User login
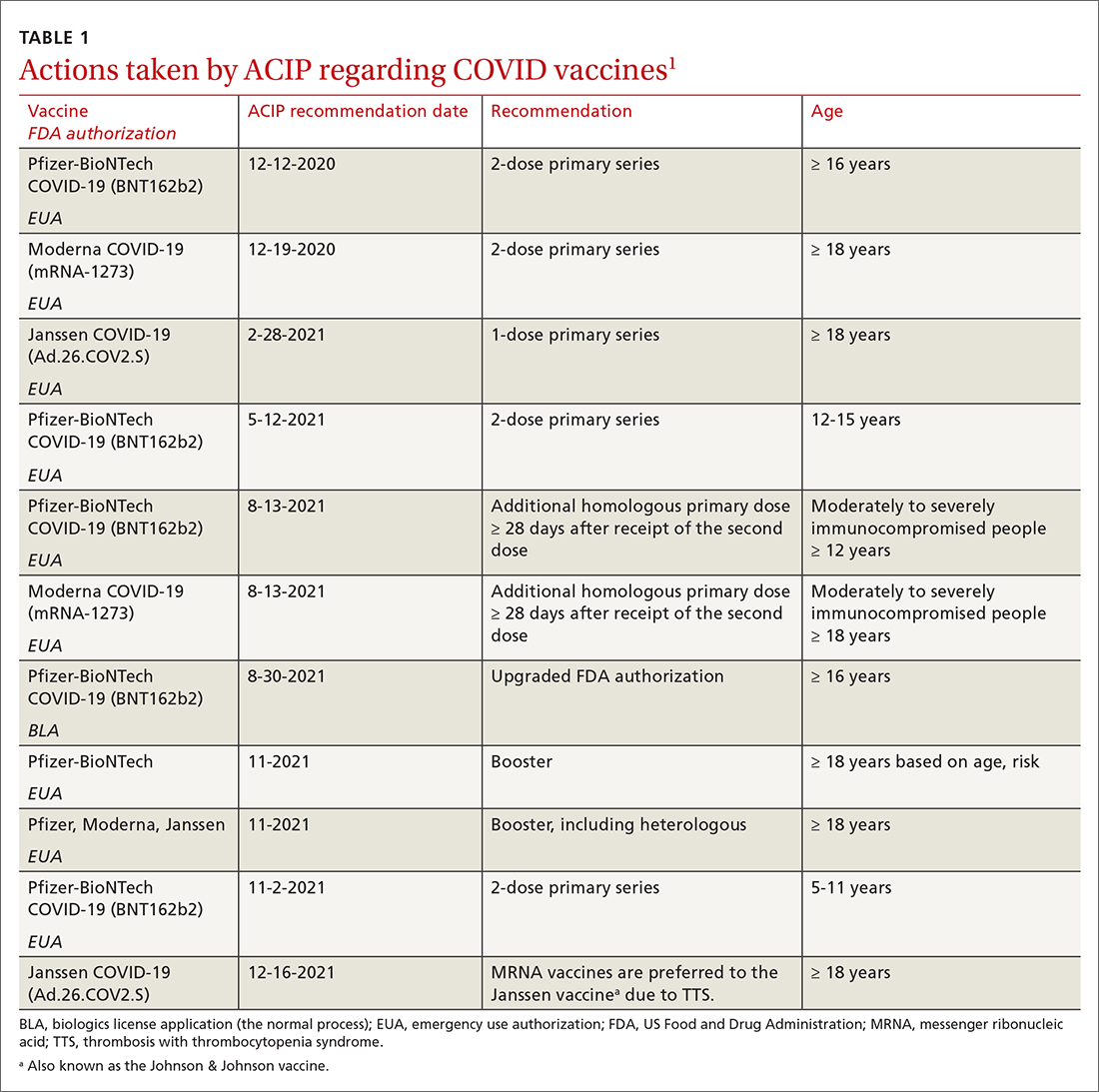
In a typical year, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) has three 1.5- to 2-day meetings to make recommendations for the use of new and existing vaccines in the US population. However, 2021 was not a typical year. Last year, ACIP held 17 meetings for a total of 127 hours. Most of these were related to vaccines to prevent COVID-19. There are now 3 COVID-19 vaccines authorized for use in the United States: the 2-dose mRNA-based Pfizer-BioNTech/Comirnaty and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and the single-dose adenovirus, vector-based Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID-19 vaccine.
