User login
Biologics yield low rates of skin clearance in real-world psoriasis study
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
AAD-NPF releases first guidelines for nonbiologic treatments of psoriasis
It’s been 11 years since monotherapy and suggest a framework for a number of off-label treatments.
The guidelines, issued jointly with the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF), were published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
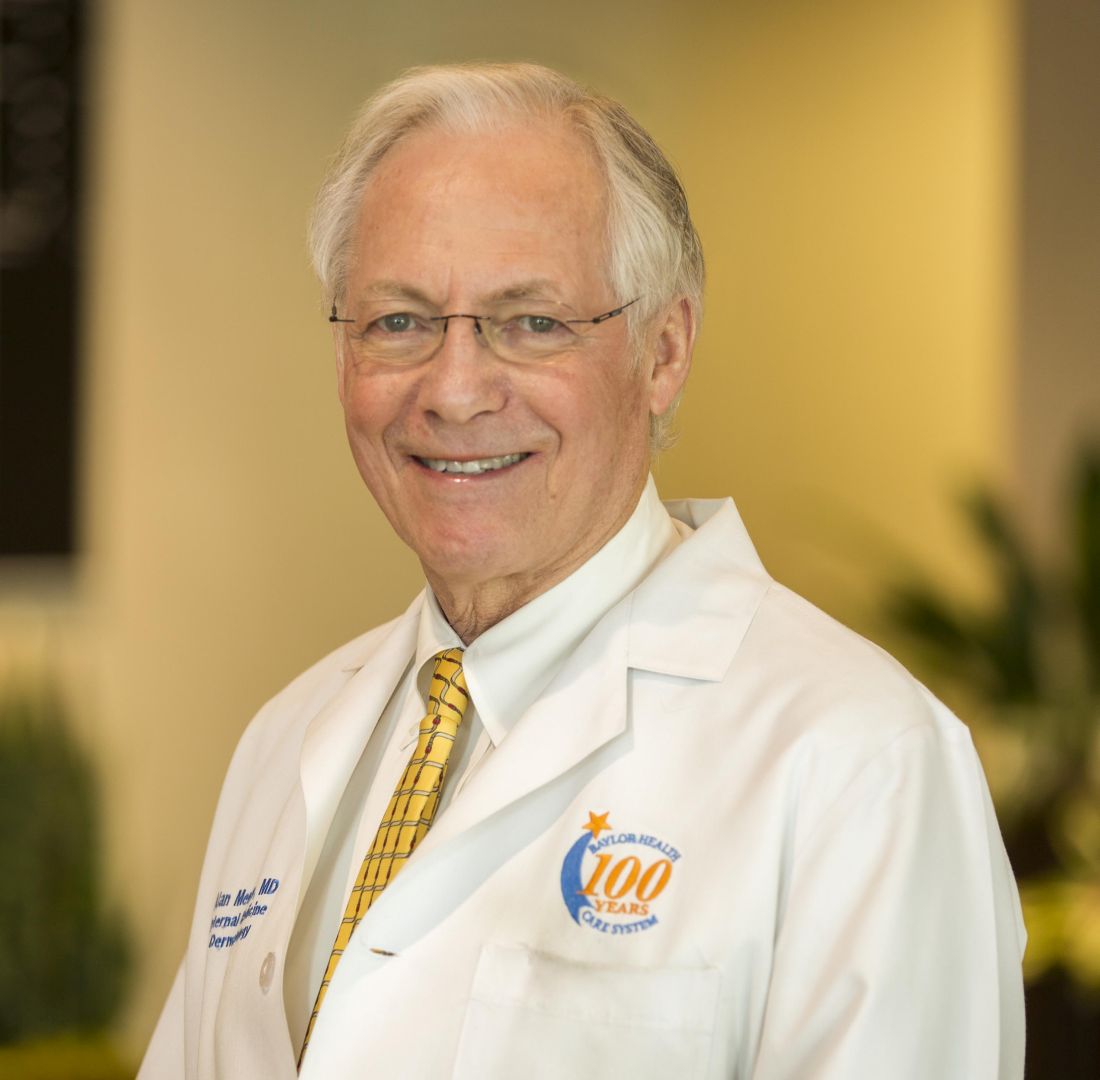
“I think we are way behind,” Alan Menter, MD, chairman of the division of dermatology at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the guideline writing committee, said in an interview. “Most other countries update their guidelines every 1 or 2 years; we were 10 years behind.” The guidelines for systemic nonbiologic drugs follow up psoriasis guidelines issued by the AAD and the NPF on pediatric patients issued earlier this year, and on phototherapy, biologic treatments, and management of comorbidities issued last year.
“A lot has happened in the last 10 years,” said cochair Craig Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “While much of the interest is on biologic agents, nonbiologics are still used quite frequently, and the guidelines for their appropriate use have changed. Use of the guidelines provides people in the health profession with the most up to date evidence-based information so they can give their patients the best care.”
The guidelines acknowledge that the medications it covers are still widely used, either by themselves or in combination with biologic agents; readily available; easy to use; and, in the case of older therapies, relatively cheap.
Methotrexate has been available since the 1970s. Given as an injection or taken orally, the guidelines recommend supplementation with folic acid to counteract methotrexate’s side effects, particularly GI upset. The guidelines note that folic acid is less expensive than folinic acid. Combination therapy with methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors is more effective than methotrexate monotherapy, with a similar side effect profile, the guidelines state.
Methotrexate is more widely used outside the United States, “but it is a very good, quick fix and it’s much safer in children and young people than it is in people with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Menter noted. “It’s still the most commonly used drug worldwide because it’s cheap, and you do have to worry about the long-term toxicity which is related the liver issues.”
The guidelines say that subcutaneous administration of methotrexate “may be particularly useful” for patients on higher doses, which when taken orally, are associated with a higher risk of GI effects.
Dr. Menter referred to a 2017 study, which reported 41% of patients treated with subcutaneous methotrexate once a week achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 score of 41% after a year of treatment, compared with 10% of those on placebo (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
The guidelines rate strength of recommendation as class A for methotrexate for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, recommend supplementation with folic or folinic acid to counteract GI complications and liver problems, and note that adalimumab and infliximab are more effective than methotrexate for cutaneous psoriasis. Class B recommendations for methotrexate and psoriasis include statements that patients should begin with a test dose, especially if they have impaired kidney function; methotrexate is effective for peripheral, but not axial, psoriatic arthritis (PsA); and TNF inhibitors are more effective than methotrexate for PsA.
Approved by the FDA in 2014 for psoriasis, apremilast, which inhibits phosphodiesterase-4, is the newest drug in the recommendations. The guidelines recommend its use for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, with a class A recommendation. Patients should start on a low dose and then build up to the 30-mg, twice-daily dose over 6 days and should be counseled about the risk of depression before starting treatment. Routine laboratory testing can be considered on an individual basis.
The guidelines also lay out three recommendations (and strength of recommendation) for cyclosporine, a drug that’s been around since the 1990s: for severe, recalcitrant cases (class A); for erythrodermic, general pustular, and palmoplantar psoriasis (class B); and as short-term therapy for psoriasis flare in patients already on another drug (class C).
