User login
Borderline personality disorder: 6 studies of psychosocial interventions
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 It is characterized by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior that often results in problems in relationships. As a result, patients with BPD tend to utilize more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or major depressive disorder.2
Some clinicians believe BPD is difficult to treat. While historically there has been little consensus on the best treatments for this disorder, current options include both pharmacologic and psychological interventions. In Part 1 of this 2-part article, we focused on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions.3 Here in Part 2, we focus on findings from 6 recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of psychosocial interventions for BPD
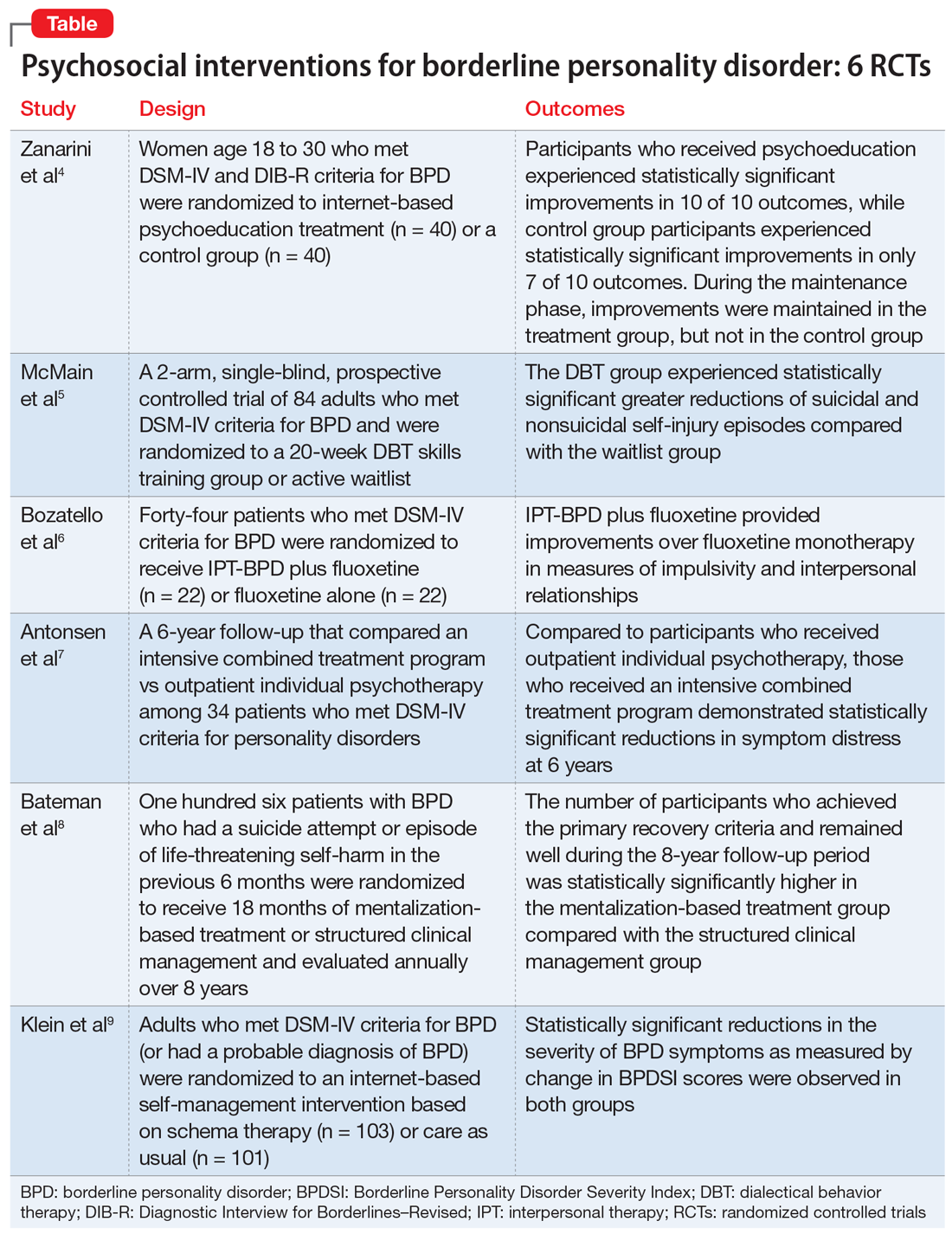
1. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi: 10.4088/JCP.16m11153
Research has shown that BPD is a treatable illness with a more favorable prognosis than previously believed. Despite this, patients often experience difficulty accessing the most up-to-date information on BPD, which can impede their treatment. A 2008 study by Zanarini et al10 of younger female patients with BPD demonstrated that immediate, in-person psychoeducation improved impulsivity and relationships. Widespread implementation of this program proved problematic, however, due to cost and personnel constraints. To resolve this issue, researchers developed an internet-based version of the program. In a 2018 follow-up study, Zanarini et al4 examined the effect of this internet-based psychoeducation program on symptoms of BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- Women (age 18 to 30) who met DSM-IV and Diagnostic Interview for Borderlines–Revised criteria for BPD were randomized to an internet-based psychoeducation treatment group (n = 40) or a control group (n = 40).
- Ten outcomes concerning symptom severity and psychosocial functioning were assessed during weeks 1 to 12 (acute phase) and at months 6, 9, and 12 (maintenance phase) using the self-report version of the Zanarini Rating Scale for BPD (ZAN-BPD), the Borderline Evaluation of Severity over Time, the Sheehan Disability Scale, the Clinically Useful Depression Outcome Scale, the Clinically Useful Anxiety Outcome Scale, and Weissman’s Social Adjustment Scale (SAS).
Outcomes
- In the acute phase, treatment group participants experienced statistically significant improvements in all 10 outcomes. Control group participants demonstrated similar results, achieving statistically significant improvements in 7 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group experienced a more significant reduction in impulsivity and improvement in psychosocial functioning as measured by the ZAN-BPD and SAS.
- In the maintenance phase, treatment group participants achieved statistically significant improvements in 9 of 10 outcomes, whereas control group participants demonstrated statistically significant improvements in only 3 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group also demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in all 4 sector scores and the total score of the ZAN-BP
Conclusions/limitations
- In patients with BPD, internet-based psychoeducation reduced symptom severity and improved psychosocial functioning, with effects lasting 1 year. Treatment group participants experienced clinically significant improvements in all outcomes measured during the acute phase of the study; most improvements were maintained over 1 year.
- While the control group initially saw similar improvements in most measurements, these improvements were not maintained as effectively over 1 year.
- Limitations include a female-only population, the restricted age range of participants, and recruitment exclusively from volunteers.
2. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148.
Standard dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an effective treatment for BPD; however, access is often limited by shortages of clinicians and resources. Therefore, it has become increasingly common for clinical settings to offer patients only the skills training component of DBT, which requires fewer resources. While several clinical trials examining brief DBT skills–only treatment for BPD have shown promising results, it is unclear how effective this intervention is at reducing suicidal or nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) episodes. McMain et al5 explored the effectiveness of brief DBT skills–only adjunctive treatment on the rates of suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this 2-arm, single-blind, prospective controlled trial, 84 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to a 20-week DBT skills training group (DBT group) or an active waitlist (WL group). No restrictions on additional psychosocial or pharmacologic treatments were imposed on either group.
- The primary outcome was the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the Lifetime Suicide Attempt Self-Injury Interview and the Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory (DSHI). Measurements occurred at baseline, 10 weeks, 20 weeks, and 3 months posttreatment (32 weeks).
- Secondary outcomes included changes in health care utilization, BPD symptoms, and coping. These were assessed using the Treatment History Interview-2, Borderline Symptom List-23, State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory, Symptom Checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R), Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)-II, Social Adjustment Scale Self-report, Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale, Distress Tolerance Scale, and Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Scale.
Outcomes
- At Week 32, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed statistically significant greater reductions in the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the LSASI but not by the DSHI. The DBT group experienced statistically significant improvements in distress tolerance and emotion regulation over the WL group at all points, but no difference on mindfulness. The DBT group achieved greater reductions in anger over time as compared to the WL group.
- At Week 20, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed significant improvements in social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms. There were no significant group differences on impulsivity. Between-group differences in the number of hospital admissions favored the DBT group at 10 and 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups with respect to the number of emergency department visits.
- Analyses of group differences in clinical improvement as measured by the SCL-90-R revealed statistically reliable and clinically significant changes in the DBT group over the WL group at 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks.
Conclusions/limitations
- Brief DBT skills training reduced suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD. Participants in the DBT group also demonstrated greater improvement in anger, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation compared to the control group. These results were evident 3 months after treatment. However, any gains in health care utilization, social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms diminished or did not differ from waitlist participants at Week 32. At that time, participants in the DBT group demonstrated a similar level of symptomatology as the WL group.
- Limitations include the use of an active waitlist control group, allowance of concurrent treatments, the absence of an active therapeutic comparator group, use of self-report measures, use of an instrument with unknown psychometric properties, and a relatively short 3-month follow-up period.
3. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156.
Psychotherapeutic options for treating BPD include DBT, mentalization-based treatment, schema-focused therapy, transference-based psychotherapy, and systems training for emotional predictability and problem solving. More recently, interpersonal therapy also has been adapted for BPD (IPT-BPD). However, thus far no trials have investigated the long-term effects of this therapy on BPD. In 2010, Bellino et al11 published a 32-week RCT examining the effect of IPT-BPD on BPD. They concluded that IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine was superior to fluoxetine alone in improving symptoms and quality of life. The present study by Bozzatello et al6 examined whether the benefits of IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine demonstrated in the 2010 study persisted over a 24-month follow-up.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2010 study by Bellino et al,11 55 outpatients who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine (combined therapy) or fluoxetine alone for 32 weeks. Forty-four participants completed a 24-month follow-up study (n = 22 for IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine, n = 22 for fluoxetine only).
- Clinical assessments were performed at 6, 12, and 24 months, and used the same instruments as the original study, including the Clinical Global Impression Scale–Severity item, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS), Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment, Satisfaction Profile (SAT-P), and the Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI).
Outcomes
- While the original study demonstrated that combined therapy had a clinically significant effect over fluoxetine alone on both HARS score and the BPDSI item “affective instability” at 32 weeks, this advantage was maintained only at the 6-month assessment.
- The improvements that the combined therapy provided over fluoxetine monotherapy on the BPDSI items of “impulsivity” and “interpersonal relationships” as well as the SAT-P factors of social and psychological functioning at 32 weeks were preserved at 24 months. No additional improvements were seen.
Conclusions/limitations
- The improvements in impulsivity, interpersonal functioning, social functioning, and psychological functioning at 32 weeks seen with IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine compared with fluoxetine alone persisted for 2 years after completing therapy; no further improvements were seen.
- The improvements to anxiety and affective instability that combined therapy demonstrated over fluoxetine monotherapy at 32 weeks were not maintained at 24 months.
- Limitations include a small sample size, exclusion of psychiatric comorbidities, and a lack of assessment of session or medication adherence.
4. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63.
While many studies have demonstrated the benefits of psychotherapy for treating personality disorders, there is limited research of how different levels of psychotherapy may impact treatment outcomes. An RCT called the Ullevål Personality Project (UPP)12 compared an intensive combined treatment program (CP) with outpatient individual psychotherapy (OIP) in patients with personality disorders. The CP program consisted of short-term day-hospital treatment followed by outpatient combined group and individual psychotherapy. The outcomes this RCT evaluated included suicide attempts, suicidal thoughts, self-injury, psychosocial functioning, symptom distress, and interpersonal and personality problems. A 6-year follow-up concluded there were no differences in outcomes between the 2 treatment groups. However, in this RCT, Antonsen et al7 examined whether CP produced statistically significant benefits over OIP in a subset of patients with BPD.
Study design
- In the UPP trial,12 117 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for personality disorders (excluding antisocial and schizotypal personality disorder) were randomized to receive 18 weeks of day hospital psychotherapy followed by CP or OIP. Fifty-two participants in the UPP were diagnosed with BPD, and 34 of these participants completed the 6-year follow-up investigation.
