User login
Resistance to azithromycin and to a lesser degree cephalosporin antibiotics was observed in patients with gonorrhea, according to an analysis of 2014 data from a national surveillance system,
“It is unclear whether these increases mark the beginning of trends, but emergence of cephalosporin and azithromycin resistance would complicate gonorrhea treatment substantially,” reported Robert D. Kirkcaldy, MD, and his colleagues. The results were published July 15 in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
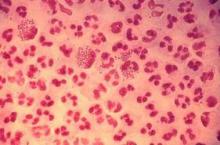
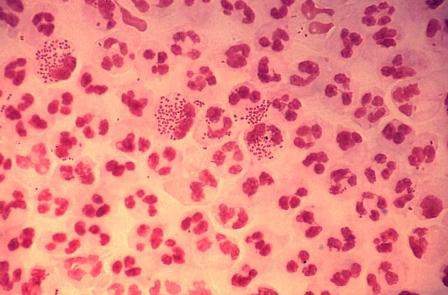
Dr. Kirkcaldy of the CDC’s Division of STD Prevention, Atlanta, and his coinvestigators evaluated 2014 data from the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP), which the CDC established in 1986 to monitor trends in antimicrobial susceptibilities of Neisseri. gonorrhoeae strains in the United States. The N. gonorrhoeae isolates are collected at 27 participating STD clinics each month from up to the first 25 men with gonococcal urethritis who present to the clinics.
In 2014, a total of 5,093 isolates were collected at the 27 sites. Among these, 25% demonstrated resistance to tetracycline, 19% to ciprofloxacin, and 16% to penicillin. At the same time, resistance to azithromycin increased from 0.6% in 2013 to 2.5% in 2014, predominantly in the Midwest.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic cefixime, meanwhile, increased from 0.1% in 2006 to 1.4% in 2010 and 2011, fell to 0.4% in 2013, and increased to 0.8% in 2014.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic ceftriaxone increased from 0.1% in 2008 to 0.4% in 2011, and decreased to 0.1% in 2013 and 2014).
“Local and state health departments can use GISP data to determine allocation of STD prevention services and resources, guide prevention planning, and communicate best treatment practices to health care providers,” the researchers wrote. “Continued surveillance, appropriate treatment, development of new antibiotics, and prevention of transmission remain the best strategies to reduce gonorrhea incidence and morbidity.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Resistance to azithromycin and to a lesser degree cephalosporin antibiotics was observed in patients with gonorrhea, according to an analysis of 2014 data from a national surveillance system,
“It is unclear whether these increases mark the beginning of trends, but emergence of cephalosporin and azithromycin resistance would complicate gonorrhea treatment substantially,” reported Robert D. Kirkcaldy, MD, and his colleagues. The results were published July 15 in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Dr. Kirkcaldy of the CDC’s Division of STD Prevention, Atlanta, and his coinvestigators evaluated 2014 data from the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP), which the CDC established in 1986 to monitor trends in antimicrobial susceptibilities of Neisseri. gonorrhoeae strains in the United States. The N. gonorrhoeae isolates are collected at 27 participating STD clinics each month from up to the first 25 men with gonococcal urethritis who present to the clinics.
In 2014, a total of 5,093 isolates were collected at the 27 sites. Among these, 25% demonstrated resistance to tetracycline, 19% to ciprofloxacin, and 16% to penicillin. At the same time, resistance to azithromycin increased from 0.6% in 2013 to 2.5% in 2014, predominantly in the Midwest.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic cefixime, meanwhile, increased from 0.1% in 2006 to 1.4% in 2010 and 2011, fell to 0.4% in 2013, and increased to 0.8% in 2014.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic ceftriaxone increased from 0.1% in 2008 to 0.4% in 2011, and decreased to 0.1% in 2013 and 2014).
“Local and state health departments can use GISP data to determine allocation of STD prevention services and resources, guide prevention planning, and communicate best treatment practices to health care providers,” the researchers wrote. “Continued surveillance, appropriate treatment, development of new antibiotics, and prevention of transmission remain the best strategies to reduce gonorrhea incidence and morbidity.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Resistance to azithromycin and to a lesser degree cephalosporin antibiotics was observed in patients with gonorrhea, according to an analysis of 2014 data from a national surveillance system,
“It is unclear whether these increases mark the beginning of trends, but emergence of cephalosporin and azithromycin resistance would complicate gonorrhea treatment substantially,” reported Robert D. Kirkcaldy, MD, and his colleagues. The results were published July 15 in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Dr. Kirkcaldy of the CDC’s Division of STD Prevention, Atlanta, and his coinvestigators evaluated 2014 data from the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP), which the CDC established in 1986 to monitor trends in antimicrobial susceptibilities of Neisseri. gonorrhoeae strains in the United States. The N. gonorrhoeae isolates are collected at 27 participating STD clinics each month from up to the first 25 men with gonococcal urethritis who present to the clinics.
In 2014, a total of 5,093 isolates were collected at the 27 sites. Among these, 25% demonstrated resistance to tetracycline, 19% to ciprofloxacin, and 16% to penicillin. At the same time, resistance to azithromycin increased from 0.6% in 2013 to 2.5% in 2014, predominantly in the Midwest.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic cefixime, meanwhile, increased from 0.1% in 2006 to 1.4% in 2010 and 2011, fell to 0.4% in 2013, and increased to 0.8% in 2014.
Resistance to the cephalosporin antibiotic ceftriaxone increased from 0.1% in 2008 to 0.4% in 2011, and decreased to 0.1% in 2013 and 2014).
“Local and state health departments can use GISP data to determine allocation of STD prevention services and resources, guide prevention planning, and communicate best treatment practices to health care providers,” the researchers wrote. “Continued surveillance, appropriate treatment, development of new antibiotics, and prevention of transmission remain the best strategies to reduce gonorrhea incidence and morbidity.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
Key clinical point: Resistance to azithromycin is emerging among patients diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Major finding: Among patients with gonorrhea, resistance to azithromycin increased from 0.6% in 2013 to 2.5% in 2014, predominantly in the Midwest.
Data source: An analysis of 5,093 Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from 27 clinics as part of the CDC’s Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project.
Disclosures: The researchers had no financial disclosures.