Acitretin is another longstanding therapy used mostly for palmar-plantar psoriasis, but it can also be used as monotherapy for plaque psoriasis as well as erythrodermic and pustular disease. It can also be used in combination with psoralens with UVA for psoriasis and combined with broadband UVB phototherapy for plaque psoriasis. The acitretin recommendations are class B.
The oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib isn’t specifically approved for psoriasis, but it is approved for RA, PsA, and ulcerative colitis. The drug targets the JAK-STAT signaling pathway that causes inflammation. The guidelines state that tofacitinib can be considered for moderate to severe psoriasis, but lists no strength of recommendation. The recommended dose is either 5 or 10 mg orally twice a day, with a caveat that the higher dose carries a higher risk of adverse events. Patients should be evaluated for getting a zoster vaccine before they begin therapy.
“We thought that, because there was probably a small chance that it might get approved for psoriasis, that we would discuss it briefly,” Dr. Menter said of tofacitinib.
Another off-label use the guidelines address is for fumaric and acid esters, also known as fumarates, which are used to in Europe to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. Dimethyl fumarate is approved for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis in the United States. The guidelines state that fumarates can be used for psoriasis, but offer no strength of recommendation. Side effects include gastrointestinal disturbance and flushing.
Other treatments that are also addressed in the guidelines include a host of systemic immunosuppressants and antimetabolites: azathioprine, hydroxyurea, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, thioguanine, and tacrolimus, none of which are FDA approved for psoriasis. They’re rarely used for psoriasis, but may have value in selected cases, the guidelines state.
Dr. Menter said that apremilast is the only oral drug in the guidelines, but they are the wave of the future for treating psoriasis. “I think there’s a tremendous potential for new oral drugs – TK2 [thymidine kinase], the JAK inhibitors, and other drugs coming down the pipelines. The majority of patients, if you ask them their preference, would like to take an oral drug rather than an injectable drug. And it would be much easier for dermatologists, they wouldn’t have to train patients on how to do the injections.”
Dr. Menter and Dr. Elmets disclosed financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Other authors/work group members also had disclosures related to pharmaceutical manufacturers, and several had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044.
It’s been 11 years since monotherapy and suggest a framework for a number of off-label treatments.
The guidelines, issued jointly with the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF), were published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“I think we are way behind,” Alan Menter, MD, chairman of the division of dermatology at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the guideline writing committee, said in an interview. “Most other countries update their guidelines every 1 or 2 years; we were 10 years behind.” The guidelines for systemic nonbiologic drugs follow up psoriasis guidelines issued by the AAD and the NPF on pediatric patients issued earlier this year, and on phototherapy, biologic treatments, and management of comorbidities issued last year.
“A lot has happened in the last 10 years,” said cochair Craig Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “While much of the interest is on biologic agents, nonbiologics are still used quite frequently, and the guidelines for their appropriate use have changed. Use of the guidelines provides people in the health profession with the most up to date evidence-based information so they can give their patients the best care.”
The guidelines acknowledge that the medications it covers are still widely used, either by themselves or in combination with biologic agents; readily available; easy to use; and, in the case of older therapies, relatively cheap.
Methotrexate has been available since the 1970s. Given as an injection or taken orally, the guidelines recommend supplementation with folic acid to counteract methotrexate’s side effects, particularly GI upset. The guidelines note that folic acid is less expensive than folinic acid. Combination therapy with methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors is more effective than methotrexate monotherapy, with a similar side effect profile, the guidelines state.
Methotrexate is more widely used outside the United States, “but it is a very good, quick fix and it’s much safer in children and young people than it is in people with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Menter noted. “It’s still the most commonly used drug worldwide because it’s cheap, and you do have to worry about the long-term toxicity which is related the liver issues.”
The guidelines say that subcutaneous administration of methotrexate “may be particularly useful” for patients on higher doses, which when taken orally, are associated with a higher risk of GI effects.
Dr. Menter referred to a 2017 study, which reported 41% of patients treated with subcutaneous methotrexate once a week achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 score of 41% after a year of treatment, compared with 10% of those on placebo (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
The guidelines rate strength of recommendation as class A for methotrexate for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, recommend supplementation with folic or folinic acid to counteract GI complications and liver problems, and note that adalimumab and infliximab are more effective than methotrexate for cutaneous psoriasis. Class B recommendations for methotrexate and psoriasis include statements that patients should begin with a test dose, especially if they have impaired kidney function; methotrexate is effective for peripheral, but not axial, psoriatic arthritis (PsA); and TNF inhibitors are more effective than methotrexate for PsA.
Approved by the FDA in 2014 for psoriasis, apremilast, which inhibits phosphodiesterase-4, is the newest drug in the recommendations. The guidelines recommend its use for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, with a class A recommendation. Patients should start on a low dose and then build up to the 30-mg, twice-daily dose over 6 days and should be counseled about the risk of depression before starting treatment. Routine laboratory testing can be considered on an individual basis.
The guidelines also lay out three recommendations (and strength of recommendation) for cyclosporine, a drug that’s been around since the 1990s: for severe, recalcitrant cases (class A); for erythrodermic, general pustular, and palmoplantar psoriasis (class B); and as short-term therapy for psoriasis flare in patients already on another drug (class C).
Acitretin is another longstanding therapy used mostly for palmar-plantar psoriasis, but it can also be used as monotherapy for plaque psoriasis as well as erythrodermic and pustular disease. It can also be used in combination with psoralens with UVA for psoriasis and combined with broadband UVB phototherapy for plaque psoriasis. The acitretin recommendations are class B.
The oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib isn’t specifically approved for psoriasis, but it is approved for RA, PsA, and ulcerative colitis. The drug targets the JAK-STAT signaling pathway that causes inflammation. The guidelines state that tofacitinib can be considered for moderate to severe psoriasis, but lists no strength of recommendation. The recommended dose is either 5 or 10 mg orally twice a day, with a caveat that the higher dose carries a higher risk of adverse events. Patients should be evaluated for getting a zoster vaccine before they begin therapy.
“We thought that, because there was probably a small chance that it might get approved for psoriasis, that we would discuss it briefly,” Dr. Menter said of tofacitinib.
Another off-label use the guidelines address is for fumaric and acid esters, also known as fumarates, which are used to in Europe to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. Dimethyl fumarate is approved for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis in the United States. The guidelines state that fumarates can be used for psoriasis, but offer no strength of recommendation. Side effects include gastrointestinal disturbance and flushing.
Other treatments that are also addressed in the guidelines include a host of systemic immunosuppressants and antimetabolites: azathioprine, hydroxyurea, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, thioguanine, and tacrolimus, none of which are FDA approved for psoriasis. They’re rarely used for psoriasis, but may have value in selected cases, the guidelines state.
Dr. Menter said that apremilast is the only oral drug in the guidelines, but they are the wave of the future for treating psoriasis. “I think there’s a tremendous potential for new oral drugs – TK2 [thymidine kinase], the JAK inhibitors, and other drugs coming down the pipelines. The majority of patients, if you ask them their preference, would like to take an oral drug rather than an injectable drug. And it would be much easier for dermatologists, they wouldn’t have to train patients on how to do the injections.”