- Symptom distress, psychosocial functioning, interpersonal problems, quality of life, personality functioning, and self-harm/suicidal thoughts/suicide attempts were assessed at baseline, 8 months, 18 months, 3 years, and 6 years using the SCL-90-R Global Severity Index (GSI), BDI, Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF), Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Quality of Life 10-point scale (QOL), Circumplex of Interpersonal Problems (CIP), and the 60-item short form of the Severity Indices of Personality Problems (SIPP-118) questionnaire.
Outcomes
- Compared to the OIP group, the CP group demonstrated statistically significant reductions in symptom distress at Year 6 as measured by the SCL-90-R GSI. Between Years 3 and 6, the CP group continued to show improvements in psychosocial functioning as demonstrated by improvements in GAF and WSAS scores. The OIP group’s scores worsened during this time. Compared to the OIP group, participants in the CP group also had significantly better outcomes on the SIPP-118 domains of self-control and identity integration.
- There were no significant differences between groups on the proportion of participants who engaged in self-harm or experienced suicidal thoughts or attempts. There were no significant differences in outcomes between the treatment groups on the CIP, BDI, or QOL.
- Participants in CP group tended to use fewer psychotropic medications than those in the OIP group over time, but this difference was not statistically significant. The 2 groups did not differ in use of health care services over the last year.
- Avoidant personality disorder (AVPD) did not have a significant moderator effect on GAF score. Comorbid AVPD was a negative predictor of GAF score, independent of the group.
Conclusions/limitations
- Both groups experienced a remission rate of 90% at 6-year follow-up. Compared with the OIP group, participants in the CP group experienced significantly greater reductions in symptom distress and improvements in self-control and identity integration at 6 years. Between Years 3 and 6, participants in the CP group experienced significant improvements in psychosocial functioning compared with OIP group participants. The 2 groups did not differ on other outcomes, including the CIP, BDI, QOL, suicidal thoughts, suicidal attempts, self-harm, and health care utilization.
- Despite statistically significant differences in GAF scores favoring the CP group over the OIP group during Years 3 to 6, GAF scores did not differ significantly in the final year, which suggests that symptomatic remission does not equal functional improvement.
- Limitations include a lack of control for intensity or length of treatment in statistical analyses, small sample size, lack of correction for multiple testing, lack of an a priori power analysis, missing data and potential violation of the missing at random assumption, use of therapists’ preferred treatment method/practice, and a lack of control for other treatments.
5. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299.
The efficacy of various psychotherapies for symptoms of BPD has been well established. However, there is limited evidence that these effects persist over time. In 2009, Bateman et al13 conducted an 18-month RCT comparing the effectiveness of outpatient mentalization-based treatment (MBT) against structured clinical management (SCM) for patients with BPD. Both groups experienced substantial improvements, but patients assigned to MBT demonstrated greater improvement in clinically significant problems, including suicide attempts and hospitalizations. In a 2021 follow-up to this study, Bateman et al8 investigated whether the MBT group’s gains in the primary outcomes (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months), social functioning, vocational engagement, and mental health service usage were maintained throughout an 8-year follow-up period.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2009 trial, Bateman et al13 randomized adult participants who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and had a suicide attempt or episode of life-threatening self-harm in the past 6 months to receive 18 months of MBT or SCM. The primary outcome was crisis events, defined as a composite of suicidal and severe self-injurious behaviors and hospitalizations. The 2021 Bateman et al8 study expanded this investigation by collecting additional data on a yearly basis for 8 years.
- Of the 134 original participants, 98 agreed to complete the follow-up. Due to attrition, the follow-up period was limited to 8 years. At each yearly visit, researchers collected information on the primary outcome, the absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months.
- Secondary measures were collected mainly through a modified version of the Client Service Receipt Inventory and included critical incidents, psychiatric and medical hospital and community services, employment and other personally meaningful activity, psychoactive medication, and other mental health treatments.
Outcomes
- The number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD at the 1-year follow-up was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. To improve participant retention, this outcome was not evaluated at later visits.
- The number of participants who achieved the primary recovery criteria of the original trial (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months) and remained well throughout the entire follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. The average number of years during which participants failed to meet recovery criteria was significantly greater in the SCM group compared with the MBT group.
- When controlling for age, treatment group was a significant predictor of recovery during the follow-up period. Overall, significantly fewer participants in the MBT group experienced critical incidents during the follow-up period.
- The SCM group used crisis mental health services for a significantly greater number of follow-up years than the MBT group, although the likelihood of ever using crisis services did not statistically differ between the groups. Both groups had similar use of outpatient mental health services, primary care services, and nonmental health medical services. Compared to the SCM group, the MBT group had significantly fewer professional support service visits and significantly fewer outpatient psychiatrist visits.
- MBT group participants spent more time in education, were less likely to be unemployed, and were less likely to use social care interventions than SCM group participants. Although those in the MBT group spent more months engaged in purposeful activity, there was no significant difference between the groups in the proportion of participants who did not engage in purposeful activity.
- The MBT group spent fewer months receiving psychotherapeutic medication compared with the SCM group. The variables that yielded significant 2-way interactions were eating disorder, substance use disorder, and physical abuse, suggesting greater benefit from MBT with these concurrent diagnoses. Younger age was associated with better outcomes.
Conclusions/limitations
- This study demonstrated that patients with BPD significantly benefited from specialized therapies such as MBT.
- At the 1 follow-up visit, the number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group.
- The number of participants who had achieved the primary recovery criteria and remained well during the 8-year follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared to the SCM group.
- Limitations include increasing attrition over time, possible allegiance effects and unmasking of research assistants, lack of self-report questionnaires, and the potentially erroneous conclusion that increased use of services equates to poorer treatment response and greater need for support.
6. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771.
Fewer than 1 in 4 patients with BPD have access to effective psychotherapies. The use of internet-based self-management interventions (SMIs) developed from evidence-based psychotherapies can help close this treatment gap. Although the efficacy of SMIs for several mental disorders has been demonstrated in multiple meta-analyses, results for BPD are mixed. In this study, Klein et al9 examined the effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an SMI based on schema therapy in addition to care as usual (CAU) in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In a 12-month, rater-blind, controlled parallel group trial, adults who had a total BPDSI score ≥15 and either a diagnosis of BPD according to DSM-IV criteria or a probable diagnosis of BPD (if they had also received a BPD diagnosis from their treating physician) were randomized to an internet-based SMI based on schema therapy called priovi (n = 103) or CAU (n = 101). Participants could complete the SMI content in approximately 6 months but were recommended to use the intervention for the entire year.
- Participation in psychotherapy and psychiatric treatment, including pharmacotherapy, was permitted. At baseline, 74% of participants were receiving psychotherapy and 88% were receiving psychiatric treatment.
- The primary outcome was change in BPDSI score at 12 months. The primary safety outcome was the number of serious adverse events at 12 months. Secondary outcomes included BPD severity, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, quality of life, uncontrolled internet use, negative treatment effects, and satisfaction with the intervention. Most assessments were measured at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 12 months.
Outcomes
- Large reductions in the severity of BPD symptoms as measured by change in BPDSI score was observed in both groups. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group, this difference was not statistically significant from the CAU group.
- There was no statistically significant difference in the number of serious adverse events between groups at any time.
Conclusions/limitations
- Treatment with SMI did not result in improved outcomes over CAU. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group compared to the CAU group, this difference was not statistically significant.
- The authors cautioned that the smaller-than-expected between-groups effect size must be interpreted against the background of an unexpectedly large effect in the CAU group. In fact, the CAU group pre/post effect was comparable to the pre/post effect of intensive specialized DBT treatment groups in previous RCTs.
- The authors also suggested that the high percentage of participants who received psychotherapy did not allow for an additional benefit from SMI.
- Limitations include recruitment method, lack of systematic assessment of accidental unblinding, high exclusion rate due to failure of the participant or treating clinician to provide confirmation of diagnosis, and the use of a serious adverse events assessment that is not psychometrically validated.
Bottom Line
Evidence from randomized controlled trials suggests that internet-based psychoeducation, brief dialectical behavior therapy skills-only treatment, interpersonal therapy, a program that combines day treatment with individual and group psychotherapy, and mentalization-based treatment can improve symptoms and quality of life for patients with borderline personality disorder.
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159(2):276-83.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(2):295-302.
3. Saeed SA, Kallis AC. Borderline personality disorder: 6 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):26-30,34-36.
4. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi:10.4088/JCP.16m11153
5. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148. doi:10.1111/acps.12664
6. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.04.014
7. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63. doi:10.1080/10503307.2015.1072283
8. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299. doi:10.1037/per0000422
9. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047771
10. Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR. A preliminary, randomized trial of psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Pers Disord. 2008;22(3):284-290.
11. Bellino S, Rinaldi C, Bogetto F. Adaptation of interpersonal psychotherapy to borderline personality disorder: a comparison of combined therapy and single pharmacotherapy. Can J Psychiatry. 2010;55(2):74-81.
12. Arnevik E, Wilberg T, Urnes Ø, et al. Psychotherapy for personality disorders: short-term day hospital psychotherapy versus outpatient individual therapy – a randomized controlled study. Eur Psychiatry. 2009,24(2):71-78. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.09.004
13. Bateman A, Fonagy P. Randomized controlled trial of outpatient mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for borderline personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(12):1355-1364.
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 It is characterized by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior that often results in problems in relationships. As a result, patients with BPD tend to utilize more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or major depressive disorder.2
Some clinicians believe BPD is difficult to treat. While historically there has been little consensus on the best treatments for this disorder, current options include both pharmacologic and psychological interventions. In Part 1 of this 2-part article, we focused on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions.3 Here in Part 2, we focus on findings from 6 recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of psychosocial interventions for BPD

1. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi: 10.4088/JCP.16m11153
Research has shown that BPD is a treatable illness with a more favorable prognosis than previously believed. Despite this, patients often experience difficulty accessing the most up-to-date information on BPD, which can impede their treatment. A 2008 study by Zanarini et al10 of younger female patients with BPD demonstrated that immediate, in-person psychoeducation improved impulsivity and relationships. Widespread implementation of this program proved problematic, however, due to cost and personnel constraints. To resolve this issue, researchers developed an internet-based version of the program. In a 2018 follow-up study, Zanarini et al4 examined the effect of this internet-based psychoeducation program on symptoms of BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- Women (age 18 to 30) who met DSM-IV and Diagnostic Interview for Borderlines–Revised criteria for BPD were randomized to an internet-based psychoeducation treatment group (n = 40) or a control group (n = 40).
- Ten outcomes concerning symptom severity and psychosocial functioning were assessed during weeks 1 to 12 (acute phase) and at months 6, 9, and 12 (maintenance phase) using the self-report version of the Zanarini Rating Scale for BPD (ZAN-BPD), the Borderline Evaluation of Severity over Time, the Sheehan Disability Scale, the Clinically Useful Depression Outcome Scale, the Clinically Useful Anxiety Outcome Scale, and Weissman’s Social Adjustment Scale (SAS).
Outcomes
- In the acute phase, treatment group participants experienced statistically significant improvements in all 10 outcomes. Control group participants demonstrated similar results, achieving statistically significant improvements in 7 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group experienced a more significant reduction in impulsivity and improvement in psychosocial functioning as measured by the ZAN-BPD and SAS.
- In the maintenance phase, treatment group participants achieved statistically significant improvements in 9 of 10 outcomes, whereas control group participants demonstrated statistically significant improvements in only 3 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group also demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in all 4 sector scores and the total score of the ZAN-BP
Conclusions/limitations
- In patients with BPD, internet-based psychoeducation reduced symptom severity and improved psychosocial functioning, with effects lasting 1 year. Treatment group participants experienced clinically significant improvements in all outcomes measured during the acute phase of the study; most improvements were maintained over 1 year.
- While the control group initially saw similar improvements in most measurements, these improvements were not maintained as effectively over 1 year.
- Limitations include a female-only population, the restricted age range of participants, and recruitment exclusively from volunteers.
2. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148.
