User login
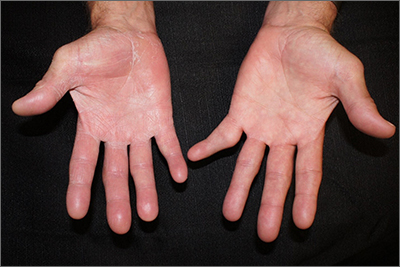
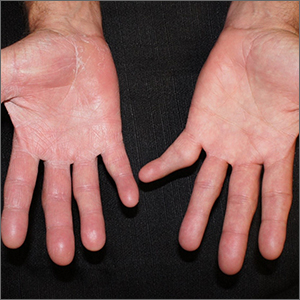
A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578
A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578