Dr. Menter and Dr. Elmets disclosed financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Other authors/work group members also had disclosures related to pharmaceutical manufacturers, and several had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044.
It’s been 11 years since monotherapy and suggest a framework for a number of off-label treatments.
The guidelines, issued jointly with the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF), were published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“I think we are way behind,” Alan Menter, MD, chairman of the division of dermatology at Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and cochair of the guideline writing committee, said in an interview. “Most other countries update their guidelines every 1 or 2 years; we were 10 years behind.” The guidelines for systemic nonbiologic drugs follow up psoriasis guidelines issued by the AAD and the NPF on pediatric patients issued earlier this year, and on phototherapy, biologic treatments, and management of comorbidities issued last year.
“A lot has happened in the last 10 years,” said cochair Craig Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. “While much of the interest is on biologic agents, nonbiologics are still used quite frequently, and the guidelines for their appropriate use have changed. Use of the guidelines provides people in the health profession with the most up to date evidence-based information so they can give their patients the best care.”
The guidelines acknowledge that the medications it covers are still widely used, either by themselves or in combination with biologic agents; readily available; easy to use; and, in the case of older therapies, relatively cheap.
Methotrexate has been available since the 1970s. Given as an injection or taken orally, the guidelines recommend supplementation with folic acid to counteract methotrexate’s side effects, particularly GI upset. The guidelines note that folic acid is less expensive than folinic acid. Combination therapy with methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors is more effective than methotrexate monotherapy, with a similar side effect profile, the guidelines state.
Methotrexate is more widely used outside the United States, “but it is a very good, quick fix and it’s much safer in children and young people than it is in people with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Menter noted. “It’s still the most commonly used drug worldwide because it’s cheap, and you do have to worry about the long-term toxicity which is related the liver issues.”
The guidelines say that subcutaneous administration of methotrexate “may be particularly useful” for patients on higher doses, which when taken orally, are associated with a higher risk of GI effects.
Dr. Menter referred to a 2017 study, which reported 41% of patients treated with subcutaneous methotrexate once a week achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 score of 41% after a year of treatment, compared with 10% of those on placebo (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
The guidelines rate strength of recommendation as class A for methotrexate for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, recommend supplementation with folic or folinic acid to counteract GI complications and liver problems, and note that adalimumab and infliximab are more effective than methotrexate for cutaneous psoriasis. Class B recommendations for methotrexate and psoriasis include statements that patients should begin with a test dose, especially if they have impaired kidney function; methotrexate is effective for peripheral, but not axial, psoriatic arthritis (PsA); and TNF inhibitors are more effective than methotrexate for PsA.
Approved by the FDA in 2014 for psoriasis, apremilast, which inhibits phosphodiesterase-4, is the newest drug in the recommendations. The guidelines recommend its use for moderate to severe psoriasis in adults, with a class A recommendation. Patients should start on a low dose and then build up to the 30-mg, twice-daily dose over 6 days and should be counseled about the risk of depression before starting treatment. Routine laboratory testing can be considered on an individual basis.
The guidelines also lay out three recommendations (and strength of recommendation) for cyclosporine, a drug that’s been around since the 1990s: for severe, recalcitrant cases (class A); for erythrodermic, general pustular, and palmoplantar psoriasis (class B); and as short-term therapy for psoriasis flare in patients already on another drug (class C).
Acitretin is another longstanding therapy used mostly for palmar-plantar psoriasis, but it can also be used as monotherapy for plaque psoriasis as well as erythrodermic and pustular disease. It can also be used in combination with psoralens with UVA for psoriasis and combined with broadband UVB phototherapy for plaque psoriasis. The acitretin recommendations are class B.
The oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib isn’t specifically approved for psoriasis, but it is approved for RA, PsA, and ulcerative colitis. The drug targets the JAK-STAT signaling pathway that causes inflammation. The guidelines state that tofacitinib can be considered for moderate to severe psoriasis, but lists no strength of recommendation. The recommended dose is either 5 or 10 mg orally twice a day, with a caveat that the higher dose carries a higher risk of adverse events. Patients should be evaluated for getting a zoster vaccine before they begin therapy.
“We thought that, because there was probably a small chance that it might get approved for psoriasis, that we would discuss it briefly,” Dr. Menter said of tofacitinib.
Another off-label use the guidelines address is for fumaric and acid esters, also known as fumarates, which are used to in Europe to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. Dimethyl fumarate is approved for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis in the United States. The guidelines state that fumarates can be used for psoriasis, but offer no strength of recommendation. Side effects include gastrointestinal disturbance and flushing.
Other treatments that are also addressed in the guidelines include a host of systemic immunosuppressants and antimetabolites: azathioprine, hydroxyurea, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, thioguanine, and tacrolimus, none of which are FDA approved for psoriasis. They’re rarely used for psoriasis, but may have value in selected cases, the guidelines state.
Dr. Menter said that apremilast is the only oral drug in the guidelines, but they are the wave of the future for treating psoriasis. “I think there’s a tremendous potential for new oral drugs – TK2 [thymidine kinase], the JAK inhibitors, and other drugs coming down the pipelines. The majority of patients, if you ask them their preference, would like to take an oral drug rather than an injectable drug. And it would be much easier for dermatologists, they wouldn’t have to train patients on how to do the injections.”
Dr. Menter and Dr. Elmets disclosed financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Other authors/work group members also had disclosures related to pharmaceutical manufacturers, and several had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Menter A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.044.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Tildrakizumab signals safe for pregnant psoriasis patients
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
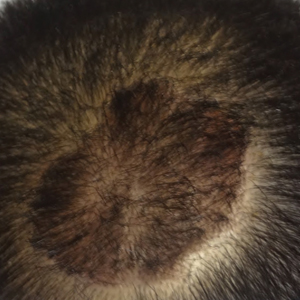
Scalp Psoriasis Considerations
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
Did You Know? Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis



Psoriasis Journal Scan: October 2019
Psoriasis Associated with Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors in Children with Inflammatory Diseases.
Buckley, L. H., Xiao, R. , Perman, M. et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Oct 23.
The study aimed to estimate the incidence rate (IR) of psoriasis in children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), and chronic noninfectious osteomyelitis (CNO) with tumor necrosis factor‐alpha inhibitor (TNFi) exposure as compared to those without TNFi exposure and to the general pediatric population. Researchers found that children with IBD, JIA, and CNO had an increased rate of psoriasis compared to the general pediatric population, with the highest rate in those with TNFi exposure.
Skin Patterning in Psoriasis by Spatial Interactions between Pathogenic Cytokines.
Ringham, L, Prusinkiewicz, P, Gniadeck R. iScience. 2019 Oct 25;20:546-553.
