User login
in Neurology.
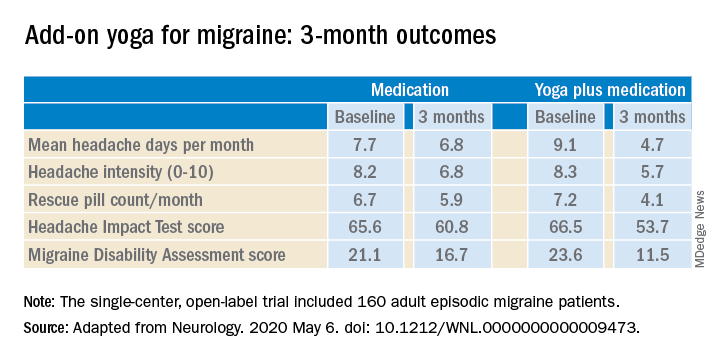
The structured yoga program resulted in “remarkably improved” outcomes at 3 months of follow-up in CONTAIN, with both headache frequency and use of medications cut in half, compared with baseline, according to the investigators.
Compared with the control group on standard antimigraine medications alone, the yoga group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in pain intensity, headache frequency, pill counts, and validated measures of disability and headache impact on daily life (see graphic).
“The good news is that practicing something as simple and accessible as yoga may help much more than medications alone. And all you need is a mat,” observed Dr. Bhatia, professor of neurology at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi.
The single-center, open-label, blinded-assessment CONTAIN trial included 160 adult episodic migraine patients ages 18-50 years experiencing 4-14 headaches per month. They were randomized to prophylactic and acute rescue medications alone or in combination with yoga instruction by a qualified yoga therapist in a class that met at the medical center 3 days per week for 1 month. This was followed by practice of the hour-long yoga program at home 5 days per week for the next 2 months, with twice-monthly telephone calls from the yoga center to encourage adherence and encouragement to call if questions arose. Both groups received counseling about the importance of lifestyle changes that may help with migraine, including diet, physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress reduction. Outcomes were assessed in an intent-to-treat analysis.
The yoga program included specific relaxation exercises, breathing techniques, meditation, and yoga postures, or asanas. The migraine-tailored program was vetted by yoga experts at five renowned Indian yoga centers.
No safety issues arose with the yoga program.
The investigators noted that the 47% reduction in migraine medication pill count and 49% decrease in headache frequency over the course of 3 months in the adjunctive yoga group have important implications, not only in a limited-resource country such as India, but also in the United States, where Americans spend an estimated $3.2 billion annually on prescription and over the counter headache medications, and the indirect cost associated with lost productivity due to migraine has been put at $13 billion per year.
Dr. Bhatia and colleagues speculated that the observed benefits of add-on yoga in migraineurs may involve previously described improved vagal tone and parasympathetic drive coupled with decreased sympathetic tone, increased nitric oxide levels, and loosening of stiff muscles, which can trigger headaches.
Real-life goals
Commenting on the research, neurologist Holly Yancy, DO, a headache specialist at the Banner Health - University Medicine Neuroscience Institute in Phoenix, said she was impressed by the high quality of this well-designed, adequately powered study of a complementary and alternative therapy.
“The primary and secondary endpoints were real-life goals of migraine treatment that we strive to achieve in clinical practice – and they were met in the study,” she observed. “To start with a month of in-house yoga classes to instill a baseline competence in yoga prior to transitioning to home practice and to provide resources for ongoing assistance for questions were nice touches.”
She noted that the control group also experienced reductions in migraine frequency, severity, and disability scores, albeit of significantly lesser magnitude than in the yoga group. This underscores how important it is in clinical practice to spend time counseling migraine patients on lifestyle choices.
“A trial such as this provides neurologists and other health care providers with an accessible, evidence-based treatment for migraines that can be used with other preventive treatments to decrease the frequency and the amount of medication their patients are taking. In addition, it is a behavioral therapy that can decrease triggers and potentially help patients cope with pain,” Dr. Yancy said.
“I suspect I’ll not hesitate to recommend yoga as an adjunctive treatment for patients in my clinic that are physically capable. I think it would be logical to try to extrapolate the concept to a chronic migraine population as well, though it would be ideal to base that recommendation on another study conducted with a chronic migraine population.”
Dr. Bhatia and his coinvestigators reported having no financial conflicts regarding their study, funded by the Government of India and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
SOURCE: Kumar A et al. Neurology. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009473.
in Neurology.

The structured yoga program resulted in “remarkably improved” outcomes at 3 months of follow-up in CONTAIN, with both headache frequency and use of medications cut in half, compared with baseline, according to the investigators.
Compared with the control group on standard antimigraine medications alone, the yoga group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in pain intensity, headache frequency, pill counts, and validated measures of disability and headache impact on daily life (see graphic).
“The good news is that practicing something as simple and accessible as yoga may help much more than medications alone. And all you need is a mat,” observed Dr. Bhatia, professor of neurology at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi.
The single-center, open-label, blinded-assessment CONTAIN trial included 160 adult episodic migraine patients ages 18-50 years experiencing 4-14 headaches per month. They were randomized to prophylactic and acute rescue medications alone or in combination with yoga instruction by a qualified yoga therapist in a class that met at the medical center 3 days per week for 1 month. This was followed by practice of the hour-long yoga program at home 5 days per week for the next 2 months, with twice-monthly telephone calls from the yoga center to encourage adherence and encouragement to call if questions arose. Both groups received counseling about the importance of lifestyle changes that may help with migraine, including diet, physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress reduction. Outcomes were assessed in an intent-to-treat analysis.
The yoga program included specific relaxation exercises, breathing techniques, meditation, and yoga postures, or asanas. The migraine-tailored program was vetted by yoga experts at five renowned Indian yoga centers.