Standard dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an effective treatment for BPD; however, access is often limited by shortages of clinicians and resources. Therefore, it has become increasingly common for clinical settings to offer patients only the skills training component of DBT, which requires fewer resources. While several clinical trials examining brief DBT skills–only treatment for BPD have shown promising results, it is unclear how effective this intervention is at reducing suicidal or nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) episodes. McMain et al5 explored the effectiveness of brief DBT skills–only adjunctive treatment on the rates of suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this 2-arm, single-blind, prospective controlled trial, 84 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to a 20-week DBT skills training group (DBT group) or an active waitlist (WL group). No restrictions on additional psychosocial or pharmacologic treatments were imposed on either group.
- The primary outcome was the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the Lifetime Suicide Attempt Self-Injury Interview and the Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory (DSHI). Measurements occurred at baseline, 10 weeks, 20 weeks, and 3 months posttreatment (32 weeks).
- Secondary outcomes included changes in health care utilization, BPD symptoms, and coping. These were assessed using the Treatment History Interview-2, Borderline Symptom List-23, State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory, Symptom Checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R), Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)-II, Social Adjustment Scale Self-report, Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale, Distress Tolerance Scale, and Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Scale.
Outcomes
- At Week 32, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed statistically significant greater reductions in the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the LSASI but not by the DSHI. The DBT group experienced statistically significant improvements in distress tolerance and emotion regulation over the WL group at all points, but no difference on mindfulness. The DBT group achieved greater reductions in anger over time as compared to the WL group.
- At Week 20, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed significant improvements in social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms. There were no significant group differences on impulsivity. Between-group differences in the number of hospital admissions favored the DBT group at 10 and 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups with respect to the number of emergency department visits.
- Analyses of group differences in clinical improvement as measured by the SCL-90-R revealed statistically reliable and clinically significant changes in the DBT group over the WL group at 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks.
Conclusions/limitations
- Brief DBT skills training reduced suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD. Participants in the DBT group also demonstrated greater improvement in anger, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation compared to the control group. These results were evident 3 months after treatment. However, any gains in health care utilization, social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms diminished or did not differ from waitlist participants at Week 32. At that time, participants in the DBT group demonstrated a similar level of symptomatology as the WL group.
- Limitations include the use of an active waitlist control group, allowance of concurrent treatments, the absence of an active therapeutic comparator group, use of self-report measures, use of an instrument with unknown psychometric properties, and a relatively short 3-month follow-up period.
3. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156.
Psychotherapeutic options for treating BPD include DBT, mentalization-based treatment, schema-focused therapy, transference-based psychotherapy, and systems training for emotional predictability and problem solving. More recently, interpersonal therapy also has been adapted for BPD (IPT-BPD). However, thus far no trials have investigated the long-term effects of this therapy on BPD. In 2010, Bellino et al11 published a 32-week RCT examining the effect of IPT-BPD on BPD. They concluded that IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine was superior to fluoxetine alone in improving symptoms and quality of life. The present study by Bozzatello et al6 examined whether the benefits of IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine demonstrated in the 2010 study persisted over a 24-month follow-up.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2010 study by Bellino et al,11 55 outpatients who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine (combined therapy) or fluoxetine alone for 32 weeks. Forty-four participants completed a 24-month follow-up study (n = 22 for IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine, n = 22 for fluoxetine only).
- Clinical assessments were performed at 6, 12, and 24 months, and used the same instruments as the original study, including the Clinical Global Impression Scale–Severity item, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS), Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment, Satisfaction Profile (SAT-P), and the Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI).
Outcomes
- While the original study demonstrated that combined therapy had a clinically significant effect over fluoxetine alone on both HARS score and the BPDSI item “affective instability” at 32 weeks, this advantage was maintained only at the 6-month assessment.
- The improvements that the combined therapy provided over fluoxetine monotherapy on the BPDSI items of “impulsivity” and “interpersonal relationships” as well as the SAT-P factors of social and psychological functioning at 32 weeks were preserved at 24 months. No additional improvements were seen.
Conclusions/limitations
- The improvements in impulsivity, interpersonal functioning, social functioning, and psychological functioning at 32 weeks seen with IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine compared with fluoxetine alone persisted for 2 years after completing therapy; no further improvements were seen.
- The improvements to anxiety and affective instability that combined therapy demonstrated over fluoxetine monotherapy at 32 weeks were not maintained at 24 months.
- Limitations include a small sample size, exclusion of psychiatric comorbidities, and a lack of assessment of session or medication adherence.
4. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63.
While many studies have demonstrated the benefits of psychotherapy for treating personality disorders, there is limited research of how different levels of psychotherapy may impact treatment outcomes. An RCT called the Ullevål Personality Project (UPP)12 compared an intensive combined treatment program (CP) with outpatient individual psychotherapy (OIP) in patients with personality disorders. The CP program consisted of short-term day-hospital treatment followed by outpatient combined group and individual psychotherapy. The outcomes this RCT evaluated included suicide attempts, suicidal thoughts, self-injury, psychosocial functioning, symptom distress, and interpersonal and personality problems. A 6-year follow-up concluded there were no differences in outcomes between the 2 treatment groups. However, in this RCT, Antonsen et al7 examined whether CP produced statistically significant benefits over OIP in a subset of patients with BPD.
Study design
- In the UPP trial,12 117 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for personality disorders (excluding antisocial and schizotypal personality disorder) were randomized to receive 18 weeks of day hospital psychotherapy followed by CP or OIP. Fifty-two participants in the UPP were diagnosed with BPD, and 34 of these participants completed the 6-year follow-up investigation.
- Symptom distress, psychosocial functioning, interpersonal problems, quality of life, personality functioning, and self-harm/suicidal thoughts/suicide attempts were assessed at baseline, 8 months, 18 months, 3 years, and 6 years using the SCL-90-R Global Severity Index (GSI), BDI, Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF), Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Quality of Life 10-point scale (QOL), Circumplex of Interpersonal Problems (CIP), and the 60-item short form of the Severity Indices of Personality Problems (SIPP-118) questionnaire.
Outcomes
- Compared to the OIP group, the CP group demonstrated statistically significant reductions in symptom distress at Year 6 as measured by the SCL-90-R GSI. Between Years 3 and 6, the CP group continued to show improvements in psychosocial functioning as demonstrated by improvements in GAF and WSAS scores. The OIP group’s scores worsened during this time. Compared to the OIP group, participants in the CP group also had significantly better outcomes on the SIPP-118 domains of self-control and identity integration.
- There were no significant differences between groups on the proportion of participants who engaged in self-harm or experienced suicidal thoughts or attempts. There were no significant differences in outcomes between the treatment groups on the CIP, BDI, or QOL.
- Participants in CP group tended to use fewer psychotropic medications than those in the OIP group over time, but this difference was not statistically significant. The 2 groups did not differ in use of health care services over the last year.
- Avoidant personality disorder (AVPD) did not have a significant moderator effect on GAF score. Comorbid AVPD was a negative predictor of GAF score, independent of the group.
Conclusions/limitations
- Both groups experienced a remission rate of 90% at 6-year follow-up. Compared with the OIP group, participants in the CP group experienced significantly greater reductions in symptom distress and improvements in self-control and identity integration at 6 years. Between Years 3 and 6, participants in the CP group experienced significant improvements in psychosocial functioning compared with OIP group participants. The 2 groups did not differ on other outcomes, including the CIP, BDI, QOL, suicidal thoughts, suicidal attempts, self-harm, and health care utilization.
- Despite statistically significant differences in GAF scores favoring the CP group over the OIP group during Years 3 to 6, GAF scores did not differ significantly in the final year, which suggests that symptomatic remission does not equal functional improvement.
- Limitations include a lack of control for intensity or length of treatment in statistical analyses, small sample size, lack of correction for multiple testing, lack of an a priori power analysis, missing data and potential violation of the missing at random assumption, use of therapists’ preferred treatment method/practice, and a lack of control for other treatments.
5. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299.
The efficacy of various psychotherapies for symptoms of BPD has been well established. However, there is limited evidence that these effects persist over time. In 2009, Bateman et al13 conducted an 18-month RCT comparing the effectiveness of outpatient mentalization-based treatment (MBT) against structured clinical management (SCM) for patients with BPD. Both groups experienced substantial improvements, but patients assigned to MBT demonstrated greater improvement in clinically significant problems, including suicide attempts and hospitalizations. In a 2021 follow-up to this study, Bateman et al8 investigated whether the MBT group’s gains in the primary outcomes (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months), social functioning, vocational engagement, and mental health service usage were maintained throughout an 8-year follow-up period.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2009 trial, Bateman et al13 randomized adult participants who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and had a suicide attempt or episode of life-threatening self-harm in the past 6 months to receive 18 months of MBT or SCM. The primary outcome was crisis events, defined as a composite of suicidal and severe self-injurious behaviors and hospitalizations. The 2021 Bateman et al8 study expanded this investigation by collecting additional data on a yearly basis for 8 years.
- Of the 134 original participants, 98 agreed to complete the follow-up. Due to attrition, the follow-up period was limited to 8 years. At each yearly visit, researchers collected information on the primary outcome, the absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months.
- Secondary measures were collected mainly through a modified version of the Client Service Receipt Inventory and included critical incidents, psychiatric and medical hospital and community services, employment and other personally meaningful activity, psychoactive medication, and other mental health treatments.
Outcomes
- The number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD at the 1-year follow-up was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. To improve participant retention, this outcome was not evaluated at later visits.
- The number of participants who achieved the primary recovery criteria of the original trial (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months) and remained well throughout the entire follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. The average number of years during which participants failed to meet recovery criteria was significantly greater in the SCM group compared with the MBT group.
- When controlling for age, treatment group was a significant predictor of recovery during the follow-up period. Overall, significantly fewer participants in the MBT group experienced critical incidents during the follow-up period.
- The SCM group used crisis mental health services for a significantly greater number of follow-up years than the MBT group, although the likelihood of ever using crisis services did not statistically differ between the groups. Both groups had similar use of outpatient mental health services, primary care services, and nonmental health medical services. Compared to the SCM group, the MBT group had significantly fewer professional support service visits and significantly fewer outpatient psychiatrist visits.
- MBT group participants spent more time in education, were less likely to be unemployed, and were less likely to use social care interventions than SCM group participants. Although those in the MBT group spent more months engaged in purposeful activity, there was no significant difference between the groups in the proportion of participants who did not engage in purposeful activity.
- The MBT group spent fewer months receiving psychotherapeutic medication compared with the SCM group. The variables that yielded significant 2-way interactions were eating disorder, substance use disorder, and physical abuse, suggesting greater benefit from MBT with these concurrent diagnoses. Younger age was associated with better outcomes.
Conclusions/limitations
- This study demonstrated that patients with BPD significantly benefited from specialized therapies such as MBT.
- At the 1 follow-up visit, the number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group.
- The number of participants who had achieved the primary recovery criteria and remained well during the 8-year follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared to the SCM group.
- Limitations include increasing attrition over time, possible allegiance effects and unmasking of research assistants, lack of self-report questionnaires, and the potentially erroneous conclusion that increased use of services equates to poorer treatment response and greater need for support.
6. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771.
Fewer than 1 in 4 patients with BPD have access to effective psychotherapies. The use of internet-based self-management interventions (SMIs) developed from evidence-based psychotherapies can help close this treatment gap. Although the efficacy of SMIs for several mental disorders has been demonstrated in multiple meta-analyses, results for BPD are mixed. In this study, Klein et al9 examined the effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an SMI based on schema therapy in addition to care as usual (CAU) in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In a 12-month, rater-blind, controlled parallel group trial, adults who had a total BPDSI score ≥15 and either a diagnosis of BPD according to DSM-IV criteria or a probable diagnosis of BPD (if they had also received a BPD diagnosis from their treating physician) were randomized to an internet-based SMI based on schema therapy called priovi (n = 103) or CAU (n = 101). Participants could complete the SMI content in approximately 6 months but were recommended to use the intervention for the entire year.
- Participation in psychotherapy and psychiatric treatment, including pharmacotherapy, was permitted. At baseline, 74% of participants were receiving psychotherapy and 88% were receiving psychiatric treatment.
- The primary outcome was change in BPDSI score at 12 months. The primary safety outcome was the number of serious adverse events at 12 months. Secondary outcomes included BPD severity, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, quality of life, uncontrolled internet use, negative treatment effects, and satisfaction with the intervention. Most assessments were measured at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 12 months.