This study shows that all known patterns of psoriasis, a common inflammatory skin disease, can be explained in terms of reaction-diffusion. Researchers constructed a computational model based on the known interactions between the main pathogenic cytokines: interleukins IL-17 and IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor TNF-α. Simulations revealed that the parameter space of the model contained all classes of psoriatic lesion patterns. They also faithfully reproduced the growth and evolution of the plaques and the response to treatment by cytokine targeting. Thus the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, may be readily understood in the framework of the stimulatory and inhibitory interactions between a few diffusing mediators.
SEfficacy of Secukinumab for Plaque Psoriasis in a Patient on Hemodialysis.
Ikuma D, Oguro M, Hoshino J, et al. CEN Case Rep. 2019 Oct 25.
The case report discusses the safety and efficiency of secukinumab on a 60-year-old patient on hemodialysis. The psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score decreased from 49.8 to 14.8 after 2 weeks and to 0 after 6 weeks, with remission being maintained after 28 months. No adverse reactions were seen. This case indicates that secukinumab may be effective for severe psoriasis in patients on hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease.
Comparison of pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab administered subcutaneously using different delivery systems in healthy volunteers and in psoriasis patients.
Bruin, G, Hockey, H‐UP, La Stella, P, et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019.
The aim of the study was to compare the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab with different devices for subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of 2 mL. Collective evidence from both studies demonstrated that 2 mL injections of secukinumab into the abdomen or thigh using different devices resulted in comparable PK characteristics and were all well tolerated without noticable local reactions.
Dual biologic therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
Thibodeaux, Quinn et al. JAAD Case Reports, Volume 5, Issue 10, 928 – 930.
This study presents a patient with severe psoriatic skin and joint disease who has been treated with multiple combinations of dual biologic therapy, including ustekinumab plus etanercept for 12 months, secukinumab plus etanercept for 6 months, and guselkumab plus etanercept for 15 months. Throughout the patient's treatment, adverse events only occurred with the ustekinumab plus etanercept combination and consisted of an increased incidence of urinary tract and upper respiratory infections, including a hospitalization for H2N1 flu.
Psoriasis Associated with Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors in Children with Inflammatory Diseases.
Buckley, L. H., Xiao, R. , Perman, M. et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Oct 23.
The study aimed to estimate the incidence rate (IR) of psoriasis in children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), and chronic noninfectious osteomyelitis (CNO) with tumor necrosis factor‐alpha inhibitor (TNFi) exposure as compared to those without TNFi exposure and to the general pediatric population. Researchers found that children with IBD, JIA, and CNO had an increased rate of psoriasis compared to the general pediatric population, with the highest rate in those with TNFi exposure.
Skin Patterning in Psoriasis by Spatial Interactions between Pathogenic Cytokines.
Ringham, L, Prusinkiewicz, P, Gniadeck R. iScience. 2019 Oct 25;20:546-553.
This study shows that all known patterns of psoriasis, a common inflammatory skin disease, can be explained in terms of reaction-diffusion. Researchers constructed a computational model based on the known interactions between the main pathogenic cytokines: interleukins IL-17 and IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor TNF-α. Simulations revealed that the parameter space of the model contained all classes of psoriatic lesion patterns. They also faithfully reproduced the growth and evolution of the plaques and the response to treatment by cytokine targeting. Thus the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, may be readily understood in the framework of the stimulatory and inhibitory interactions between a few diffusing mediators.
SEfficacy of Secukinumab for Plaque Psoriasis in a Patient on Hemodialysis.
Ikuma D, Oguro M, Hoshino J, et al. CEN Case Rep. 2019 Oct 25.
The case report discusses the safety and efficiency of secukinumab on a 60-year-old patient on hemodialysis. The psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score decreased from 49.8 to 14.8 after 2 weeks and to 0 after 6 weeks, with remission being maintained after 28 months. No adverse reactions were seen. This case indicates that secukinumab may be effective for severe psoriasis in patients on hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease.
Comparison of pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab administered subcutaneously using different delivery systems in healthy volunteers and in psoriasis patients.
Bruin, G, Hockey, H‐UP, La Stella, P, et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019.
The aim of the study was to compare the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab with different devices for subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of 2 mL. Collective evidence from both studies demonstrated that 2 mL injections of secukinumab into the abdomen or thigh using different devices resulted in comparable PK characteristics and were all well tolerated without noticable local reactions.
Dual biologic therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
Thibodeaux, Quinn et al. JAAD Case Reports, Volume 5, Issue 10, 928 – 930.
This study presents a patient with severe psoriatic skin and joint disease who has been treated with multiple combinations of dual biologic therapy, including ustekinumab plus etanercept for 12 months, secukinumab plus etanercept for 6 months, and guselkumab plus etanercept for 15 months. Throughout the patient's treatment, adverse events only occurred with the ustekinumab plus etanercept combination and consisted of an increased incidence of urinary tract and upper respiratory infections, including a hospitalization for H2N1 flu.
Psoriasis Associated with Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors in Children with Inflammatory Diseases.
Buckley, L. H., Xiao, R. , Perman, M. et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Oct 23.
The study aimed to estimate the incidence rate (IR) of psoriasis in children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), and chronic noninfectious osteomyelitis (CNO) with tumor necrosis factor‐alpha inhibitor (TNFi) exposure as compared to those without TNFi exposure and to the general pediatric population. Researchers found that children with IBD, JIA, and CNO had an increased rate of psoriasis compared to the general pediatric population, with the highest rate in those with TNFi exposure.
Skin Patterning in Psoriasis by Spatial Interactions between Pathogenic Cytokines.
Ringham, L, Prusinkiewicz, P, Gniadeck R. iScience. 2019 Oct 25;20:546-553.
This study shows that all known patterns of psoriasis, a common inflammatory skin disease, can be explained in terms of reaction-diffusion. Researchers constructed a computational model based on the known interactions between the main pathogenic cytokines: interleukins IL-17 and IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor TNF-α. Simulations revealed that the parameter space of the model contained all classes of psoriatic lesion patterns. They also faithfully reproduced the growth and evolution of the plaques and the response to treatment by cytokine targeting. Thus the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, may be readily understood in the framework of the stimulatory and inhibitory interactions between a few diffusing mediators.
SEfficacy of Secukinumab for Plaque Psoriasis in a Patient on Hemodialysis.
Ikuma D, Oguro M, Hoshino J, et al. CEN Case Rep. 2019 Oct 25.
The case report discusses the safety and efficiency of secukinumab on a 60-year-old patient on hemodialysis. The psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score decreased from 49.8 to 14.8 after 2 weeks and to 0 after 6 weeks, with remission being maintained after 28 months. No adverse reactions were seen. This case indicates that secukinumab may be effective for severe psoriasis in patients on hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease.
Comparison of pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab administered subcutaneously using different delivery systems in healthy volunteers and in psoriasis patients.
Bruin, G, Hockey, H‐UP, La Stella, P, et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019.
The aim of the study was to compare the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of secukinumab with different devices for subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of 2 mL. Collective evidence from both studies demonstrated that 2 mL injections of secukinumab into the abdomen or thigh using different devices resulted in comparable PK characteristics and were all well tolerated without noticable local reactions.