No safety issues arose with the yoga program.
The investigators noted that the 47% reduction in migraine medication pill count and 49% decrease in headache frequency over the course of 3 months in the adjunctive yoga group have important implications, not only in a limited-resource country such as India, but also in the United States, where Americans spend an estimated $3.2 billion annually on prescription and over the counter headache medications, and the indirect cost associated with lost productivity due to migraine has been put at $13 billion per year.
Dr. Bhatia and colleagues speculated that the observed benefits of add-on yoga in migraineurs may involve previously described improved vagal tone and parasympathetic drive coupled with decreased sympathetic tone, increased nitric oxide levels, and loosening of stiff muscles, which can trigger headaches.
Real-life goals
Commenting on the research, neurologist Holly Yancy, DO, a headache specialist at the Banner Health - University Medicine Neuroscience Institute in Phoenix, said she was impressed by the high quality of this well-designed, adequately powered study of a complementary and alternative therapy.
“The primary and secondary endpoints were real-life goals of migraine treatment that we strive to achieve in clinical practice – and they were met in the study,” she observed. “To start with a month of in-house yoga classes to instill a baseline competence in yoga prior to transitioning to home practice and to provide resources for ongoing assistance for questions were nice touches.”
She noted that the control group also experienced reductions in migraine frequency, severity, and disability scores, albeit of significantly lesser magnitude than in the yoga group. This underscores how important it is in clinical practice to spend time counseling migraine patients on lifestyle choices.
“A trial such as this provides neurologists and other health care providers with an accessible, evidence-based treatment for migraines that can be used with other preventive treatments to decrease the frequency and the amount of medication their patients are taking. In addition, it is a behavioral therapy that can decrease triggers and potentially help patients cope with pain,” Dr. Yancy said.
“I suspect I’ll not hesitate to recommend yoga as an adjunctive treatment for patients in my clinic that are physically capable. I think it would be logical to try to extrapolate the concept to a chronic migraine population as well, though it would be ideal to base that recommendation on another study conducted with a chronic migraine population.”
Dr. Bhatia and his coinvestigators reported having no financial conflicts regarding their study, funded by the Government of India and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
SOURCE: Kumar A et al. Neurology. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009473.
in Neurology.

The structured yoga program resulted in “remarkably improved” outcomes at 3 months of follow-up in CONTAIN, with both headache frequency and use of medications cut in half, compared with baseline, according to the investigators.
Compared with the control group on standard antimigraine medications alone, the yoga group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in pain intensity, headache frequency, pill counts, and validated measures of disability and headache impact on daily life (see graphic).
“The good news is that practicing something as simple and accessible as yoga may help much more than medications alone. And all you need is a mat,” observed Dr. Bhatia, professor of neurology at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi.
The single-center, open-label, blinded-assessment CONTAIN trial included 160 adult episodic migraine patients ages 18-50 years experiencing 4-14 headaches per month. They were randomized to prophylactic and acute rescue medications alone or in combination with yoga instruction by a qualified yoga therapist in a class that met at the medical center 3 days per week for 1 month. This was followed by practice of the hour-long yoga program at home 5 days per week for the next 2 months, with twice-monthly telephone calls from the yoga center to encourage adherence and encouragement to call if questions arose. Both groups received counseling about the importance of lifestyle changes that may help with migraine, including diet, physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress reduction. Outcomes were assessed in an intent-to-treat analysis.
The yoga program included specific relaxation exercises, breathing techniques, meditation, and yoga postures, or asanas. The migraine-tailored program was vetted by yoga experts at five renowned Indian yoga centers.
No safety issues arose with the yoga program.
The investigators noted that the 47% reduction in migraine medication pill count and 49% decrease in headache frequency over the course of 3 months in the adjunctive yoga group have important implications, not only in a limited-resource country such as India, but also in the United States, where Americans spend an estimated $3.2 billion annually on prescription and over the counter headache medications, and the indirect cost associated with lost productivity due to migraine has been put at $13 billion per year.
Dr. Bhatia and colleagues speculated that the observed benefits of add-on yoga in migraineurs may involve previously described improved vagal tone and parasympathetic drive coupled with decreased sympathetic tone, increased nitric oxide levels, and loosening of stiff muscles, which can trigger headaches.
Real-life goals
Commenting on the research, neurologist Holly Yancy, DO, a headache specialist at the Banner Health - University Medicine Neuroscience Institute in Phoenix, said she was impressed by the high quality of this well-designed, adequately powered study of a complementary and alternative therapy.
“The primary and secondary endpoints were real-life goals of migraine treatment that we strive to achieve in clinical practice – and they were met in the study,” she observed. “To start with a month of in-house yoga classes to instill a baseline competence in yoga prior to transitioning to home practice and to provide resources for ongoing assistance for questions were nice touches.”
She noted that the control group also experienced reductions in migraine frequency, severity, and disability scores, albeit of significantly lesser magnitude than in the yoga group. This underscores how important it is in clinical practice to spend time counseling migraine patients on lifestyle choices.
“A trial such as this provides neurologists and other health care providers with an accessible, evidence-based treatment for migraines that can be used with other preventive treatments to decrease the frequency and the amount of medication their patients are taking. In addition, it is a behavioral therapy that can decrease triggers and potentially help patients cope with pain,” Dr. Yancy said.
“I suspect I’ll not hesitate to recommend yoga as an adjunctive treatment for patients in my clinic that are physically capable. I think it would be logical to try to extrapolate the concept to a chronic migraine population as well, though it would be ideal to base that recommendation on another study conducted with a chronic migraine population.”
Dr. Bhatia and his coinvestigators reported having no financial conflicts regarding their study, funded by the Government of India and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
SOURCE: Kumar A et al. Neurology. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009473.
FROM NEUROLOGY