Outcomes
- Large reductions in the severity of BPD symptoms as measured by change in BPDSI score was observed in both groups. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group, this difference was not statistically significant from the CAU group.
- There was no statistically significant difference in the number of serious adverse events between groups at any time.
Conclusions/limitations
- Treatment with SMI did not result in improved outcomes over CAU. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group compared to the CAU group, this difference was not statistically significant.
- The authors cautioned that the smaller-than-expected between-groups effect size must be interpreted against the background of an unexpectedly large effect in the CAU group. In fact, the CAU group pre/post effect was comparable to the pre/post effect of intensive specialized DBT treatment groups in previous RCTs.
- The authors also suggested that the high percentage of participants who received psychotherapy did not allow for an additional benefit from SMI.
- Limitations include recruitment method, lack of systematic assessment of accidental unblinding, high exclusion rate due to failure of the participant or treating clinician to provide confirmation of diagnosis, and the use of a serious adverse events assessment that is not psychometrically validated.
Bottom Line
Evidence from randomized controlled trials suggests that internet-based psychoeducation, brief dialectical behavior therapy skills-only treatment, interpersonal therapy, a program that combines day treatment with individual and group psychotherapy, and mentalization-based treatment can improve symptoms and quality of life for patients with borderline personality disorder.
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 It is characterized by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior that often results in problems in relationships. As a result, patients with BPD tend to utilize more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or major depressive disorder.2
Some clinicians believe BPD is difficult to treat. While historically there has been little consensus on the best treatments for this disorder, current options include both pharmacologic and psychological interventions. In Part 1 of this 2-part article, we focused on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions.3 Here in Part 2, we focus on findings from 6 recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of psychosocial interventions for BPD

1. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi: 10.4088/JCP.16m11153
Research has shown that BPD is a treatable illness with a more favorable prognosis than previously believed. Despite this, patients often experience difficulty accessing the most up-to-date information on BPD, which can impede their treatment. A 2008 study by Zanarini et al10 of younger female patients with BPD demonstrated that immediate, in-person psychoeducation improved impulsivity and relationships. Widespread implementation of this program proved problematic, however, due to cost and personnel constraints. To resolve this issue, researchers developed an internet-based version of the program. In a 2018 follow-up study, Zanarini et al4 examined the effect of this internet-based psychoeducation program on symptoms of BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- Women (age 18 to 30) who met DSM-IV and Diagnostic Interview for Borderlines–Revised criteria for BPD were randomized to an internet-based psychoeducation treatment group (n = 40) or a control group (n = 40).
- Ten outcomes concerning symptom severity and psychosocial functioning were assessed during weeks 1 to 12 (acute phase) and at months 6, 9, and 12 (maintenance phase) using the self-report version of the Zanarini Rating Scale for BPD (ZAN-BPD), the Borderline Evaluation of Severity over Time, the Sheehan Disability Scale, the Clinically Useful Depression Outcome Scale, the Clinically Useful Anxiety Outcome Scale, and Weissman’s Social Adjustment Scale (SAS).
Outcomes
- In the acute phase, treatment group participants experienced statistically significant improvements in all 10 outcomes. Control group participants demonstrated similar results, achieving statistically significant improvements in 7 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group experienced a more significant reduction in impulsivity and improvement in psychosocial functioning as measured by the ZAN-BPD and SAS.
- In the maintenance phase, treatment group participants achieved statistically significant improvements in 9 of 10 outcomes, whereas control group participants demonstrated statistically significant improvements in only 3 of 10 outcomes.
- Compared to the control group, the treatment group also demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in all 4 sector scores and the total score of the ZAN-BP
Conclusions/limitations
- In patients with BPD, internet-based psychoeducation reduced symptom severity and improved psychosocial functioning, with effects lasting 1 year. Treatment group participants experienced clinically significant improvements in all outcomes measured during the acute phase of the study; most improvements were maintained over 1 year.
- While the control group initially saw similar improvements in most measurements, these improvements were not maintained as effectively over 1 year.
- Limitations include a female-only population, the restricted age range of participants, and recruitment exclusively from volunteers.
2. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148.
Standard dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an effective treatment for BPD; however, access is often limited by shortages of clinicians and resources. Therefore, it has become increasingly common for clinical settings to offer patients only the skills training component of DBT, which requires fewer resources. While several clinical trials examining brief DBT skills–only treatment for BPD have shown promising results, it is unclear how effective this intervention is at reducing suicidal or nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI) episodes. McMain et al5 explored the effectiveness of brief DBT skills–only adjunctive treatment on the rates of suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this 2-arm, single-blind, prospective controlled trial, 84 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to a 20-week DBT skills training group (DBT group) or an active waitlist (WL group). No restrictions on additional psychosocial or pharmacologic treatments were imposed on either group.
- The primary outcome was the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the Lifetime Suicide Attempt Self-Injury Interview and the Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory (DSHI). Measurements occurred at baseline, 10 weeks, 20 weeks, and 3 months posttreatment (32 weeks).
- Secondary outcomes included changes in health care utilization, BPD symptoms, and coping. These were assessed using the Treatment History Interview-2, Borderline Symptom List-23, State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory, Symptom Checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R), Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)-II, Social Adjustment Scale Self-report, Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale, Distress Tolerance Scale, and Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Scale.
Outcomes
- At Week 32, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed statistically significant greater reductions in the frequency of suicidal and NSSI episodes as measured by the LSASI but not by the DSHI. The DBT group experienced statistically significant improvements in distress tolerance and emotion regulation over the WL group at all points, but no difference on mindfulness. The DBT group achieved greater reductions in anger over time as compared to the WL group.
- At Week 20, compared to the WL group, the DBT group showed significant improvements in social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms. There were no significant group differences on impulsivity. Between-group differences in the number of hospital admissions favored the DBT group at 10 and 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups with respect to the number of emergency department visits.
- Analyses of group differences in clinical improvement as measured by the SCL-90-R revealed statistically reliable and clinically significant changes in the DBT group over the WL group at 20 weeks, but not at 32 weeks.
Conclusions/limitations
- Brief DBT skills training reduced suicidal and NSSI episodes in patients with BPD. Participants in the DBT group also demonstrated greater improvement in anger, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation compared to the control group. These results were evident 3 months after treatment. However, any gains in health care utilization, social adjustment, symptom distress, and borderline symptoms diminished or did not differ from waitlist participants at Week 32. At that time, participants in the DBT group demonstrated a similar level of symptomatology as the WL group.
- Limitations include the use of an active waitlist control group, allowance of concurrent treatments, the absence of an active therapeutic comparator group, use of self-report measures, use of an instrument with unknown psychometric properties, and a relatively short 3-month follow-up period.
3. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156.
Psychotherapeutic options for treating BPD include DBT, mentalization-based treatment, schema-focused therapy, transference-based psychotherapy, and systems training for emotional predictability and problem solving. More recently, interpersonal therapy also has been adapted for BPD (IPT-BPD). However, thus far no trials have investigated the long-term effects of this therapy on BPD. In 2010, Bellino et al11 published a 32-week RCT examining the effect of IPT-BPD on BPD. They concluded that IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine was superior to fluoxetine alone in improving symptoms and quality of life. The present study by Bozzatello et al6 examined whether the benefits of IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine demonstrated in the 2010 study persisted over a 24-month follow-up.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2010 study by Bellino et al,11 55 outpatients who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine (combined therapy) or fluoxetine alone for 32 weeks. Forty-four participants completed a 24-month follow-up study (n = 22 for IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine, n = 22 for fluoxetine only).
- Clinical assessments were performed at 6, 12, and 24 months, and used the same instruments as the original study, including the Clinical Global Impression Scale–Severity item, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS), Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment, Satisfaction Profile (SAT-P), and the Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI).
Outcomes
- While the original study demonstrated that combined therapy had a clinically significant effect over fluoxetine alone on both HARS score and the BPDSI item “affective instability” at 32 weeks, this advantage was maintained only at the 6-month assessment.
- The improvements that the combined therapy provided over fluoxetine monotherapy on the BPDSI items of “impulsivity” and “interpersonal relationships” as well as the SAT-P factors of social and psychological functioning at 32 weeks were preserved at 24 months. No additional improvements were seen.
Conclusions/limitations
- The improvements in impulsivity, interpersonal functioning, social functioning, and psychological functioning at 32 weeks seen with IPT-BPD plus fluoxetine compared with fluoxetine alone persisted for 2 years after completing therapy; no further improvements were seen.
- The improvements to anxiety and affective instability that combined therapy demonstrated over fluoxetine monotherapy at 32 weeks were not maintained at 24 months.
- Limitations include a small sample size, exclusion of psychiatric comorbidities, and a lack of assessment of session or medication adherence.
4. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63.
While many studies have demonstrated the benefits of psychotherapy for treating personality disorders, there is limited research of how different levels of psychotherapy may impact treatment outcomes. An RCT called the Ullevål Personality Project (UPP)12 compared an intensive combined treatment program (CP) with outpatient individual psychotherapy (OIP) in patients with personality disorders. The CP program consisted of short-term day-hospital treatment followed by outpatient combined group and individual psychotherapy. The outcomes this RCT evaluated included suicide attempts, suicidal thoughts, self-injury, psychosocial functioning, symptom distress, and interpersonal and personality problems. A 6-year follow-up concluded there were no differences in outcomes between the 2 treatment groups. However, in this RCT, Antonsen et al7 examined whether CP produced statistically significant benefits over OIP in a subset of patients with BPD.
Study design
- In the UPP trial,12 117 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for personality disorders (excluding antisocial and schizotypal personality disorder) were randomized to receive 18 weeks of day hospital psychotherapy followed by CP or OIP. Fifty-two participants in the UPP were diagnosed with BPD, and 34 of these participants completed the 6-year follow-up investigation.
- Symptom distress, psychosocial functioning, interpersonal problems, quality of life, personality functioning, and self-harm/suicidal thoughts/suicide attempts were assessed at baseline, 8 months, 18 months, 3 years, and 6 years using the SCL-90-R Global Severity Index (GSI), BDI, Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF), Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Quality of Life 10-point scale (QOL), Circumplex of Interpersonal Problems (CIP), and the 60-item short form of the Severity Indices of Personality Problems (SIPP-118) questionnaire.
Outcomes
- Compared to the OIP group, the CP group demonstrated statistically significant reductions in symptom distress at Year 6 as measured by the SCL-90-R GSI. Between Years 3 and 6, the CP group continued to show improvements in psychosocial functioning as demonstrated by improvements in GAF and WSAS scores. The OIP group’s scores worsened during this time. Compared to the OIP group, participants in the CP group also had significantly better outcomes on the SIPP-118 domains of self-control and identity integration.
- There were no significant differences between groups on the proportion of participants who engaged in self-harm or experienced suicidal thoughts or attempts. There were no significant differences in outcomes between the treatment groups on the CIP, BDI, or QOL.
- Participants in CP group tended to use fewer psychotropic medications than those in the OIP group over time, but this difference was not statistically significant. The 2 groups did not differ in use of health care services over the last year.
- Avoidant personality disorder (AVPD) did not have a significant moderator effect on GAF score. Comorbid AVPD was a negative predictor of GAF score, independent of the group.
Conclusions/limitations
- Both groups experienced a remission rate of 90% at 6-year follow-up. Compared with the OIP group, participants in the CP group experienced significantly greater reductions in symptom distress and improvements in self-control and identity integration at 6 years. Between Years 3 and 6, participants in the CP group experienced significant improvements in psychosocial functioning compared with OIP group participants. The 2 groups did not differ on other outcomes, including the CIP, BDI, QOL, suicidal thoughts, suicidal attempts, self-harm, and health care utilization.
- Despite statistically significant differences in GAF scores favoring the CP group over the OIP group during Years 3 to 6, GAF scores did not differ significantly in the final year, which suggests that symptomatic remission does not equal functional improvement.
- Limitations include a lack of control for intensity or length of treatment in statistical analyses, small sample size, lack of correction for multiple testing, lack of an a priori power analysis, missing data and potential violation of the missing at random assumption, use of therapists’ preferred treatment method/practice, and a lack of control for other treatments.
5. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299.
The efficacy of various psychotherapies for symptoms of BPD has been well established. However, there is limited evidence that these effects persist over time. In 2009, Bateman et al13 conducted an 18-month RCT comparing the effectiveness of outpatient mentalization-based treatment (MBT) against structured clinical management (SCM) for patients with BPD. Both groups experienced substantial improvements, but patients assigned to MBT demonstrated greater improvement in clinically significant problems, including suicide attempts and hospitalizations. In a 2021 follow-up to this study, Bateman et al8 investigated whether the MBT group’s gains in the primary outcomes (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months), social functioning, vocational engagement, and mental health service usage were maintained throughout an 8-year follow-up period.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In the 2009 trial, Bateman et al13 randomized adult participants who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and had a suicide attempt or episode of life-threatening self-harm in the past 6 months to receive 18 months of MBT or SCM. The primary outcome was crisis events, defined as a composite of suicidal and severe self-injurious behaviors and hospitalizations. The 2021 Bateman et al8 study expanded this investigation by collecting additional data on a yearly basis for 8 years.
- Of the 134 original participants, 98 agreed to complete the follow-up. Due to attrition, the follow-up period was limited to 8 years. At each yearly visit, researchers collected information on the primary outcome, the absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months.
- Secondary measures were collected mainly through a modified version of the Client Service Receipt Inventory and included critical incidents, psychiatric and medical hospital and community services, employment and other personally meaningful activity, psychoactive medication, and other mental health treatments.
Outcomes
- The number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD at the 1-year follow-up was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. To improve participant retention, this outcome was not evaluated at later visits.
- The number of participants who achieved the primary recovery criteria of the original trial (absence of severe self-harm, suicide attempts, and inpatient admissions in the previous 12 months) and remained well throughout the entire follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared with the SCM group. The average number of years during which participants failed to meet recovery criteria was significantly greater in the SCM group compared with the MBT group.
- When controlling for age, treatment group was a significant predictor of recovery during the follow-up period. Overall, significantly fewer participants in the MBT group experienced critical incidents during the follow-up period.
- The SCM group used crisis mental health services for a significantly greater number of follow-up years than the MBT group, although the likelihood of ever using crisis services did not statistically differ between the groups. Both groups had similar use of outpatient mental health services, primary care services, and nonmental health medical services. Compared to the SCM group, the MBT group had significantly fewer professional support service visits and significantly fewer outpatient psychiatrist visits.
- MBT group participants spent more time in education, were less likely to be unemployed, and were less likely to use social care interventions than SCM group participants. Although those in the MBT group spent more months engaged in purposeful activity, there was no significant difference between the groups in the proportion of participants who did not engage in purposeful activity.
- The MBT group spent fewer months receiving psychotherapeutic medication compared with the SCM group. The variables that yielded significant 2-way interactions were eating disorder, substance use disorder, and physical abuse, suggesting greater benefit from MBT with these concurrent diagnoses. Younger age was associated with better outcomes.
Conclusions/limitations
- This study demonstrated that patients with BPD significantly benefited from specialized therapies such as MBT.
- At the 1 follow-up visit, the number of participants who met diagnostic criteria for BPD was significantly lower in the MBT group compared with the SCM group.
- The number of participants who had achieved the primary recovery criteria and remained well during the 8-year follow-up period was significantly higher in the MBT group compared to the SCM group.
- Limitations include increasing attrition over time, possible allegiance effects and unmasking of research assistants, lack of self-report questionnaires, and the potentially erroneous conclusion that increased use of services equates to poorer treatment response and greater need for support.
6. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771.
Fewer than 1 in 4 patients with BPD have access to effective psychotherapies. The use of internet-based self-management interventions (SMIs) developed from evidence-based psychotherapies can help close this treatment gap. Although the efficacy of SMIs for several mental disorders has been demonstrated in multiple meta-analyses, results for BPD are mixed. In this study, Klein et al9 examined the effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an SMI based on schema therapy in addition to care as usual (CAU) in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In a 12-month, rater-blind, controlled parallel group trial, adults who had a total BPDSI score ≥15 and either a diagnosis of BPD according to DSM-IV criteria or a probable diagnosis of BPD (if they had also received a BPD diagnosis from their treating physician) were randomized to an internet-based SMI based on schema therapy called priovi (n = 103) or CAU (n = 101). Participants could complete the SMI content in approximately 6 months but were recommended to use the intervention for the entire year.
- Participation in psychotherapy and psychiatric treatment, including pharmacotherapy, was permitted. At baseline, 74% of participants were receiving psychotherapy and 88% were receiving psychiatric treatment.
- The primary outcome was change in BPDSI score at 12 months. The primary safety outcome was the number of serious adverse events at 12 months. Secondary outcomes included BPD severity, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, quality of life, uncontrolled internet use, negative treatment effects, and satisfaction with the intervention. Most assessments were measured at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 12 months.
Outcomes
- Large reductions in the severity of BPD symptoms as measured by change in BPDSI score was observed in both groups. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group, this difference was not statistically significant from the CAU group.
- There was no statistically significant difference in the number of serious adverse events between groups at any time.
Conclusions/limitations
- Treatment with SMI did not result in improved outcomes over CAU. Although the average reduction in BPDSI score was greater in the SMI group compared to the CAU group, this difference was not statistically significant.
- The authors cautioned that the smaller-than-expected between-groups effect size must be interpreted against the background of an unexpectedly large effect in the CAU group. In fact, the CAU group pre/post effect was comparable to the pre/post effect of intensive specialized DBT treatment groups in previous RCTs.
- The authors also suggested that the high percentage of participants who received psychotherapy did not allow for an additional benefit from SMI.
- Limitations include recruitment method, lack of systematic assessment of accidental unblinding, high exclusion rate due to failure of the participant or treating clinician to provide confirmation of diagnosis, and the use of a serious adverse events assessment that is not psychometrically validated.
Bottom Line
Evidence from randomized controlled trials suggests that internet-based psychoeducation, brief dialectical behavior therapy skills-only treatment, interpersonal therapy, a program that combines day treatment with individual and group psychotherapy, and mentalization-based treatment can improve symptoms and quality of life for patients with borderline personality disorder.
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159(2):276-83.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(2):295-302.
3. Saeed SA, Kallis AC. Borderline personality disorder: 6 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):26-30,34-36.
4. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi:10.4088/JCP.16m11153
5. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148. doi:10.1111/acps.12664
6. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.04.014
7. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63. doi:10.1080/10503307.2015.1072283
8. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299. doi:10.1037/per0000422
9. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047771
10. Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR. A preliminary, randomized trial of psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Pers Disord. 2008;22(3):284-290.
11. Bellino S, Rinaldi C, Bogetto F. Adaptation of interpersonal psychotherapy to borderline personality disorder: a comparison of combined therapy and single pharmacotherapy. Can J Psychiatry. 2010;55(2):74-81.
12. Arnevik E, Wilberg T, Urnes Ø, et al. Psychotherapy for personality disorders: short-term day hospital psychotherapy versus outpatient individual therapy – a randomized controlled study. Eur Psychiatry. 2009,24(2):71-78. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.09.004
13. Bateman A, Fonagy P. Randomized controlled trial of outpatient mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for borderline personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(12):1355-1364.
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159(2):276-83.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(2):295-302.
3. Saeed SA, Kallis AC. Borderline personality disorder: 6 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):26-30,34-36.
4. Zanarini MC, Conkey LC, Temes CM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of web-based psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(3):16m11153. doi:10.4088/JCP.16m11153
5. McMain SF, Guimond T, Barnhart R, et al. A randomized trial of brief dialectical behaviour therapy skills training in suicidal patients suffering from borderline disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135(2):138-148. doi:10.1111/acps.12664
6. Bozzatello P, Bellino S. Combined therapy with interpersonal psychotherapy adapted for borderline personality disorder: a two-years follow-up. Psychiatry Res. 2016;240:151-156. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.04.014
7. Antonsen BT, Kvarstein EH, Urnes Ø, et al. Favourable outcome of long-term combined psychotherapy for patients with borderline personality disorder: six-year follow-up of a randomized study. Psychother Res. 2017;27(1):51-63. doi:10.1080/10503307.2015.1072283
8. Bateman A, Constantinou MP, Fonagy P, et al. Eight-year prospective follow-up of mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for people with borderline personality disorder. Personal Disord. 2021;12(4):291-299. doi:10.1037/per0000422
9. Klein JP, Hauer-von Mauschwitz A, Berger T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of the adjunctive use of an internet-based self-management intervention for borderline personality disorder in addition to care as usual: results from a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e047771. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047771
10. Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR. A preliminary, randomized trial of psychoeducation for women with borderline personality disorder. J Pers Disord. 2008;22(3):284-290.
11. Bellino S, Rinaldi C, Bogetto F. Adaptation of interpersonal psychotherapy to borderline personality disorder: a comparison of combined therapy and single pharmacotherapy. Can J Psychiatry. 2010;55(2):74-81.
12. Arnevik E, Wilberg T, Urnes Ø, et al. Psychotherapy for personality disorders: short-term day hospital psychotherapy versus outpatient individual therapy – a randomized controlled study. Eur Psychiatry. 2009,24(2):71-78. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.09.004
13. Bateman A, Fonagy P. Randomized controlled trial of outpatient mentalization-based treatment versus structured clinical management for borderline personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(12):1355-1364.
Borderline personality disorder: 6 studies of biological interventions
FIRST OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is marked by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior, often resulting in problems in relationships. BPD is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 Patients with BPD tend to use more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or those with major depressive disorder (MDD).2 However, there has been little consensus on the best treatment(s) for this serious and debilitating disorder, and some clinicians view BPD as difficult to treat.
Current treatments for BPD include psychological and pharmacological interventions. Neuromodulation techniques, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, may also positively affect BPD symptomatology. In recent years, there have been some promising findings in the treatment of BPD. In this 2-part article, we focus on current (within the last 5 years) findings from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of BPD treatments. Here in Part 1, we focus on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions (Table,3-8). In Part 2, we will focus on RCTs that investigated psychological interventions.