Dual biologic therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
Thibodeaux, Quinn et al. JAAD Case Reports, Volume 5, Issue 10, 928 – 930.
This study presents a patient with severe psoriatic skin and joint disease who has been treated with multiple combinations of dual biologic therapy, including ustekinumab plus etanercept for 12 months, secukinumab plus etanercept for 6 months, and guselkumab plus etanercept for 15 months. Throughout the patient's treatment, adverse events only occurred with the ustekinumab plus etanercept combination and consisted of an increased incidence of urinary tract and upper respiratory infections, including a hospitalization for H2N1 flu.
Role of Psoriasis in the Development of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
1. O’Brien T, Power DG. Metastatic Merkel-cell carcinoma: the dawn of a new era. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;11:2018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224924.
2. Del Marmol V, Lebbé C. New perspectives in Merkel cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019;31:72-83.
3. Garcia-Carbonero R, Marquez-Rodas I, de la Cruz-Merino L, et al. Recent therapeutic advances and change in treatment paradigm of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma [published online April 8, 2019]. Oncologist. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0718.
4. Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
5. Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
6. Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
7. Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
8. Yousif J, Yousif B, Kuriata MA. Complete remission of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma in a patient with severe psoriasis. Cutis. 2018;101:E24-E27.
9. Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
10. Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
11. Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
12. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Merkel cell carcinoma. Published October 3, 2016. http://merkelcell.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/MccNccn.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2019.
13. Coggshall K, Tello TL, North JP, Yu SS. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and review: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:433-442.
14. Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
15. Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
1. O’Brien T, Power DG. Metastatic Merkel-cell carcinoma: the dawn of a new era. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;11:2018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224924.
2. Del Marmol V, Lebbé C. New perspectives in Merkel cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019;31:72-83.
3. Garcia-Carbonero R, Marquez-Rodas I, de la Cruz-Merino L, et al. Recent therapeutic advances and change in treatment paradigm of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma [published online April 8, 2019]. Oncologist. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0718.
4. Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
5. Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
6. Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
7. Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
8. Yousif J, Yousif B, Kuriata MA. Complete remission of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma in a patient with severe psoriasis. Cutis. 2018;101:E24-E27.
9. Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
10. Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
11. Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
12. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Merkel cell carcinoma. Published October 3, 2016. http://merkelcell.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/MccNccn.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2019.
13. Coggshall K, Tello TL, North JP, Yu SS. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and review: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:433-442.
14. Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
15. Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
1. O’Brien T, Power DG. Metastatic Merkel-cell carcinoma: the dawn of a new era. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;11:2018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224924.
2. Del Marmol V, Lebbé C. New perspectives in Merkel cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019;31:72-83.
3. Garcia-Carbonero R, Marquez-Rodas I, de la Cruz-Merino L, et al. Recent therapeutic advances and change in treatment paradigm of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma [published online April 8, 2019]. Oncologist. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0718.
4. Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
5. Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
6. Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
7. Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
8. Yousif J, Yousif B, Kuriata MA. Complete remission of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma in a patient with severe psoriasis. Cutis. 2018;101:E24-E27.
9. Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
10. Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
11. Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
12. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Merkel cell carcinoma. Published October 3, 2016. http://merkelcell.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/MccNccn.pdf. Accessed September 10, 2019.
13. Coggshall K, Tello TL, North JP, Yu SS. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and review: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:433-442.
14. Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
15. Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
Did You Know? Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease



Psoriasis comorbidities: Biologics may help
SEATTLE – Psoriasis is a complex condition, made more difficult by comorbidities. Psoriatic arthritis is the most common and is frequently discussed. But mental health issues and cardiovascular events also co-occur and can present major complications, according to Jashin Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, who discussed psoriasis comorbidities at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium.
Mental health–related issues associated with psoriasis (Psychiatr Danub. 2017 Dec;29[4]:401-6) include sleep disorders (prevalence, 62%), sexual dysfunction (46%), personality disorder (35%), anxiety (30%), adjustment (29%), and depressive disorders (28%); 25% of patients have an accompanying substance abuse disorder. Suicidal ideation and suicidal depression are particularly concerning, and a meta-analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77[3]:425-40.e2) showed a 44% increased risk of suicidal ideation associated with psoriasis.
Such problems aren’t surprising, since psoriasis is a lifelong disease, and many patients’ symptoms aren’t adequately controlled. “A lot of these patients get topical therapies, which is probably not enough, especially if they have severe disease,” said Dr. Wu in an interview.
Dermatologists can sometimes be nervous about biologics because of concerns over increased risk of infection or cancer. That can lead to conservative, topical treatment. Dr. Wu feels that rare side effects shouldn’t deter from aggressive treatment, when appropriate. “It’s better to treat the patient to make sure they’re clear, which may improve their comorbidities as well. In general, if you’re worried, you can send them to other specialists to do monitoring,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Different treatment methods may influence mental health outcomes, according to the PSOLAR study (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78[1]:70-80). It examined the issue prospectively with over 12,000 psoriasis patients, and found a depression incidence of 3.01 per 100-patient years when treated with biologics, compared with 5.85 for phototherapy and 5.70 for conventional therapy. Put another way, exposure to biologics was associated with a reduced risk of depression, compared with conventional therapies (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .0367). “It seems to show that biologics have a better improvement of depression symptoms, compared to phototherapy or oral therapy,” said Dr. Wu.
Those results suggest that dermatologists should be on the lookout for mental health issues, though that is a challenge for someone not trained in the field. Dr. Wu takes a simple approach. “I like just asking open-ended questions, like how they’re doing, and if you get a sense that maybe they’re depressed, ask more specific questions about their mood, how they’re feeling, how things are at work, how things are at home.” When things aren’t right, “the key is to try to get them on something that’s going to clear them very quickly. If it’s severe disease, use a biologic that’s going to clear it very quickly,” he added.
Unfortunately, just being clear isn’t a complete guarantee of improved mental health. Dr. Wu had two patients who committed suicide despite significant skin improvement. Patients may have between-visit flare-ups, or regular injections may be a reminder that psoriasis is an ongoing health struggle. Or patients may have other psychological concerns. That underlines the importance of awareness of mental health issues. “You don’t need to refer everyone [to a mental health specialist], but you should have a rolodex where you have someone you can send a patient to if you’re worried,” said Dr. Wu.
As with mental health issues, psoriasis patients are also at elevated risk for a wide range of cardiovascular comorbidities, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and high blood pressure. “As a dermatologist, you may not want to screen for these things, but you can send them to their primary care doctor or a cardiologist,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Also like mental health issues, there is evidence that treatment with biologics may have an outsized protective effect. One study (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 24. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14951) led by Dr. Wu showed that treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitor led to a significant reduction in major adverse cardiac events, compared with topical therapy (propensity score–adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98), while phototherapy or oral therapy trended towards an increased risk (adjusted HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.00-1.28). Another analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jan;76[1]:81-90) from Dr. Wu’s group that included about 380,000 psoriasis patients found that treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors was associated with fewer major cardiovascular events, compared with treatment with methotrexate (adjusted HR, 0.55; P less than .0001). Individual analyses showed associated reductions in stroke or transient ischemic attack (aHR, 0.55; P less than .0001), unstable angina (aHR, 0.58; P = .0024), and MI (aHR, 0.49; P = .0002). TNF-alpha inhibitors also seem to beat out phototherapy with respect to major cardiovascular events (aHR, 0.77; P = .046. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jul;79[1]:60-6).