TABLE 11 includes the actions taken by the ACIP from late 2020 through 2021 related to COVID-19 vaccines. All of these recommendations except 1 occurred after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the product using an emergency use authorization (EUA). The exception is the recommendation for use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) for those ages 16 years and older, which was approved under the normal process 8 months after widespread use under an EUA.
Hepatitis B vaccine now for all nonimmune adults up through 59 years
Since the introduction of hepatitis B (HepB) vaccines in 1980, the incidence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections in the United States has been reduced dramatically; there were an estimated 287,000 cases in 19852 and 19,200 in 2014.3 However, the incidence among adults has not declined in recent years and among someage groups has actually increased. Among those ages 40 to 49 years, the rate went from 1.9 per 100,000 in 20114 to 2.7 per 100,000 population in 2019.5 In those ages 50 to 59, there was an increase from 1.1 to 1.6 per 100,000 population over the same period of time.4,5
Recommendations for using HepB vaccine in adults have been based on risk that involves individual behavior, occupation, and medical conditions (TABLE 26). The presence of these risk factors is often unknown to medical professionals, who rarely ask about or document them. And patients can be reluctant to disclose them for fear of being stigmatized. The consequence has been a low rate of vaccination in at-risk adults.
At its November 2021 meeting, ACIP accepted the advice of the Hepatitis Work Group to move to a universal adult recommendation through age 59.7 ACIP believed that the incidence of acute infection in those ages 60 and older was too low to merit a universal recommendation. The new recommendation states that
Multiple HepB vaccine products are available for adults. Two are recombinant-based and require 3 doses: Engerix-B (GlaxoSmithKline) and Recombivax HB (Merck). One is recombinant based and requires only 2 doses: Heplisav-B (Dynavax Technologies). A new product recently approved by the FDA, PREHEVBRIO (VBI Vaccines), is another recombinant 3-dose option that the ACIP will consider early in 2022. HepB and HepA vaccines can also be co-administered with Twinrix (GlaxoSmithKline).
Pneumococcal vaccines: New PCV vaccines alter prescribing choices
The ACIP recommendations for pneumococcal vaccines in adults have been very confusing, involving 2 vaccines: PCV13 (Prevnar13, Pfizer) and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23, Merck). Both PCV13 and PPSV23 given in series were recommended for immunocompromised patients, but only PPSV23 was recommended for those with chronic medical conditions. For those 65 and older, PPSV23 was recommended for all individuals (including those with no chronic or immunocompromising condition), and PCV13 was recommended for those with immunocompromising conditions. Other adults in this older age group could receive PCV13 based on individual risk and shared clinical decision making.8
Continue to: This past year...
This past year, 2 new PCV vaccines were approved by the FDA: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance, Merck) and PCV20 (Prevnar20, Pfizer). While considering these new vaccines, the ACIP re-assessed its entire approval of pneumococcal vaccines. First, they retained the cutoff for universal pneumococcal vaccination at 65 years. For those younger than 65, they combined chronic medical conditions and immunocompromising conditions into a single at-risk group (TABLE 39). They then issued the same recommendation for older adults and those younger than 65 with risks: to receive a PCV vaccine, either PCV15 or PCV20. If they receive PCV15, it should be followed by PPSV23. PPSV23 is not recommended for those who receive PCV20. Therefore,
Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) has been licensed and recommended in the United States since 2017 in a 2-dose schedule for adults ages 50 years and older. In the summer of 2021, the FDA expanded the indication for use of RZV to include individuals 18 to 49 years of age who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy. In October, the ACIP agreed and recommended 2 RZV doses for those 19 years and older in these risk groups (TABLE 410).
This recommendation was based on the elevated risk of herpes zoster documented in those with immune-suppressing conditions and therapies. In the conditions studied, the incidence in these younger adults exceeded that for older adults, for whom the vaccine is recommended.10 There are many immune conditions and immune-suppressing medications. The ACIP Zoster Work Group did not have efficacy and safety information on the use of RZV in each one of them, even though their recommendation includes them all. Many of these patients are under the care of specialists whose specialty societies had been recommending zoster vaccine for their patients, off label, prior to the FDA authorization.