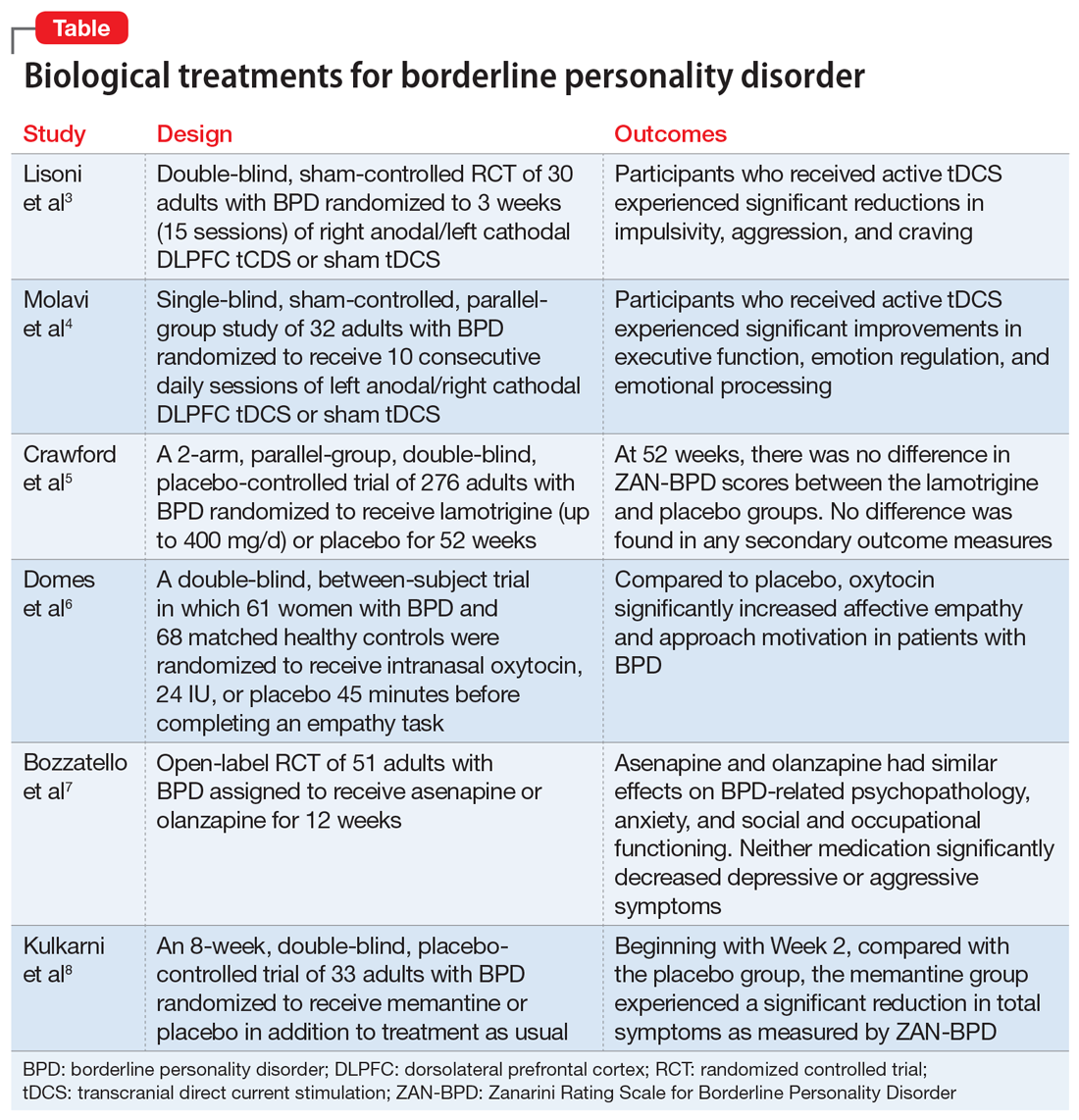
1. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
Impulsivity has been described as the core feature of BPD that best explains its behavioral, cognitive, and clinical manifestations. Studies have repeatedly demonstrated the role of the prefrontal cortex in modulating impulsivity. Dysfunction of the
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In a double-blind, sham-controlled trial, adults who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for BPD were randomized to 3 weeks (15 sessions) of right anodal/left cathodal DLPFC tCDS (n = 15) or sham tDCS (n = 15). This study included patients with comorbid psychiatric disorders, including substance use disorders. Discontinuation or alteration of existing medications was not allowed.
- The presence, severity, and change over time of BPD core symptoms was assessed at baseline and after 3 weeks using several clinical scales, self-questionnaires, and neuropsychological tests, including the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11 (BIS-11), Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BP-AQ), Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Irritability-Depression Anxiety Scale (IDA), Visual Analog Scales (VAS), and Iowa Gambling Task.
Outcomes
- Participants in the active tDCS group experienced significant reductions in impulsivity, aggression, and craving as measured by the BIS-11, BP-AQ, and VAS.
- Compared to the sham group, the active tDCS group had greater reductions in HAM-D and BDI scores.
- HAM-A and IDA scores were improved in both groups, although the active tDCS group showed greater reductions in IDA scores compared with the sham group.
- As measured by DERS, active tDCS did not improve affective dysregulation more than sham tDCS.
Conclusions/limitations
- Bilateral tDCS targeting the right DLPFC with anodal stimulation is a safe, well-tolerated technique that may modulate core dimensions of BPD, including impulsivity, aggression, and craving.
- Excitatory anodal stimulation of the right DLFPC coupled with inhibitory cathodal stimulation on the left DLPFC may be an effective montage for targeting impulsivity in patients with BPD.
- Study limitations include a small sample size, use of targeted questionnaires only, inclusion of patients with BPD who also had certain comorbid psychiatric disorders, lack of analysis of the contributions of medications, lack of functional neuroimaging, and lack of a follow-up phase.
2. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
Emotional dysregulation is considered a core feature of BPD psychopathology and is closely associated with executive dysfunction and cognitive control. Manifestations of executive dysfunction include aggressiveness, impulsive decision-making, disinhibition, and self-destructive behaviors. Neuroimaging of patients with BPD has shown enhanced activity in the insula, posterior cingulate cortex, and amygdala, with reduced activity in the medial PFC, subgenual anterior cingulate cortex, and DLPFC. Molavi et al4 postulated that increasing DLPFC activation with left anodal tDCS would result in improved executive functioning and emotion dysregulation in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this single-blind, sham-controlled, parallel-group study, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were randomized to receive 10 consecutive daily sessions of left anodal/right cathodal DLPFC tDCS (n = 16) or sham tDCS (n = 16).
- The effect of tDCS on executive dysfunction, emotion dysregulation, and emotional processing was measured using the Executive Skills Questionnaire for Adults (ESQ), Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ), and Emotional Processing Scale (EPS). Measurements occurred at baseline and after 10 sessions of active or sham tDCS.
Outcomes
- Participants who received active tDCS experienced significant improvements in ESQ overall score and most of the executive function domains measured by the ESQ.
- Those in the active tDCS group also experienced significant improvement in emotion regulation as measured by the cognitive reappraisal subscale (but not the expressive suppression subscale) of the ERQ after the intervention.
- Overall emotional processing as measured by the EPS was significantly improved in the active tDCS group following the intervention.
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated bilateral left anodal/right cathodal tDCS stimulation of the DLPFC significantly improved executive functioning and aspects of emotion regulation and emotional processing in patients with BPD. This improvement was presumed to be the result of increased activity of left DLPFC.
- Study limitations include a single-blind design, lack of follow-up to assess durability and stability of response over time, reliance on self-report measures, lack of functional neuroimaging, and limited focality of tDCS.
3. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
One of the hallmark symptoms of BPD is mood dysregulation. Current treatment guidelines recommend the use of mood stabilizers for BPD despite limited quality evidence of effectiveness and a lack of FDA-approved medications with this indication. In this RCT, Crawford et al5 examined whether lamotrigine is a clinically effective and cost-effective treatment for people with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In this 2-arm, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 276 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive lamotrigine (up to 400 mg/d) or placebo for 52 weeks.
- The primary outcome was the score on the Zanarini Rating Scale for Borderline Personality Disorder (ZAN-BPD) at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included depressive symptoms, deliberate self-harm, social functioning, health-related quality of life, resource use and costs, treatment adverse effects, and adverse events. These were assessed using the BDI; Acts of Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory; Social Functioning Questionnaire; Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test; and the EQ-5D-3L.
Outcomes
- Mean ZAN-BPD score decreased at 12 weeks in both groups, after which time the score remained stable.
- There was no difference in ZAN-BPD scores at 52 weeks between treatment arms. No difference was found in any secondary outcome measures.
- Difference in costs between groups was not significant.
Conclusions/limitations
- There was no evidence that lamotrigine led to clinical improvements in BPD symptomatology, social functioning, health-related quality of life, or substance use.
- Lamotrigine is neither clinically effective nor a cost-effective use of resources in the treatment of BPD.
- Limitations include a low level of adherence.
4. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
A core feature of BPD is impairment in empathy; adequate empathy is required for intact social functioning. Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that helps regulate complex social cognition and behavior. Prior research has found that oxytocin administration enhances emotion regulation and empathy. Women with BPD have been observed to have lower levels of oxytocin. Domes et al6 conducted an RCT to see if oxytocin could have a beneficial effect on social approach and social cognition in women with BPD.
Study design
- In a double-blind, placebo-controlled, between-subject trial, 61 women who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and 68 matched healthy controls were randomized to receive intranasal oxytocin, 24 IU, or placebo 45 minutes before completing an empathy task.
- An extended version of the Multifaceted Empathy Test was used to assess empathy and approach motivation.
Outcomes
- For cognitive empathy, patients with BPD exhibited significantly lower overall performance compared to controls. There was no effect of oxytocin on this performance in either group.
- Patients with BPD had significantly lower affective empathy compared with controls. After oxytocin administration, patients with BPD had significantly higher affective empathy than those with BPD who received placebo, reaching the level of healthy controls who received placebo.
- For positive stimuli, patients with BPD showed lower affective empathy than controls. Oxytocin treatment increased affective empathy in both groups.
- For negative stimuli, oxytocin increased affective empathy more in patients with BPD than in controls.
- Patients with BPD demonstrated less approach motivation than controls. Oxytocin increased approach motivation more in patients with BPD than in controls. For approach motivation toward positive stimuli, oxytocin had a significant effect on patients with BPD.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations...
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients with BPD showed reduced cognitive and affective empathy and less approach behavior motivation than healthy controls.
- Patients with BPD who received oxytocin attained a level of affective empathy and approach motivation similar to that of healthy controls who received placebo. For positive stimuli, both groups exhibited comparable improvements from oxytocin. For negative stimuli, patients with BPD patients showed significant improvement with oxytocin, whereas healthy controls received no such benefit.
- Limitations include the use of self-report scales, lack of a control group, and inclusion of patients using psychotherapeutic medications. The study lacks generalizability because only women were included; the effect of exogenous oxytocin on men may differ.
5. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
The last decade has seen a noticeable shift in clinical practice from the use of antidepressants to mood stabilizers and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) in the treatment of BPD. Studies have demonstrated therapeutic effects of antipsychotic drugs across a wide range of BPD symptoms. Among SGAs, olanzapine is the most extensively studied across case reports, open-label studies, and RCTs of patients with BPD. In an RCT, Bozzatello et al7 compared the efficacy and tolerability of asenapine to olanzapine.
Study design
- In this open-label RCT, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were assigned to receive asenapine (n = 25) or olanzapine (n = 26) for 12 weeks.
- Study measurements included the Clinical Global Impression Scale, Severity item, HAM-D, HAM-A, Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale, Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI), BIS-11, Modified Overt Aggression Scale, and Dosage Record Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale.
Outcomes
- Asenapine and olanzapine had similar effects on BPD-related psychopathology, anxiety, and social and occupational functioning.
- Neither medication significantly decreased depressive or aggressive symptoms.
- Asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the affective instability score of the BPDSI.
- Akathisia and restlessness/anxiety were more common with asenapine, and somnolence and fatigue were more common with olanzapine.
Conclusions/limitations
- The overall efficacy of asenapine was not different from olanzapine, and both medications were well-tolerated.
- Neither medication led to an improvement in depression or aggression, but asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the severity of affective instability.
- Limitations include an open-label design, lack of placebo group, small sample size, high drop-out rate, exclusion of participants with co-occurring MDD and substance abuse/dependence, lack of data on prior pharmacotherapies and psychotherapies, and lack of power to detect a difference on the dissociation/paranoid ideation item of BPDSI.
6. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8
It has been hypothesized that glutamate dysregulation and excitotoxicity are crucial to the development of the cognitive disturbances that underlie BPD. As such, glutamate modulators such as memantine hold promise for the treatment of BPD. In this RCT, Kulkarni et al8 examined the efficacy and tolerability of memantine compared with treatment as usual in patients with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adults diagnosed with BPD according to the Diagnostic Interview for Borderline Patients were randomized to receive memantine (n = 17) or placebo (n = 16) in addition to treatment as usual. Treatment as usual included the use of antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics as well as psychotherapy and other psychosocial interventions.
- Patients were initiated on placebo or memantine, 10 mg/d. Memantine was increased to 20 mg/d after 7 days.
- ZAN-BPD score was the primary outcome and was measured at baseline and 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks. An adverse effects questionnaire was administered every 2 weeks to assess tolerability.
Outcomes
- During the first 2 weeks of treatment, there were no significant improvements in ZAN-BPD score in the memantine group compared with the placebo group.
- Beginning with Week 2, compared with the placebo group, the memantine group experienced a significant reduction in total symptoms as measured by ZAN-BPD.
- There were no statistically significant differences in adverse events between groups.
Conclusions/limitations
- Memantine appears to be a well-tolerated treatment option for patients with BPD and merits further study.
- Limitations include a small sample size, and an inability to reach plateau of ZAN-BPD total score in either group. Also, there is considerable individual variability in memantine steady-state plasma concentrations, but plasma levels were not measured in this study.