More direct evidence of the benefit of biologics comes from the CANTOS trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Sep 21;377[12]:1119-31), which randomized more than 10,000 patients with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes to receive the IL-1 beta-blocker canakinumab or placebo. Canakinumab was associated with significant reductions in nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death at 150 mg (HR, 0.85; P = .021) and 300 mg (HR, 0.86; P = .031), but not at 50 mg.
The bottom line, said Dr. Wu, is that psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis should be treated early with TNF-alpha inhibitors or IL-17 inhibitors in an effort to improve mental health, cardiovascular, and psoriatic arthritis outcomes.
Dr. Wu has been a consultant or speaker for, or done research on behalf of, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Regeneron, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America.
The meeting is jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
SEATTLE – Psoriasis is a complex condition, made more difficult by comorbidities. Psoriatic arthritis is the most common and is frequently discussed. But mental health issues and cardiovascular events also co-occur and can present major complications, according to Jashin Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, who discussed psoriasis comorbidities at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium.
Mental health–related issues associated with psoriasis (Psychiatr Danub. 2017 Dec;29[4]:401-6) include sleep disorders (prevalence, 62%), sexual dysfunction (46%), personality disorder (35%), anxiety (30%), adjustment (29%), and depressive disorders (28%); 25% of patients have an accompanying substance abuse disorder. Suicidal ideation and suicidal depression are particularly concerning, and a meta-analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77[3]:425-40.e2) showed a 44% increased risk of suicidal ideation associated with psoriasis.
Such problems aren’t surprising, since psoriasis is a lifelong disease, and many patients’ symptoms aren’t adequately controlled. “A lot of these patients get topical therapies, which is probably not enough, especially if they have severe disease,” said Dr. Wu in an interview.
Dermatologists can sometimes be nervous about biologics because of concerns over increased risk of infection or cancer. That can lead to conservative, topical treatment. Dr. Wu feels that rare side effects shouldn’t deter from aggressive treatment, when appropriate. “It’s better to treat the patient to make sure they’re clear, which may improve their comorbidities as well. In general, if you’re worried, you can send them to other specialists to do monitoring,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Different treatment methods may influence mental health outcomes, according to the PSOLAR study (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78[1]:70-80). It examined the issue prospectively with over 12,000 psoriasis patients, and found a depression incidence of 3.01 per 100-patient years when treated with biologics, compared with 5.85 for phototherapy and 5.70 for conventional therapy. Put another way, exposure to biologics was associated with a reduced risk of depression, compared with conventional therapies (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .0367). “It seems to show that biologics have a better improvement of depression symptoms, compared to phototherapy or oral therapy,” said Dr. Wu.
Those results suggest that dermatologists should be on the lookout for mental health issues, though that is a challenge for someone not trained in the field. Dr. Wu takes a simple approach. “I like just asking open-ended questions, like how they’re doing, and if you get a sense that maybe they’re depressed, ask more specific questions about their mood, how they’re feeling, how things are at work, how things are at home.” When things aren’t right, “the key is to try to get them on something that’s going to clear them very quickly. If it’s severe disease, use a biologic that’s going to clear it very quickly,” he added.
Unfortunately, just being clear isn’t a complete guarantee of improved mental health. Dr. Wu had two patients who committed suicide despite significant skin improvement. Patients may have between-visit flare-ups, or regular injections may be a reminder that psoriasis is an ongoing health struggle. Or patients may have other psychological concerns. That underlines the importance of awareness of mental health issues. “You don’t need to refer everyone [to a mental health specialist], but you should have a rolodex where you have someone you can send a patient to if you’re worried,” said Dr. Wu.
As with mental health issues, psoriasis patients are also at elevated risk for a wide range of cardiovascular comorbidities, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and high blood pressure. “As a dermatologist, you may not want to screen for these things, but you can send them to their primary care doctor or a cardiologist,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Also like mental health issues, there is evidence that treatment with biologics may have an outsized protective effect. One study (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 24. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14951) led by Dr. Wu showed that treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitor led to a significant reduction in major adverse cardiac events, compared with topical therapy (propensity score–adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98), while phototherapy or oral therapy trended towards an increased risk (adjusted HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.00-1.28). Another analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jan;76[1]:81-90) from Dr. Wu’s group that included about 380,000 psoriasis patients found that treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors was associated with fewer major cardiovascular events, compared with treatment with methotrexate (adjusted HR, 0.55; P less than .0001). Individual analyses showed associated reductions in stroke or transient ischemic attack (aHR, 0.55; P less than .0001), unstable angina (aHR, 0.58; P = .0024), and MI (aHR, 0.49; P = .0002). TNF-alpha inhibitors also seem to beat out phototherapy with respect to major cardiovascular events (aHR, 0.77; P = .046. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jul;79[1]:60-6).
More direct evidence of the benefit of biologics comes from the CANTOS trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Sep 21;377[12]:1119-31), which randomized more than 10,000 patients with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes to receive the IL-1 beta-blocker canakinumab or placebo. Canakinumab was associated with significant reductions in nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death at 150 mg (HR, 0.85; P = .021) and 300 mg (HR, 0.86; P = .031), but not at 50 mg.
The bottom line, said Dr. Wu, is that psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis should be treated early with TNF-alpha inhibitors or IL-17 inhibitors in an effort to improve mental health, cardiovascular, and psoriatic arthritis outcomes.
Dr. Wu has been a consultant or speaker for, or done research on behalf of, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Regeneron, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America.
The meeting is jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
SEATTLE – Psoriasis is a complex condition, made more difficult by comorbidities. Psoriatic arthritis is the most common and is frequently discussed. But mental health issues and cardiovascular events also co-occur and can present major complications, according to Jashin Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, who discussed psoriasis comorbidities at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium.
Mental health–related issues associated with psoriasis (Psychiatr Danub. 2017 Dec;29[4]:401-6) include sleep disorders (prevalence, 62%), sexual dysfunction (46%), personality disorder (35%), anxiety (30%), adjustment (29%), and depressive disorders (28%); 25% of patients have an accompanying substance abuse disorder. Suicidal ideation and suicidal depression are particularly concerning, and a meta-analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77[3]:425-40.e2) showed a 44% increased risk of suicidal ideation associated with psoriasis.
Such problems aren’t surprising, since psoriasis is a lifelong disease, and many patients’ symptoms aren’t adequately controlled. “A lot of these patients get topical therapies, which is probably not enough, especially if they have severe disease,” said Dr. Wu in an interview.