Rabies vaccine is now available in 2-dose schedule
People who should receive rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with rabies vaccine include laboratory personnel who work with rabies virus, biologists who work with bats, animal care professionals, wildlife biologists, veterinarians, and travelers who may be at risk of encountering rabid dogs. The recommendation has been for 3 doses of rabies vaccine at 0, 7, and 21-28 days. The ACIP voted at its June 2021 meeting to adopt a 2-dose PrEP schedule of 0 and 7 days.11 This will be especially helpful to travelers who want to complete the recommended doses prior to departure. Those who have sustained risk over time can elect to have a third dose after 21 days and before 3 years, or elect to have titers checked. More detailed clinical advice will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2022.
Dengue vaccine: New rec for those 9-16 years
In 2019, the FDA approved the first dengue vaccine for use in the United States for children 9 to 16 years old who had laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and who were living in an area where dengue is endemic. The CYD-TDV dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is a live-attenuated tetravalent vaccine built on a yellow fever vaccine backbone. Its effectiveness is 82% for prevention of symptomatic dengue, 79% for prevention of dengue-associated hospitalizations, and 84% against severe dengue.12
Continue to: Dengue viruses...
Dengue viruses (DENV) are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. There are 4 serotypes of dengue, and all 4 appear to be circulating in most endemic countries. Clinical disease varies from a mild febrile illness to severe disease. The most common clinical presentation includes sudden onset of fever, headache, retro-orbital pain, myalgia and arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea.
Severe disease includes plasma leakage, shock, respiratory distress, severe bleeding, and organ failure. While severe dengue can occur with a primary infection, a second infection with a different DENV increases the risk of severe dengue. A small increased risk of severe dengue occurs when dengue infection occurs after vaccination in those with no evidence of previous dengue infection. It is felt that the vaccine serves as a primary infection that increases the risk of severe dengue with subsequent infections. This is the reason that the vaccine is recommended only for those with a documented previous dengue infection.
At its June 2021 meeting, the ACIP recommended 3-doses of Dengvaxia, administered at 0, 6, and 12 months, for individuals 9 to 16 years of age who have laboratory confirmation of previous dengue infection and live in endemic areas.12 These areas include the territories and affiliated states of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, US Virgin Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. Puerto Rico accounts for 85% of the population of these areas and 95% of reported dengue cases.12The reason for the delay between FDA approval and the ACIP recommendation was the need to wait for a readily available, accurate laboratory test to confirm previous dengue infection, which is now available. There are other dengue vaccines in development including 2 live-attenuated, tetravalent vaccine candidates in Phase 3 trials.
1. ACIP. COVID-19 vaccine recommendations. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc-specific/covid-19.html
2. CDC. Division of viral hepatitis. Disease burden from viral hepatitis A, B, and C in the United States. Accessed February 8 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/PDFs/disease_burden.pdf
3. CDC. Surveillance for viral hepatitis – United States, 2014. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2014surveillance/commentary.htm#:~:text=HEPATITIS%20B-,Acute%20Hepatitis%20B,B%20cases%20occurred%20in%202014
4. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance: United States, 2011. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2011surveillance/pdfs/2011HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf
5. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance report, 2019. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2019surveillance/HepB.htm
6. Schillie S, Harris A, Link-Gelles R, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of a hepatitis B vaccine with a novel adjuvant. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:455-458.
7. CDC. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Meeting recommendations, November 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/index.html
8. Matanock A, Lee G, Gierke R, et al. Use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine among adults aged ≥65 years: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1069-1075.
9. Kobayashi M. Considerations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in U.S. adults. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-02/24-25/05-Pneumococcal-Kobayashi.pdf
10. Anderson TC, Masters NB, Guo A, et al. Use of recombinant zoster vaccine in immunocompromised adults aged ≥19 years: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:80-84.
11. CDC. ACIP recommendations. June 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html
12. Paz-Bailey G. Dengue vaccine. Evidence to recommendation framework. Presented to the ACIP June 24, 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-Dengue-Paz-Bailey-508.pdf
In a typical year, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) has three 1.5- to 2-day meetings to make recommendations for the use of new and existing vaccines in the US population. However, 2021 was not a typical year. Last year, ACIP held 17 meetings for a total of 127 hours. Most of these were related to vaccines to prevent COVID-19. There are now 3 COVID-19 vaccines authorized for use in the United States: the 2-dose mRNA-based Pfizer-BioNTech/Comirnaty and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and the single-dose adenovirus, vector-based Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID-19 vaccine.