Bottom Line
Findings from small randomized controlled trials suggest that transcranial direct current stimulation, oxytocin, asenapine, olanzapine, and memantine may have beneficial effects on some core symptoms of borderline personality disorder. These findings need to be replicated in larger studies.
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002; 159:276-283.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:295-302.
3. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
4. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
5. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
6. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
7. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
8. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8
FIRST OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is marked by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior, often resulting in problems in relationships. BPD is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 Patients with BPD tend to use more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or those with major depressive disorder (MDD).2 However, there has been little consensus on the best treatment(s) for this serious and debilitating disorder, and some clinicians view BPD as difficult to treat.
Current treatments for BPD include psychological and pharmacological interventions. Neuromodulation techniques, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, may also positively affect BPD symptomatology. In recent years, there have been some promising findings in the treatment of BPD. In this 2-part article, we focus on current (within the last 5 years) findings from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of BPD treatments. Here in Part 1, we focus on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions (Table,3-8). In Part 2, we will focus on RCTs that investigated psychological interventions.

1. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
Impulsivity has been described as the core feature of BPD that best explains its behavioral, cognitive, and clinical manifestations. Studies have repeatedly demonstrated the role of the prefrontal cortex in modulating impulsivity. Dysfunction of the
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In a double-blind, sham-controlled trial, adults who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for BPD were randomized to 3 weeks (15 sessions) of right anodal/left cathodal DLPFC tCDS (n = 15) or sham tDCS (n = 15). This study included patients with comorbid psychiatric disorders, including substance use disorders. Discontinuation or alteration of existing medications was not allowed.
- The presence, severity, and change over time of BPD core symptoms was assessed at baseline and after 3 weeks using several clinical scales, self-questionnaires, and neuropsychological tests, including the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11 (BIS-11), Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BP-AQ), Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Irritability-Depression Anxiety Scale (IDA), Visual Analog Scales (VAS), and Iowa Gambling Task.
Outcomes
- Participants in the active tDCS group experienced significant reductions in impulsivity, aggression, and craving as measured by the BIS-11, BP-AQ, and VAS.
- Compared to the sham group, the active tDCS group had greater reductions in HAM-D and BDI scores.
- HAM-A and IDA scores were improved in both groups, although the active tDCS group showed greater reductions in IDA scores compared with the sham group.
- As measured by DERS, active tDCS did not improve affective dysregulation more than sham tDCS.
Conclusions/limitations
- Bilateral tDCS targeting the right DLPFC with anodal stimulation is a safe, well-tolerated technique that may modulate core dimensions of BPD, including impulsivity, aggression, and craving.
- Excitatory anodal stimulation of the right DLFPC coupled with inhibitory cathodal stimulation on the left DLPFC may be an effective montage for targeting impulsivity in patients with BPD.
- Study limitations include a small sample size, use of targeted questionnaires only, inclusion of patients with BPD who also had certain comorbid psychiatric disorders, lack of analysis of the contributions of medications, lack of functional neuroimaging, and lack of a follow-up phase.
2. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
Emotional dysregulation is considered a core feature of BPD psychopathology and is closely associated with executive dysfunction and cognitive control. Manifestations of executive dysfunction include aggressiveness, impulsive decision-making, disinhibition, and self-destructive behaviors. Neuroimaging of patients with BPD has shown enhanced activity in the insula, posterior cingulate cortex, and amygdala, with reduced activity in the medial PFC, subgenual anterior cingulate cortex, and DLPFC. Molavi et al4 postulated that increasing DLPFC activation with left anodal tDCS would result in improved executive functioning and emotion dysregulation in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this single-blind, sham-controlled, parallel-group study, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were randomized to receive 10 consecutive daily sessions of left anodal/right cathodal DLPFC tDCS (n = 16) or sham tDCS (n = 16).
- The effect of tDCS on executive dysfunction, emotion dysregulation, and emotional processing was measured using the Executive Skills Questionnaire for Adults (ESQ), Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ), and Emotional Processing Scale (EPS). Measurements occurred at baseline and after 10 sessions of active or sham tDCS.
Outcomes
- Participants who received active tDCS experienced significant improvements in ESQ overall score and most of the executive function domains measured by the ESQ.
- Those in the active tDCS group also experienced significant improvement in emotion regulation as measured by the cognitive reappraisal subscale (but not the expressive suppression subscale) of the ERQ after the intervention.
- Overall emotional processing as measured by the EPS was significantly improved in the active tDCS group following the intervention.
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated bilateral left anodal/right cathodal tDCS stimulation of the DLPFC significantly improved executive functioning and aspects of emotion regulation and emotional processing in patients with BPD. This improvement was presumed to be the result of increased activity of left DLPFC.
- Study limitations include a single-blind design, lack of follow-up to assess durability and stability of response over time, reliance on self-report measures, lack of functional neuroimaging, and limited focality of tDCS.
3. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
One of the hallmark symptoms of BPD is mood dysregulation. Current treatment guidelines recommend the use of mood stabilizers for BPD despite limited quality evidence of effectiveness and a lack of FDA-approved medications with this indication. In this RCT, Crawford et al5 examined whether lamotrigine is a clinically effective and cost-effective treatment for people with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In this 2-arm, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 276 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive lamotrigine (up to 400 mg/d) or placebo for 52 weeks.
- The primary outcome was the score on the Zanarini Rating Scale for Borderline Personality Disorder (ZAN-BPD) at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included depressive symptoms, deliberate self-harm, social functioning, health-related quality of life, resource use and costs, treatment adverse effects, and adverse events. These were assessed using the BDI; Acts of Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory; Social Functioning Questionnaire; Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test; and the EQ-5D-3L.
Outcomes
- Mean ZAN-BPD score decreased at 12 weeks in both groups, after which time the score remained stable.
- There was no difference in ZAN-BPD scores at 52 weeks between treatment arms. No difference was found in any secondary outcome measures.
- Difference in costs between groups was not significant.
Conclusions/limitations
- There was no evidence that lamotrigine led to clinical improvements in BPD symptomatology, social functioning, health-related quality of life, or substance use.
- Lamotrigine is neither clinically effective nor a cost-effective use of resources in the treatment of BPD.
- Limitations include a low level of adherence.
4. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
A core feature of BPD is impairment in empathy; adequate empathy is required for intact social functioning. Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that helps regulate complex social cognition and behavior. Prior research has found that oxytocin administration enhances emotion regulation and empathy. Women with BPD have been observed to have lower levels of oxytocin. Domes et al6 conducted an RCT to see if oxytocin could have a beneficial effect on social approach and social cognition in women with BPD.
Study design
- In a double-blind, placebo-controlled, between-subject trial, 61 women who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and 68 matched healthy controls were randomized to receive intranasal oxytocin, 24 IU, or placebo 45 minutes before completing an empathy task.
- An extended version of the Multifaceted Empathy Test was used to assess empathy and approach motivation.
Outcomes
- For cognitive empathy, patients with BPD exhibited significantly lower overall performance compared to controls. There was no effect of oxytocin on this performance in either group.
- Patients with BPD had significantly lower affective empathy compared with controls. After oxytocin administration, patients with BPD had significantly higher affective empathy than those with BPD who received placebo, reaching the level of healthy controls who received placebo.
- For positive stimuli, patients with BPD showed lower affective empathy than controls. Oxytocin treatment increased affective empathy in both groups.
- For negative stimuli, oxytocin increased affective empathy more in patients with BPD than in controls.
- Patients with BPD demonstrated less approach motivation than controls. Oxytocin increased approach motivation more in patients with BPD than in controls. For approach motivation toward positive stimuli, oxytocin had a significant effect on patients with BPD.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations...
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients with BPD showed reduced cognitive and affective empathy and less approach behavior motivation than healthy controls.
- Patients with BPD who received oxytocin attained a level of affective empathy and approach motivation similar to that of healthy controls who received placebo. For positive stimuli, both groups exhibited comparable improvements from oxytocin. For negative stimuli, patients with BPD patients showed significant improvement with oxytocin, whereas healthy controls received no such benefit.
- Limitations include the use of self-report scales, lack of a control group, and inclusion of patients using psychotherapeutic medications. The study lacks generalizability because only women were included; the effect of exogenous oxytocin on men may differ.
5. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
The last decade has seen a noticeable shift in clinical practice from the use of antidepressants to mood stabilizers and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) in the treatment of BPD. Studies have demonstrated therapeutic effects of antipsychotic drugs across a wide range of BPD symptoms. Among SGAs, olanzapine is the most extensively studied across case reports, open-label studies, and RCTs of patients with BPD. In an RCT, Bozzatello et al7 compared the efficacy and tolerability of asenapine to olanzapine.
Study design
- In this open-label RCT, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were assigned to receive asenapine (n = 25) or olanzapine (n = 26) for 12 weeks.
- Study measurements included the Clinical Global Impression Scale, Severity item, HAM-D, HAM-A, Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale, Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI), BIS-11, Modified Overt Aggression Scale, and Dosage Record Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale.
Outcomes
- Asenapine and olanzapine had similar effects on BPD-related psychopathology, anxiety, and social and occupational functioning.
- Neither medication significantly decreased depressive or aggressive symptoms.
- Asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the affective instability score of the BPDSI.
- Akathisia and restlessness/anxiety were more common with asenapine, and somnolence and fatigue were more common with olanzapine.
Conclusions/limitations
- The overall efficacy of asenapine was not different from olanzapine, and both medications were well-tolerated.
- Neither medication led to an improvement in depression or aggression, but asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the severity of affective instability.
- Limitations include an open-label design, lack of placebo group, small sample size, high drop-out rate, exclusion of participants with co-occurring MDD and substance abuse/dependence, lack of data on prior pharmacotherapies and psychotherapies, and lack of power to detect a difference on the dissociation/paranoid ideation item of BPDSI.
6. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8
It has been hypothesized that glutamate dysregulation and excitotoxicity are crucial to the development of the cognitive disturbances that underlie BPD. As such, glutamate modulators such as memantine hold promise for the treatment of BPD. In this RCT, Kulkarni et al8 examined the efficacy and tolerability of memantine compared with treatment as usual in patients with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adults diagnosed with BPD according to the Diagnostic Interview for Borderline Patients were randomized to receive memantine (n = 17) or placebo (n = 16) in addition to treatment as usual. Treatment as usual included the use of antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics as well as psychotherapy and other psychosocial interventions.
- Patients were initiated on placebo or memantine, 10 mg/d. Memantine was increased to 20 mg/d after 7 days.
- ZAN-BPD score was the primary outcome and was measured at baseline and 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks. An adverse effects questionnaire was administered every 2 weeks to assess tolerability.
Outcomes
- During the first 2 weeks of treatment, there were no significant improvements in ZAN-BPD score in the memantine group compared with the placebo group.
- Beginning with Week 2, compared with the placebo group, the memantine group experienced a significant reduction in total symptoms as measured by ZAN-BPD.
- There were no statistically significant differences in adverse events between groups.
Conclusions/limitations
- Memantine appears to be a well-tolerated treatment option for patients with BPD and merits further study.
- Limitations include a small sample size, and an inability to reach plateau of ZAN-BPD total score in either group. Also, there is considerable individual variability in memantine steady-state plasma concentrations, but plasma levels were not measured in this study.
Bottom Line
Findings from small randomized controlled trials suggest that transcranial direct current stimulation, oxytocin, asenapine, olanzapine, and memantine may have beneficial effects on some core symptoms of borderline personality disorder. These findings need to be replicated in larger studies.
FIRST OF 2 PARTS
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is marked by an ongoing pattern of mood instability, cognitive distortions, problems with self-image, and impulsive behavior, often resulting in problems in relationships. BPD is associated with serious impairment in psychosocial functioning.1 Patients with BPD tend to use more mental health services than patients with other personality disorders or those with major depressive disorder (MDD).2 However, there has been little consensus on the best treatment(s) for this serious and debilitating disorder, and some clinicians view BPD as difficult to treat.
Current treatments for BPD include psychological and pharmacological interventions. Neuromodulation techniques, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, may also positively affect BPD symptomatology. In recent years, there have been some promising findings in the treatment of BPD. In this 2-part article, we focus on current (within the last 5 years) findings from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of BPD treatments. Here in Part 1, we focus on 6 studies that evaluated biological interventions (Table,3-8). In Part 2, we will focus on RCTs that investigated psychological interventions.

1. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
Impulsivity has been described as the core feature of BPD that best explains its behavioral, cognitive, and clinical manifestations. Studies have repeatedly demonstrated the role of the prefrontal cortex in modulating impulsivity. Dysfunction of the
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In a double-blind, sham-controlled trial, adults who met DSM-IV-TR criteria for BPD were randomized to 3 weeks (15 sessions) of right anodal/left cathodal DLPFC tCDS (n = 15) or sham tDCS (n = 15). This study included patients with comorbid psychiatric disorders, including substance use disorders. Discontinuation or alteration of existing medications was not allowed.
- The presence, severity, and change over time of BPD core symptoms was assessed at baseline and after 3 weeks using several clinical scales, self-questionnaires, and neuropsychological tests, including the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11 (BIS-11), Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BP-AQ), Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Irritability-Depression Anxiety Scale (IDA), Visual Analog Scales (VAS), and Iowa Gambling Task.
Outcomes
- Participants in the active tDCS group experienced significant reductions in impulsivity, aggression, and craving as measured by the BIS-11, BP-AQ, and VAS.
- Compared to the sham group, the active tDCS group had greater reductions in HAM-D and BDI scores.
- HAM-A and IDA scores were improved in both groups, although the active tDCS group showed greater reductions in IDA scores compared with the sham group.
- As measured by DERS, active tDCS did not improve affective dysregulation more than sham tDCS.
Conclusions/limitations
- Bilateral tDCS targeting the right DLPFC with anodal stimulation is a safe, well-tolerated technique that may modulate core dimensions of BPD, including impulsivity, aggression, and craving.
- Excitatory anodal stimulation of the right DLFPC coupled with inhibitory cathodal stimulation on the left DLPFC may be an effective montage for targeting impulsivity in patients with BPD.
- Study limitations include a small sample size, use of targeted questionnaires only, inclusion of patients with BPD who also had certain comorbid psychiatric disorders, lack of analysis of the contributions of medications, lack of functional neuroimaging, and lack of a follow-up phase.
2. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
Emotional dysregulation is considered a core feature of BPD psychopathology and is closely associated with executive dysfunction and cognitive control. Manifestations of executive dysfunction include aggressiveness, impulsive decision-making, disinhibition, and self-destructive behaviors. Neuroimaging of patients with BPD has shown enhanced activity in the insula, posterior cingulate cortex, and amygdala, with reduced activity in the medial PFC, subgenual anterior cingulate cortex, and DLPFC. Molavi et al4 postulated that increasing DLPFC activation with left anodal tDCS would result in improved executive functioning and emotion dysregulation in patients with BPD.
Study design
- In this single-blind, sham-controlled, parallel-group study, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were randomized to receive 10 consecutive daily sessions of left anodal/right cathodal DLPFC tDCS (n = 16) or sham tDCS (n = 16).
- The effect of tDCS on executive dysfunction, emotion dysregulation, and emotional processing was measured using the Executive Skills Questionnaire for Adults (ESQ), Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ), and Emotional Processing Scale (EPS). Measurements occurred at baseline and after 10 sessions of active or sham tDCS.
Outcomes
- Participants who received active tDCS experienced significant improvements in ESQ overall score and most of the executive function domains measured by the ESQ.
- Those in the active tDCS group also experienced significant improvement in emotion regulation as measured by the cognitive reappraisal subscale (but not the expressive suppression subscale) of the ERQ after the intervention.
- Overall emotional processing as measured by the EPS was significantly improved in the active tDCS group following the intervention.
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated bilateral left anodal/right cathodal tDCS stimulation of the DLPFC significantly improved executive functioning and aspects of emotion regulation and emotional processing in patients with BPD. This improvement was presumed to be the result of increased activity of left DLPFC.
- Study limitations include a single-blind design, lack of follow-up to assess durability and stability of response over time, reliance on self-report measures, lack of functional neuroimaging, and limited focality of tDCS.
3. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
One of the hallmark symptoms of BPD is mood dysregulation. Current treatment guidelines recommend the use of mood stabilizers for BPD despite limited quality evidence of effectiveness and a lack of FDA-approved medications with this indication. In this RCT, Crawford et al5 examined whether lamotrigine is a clinically effective and cost-effective treatment for people with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In this 2-arm, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 276 adults who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD were randomized to receive lamotrigine (up to 400 mg/d) or placebo for 52 weeks.
- The primary outcome was the score on the Zanarini Rating Scale for Borderline Personality Disorder (ZAN-BPD) at 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes included depressive symptoms, deliberate self-harm, social functioning, health-related quality of life, resource use and costs, treatment adverse effects, and adverse events. These were assessed using the BDI; Acts of Deliberate Self-Harm Inventory; Social Functioning Questionnaire; Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test; and the EQ-5D-3L.
Outcomes
- Mean ZAN-BPD score decreased at 12 weeks in both groups, after which time the score remained stable.
- There was no difference in ZAN-BPD scores at 52 weeks between treatment arms. No difference was found in any secondary outcome measures.
- Difference in costs between groups was not significant.
Conclusions/limitations
- There was no evidence that lamotrigine led to clinical improvements in BPD symptomatology, social functioning, health-related quality of life, or substance use.
- Lamotrigine is neither clinically effective nor a cost-effective use of resources in the treatment of BPD.
- Limitations include a low level of adherence.
4. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
A core feature of BPD is impairment in empathy; adequate empathy is required for intact social functioning. Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that helps regulate complex social cognition and behavior. Prior research has found that oxytocin administration enhances emotion regulation and empathy. Women with BPD have been observed to have lower levels of oxytocin. Domes et al6 conducted an RCT to see if oxytocin could have a beneficial effect on social approach and social cognition in women with BPD.
Study design
- In a double-blind, placebo-controlled, between-subject trial, 61 women who met DSM-IV criteria for BPD and 68 matched healthy controls were randomized to receive intranasal oxytocin, 24 IU, or placebo 45 minutes before completing an empathy task.
- An extended version of the Multifaceted Empathy Test was used to assess empathy and approach motivation.
Outcomes
- For cognitive empathy, patients with BPD exhibited significantly lower overall performance compared to controls. There was no effect of oxytocin on this performance in either group.
- Patients with BPD had significantly lower affective empathy compared with controls. After oxytocin administration, patients with BPD had significantly higher affective empathy than those with BPD who received placebo, reaching the level of healthy controls who received placebo.
- For positive stimuli, patients with BPD showed lower affective empathy than controls. Oxytocin treatment increased affective empathy in both groups.
- For negative stimuli, oxytocin increased affective empathy more in patients with BPD than in controls.
- Patients with BPD demonstrated less approach motivation than controls. Oxytocin increased approach motivation more in patients with BPD than in controls. For approach motivation toward positive stimuli, oxytocin had a significant effect on patients with BPD.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations...
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients with BPD showed reduced cognitive and affective empathy and less approach behavior motivation than healthy controls.
- Patients with BPD who received oxytocin attained a level of affective empathy and approach motivation similar to that of healthy controls who received placebo. For positive stimuli, both groups exhibited comparable improvements from oxytocin. For negative stimuli, patients with BPD patients showed significant improvement with oxytocin, whereas healthy controls received no such benefit.
- Limitations include the use of self-report scales, lack of a control group, and inclusion of patients using psychotherapeutic medications. The study lacks generalizability because only women were included; the effect of exogenous oxytocin on men may differ.
5. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
The last decade has seen a noticeable shift in clinical practice from the use of antidepressants to mood stabilizers and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) in the treatment of BPD. Studies have demonstrated therapeutic effects of antipsychotic drugs across a wide range of BPD symptoms. Among SGAs, olanzapine is the most extensively studied across case reports, open-label studies, and RCTs of patients with BPD. In an RCT, Bozzatello et al7 compared the efficacy and tolerability of asenapine to olanzapine.
Study design
- In this open-label RCT, adults who met DSM-5 criteria for BPD were assigned to receive asenapine (n = 25) or olanzapine (n = 26) for 12 weeks.
- Study measurements included the Clinical Global Impression Scale, Severity item, HAM-D, HAM-A, Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale, Borderline Personality Disorder Severity Index (BPDSI), BIS-11, Modified Overt Aggression Scale, and Dosage Record Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale.
Outcomes
- Asenapine and olanzapine had similar effects on BPD-related psychopathology, anxiety, and social and occupational functioning.
- Neither medication significantly decreased depressive or aggressive symptoms.
- Asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the affective instability score of the BPDSI.
- Akathisia and restlessness/anxiety were more common with asenapine, and somnolence and fatigue were more common with olanzapine.
Conclusions/limitations
- The overall efficacy of asenapine was not different from olanzapine, and both medications were well-tolerated.
- Neither medication led to an improvement in depression or aggression, but asenapine was superior to olanzapine in reducing the severity of affective instability.
- Limitations include an open-label design, lack of placebo group, small sample size, high drop-out rate, exclusion of participants with co-occurring MDD and substance abuse/dependence, lack of data on prior pharmacotherapies and psychotherapies, and lack of power to detect a difference on the dissociation/paranoid ideation item of BPDSI.
6. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8
It has been hypothesized that glutamate dysregulation and excitotoxicity are crucial to the development of the cognitive disturbances that underlie BPD. As such, glutamate modulators such as memantine hold promise for the treatment of BPD. In this RCT, Kulkarni et al8 examined the efficacy and tolerability of memantine compared with treatment as usual in patients with BPD.
Continue to: Study design...
Study design
- In an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, adults diagnosed with BPD according to the Diagnostic Interview for Borderline Patients were randomized to receive memantine (n = 17) or placebo (n = 16) in addition to treatment as usual. Treatment as usual included the use of antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics as well as psychotherapy and other psychosocial interventions.
- Patients were initiated on placebo or memantine, 10 mg/d. Memantine was increased to 20 mg/d after 7 days.
- ZAN-BPD score was the primary outcome and was measured at baseline and 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks. An adverse effects questionnaire was administered every 2 weeks to assess tolerability.
Outcomes
- During the first 2 weeks of treatment, there were no significant improvements in ZAN-BPD score in the memantine group compared with the placebo group.
- Beginning with Week 2, compared with the placebo group, the memantine group experienced a significant reduction in total symptoms as measured by ZAN-BPD.
- There were no statistically significant differences in adverse events between groups.
Conclusions/limitations
- Memantine appears to be a well-tolerated treatment option for patients with BPD and merits further study.
- Limitations include a small sample size, and an inability to reach plateau of ZAN-BPD total score in either group. Also, there is considerable individual variability in memantine steady-state plasma concentrations, but plasma levels were not measured in this study.
Bottom Line
Findings from small randomized controlled trials suggest that transcranial direct current stimulation, oxytocin, asenapine, olanzapine, and memantine may have beneficial effects on some core symptoms of borderline personality disorder. These findings need to be replicated in larger studies.
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002; 159:276-283.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:295-302.
3. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
4. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
5. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
6. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
7. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
8. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8
1. Skodol AE, Gunderson JG, McGlashan TM, et al. Functional impairment in patients with schizotypal, borderline, avoidant, or obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2002; 159:276-283.
2. Bender DS, Dolan RT, Skodol AE, et al. Treatment utilization by patients with personality disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:295-302.
3. Lisoni J, Miotto P, Barlati S, et al. Change in core symptoms of borderline personality disorder by tDCS: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2020;291:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113261
4. Molavi P, Aziziaram S, Basharpoor S, et al. Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: a randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
5. Crawford MJ, Sanatinia R, Barrett B, et al; LABILE study team. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of lamotrigine in borderline personality disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(8):756-764. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17091006
6. Domes G, Ower N, von Dawans B, et al. Effects of intranasal oxytocin administration on empathy and approach motivation in women with borderline personality disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0658-4
7. Bozzatello P, Rocca P, Uscinska M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of asenapine compared with olanzapine in borderline personality disorder: an open-label randomized controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2017;31(9):809-819. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0458-4
8. Kulkarni J, Thomas N, Hudaib AR, et al. Effect of the glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as adjunctive treatment in borderline personality disorder: an exploratory, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(2):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-0506-8

