User login
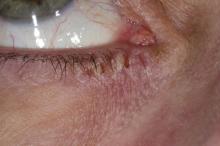
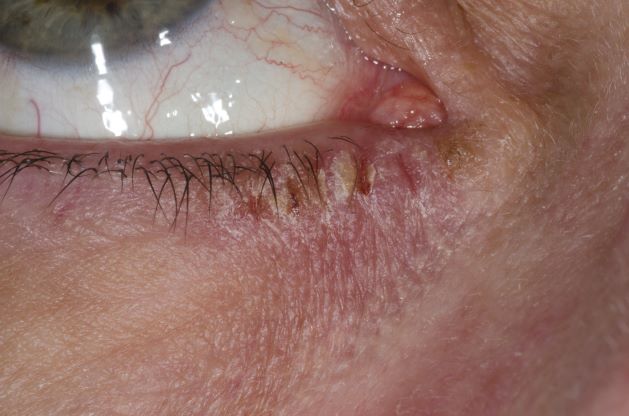
This patient has the “atopic triad” of allergies, asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis around the eyes and on the eyelids often develops in teenage years and adulthood but may also occur in older persons. Occasionally, it can be the only manifestation of atopic dermatitis. The upper eyelids may appear scaly and fissured. The so-called "allergic shiners" (symmetric, dark circles beneath the lower eyelid) and Dennie-Morgan lines (extra skin folds under the lower eyelid) are often present.
The thin skin of the eyelids is particularly sensitive to irritants and allergens and is thus prone to develop dermatitis. Contact with the same trigger may not lead to a rash on other areas of skin. Upper, lower or both eyelids on one or both sides can be affected. The patient may report itching, stinging or burning, and the lids are red and scaly. They may swell. With persistence of the dermatitis, the eyelids become thickened with increased skin markings (lichenification). The eyelid margins may become involved (blepharitis). The appearance is similar, whatever the cause.
The basis of treatment for atopic dermatitis is to provide moisturization for dryness, allay pruritus, and manage inflammation of the eczematous lesions. Conservative initial management of eyelid dermatitis also includes gentle skin care and avoidance of fragrance and other known irritants in personal care, hair, and facial skin care products. Bland, fragrance-free emollients, such as petrolatum, may be applied directly to the eyelids.
Topical corticosteroids are one therapeutic option for eyelid dermatitis. However, only low-potency topical corticosteroids are safe, and only for short-term use, on the eyelids. Typically, they are used twice daily for 2-4 weeks. However, even with low-potency topical corticosteroids, the eyelids remain vulnerable to thinning, even atrophy. Because of these issues, topical calcineurin inhibitors are often the preferred treatment.
Patients with atopic dermatitis have an increased risk of comorbid eye diseases, including keratitis, conjunctivitis, and keratoconus. A careful clinical examination for associated erythema, crusting, and blepharitis many prompt a referral to an ophthalmologist.
Brian S. Kim, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Dermatology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brian S. Kim, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This patient has the “atopic triad” of allergies, asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis around the eyes and on the eyelids often develops in teenage years and adulthood but may also occur in older persons. Occasionally, it can be the only manifestation of atopic dermatitis. The upper eyelids may appear scaly and fissured. The so-called "allergic shiners" (symmetric, dark circles beneath the lower eyelid) and Dennie-Morgan lines (extra skin folds under the lower eyelid) are often present.
The thin skin of the eyelids is particularly sensitive to irritants and allergens and is thus prone to develop dermatitis. Contact with the same trigger may not lead to a rash on other areas of skin. Upper, lower or both eyelids on one or both sides can be affected. The patient may report itching, stinging or burning, and the lids are red and scaly. They may swell. With persistence of the dermatitis, the eyelids become thickened with increased skin markings (lichenification). The eyelid margins may become involved (blepharitis). The appearance is similar, whatever the cause.
The basis of treatment for atopic dermatitis is to provide moisturization for dryness, allay pruritus, and manage inflammation of the eczematous lesions. Conservative initial management of eyelid dermatitis also includes gentle skin care and avoidance of fragrance and other known irritants in personal care, hair, and facial skin care products. Bland, fragrance-free emollients, such as petrolatum, may be applied directly to the eyelids.
Topical corticosteroids are one therapeutic option for eyelid dermatitis. However, only low-potency topical corticosteroids are safe, and only for short-term use, on the eyelids. Typically, they are used twice daily for 2-4 weeks. However, even with low-potency topical corticosteroids, the eyelids remain vulnerable to thinning, even atrophy. Because of these issues, topical calcineurin inhibitors are often the preferred treatment.
Patients with atopic dermatitis have an increased risk of comorbid eye diseases, including keratitis, conjunctivitis, and keratoconus. A careful clinical examination for associated erythema, crusting, and blepharitis many prompt a referral to an ophthalmologist.
Brian S. Kim, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Dermatology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brian S. Kim, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This patient has the “atopic triad” of allergies, asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis around the eyes and on the eyelids often develops in teenage years and adulthood but may also occur in older persons. Occasionally, it can be the only manifestation of atopic dermatitis. The upper eyelids may appear scaly and fissured. The so-called "allergic shiners" (symmetric, dark circles beneath the lower eyelid) and Dennie-Morgan lines (extra skin folds under the lower eyelid) are often present.
The thin skin of the eyelids is particularly sensitive to irritants and allergens and is thus prone to develop dermatitis. Contact with the same trigger may not lead to a rash on other areas of skin. Upper, lower or both eyelids on one or both sides can be affected. The patient may report itching, stinging or burning, and the lids are red and scaly. They may swell. With persistence of the dermatitis, the eyelids become thickened with increased skin markings (lichenification). The eyelid margins may become involved (blepharitis). The appearance is similar, whatever the cause.
The basis of treatment for atopic dermatitis is to provide moisturization for dryness, allay pruritus, and manage inflammation of the eczematous lesions. Conservative initial management of eyelid dermatitis also includes gentle skin care and avoidance of fragrance and other known irritants in personal care, hair, and facial skin care products. Bland, fragrance-free emollients, such as petrolatum, may be applied directly to the eyelids.
Topical corticosteroids are one therapeutic option for eyelid dermatitis. However, only low-potency topical corticosteroids are safe, and only for short-term use, on the eyelids. Typically, they are used twice daily for 2-4 weeks. However, even with low-potency topical corticosteroids, the eyelids remain vulnerable to thinning, even atrophy. Because of these issues, topical calcineurin inhibitors are often the preferred treatment.
Patients with atopic dermatitis have an increased risk of comorbid eye diseases, including keratitis, conjunctivitis, and keratoconus. A careful clinical examination for associated erythema, crusting, and blepharitis many prompt a referral to an ophthalmologist.
Brian S. Kim, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Dermatology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri
Brian S. Kim, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A 21-year-old woman presents with burning, itchy red eyes that she rubs incessantly. On examination, she has an erythematic, scaly, pruritic rash on the upper and lower eyelids and below her eyes. She has no other outbreaks on the rest of her skin except for mild acne. A moisturizer has provided minimal relief for the itching but has not helped with the rash. She has a history of asthma, for which she uses an inhaler, and of hay fever, for which she takes an antihistamine. She also reports that she has had two episodes of conjunctivitis within the past year, which were treated with antibiotic eye drops.