TABLE 11 includes the actions taken by the ACIP from late 2020 through 2021 related to COVID-19 vaccines. All of these recommendations except 1 occurred after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the product using an emergency use authorization (EUA). The exception is the recommendation for use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) for those ages 16 years and older, which was approved under the normal process 8 months after widespread use under an EUA.
Hepatitis B vaccine now for all nonimmune adults up through 59 years
Since the introduction of hepatitis B (HepB) vaccines in 1980, the incidence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections in the United States has been reduced dramatically; there were an estimated 287,000 cases in 19852 and 19,200 in 2014.3 However, the incidence among adults has not declined in recent years and among someage groups has actually increased. Among those ages 40 to 49 years, the rate went from 1.9 per 100,000 in 20114 to 2.7 per 100,000 population in 2019.5 In those ages 50 to 59, there was an increase from 1.1 to 1.6 per 100,000 population over the same period of time.4,5
Recommendations for using HepB vaccine in adults have been based on risk that involves individual behavior, occupation, and medical conditions (TABLE 26). The presence of these risk factors is often unknown to medical professionals, who rarely ask about or document them. And patients can be reluctant to disclose them for fear of being stigmatized. The consequence has been a low rate of vaccination in at-risk adults.
At its November 2021 meeting, ACIP accepted the advice of the Hepatitis Work Group to move to a universal adult recommendation through age 59.7 ACIP believed that the incidence of acute infection in those ages 60 and older was too low to merit a universal recommendation. The new recommendation states that
Multiple HepB vaccine products are available for adults. Two are recombinant-based and require 3 doses: Engerix-B (GlaxoSmithKline) and Recombivax HB (Merck). One is recombinant based and requires only 2 doses: Heplisav-B (Dynavax Technologies). A new product recently approved by the FDA, PREHEVBRIO (VBI Vaccines), is another recombinant 3-dose option that the ACIP will consider early in 2022. HepB and HepA vaccines can also be co-administered with Twinrix (GlaxoSmithKline).
Pneumococcal vaccines: New PCV vaccines alter prescribing choices
The ACIP recommendations for pneumococcal vaccines in adults have been very confusing, involving 2 vaccines: PCV13 (Prevnar13, Pfizer) and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23, Merck). Both PCV13 and PPSV23 given in series were recommended for immunocompromised patients, but only PPSV23 was recommended for those with chronic medical conditions. For those 65 and older, PPSV23 was recommended for all individuals (including those with no chronic or immunocompromising condition), and PCV13 was recommended for those with immunocompromising conditions. Other adults in this older age group could receive PCV13 based on individual risk and shared clinical decision making.8
Continue to: This past year...
This past year, 2 new PCV vaccines were approved by the FDA: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance, Merck) and PCV20 (Prevnar20, Pfizer). While considering these new vaccines, the ACIP re-assessed its entire approval of pneumococcal vaccines. First, they retained the cutoff for universal pneumococcal vaccination at 65 years. For those younger than 65, they combined chronic medical conditions and immunocompromising conditions into a single at-risk group (TABLE 39). They then issued the same recommendation for older adults and those younger than 65 with risks: to receive a PCV vaccine, either PCV15 or PCV20. If they receive PCV15, it should be followed by PPSV23. PPSV23 is not recommended for those who receive PCV20. Therefore,
Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) has been licensed and recommended in the United States since 2017 in a 2-dose schedule for adults ages 50 years and older. In the summer of 2021, the FDA expanded the indication for use of RZV to include individuals 18 to 49 years of age who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy. In October, the ACIP agreed and recommended 2 RZV doses for those 19 years and older in these risk groups (TABLE 410).
This recommendation was based on the elevated risk of herpes zoster documented in those with immune-suppressing conditions and therapies. In the conditions studied, the incidence in these younger adults exceeded that for older adults, for whom the vaccine is recommended.10 There are many immune conditions and immune-suppressing medications. The ACIP Zoster Work Group did not have efficacy and safety information on the use of RZV in each one of them, even though their recommendation includes them all. Many of these patients are under the care of specialists whose specialty societies had been recommending zoster vaccine for their patients, off label, prior to the FDA authorization.