Dermatologists can sometimes be nervous about biologics because of concerns over increased risk of infection or cancer. That can lead to conservative, topical treatment. Dr. Wu feels that rare side effects shouldn’t deter from aggressive treatment, when appropriate. “It’s better to treat the patient to make sure they’re clear, which may improve their comorbidities as well. In general, if you’re worried, you can send them to other specialists to do monitoring,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Different treatment methods may influence mental health outcomes, according to the PSOLAR study (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78[1]:70-80). It examined the issue prospectively with over 12,000 psoriasis patients, and found a depression incidence of 3.01 per 100-patient years when treated with biologics, compared with 5.85 for phototherapy and 5.70 for conventional therapy. Put another way, exposure to biologics was associated with a reduced risk of depression, compared with conventional therapies (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .0367). “It seems to show that biologics have a better improvement of depression symptoms, compared to phototherapy or oral therapy,” said Dr. Wu.
Those results suggest that dermatologists should be on the lookout for mental health issues, though that is a challenge for someone not trained in the field. Dr. Wu takes a simple approach. “I like just asking open-ended questions, like how they’re doing, and if you get a sense that maybe they’re depressed, ask more specific questions about their mood, how they’re feeling, how things are at work, how things are at home.” When things aren’t right, “the key is to try to get them on something that’s going to clear them very quickly. If it’s severe disease, use a biologic that’s going to clear it very quickly,” he added.
Unfortunately, just being clear isn’t a complete guarantee of improved mental health. Dr. Wu had two patients who committed suicide despite significant skin improvement. Patients may have between-visit flare-ups, or regular injections may be a reminder that psoriasis is an ongoing health struggle. Or patients may have other psychological concerns. That underlines the importance of awareness of mental health issues. “You don’t need to refer everyone [to a mental health specialist], but you should have a rolodex where you have someone you can send a patient to if you’re worried,” said Dr. Wu.
As with mental health issues, psoriasis patients are also at elevated risk for a wide range of cardiovascular comorbidities, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and high blood pressure. “As a dermatologist, you may not want to screen for these things, but you can send them to their primary care doctor or a cardiologist,” Dr. Wu said in the interview.
Also like mental health issues, there is evidence that treatment with biologics may have an outsized protective effect. One study (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 24. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14951) led by Dr. Wu showed that treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitor led to a significant reduction in major adverse cardiac events, compared with topical therapy (propensity score–adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98), while phototherapy or oral therapy trended towards an increased risk (adjusted HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.00-1.28). Another analysis (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jan;76[1]:81-90) from Dr. Wu’s group that included about 380,000 psoriasis patients found that treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors was associated with fewer major cardiovascular events, compared with treatment with methotrexate (adjusted HR, 0.55; P less than .0001). Individual analyses showed associated reductions in stroke or transient ischemic attack (aHR, 0.55; P less than .0001), unstable angina (aHR, 0.58; P = .0024), and MI (aHR, 0.49; P = .0002). TNF-alpha inhibitors also seem to beat out phototherapy with respect to major cardiovascular events (aHR, 0.77; P = .046. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jul;79[1]:60-6).
More direct evidence of the benefit of biologics comes from the CANTOS trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Sep 21;377[12]:1119-31), which randomized more than 10,000 patients with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes to receive the IL-1 beta-blocker canakinumab or placebo. Canakinumab was associated with significant reductions in nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death at 150 mg (HR, 0.85; P = .021) and 300 mg (HR, 0.86; P = .031), but not at 50 mg.
The bottom line, said Dr. Wu, is that psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis should be treated early with TNF-alpha inhibitors or IL-17 inhibitors in an effort to improve mental health, cardiovascular, and psoriatic arthritis outcomes.
Dr. Wu has been a consultant or speaker for, or done research on behalf of, AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Regeneron, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America.
The meeting is jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM COASTAL DERM
Psoriasis Journal Scan: September 2019
Psychological and Sexual Consequences of Psoriasis Vulgaris on Patients and Their Partners.
Alariny AF, Farid CI, Elweshahi HM, Abbood SS. J Sex Med. 2019 Sep 18.
In a comparative cross-sectional study that aimed to evaluate the psychopathological and sexual aspects of psoriasis vulgaris in patients and their partners, the sample included 220 psoriasis vulgaris patients (110 males and 110 females), their consenting partners, and 220 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. The main outcome measures were frequency of depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and sexual dysfunction in psoriasis vulgaris patients, partners, and controls; the domains of sexual function affected in the studied groups; and the etiology of erectile dysfunction in affected psoriatic males.
Ceramide- and Keratolytic-containing Body Cleanser and Cream Application in Patients with Psoriasis: Outcomes from a Consumer Usage Study.
Del Rosso JQ. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Jul;12(7):18-21
Ceramides are epidermal lipids that play an essential role in stratum corneum function, including maintaining physiologic permeability barrier properties. The role of ceramides in the maintenance and repair of epidermal barrier function is believed to be valuable in the treatment of psoriasis. Normalization of corneocyte desquamation and the incorporation of agents that promote desquamation to reduce hyperkeratosis are also regarded as key factors in psoriasis management. Based on results reported by the study patients, the evaluated ceramide/keratolytic-containing cream and cleanser both yielded a high level of patient acceptance regarding improvement in skin characteristics in patients with psoriasis, including when used as a combination adjunctive regimen.
Split thickness skin graft in active psoriasis in patient with clear cell variant squamous cell carcinoma.
Scupham L, Ingle A. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Sep 16;12(9).
The case report discusses split thickness skin grafting in a patient with active psoriasis. This also reports a case of a rare variant of squamous cell carcinoma.
Epicardial Adipose Tissue Inflammation Can Cause the Distinctive Pattern of Cardiovascular Disorders Seen in Psoriasis.
Packer M. Am J Med. 2019 Sep 11.
Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disorder that can target adipose tissue; the resulting adipocyte dysfunction is manifest clinically as the metabolic syndrome, which is present in ≈20-40% of patients. Epicardial adipose tissue inflammation is likely responsible for a distinctive pattern of cardiovascular disorders, consisting of: accelerated coronary atherosclerosis leading to myocardial infarction, atrial myopathy leading to atrial fibrillation and thromboembolic stroke, and ventricular myopathy leading to heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. If cardiovascular inflammation drives these risks, then treatments that focus on blood pressure, lipids and glucose will not ameliorate the burden of cardiovascular disease in patients with psoriasis, especially in those who are young and have severe inflammation. Instead, interventions that alleviate systemic and adipose tissue inflammation may not only minimize the risks of atrial fibrillation and heart failure, but may also have favorable effects on the severity of psoriasis. Viewed from this perspective, the known link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease is not related to the influence of the individual diagnostic components of the metabolic syndrome.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound can improve referrals from dermatology to rheumatology for patients with psoriasis.
Solmaz D, Bakirci S, Al Onazi A, Al Osaimi N, Fahim S, Aydin SZ. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Sep 10.
Psoriasis affects 1-3% of the population and up to 1/3 of psoriasis patients have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Non-specific musculoskeletal complaints are even higher, being around 50%. Detecting early signs of PsA and early treatments are crucial to improve the outcomes to prevent progressive, damaging arthritis. Due to the high frequency of non-specific pain in psoriasis, it is not possible for every psoriasis patient with joint pain to be assessed by a rheumato
Psychological and Sexual Consequences of Psoriasis Vulgaris on Patients and Their Partners.
