukizawa H, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by topical diphenhydramine. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:994-995. doi:10.1684/ejd.2011.1500
- Reynolds KA, Pithadia DJ, Lee EB, et al. Generalized pustular psoriasis: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations,diagnosis, and treatment. Cutis. 2022;110:19-25. doi:10.12788/cutis.0579
- Isom J, Braswell DS, Siroy A, et al. Clinical and histopathologic features differentiating acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and pustular psoriasis: a retrospective series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:265-267. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.015
- Fealey RD, Hebert AA. Disorders of the eccrine sweat glands and sweating. In: Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine.8th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2012:946.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Marchiony Hunt K, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:1329-1363.
- Elmas ÖF, Akdeniz N, Atasoy M, et al. Contact dermatitis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:176-192. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.003
- Hull CM, Zone JZ. Dermatitis herpetiforms and linear IgA bullous dermatosis. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:527-537.
- Yamagami J, Nakamura Y, Nagao K, et al. Vancomycin mediates IgA autoreactivity in drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:1473-1480.
- Bullous acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to oral terbinafine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:P115. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.10.468
- Hausermann P, Scherer K, Weber M, et al. Ciprofloxacin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis mimicking bullous drug eruption confirmed by a positive patch test. Dermatology. 2005;211:277-280. doi:10.1159/000087024
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Secondary to Application of Tapinarof Cream 1%
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Secondary to Application of Tapinarof Cream 1%
PRACTICE POINTS
- Tapinarof cream 1% can be absorbed systemically and cause acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP).
- Clinical configuration and histology can be useful to distinguish AGEP from mimickers.
- Topical application of drugs in general, particularly over large body surface areas, may lead to systemic drug eruptions.
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection of Pharyngeal Origin: Test All Anatomic Sites
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.
A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.
Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
Practice Points
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections of the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx can disseminate and cause fever, joint pain, and hemorrhagic papulovesicles that can mimic other serious conditions and require dermatologic expertise to confirm.
- Patients with suspected disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) as well as patients who are asymptomatic and at increased risk should have all possible anatomic sites of infection—the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx—tested with the appropriate molecular assays and culture when appropriate.
- Appropriate recognition and treatment of DGI is vital, as undertreatment can result in serious complications and contribute to the increasing global public health threat of antimicrobial-resistant gonococcal infections.