User login
To the Editor:
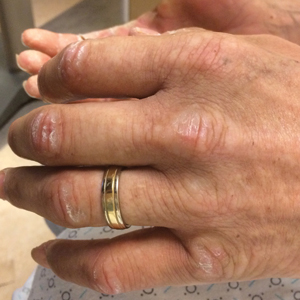
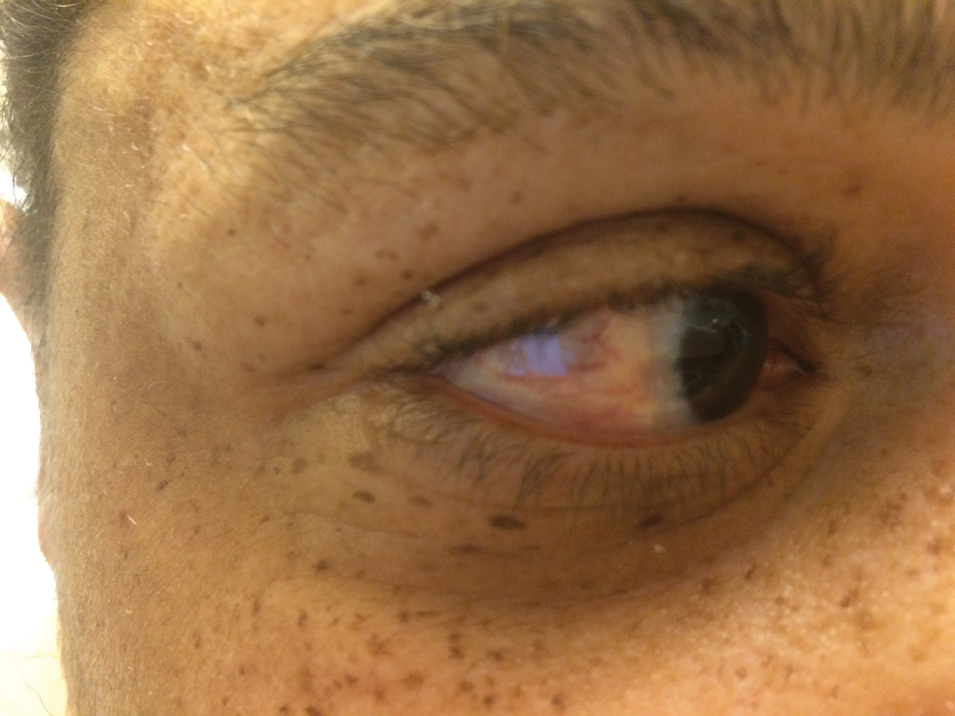
A 44-year-old man with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicated by lupus nephritis, end-stage renal disease, and antiphospholipid syndrome was evaluated for progressive skin tightening over the last 3 years, predominantly on the hands but also involving the feet, legs, and arms. Physical examination revealed multiple flesh-colored to hypopigmented, bound-down, indurated, fissured plaques over the distal upper and lower extremities, most prominent over the hands (Figure 1). Yellow plaques appeared on the lateral sclera of both eyes (Figure 2). A diagnosis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) was supported by typical findings on punch biopsy, including a proliferation of dermal fibroblasts with thickened collagen bundles and mucin deposition.
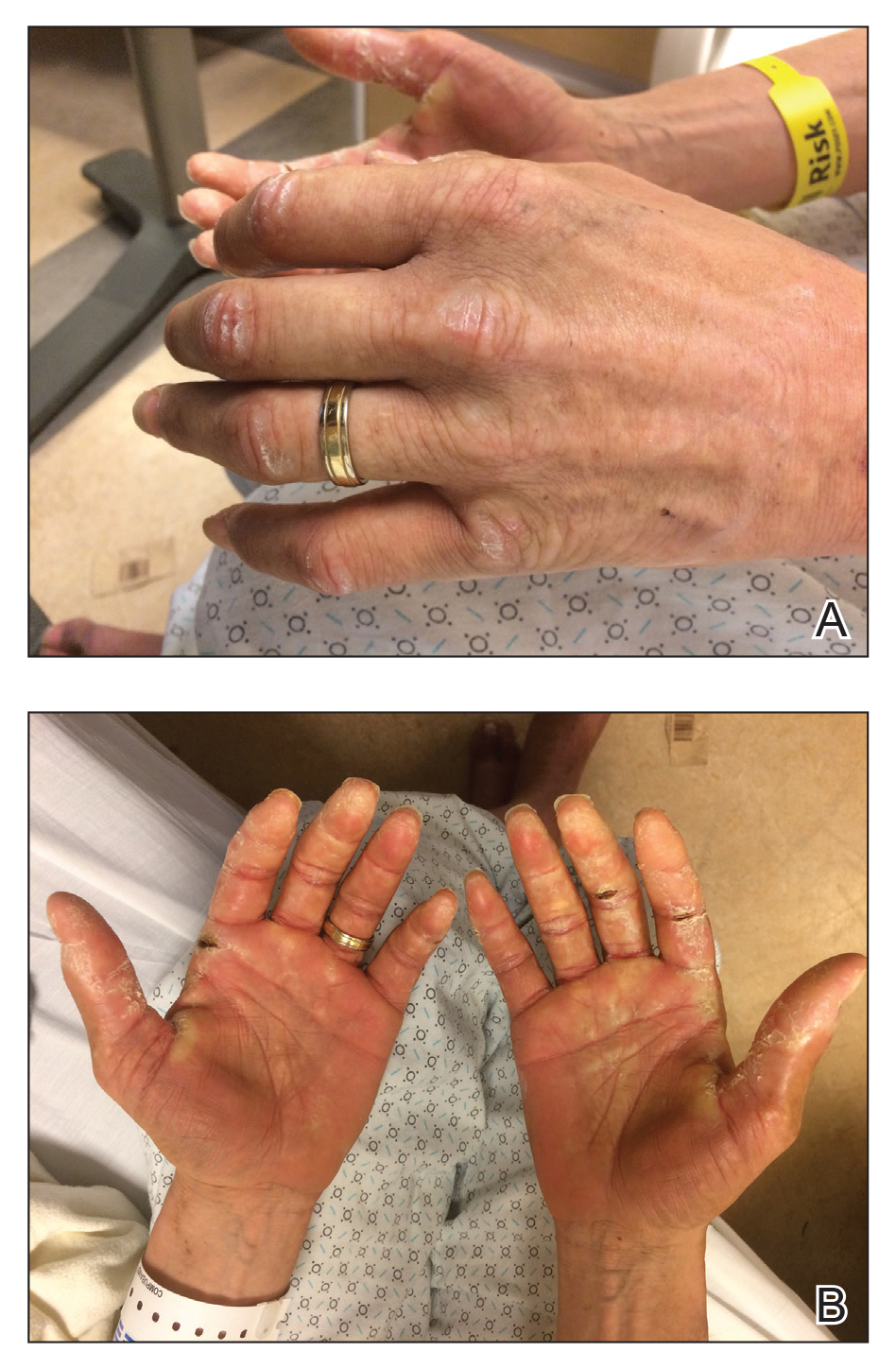
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, also known as nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy, is characterized by fibrotic plaques and nodules that tend to be bilateral.1 The chronic course of this disease often is accompanied by flexion contractures. Yellow scleral plaques caused by calcium phosphate deposition are present in up to 75% of cases and are more specific to a diagnosis of NSF in patients younger than 45 years.1,2 A strong association exists between NSF and gadolinium contrast agents in patients with acute renal failure; our patient later confirmed multiple gadolinium exposures years prior. Deposits of gadolinium have even been found in NSF skin lesions.2
- Stone JH. A Clinician’s Pearls & Myths in Rheumatology. Springer London; 2009.
- Barker-Griffith A, Goldberg J, Abraham JL. Ocular pathologic features and gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129:661-663.
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old man with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicated by lupus nephritis, end-stage renal disease, and antiphospholipid syndrome was evaluated for progressive skin tightening over the last 3 years, predominantly on the hands but also involving the feet, legs, and arms. Physical examination revealed multiple flesh-colored to hypopigmented, bound-down, indurated, fissured plaques over the distal upper and lower extremities, most prominent over the hands (Figure 1). Yellow plaques appeared on the lateral sclera of both eyes (Figure 2). A diagnosis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) was supported by typical findings on punch biopsy, including a proliferation of dermal fibroblasts with thickened collagen bundles and mucin deposition.

Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, also known as nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy, is characterized by fibrotic plaques and nodules that tend to be bilateral.1 The chronic course of this disease often is accompanied by flexion contractures. Yellow scleral plaques caused by calcium phosphate deposition are present in up to 75% of cases and are more specific to a diagnosis of NSF in patients younger than 45 years.1,2 A strong association exists between NSF and gadolinium contrast agents in patients with acute renal failure; our patient later confirmed multiple gadolinium exposures years prior. Deposits of gadolinium have even been found in NSF skin lesions.2

To the Editor:
A 44-year-old man with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) complicated by lupus nephritis, end-stage renal disease, and antiphospholipid syndrome was evaluated for progressive skin tightening over the last 3 years, predominantly on the hands but also involving the feet, legs, and arms. Physical examination revealed multiple flesh-colored to hypopigmented, bound-down, indurated, fissured plaques over the distal upper and lower extremities, most prominent over the hands (Figure 1). Yellow plaques appeared on the lateral sclera of both eyes (Figure 2). A diagnosis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) was supported by typical findings on punch biopsy, including a proliferation of dermal fibroblasts with thickened collagen bundles and mucin deposition.

Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, also known as nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy, is characterized by fibrotic plaques and nodules that tend to be bilateral.1 The chronic course of this disease often is accompanied by flexion contractures. Yellow scleral plaques caused by calcium phosphate deposition are present in up to 75% of cases and are more specific to a diagnosis of NSF in patients younger than 45 years.1,2 A strong association exists between NSF and gadolinium contrast agents in patients with acute renal failure; our patient later confirmed multiple gadolinium exposures years prior. Deposits of gadolinium have even been found in NSF skin lesions.2

- Stone JH. A Clinician’s Pearls & Myths in Rheumatology. Springer London; 2009.
- Barker-Griffith A, Goldberg J, Abraham JL. Ocular pathologic features and gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129:661-663.
- Stone JH. A Clinician’s Pearls & Myths in Rheumatology. Springer London; 2009.
- Barker-Griffith A, Goldberg J, Abraham JL. Ocular pathologic features and gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129:661-663.
Practice Points
- It is important to examine the eyes in a patient with sclerotic skin changes on physical examination.
- The presence of yellow scleral plaques strongly is associated with a diagnosis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.