Alariny AF, Farid CI, Elweshahi HM, Abbood SS. J Sex Med. 2019 Sep 18.
In a comparative cross-sectional study that aimed to evaluate the psychopathological and sexual aspects of psoriasis vulgaris in patients and their partners, the sample included 220 psoriasis vulgaris patients (110 males and 110 females), their consenting partners, and 220 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. The main outcome measures were frequency of depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and sexual dysfunction in psoriasis vulgaris patients, partners, and controls; the domains of sexual function affected in the studied groups; and the etiology of erectile dysfunction in affected psoriatic males.
Ceramide- and Keratolytic-containing Body Cleanser and Cream Application in Patients with Psoriasis: Outcomes from a Consumer Usage Study.
Del Rosso JQ. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Jul;12(7):18-21
Ceramides are epidermal lipids that play an essential role in stratum corneum function, including maintaining physiologic permeability barrier properties. The role of ceramides in the maintenance and repair of epidermal barrier function is believed to be valuable in the treatment of psoriasis. Normalization of corneocyte desquamation and the incorporation of agents that promote desquamation to reduce hyperkeratosis are also regarded as key factors in psoriasis management. Based on results reported by the study patients, the evaluated ceramide/keratolytic-containing cream and cleanser both yielded a high level of patient acceptance regarding improvement in skin characteristics in patients with psoriasis, including when used as a combination adjunctive regimen.
Split thickness skin graft in active psoriasis in patient with clear cell variant squamous cell carcinoma.
Scupham L, Ingle A. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Sep 16;12(9).
The case report discusses split thickness skin grafting in a patient with active psoriasis. This also reports a case of a rare variant of squamous cell carcinoma.
Epicardial Adipose Tissue Inflammation Can Cause the Distinctive Pattern of Cardiovascular Disorders Seen in Psoriasis.
Packer M. Am J Med. 2019 Sep 11.
Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disorder that can target adipose tissue; the resulting adipocyte dysfunction is manifest clinically as the metabolic syndrome, which is present in ≈20-40% of patients. Epicardial adipose tissue inflammation is likely responsible for a distinctive pattern of cardiovascular disorders, consisting of: accelerated coronary atherosclerosis leading to myocardial infarction, atrial myopathy leading to atrial fibrillation and thromboembolic stroke, and ventricular myopathy leading to heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. If cardiovascular inflammation drives these risks, then treatments that focus on blood pressure, lipids and glucose will not ameliorate the burden of cardiovascular disease in patients with psoriasis, especially in those who are young and have severe inflammation. Instead, interventions that alleviate systemic and adipose tissue inflammation may not only minimize the risks of atrial fibrillation and heart failure, but may also have favorable effects on the severity of psoriasis. Viewed from this perspective, the known link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease is not related to the influence of the individual diagnostic components of the metabolic syndrome.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound can improve referrals from dermatology to rheumatology for patients with psoriasis.
Solmaz D, Bakirci S, Al Onazi A, Al Osaimi N, Fahim S, Aydin SZ. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Sep 10.
Psoriasis affects 1-3% of the population and up to 1/3 of psoriasis patients have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Non-specific musculoskeletal complaints are even higher, being around 50%. Detecting early signs of PsA and early treatments are crucial to improve the outcomes to prevent progressive, damaging arthritis. Due to the high frequency of non-specific pain in psoriasis, it is not possible for every psoriasis patient with joint pain to be assessed by a rheumato
Psychological and Sexual Consequences of Psoriasis Vulgaris on Patients and Their Partners.
Alariny AF, Farid CI, Elweshahi HM, Abbood SS. J Sex Med. 2019 Sep 18.
In a comparative cross-sectional study that aimed to evaluate the psychopathological and sexual aspects of psoriasis vulgaris in patients and their partners, the sample included 220 psoriasis vulgaris patients (110 males and 110 females), their consenting partners, and 220 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. The main outcome measures were frequency of depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and sexual dysfunction in psoriasis vulgaris patients, partners, and controls; the domains of sexual function affected in the studied groups; and the etiology of erectile dysfunction in affected psoriatic males.
Ceramide- and Keratolytic-containing Body Cleanser and Cream Application in Patients with Psoriasis: Outcomes from a Consumer Usage Study.
Del Rosso JQ. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Jul;12(7):18-21
Ceramides are epidermal lipids that play an essential role in stratum corneum function, including maintaining physiologic permeability barrier properties. The role of ceramides in the maintenance and repair of epidermal barrier function is believed to be valuable in the treatment of psoriasis. Normalization of corneocyte desquamation and the incorporation of agents that promote desquamation to reduce hyperkeratosis are also regarded as key factors in psoriasis management. Based on results reported by the study patients, the evaluated ceramide/keratolytic-containing cream and cleanser both yielded a high level of patient acceptance regarding improvement in skin characteristics in patients with psoriasis, including when used as a combination adjunctive regimen.
Split thickness skin graft in active psoriasis in patient with clear cell variant squamous cell carcinoma.
Scupham L, Ingle A. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Sep 16;12(9).
The case report discusses split thickness skin grafting in a patient with active psoriasis. This also reports a case of a rare variant of squamous cell carcinoma.
Epicardial Adipose Tissue Inflammation Can Cause the Distinctive Pattern of Cardiovascular Disorders Seen in Psoriasis.
Packer M. Am J Med. 2019 Sep 11.
Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disorder that can target adipose tissue; the resulting adipocyte dysfunction is manifest clinically as the metabolic syndrome, which is present in ≈20-40% of patients. Epicardial adipose tissue inflammation is likely responsible for a distinctive pattern of cardiovascular disorders, consisting of: accelerated coronary atherosclerosis leading to myocardial infarction, atrial myopathy leading to atrial fibrillation and thromboembolic stroke, and ventricular myopathy leading to heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. If cardiovascular inflammation drives these risks, then treatments that focus on blood pressure, lipids and glucose will not ameliorate the burden of cardiovascular disease in patients with psoriasis, especially in those who are young and have severe inflammation. Instead, interventions that alleviate systemic and adipose tissue inflammation may not only minimize the risks of atrial fibrillation and heart failure, but may also have favorable effects on the severity of psoriasis. Viewed from this perspective, the known link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease is not related to the influence of the individual diagnostic components of the metabolic syndrome.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound can improve referrals from dermatology to rheumatology for patients with psoriasis.
Solmaz D, Bakirci S, Al Onazi A, Al Osaimi N, Fahim S, Aydin SZ. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Sep 10.
Psoriasis affects 1-3% of the population and up to 1/3 of psoriasis patients have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Non-specific musculoskeletal complaints are even higher, being around 50%. Detecting early signs of PsA and early treatments are crucial to improve the outcomes to prevent progressive, damaging arthritis. Due to the high frequency of non-specific pain in psoriasis, it is not possible for every psoriasis patient with joint pain to be assessed by a rheumato