User login
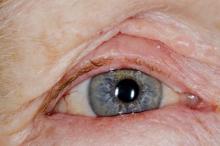
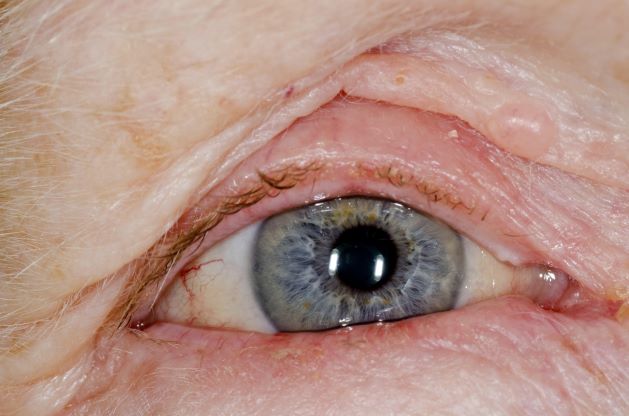
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 71-year-old woman was referred for an ophthalmologic examination by her dermatologist. The patient reports recent onset of red, swollen eyelids; ocular itching; and a burning sensation. Prior medical history includes severe atopic dermatitis, type 2 diabetes, and osteoarthritis. Current medications include metformin 1000 mg/d, celecoxib 200 mg/d, and clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream twice daily. The patient began receiving subcutaneous dupilumab 300 mg/once every 2 weeks about 6 weeks earlier.