Rabies vaccine is now available in 2-dose schedule
People who should receive rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with rabies vaccine include laboratory personnel who work with rabies virus, biologists who work with bats, animal care professionals, wildlife biologists, veterinarians, and travelers who may be at risk of encountering rabid dogs. The recommendation has been for 3 doses of rabies vaccine at 0, 7, and 21-28 days. The ACIP voted at its June 2021 meeting to adopt a 2-dose PrEP schedule of 0 and 7 days.11 This will be especially helpful to travelers who want to complete the recommended doses prior to departure. Those who have sustained risk over time can elect to have a third dose after 21 days and before 3 years, or elect to have titers checked. More detailed clinical advice will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2022.
Dengue vaccine: New rec for those 9-16 years
In 2019, the FDA approved the first dengue vaccine for use in the United States for children 9 to 16 years old who had laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and who were living in an area where dengue is endemic. The CYD-TDV dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is a live-attenuated tetravalent vaccine built on a yellow fever vaccine backbone. Its effectiveness is 82% for prevention of symptomatic dengue, 79% for prevention of dengue-associated hospitalizations, and 84% against severe dengue.12
Continue to: Dengue viruses...
Dengue viruses (DENV) are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. There are 4 serotypes of dengue, and all 4 appear to be circulating in most endemic countries. Clinical disease varies from a mild febrile illness to severe disease. The most common clinical presentation includes sudden onset of fever, headache, retro-orbital pain, myalgia and arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea.
Severe disease includes plasma leakage, shock, respiratory distress, severe bleeding, and organ failure. While severe dengue can occur with a primary infection, a second infection with a different DENV increases the risk of severe dengue. A small increased risk of severe dengue occurs when dengue infection occurs after vaccination in those with no evidence of previous dengue infection. It is felt that the vaccine serves as a primary infection that increases the risk of severe dengue with subsequent infections. This is the reason that the vaccine is recommended only for those with a documented previous dengue infection.
At its June 2021 meeting, the ACIP recommended 3-doses of Dengvaxia, administered at 0, 6, and 12 months, for individuals 9 to 16 years of age who have laboratory confirmation of previous dengue infection and live in endemic areas.12 These areas include the territories and affiliated states of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, US Virgin Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. Puerto Rico accounts for 85% of the population of these areas and 95% of reported dengue cases.12The reason for the delay between FDA approval and the ACIP recommendation was the need to wait for a readily available, accurate laboratory test to confirm previous dengue infection, which is now available. There are other dengue vaccines in development including 2 live-attenuated, tetravalent vaccine candidates in Phase 3 trials.
In a typical year, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) has three 1.5- to 2-day meetings to make recommendations for the use of new and existing vaccines in the US population. However, 2021 was not a typical year. Last year, ACIP held 17 meetings for a total of 127 hours. Most of these were related to vaccines to prevent COVID-19. There are now 3 COVID-19 vaccines authorized for use in the United States: the 2-dose mRNA-based Pfizer-BioNTech/Comirnaty and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines and the single-dose adenovirus, vector-based Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID-19 vaccine.
TABLE 11 includes the actions taken by the ACIP from late 2020 through 2021 related to COVID-19 vaccines. All of these recommendations except 1 occurred after the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the product using an emergency use authorization (EUA). The exception is the recommendation for use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) for those ages 16 years and older, which was approved under the normal process 8 months after widespread use under an EUA.
Hepatitis B vaccine now for all nonimmune adults up through 59 years
Since the introduction of hepatitis B (HepB) vaccines in 1980, the incidence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections in the United States has been reduced dramatically; there were an estimated 287,000 cases in 19852 and 19,200 in 2014.3 However, the incidence among adults has not declined in recent years and among someage groups has actually increased. Among those ages 40 to 49 years, the rate went from 1.9 per 100,000 in 20114 to 2.7 per 100,000 population in 2019.5 In those ages 50 to 59, there was an increase from 1.1 to 1.6 per 100,000 population over the same period of time.4,5
Recommendations for using HepB vaccine in adults have been based on risk that involves individual behavior, occupation, and medical conditions (TABLE 26). The presence of these risk factors is often unknown to medical professionals, who rarely ask about or document them. And patients can be reluctant to disclose them for fear of being stigmatized. The consequence has been a low rate of vaccination in at-risk adults.
