User login
Liver biopsy will reveal the cause of the liver dysfunction and confirm whether this patient has small cell lung cancer (SCLC), as suspected, and whether it has spread to the liver. This will affect chemotherapy options.
Most cases of SCLC will present in advanced stages, be inoperable, and have a dismal prognosis. Only about 5% of patients present at an early stage (Ia, Ib, or IIa). The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend that patients with advanced disease be managed with aggressive chemoradiation therapy and immunotherapy.
SCLC is the most aggressive lung cancer subtype. It is almost always associated with smoking. It accounts for 10%-15% of all lung cancers. Rapid tumor growth may lead to obstruction of major airways, with distal collapse leading to postobstructive pneumonitis, infection, and fever. About 70% of patients show metastatic spread at presentation, and the liver is one of the most common sites of metastasis.
Unlike non-SCLC, for which the prognosis has improved in part because of several new drug approvals from the US Food and Drug Administration, the prognosis for SCLC has not changed substantially in the past two decades and remains poor. However, with immunotherapy, the outlook may be improving. The NCCN recommends atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide for first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage SCLC. Furthermore, the approval of durvalumab in combination with chemotherapy and the approval of lurbinectedin, a novel chemotherapy agent approved for second-line treatment of SCLC, have added to the therapeutic options for patients with advanced SCLC.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
Liver biopsy will reveal the cause of the liver dysfunction and confirm whether this patient has small cell lung cancer (SCLC), as suspected, and whether it has spread to the liver. This will affect chemotherapy options.
Most cases of SCLC will present in advanced stages, be inoperable, and have a dismal prognosis. Only about 5% of patients present at an early stage (Ia, Ib, or IIa). The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend that patients with advanced disease be managed with aggressive chemoradiation therapy and immunotherapy.
SCLC is the most aggressive lung cancer subtype. It is almost always associated with smoking. It accounts for 10%-15% of all lung cancers. Rapid tumor growth may lead to obstruction of major airways, with distal collapse leading to postobstructive pneumonitis, infection, and fever. About 70% of patients show metastatic spread at presentation, and the liver is one of the most common sites of metastasis.
Unlike non-SCLC, for which the prognosis has improved in part because of several new drug approvals from the US Food and Drug Administration, the prognosis for SCLC has not changed substantially in the past two decades and remains poor. However, with immunotherapy, the outlook may be improving. The NCCN recommends atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide for first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage SCLC. Furthermore, the approval of durvalumab in combination with chemotherapy and the approval of lurbinectedin, a novel chemotherapy agent approved for second-line treatment of SCLC, have added to the therapeutic options for patients with advanced SCLC.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
Liver biopsy will reveal the cause of the liver dysfunction and confirm whether this patient has small cell lung cancer (SCLC), as suspected, and whether it has spread to the liver. This will affect chemotherapy options.
Most cases of SCLC will present in advanced stages, be inoperable, and have a dismal prognosis. Only about 5% of patients present at an early stage (Ia, Ib, or IIa). The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend that patients with advanced disease be managed with aggressive chemoradiation therapy and immunotherapy.
SCLC is the most aggressive lung cancer subtype. It is almost always associated with smoking. It accounts for 10%-15% of all lung cancers. Rapid tumor growth may lead to obstruction of major airways, with distal collapse leading to postobstructive pneumonitis, infection, and fever. About 70% of patients show metastatic spread at presentation, and the liver is one of the most common sites of metastasis.
Unlike non-SCLC, for which the prognosis has improved in part because of several new drug approvals from the US Food and Drug Administration, the prognosis for SCLC has not changed substantially in the past two decades and remains poor. However, with immunotherapy, the outlook may be improving. The NCCN recommends atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide for first-line treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage SCLC. Furthermore, the approval of durvalumab in combination with chemotherapy and the approval of lurbinectedin, a novel chemotherapy agent approved for second-line treatment of SCLC, have added to the therapeutic options for patients with advanced SCLC.
Maurie Markman, MD, President, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
Maurie Markman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Merck
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Novis; Glaxo Smith Kline
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Novis; GSK; Merck
A 64-year-old man presents with shortness of breath, a productive cough, chest pain, some fatigue, anorexia, a recent 15-lb weight loss, jaundice, and a history of type 2 diabetes. He is a college professor and has a 35–pack-year smoking history; he quit 3 years ago.
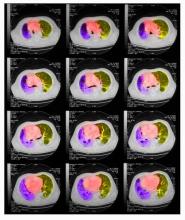
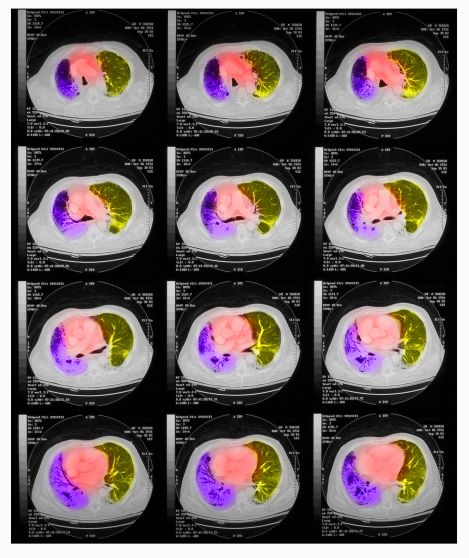
On physical examination, he has dullness to percussion and decreased breath sounds. His laboratory data reveal elevated serum liver enzyme levels. Chest radiography shows a left hilar mass and a 5.6-cm left upper lobe mass. CT reveals a hilar mass with a bilateral mediastinal extension and pneumonia. PET shows activity in the left upper lobe mass, with supraclavicular nodal areas and liver lesions. MRI shows that there are no metastases to the brain.