At its November 2021 meeting, ACIP accepted the advice of the Hepatitis Work Group to move to a universal adult recommendation through age 59.7 ACIP believed that the incidence of acute infection in those ages 60 and older was too low to merit a universal recommendation. The new recommendation states that
Multiple HepB vaccine products are available for adults. Two are recombinant-based and require 3 doses: Engerix-B (GlaxoSmithKline) and Recombivax HB (Merck). One is recombinant based and requires only 2 doses: Heplisav-B (Dynavax Technologies). A new product recently approved by the FDA, PREHEVBRIO (VBI Vaccines), is another recombinant 3-dose option that the ACIP will consider early in 2022. HepB and HepA vaccines can also be co-administered with Twinrix (GlaxoSmithKline).
Pneumococcal vaccines: New PCV vaccines alter prescribing choices
The ACIP recommendations for pneumococcal vaccines in adults have been very confusing, involving 2 vaccines: PCV13 (Prevnar13, Pfizer) and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23, Merck). Both PCV13 and PPSV23 given in series were recommended for immunocompromised patients, but only PPSV23 was recommended for those with chronic medical conditions. For those 65 and older, PPSV23 was recommended for all individuals (including those with no chronic or immunocompromising condition), and PCV13 was recommended for those with immunocompromising conditions. Other adults in this older age group could receive PCV13 based on individual risk and shared clinical decision making.8
Continue to: This past year...
This past year, 2 new PCV vaccines were approved by the FDA: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance, Merck) and PCV20 (Prevnar20, Pfizer). While considering these new vaccines, the ACIP re-assessed its entire approval of pneumococcal vaccines. First, they retained the cutoff for universal pneumococcal vaccination at 65 years. For those younger than 65, they combined chronic medical conditions and immunocompromising conditions into a single at-risk group (TABLE 39). They then issued the same recommendation for older adults and those younger than 65 with risks: to receive a PCV vaccine, either PCV15 or PCV20. If they receive PCV15, it should be followed by PPSV23. PPSV23 is not recommended for those who receive PCV20. Therefore,
Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) has been licensed and recommended in the United States since 2017 in a 2-dose schedule for adults ages 50 years and older. In the summer of 2021, the FDA expanded the indication for use of RZV to include individuals 18 to 49 years of age who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to known disease or therapy. In October, the ACIP agreed and recommended 2 RZV doses for those 19 years and older in these risk groups (TABLE 410).
This recommendation was based on the elevated risk of herpes zoster documented in those with immune-suppressing conditions and therapies. In the conditions studied, the incidence in these younger adults exceeded that for older adults, for whom the vaccine is recommended.10 There are many immune conditions and immune-suppressing medications. The ACIP Zoster Work Group did not have efficacy and safety information on the use of RZV in each one of them, even though their recommendation includes them all. Many of these patients are under the care of specialists whose specialty societies had been recommending zoster vaccine for their patients, off label, prior to the FDA authorization.
Rabies vaccine is now available in 2-dose schedule
People who should receive rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with rabies vaccine include laboratory personnel who work with rabies virus, biologists who work with bats, animal care professionals, wildlife biologists, veterinarians, and travelers who may be at risk of encountering rabid dogs. The recommendation has been for 3 doses of rabies vaccine at 0, 7, and 21-28 days. The ACIP voted at its June 2021 meeting to adopt a 2-dose PrEP schedule of 0 and 7 days.11 This will be especially helpful to travelers who want to complete the recommended doses prior to departure. Those who have sustained risk over time can elect to have a third dose after 21 days and before 3 years, or elect to have titers checked. More detailed clinical advice will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in 2022.
Dengue vaccine: New rec for those 9-16 years
In 2019, the FDA approved the first dengue vaccine for use in the United States for children 9 to 16 years old who had laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and who were living in an area where dengue is endemic. The CYD-TDV dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is a live-attenuated tetravalent vaccine built on a yellow fever vaccine backbone. Its effectiveness is 82% for prevention of symptomatic dengue, 79% for prevention of dengue-associated hospitalizations, and 84% against severe dengue.12
Continue to: Dengue viruses...
Dengue viruses (DENV) are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. There are 4 serotypes of dengue, and all 4 appear to be circulating in most endemic countries. Clinical disease varies from a mild febrile illness to severe disease. The most common clinical presentation includes sudden onset of fever, headache, retro-orbital pain, myalgia and arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea.
Severe disease includes plasma leakage, shock, respiratory distress, severe bleeding, and organ failure. While severe dengue can occur with a primary infection, a second infection with a different DENV increases the risk of severe dengue. A small increased risk of severe dengue occurs when dengue infection occurs after vaccination in those with no evidence of previous dengue infection. It is felt that the vaccine serves as a primary infection that increases the risk of severe dengue with subsequent infections. This is the reason that the vaccine is recommended only for those with a documented previous dengue infection.
At its June 2021 meeting, the ACIP recommended 3-doses of Dengvaxia, administered at 0, 6, and 12 months, for individuals 9 to 16 years of age who have laboratory confirmation of previous dengue infection and live in endemic areas.12 These areas include the territories and affiliated states of Puerto Rico, American Samoa, US Virgin Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Republic of Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. Puerto Rico accounts for 85% of the population of these areas and 95% of reported dengue cases.12The reason for the delay between FDA approval and the ACIP recommendation was the need to wait for a readily available, accurate laboratory test to confirm previous dengue infection, which is now available. There are other dengue vaccines in development including 2 live-attenuated, tetravalent vaccine candidates in Phase 3 trials.
1. ACIP. COVID-19 vaccine recommendations. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc-specific/covid-19.html
2. CDC. Division of viral hepatitis. Disease burden from viral hepatitis A, B, and C in the United States. Accessed February 8 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/PDFs/disease_burden.pdf
3. CDC. Surveillance for viral hepatitis – United States, 2014. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2014surveillance/commentary.htm#:~:text=HEPATITIS%20B-,Acute%20Hepatitis%20B,B%20cases%20occurred%20in%202014
4. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance: United States, 2011. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2011surveillance/pdfs/2011HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf
5. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance report, 2019. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2019surveillance/HepB.htm
6. Schillie S, Harris A, Link-Gelles R, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of a hepatitis B vaccine with a novel adjuvant. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:455-458.
7. CDC. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Meeting recommendations, November 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/index.html
8. Matanock A, Lee G, Gierke R, et al. Use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine among adults aged ≥65 years: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1069-1075.
9. Kobayashi M. Considerations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in U.S. adults. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-02/24-25/05-Pneumococcal-Kobayashi.pdf
10. Anderson TC, Masters NB, Guo A, et al. Use of recombinant zoster vaccine in immunocompromised adults aged ≥19 years: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:80-84.
11. CDC. ACIP recommendations. June 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html
12. Paz-Bailey G. Dengue vaccine. Evidence to recommendation framework. Presented to the ACIP June 24, 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-Dengue-Paz-Bailey-508.pdf
1. ACIP. COVID-19 vaccine recommendations. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/vacc-specific/covid-19.html
2. CDC. Division of viral hepatitis. Disease burden from viral hepatitis A, B, and C in the United States. Accessed February 8 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/PDFs/disease_burden.pdf
3. CDC. Surveillance for viral hepatitis – United States, 2014. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2014surveillance/commentary.htm#:~:text=HEPATITIS%20B-,Acute%20Hepatitis%20B,B%20cases%20occurred%20in%202014
4. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance: United States, 2011. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2011surveillance/pdfs/2011HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf
5. CDC. Viral hepatitis surveillance report, 2019. Hepatitis B. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2019surveillance/HepB.htm
6. Schillie S, Harris A, Link-Gelles R, et al. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for use of a hepatitis B vaccine with a novel adjuvant. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:455-458.
7. CDC. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Meeting recommendations, November 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/index.html
8. Matanock A, Lee G, Gierke R, et al. Use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine among adults aged ≥65 years: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1069-1075.
9. Kobayashi M. Considerations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in U.S. adults. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-02/24-25/05-Pneumococcal-Kobayashi.pdf
10. Anderson TC, Masters NB, Guo A, et al. Use of recombinant zoster vaccine in immunocompromised adults aged ≥19 years: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:80-84.
11. CDC. ACIP recommendations. June 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html
12. Paz-Bailey G. Dengue vaccine. Evidence to recommendation framework. Presented to the ACIP June 24, 2021. Accessed February 8, 2022. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/03-Dengue-Paz-Bailey-508.pdf